Klotho Exerts an Emerging Role in Cytokinesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.2. Immunoprecipitation, Mass Spectrometry and Pathway Analysis
2.3. Western Blotting Analysis
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining, Confocal Microscopy, Live Cell Image, and 3D Structure Reconstruction Analysis
2.5. Zebrafish Embryo Staging and Morpholino Injection
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
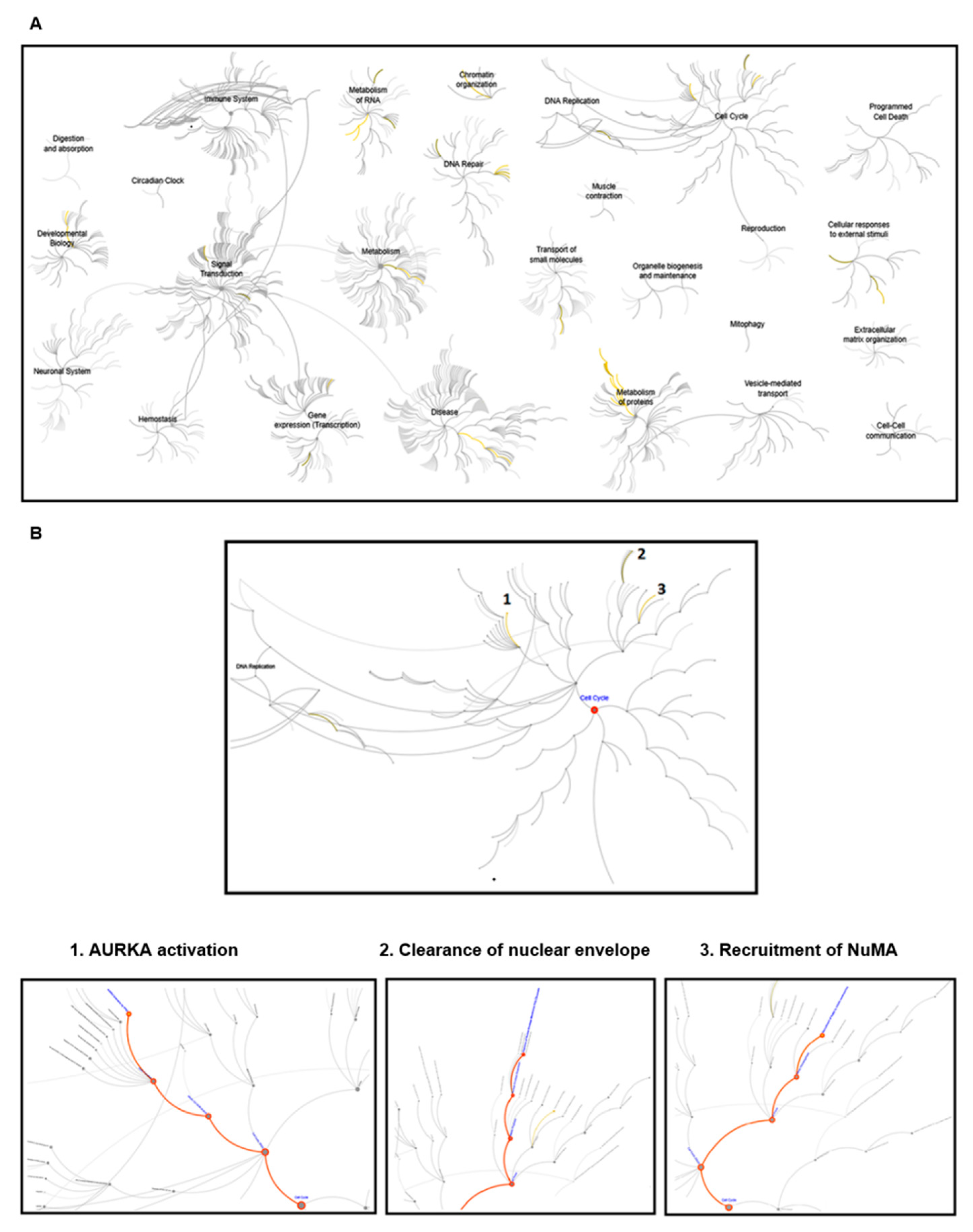
3.1. Reactome Pathway Analysis of Klotho
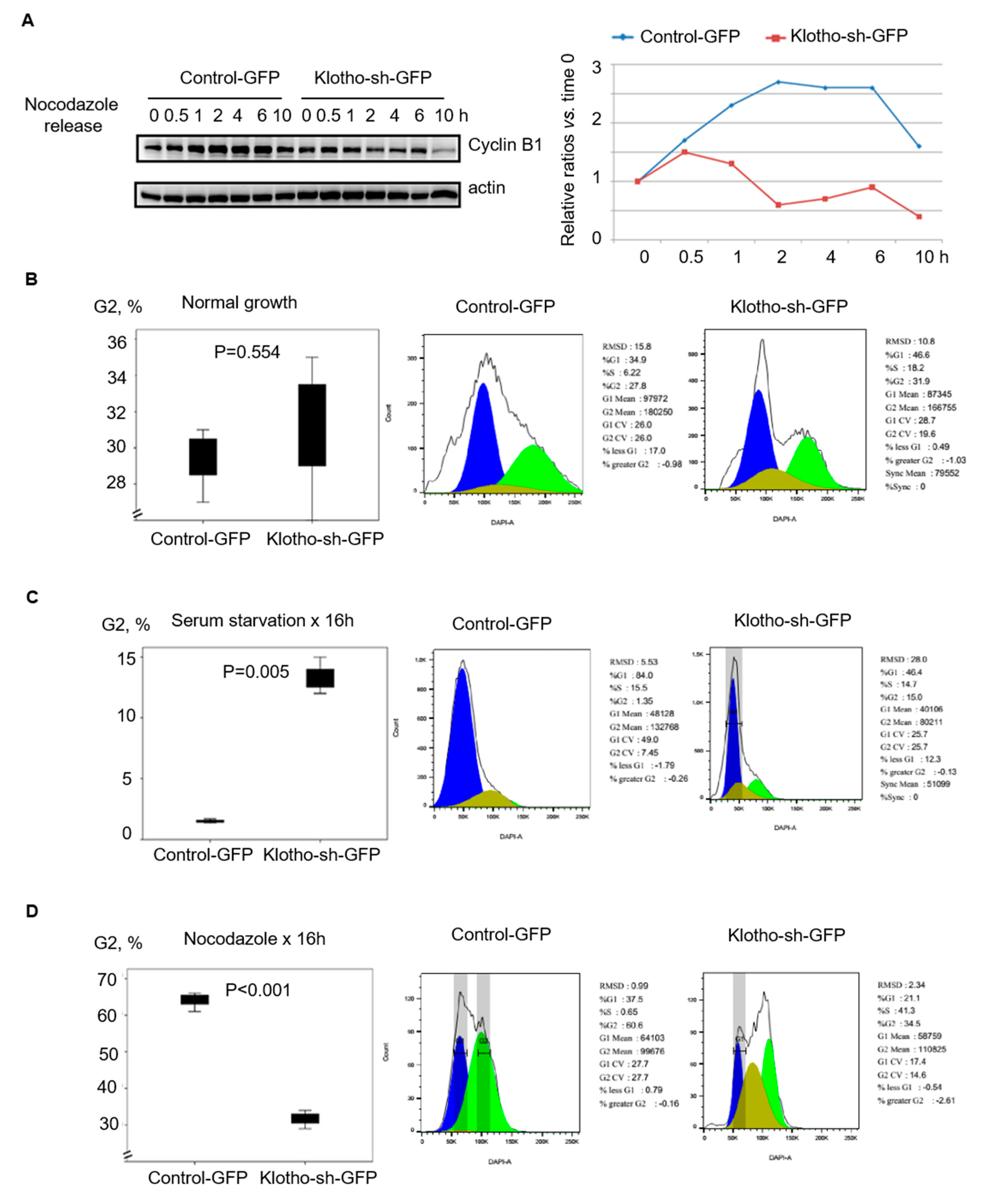
3.2. Klotho Depletion Caused Aberrant Cell Cycle
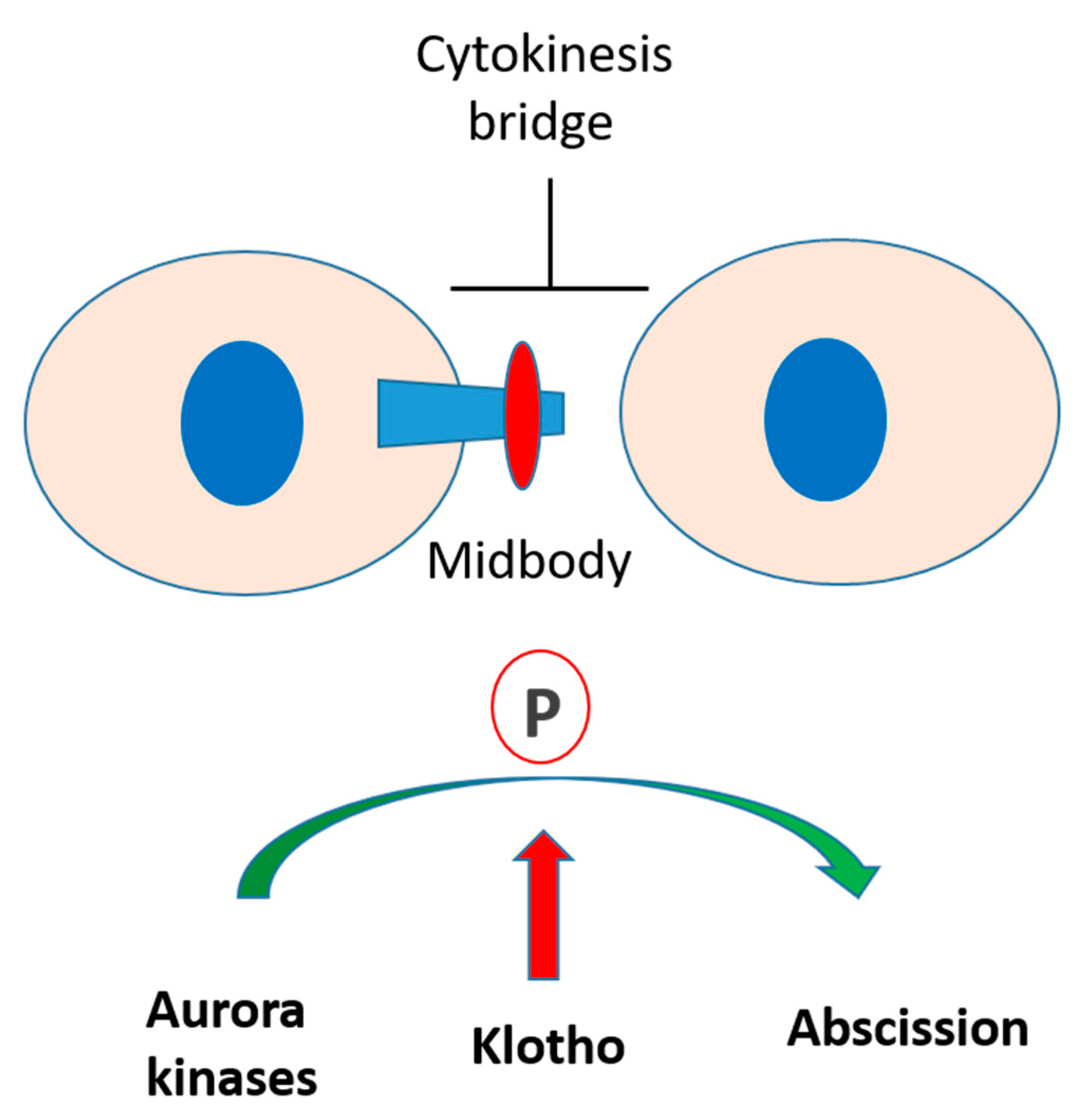
3.3. Klotho Depletion Induced Cytokinesis Bridge Abscission Delay
3.4. Klotho Depletion Impairs Aurora Kinase Activation
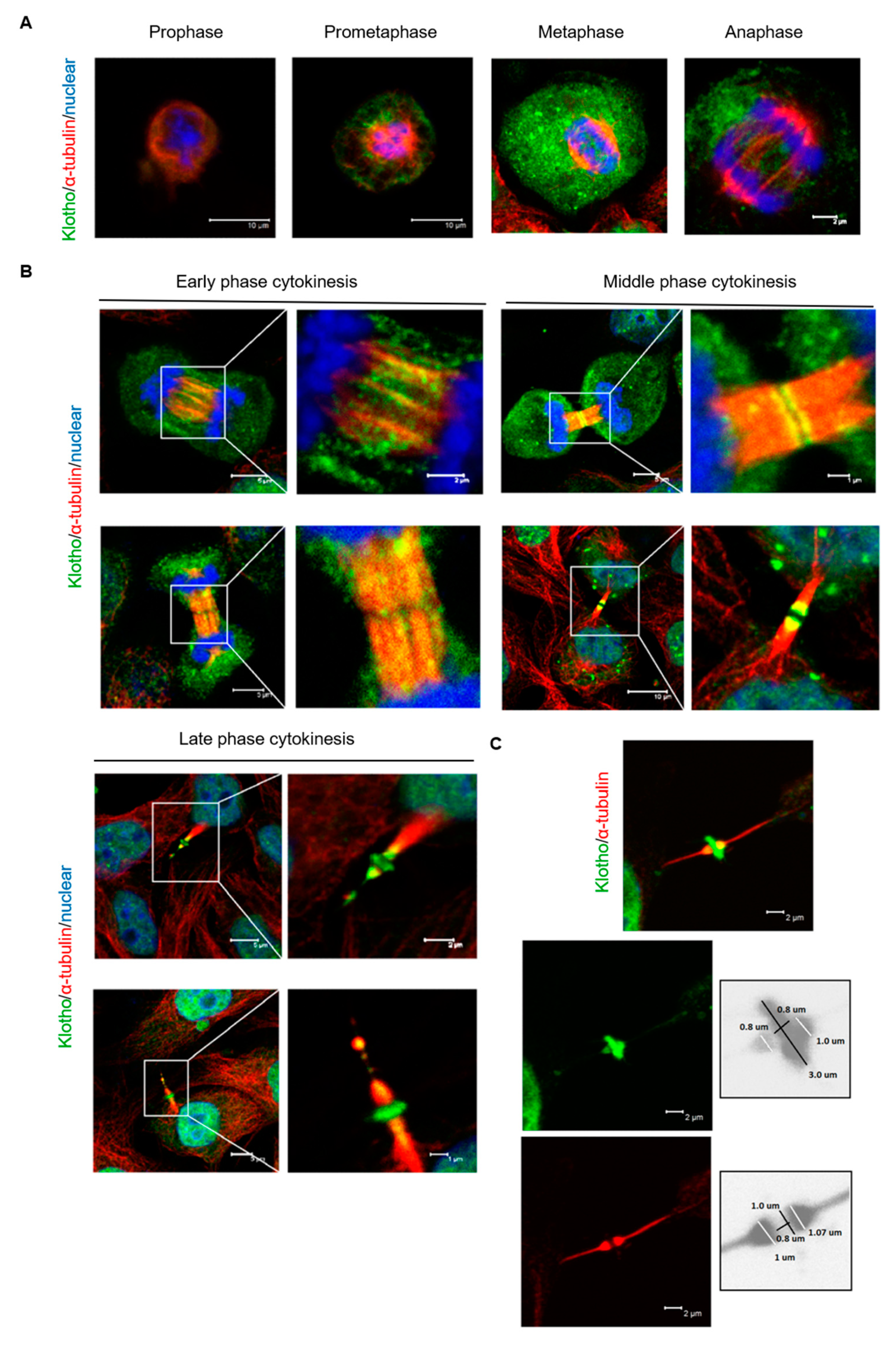
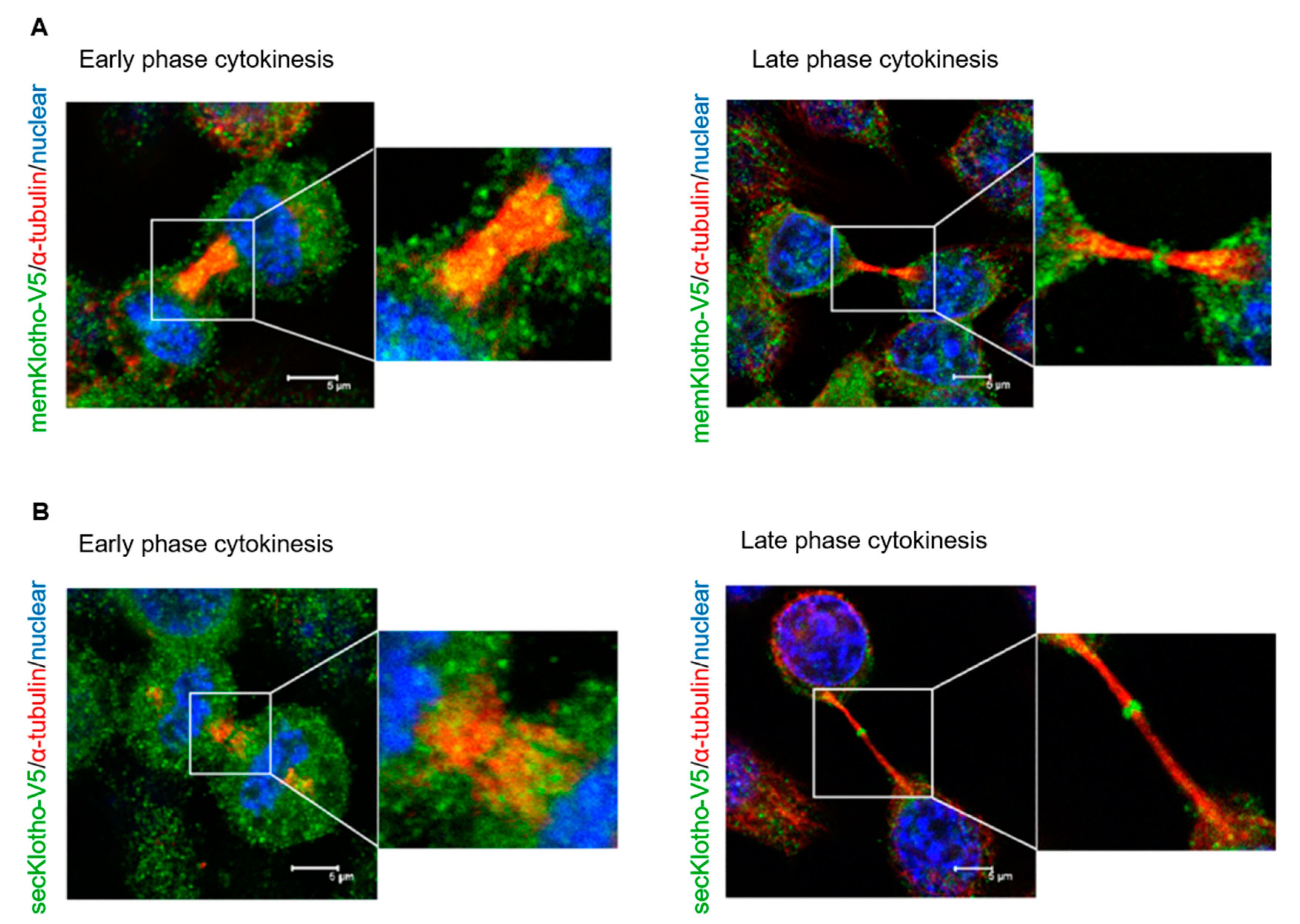
3.5. The Spatial Localization of Klotho in the Midbody Relating with Cytokinetic Protein Kinases
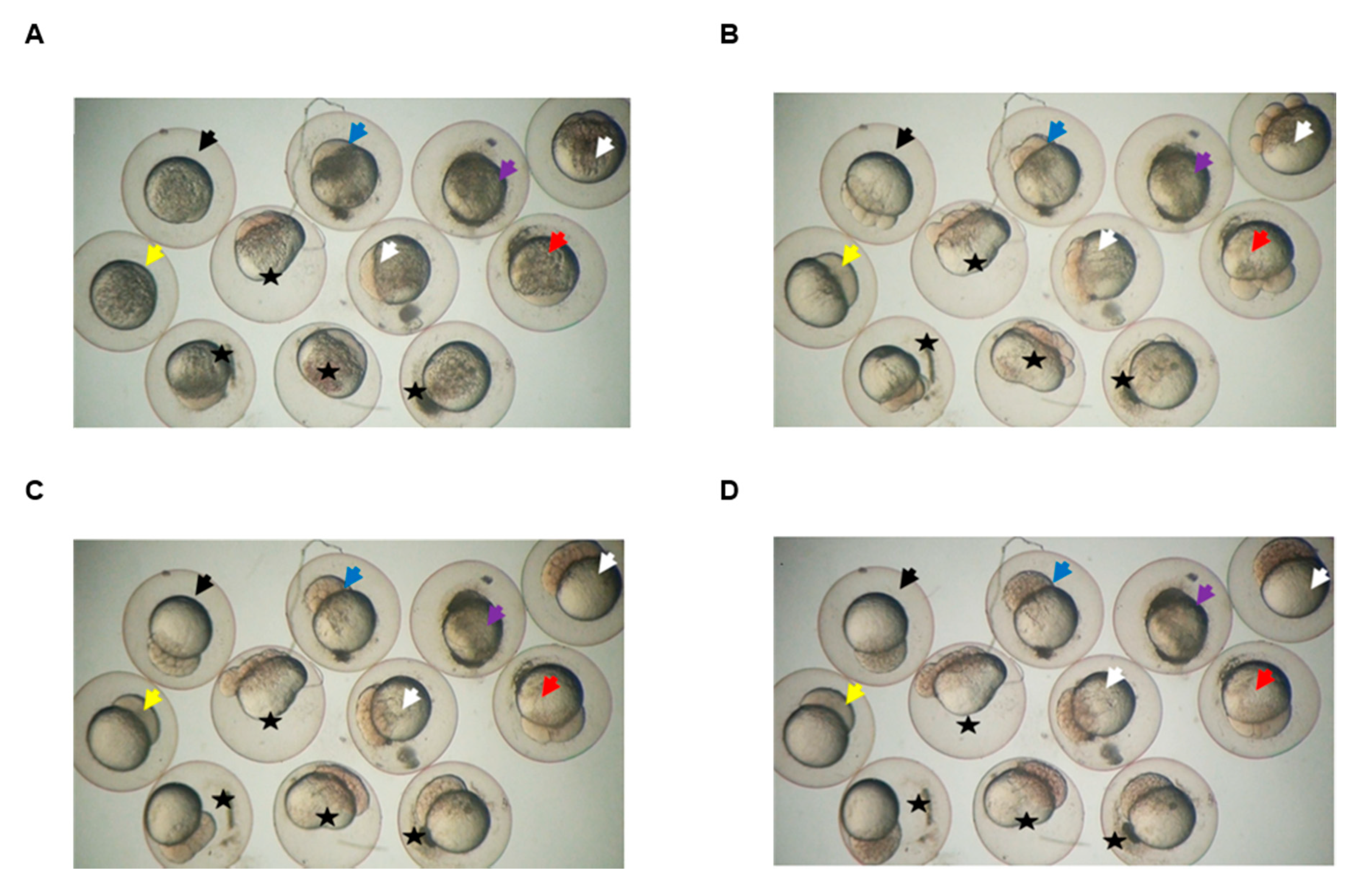
3.6. Klotho Depletion Causes Embryo Cleavage Defects in Zebrafish
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KL | Klotho |
| hpf | Hours post-fertilization |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| MO | Morpholino |
References
- Matsumura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Shiraki-Iida, T.; Nagai, R.; Kuro-o, M.; Nabeshima, Y. Identification of the human klotho gene and its two transcripts encoding membrane and secreted klotho protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 242, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuro-o, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Suga, T.; Utsugi, T.; Ohyama, Y.; Kurabayashi, M.; Kaname, T.; Kume, E.; et al. Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 1997, 390, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosu, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Clark, J.D.; Pastor, J.V.; Nandi, A.; Gurnani, P.; McGuinness, O.P.; Chikuda, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, H.; et al. Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 2005, 309, 1829–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arking, D.E.; Krebsova, A.; Macek, M.; Arking, A.; Mian, I.S.; Fried, L.; Hamosh, A.; Dey, S.; McIntosh, I.; Dietz, H.C. Association of human aging with a functional variant of klotho. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urakawa, I.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shimada, T.; Iijima, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Okawa, K.; Fujita, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Yamashita, T. Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 2006, 444, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, T.; Ohnishi, M.; Razzaque, M.S. Inactivation of klotho function induces hyperphosphatemia even in presence of high serum fibroblast growth factor 23 levels in a genetically engineered hypophosphatemic (Hyp) mouse model. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3702–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaque, M.S. The FGF23-Klotho axis: Endocrine regulation of phosphate homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Hoefs, S.; Van Der Kemp, A.W.; Topala, C.N.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G. The beta-glucuronidase klotho hydrolyzes and activates the TRPV5 channel. Science 2005, 310, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, D.; Razzaque, M.S.; DeLuca, S.; Rector, T.L.; Hou, B.; Kang, K.; Goetz, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Kuro-O, M.; Olsen, B.R.; et al. FGF-23-Klotho signaling stimulates proliferation and prevents vitamin D-induced apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 182, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, Z. Antiaging gene Klotho attenuates pancreatic β-cell apoptosis in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2015, 64, 4298–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, E.A.; Olauson, H.; Larsson, T.; Catrina, S.B. Effect of systemically increasing human full-length Klotho on glucose metabolism in db/db mice. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 113, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltese, G.; Psefteli, P.M.; Rizzo, B.; Srivastava, S.; Gnudi, L.; Mann, G.E.; Siow, R.C.M. The anti-ageing hormone klotho induces Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defenses in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Huang, Z.; Zou, J.; Yang, D.; Hu, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, L.; Liao, X. Klotho protects the heart from hyperglycemia-induced injury by inactivating ROS and NF-κB-mediated inflammation both in vitro and in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1864, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Mogilner, A.; Maresca, T.J. Classical and Emerging Regulatory Mechanisms of Cytokinesis in Animal Cells. Biology 2019, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.D.; O’Shaughnessy, B. Molecular Mechanism of Cytokinesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 8, 661–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.; O’Connor, P.M. Methods for synchronizing cells at specific stages of the cell cycle. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2001, 8.3.1–8.3.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Jupe, S.; Matthews, L.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Gillespie, M.; Garapati, P.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Korninger, F.; May, B.; et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D481–D487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Lee, G.H. Novel and unexpected functions of zebrafish CCAAT box binding transcription factor (NF-Y) B subunit during cartilages development. Bone 2009, 44, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Z. Molecular basis of Klotho: From gene to function in aging. Endocr. Rev. 2015, 36, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bian, M.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C. Roles of Aurora kinases in mitosis and tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, Z.I.; Audusseau, M.; Riparbelli, M.G.; Callaini, G.; D’Avino, P.P. Citron kinase controls a molecular network required for midbody formation in cytokinesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9782–9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, M.; Camera, P.; Dema, A.; Bianchi, F.; Berto, G.; Scarpa, E.; Germena, G.; Di Cunto, F. Citron kinase controls abscission through RhoA and anillin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3768–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, C.; Bassi, Z.I.; Debski, J.; Gottardo, M.; Callaini, G.; Dadlez, M.; D’Avino, P.P. Cross-regulation between Aurora B and Citron kinase controls midbody architecture in cytokinesis. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, D.R. Cytokinesis and the establishment of early embryonic cell polarity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, L.R.; Megraw, T. Cytokinesis: RhoGEFs control a developmental cleavage switch. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R916–R917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalhoub, V.; Ward, S.C.; Sun, B.; Stevens, J.; Renshaw, L.; Hawkins, N.; Richards, W.G. Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) and alpha-klotho stimulate osteoblastic MC3T3.E1 cell proliferation and inhibit mineralization. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2011, 89, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Sun, Z. The antiaging gene klotho regulates proliferation and differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.K.; Coughlin, M.; Mitchison, T.J. Midbody assembly and its regulation during cytokinesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa, B.; Gerlich, D.W. Cytokinetic abscission: Molecular mechanisms and temporal control. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skop, A.R.; Liu, H.; Yates, J.; Meyer, B.J.; Heald, R. Dissection of the mammalian midbody proteome reveals conserved cytokinesis mechanisms. Science 2004, 305, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, O.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Maiato, H. Late mitotic functions of Aurora kinases. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severson, A.F.; Hamill, D.R.; Carter, J.C.; Schumacher, J.; Bowerman, B. The aurora-related kinase AIR-2 recruits ZEN-4/CeMKLP1 to the mitotic spindle at metaphase and is required for cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, M.; Kaitna, S.; Glotzer, M. Central spindle assembly and cytokinesis require a kinesin-like protein/RhoGAP complex with microtubule bundling activity. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, B.G.; Lampson, M.A.; Foley, E.A.; Rosasco-Nitcher, S.; Le, K.V.; Tobelmann, P.; Brautigan, D.L.; Stukenberg, P.T.; Kapoor, T.M. Midzone activation of aurora B in anaphase produces an intracellular phosphorylation gradient. Nature 2008, 453, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, R.; Tsukada, Y.; Kamasaki, T.; Poser, I.; Yoda, K.; Gerlich, D.W.; Goshima, G. Aurora B and Kif2A control microtubule length for assembly of a functional central spindle during anaphase. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaule, P.; Furuyashiki, T.; Eda, M.; Bito, H.; Ishizaki, T.; Narumiya, S. Citron, a Rho target that affects contractility during cytokinesis. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2000, 49, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Maresca, T.J. Microtubule plus-ends act as physical signaling hubs to activate RhoA during cytokinesis. Elife 2019, 8, e38968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetake, Y.; Sluder, G. Cell cycle progression after cleavage failure: Mammalian somatic cells do not possess a “tetraploidy checkpoint”. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovitz, L.; Rubinek, T.; Ligumsky, H.; Bose, S.; Barshack, I.; Avivi, C.; Kaufman, B.; Wolf, I. KL1 internal repeat mediates klotho tumor suppressor activities and inhibits bFGF and IGF-I signaling in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4254–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Xie, B.; Ren, F.; Liu, D.C.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, J. Restoration of klotho expression induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Oncol. 2013, 36, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X.; Huang, L.Y.; Peng, J.J.; Liang, L.; Shi, D.B.; Zheng, H.T.; Cai, S.J. Klotho suppresses growth and invasion of colon cancer cells through inhibition of IGF1R-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.-Y.; Chou, C.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Lo, K.-C.; Liou, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-H. Klotho Exerts an Emerging Role in Cytokinesis. Genes 2020, 11, 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091048
Sun C-Y, Chou C-Y, Hsieh Y-Y, Lo K-C, Liou Y-L, Chen Y-H. Klotho Exerts an Emerging Role in Cytokinesis. Genes. 2020; 11(9):1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chiao-Yin, Chi-Yuan Chou, Yu-Ying Hsieh, Kang-Chieh Lo, Yan-Liang Liou, and Yau-Hung Chen. 2020. "Klotho Exerts an Emerging Role in Cytokinesis" Genes 11, no. 9: 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091048
APA StyleSun, C.-Y., Chou, C.-Y., Hsieh, Y.-Y., Lo, K.-C., Liou, Y.-L., & Chen, Y.-H. (2020). Klotho Exerts an Emerging Role in Cytokinesis. Genes, 11(9), 1048. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11091048




