Exome Sequencing Identifies a Novel FBN1 Variant in a Pakistani Family with Marfan Syndrome That Includes Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Family Recruitment and Clinical Diagnosis
2.2. DNA Isolation and Whole Exome Sequencing
2.3. Variant’s Annotation and Filtering
2.4. Sanger Validation
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Manifestations
3.2. Genetic Analysis
3.3. Variant’s Validation and Segregation
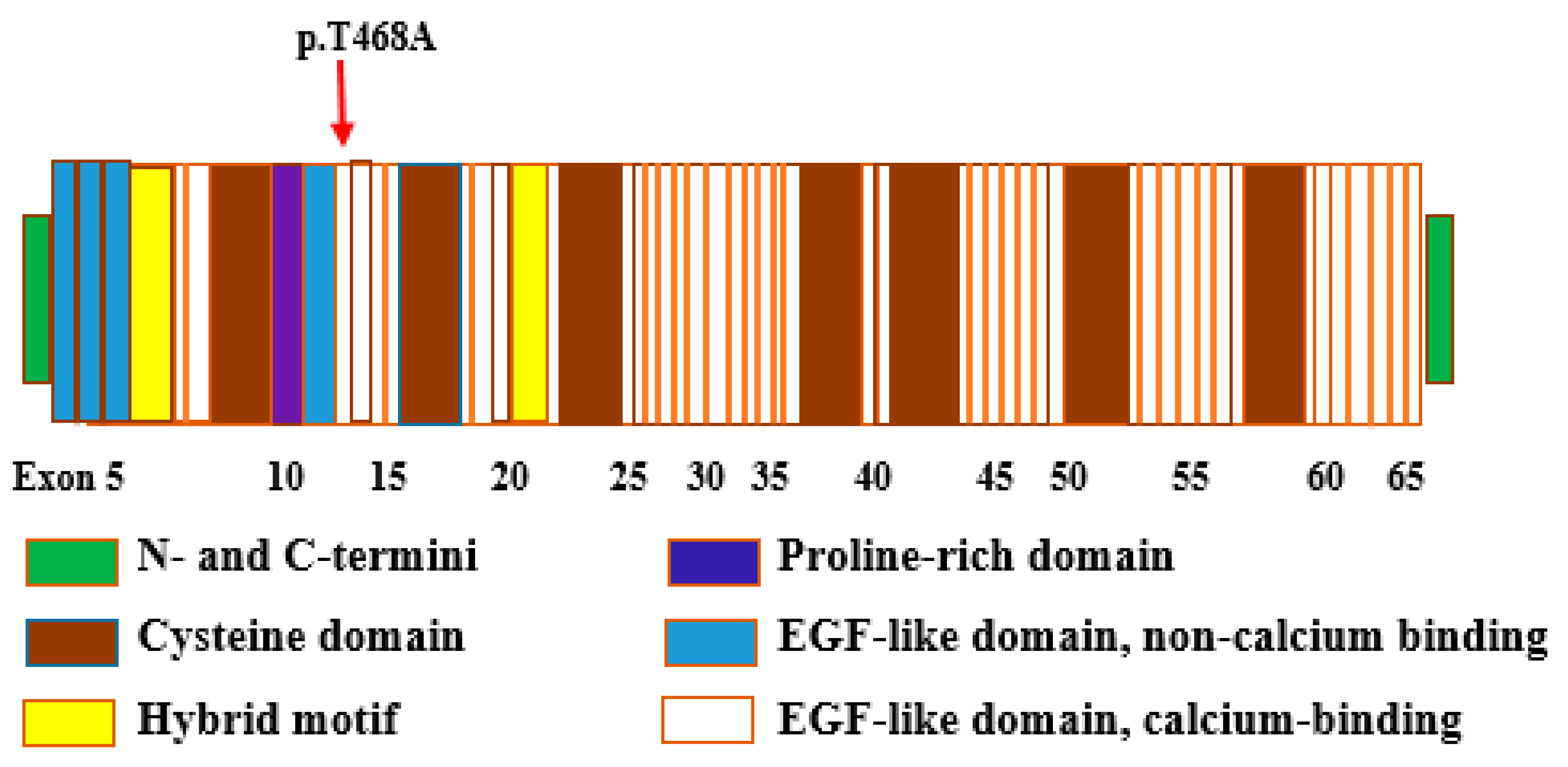
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Web Resources
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wexler, R.; Elton, T.; Pleister, A.; Feldman, D. Cardiomyopathy: An overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2009, 79, 778. [Google Scholar]
- Maron, B.J.; Towbin, J.A.; Thiene, G.; Antzelevitch, C.; Corrado, D.; Arnett, D.; Moss, A.J.; Seidman, C.E.; Young, J.B. Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: An American Heart Association scientific statement from the council on clinical cardiology, heart failure and transplantation committee; quality of care and outcomes research and functional genomics and translational biology interdisciplinary working groups; and council on epidemiology and prevention. Circulation 2006, 113, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger, R.E.; Jordan, E. Dilated Cardiomyopathy Overview. Genereviews® [Internet]; 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1309/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK1309.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2021).
- Rosenbaum, A.N.; Agre, K.E.; Pereira, N.L. Genetics of dilated cardiomyopathy: Practical implications for heart failure management. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isekame, Y.; Gati, S.; Aragon-Martin, J.A.; Bastiaenen, R.; Seshasai, S.R.K.; Child, A. Cardiovascular management of adults with Marfan syndrome. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2016, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayal, U.; Prasad, S.; Cook, S.A. Genetics and genomics of dilated cardiomyopathy and systolic heart failure. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weintraub, R.G.; Semsarian, C.; Macdonald, P. Dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2017, 390, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, R.E.; Morales, A.; Siegfried, J.D. Clinical and genetic issues in dilated cardiomyopathy: A review for genetics professionals. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piran, S.; Liu, P.; Morales, A.; Hershberger, R.E. Where genome meets phenome: Rationale for integrating genetic and protein biomarkers in the diagnosis and management of dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merlo, M.; Cannata, A.; Gobbo, M.; Stolfo, D.; Elliott, P.M.; Sinagra, G. Evolving concepts in dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herman, D.S.; Lam, L.; Taylor, M.R.; Wang, L.; Teekakirikul, P.; Christodoulou, D.; Conner, L.; DePalma, S.R.; McDonough, B.; Sparks, E. Truncations of titin causing dilated cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hershberger, R.E.; Hedges, D.J.; Morales, A. Dilated cardiomyopathy: The complexity of a diverse genetic architecture. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, D.P.; Dietz, H.C. Marfan’s syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, A.; Alaerts, M.; Van Laer, L.; Loeys, B. Marfan syndrome and related disorders: 25 years of gene discovery. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijboom, L.J.; Timmermans, J.; Van Tintelen, J.P.; Nollen, G.J.; De Backer, J.; Van Den Berg, M.P.; Boers, G.H.; Mulder, B.J. Evaluation of left ventricular dimensions and function in Marfan’s syndrome without significant valvular regurgitation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatrath, R.; Beauchesne, L.M.; Connolly, H.M.; Michels, V.V.; Driscoll, D.J. Left ventricular function in the Marfan syndrome without significant valvular regurgitation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 914–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, A.; Nisula, L.; Keto, P.; Hekali, P.; Viitasalo, M.; Kaitila, L.; Kupari, M. Left ventricular function in children with the Marfan syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 1994, 15, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciani, M.C.; Giurlani, L.; Chelucci, A.; Pepe, G.; Giusti, B.; Brunelli, T.; Attanasio, M.; Martinucci, P.; Fattori, R.; Abbatea, R. Diastolic subclinical primary alterations in Marfan syndrome and Marfan-related disorders. Clin. Cardiol. Int. Index. Peer-Rev. J. Adv. Treat. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2002, 25, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, L.Y.; Keene, D.R.; Renard, M.; De Backer, J. FBN1: The disease-causing gene for Marfan syndrome and other genetic disorders. Gene 2016, 591, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbloom, J.; Abrams, W.; Mecham, R. Extracellular matrix 4: The elastic fiber. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stheneur, C.; Collod-Béroud, G.; Faivre, L.; Buyck, J.F.; Gouya, L.; Le Parc, J.-M.; Moura, B.; Muti, C.; Grandchamp, B.; Sultan, G. Identification of the minimal combination of clinical features in probands for efficient mutation detection in the FBN1 gene. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Gong, B. A novel FBN1 mutation causes autosomal dominant Marfan syndrome. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7321–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; Del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; O’connor, T.D.; Jun, G.; Kang, H.M.; Abecasis, G.; Leal, S.M.; Gabriel, S.; Rieder, M.J.; Altshuler, D.; Shendure, J. Analysis of 6515 exomes reveals the recent origin of most human protein-coding variants. Nature 2013, 493, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consortium, G.P. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, E.M.; Halees, A.; Itan, Y.; Spencer, E.G.; He, Y.; Azab, M.A.; Gabriel, S.B.; Belkadi, A.; Boisson, B.; Abel, L. Characterization of Greater Middle Eastern genetic variation for enhanced disease gene discovery. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, X.; Boerwinkle, E.; Liu, X. In silico prediction of splice-altering single nucleotide variants in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 13534–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Boerwinkle, E. dbNSFP v3.0: A one-stop database of functional predictions and annotations for human nonsynonymous and splice-site SNVs. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koressaar, T.; Remm, M. Enhancements and modifications of primer design program Primer3. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1289–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dietz, H.C.; Pyeritz, R.E. Mutations in the human gene for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) in the Marfan syndrome and related disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteman, P.; Handford, P.A. Defective secretion of recombinant fragments of fibrillin-1: Implications of protein misfolding for the pathogenesis of Marfan syndrome and related disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y. Novel FBN1 mutations are responsible for cardiovascular manifestations of Marfan syndrome. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, G.; Giusti, B.; Sticchi, E.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Nistri, S. Marfan syndrome: Current perspectives. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2016, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vollbrandt, T.; Tiedemann, K.; El-Hallous, E.; Lin, G.; Brinckmann, J.; John, H.; Bätge, B.; Notbohm, H.; Reinhardt, D.P. Consequences of cysteine mutations in calcium-binding epidermal growth factor modules of fibrillin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32924–32931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, F.; Dietz, H.C. Marfan syndrome: From molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2007, 17, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, G.; Lapini, I.; Evangelisti, L.; Attanasio, M.; Giusti, B.; Lucarini, L.; Fattori, R.; Pellicanò, G.; Scrivanti, M.; Porciani, M.C. Is ectopia lentis in some cases a mild phenotypic expression of Marfan syndrome? Need for a long-term follow-up. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Micheal, S.; Khan, M.I.; Akhtar, F.; Weiss, M.M.; Islam, F.; Ali, M.; Qamar, R.; Maugeri, A.; den Hollander, A.I. Identification of a novel FBN1 gene mutation in a large Pakistani family with Marfan syndrome. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dureau, P. Pathophysiology of zonular diseases. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2008, 19, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, D.V.; Bernard, S.E.; Lomas, A.; Morgan, A.; Humphries, J.; Shuttleworth, C.A.; Humphries, M.J.; Kielty, C.M. Cell adhesion to fibrillin-1 molecules and microfibrils is mediated by α5β1 and αvβ3 integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34605–34616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jovanović, J.; Takagi, J.; Choulier, L.; Abrescia, N.G.; Stuart, D.I.; van der Merwe, P.A.; Mardon, H.J.; Handford, P.A. αvβ6 is a novel receptor for human fibrillin-1: Comparative studies of molecular determinants underlying integrin-RGD affinity and specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6743–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neptune, E.R.; Frischmeyer, P.A.; Arking, D.E.; Myers, L.; Bunton, T.E.; Gayraud, B.; Ramirez, F.; Sakai, L.Y.; Dietz, H.C. Dysregulation of TGF-β activation contributes to pathogenesis in Marfan syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayraud, B.; Keene, D.R.; Sakai, L.Y.; Ramirez, F. New insights into the assembly of extracellular microfibrils from the analysis of the fibrillin 1 mutation in the tight skin mouse. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

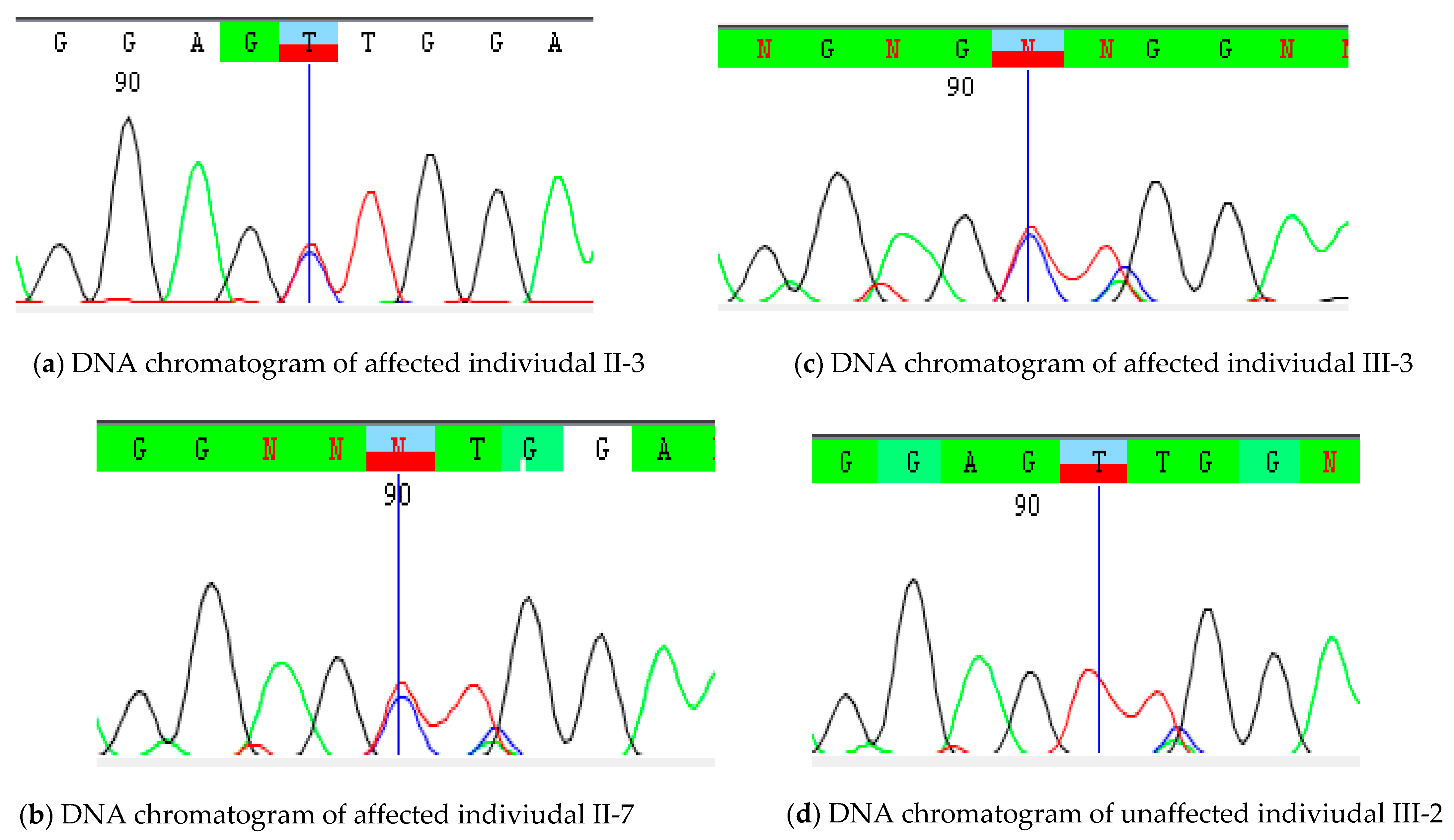
| Patients | II-3 | II-5 | II-7 | III-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 63 | 57 | 47 | 16 |
| Age at the time of onset | 58 | 53 | 42 | 16 |
| Gender | Male | Male | Male | Male |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||
| LVEDD (mm) | 46 | 50 | 53 | 42 |
| LVEF (%) | 65 | 71 | 59 | 60 |
| FS (%) | 35 | 40 | 32 | 36 |
| MV E (m/sec) | 0.86 ± 1.6 | 0.74 ± 1.4 | 0.83 ± 0.2 | 0.72 ± 1.9 |
| MV A (m/sec) | 0.56 ± 0.13 | 0.51 ± 0.11 | 0.47 ± 0.18 | 0.49 ± 0.15 |
| E/A ratio | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 1.6 ± 0.3 |
| DTE (msec) | 199 ± 32 | 171.6 ± 41.5 | 174.3 ± 63.2 | 165 ± 37.1 |
| IVRT (msec) | 73 ± 13 | 68 ± 15 | 72.4 ± 10 | 70.2 ± 14.1 |
| Mitral valve regurgitation | +1 | +1 | +1 | − |
| Skeletal system | ||||
| Height (cm) | 185 | 187 | 178 | 173.58 |
| Arm Span (cm) | 196.1 | 198.22 | 190.46 | 184 |
| Arm span to height ratio | 1.06 | 1.06 | 1.07 | 1.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farooqi, N.; Metherell, L.A.; Schrauwen, I.; Acharya, A.; Khan, Q.; Nouel Saied, L.M.; Ali, Y.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Jalil, F.; Leal, S.M. Exome Sequencing Identifies a Novel FBN1 Variant in a Pakistani Family with Marfan Syndrome That Includes Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction. Genes 2021, 12, 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121915
Farooqi N, Metherell LA, Schrauwen I, Acharya A, Khan Q, Nouel Saied LM, Ali Y, El-Serehy HA, Jalil F, Leal SM. Exome Sequencing Identifies a Novel FBN1 Variant in a Pakistani Family with Marfan Syndrome That Includes Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121915
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarooqi, Nadia, Louise A. Metherell, Isabelle Schrauwen, Anushree Acharya, Qayum Khan, Liz M. Nouel Saied, Yasir Ali, Hamed A. El-Serehy, Fazal Jalil, and Suzanne M. Leal. 2021. "Exome Sequencing Identifies a Novel FBN1 Variant in a Pakistani Family with Marfan Syndrome That Includes Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction" Genes 12, no. 12: 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121915
APA StyleFarooqi, N., Metherell, L. A., Schrauwen, I., Acharya, A., Khan, Q., Nouel Saied, L. M., Ali, Y., El-Serehy, H. A., Jalil, F., & Leal, S. M. (2021). Exome Sequencing Identifies a Novel FBN1 Variant in a Pakistani Family with Marfan Syndrome That Includes Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction. Genes, 12(12), 1915. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121915






