Quantitative Phosphoproteomics of cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and Wild Type in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
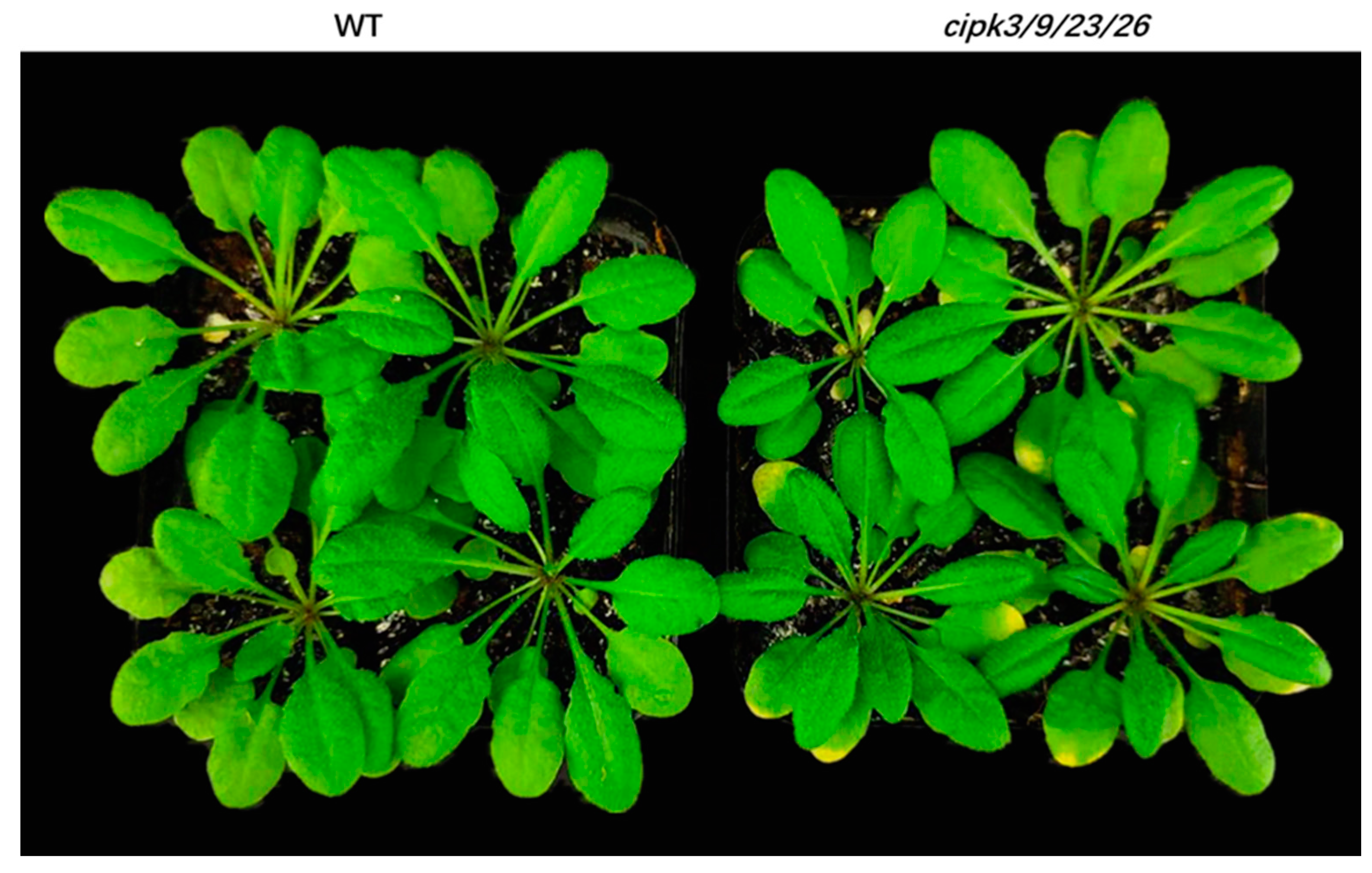
2.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
2.2. Protein Extraction and Trypsin Digestion
2.3. TMT Labeling and Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Fractionation
2.4. Modified Enrichment and LC-MS/MS Analyses
2.5. Database Search and LC-MS/MS Data Analyses
3. Results
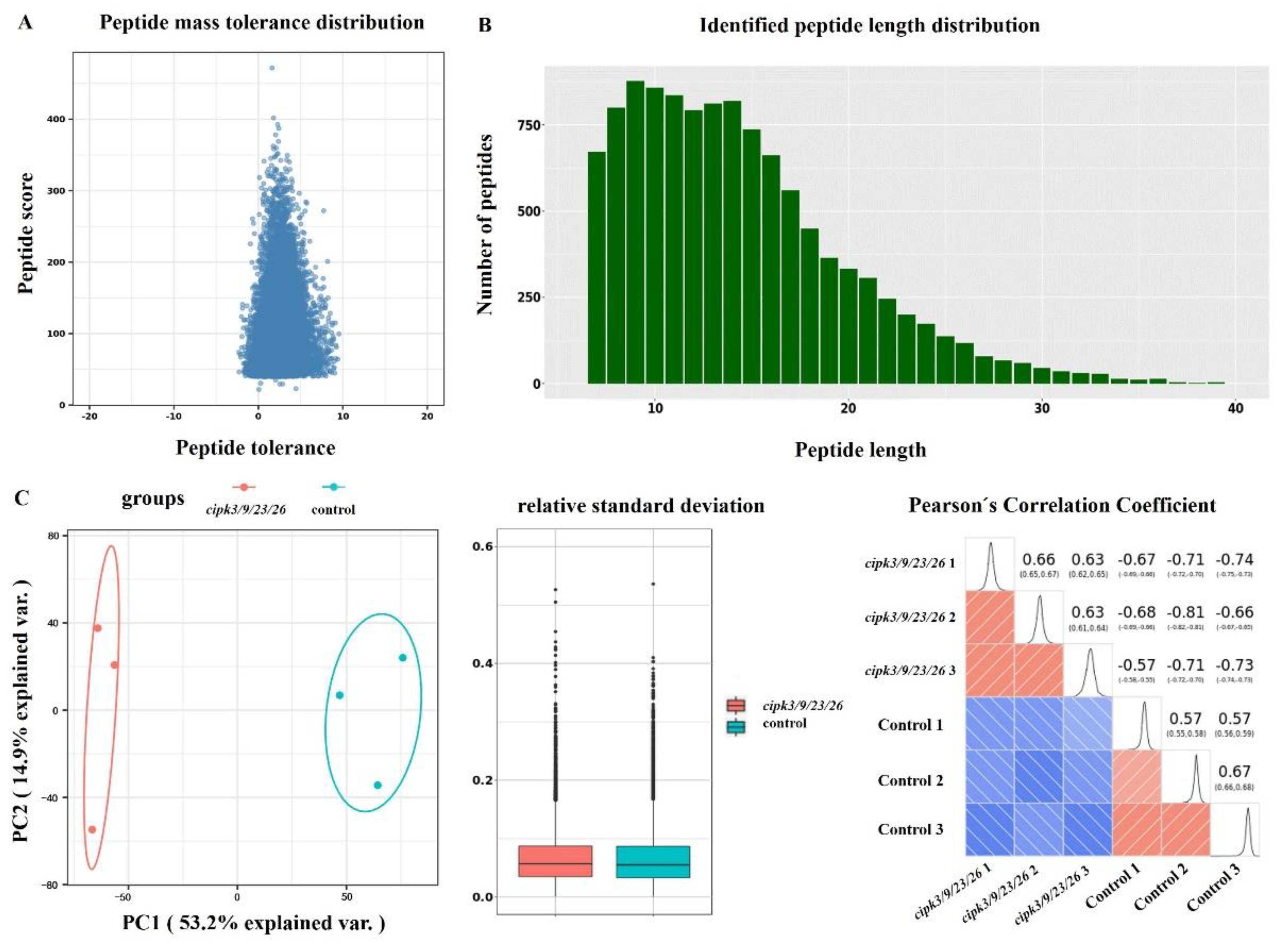
3.1. Quantitative Phosphoproteomic Data Analysis
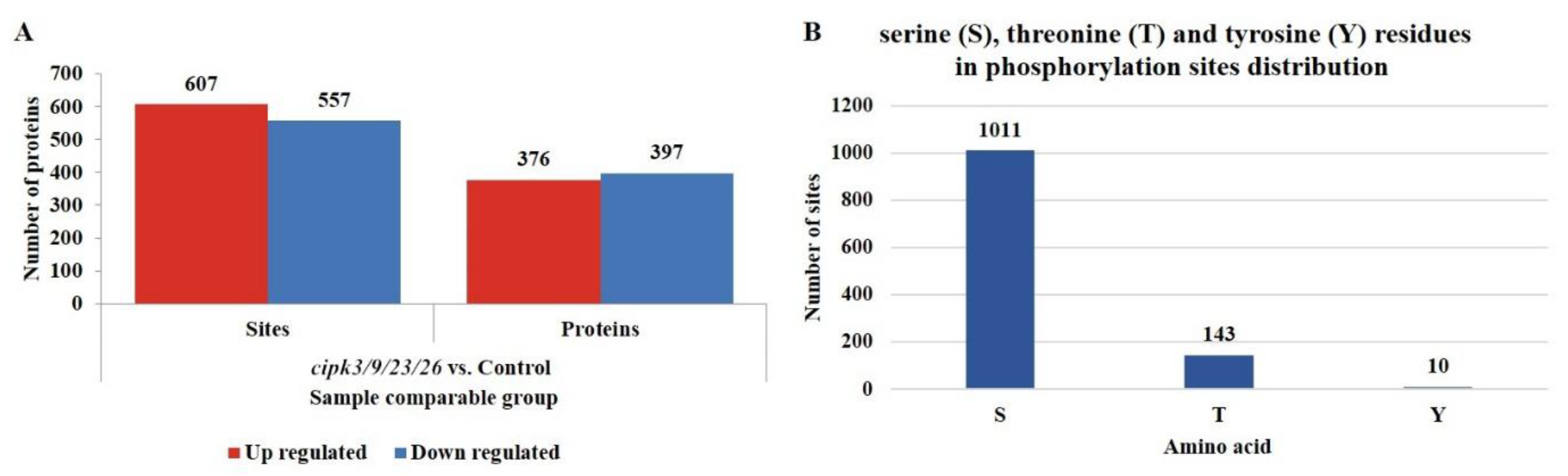
3.2. Identification of Differential Phosphorylation Modification Sites and Proteins in the cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and WT
3.3. Motif Analysis of cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant Phosphoprotein Modification
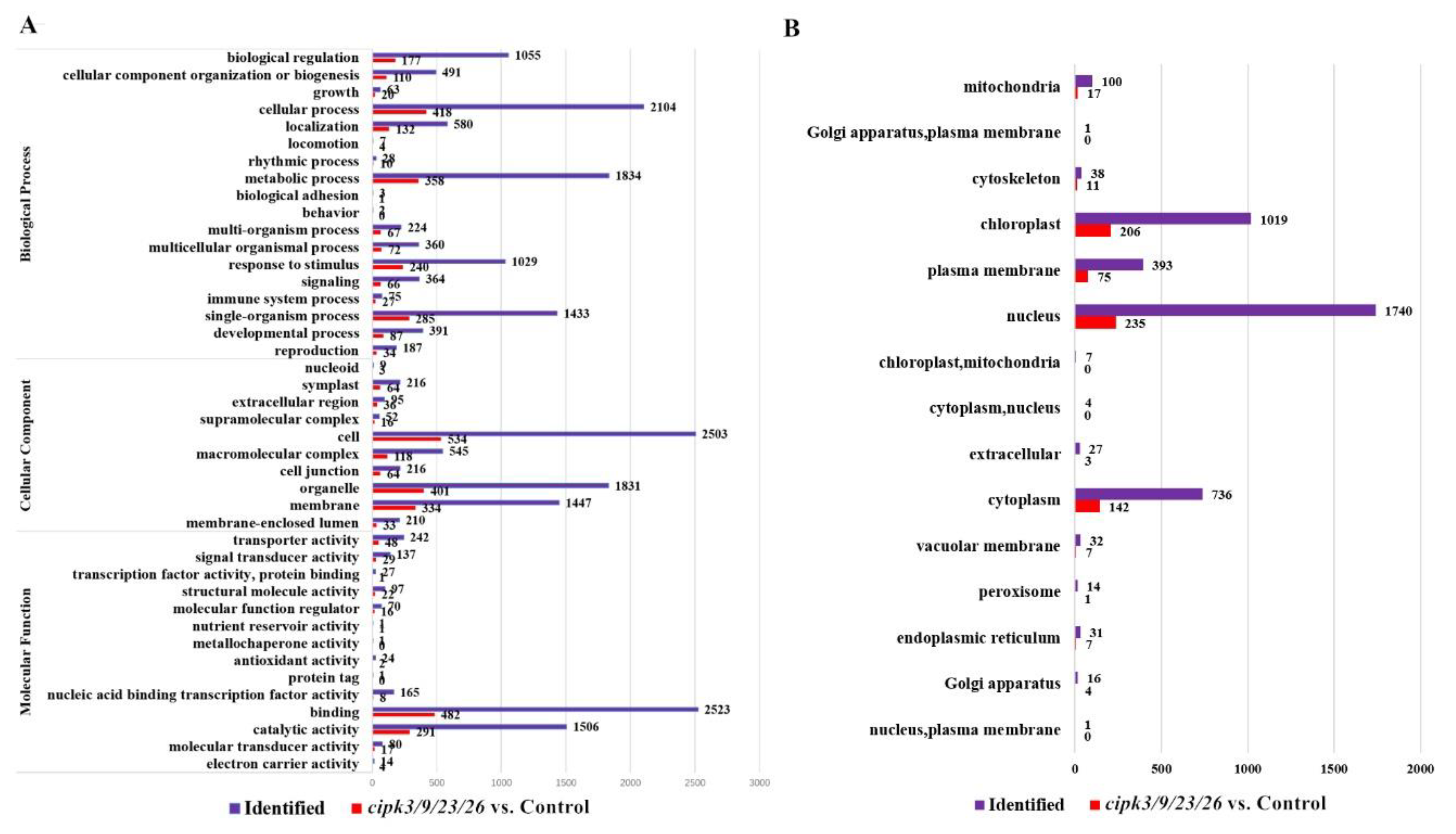
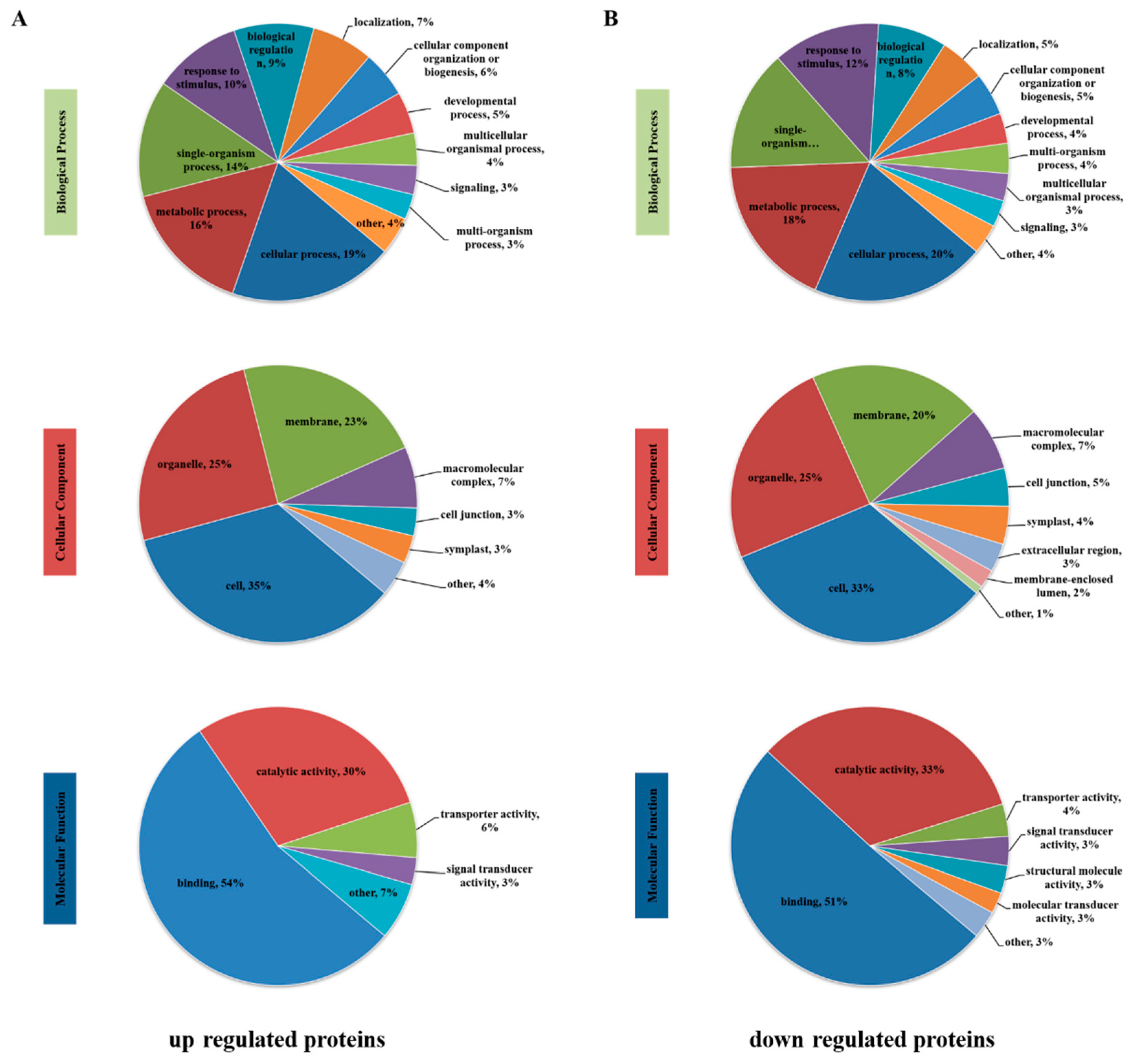
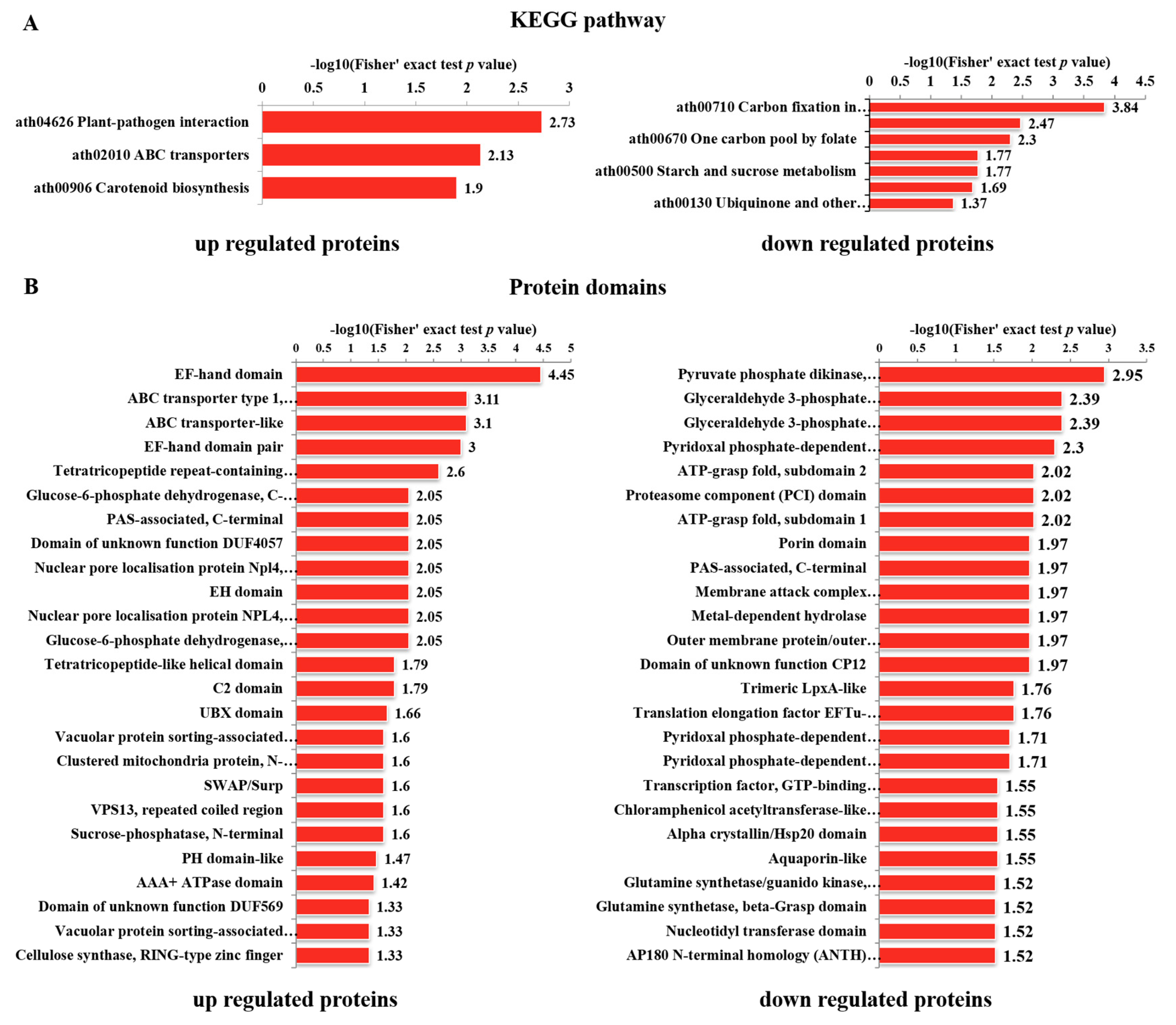
3.4. Functional Classification of Differentially Phosphorylated Proteins
3.5. Differential Expression of Related Phosphoproteins between the cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and WT
3.6. Enrichment Analyses of DPPs
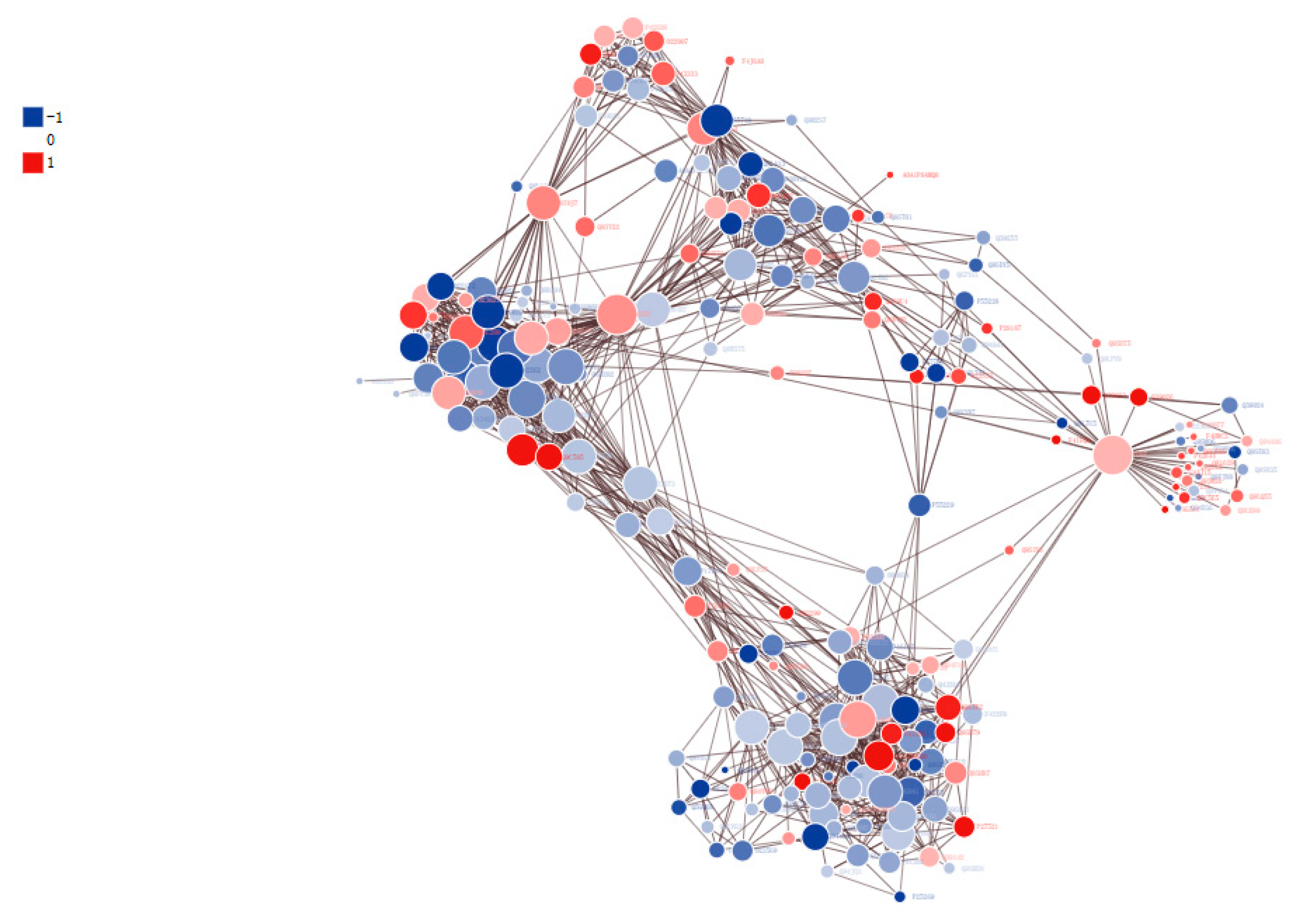
3.7. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks of DPPs
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of the Cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant to Magnesium Toxicity
4.2. Transport-Related Proteins
4.3. Signal Transduction and Protein Kinases
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grusak, M.A.; Broadley, M.R.; White, P.J. Plant macro-and micronutrient minerals. In Encyclopedia Life Sciences; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, S. The CBL–CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Kanwar, P.; Singh, A.; Steinhorst, L.; Pandey, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Tokas, I.; Sanyal, S.K.; Kim, B.-G.; Lee, S.-C.; et al. Calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase CIPK21 regulates osmotic and salt stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Kanwar, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Sharma, C.; Kumar, A.; Pandey, G.K. Arabidopsis CBL interacting protein kinase 3 interacts with ABR1, an APETALA2 domain transcription factor, to regulate ABA responses. Plant Sci. 2017, 254, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerendás, J.; Führs, H. The significance of magnesium for crop quality. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhao, F.-G.; Garcia, V.J.; Kleist, T.J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.-X.; Luan, S. Tonoplast CBL-CIPK calcium signaling network regulates magnesium homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3134–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogami, J.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Tsukiori, Y.; Nakagami, H.; Nomura, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Nishida, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Ishida, T.; et al. Two distinct families of protein kinases are required for plant growth under high external Mg2+ concentrations in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1039–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Hou, Y.; Tong, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Nallamilli, B.R.; Zhang, J. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of early seed development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Li, J.; Koh, J.; Dufresne, C.; Yang, N.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Duong, B.V.; Chen, S.; et al. Quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics of sugar beet monosomic addition line M14 in response to salt stress. J. Proteom. 2016, 143, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, X.; Qiu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.; Hou, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J. A phosphoproteomic landscape of rice (Oryza sativa) tissues. Physiol. Plant 2017, 160, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, D.; Konrad, K.R.; Bemm, F.; Nebioglu, M.G.P.; Lorey, C.; Duscha, K.; Güthoff, T.; Herrmann, J.; Ferjani, A.; Cuin, T.A.; et al. High V-PPase activity is beneficial under high salt loads, but detrimental without salinity. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, H.; Burla, B.; Kretzschmar, T.; Lee, Y.; Martinoia, E. Plant ABC transporters. Arab. Book 2011, 9, e0153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidler, M.; Hassa, P.O.; Hasan, S.; Ringli, C.; Dudler, R. Involvement of an ABC transporter in a developmental pathway regulating hypocotyl cell elongation in the light. Plant Cell. 1998, 10, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.R.; Miller, N.D.; Splitt, B.L.; Wu, G.; Spalding, E.P. Separating the roles of acropetal and basipetal auxin transport on gravitropism with mutations in two Arabidopsis multidrug resistance-like ABC transporter genes. Plant Cell. 2007, 19, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, M.; Schuetz, M.; Lin, B.S.; Chanis, C.; Hamberger, B.; Western, T.L.; Ehlting, J.; Samuels, A.L. ABC transporters coordinately expressed during lignification of Arabidopsis stems include a set of ABCBs associated with auxin transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, M.; Yang, H.; Richter, G.L.; Cheng, Y.; Mlodzinska, E.; Wang, X.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Carraro, N.; Petrasek, J.; Zazimalova, E.; et al. The Arabidopsis concentration-dependent influx/efflux transporter ABCB4 regulates cellular auxin levels in the root epidermis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenness, M.K.; Carraro, N.; Pritchard, C.A.; Murphy, A.S. The Arabidopsis ATP-BINDING CASSETTE transporter ABCB21 Regulates auxin levels in cotyledons, the root pericycle, and leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanke, D.; Üner Kolukisaoglu, H. An update on the ABCC transporter family in plants: Many genes, many proteins, but how many functions? Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Miller, A.J.; Zhao, F.-J. The C-type ATP-binding cassette transporter OsABCC7 is involved in the root-to-shoot translocation of arsenic in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, C.A.; Hanselaer, S.; Soares, E.V. ABCC subfamily vacuolar transporters are involved in Pb (lead) detoxification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasinski, M.; Banasiak, J.; Radom, M.; Kalitkiewicz, A.; Figlerowicz, M. Full-size ABC transporters from the ABCG subfamily in Medicago truncatula. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ruocco, M.; Ambrosino, P.; Lanzuise, S.; Woo, S.L.; Lorito, M. Four potato (Solanum tuberosum) ABCG transporters and their expression in response to abiotic factors and Phytophthora infestans infection. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhara, A.; Raichaudhuri, A. ABCG transporter proteins with beneficial activity on plants. Phytochemistry. 2021, 184, 112663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickerton, P.D.; Pittman, J.K. Role of cation/proton exchangers in abiotic stress signaling and stress tolerance in plants. In Elucidation of Abiotic Stress Signaling in Plants; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 95–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Ji, W.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Bai, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y. GsAPK, an ABA-activated and calcium-independent SnRK2-type kinase from G. soja, mediates the regulation of plant tolerance to salinity and ABA stress. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Liu, J.; Bi, D.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. MEKK1, MKK1/MKK2 and MPK4 function together in a mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to regulate innate immunity in plants. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Qu, N.; Gao, M.H.; Zhang, Z.B.; Ding, X.J.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.Z.; Dong, O.X.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; et al. The MEKK1-MKK1/MKK2-MPK4 kinase cascade negatively regulates immunity mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, J.; Kong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ba, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Disruption of PAMP-induced MAP kinase cascade by a Pseudomonas syringae effector activates plant immunity mediated by the NB-LRR protein SUMM2. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Z.; Wang, P.C.; Si, T.; Hsu, C.C.; Wang, L.; Zayed, O.; Yu, Z.P.; Zhu, Y.F.; Dong, J.; Tao, W.A.; et al. MAP kinase cascades regulate the cold response by modulating ICE1 protein stability. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 618–629.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.C.; Wang, Z.-R.; Jiang, X.-X.; Shi, Y.-F.; Tian, S.-N.; Braun, E.; Mei, Y.; Qiu, W.-L.; et al. The MAPK kinase kinase GmMEKK1 regulates cell death and defense responses. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Bian, C.; Guo, X.; Di, R.; Dong, J. The MAPK substrate MASS proteins regulate stomatal development in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Brownlee, C.; Hetherington, A.M. Calcium ions as second messengers in guard cell signal transduction. Physiol. Plant. 1997, 100, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.C.; Chung, W.S.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, K.J.; Park, H.C.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, M.J. Involvement of specific calmodulin isoforms in salicylic acid-independent activation of plant disease resistance responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yang, T.; Li, W.M.J. Calmodulin gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and Botrytis cinerea infection in tomato fruit. Plants 2014, 3, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Gilroy, S.; Chehab, E.W.; Braam, J. CML24 is involved in root mechanoresponses and cortical microtubule orientation in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 30, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, M.; Qiao, Z.; Bao, C.-C.; Zhang, W. Arabidopsis thaliana calmodulin-like protein CML24 regulates pollen tube growth by modulating the actin cytoskeleton and controlling the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cheval, C.; Laohavisit, A.; Hocking, B.; Chiasson, D.; Olsson, T.S.G.; Shirasu, K.; Faulkner, C.; Gilliham, M. A calmodulin-like protein regulates plasmodesmal closure during bacterial immune responses. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, I.C.; Murata, Y.; Yang, Y.; Munemasa, S.; Wang, Y.-F.; Andreoli, S.; Tiriac, H.; Alonso, J.M.; Harper, J.F.; Ecker, J.R.; et al. CDPKs CPK6 and CPK3 function in ABA regulation of guard cell S-type anion-and Ca2+-permeable channels and stomatal closure. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.J.; Wei, F.J.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.-J.; Ratnasekera, D.; Liu, W.-X.; Wu, W.-H. Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK10 functions in abscisic acid-and Ca2+-mediated stomatal regulation in response to drought stress. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, S.; Ehlert, B.; Liese, A.; Kurth, J.; Cazalé, A.-C.; Romeis, T. Calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK21 functions in abiotic stress response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Hu, W.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Luo, Q.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, S.; Sun, T.; et al. A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK9 positively regulates drought stress tolerance and spikelet fertility. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Hakata, M.; Nakamura, H.; Aoki, N.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Hirochika, H.; Ohsugi, R. Functional characterisation of OsCPK21, a calcium-dependent protein kinase that confers salt tolerance in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 75, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatek, K.N.; Wilson, R.S.; Ahsan, N.; Tritz, R.L.; Thelen, J.J. Multisite phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins by calcium-dependent protein kinases. Biochem. J. 2014, 459, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Motif | Motif Score | Foreground | Background | Fold Increase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matches | Size | Matches | Size | |||
| xxxxPx_S_PxRxxx | 39.87 | 61 | 8351 | 255 | 952,659 | 27.3 |
| xxxxPx_S_PRxxxx | 40.29 | 53 | 8290 | 219 | 952,404 | 27.8 |
| xxxxPx_S_PKxxxx | 39.63 | 41 | 8237 | 169 | 952,185 | 28.0 |
| xxxxxx_S_PRxxxx | 32.00 | 300 | 8196 | 2586 | 952,016 | 13.5 |
| xxxxPx_S_Pxxxxx | 32.00 | 281 | 7896 | 3314 | 949,430 | 10.2 |
| xxxxxx_S_PxRxxx | 32.00 | 246 | 7615 | 2235 | 946,116 | 13.7 |
| xxxRxx_S_PxPxxx | 38.69 | 47 | 7369 | 229 | 943,881 | 26.3 |
| xxxxxx_S_PxxxRx | 32.00 | 199 | 7322 | 2288 | 943,652 | 11.2 |
| xxxxxx_S_PKxxxx | 29.51 | 163 | 7123 | 2114 | 941,364 | 10.2 |
| xxxRSx_S_xPxxxx | 38.04 | 45 | 6960 | 388 | 939,250 | 15.7 |
| xxxxxx_S_PxxxxR | 30.02 | 149 | 6915 | 1948 | 938,862 | 10.4 |
| xLxRxx_S_xxxxxx | 32.00 | 292 | 6766 | 5590 | 936,914 | 7.2 |
| xxxxxR_S_Pxxxxx | 27.82 | 112 | 6474 | 1486 | 931,324 | 10.8 |
| xxxxxG_S_Pxxxxx | 27.98 | 124 | 6362 | 1797 | 929,838 | 10.1 |
| xxxRSx_S_xxxxxx | 32.00 | 234 | 6238 | 5119 | 928,041 | 6.8 |
| xxxxxx_S_PxxRxx | 25.38 | 93 | 6004 | 1423 | 922,922 | 10.0 |
| xxxxxx_S_Pxxxxx | 16.00 | 930 | 5911 | 29,886 | 921,499 | 4.9 |
| xxxRxx_S_Fxxxxx | 32.00 | 116 | 4981 | 1886 | 891,613 | 11.0 |
| xxxRxx_S_xDxxxx | 28.35 | 85 | 4865 | 1907 | 889,727 | 8.2 |
| xxxxxx_S_DDExxx | 38.28 | 46 | 4780 | 478 | 887,820 | 17.9 |
| xxxxxx_S_DGExxx | 39.07 | 28 | 4734 | 235 | 887,342 | 22.3 |
| xMxRxx_S_xxxxxx | 25.45 | 48 | 4706 | 986 | 887,107 | 9.2 |
| xxxxxx_S_DxExxx | 32.00 | 112 | 4658 | 3395 | 886,121 | 6.3 |
| xxxRxx_S_xPxxxx | 24.23 | 63 | 4546 | 1741 | 882,726 | 7.0 |
| xxxxxG_S_Gxxxxx | 25.21 | 99 | 4483 | 5462 | 880,985 | 3.6 |
| xLxKSx_S_xxxxxx | 38.37 | 29 | 4384 | 497 | 875,523 | 11.7 |
| xxxxxD_S_DxDxxx | 39.45 | 37 | 4355 | 422 | 875,026 | 17.6 |
| xxxRxx_S_xExxxx | 23.85 | 65 | 4318 | 2050 | 874,604 | 6.4 |
| xxxKxx_S_Fxxxxx | 32.00 | 85 | 4253 | 2802 | 872,554 | 6.2 |
| xxxRxx_S_xGxxxx | 32.00 | 66 | 4168 | 2312 | 869,752 | 6.0 |
| xxxxxx_S_ExExxx | 32.00 | 105 | 4102 | 5008 | 867,440 | 4.4 |
| xxxxxx_S_DxGxxx | 24.52 | 55 | 3997 | 2966 | 862,432 | 4.0 |
| xxxxxx_S_DxDxxx | 32.00 | 86 | 3942 | 3168 | 859,466 | 5.9 |
| xxxxxG_S_Fxxxxx | 25.25 | 52 | 3856 | 2487 | 856,298 | 4.6 |
| xxxxRx_S_xDxxxx | 26.26 | 54 | 3804 | 2257 | 853,811 | 5.4 |
| xxxxxx_S_ExGxxx | 24.29 | 53 | 3750 | 3143 | 851,554 | 3.8 |
| xLxKxx_S_xxxxxx | 24.76 | 71 | 3697 | 4574 | 848,411 | 3.6 |
| xxxxSx_S_Fxxxxx | 29.03 | 68 | 3626 | 4094 | 843,837 | 3.9 |
| xxxxxG_S_xxxxxx | 16.00 | 338 | 3558 | 47,187 | 839,743 | 1.7 |
| xxxRxx_S_xxxxxx | 16.00 | 314 | 3220 | 25,377 | 792,556 | 3.0 |
| xxxxSR_S_xxxxxx | 24.33 | 54 | 2906 | 4112 | 767,179 | 3.5 |
| xxxxxx_S_xExxxx | 16.00 | 303 | 2852 | 43,739 | 763,067 | 1.9 |
| xxxxxx_S_xGxxxx | 16.00 | 285 | 2549 | 48,192 | 719,328 | 1.7 |
| xxxxxx_S_xPxSPx | 39.01 | 29 | 2264 | 388 | 671,136 | 22.2 |
| xxxxxx_S_xDxxxx | 16.00 | 261 | 2235 | 37,147 | 670,748 | 2.1 |
| xxxxxx_S_GPLxxx | 39.06 | 24 | 1974 | 245 | 633,601 | 31.4 |
| xxRxxx_S_xPxxxx | 23.73 | 34 | 1950 | 2060 | 633,356 | 5.4 |
| xxxxRx_S_xSxxxx | 29.92 | 74 | 1916 | 4763 | 631,296 | 5.1 |
| xxxxxx_S_FRxxxx | 27.42 | 33 | 1842 | 1453 | 626,533 | 7.7 |
| RxxSxx_S_xxxxxx | 20.27 | 49 | 1809 | 4205 | 625,080 | 4.0 |
| xxxxxD_S_xxxxxx | 12.49 | 167 | 1760 | 32,542 | 620,875 | 1.8 |
| xxxxxx_S_xPxxxx | 13.05 | 172 | 1593 | 34,988 | 588,333 | 1.8 |
| xxxKxx_S_xxxxxx | 10.30 | 139 | 1421 | 30,182 | 553,345 | 1.8 |
| xxxxxx_S_xRxxxx | 12.48 | 149 | 1282 | 32,477 | 523,163 | 1.9 |
| xxxxxx_S_Fxxxxx | 9.38 | 99 | 1133 | 21,946 | 490,686 | 2.0 |
| xxxxSx_S_xNxxxx | 15.13 | 31 | 1034 | 3443 | 468,740 | 4.1 |
| xxxxxx_S_Dxxxxx | 7.27 | 82 | 1003 | 20,145 | 465,297 | 1.9 |
| xxxxxx_S_xxGxxx | 7.96 | 98 | 921 | 25,916 | 445,152 | 1.8 |
| xxxxxx_S_xKxxxx | 8.29 | 115 | 823 | 33,536 | 419,236 | 1.7 |
| xxxxPx_T_Pxxxxx | 32.00 | 143 | 1057 | 2335 | 529,615 | 30.7 |
| xxxxxx_T_PxRxxx | 27.88 | 63 | 914 | 1278 | 527,280 | 28.4 |
| xxxxxx_T_PRxxxx | 24.65 | 48 | 851 | 1115 | 526,002 | 26.6 |
| xxxxxx_T_PTxxxx | 24.66 | 54 | 803 | 1470 | 524,887 | 24.0 |
| xxxxxx_T_PKxxxx | 23.80 | 47 | 749 | 1406 | 523,417 | 23.4 |
| xxxxxx_T_Pxxxxx | 16.00 | 239 | 702 | 19,445 | 522,011 | 9.1 |
| xxxRxx_T_xxxxxx | 16.00 | 83 | 463 | 25,391 | 502,566 | 3.5 |
| xxxxxx_T_xExxxx | 10.57 | 63 | 380 | 31,767 | 477,175 | 2.5 |
| xxxxxx_T_Dxxxxx | 6.44 | 38 | 317 | 21,640 | 445,408 | 2.5 |
| Protein Accession | Position | Ratio | Protein Description | Modified Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9ZR72 | 1014 | 1.49 | ABC transporter B family member 1 | KTEIEPDDPDT(0.203)T(0.797)PVPDR |
| Q9ZR72 | 642 | 1.386 | ABC transporter B family member 1 | NS(0.016)S(0.979)Y(0.005)GRS(0.965)PY(0.005)S(0.03)R |
| Q9LJX0 | 624 | 1.262 | ABC transporter B family member 19 | T(0.157)RS(0.831)T(0.094)RLS(0.917)HS(0.32)LS(0.672)T(0.008)K |
| Q9LJX0 | 620 | 1.405 | ABC transporter B family member 19 | T(0.157)RS(0.831)T(0.094)RLS(0.917)HS(0.32)LS(0.672)T(0.008)K |
| Q9LJX0 | 611 | 1.335 | ABC transporter B family member 19 | DFS(0.999)NPS(0.001)TR |
| Q9M1Q9 | 660 | 1.554 | ABC transporter B family member 21 | LSMES(1)MKR |
| Q0WML0 | 639 | 1.252 | ABC transporter B family member 27 | QLQS(0.009)S(0.086)S(0.889)S(0.016)VTTL |
| Q9C8G9 | 1485 | 1.778 | ABC transporter C family member 1 | S(0.007)IT(0.993)LENKR |
| Q9LZJ5 | 897 | 1.403 | ABC transporter C family member 14 | SIS(1)IES(1)PRQPKS(1)PK |
| Q9LZJ5 | 894 | 1.615 | ABC transporter C family member 14 | SIS(1)IES(1)PRQPKS(1)PK |
| Q9LZJ5 | 903 | 1.345 | ABC transporter C family member 14 | SIS(1)IES(1)PRQPKS(1)PK |
| Q9C8K2 | 667 | 1.237 | ABC transporter G family member 12 | KVPS(0.003)LS(0.162)S(0.162)LS(0.68)S(0.994)RR |
| Q9C8K2 | 666 | 1.289 | ABC transporter G family member 12 | KVPSLS(0.003)S(0.009)LS(0.9)S(0.088)RR |
| Q9C8K2 | 661 | 1.245 | ABC transporter G family member 12 | KVPS(0.999)LS(0.002)S(0.009)LS(0.829)S(0.162)R |
| Q93YS4 | 71 | 1.29 | ABC transporter G family member 22 | LMGMS(0.996)PGRS(0.175)S(0.806)GAGT(0.022)HIR |
| Q93YS4 | 66 | 1.428 | ABC transporter G family member 22 | RLMGMS(1)PGR |
| Q9XIE2 | 40 | 1.266 | ABC transporter G family member 36 | NIEDIFSS(0.003)GS(0.997)R |
| A0A1P8AZ84 | 586 | 2.017 | p-glycoprotein 6 | QKS(0.888)NGS(0.116)DPES(0.988)PIS(0.007)PLLISDPQNER |
| A0A1P8AZ84 | 610 | 1.419 | p-glycoprotein 6 | S(0.002)HS(0.997)QT(0.001)FSRPLGHSDDTSASVK |
| A0A1P8AZ84 | 593 | 1.548 | p-glycoprotein 6 | QKS(0.888)NGS(0.116)DPES(0.988)PIS(0.007)PLLISDPQNER |
| Q9S7Z8 | 235 | 1.326 | Auxin efflux carrier component 3 | PSNLTGAEIYS(1)LS(0.003)T(0.201)T(0.797)PR |
| F4IS06 | 38 | 1.674 | Vacuolar cation/proton exchanger | TAHNMS(0.993)S(0.119)S(0.539)S(0.348)LRK |
| Q9ZV07 | 282 | 1.214 | Probable aquaporin PIP2-6 | S(1)QLHELHA |
| A0A1P8AU30 | 30 | 1.27 | Cationic amino acid transporter 9 | S(0.012)KS(0.986)LPPPS(0.001)S(0.001)QT(0.001)AVR |
| Q9ZTZ7 | 120 | 1.733 | K(+) efflux antiporter 1, chloroplastic | IGES(0.002)S(0.013)ES(0.864)S(0.121)DETEATDLK |
| Q8W4J2 | 527 | 1.374 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 16 | T(0.237)QPCKS(0.763)NRGDEDCATAAEGPSR |
| Q94A06 | 27 | 1.235 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | FLT(0.096)QS(0.9)GT(0.005)FKDGDLR |
| Q9C9U4 | 530 | 1.742 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 15 | ASQQAEGTENGGGGGYS(1)AR |
| Q39026 | 221 | 2.126 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | VTSESDFMT(1)EY(1)VVTR |
| Q39026 | 223 | 2.106 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 | VTSESDFMT(1)EY(1)VVTR |
| Q39023 | 198 | 2.156 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | PTSENDFMT(1)EY(1)VVTR |
| Q39023 | 196 | 2.309 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 | PTSENDFMT(1)EY(1)VVTR |
| Q39024 | 195 | 0.637 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 | T(0.036)KS(0.908)ET(0.056)DFMTEYVVTR |
| Q9SSC1 | 98 | 1.208 | MAPK kinase substrate protein At1g80180 | VS(1)PAVDPPS(1)PR |
| Q9SSC1 | 16 | 1.429 | MAPK kinase substrate protein At1g80180 | RQGS(1)S(1)GIVWDDR |
| Q9SSC1 | 17 | 1.33 | MAPK kinase substrate protein At1g80180 | RQGS(1)S(1)GIVWDDR |
| Q9SSC1 | 82 | 0.464 | MAPK kinase substrate protein At1g80180 | S(0.013)RS(0.987)NGGGAIR |
| F4IVN6 | 80 | 1.251 | Calmodulin 5 | MKDT(0.998)DS(0.002)EEELK |
| F4IVN6 | 82 | 1.21 | Calmodulin 5 | MKDT(0.017)DS(0.983)EEELK |
| P30188 | 27 | 1.812 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML35 | AS(0.008)VS(0.183)RS(0.803)EPS(0.501)S(0.501)FS(0.002)S(0.002)NASSSSSDGSYGNLK |
| P30188 | 11 | 0.765 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML35 | LAASLNRLS(1)PK |
| P30188 | 44 | 0.208 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML35 | SEPSSFSSNASSSSSDGS(1)YGNLK |
| P25070 | 46 | 1.215 | Calcium-binding protein CML24 | ALS(0.937)PT(0.059)AS(0.004)PEETVTMMK |
| Q8L3R2 | 159 | 0.593 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML41 | GSGCIT(1)PK |
| Q8L3R2 | 26 | 1.321 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML41 | LNLS(1)FQNR |
| Q8L3R2 | 47 | 0.566 | Probable calcium-binding protein CML41 | SNSS(0.001)S(0.003)T(0.017)LNS(0.98)PRS(1)NSDDNNNIK |
| Q38868 | 69 | 1.208 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 9 | AAAAAPGLS(1)PK |
| Q38868 | 51 | 1.627 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 9 | TTQQPEKPGS(0.997)VNS(0.003)QPPPWR |
| Q38868 | 78 | 1.889 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 9 | S(0.001)NS(0.999)ILENAFEDVK |
| Q9ZSA2 | 244 | 0.432 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 21 | DIVGS(1)AYYVAPEVLR |
| Q9ZSA2 | 53 | 1.322 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 21 | PMTQPIHQQIS(0.964)T(0.036)PSSNPVSVR |
| Q9ZSA2 | 414 | 1.449 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 21 | LGS(0.997)RLS(0.003)ETEVK |
| Q9ZSA2 | 417 | 0.744 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 21 | LS(0.971)ET(0.029)EVK |
| Q9M9V8 | 40 | 0.394 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 10 | LNPFAGDFT(0.002)RS(0.998)PAPIR |
| Q8W4I7 | 18 | 0.712 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 13 | EDVKS(1)NY(0.001)S(0.999)GHDHAR |
| Q8W4I7 | 21 | 0.454 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 13 | SNYS(1)GHDHAR |
| Q8W4I7 | 43 | 0.511 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 13 | VLS(1)DVPKENIEDR |
| Q42479 | 18 | 1.485 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 3 | SSDPPPSS(0.005)S(0.768)S(0.175)S(0.041)S(0.009)S(0.002)GNVVHHVKPAGER |
| Q06850 | 130 | 0.778 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 | RVS(0.076)S(0.924)AGLR |
| Q06850 | 64 | 1.878 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 | LSDEVQNKPPEQVT(0.997)MPKPGT(0.003)DVETK |
| Q06850 | 129 | 0.549 | Calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 | RVS(0.994)S(0.006)AGLR |
| P46077 | 248 | 1.31 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 phi | DNLTLWTSDMQDES(1)PEEIKEAAAPKPAEEQK |
| P42644 | 238 | 1.575 | 14-3-3-like protein GF14 psi | DNLTLWTSDMT(1)DEAGDEIK |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhen, Y. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics of cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and Wild Type in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes 2021, 12, 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111759
Yin Z, Shi J, Zhen Y. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics of cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and Wild Type in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes. 2021; 12(11):1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111759
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Ziyi, Jisen Shi, and Yan Zhen. 2021. "Quantitative Phosphoproteomics of cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and Wild Type in Arabidopsis thaliana" Genes 12, no. 11: 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111759
APA StyleYin, Z., Shi, J., & Zhen, Y. (2021). Quantitative Phosphoproteomics of cipk3/9/23/26 Mutant and Wild Type in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes, 12(11), 1759. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111759






