A DSG1 Frameshift Variant in a Rottweiler Dog with Footpad Hyperkeratosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animal Selection
2.3. Histopathological Examinations
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.6. Variant Calling
2.7. Gene Analysis
2.8. Sanger Sequencing
3. Results
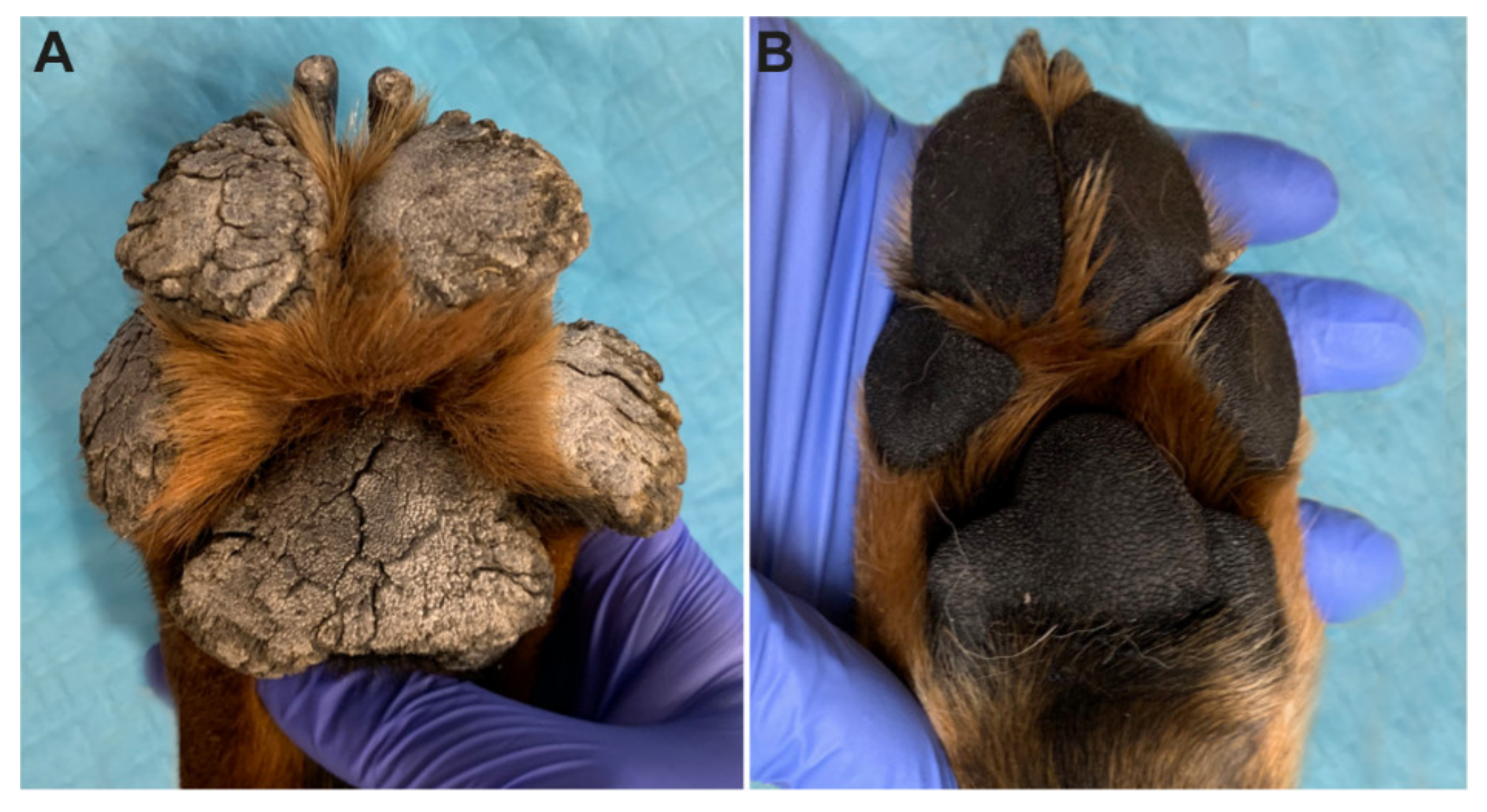
3.1. Clinical Examination
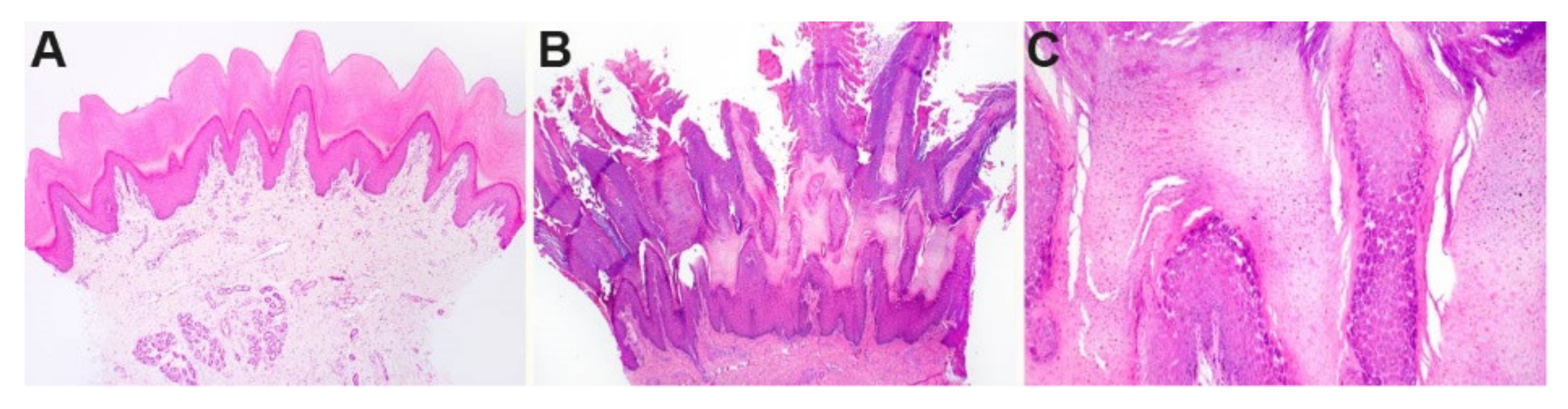
3.2. Histopathological Findings
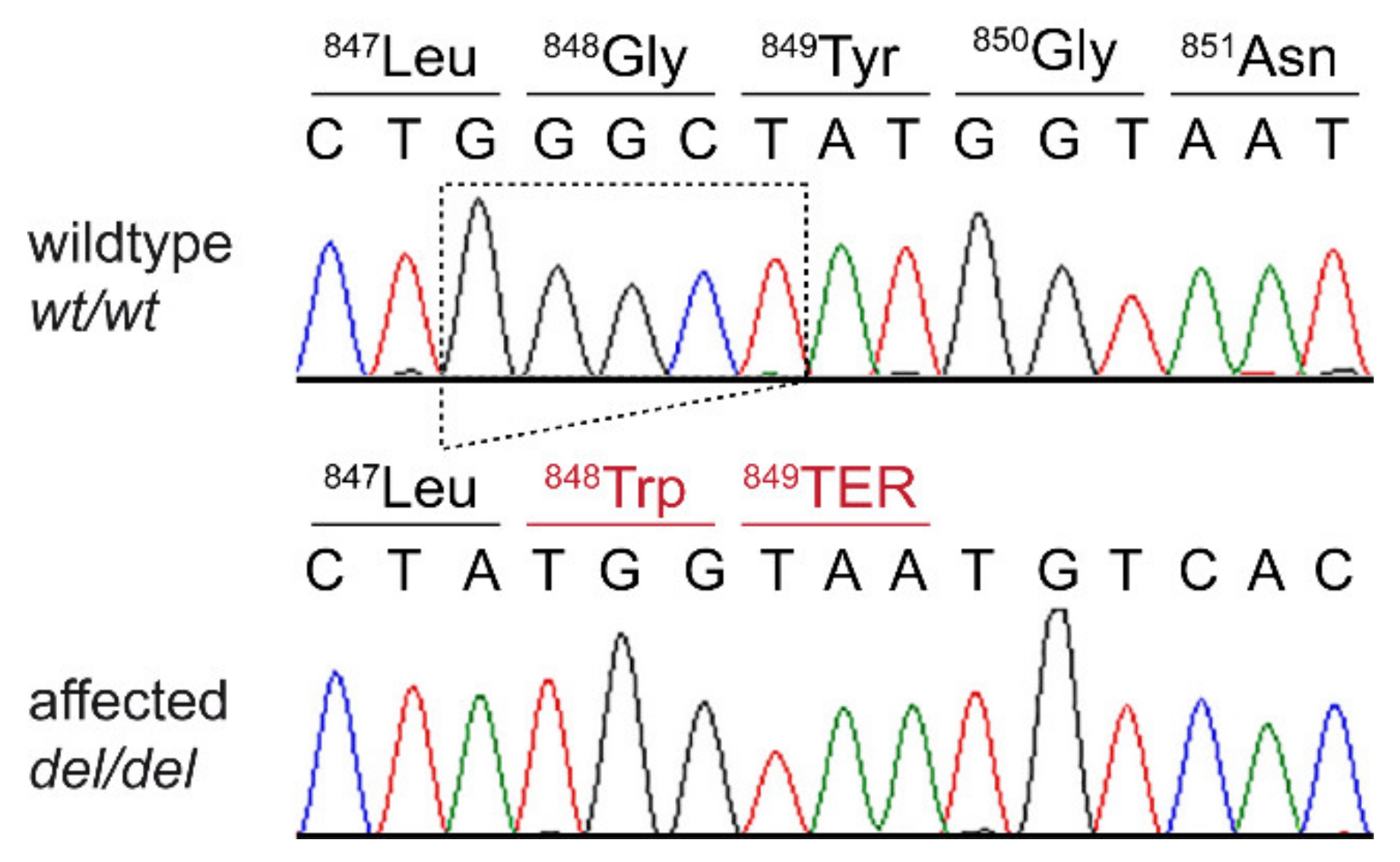
3.3. Genetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemke, J.R.; Kernland-Lang, K.; Hörtnagel, K.; Itin, P. Monogenic human skin disorders. Dermatology 2014, 229, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Technau-Hafsi, K. Palmoplantar keratodermas: Clinical and genetic aspects. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2016, 14, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohler, E.; Mamai, O.; Hirst, J.; Zamiri, M.; Horn, H.; Nomura, T.; Irvine, A.D.; Moran, B.; Wilson, N.J.; Smith, F.J.D.; et al. Haploinsufficiency for AAGAB causes clinically heterogenous forms of punctate palmoplantar keratoderma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giehl, K.A.; Eckstein, G.N.; Pasternack, S.M.; Praetzel-Wunder, S.; Ruzicka, T.; Lichtner, P.; Seidl, K.; Rogers, M.; Graf, E.; Langbein, L.; et al. Nonsense mutations in AAGAB cause punctate palmoplantar keratoderma type Buschke-Fischer-Brauer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaydon, D.C.; Lind, L.K.; Plagnol, V.; Linton, K.J.; Smith, F.J.D.; Wilson, N.J.; McLean, W.H.I.; Munro, C.S.; South, A.P.; Leigh, I.M.; et al. Mutations in AQP5, encoding a water-channel protein, cause autosomal-dominant diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs-Telem, D.; Sarig, O.; van Steensel, M.A.M.; Isakov, O.; Israeli, S.; Nousbeck, J.; Richard, K.; Winnepenninckx, V.; Vernooij, M.; Shomron, N.; et al. Familial pityriasis rubra pilaris is caused by mutations in CARD14. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.-R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.-G.; Sun, L.-D.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tang, X.-F.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies a COL14A1 mutation in a large Chinese pedigree with punctate palmoplantar keratoderma. J. Med. Genet. 2012, 49, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toomes, C.; James, J.; Wood, A.J.; Wu, C.L.; McCormick, D.; Lench, N.; Hewitt, C.; Moynihan, L.; Roberts, E.; Woods, C.G.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the cathepsin C gene result in periodontal disease and palmoplantar keratosis. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickman, L.; Simrak, D.; Stevens, H.P.; Hunt, D.M.; King, I.A.; Bryant, S.P.; Eady, R.A.J.; Leigh, I.M.; Arnemann, J.; Magee, A.I.; et al. N-terminal deletion in a desmosomal cadherin causes the autosomal dominant skin disease striate palmoplantar keratoderma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.K.; McKenna, K.E.; Purkis, P.E.; Green, K.J.; Eady, R.A.J.; Leigh, I.M.; Hughes, A.E. Haploinsufficiency of desmoplakin causes a striate subtype of palmoplantar keratoderma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eytan, O.; Morice-Picard, F.; Sarig, O.; Ezzedine, K.; Isakov, O.; Li, Q.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Shomron, N.; Goldsmith, T.; Fuchs-Telem, D.; et al. Cole disease results from mutations in ENPP1. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruthappu, T.; McGinty, L.A.; Blaydon, D.C.; Fell, B.; Määttä, A.; Duit, R.; Hawkins, T.; Braun, K.M.; Simpson, M.A.; O’Toole, E.A.; et al. Recessive mutation in FAM83G associated with palmoplantar keratoderma and exuberant scalp hair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Lin, Z.; Lee, M.; Jia, X.; Ren, Y.; Dai, L.; Guan, L.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; et al. Exome sequencing reveals mutation in GJA1 as a cause of keratoderma-hypotrichosis-leukonychia totalis syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heathcote, K.; Syrris, P.; Carter, N.D.; Patton, M.A. A connexin 26 mutation causes a syndrome of sensorineural hearing loss and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis (MIM 148350). J. Med. Genet. 2000, 37, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G.; Smith, L.E.; Bailey, R.A.; Itin, P.; Hohl, D.; Epstein, E.H., Jr.; DiGiovanna, J.J.; Compton, J.G.; Bale, S.J. Mutations in the human connexin gene GJB3 cause erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macari, F.; Landau, M.; Cousin, P.; Mevorah, B.; Brenner, S.; Panizzon, R.; Schorderet, D.F.; Hohl, D.; Huber, M. Mutation in the gene for connexin 30.3 in a family with erythrokeratodermia variabilis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamartine, J.; Essenfelder, G.M.; Kibar, Z.; Lanneluc, I.; Callouet, E.; Laoudj, D.; Lemaitre, G.; Hand, C.; Haylick, S.J.; Zonana, J.; et al. Mutations in GJB6 cause hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKoy, G.; Protonotarios, N.; Crosby, A.; Tsatsopoulou, A.; Anastasakis, A.; Coonar, A.; Norman, M.; Baboonian, C.; Jeffery, S.; McKenna, W.J. Identification of a deletion in plakoglobin in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy with palmoplantar keratoderma and woolly hair (Naxos disease). Lancet 2000, 355, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramot, Y.; Molho-Pessach, V.; Meir, T.; Alper-Pinus, R.; Siam, I.; Tams, S.; Babay, S.; Zlotogorski, A. Mutation in KANK2, encoding a sequestering protein for steroid receptor coactivators, causes keratoderma and woolly hair. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimonis, V.; DiGiovanna, J.J.; Yang, J.M.; Doyle, S.Z.; Bale, S.J.; Compton, J.G. A mutation in the V1 end domain of keratin 1 in non-epidermolytic palmar-plantarkeratoderma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 103, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, P.E.; Haley, J.L.; Kansky, A.; Rothnagel, J.A.; Jones, D.O.; Turner, R.J. Mutation of a type II keratin gene (K6a) in pachyonychia congenita. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, F.J.D.; Jonkman, M.F.; van Goor, H.; Coleman, C.M.; Covello, S.P.; Uitto, J.; McLean, W.H.I. A mutation in human keratin K6b produces a phenocopy of the K17 disorder pachyonychia congenita type 2. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.J.; Messenger, A.G.; Leachman, S.A.; O’Toole, E.A.; Lane, E.B.; McLean, W.H.I.; Smith, F.J.D. Keratin K6c mutations cause focal palmoplantar keratoderma. J. Investig. Derm. 2010, 130, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.; Hennies, H.-C.; Langbein, L.; Digweed, M.; Mischke, D.; Drechsler, M.; Schrock, E.; Royer-Pokora, B.; Franke, W.W.; Sperling, K.; et al. Keratin 9 gene mutations in epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (EPPK). Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsher, M.K.; Navsaria, H.A.; Stevens, H.P.; Ratnavel, R.C.; Purkis, P.E.; McLean, W.H.; Cook, L.J.; Griffiths, W.A.D.; Geschmeissner, S.; Spurr, N.; et al. Novel mutations in keratin 16 gene underly focal nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (NEPPK) in two families. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, W.H.I.; Rugg, E.L.; Lunny, D.P.; Morley, S.M.; Lane, E.B.; Swensson, O.; Dopping-Hepenstal, P.J.C.; Griffiths, W.A.D.; Eady, R.A.J.; Higgins, C.; et al. Keratin 16 and keratin 17 mutations cause pachyonychia congenita. Nat. Genet. 1995, 9, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, E.; Monaco, A.P.; McGrath, J.A.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Camisa, C.; Hovnanian, A.; Weeks, D.E.; Lathrop, M.; Uitto, J.; Christiano, A.M. A molecular defect in loricrin, the major component of the cornified cell envelope, underlies Vohwinkel’s syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlqvist, J.; Klar, J.; Tiwari, N.; Schuster, J.; Torma, H.; Badhai, J.; Pujol, R.; van Steensel, M.A.M.; Brinkhuizen, T.; Gijezen, L.; et al. A single-nucleotide deletion in the POMP 5-prime UTR causes a transcriptional switch and altered epidermal proteasome distribution in KLICK genodermatosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courcet, J.-B.; Elalaoui, S.C.; Duplomb, L.; Tajir, M.; Riviere, J.-B.; Thevenon, J.; Gigot, N.; Marle, N.; Aral, B.; Duffourd, Y.; et al. Autosomal-recessive SASH1 variants associated with a new genodermatosis with pigmentation defects, palmoplantar keratoderma and skin carcinoma. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 957–962. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, A.; Shiohama, A.; Sasaki, T.; Nakabayashi, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Atsugi, T.; Sato, S.; Shimizu, A.; Mikami, S.; Tanizaki, H.; et al. Mutations in SERPINB7, encoding a member of the serine protease inhibitor superfamily, cause Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Bouadjar, B.; Heilig, R.; Huber, M.; Lefevre, C.; Jobard, F.; Macari, F.; Bakija-Konsuo, A.; Ait-Belkacem, F.; Weissenbach, J.; et al. Mutations in the gene encoding SLURP-1 in mal de Meleda. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natt, E.; Kida, K.; Odievre, M.; Di Rocco, M.; Scherer, G. Point mutations in the tyrosine aminotransferase gene in tyrosinemia type II. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9297–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.; Rettler, I.; Bernasconi, K.; Frenk, E.; Lavrijsen, S.P.M.; Ponec, M.; Bon, A.; Lautenschlager, S.; Schorderet, D.F.; Hohl, D. Mutations of keratinocyte transglutaminase in lamellar ichthyosis. Science 1995, 267, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zeng, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Glusman, G.; Roach, J.; Etheridge, A.; et al. A gain-of-function mutation in TRPV3 causes focal palmoplantar keratoderma in a Chinese family. J. Investig. Derm. 2015, 135, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohring, A.; Stamm, T.; Spaich, C.; Haase, C.; Spree, K.; Hehr, U.; Hoffmann, M.; Ledig, S.; Sel, S.; Wieacker, P.; et al. WNT10A mutations are a frequent cause of a broad spectrum of ectodermal dysplasias with sex-biased manifestation pattern in heterozygotes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drögemüller, M.; Jagannathan, V.; Becker, D.; Drögemüller, C.; Schelling, C.; Plassais, J.; Kaerle, C.; Dufaure de Citres, C.; Thomas, A.; Müller, E.J.; et al. A mutation in the FAM83G gene in dogs with hereditary footpad hyperkeratosis (HFH). PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, P.; Fellay, A.K.; Sayar, B.S.; Hariton, W.V.J.; Wiener, D.J.; Galichet, A.; Müller, E.J.; Roosje, P.J. FAM83G/Fam83g genetic variants affect canine and murine hair formation. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.; Dingwell, K.S.; Herhaus, L.; Gourlay, R.; Macartney, T.; Campbell, D.; Smith, J.C.; Sapkota, G.P. Protein associated with SMAD1 (PAWS1/FAM83G) is a substrate for type I bone morphogenetic protein receptors and modulates bone morphogenetic protein signalling. Open Biol. 2014, 4, 130210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozatzi, P.; Dingwell, K.S.; Wu, K.Z.; Cooper, F.; Cummins, T.D.; Hutchinson, L.D.; Vogt, J.; Wood, N.T.; Macartney, T.J.; Varghese, J.; et al. PAWS1 controls Wnt signalling through association with casein kinase 1α. EMBO Rep. 2018, 19, e44807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radden, L.A.; Child, K.M.; Adkins, E.B.; Spacek, D.V.; Feliciano, A.M.; King, T.R. The wooly mutation (wly) on mouse chromosome 11 is associated with a genetic defect in Fam83g. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassais, J.; Guaguère, E.; Lagoutte, L.; Guillory, A.S.; de Citres, C.D.; Degorce-Rubiales, F.; Delverdier, M.; Vaysse, A.; Quignon, P.; Bleuart, C.; et al. A spontaneous KRT16 mutation in a dog breed: A model for human focal non-epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (FNEPPK). J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannathan, V.; Drögemüller, C.; Leeb, T.; Dog Biomedical Variant Database Consortium (DBVDC). A comprehensive biomedical variant catalogue based on whole genome sequences of 582 dogs and eight wolves. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang le, L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Najor, N.A.; Green, K.J. Desmosomes: Regulators of cellular signaling and adhesion in epidermal health and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a015297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulu, L.; Kusumi, A.; Steinberg, M.S.; Klaus-Kovtun, V.; Stanley, J.R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal core protein in pemphigus foliaceus. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, D.M.; Rickman, L.; Whittock, N.V.; Eady, R.A.; Simrak, D.; Dopping-Hepenstal, P.J.; Stevens, H.P.; Armstrong, D.K.; Hennies, H.C.; Küster, W.; et al. Spectrum of dominant mutations in the desmosomal cadherin desmoglein 1, causing the skin disease striate palmoplantar keratoderma. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 9, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelov, L.; Sarig, O.; Harmon, R.M.; Rapaport, D.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Isakov, O.; Koetsier, J.L.; Gat, A.; Goldberg, I.; Bergman, R.; et al. Desmoglein 1 deficiency results in severe dermatitis, multiple allergies and metabolic wasting. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C.; Jakob, T.; He, Y.; Kiritsi, D.; Hausser, I.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Loss of desmoglein 1 associated with palmoplantar keratoderma, ermatitis and multiple allergies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlipf, N.A.; Vahlquist, A.; Teigen, N.; Virtanen, M.; Dragomir, A.; Fismen, S.; Barenboim, M.; Manke, T.; Rösler, B.; Zimmer, A.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel autosomal recessive DSG1 mutations associated with mild SAM syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Phenotype | Inheritance a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAGAB | Palmoplantar keratoderma, punctate type IA; PPKP1A | AD | [3,4] |
| AQP5 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, Bothnian type | AD | [5] |
| CARD5 | Pityriasis rubra pilaris | AD | [6] |
| COL14A1 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, punctate type IB; PPKP1B | AD | [7] |
| CTSC | Papillon-Lefevre syndrome | AR | [8] |
| DSG1 | Palmoplantar keratoderma I, striate, focal, or diffuse; PPKS1 | AD | [9] |
| DSP | Palmoplantar keratoderma II, striate, focal, or diffuse; PPKS2 | AD | [10] |
| ENPP1 | Cole disease | AD | [11] |
| FAM83G | Palmoplantar keratoderma and exuberant scalp hair. | AR | [12] |
| GJA1 | Palmoplantar keratoderma with congenital alopecia | AD | [13] |
| GJB2 | Keratoderma, palmoplantar, with deafness | AD | [14] |
| GJB3 | Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 1 | AD or AR | [15] |
| GJB4 | Erythrokeratodermia variabilis et progressiva 2 | AD | [16] |
| GJB6 | Ectodermal dysplasia 2, Clouston type | AD | [17] |
| JUP | Naxos disease | AR | [18] |
| KANK2 | Palmoplantar keratoderma and woolly hair | AR | [19] |
| KRT1 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, epidermolytic or nonepidermolytic | AD | [20] |
| KRT6A | Pachyonychia congenita 3 | AD | [21] |
| KRT6B | Pachyonychia congenita 4 | AD | [22] |
| KRT6C | Palmoplantar keratoderma, nonepidermolytic, focal or diffuse | AD | [23] |
| KRT9 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, epidermolytic | AD | [24] |
| KRT16 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, nonepidermolytic, focal 1, FNEPPK1 | AD | [25,26] |
| KRT17 | Pachyonychia congenita 2 | AD | [26] |
| LOR | Vohwinkel syndrome with ichthyosis | AD | [27] |
| POMP | Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma | AR | [28] |
| SASH1 | Cancer, alopecia, pigment dyscrasia, onychodystrophy, and keratoderma | AR | [29] |
| SERPINB7 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, Nagashima type; PPKN | AR | [30] |
| SLURP1 | Meleda disease | AR | [31] |
| TAT | Tyrosinemia, type II | AR | [32] |
| TGM1 | Ichthyosis, congenital, autosomal recessive 1 | AR | [33] |
| TRPV3 | Palmoplantar keratoderma, nonepidermolytic, focal 2; FNEPPK2 | AD | [34] |
| WNT10A | Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome | AR | [35] |
| Filtering Step | Homozygous Variants | Heterozygous Variants |
|---|---|---|
| All variants in the affected Rottweiler | 3,310,269 | 2,516,875 |
| Private variants | 842 | 3290 |
| Protein-changing private variants | 4 | 25 |
| Private variants in known candidate genes | 1 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Backel, K.A.; Kiener, S.; Jagannathan, V.; Casal, M.L.; Leeb, T.; Mauldin, E.A. A DSG1 Frameshift Variant in a Rottweiler Dog with Footpad Hyperkeratosis. Genes 2020, 11, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040469
Backel KA, Kiener S, Jagannathan V, Casal ML, Leeb T, Mauldin EA. A DSG1 Frameshift Variant in a Rottweiler Dog with Footpad Hyperkeratosis. Genes. 2020; 11(4):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040469
Chicago/Turabian StyleBackel, Katherine A., Sarah Kiener, Vidhya Jagannathan, Margret L. Casal, Tosso Leeb, and Elizabeth A. Mauldin. 2020. "A DSG1 Frameshift Variant in a Rottweiler Dog with Footpad Hyperkeratosis" Genes 11, no. 4: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040469
APA StyleBackel, K. A., Kiener, S., Jagannathan, V., Casal, M. L., Leeb, T., & Mauldin, E. A. (2020). A DSG1 Frameshift Variant in a Rottweiler Dog with Footpad Hyperkeratosis. Genes, 11(4), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040469






