Assessment of Genotoxicity in Human Cells Exposed to Modulated Electromagnetic Fields of Wireless Communication Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Models and Culture Procedures
2.2. Exposure Equipment and wEMF Signal Modulations
2.3. Assessment of Genotoxicity
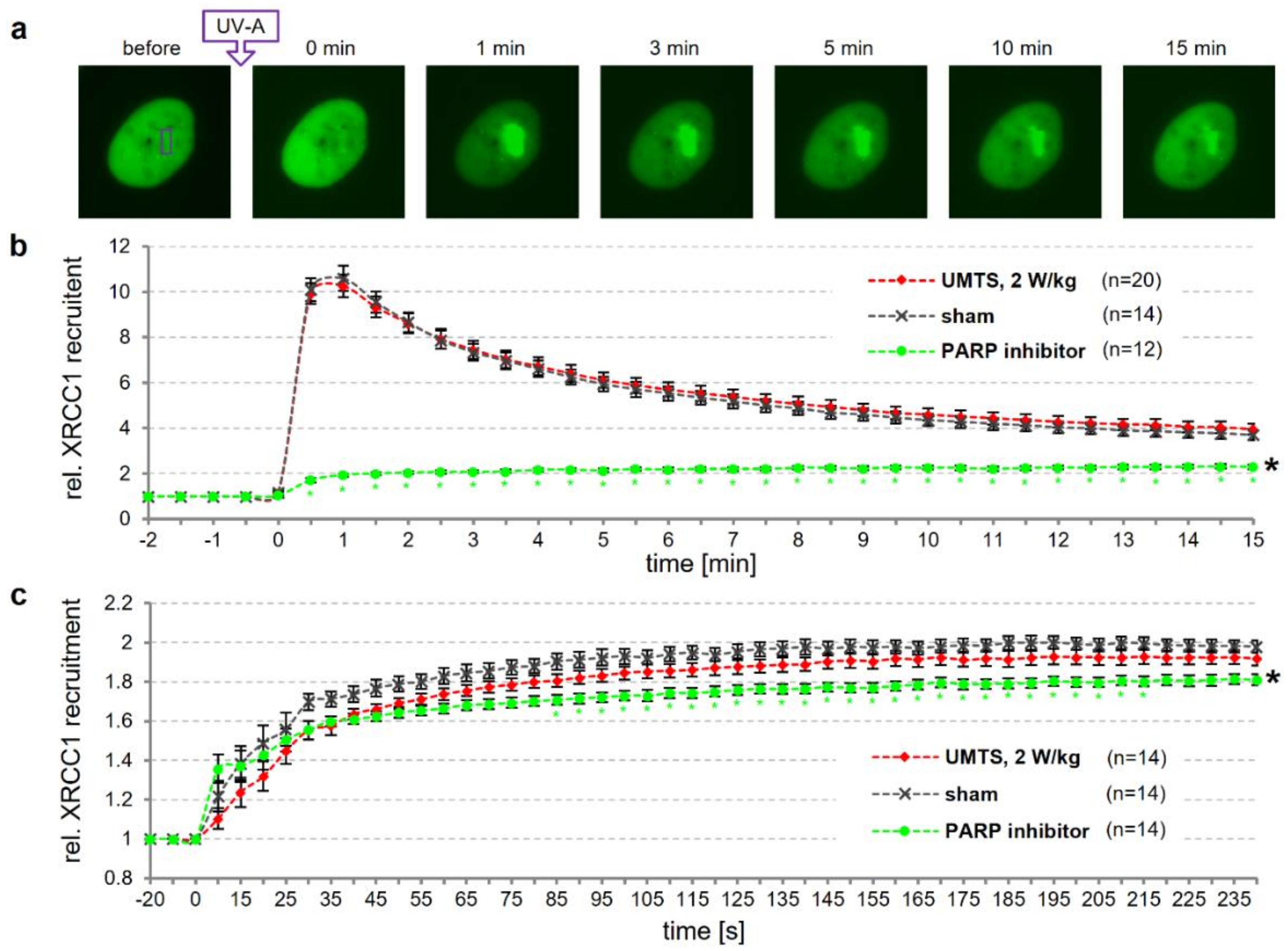
2.4. Live Cell Imaging of XRCC1 Recruitment
3. Results
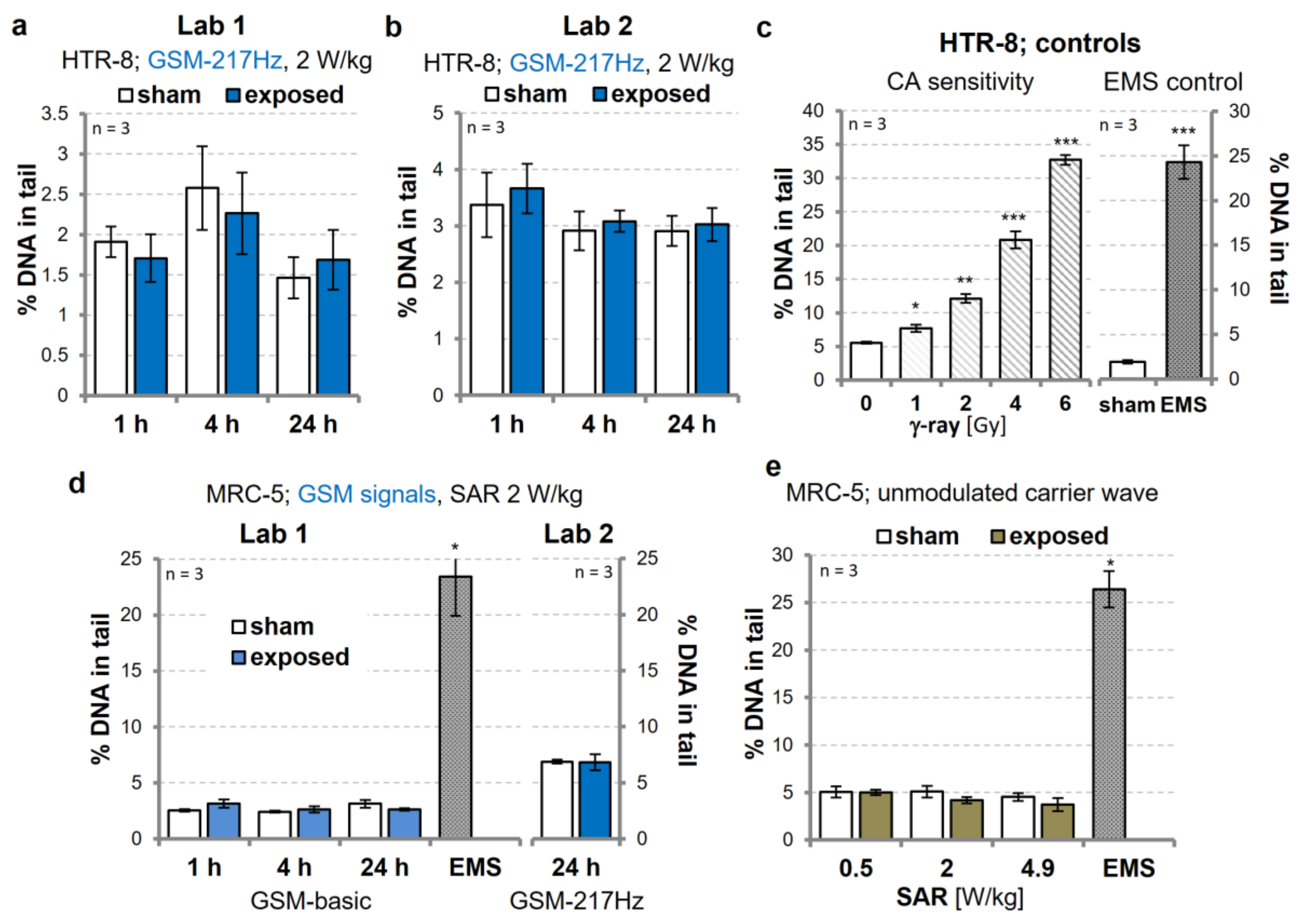
3.1. Replication Experiments on Genotoxic Effects of GSM-Modulated Signals
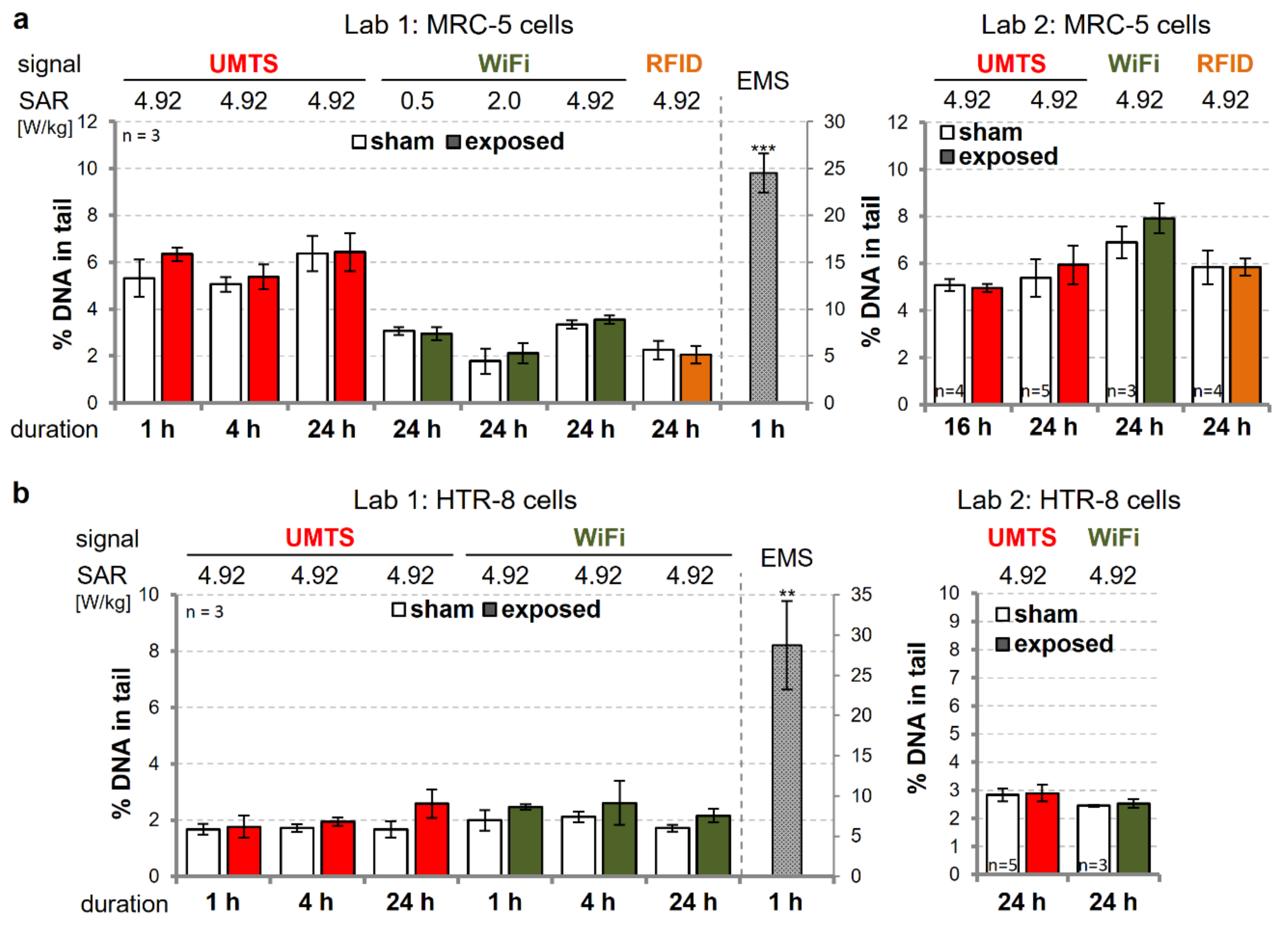
3.2. Investigation of the Genotoxic Potential of UMTS-, WiFi-, and RFID-Modulated wEMF
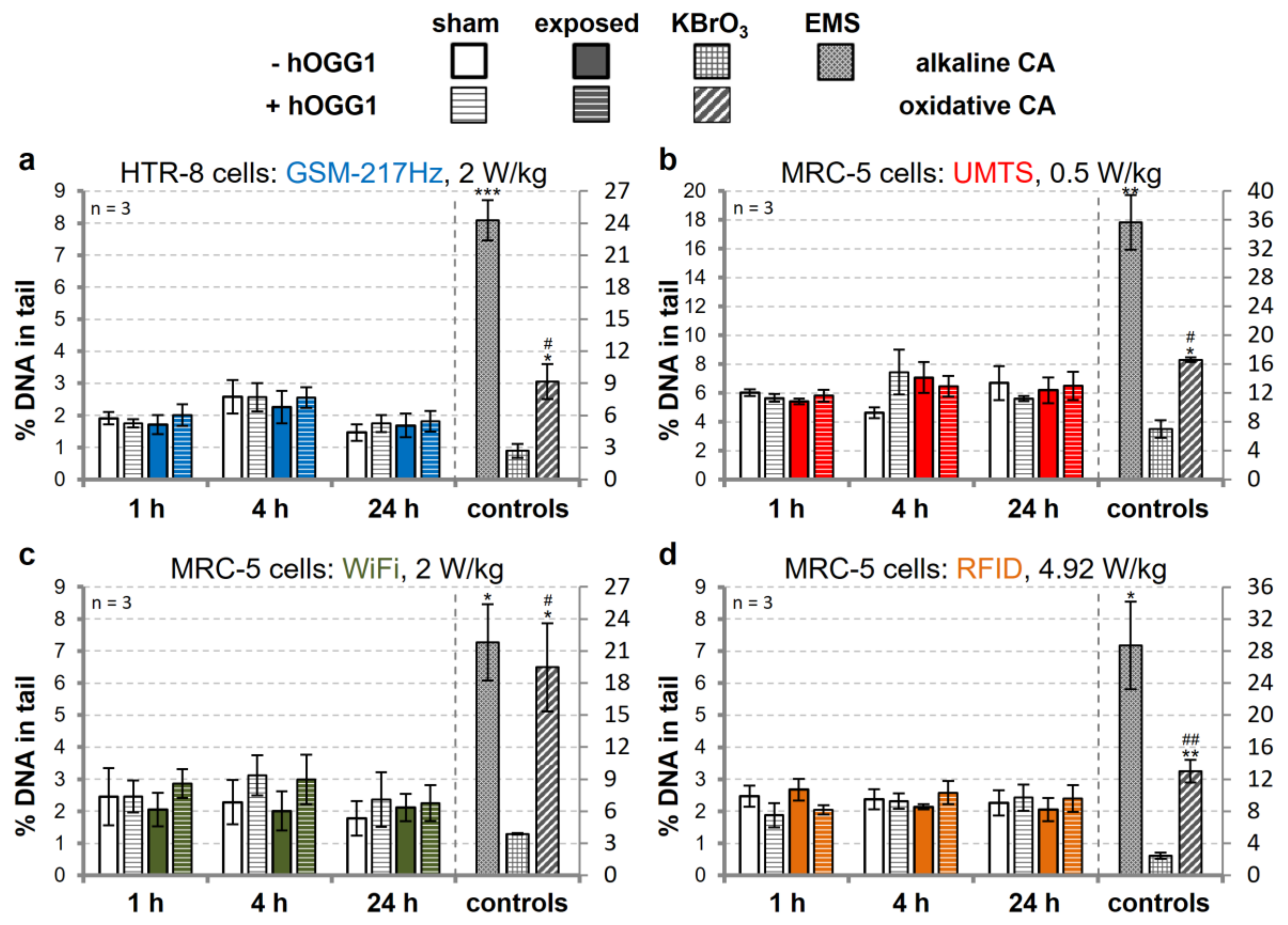
3.3. Modulation of DNA Repair Capacity does not Reveal wEMF-Dependent DNA Damage
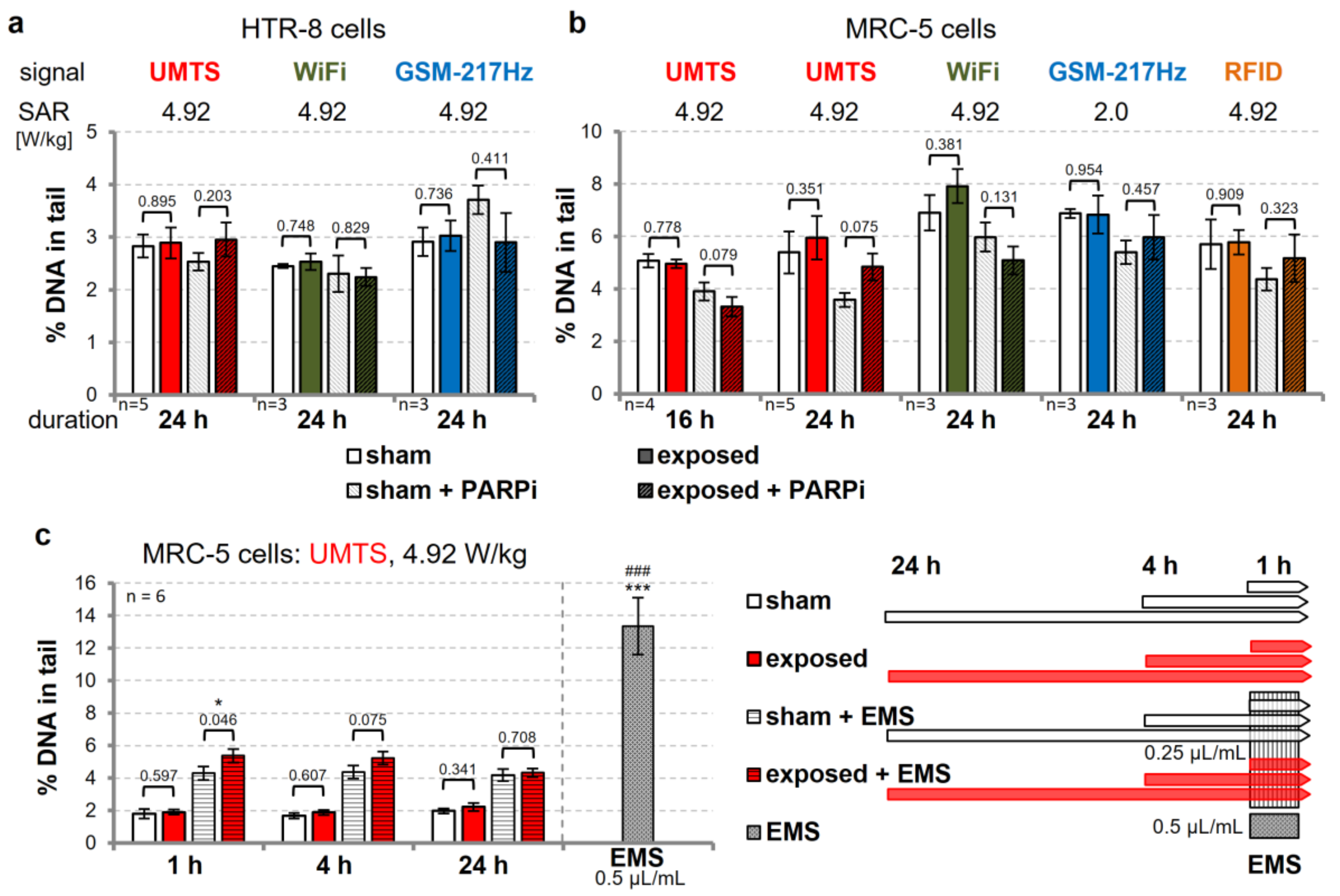
3.4. Dynamics of DNA Repair is not Affected by UMTS Exposure
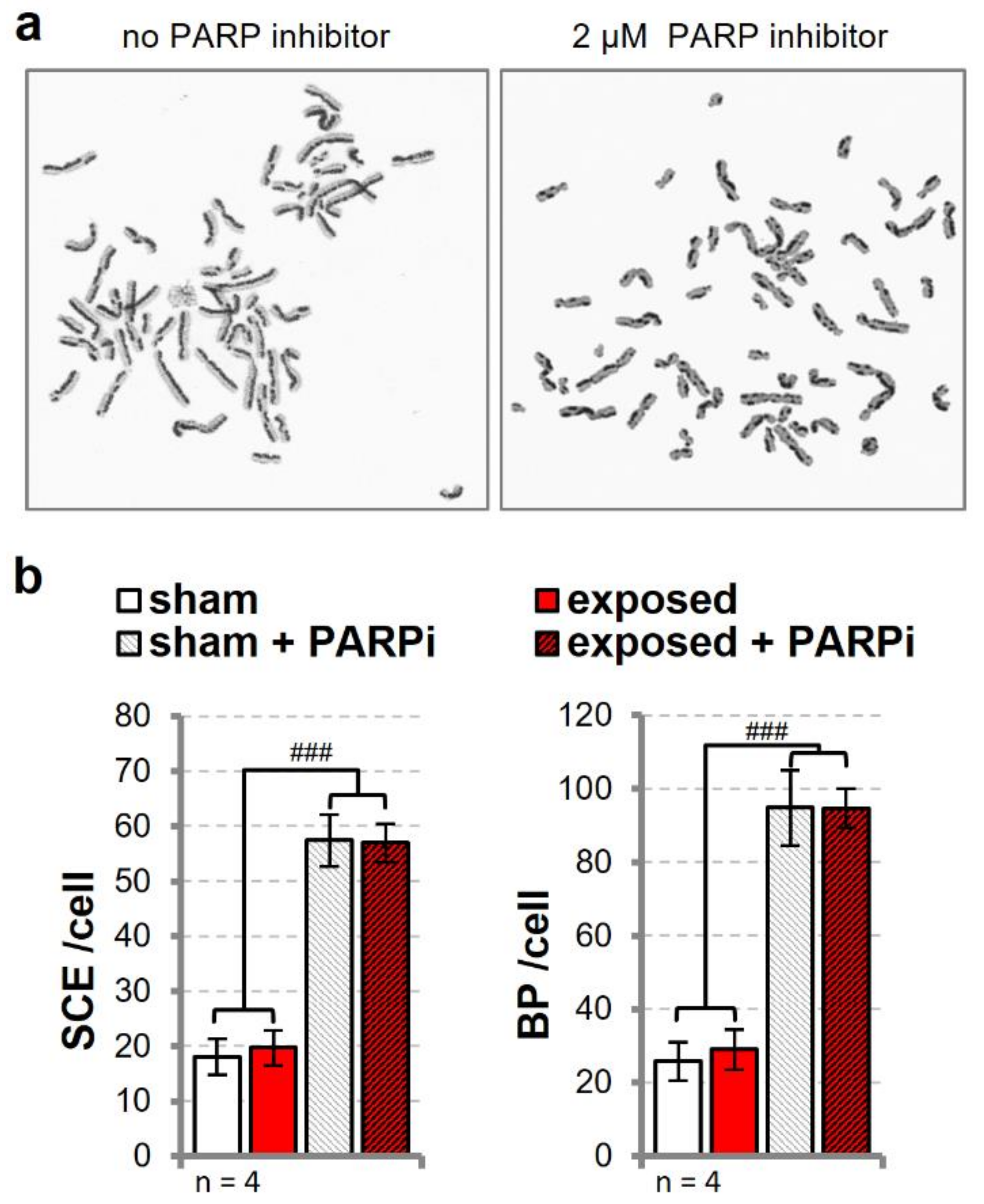
3.5. Sister Chromatid Exchange is Unaffected in Cells Exposed to UMTS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyde, M.; Cesta, M.; Blystone, C.; Elmore, S.; Foster, P.; Hooth, M.; Kissling, G.; Malarkey, D.; Sills, R.; Stout, M.; et al. Report of Partial findings from the National Toxicology Program Carcinogenesis Studies of Cell Phone Radiofrequency Radiation in Hsd: Sprague Dawley® SD rats (Whole Body Exposures). BioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcioni, L.; Bua, L.; Tibaldi, E.; Lauriola, M.; De Angelis, L.; Gnudi, F.; Mandrioli, D.; Manservigi, M.; Manservisi, F.; Manzoli, I.; et al. Report of final results regarding brain and heart tumors in Sprague-Dawley rats exposed from prenatal life until natural death to mobile phone radiofrequency field representative of a 1.8 GHz GSM base station environmental emission. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Roe, S.L.; Wyde, M.E.; Stout, M.D.; Winters, J.W.; Hobbs, C.A.; Shepard, K.G.; Green, A.S.; Kissling, G.E.; Shockley, K.R.; Tice, R.R.; et al. Evaluation of the genotoxicity of cell phone radiofrequency radiation in male and female rats and mice following subchronic exposure. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, M.; Goodman, R. Electromagnetic fields stress living cells. Pathophysiology 2009, 16, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juutilainen, J.; Hoyto, A.; Kumlin, T.; Naarala, J. Review of possible modulation-dependent biological effects of radiofrequency fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2011, 32, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacic, P.; Somanathan, R. Electromagnetic fields: Mechanism, cell signaling, other bioprocesses, toxicity, radicals, antioxidants and beneficial effects. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2010, 30, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.L.; Singh, N.P.; Lai, H. Electromagnetic fields and DNA damage. Pathophysiology 2009, 16, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalaxmi; Prihoda, T.J. Comprehensive Review of Quality of Publications and Meta-analysis of Genetic Damage in Mammalian Cells Exposed to Non-Ionizing Radiofrequency Fields. Radiat. Res. 2019, 191, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simko, M.; Remondini, D.; Zeni, O.; Scarfi, M.R. Quality matters: Systematic analysis of endpoints related to “cellular life” in vitro data of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tice, R.R.; Agurell, E.; Anderson, D.; Burlinson, B.; Hartmann, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Miyamae, Y.; Rojas, E.; Ryu, J.C.; Sasaki, Y.F. Single cell gel/comet assay: Guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkez, H.; Arslan, M.E.; Ozdemir, O. Genotoxicity testing: Progress and prospects for the next decade. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glei, M.; Schneider, T.; Schlormann, W. Comet assay: An essential tool in toxicological research. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2315–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, R.K. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields do not interact directly with DNA. Bioelectromagnetics 1998, 19, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.S.; O’Shea, V.L.; Kundu, S. Base-excision repair of oxidative DNA damage. Nature 2007, 447, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortini, P.; Dogliotti, E. Base damage and single-strand break repair: Mechanisms and functional significance of short-and long-patch repair subpathways. DNA Repair 2007, 6, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.B.; Klungland, A.; Rognes, T.; Leiros, I. DNA repair in mammalian cells: Base excision repair: The long and short of it. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svilar, D.; Goellner, E.M.; Almeida, K.H.; Sobol, R.W. Base excision repair and lesion-dependent subpathways for repair of oxidative DNA damage. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2491–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen-Bauer, A.; Solvang-Garten, K.; Sundheim, O.; Pena-Diaz, J.; Andersen, S.; Slupphaug, G.; Krokan, H.E.; Wilson, D.M.; Akbari, M.; Otterlei, M. XRCC1 coordinates disparate responses and multiprotein repair complexes depending on the nature and context of the DNA damage. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2011, 52, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldecott, K.W. XRCC1 protein; Form and function. DNA Repair 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschaeve, L.; Juutilainen, J.; Lagroye, I.; Miyakoshi, J.; Saunders, R.; De Seze, R.; Tenforde, T.; Van Rongen, E.; Veyret, B.; Xu, Z. In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity of radiofrequency fields. Mutat. Res. 2010, 705, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.H.; Hawley, T.S.; Hawley, R.G.; MacDougall, J.R.; Kerbel, R.S.; Khoo, N.; Lala, P.K. Establishment and characterization of first trimester human trophoblast cells with extended lifespan. Exp. Cell Res. 1993, 206, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzellitti, S.; Valbonesi, P.; Ciancaglini, N.; Biondi, C.; Contin, A.; Bersani, F.; Fabbri, E. Transient DNA damage induced by high-frequency electromagnetic fields (GSM 1.8 GHz) in the human trophoblast HTR-8/SVneo cell line evaluated with the alkaline comet assay. Mutat. Res. 2010, 683, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diem, E.; Schwarz, C.; Adlkofer, F.; Jahn, O.; Rudiger, H. Non-thermal DNA breakage by mobile-phone radiation (1800 MHz) in human fibroblasts and in transformed GFSH-R17 rat granulosa cells in vitro. Mutat. Res. 2005, 583, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobkin, D.M. The RF in RFID: Passive UHF RFID in Practice, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Burlington, VT, USA, 2008; pp. 1–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPCglobal. EPC Radio-Frequency Identity Protocols Class-1 Generation-2 UHF RFID. (v1.2.0). 2008. Available online: https://www.gs1.org/sites/default/files/docs/epc/uhfc1g2_1_2_0-standard-20080511.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2011).
- Andersen, J.B.; Mogensen, P.E.; Pedersen, G.F. Power variations of wireless communication systems. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 31, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuderer, J. EMF Risk Assessment: “In Vitro” Research and Sleep Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verloock, L.; Joseph, W.; Vermeeren, G.; Martens, L. Procedure for assessment of general public exposure from WLAN in offices and in wireless sensor network testbed. Health Phys. 2010, 98, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE Std 802.11g-2003, Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications, Amendment 4: Further Higher Data Rate Extension in the 2.4 GHz Band; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Yu, T.W.; Phillips, B.J.; Schmezer, P. The effect of various antioxidants and other modifying agents on oxygen-radical-generated DNA damage in human lymphocytes in the COMET assay. Mutat. Res. 1994, 307, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancsits, S.; Diem, E.; Pilger, A.; Rudiger, H.W.; Jahn, O. Induction of DNA strand breaks by intermittent exposure to extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic fields in human diploid fibroblasts. Mutat. Res. 2002, 519, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.C.; O’Donovan, M.R.; Martin, E.A. hOGG1 recognizes oxidative damage using the comet assay with greater specificity than FPG or ENDOIII. Mutagenesis 2006, 21, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunada, S.; Haskins, J.S.; Kato, T.A. Sister Chromatid Exchange as a Genotoxic Stress Marker. In Radiation Cytogenetics: Methods and Protocols; Kato, T.A., Wilson, P.F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, L.; Nakajima, S.; Oohata, Y.; Takao, M.; Okano, S.; Masutani, M.; Wilson, S.H.; Yasui, A. In situ analysis of repair processes for oxidative DNA damage in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13738–13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, M.R.; Sabatini, D.M.; Carpenter, A.E. CellProfiler: Free, versatile software for automated biological image analysis. BioTechniques 2007, 42, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focke, F.; Schuermann, D.; Kuster, N.; Schär, P. DNA fragmentation in human fibroblasts under extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure. Mutat. Res. 2010, 683, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forchhammer, L.; Brauner, E.V.; Folkmann, J.K.; Danielsen, P.H.; Nielsen, C.; Jensen, A.; Loft, S.; Friis, G.; Moller, P. Variation in assessment of oxidatively damaged DNA in mononuclear blood cells by the comet assay with visual scoring. Mutagenesis 2008, 23, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markkanen, E. Not breathing is not an option: How to deal with oxidative DNA damage. DNA Repair 2017, 59, 82–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. 8-oxoG DNA glycosylase-1 inhibition sensitizes Neuro-2a cells to oxidative DNA base damage induced by 900 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wei, X.; Fei, Y.; Su, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z. Mobile phone signal exposure triggers a hormesis-like effect in Atm(+/+) and Atm(-/-) mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, L.M.; Xu, Y.; Hornyak, P.; Garces, F.; Zeng, Z.; Hailstone, R.; Matthews, S.J.; Caldecott, K.W.; Oliver, A.W.; Pearl, L.H. Efficient single-strand break repair requires binding to both poly(ADP-ribose) and DNA by the central BRCT domain of XRCC1. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 573–581.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, M.; Patel, A.; Hendzel, M.J.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Poirier, G.G. PARP inhibition: PARP1 and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, N.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Non-Ionizing Radiation, Part 2: Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields; WHO Press: Lyon, France, 2013; Volume 102, pp. 1–460. [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann, P.; Bohnenberger, S.; Greinert, R.; Hermann-Then, B.; Heselich, A.; Klug, S.J.; Koenig, J.; Kuhr, K.; Kuster, N.; Merker, M.; et al. Influence of GSM signals on human peripheral lymphocytes: Study of genotoxicity. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, C.; Kratochvil, E.; Pilger, A.; Kuster, N.; Adlkofer, F.; Rüdiger, H.W. Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (UMTS, 1950 MHz) induce genotoxic effects in vitro in human fibroblasts but not in lymphocytes. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2008, 81, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lixia, S.; Yao, K.; Kaijun, W.; Deqiang, L.; Huajun, H.; Xiangwei, G.; Baohong, W.; Wei, Z.; Jianling, L.; Wei, W. Effects of 1.8 GHz radiofrequency field on DNA damage and expression of heat shock protein 70 in human lens epithelial cells. Mutat. Res. 2006, 602, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, J.; Hakulinen, P.; Maki-Paakkanen, J.; Juutilainen, J.; Naarala, J. Enhancement of chemically induced reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells by 872 MHz radiofrequency radiation. Mutat. Res. 2009, 662, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, N.; Komatsubara, Y.; Takeda, H.; Hirose, H.; Sekijima, M.; Nojima, T.; Miyakoshi, J. DNA strand breaks are not induced in human cells exposed to 2.1425 GHz band CW and W-CDMA modulated radiofrequency fields allocated to mobile radio base stations. Bioelectromagnetics 2006, 27, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speit, G.; Schütz, P.; Hoffmann, H. Genotoxic effects of exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMF) in cultured mammalian cells are not independently reproducible. Mutat. Res. 2007, 626, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijian, C.; Xiaoxue, L.; Yezhen, L.; Deqiang, L.; Shijie, C.; Lifen, J.; Jianlin, L.; Jiliang, H. Influence of 1.8-GHz (GSM) radiofrequency radiation (RFR) on DNA damage and repair induced by X-rays in human leukocytes in vitro. Mutat. Res. 2009, 677, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Chen, C.; Sun, C.; Zhang, D.; Murbach, M.; Kuster, N.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, Z. Cell type-dependent induction of DNA damage by 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields does not result in significant cellular dysfunctions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Wei, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, G. RF-EMF exposure at 1800 MHz did not elicit DNA damage or abnormal cellular behaviors in different neurogenic cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Serori, H.; Ferk, F.; Kundi, M.; Bileck, A.; Gerner, C.; Misik, M.; Nersesyan, A.; Waldherr, M.; Murbach, M.; Lah, T.T.; et al. Mobile phone specific electromagnetic fields induce transient DNA damage and nucleotide excision repair in serum-deprived human glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gläser, K.; Rohland, M.; Kleine-Ostmann, T.; Schrader, T.; Stopper, H.; Hintzsche, H. Effect of Radiofrequency Radiation on Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Radiat. Res. 2016, 186, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, T.J.; Yamamoto, K.N.; Hirota, K.; Takeda, S. Mutant cells defective in DNA repair pathways provide a sensitive high-throughput assay for genotoxicity. DNA Repair 2010, 9, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zong, L.; Sun, Y.; Prihoda, T.J.; Tong, J.; Cao, Y. Adaptive response in mouse bone marrow stromal cells exposed to 900MHz radiofrequency fields: Impact of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Mutat. Res. 2017, 820, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannino, A.; Zeni, O.; Romeo, S.; Lioi, M.B.; Scarfi, M.R. Treatment with 3-Aminobenzamide Negates the Radiofrequency-Induced Adaptive Response in Two Cell Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naarala, J.; Kolehmainen, M.; Juutilainen, J. Electromagnetic fields, genomic instability and cancer: A systems biological view. Genes 2019, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duez, P.; Dehon, G.; Kumps, A.; Dubois, J. Statistics of the Comet assay: A key to discriminate between genotoxic effects. Mutagenesis 2003, 18, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, D.P.; Omori, T. Statistical issues in the use of the comet assay. Mutagenesis 2008, 23, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchhammer, L.; Ersson, C.; Loft, S.; Moller, L.; Godschalk, R.W.; Van Schooten, F.J.; Jones, G.D.; Higgins, J.A.; Cooke, M.; Mistry, V.; et al. Inter-laboratory variation in DNA damage using a standard comet assay protocol. Mutagenesis 2012, 27, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchhammer, L.; Johansson, C.; Loft, S.; Moller, L.; Godschalk, R.W.; Langie, S.A.; Jones, G.D.; Kwok, R.W.; Collins, A.R.; Azqueta, A.; et al. Variation in the measurement of DNA damage by comet assay measured by the ECVAG inter-laboratory validation trial. Mutagenesis 2010, 25, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schuermann, D.; Ziemann, C.; Barekati, Z.; Capstick, M.; Oertel, A.; Focke, F.; Murbach, M.; Kuster, N.; Dasenbrock, C.; Schär, P. Assessment of Genotoxicity in Human Cells Exposed to Modulated Electromagnetic Fields of Wireless Communication Devices. Genes 2020, 11, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040347
Schuermann D, Ziemann C, Barekati Z, Capstick M, Oertel A, Focke F, Murbach M, Kuster N, Dasenbrock C, Schär P. Assessment of Genotoxicity in Human Cells Exposed to Modulated Electromagnetic Fields of Wireless Communication Devices. Genes. 2020; 11(4):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040347
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchuermann, David, Christina Ziemann, Zeinab Barekati, Myles Capstick, Antje Oertel, Frauke Focke, Manuel Murbach, Niels Kuster, Clemens Dasenbrock, and Primo Schär. 2020. "Assessment of Genotoxicity in Human Cells Exposed to Modulated Electromagnetic Fields of Wireless Communication Devices" Genes 11, no. 4: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040347
APA StyleSchuermann, D., Ziemann, C., Barekati, Z., Capstick, M., Oertel, A., Focke, F., Murbach, M., Kuster, N., Dasenbrock, C., & Schär, P. (2020). Assessment of Genotoxicity in Human Cells Exposed to Modulated Electromagnetic Fields of Wireless Communication Devices. Genes, 11(4), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11040347






