Rapid Direct Nucleic Acid Amplification Test without RNA Extraction for SARS-CoV-2 Using a Portable PCR Thermocycler
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Controls Used for Assay Development
2.2. Collection and Processing of Sputum and Nasal Exudate Samples
2.3. Primer and Probes
2.4. RT-qPCR and DIRECT-PCR
2.5. DIRECT-PCR of SARS-CoV-2 N Gene in Sputum and Nasal Exudate
2.6. Optimization of Fast DIRECT-PCR Assay
2.7. Performance of Portable Real-Time Thermocycler
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
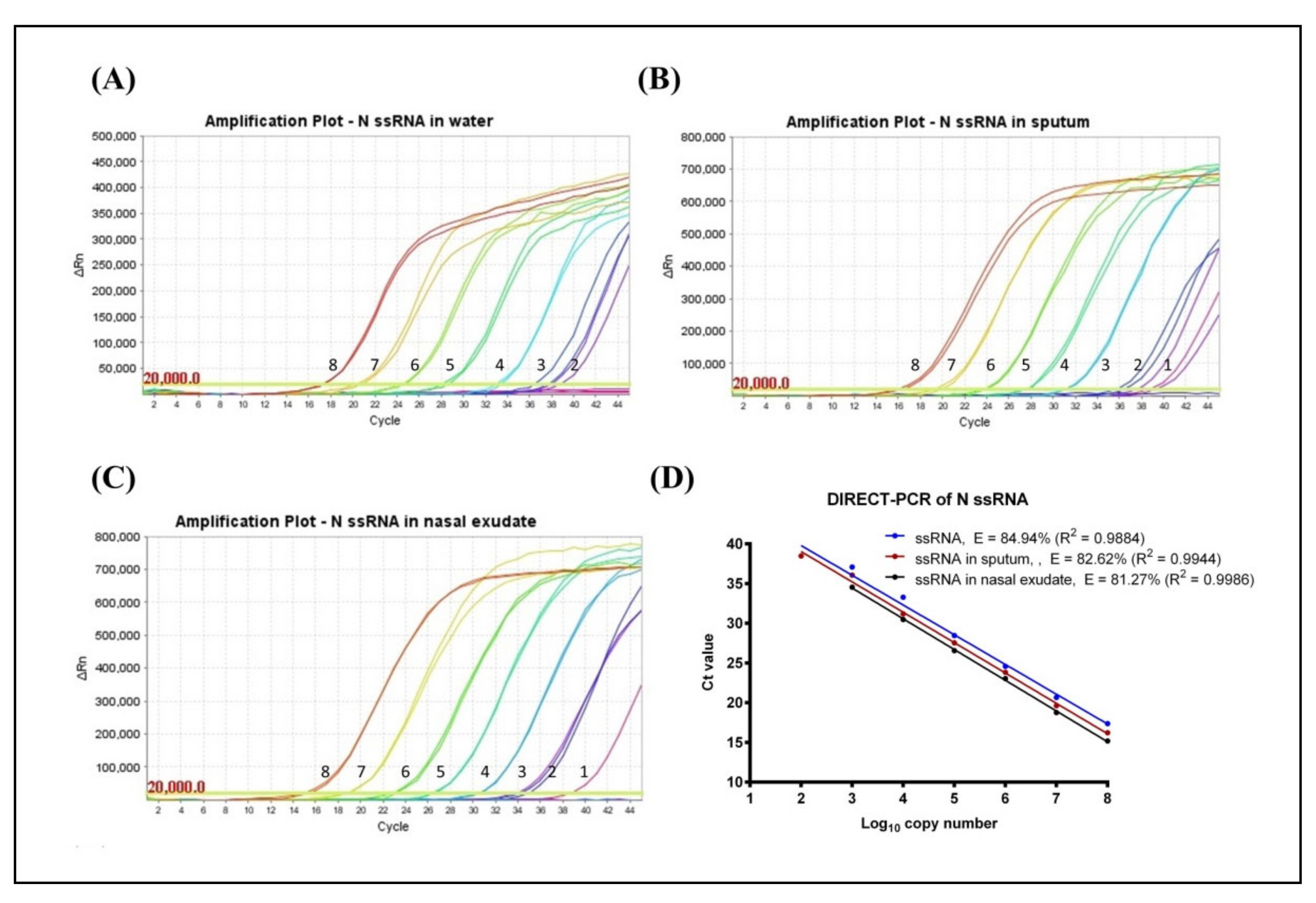
3.1. Determination of LoD and Amplification Efficiency (E)
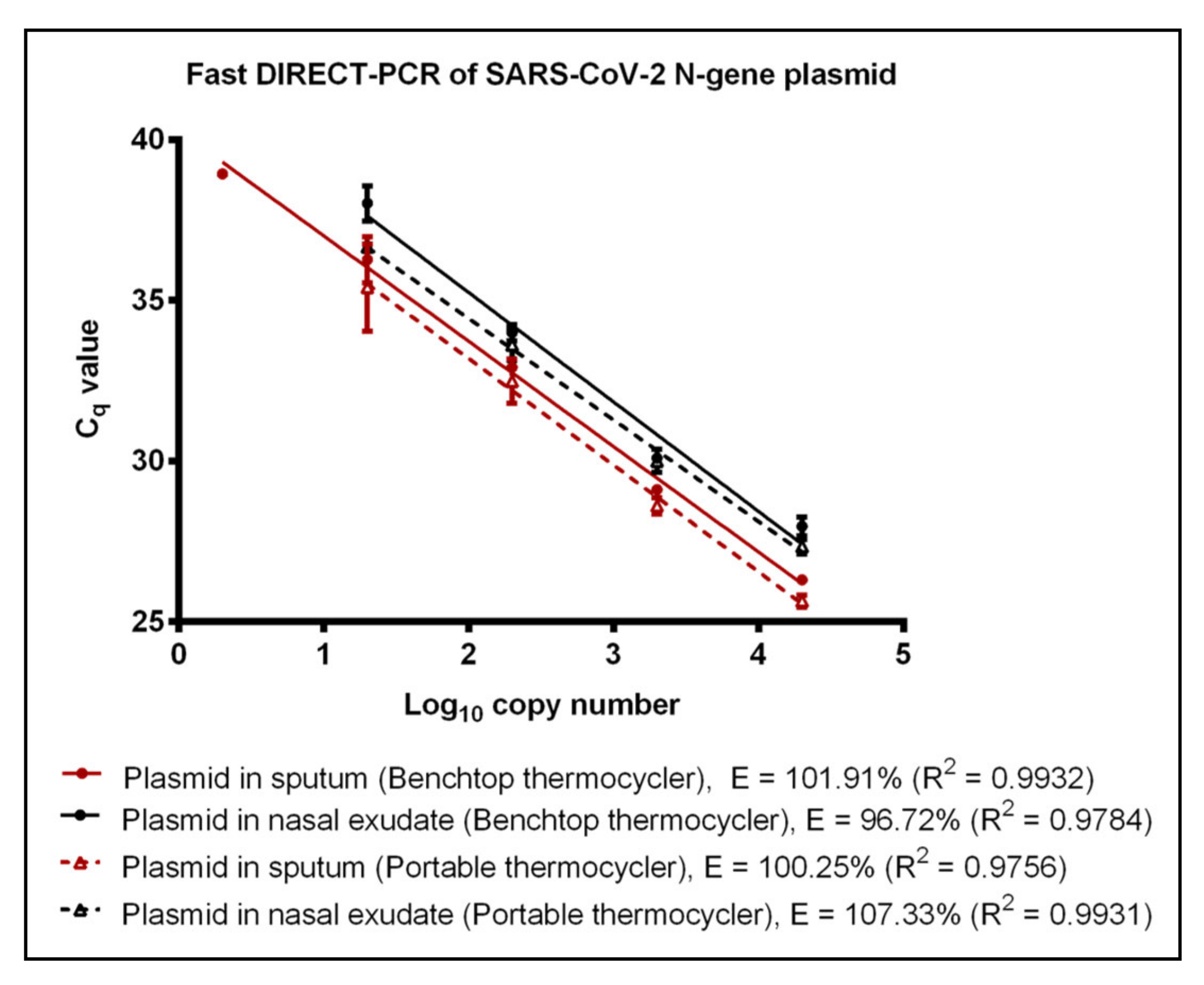
3.2. Evaluation of Fast DIRECT-PCR Assay
3.3. Performance of Portable Thermocycler
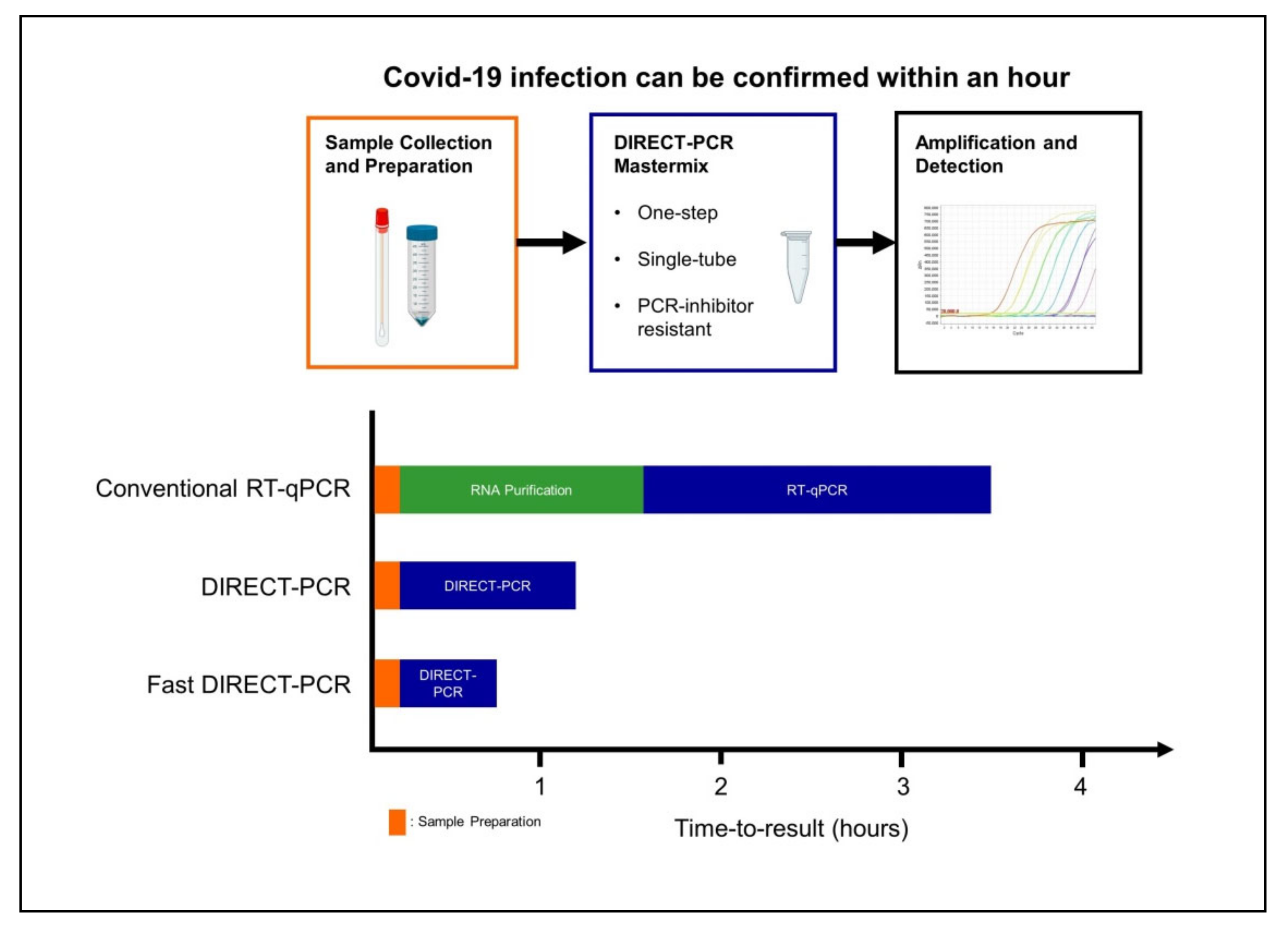
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- WHO. COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Beeching, N.J.; E Fletcher, T.; Beadsworth, M.B.J. Covid-19: Testing times. BMJ 2020, 369, m1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Y.; Li, Z.; Chua, Y.X.; Chaw, W.L.; Zhao, Z.; Er, B.; Pung, R.; Chiew, C.J.; Lye, D.C.; Heng, D.; et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Surveillance and Containment Measures for the First 100 Patients with COVID-19 in Singapore — January 2–February 29, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.E.L.; Leo, Y.S.; Tan, C.C. COVID-19 in Singapore—Current Experience. JAMA 2020, 323, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOH. Updates on COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) Local Situation. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sg/covid-19 (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Zhang, Y.-Z. Novel 2019 coronavirus genome. Available online: http://virological.org/t/novel-2019-coronavirus-genome/319 (accessed on 22 March 2020).
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Laboratory testing for 2019-nCoV in humans. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technical-guidance/laboratory-guidance (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- NUS. SSHSPH COVID-19 Science Report; Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases; WHO/COVID-19/laboratory/2020.5; World Health Organization: 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/10665-331501 (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Nguyen, T.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Paving the Road for Rapid Detection and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Micromachines 2020, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.E.; Li, Z.; Chiew, C.J.; Yong, S.E.; Toh, M.P.; Lee, V.J. Presymptomatic Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 — Singapore, January 23–March 16, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lau, E.H.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.; Lau, Y.C.; Wong, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Tan, X.; et al. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Helgason, A.; Jonsson, H.; Magnusson, O.T.; Melsted, P.; Norddahl, G.L.; Saemundsdottir, J.; Sigurdsson, A.; Sulem, P.; Agustsdottir, A.B.; et al. Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the Icelandic Population. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, C. Fast, portable tests come online to curb coronavirus pandemic. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Babady, N.E.; Theel, E.S.; Storch, G.A.; Pinsky, B.A.; George, K.S.; Smith, T.C.; Bertuzzi, S. Report from the American Society for Microbiology COVID-19 International Summit, 23 March 2020: Value of Diagnostic Testing for SARS–CoV-2/COVID-19. mBio. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, S.P.; Ayi, T.C.; Mustaffa, S.B.; Loo, S.; Tan, B.H.; Yap, E.P.H. Direct RT-PCR detection of Dengue 1-4 virus from crude samples for rapid point-of-care diagnosis. In Proceedings of the SingHealth Duke-NUS Scientific Congress, Singapore, 23–24 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, N.; Perrais, B.; Martin, K.; Kumar, A.; Hobman, T.C.; Cabalfin-Chua, M.N.; Donaldo, M.E.; Painaga, M.S.S.; Gaite, J.Y.; Tran, V.; et al. A Direct from Blood/Plasma Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction for Dengue Virus Detection in Point-of-Care Settings. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, B.; Bessaud, M.; Grandadam, M.; Murri, S.; Tolou, H.J.; Peyrefitte, C.N. Development of a TaqMan® RT-PCR assay without RNA extraction step for the detection and quantification of African Chikungunya viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 124, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, N.; Nakayama, H.; Yoshizumi, S.; Miyoshi, M.; Tonoike, H.; Shirasaki, Y.; Kojima, K.; Ishida, S. Detection of noroviruses in fecal specimens by direct RT-PCR without RNA purification. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachofen, C.; Willoughby, K.; Zadoks, R.; Burr, P.; Mellor, D.; Russell, G.C. Direct RT-PCR from serum enables fast and cost-effective phylogenetic analysis of bovine viral diarrhoea virus. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 190, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; He, J.-A.; Wang, W.; Xia, Y.; Song, L.; Chen, Z.-H.; Zuo, H.-Z.; Tan, X.-P.; Ho, A.H.-P.; Kong, S.-K.; et al. Development of a direct reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (dirRT-qPCR) assay for clinical Zika diagnosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 85, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.T.; Zovanyi, A.M.; Christensen, D.R.; Koehler, J.W.; Minogue, T.D. Evaluation of Inhibitor-Resistant Real-Time PCR Methods for Diagnostics in Clinical and Environmental Samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC, C. Specific primers and probes for detection 2019 novel coronavirus. Available online: http://ivdc.chinacdc.cn/kyjz/202001/t20200121_211337.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- CDC. Research Use Only 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-time RT-PCR Primer and Probe Information. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/rt-pcr-panel-primer-probes.html (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shen, C.; Wang, F.; Jing, Y.; Li, J.-X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Xing, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Evaluating the accuracy of different respiratory specimens in the laboratory diagnosis and monitoring the viral shedding of 2019-nCoV infections 2020. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.; Wang, Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. COVID 19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) - Global research and innovation forum: Towards a research roadmap. Available online: https://www.who.int/blueprint/priority-diseases/key-action/Global_Research_Forum_FINAL_VERSION_for_web_14_feb_2020.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Bruce, E.A.; Huang, M.-L.; Perchetti, G.A.; Tighe, S.W.; Laaguiby, P.; Hoffman, J.J.; Gerrard, D.L.; Nalla, A.K.; Wei, Y.; Greninger, A.L.; et al. DIRECT RT-qPCR DETECTION OF SARS-CoV-2 RNA FROM PATIENT NASOPHARYNGEAL SWABS WITHOUT AN RNA EXTRACTION STEP 2020. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sentmanat, M.; Kouranova, E.; Cui, X. One-step RNA extraction for RT-qPCR detection of 2019-nCoV 2020. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam, A.; Wong, S.S. The Potential Use of Unprocessed Sample for RT-qPCR Detection of COVID-19 without an RNA Extraction Step 2020. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, P.R.; Turner, M.; Shin, G.Y.; Nastouli, E.; Levett, L. Extraction-free COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) diagnosis by RT-PCR to increase capacity for national testing programmes during a pandemic. In bioRxiv 2020; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Merindol, N.; Pépin, G.; Marchand, C.; Rheault, M.; Peterson, C.; Poirier, A.; Germain, H.; Danylo, A. Optimization of SARS-CoV-2 detection by RT-QPCR without RNA extraction 2020. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Smyrlaki, I.; Ekman, M.; Lentini, A.; Vondracek, M.; Papanicoloau, N.; Aarum, J.; Safari, H.; Muradrasoli, S.; Albert, J.; Högberg, B.; et al. Massive and rapid COVID-19 testing is feasible by extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR 2020. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.R.; Atkinson, L.; Shah, D.; Harris, K. Validation of an extraction-free RT-PCR protocol for detection of SARS-CoV2 RNA 2020. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.R.; Mirza, F.; Al-Hail, H.; Sundararaju, S.; Xaba, T.; Iqbal, M.; Alhussain, H.; Yassine, H.M.; Lopez, A.P.; Tang, P. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by direct RT-qPCR on nasopharyngeal specimens without extraction of viral RNA 2020. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard, A.S.; Rosenstierne, M.W. An alternative workflow for molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2 – escape from the NA extraction kit-shortage, Copenhagen, Denmark, March 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Benchtop Thermocycler | Portable Thermocycler | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCR | Mastermix Volume per Reaction (µL) | Mastermix Used | Template | Matrix | LoD (Cq Mean ± S.D) | PCR Efficiency (%) | R2 | LoD (Cq Mean ± S.D) | PCR Efficiency (%) | R2 |
| RT-qPCR | 20 | Invitrogen SuperScript™ III Platinum™ One-Step RT-qPCR Kit | ssRNA | Water | 120 (40.67 ± 0.29) | 84.30 | 0.9994 | 120 (38.70 ± 0.10) | 86.26 | 0.9985 |
| Sputum | No amplification | No amplification | ||||||||
| Nasal Exudate | No amplification | No amplification | ||||||||
| DIRECT-PCR | 20 | VitaNavi Direct One-Step S/P RT-qPCR TaqProbe Kit | ssRNA | Water | 120 (38.48 ± 0.57) | 84.94 | 0.9884 | 120 (36.99^) | 88.35 | 0.9729 |
| Sputum | 12 (38.79^) | 82.62 | 0.9944 | 12 (38.10^) | 88.64 | 0.9924 | ||||
| Nasal Exudate | 12 (38.72^) | 81.27 | 0.9986 | 1200 (36.47 ± 0.23) | 77.45 | 0.9976 | ||||
| Fast DIRECT-PCR | 10 | VitaNavi Direct One-Step S/P RT-qPCR TaqProbe Kit | ssRNA | Water | 600 (39.42^) | 81.72 | 0.9859 | 600 (36.63^) | 89.37 | 0.9639 |
| Sputum | 6 (39.28^) | 76.03 | 0.9824 | 600 (36.25 ± 0.46) | 85.52 | 0.9784 | ||||
| Nasal Exudate | 60 (39.34^) | 69.23 | 0.9865 | 60 (36.90^) | 81.08 | 0.9775 | ||||
| Plasmid | Water | 2 (39.75^) | 119.25 | 0.9896 | 20 (36.56 ± 0.26) | 113.17 | 0.9669 | |||
| Sputum | 2 (38.93^) | 101.91 | 0.9932 | 20 (35.40 ± 1.35) | 100.25 | 0.9756 | ||||
| Nasal Exudate | 20 (38.02 ± 0.55) | 96.72 | 0.9784 | 20 (36.66 ± 0.08) | 107.33 | 0.9931 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wee, S.K.; Sivalingam, S.P.; Yap, E.P.H. Rapid Direct Nucleic Acid Amplification Test without RNA Extraction for SARS-CoV-2 Using a Portable PCR Thermocycler. Genes 2020, 11, 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060664
Wee SK, Sivalingam SP, Yap EPH. Rapid Direct Nucleic Acid Amplification Test without RNA Extraction for SARS-CoV-2 Using a Portable PCR Thermocycler. Genes. 2020; 11(6):664. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060664
Chicago/Turabian StyleWee, Soon Keong, Suppiah Paramalingam Sivalingam, and Eric Peng Huat Yap. 2020. "Rapid Direct Nucleic Acid Amplification Test without RNA Extraction for SARS-CoV-2 Using a Portable PCR Thermocycler" Genes 11, no. 6: 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060664
APA StyleWee, S. K., Sivalingam, S. P., & Yap, E. P. H. (2020). Rapid Direct Nucleic Acid Amplification Test without RNA Extraction for SARS-CoV-2 Using a Portable PCR Thermocycler. Genes, 11(6), 664. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060664





