Genetic and Epigenetic Modification of Rat Liver Progenitor Cells via HNF4α Transduction and 5’ Azacytidine Treatment: An Integrated miRNA and mRNA Expression Profile Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Vector Construction and Production
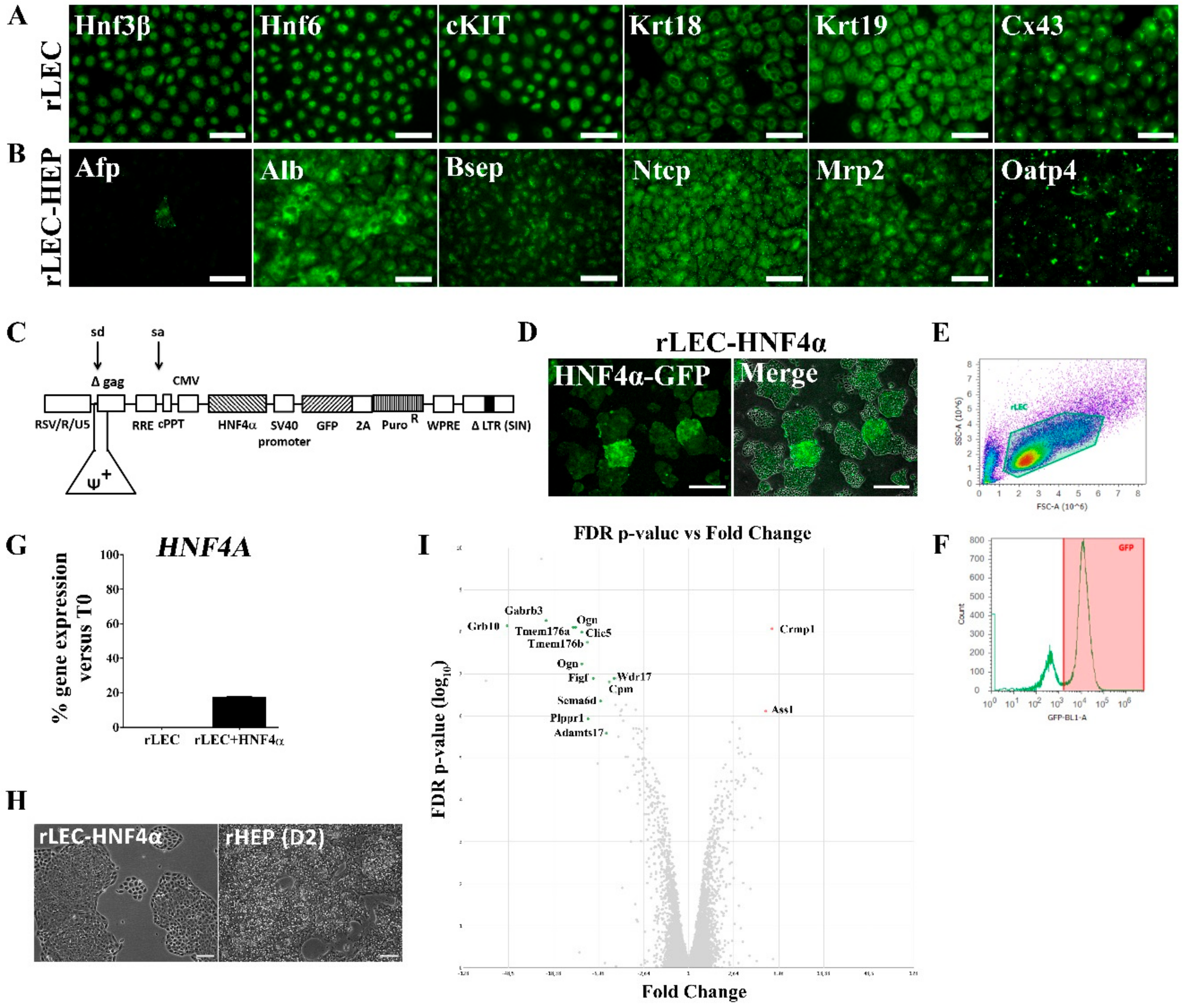
2.4. Isolation, Cultivation and Transduction of rLEC
2.5. Hepatic Differentiation of rLEC
2.6. Isolation of Hepatocytes
2.7. Morphological analysis
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. RNA Isolation
2.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.12. qPCR Data Analysis
2.13. Microarray Profiling of mRNAs
2.14. Microarray Profiling of MicroRNAs
2.15. Data Mining
3. Results
3.1. Ectopic HNF4α Expression Does Not Cause Major Changes to the Transcriptome of Naïve rLEC
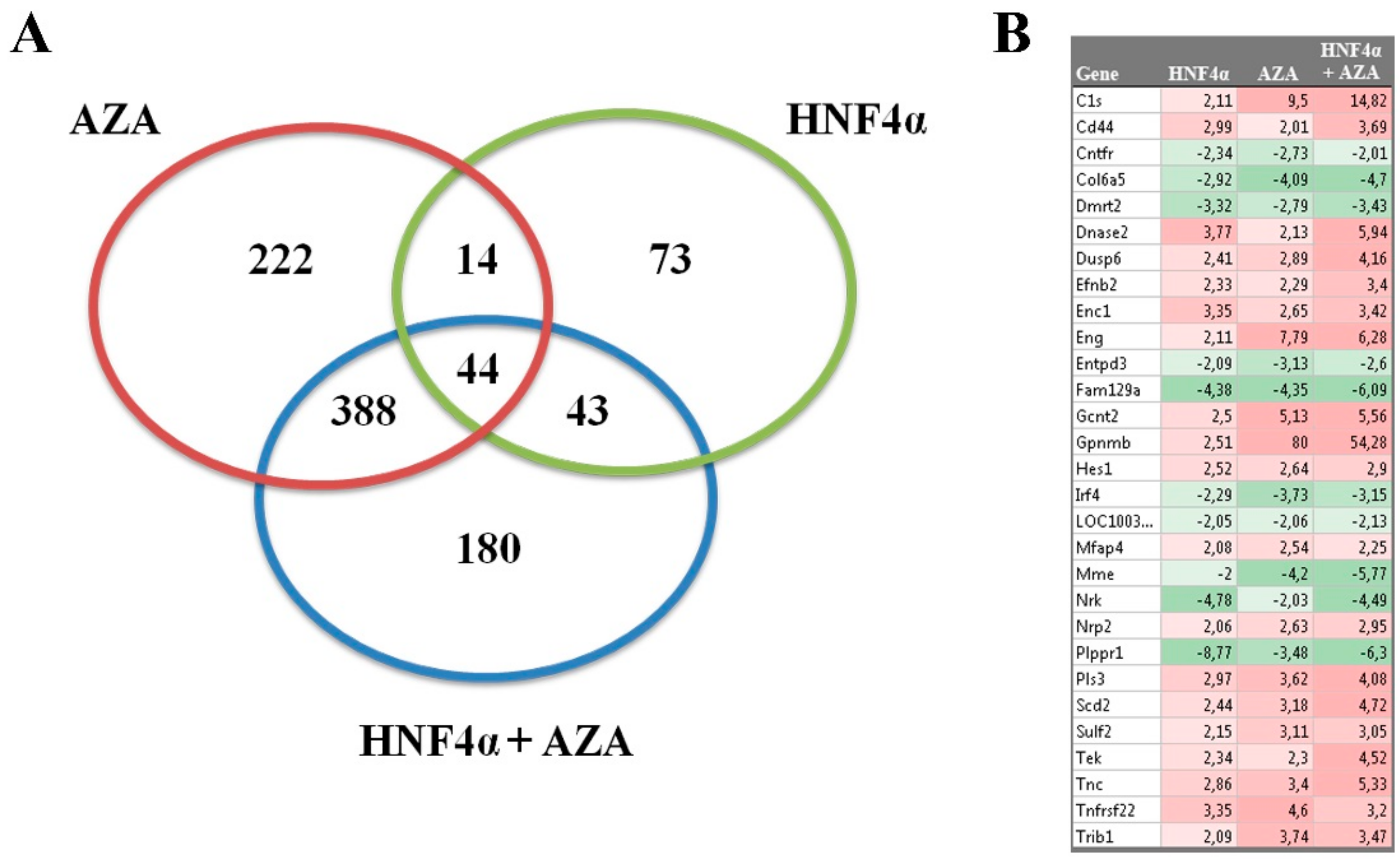
3.2. AZA exposure Significantly Alters the Transcriptome of Naïve rLEC
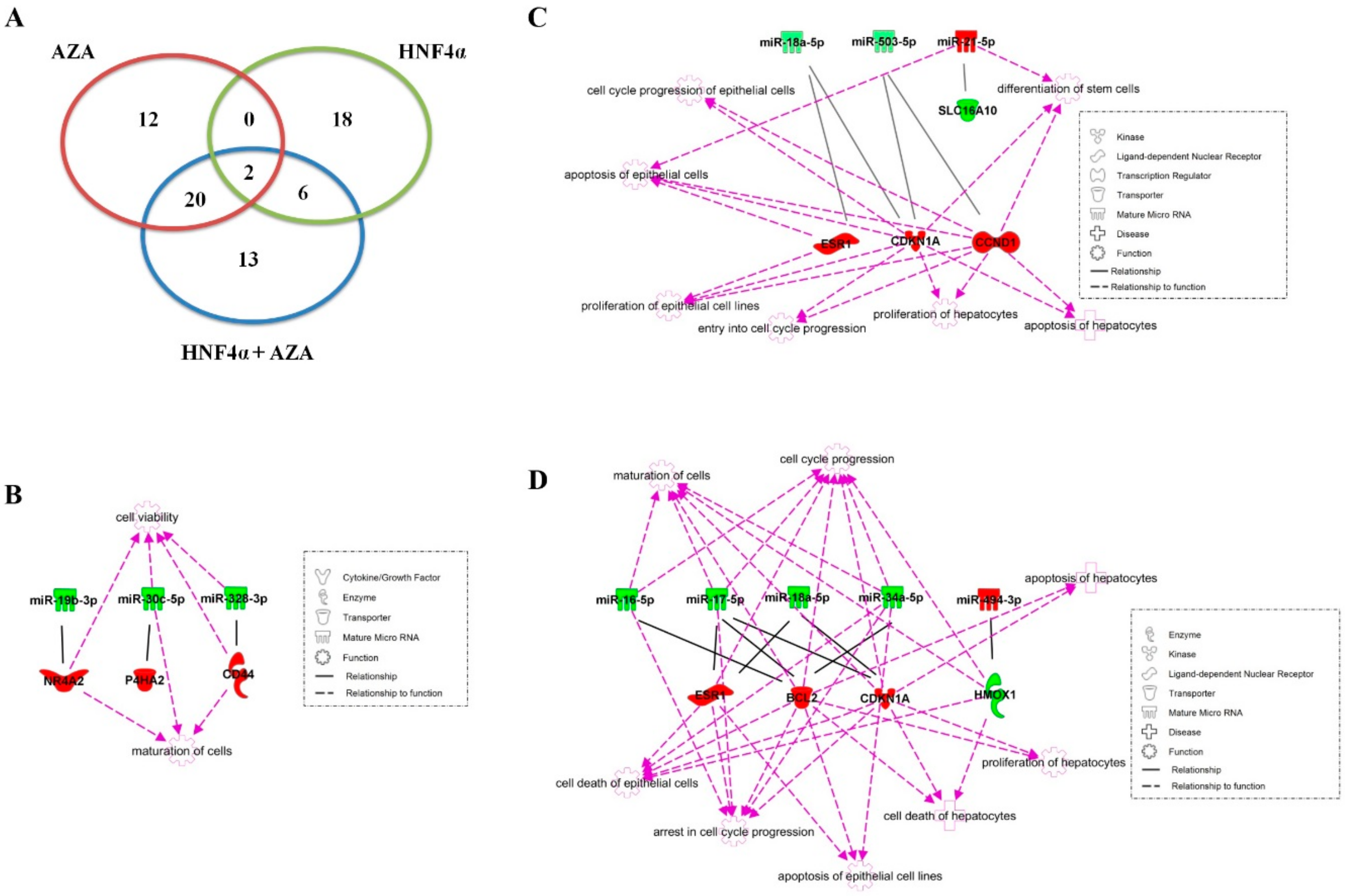
3.3. MicroRNA Expression Profile of rLEC is Significantly Altered by HNF4α Transduction and AZA Exposure
4. Discussion
4.1. Genome-Wide Analysis of Both miRNA and mRNA Expression
4.2. Evaluation of the LETFs Network
4.3. Linking miRNA–mRNA Target Interactions to Functional Pathways
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Clément, B.; Baffet, G.; Beaumont, C.; Morel-Chany, E.; Glaise, D.; Guillouzo, A. Maintenance and reversibility of active albumin secretion by adult rat hepatocytes co-cultured with another liver epithelial cell type. Exp. Cell Res. 1983, 143, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, V.; Vandenberghe, Y.; Callaerts, A.; Verleye, G.; Cornet, M.; Mertens, K.; Sonck, W.; Vercruysse, A. Phase I and phase II xenobiotic biotransformation in cultures and co-cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 40, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, V.; Akrawi, M.; Vandenberghe, Y.; Shephard, E.; Phillips, I.; Vercruysse, A. Co-cultures of rat hepatocytes in the study of valproate toxicity. Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 1992, 15, 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Snykers, S.; De Kock, J.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Differentiation of neonatal rat epithelial cells from biliary origin into immature hepatic cells by sequential exposure to hepatogenic cytokines and growth factors reflecting liver development. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kock, J.; Snykers, S.; Branson, S.; Jagtap, S.A.; Gaspar, J.; Sachinidis, A.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. A Liver-Derived Rat Epithelial Cell Line from Biliary Origin Acquires Hepatic Functions Upon Sequential Exposure to Hepatogenic Growth Factors and Cytokines. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4523–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y.L. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha regulation of bile acid and drug metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, F.J. Regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha-mediated transcription. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 23, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátrai, J.; Cantore, A.; Bartholomae, C.C.; Annoni, A.; Wang, W.; Acosta-Sanchez, A.; Samara-Kuko, E.; De Waele, L.; Ma, L.; Genovese, P.; et al. Hepatocyte-targeted expression by integrase-defective lentiviral vectors induces antigen-specific tolerance in mice with low genotoxic risk. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkens, T.; Vanhaecke, T.; Papeleu, P.; Elaut, G.; Vinken, M.; Snykers, S.; Rogiers, V. Rat hepatocyte cultures: Conventional monolayer and cocultures with rat liver epithelial cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 320, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Papeleu, P.; Vanhaecke, T.; Henkens, T.; Elaut, G.; Vinken, M.; Snykers, S.; Rogiers, V. Isolation of rat hepatocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 320, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- De Kock, J.; Meuleman, P.; Raicevic, G.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Branson, S.; Meganathan, K.; De Boe, V.; Sachinidis, A.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Vanhaecke, T.; et al. Human skin-derived precursor cells are poorly immunogenic and modulate the allogeneic immune response. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2215–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraczek, J.; Vinken, M.; Tourwé, D.; Vanhaecke, T.; Rogiers, V. Synergetic effects of DNA demethylation and histone deacetylase inhibition in primary rat hepatocytes. Invest. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacob, R.; Rüdrich, U.; Rothe, M.; Kirsch, S.; Maasoumy, B.; Narain, N.; Verfaillie, C.M.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Iken, M.; Popescu, I.; et al. Induction of a mature hepatocyte phenotype in adult liver derived progenitor cells by ectopic expression of transcription factors. Stem Cell Res. 2011, 6, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alison, M.R.; Islam, S.; Lim, S. Stem cells in liver regeneration, fibrosis and cancer: The good, the bad and the ugly. J. Pathol. 2009, 217, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snykers, S.; Henkens, T.; De Rop, E.; Vinken, M.; Fraczek, J.; De Kock, J.; De Prins, E.; Geerts, A.; Rogiers, V.; Vanhaecke, T. Role of epigenetics in liver-specific gene transcription, hepatocyte differentiation and stem cell reprogrammation. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLaForest, A.; Nagaoka, M.; Si-Tayeb, K.; Noto, F.K.; Konopka, G.; Battle, M.A.; Duncan, S.A. HNF4A is essential for specification of hepatic progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells. Development 2011, 138, 4143–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Chung, T.-H.; Huang, G.; Zhou, J.; Yan, J.; Ahmann, G.J.; Fonseca, R.; Chng, W.J. Genome-wide pharmacologic unmasking identifies tumor suppressive microRNAs in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26508–26518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, C.; Culmes, M.; Schyschka, L.; Yan, X.; Damm, G.; Wang, Z.; Kleeff, J.; Thasler, W.E.; Hengstler, J.; Stöckle, U.; et al. Decrease of global methylation improves significantly hepatic differentiation of Ad-MSCs: Possible future application for urea detoxification. Cell Transplant. 2013, 22, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.L.; Yeh, P.H.; Tsai, C.Y.; Ting, C.T.; Chiu, Y.H.; Tao, M.H.; Li, W.C.; Hung, S.C. Efficient programming of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived hepatocytes by epigenetic regulations. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, T.; Heraud, P.; Parnpai, R. Effect of Chromatin-Remodeling Agents in Hepatic Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3038764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Burke, P.A. The role of microRNAs in hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha expression and transactivation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, S.; Nakajima, M.; Kida, K.; Yamaura, Y.; Fukami, T.; Yokoi, T. MicroRNAs regulate human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha, modulating the expression of metabolic enzymes and cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, A.; Li, L.; Gaedigk, A.; Bradford, L.D.; Benson, E.A.; Flockhart, D.A.; Skaar, T.C. In silico and in vitro identification of microRNAs that regulate hepatic nuclear factor 4α expression. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Park, H.; Pak, H.-J.; Yang, D.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, W.-J.; Park, S.-J.; Cho, J.-A.; Lee, K.-W. miR-34a inhibits differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells by regulating cell cycle and senescence induction. Differentiation 2015, 90, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.H.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Holterman, A.-X.L.; Wang, X. Transcription factors in liver development, differentiation, and regeneration. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1331–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Sevinç, G.G.; Ersoy, N.; Basak, O.; Kaplan, K.; Sevinç, K.; Ozel, E.; Sengun, B.; Enustun, E.; Ozcimen, B.; et al. Robust, Long-Term Culture of Endoderm-Derived Hepatic Organoids for Disease Modeling. Stem Cell Reports 2019, 13, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausa, F.M.; Tan, Y.; Costa, R.H. Association between hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 (HNF-6) and FoxA2 DNA binding domains stimulates FoxA2 transcriptional activity but inhibits HNF-6 DNA binding. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Tang, W.; Yuan, Q.; Hui, L.; Wang, X.; Xie, X. Chemical Cocktails Enable Hepatic Reprogramming of Mouse Fibroblasts with a Single Transcription Factor. Stem Cell Reports 2017, 9, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovén, J.; Zinin, N.; Wahlström, T.; Müller, I.; Brodin, P.; Fredlund, E.; Ribacke, U.; Pivarcsi, A.; Påhlman, S.; Henriksson, M. MYCN-regulated microRNAs repress estrogen receptor-alpha (ESR1) expression and neuronal differentiation in human neuroblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Yeh, S.-H.; Lu, C.-C.; Yu, S.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, D.-S.; Chen, P.-J. MicroRNA-18a prevents estrogen receptor-alpha expression, promoting proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Ou, C.; Xia, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, D. MiR-503 inhibited cell proliferation of human breast cancer cells by suppressing CCND1 expression. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8697–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-Y.; Wu, H.-J.; Ma, H.-D.; Xu, L.-P.; Huo, Y.; Yin, L.-R. MicroRNA-503 suppresses proliferation and cell-cycle progression of endometrioid endometrial cancer by negatively regulating cyclin D1. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3768–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Sue, Y.-M.; Liu, C.-T.; Cheng, T.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chen, T.-H. MicroRNA-328 inhibits renal tubular cell epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting the CD44 in pressure-induced renal fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchini, C.; Amicone, L.; Alonzi, T.; Marchetti, A.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M. Molecular mechanisms controlling the phenotype and the EMT/MET dynamics of hepatocyte. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Späth, G.F.; Weiss, M.C. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 provokes expression of epithelial marker genes, acting as a morphogen in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 140, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, J.M.; Soane, L. Multiple functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Gong, B.; Wang, H.; Yu, D.; Zhao, G.; Lin, L.; Tang, W.; Yu, H.; Bao, S.; Xie, Q. miR-15b and miR-16 regulate TNF mediated hepatocyte apoptosis via BCL2 in acute liver failure. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherr, M.; Elder, A.; Battmer, K.; Barzan, D.; Bomken, S.; Ricke-Hoch, M.; Schröder, A.; Venturini, L.; Blair, H.J.; Vormoor, J.; et al. Differential expression of miR-17~92 identifies BCL2 as a therapeutic target in BCR-ABL-positive B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 28, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Wei, G.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. Downregulation of Bcl-2 expression by miR-34a mediates palmitate-induced Min6 cells apoptosis. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 258695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, G.T.; Gerin, I.; Feng, Y.; Kaczorowski, A.J.; Kuick, R.; Love, R.E.; Zhai, Y.; Giordano, T.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Moore, B.B.; et al. p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor genes. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, L.L.; Midwinter, R.G.; Ni, J.; Hamid, H.A.; Parish, C.R.; Stocker, R. New insights into intracellular locations and functions of heme oxygenase-1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1723–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaseelan, K.; Lim, K.Y.; Armugam, A. MicroRNA expression in the blood and brain of rats subjected to transient focal ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2008, 39, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antibody | Type | Order ID | Species | Dilution | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-Afp | polyclonal | sc-8108 | goat | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Hnf3β | polyclonal | sc-6554 | goat | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-c-kit | polyclonal | sc-1494 | goat | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Oatp4 | polyclonal | sc-134461 | rabbit | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Ntcp | polyclonal | sc-107029 | goat | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Hnf6 | polyclonal | sc-13050 | rabbit | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Cx43 | polyclonal | C6219 | rabbit | 1/100 | SA |
| anti-Krt18 | monoclonal | F4772 | mouse | 1/50 | SA |
| anti-Krt19 | monoclonal | C7159 | mouse | 1/20 | SA |
| anti-Mrp2 | monoclonal | sc-59611 | mouse | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Bsep | monoclonal | sc-74500 | mouse | 1/50 | SC |
| anti-Alb | polyclonal | A110-125 | rabbit | 1/50 | BL |
| anti-rabbit | Dylight-488 | 711-485-152 | donkey | 1/500 | JI |
| anti-mouse | Dylight-488 | 715-485-150 | donkey | 1/500 | JI |
| anti-goat | Dylight-488 | 711-485-152 | donkey | 1/500 | JI |
| Gene | Assay-On-Demand ID | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Rn01775763_g1 | 174 |
| B2M | Rn00560865_m1 | 58 |
| UBC | Rn01789812_g1 | 88 |
| ACTB * | Rn00667869_m1 | 91 |
| 18S | Hs99999901_s1 | 187 |
| HMBS * | Rn00565886_m1 | 99 |
| HNF4A | Rn04339144_m1 | 53 |
| AZA | HNF4α Transduction | HNF4α Transduction + AZA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular and Cellular Functions | Amount of Genes | Molecular and Cellular Functions | Amount of Genes | Molecular and Cellular Functions | Amount of Genes |
| Cellular growth and proliferation | 91 | Cellular assembly and organisation | 15 | Cellular growth and proliferation | 95 |
| Cell death and survival | 76 | Cellular compromise | 8 | Cell death and survival | 73 |
| Cellular movement | 37 | Cellular growth and proliferation | 20 | Cellular movement | 37 |
| Lipid metabolism | 29 | Gene expression | 13 | Cellular assembly and organisation | 57 |
| Small molecule biochemistry | 17 | Cell-to-cell signaling and interaction | 16 | Cellular function and maintenance | 59 |
| HNF4α Transduction | AZA | HNF4α Transduction + AZA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Fold Change | Fold Change | Fold Change |
| HNF1A | 1.01 | 1.01 | −1.01 |
| HNF3B (FOXA2) | 1.1 | 1.83 * | 1.54* |
| HNF4A | 2.88 * | −1.03 | 4.37 *$ |
| HNF6 | 1.04 | 1.09 | −1.04 |
| CEBPA | −1.38 * | −1.37 * | −1.36 * |
| HNF4α Transduction | AZA | HNF4α Transduction + AZA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Fold Change | p-Value | Fold Change | p-Value | Fold Change | p-Value |
| BCL2 | 1.36 * | 0.001289 | 1.78 * | 0.000086 | 2.47 * | 0.000012 |
| CCND1 | 1.08 | 0.806816 | 2.26 * | 0.000349 | 1.77 * | 0.000081 |
| CD44 | 2.99 * | 0.000012 | 2.01 * | 0.000148 | 3.69 * | 0.000019 |
| CDKN1A | 1.76 * | 0.018413 | 17.19 * | 0.000020 | 3.4 * | 0.000802 |
| ERS1 | 1.01 | 0.834552 | 2.35 * | 0.000142 | 2.72 * | 0.000082 |
| HMOX1 | −1.02 | 0.954842 | −2.98 * | 0.004230 | −2.99 * | 0.001001 |
| NR4A2 | 3.77 * | 0.019828 | 5.16 * | 0.009264 | 9.17 * | 0.002329 |
| P4HA2 | 2.19 * | 0.000041 | −2.27 * | 0.000048 | 1.14 * | 0.001325 |
| SLC16A10 | 1.19 | 0.261210 | −2.58 * | 0.001054 | −1.23 * | 0.011956 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolleyn, J.; Rombaut, M.; Nair, N.; Branson, S.; Heymans, A.; Chuah, M.; VandenDriessche, T.; Rogiers, V.; De Kock, J.; Vanhaecke, T. Genetic and Epigenetic Modification of Rat Liver Progenitor Cells via HNF4α Transduction and 5’ Azacytidine Treatment: An Integrated miRNA and mRNA Expression Profile Analysis. Genes 2020, 11, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050486
Bolleyn J, Rombaut M, Nair N, Branson S, Heymans A, Chuah M, VandenDriessche T, Rogiers V, De Kock J, Vanhaecke T. Genetic and Epigenetic Modification of Rat Liver Progenitor Cells via HNF4α Transduction and 5’ Azacytidine Treatment: An Integrated miRNA and mRNA Expression Profile Analysis. Genes. 2020; 11(5):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050486
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolleyn, Jennifer, Matthias Rombaut, Nisha Nair, Steven Branson, Anja Heymans, Marinee Chuah, Thierry VandenDriessche, Vera Rogiers, Joery De Kock, and Tamara Vanhaecke. 2020. "Genetic and Epigenetic Modification of Rat Liver Progenitor Cells via HNF4α Transduction and 5’ Azacytidine Treatment: An Integrated miRNA and mRNA Expression Profile Analysis" Genes 11, no. 5: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050486
APA StyleBolleyn, J., Rombaut, M., Nair, N., Branson, S., Heymans, A., Chuah, M., VandenDriessche, T., Rogiers, V., De Kock, J., & Vanhaecke, T. (2020). Genetic and Epigenetic Modification of Rat Liver Progenitor Cells via HNF4α Transduction and 5’ Azacytidine Treatment: An Integrated miRNA and mRNA Expression Profile Analysis. Genes, 11(5), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050486






