Novel Mutations in CLPP, LARS2, CDH23, and COL4A5 Identified in Familial Cases of Prelingual Hearing Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Exome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analyses
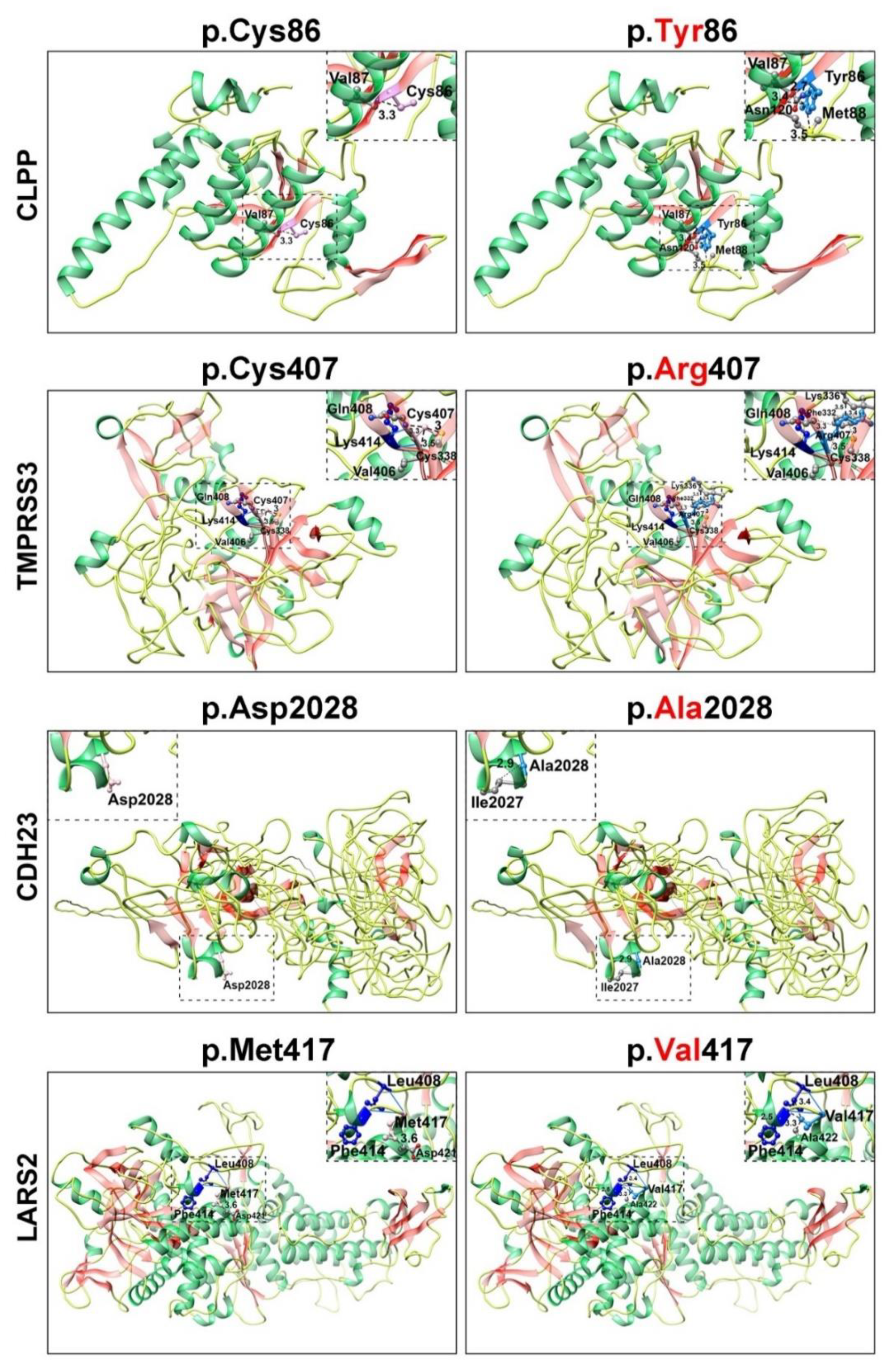
2.3. Structural Modeling
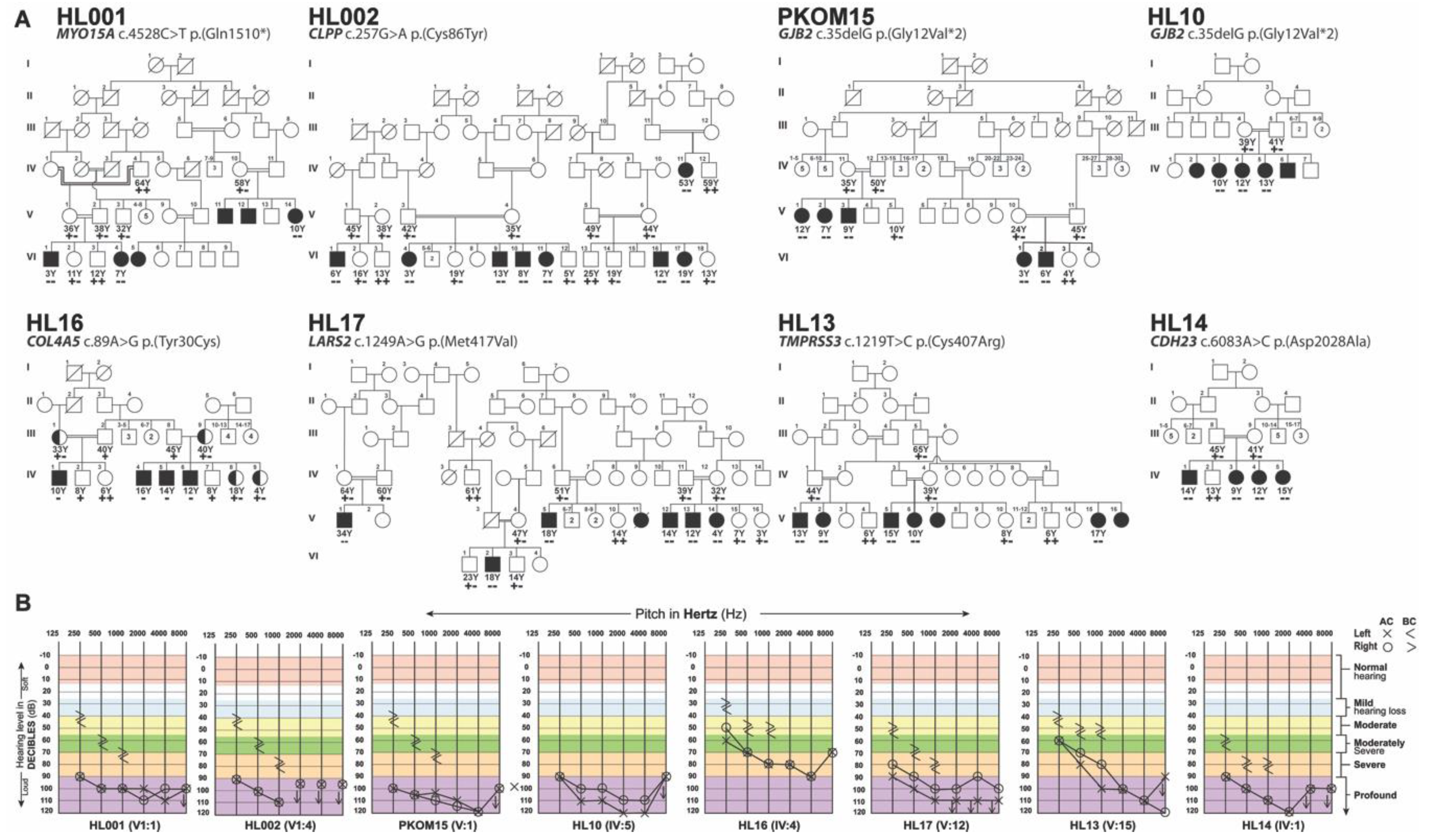
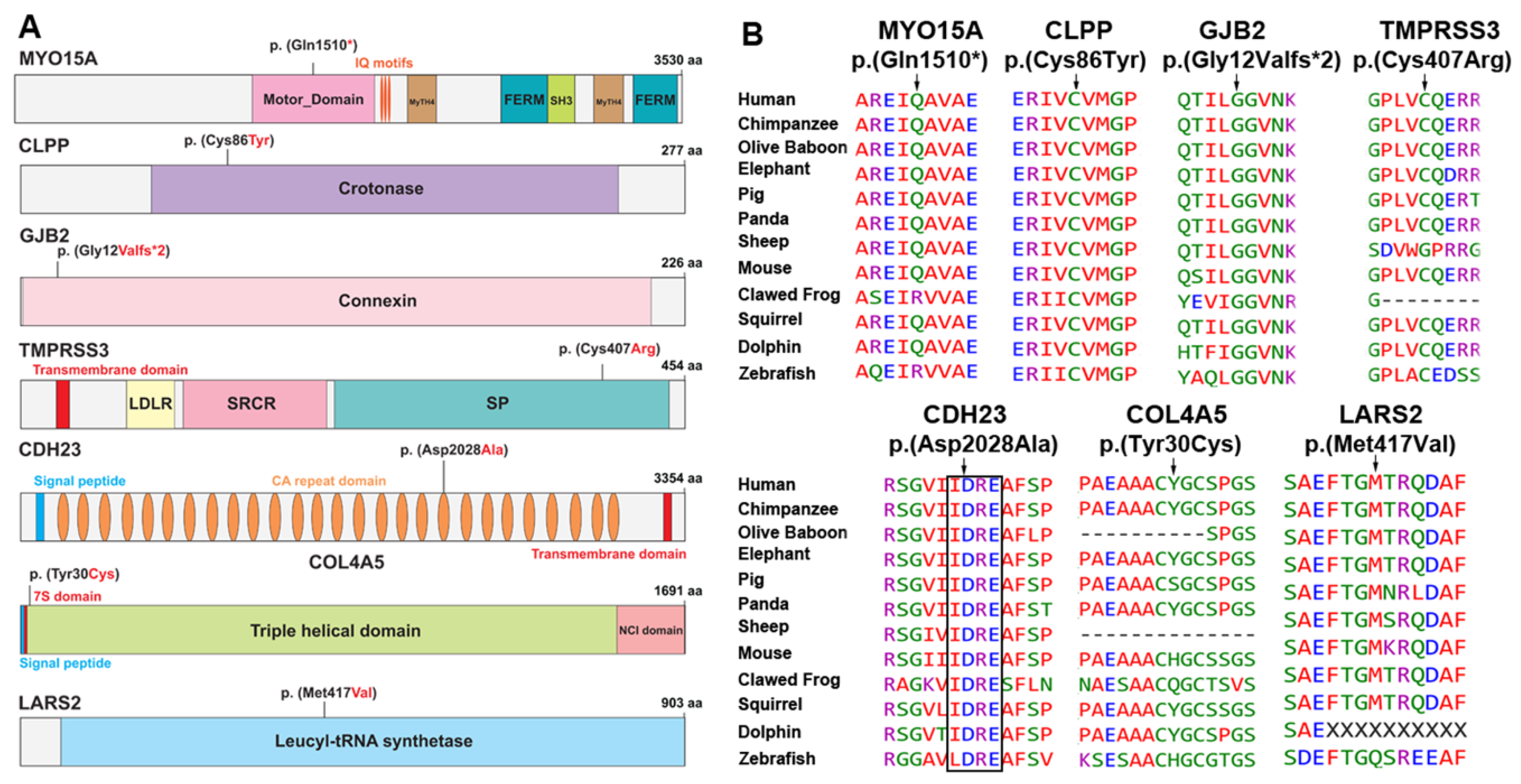
3. Results
| Family | Gene | cDNA Change | Protein Change | CADD | ExAC | Mutation Taster | Mutation Assessor | Polyphen 2 | SIFT | ACMG Classification (Criteria Used) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HL001 | MYO15A | c.4528C>T | p.(Gln1510*) | 42 | 8 × 10−6 | Disease causing | N/A | N/A | N/A | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5) | [30] |
| HL002 | CLPP | c.257G>A | p.(Cys86Tyr) | 33 | 0 | Disease causing | Low | Probably damaging | Damaging | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP3) | This study |
| HL10 | GJB2 | c.35delG | p.(Gly12Valfs*2) | N/A | 0.006 | Disease causing | Medium | Probably damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PVS1, PS3, PM1, PP3, BS2) | [31] |
| PKOM15 | GJB2 | c.35delG | p.(Gly12Valfs*2) | N/A | 0.006 | Disease causing | Medium | Probably damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PVS1, PS3, PM1, PP3, BS2) | [31] |
| HL13 | TMPRSS3 | c.1219T>C | p.(Cys407Arg) | 27.5 | 0.00005 | Disease causing | Medium | Possibly damaging | Tolerated | Pathogenic (PS1, PM1, PM2, PP2, PP3, PP5) | [32] |
| HL14 | CDH23 | c.6083A>C | p.(Asp2028Ala) | 21.9 | 0.00001 | Disease causing | High | Possibly damaging | Damaging | Likely pathogenic (PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5, BP1) | This study |
| HL16 | COL4A5 | c.89A>G | p.(Tyr30Cys) | 22.8 | 0.0003 | Benign | Neutral | Possibly damaging | Tolerated | Benign (PM1, PP2, BS1, BS2, BP4) | This study |
| HL17 | LARS2 | c.1249A>G | p.(Met417Val) | 16.83 | 0.00002 | Disease causing | Medium | Benign | Tolerated | Uncertain significance (PM2, PP2, BP4) | This study |
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morton, C.C.; Nance, W.E. Newborn hearing screening—A silent revolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, N.E. Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 630, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Camp, G.; Smith, R.J.H. Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage. 2019. Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Friedman, T.B.; Griffith, A.J. Human nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2003, 4, 341–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.C.; Kelly, M.C.; Hoa, M.; Morell, R.J.; Kelley, M.W. Single-cell RNA-Seq resolves cellular complexity in sensory organs from the neonatal inner ear. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkon, R.; Milon, B.; Morrison, L.; Shah, M.; Vijayakumar, S.; Racherla, M.; Leitch, C.C.; Silipino, L.; Hadi, S.; Weiss-Gayet, M.; et al. RFX transcription factors are essential for hearing in mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertzano, R.; Elkon, R. High throughput gene expression analysis of the inner ear. Hear. Res. 2012, 288, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pecka, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Soukup, G.A.; Beisel, K.W.; He, D.Z.Z. Characterization of Transcriptomes of Cochlear Inner and Outer Hair Cells. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11085–11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheffer, D.I.; Shen, J.; Corey, D.P.; Chen, Z.Y. Gene Expression by Mouse Inner Ear Hair Cells during Development. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6366–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayadi, A.; Birling, M.C.; Bottomley, J.; Bussell, J.; Fuchs, H.; Fray, M.; Gailus-Durner, V.; Greenaway, S.; Houghton, R.; Karp, N.; et al. Mouse large-scale phenotyping initiatives: Overview of the European Mouse Disease Clinic (EUMODIC) and of the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Mouse Genetics Project. Mamm. Genome 2012, 23, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.D.; Hardisty-Hughes, R.E.; Mburu, P. Quiet as a mouse: Dissecting the molecular and genetic basis of hearing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Nicholson, G.; Selloum, M.; White, J.; Morgan, H.; Ramirez-Solis, R.; Sorg, T.; Wells, S.; Fuchs, H.; Fray, M.; et al. Analysis of mammalian gene function through broad-based phenotypic screens across a consortium of mouse clinics. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, P.K.; Bowl, M.R.; Jeyarajan, P.; Wisby, L.; Blease, A.; Goldsworthy, M.E.; Simon, M.M.; Greenaway, S.; Michel, V.; Barnard, A.; et al. Novel gene function revealed by mouse mutagenesis screens for models of age-related disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwander, M.; Sczaniecka, A.; Grillet, N.; Bailey, J.S.; Avenarius, M.; Najmabadi, H.; Steffy, B.M.; Federe, G.C.; Lagler, E.A.; Banan, R.; et al. A forward genetics screen in mice identifies recessive deafness traits and reveals that pejvakin is essential for outer hair cell function. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stottmann, R.W.; Moran, J.L.; Turbe-Doan, A.; Driver, E.; Kelley, M.; Beier, D.R. Focusing forward genetics: A tripartite ENU screen for neurodevelopmental mutations in the mouse. Genetics 2011, 188, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ammar-Khodja, F.; Bonnet, C.; Dahmani, M.; Ouhab, S.; Lefevre, G.M.; Ibrahim, H.; Hardelin, J.P.; Weil, D.; Louha, M.; Petit, C. Diversity of the causal genes in hearing impaired Algerian individuals identified by whole exome sequencing. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2015, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bademci, G.; Foster, J.; Mahdieh, N.; Bonyadi, M.; Duman, D.; Cengiz, F.B.; Menendez, I.; Diaz-Horta, O.; Shirkavand, A.; Zeinali, S.; et al. Comprehensive analysis via exome sequencing uncovers genetic etiology in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness in a large multiethnic cohort. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masindova, I.; Soltysova, A.; Varga, L.; Matyas, P.; Ficek, A.; Huckova, M.; Surova, M.; Safka-Brozkova, D.; Anwar, S.; Bene, J.; et al. MARVELD2 (DFNB49) mutations in the hearing impaired Central European Roma population—Prevalence, clinical impact and the common origin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, C.G.; Gasmelseed, N.M.; Mergani, A.; Maqzoub, M.M.A.; Muntau, B.; Thye, T.; Horstmann, R.D. Novel TMC1 structural and splice variants associated with congenital nonsyndromic deafness in a Sudanese pedigree. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 25, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Z.; Bonnet, C.; Zainine, R.; Louha, M.; Bouyacoub, Y.; Laroussi, N.; Chargui, M.; Kefi, R.; Jonard, L.; Dorboz, I.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies new causative mutations in Tunisian families with non-syndromic deafness. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozzi, D.; Morgan, A.; Vuckovic, D.; Eustacchio, A.D.; Abdulhadi, K.; Rubinato, E.; Badii, R.; Gasparini, P.; Girotto, G. Hereditary hearing loss: A 96 gene targeted sequencing protocol reveals novel alleles in a series of Italian and Qatari patients. Gene 2014, 542, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittles, A. Consanguinity and its relevance to clinical genetics. Clin. Genet. 2001, 60, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, R.; Bittles, A.H. The prevalence and demographic characteristics of consanguineous marriages in Pakistan. J. Biosoc. Sci. 1998, 30, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimberg, J.; Nawoschik, S.; Belluscio, L.; McKee, R.; Turck, A.; Eisenberg, A. A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noman, M.; Ishaq, R.; Bukhari, S.A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Riazuddin, S. Delineation of Homozygous Variants Associated with Prelingual Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Pakistani Families. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riazuddin, S.; Hussain, M.; Razzaq, A.; Iqbal, Z.; Shahzad, M.; Polla, D.L.; Song, Y.; Beusekom, E.V.; Khan, A.A.; Roca, L.T.; et al. Exome sequencing of Pakistani consanguineous families identifies 30 novel candidate genes for recessive intellectual disability. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1604–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maquat, L.E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Splicing, translation and mRNP dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyantseva, I.A.; Boger, E.T.; Naz, S.; Frolenkov, G.I.; Sellers, J.R.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Griffith, A.J.; Friedman, T.B. Myosin-XVa is required for tip localization of whirlin and differential elongation of hair-cell stereocilia. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delprat, B.; Michel, V.; Goodyear, R.; Yamasaki, Y.; Michalski, N.; Amraoui, A.; Perfettini, I.; Legrain, P.; Richardson, G.; Hardelin, J.P.; et al. Myosin XVa and whirlin, two deafness gene products required for hair bundle growth, are located at the stereocilia tips and interact directly. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Bird, J.E.; Faridi, R.; Shahzad, M.; Shah, S.; Lee, K.; Khan, S.N.; Imtiaz, A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Riazuddin, S.; et al. Mutational Spectrum of MYO15A and the Molecular Mechanisms of DFNB3 Human Deafness. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelsell, D.P.; Dunlop, J.; Stevens, H.P.; Lench, N.J.; Liang, J.N.; Parry, G.; Mueller, R.F.; Leigh, I.M. Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature 1997, 387, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, T.B.; Wattenhofer, M.; Riazuddin, S.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Scott, H.S.; Kudoh, J.; Shibuya, K.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Tamir, B.B.; Radhakrishna, U.; et al. Novel mutations of TMPRSS3 in four DFNB8/B10 families segregating congenital autosomal recessive deafness. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 38, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akil, O.; Seal, R.P.; Burke, K.; Wang, C.; Alemi, A.; During, M.; Edwards, R.H.; Lustig, L.R. Restoration of hearing in the VGLUT3 knockout mouse using virally mediated gene therapy. Neuron 2012, 75, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alagramam, K.N.; Gopal, S.R.; Geng, R.; Chen, D.; Nemet, I.; Lee, R.; Tian, G.; Miyagi, G.; Malagu, K.F.; Lock, C.J.; et al. A small molecule mitigates hearing loss in a mouse model of Usher syndrome III. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Askew, C.; Rochat, C.; Pan, B.; Asai, Y.; Ahmed, H.; Child, E.; Schneider, B.L.; Aebischer, P.; Holt, J.R. Tmc gene therapy restores auditory function in deaf mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 295ra108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lentz, J.J.; Jodelka, F.M.; Hinrich, H.L.; McCaffrey, K.E.; Farris, H.E.; Spalitta, M.J.; Bazan, N.G.; Duelli, D.M.; Rigo, F.; Hastings, M.L. Rescue of hearing and vestibular function by antisense oligonucleotides in a mouse model of human deafness. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emma M Jenkinson, E.M.; Rehman, A.; Walsh, T.; Smith, J.; Lee, K.; Morell, R.J.; Drummond, M.C.; Khan, S.N.; Naeem, M.A.; Rauf, B.; et al. Perrault syndrome is caused by recessive mutations in CLPP, encoding a mitochondrial ATP-dependent chambered protease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierce, S.B.; Gersak, J.; Cohen, R.M.; Walsh, T.; Lee, M.K.; Malach, D.; Klevit, R.E.; King, M.; Lahad, E. Mutations in LARS2, encoding mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase, lead to premature ovarian failure and hearing loss in Perrault syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 92, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bork, J.M.; Peters, L.M.; Riazuddin, S.; Bernstein, S.L.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Ness, S.L.; Polomeno, R.; Ramesh, A.; Schloss, M.; Srisailpathy, C.R.; et al. Usher syndrome 1D and nonsyndromic autosomal recessive deafness DFNB12 are caused by allelic mutations of the novel cadherin-like gene CDH23. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brouwer, A.P.M.; Pennings, R.J.E.; Roeters, M.; Hauwe, P.V.; Astuto, L.M.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; Huygen, P.L.M.; Helm, B.; Deutman, A.F.; Bork, J.M.; et al. Mutations in the calcium-binding motifs of CDH23 and the 35delG mutation in GJB2 cause hearing loss in one family. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuto, L.M.; Bork, J.M.; Weston, M.D.; Askew, J.W.; Fields, R.R.; Orten, D.J.; Ohliger, S.J.; Riazuddin, S.; Morell, R.J.; Khan, S.N.; et al. CDH23 mutation and phenotype heterogeneity: A profile of 107 diverse families with Usher syndrome and nonsyndromic deafness. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, D.F.; Hostikka, S.L.; Zhou, J.; Chow, L.T.; Oliphant, A.R.; Gerken, S.C.; Gregory, M.C.; Skolnick, M.H.; Atkin, C.L.; Tryggvason, K.; et al. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science 1990, 248, 1224–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zafar, S.; Shahzad, M.; Ishaq, R.; Yousaf, A.; Shaikh, R.S.; Akram, J.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Riazuddin, S. Novel Mutations in CLPP, LARS2, CDH23, and COL4A5 Identified in Familial Cases of Prelingual Hearing Loss. Genes 2020, 11, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090978
Zafar S, Shahzad M, Ishaq R, Yousaf A, Shaikh RS, Akram J, Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S. Novel Mutations in CLPP, LARS2, CDH23, and COL4A5 Identified in Familial Cases of Prelingual Hearing Loss. Genes. 2020; 11(9):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090978
Chicago/Turabian StyleZafar, Saba, Mohsin Shahzad, Rafaqat Ishaq, Ayesha Yousaf, Rehan S. Shaikh, Javed Akram, Zubair M. Ahmed, and Saima Riazuddin. 2020. "Novel Mutations in CLPP, LARS2, CDH23, and COL4A5 Identified in Familial Cases of Prelingual Hearing Loss" Genes 11, no. 9: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090978
APA StyleZafar, S., Shahzad, M., Ishaq, R., Yousaf, A., Shaikh, R. S., Akram, J., Ahmed, Z. M., & Riazuddin, S. (2020). Novel Mutations in CLPP, LARS2, CDH23, and COL4A5 Identified in Familial Cases of Prelingual Hearing Loss. Genes, 11(9), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11090978





