Estradiol Enhances Anorectic Effect of Apolipoprotein A-IV through ERα-PI3K Pathway in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Culture and Treatment of Primary Cultured Neuronal Cells
2.4. Surgical Procedure for i4vt Cannula Implantation
2.5. Ovariectomy (OVX)
2.6. pAkt/Akt Levels Determined by Immunoblot Analyses
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
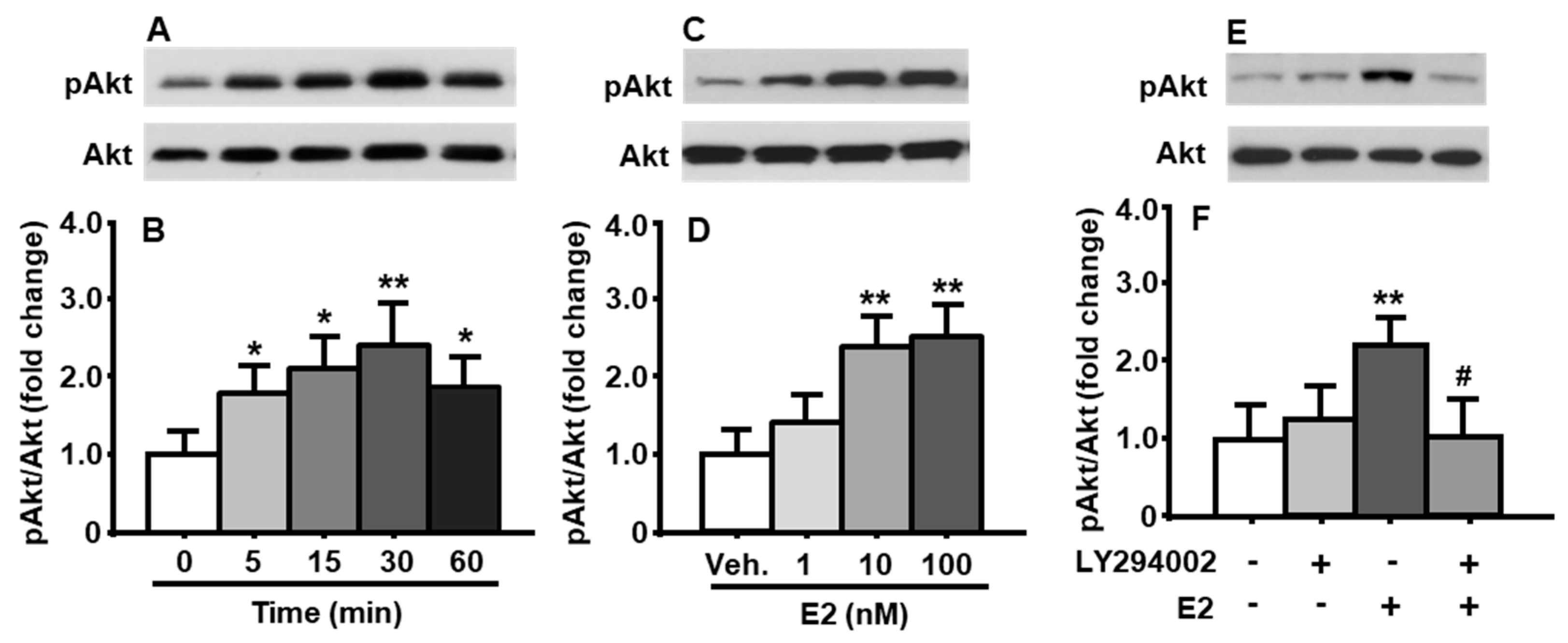
3.1. Akt Was Phosphorylated by E2 in Cultured Neuronal Cells
3.2. E2 Concentration-Dependently Increased Akt Phosphorylation
3.3. E2-Induced Phosphorylation of Akt Was Attenuated after Pretreatment of PI3K Inhibitor
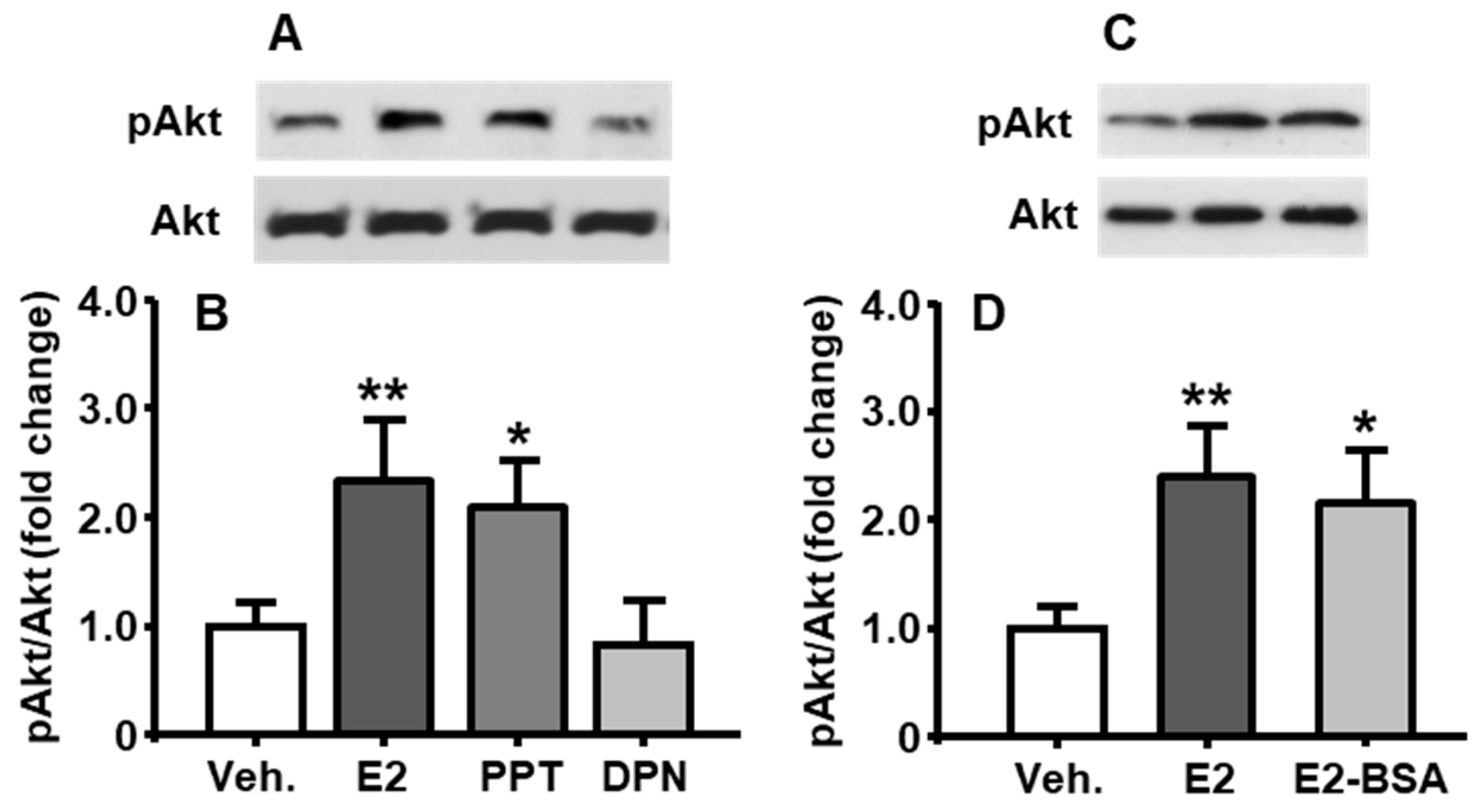
3.4. E2-Induced Activation of PI3K/Akt Pathway Was Mediated through ERα
3.5. Membrane-Associated ER Mediated E2-Induced PI3K Activation
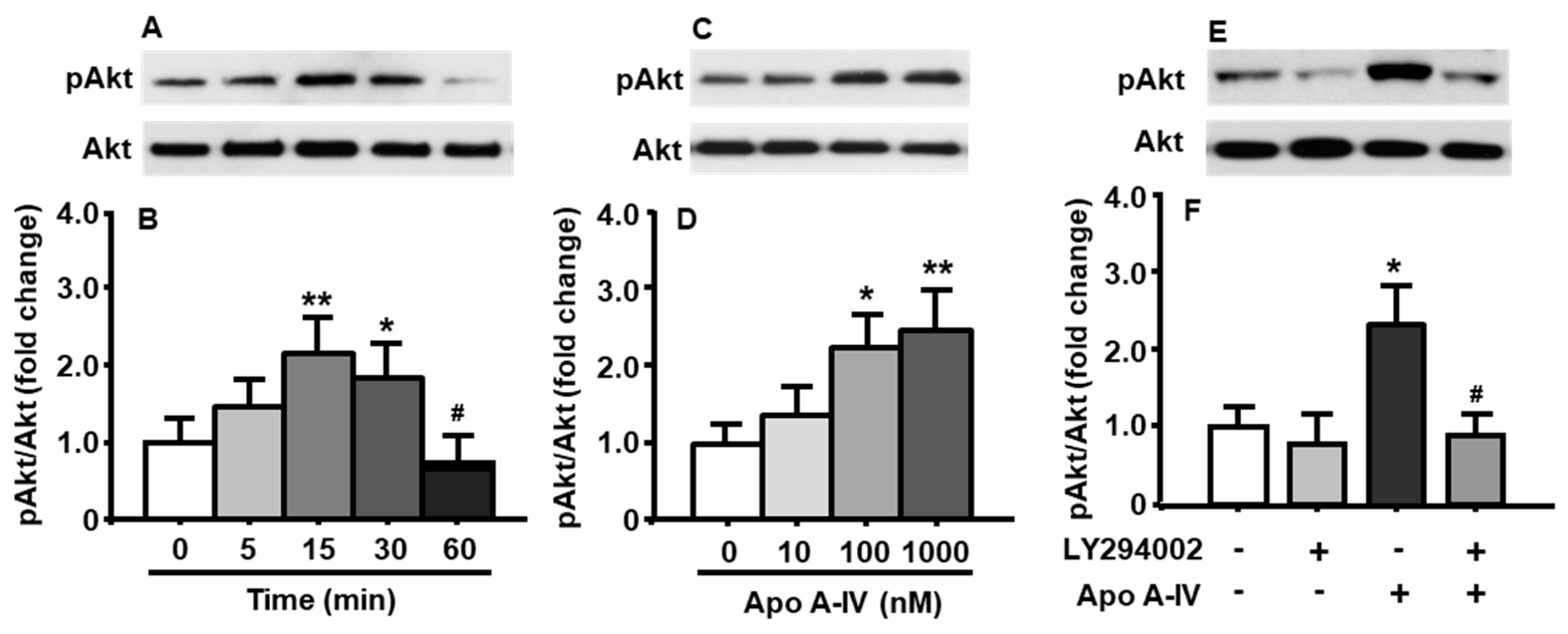
3.6. Effects of apoA-IV Treatment on the Phosphorylation of Akt
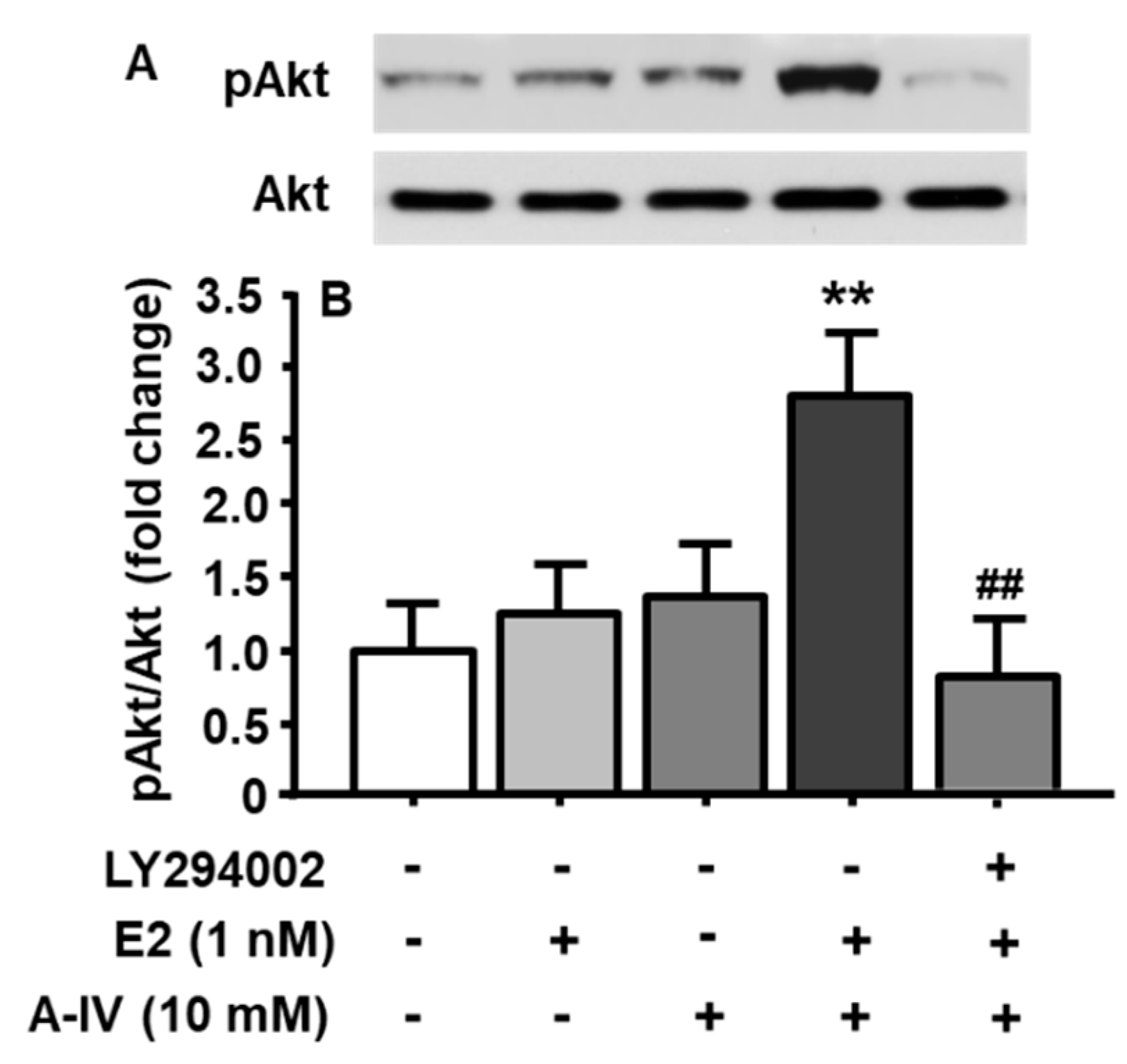
3.7. Synergistic Interaction of E2 and apoA-IV in PI3K/Akt Activation of Neuronal Cells
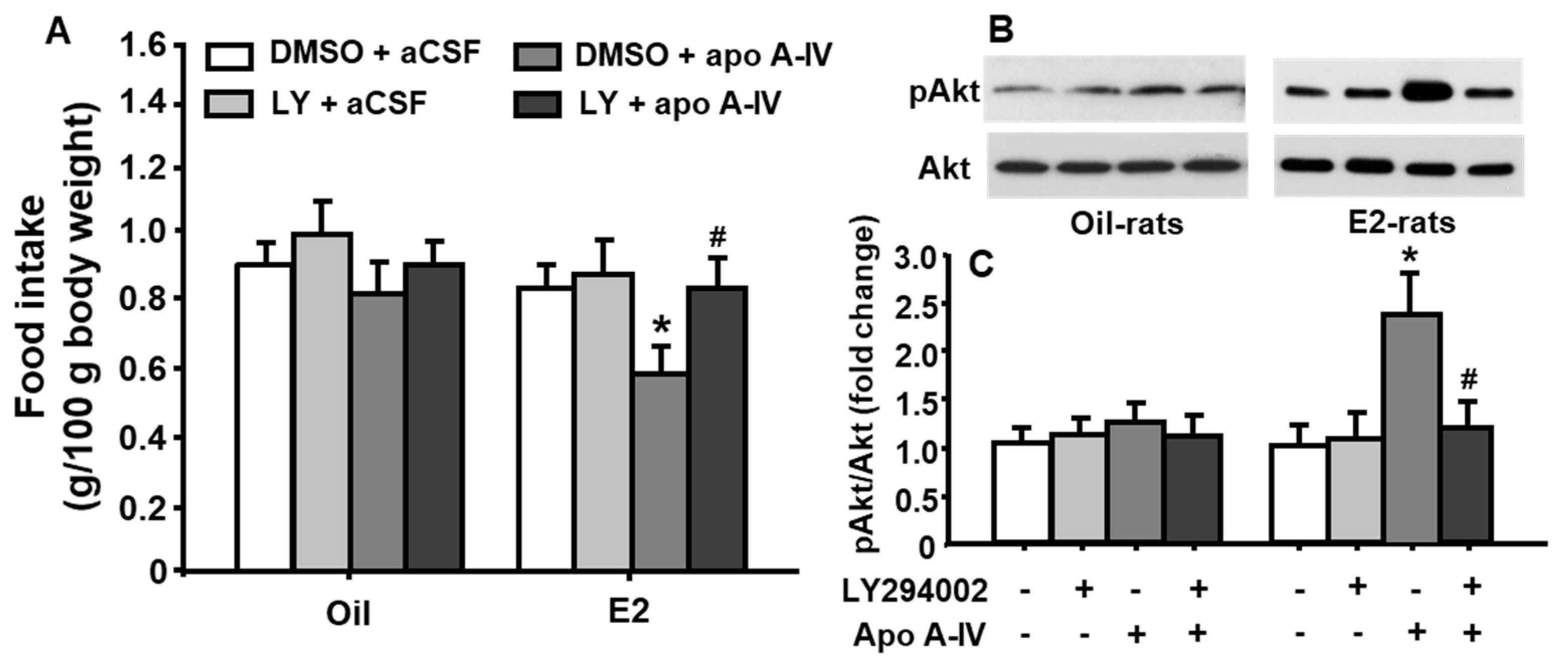
3.8. Central Inhibition of PI3K/Akt Signaling Significantly Diminished apoA-IV’s Anorectic Action in E2-Treated OVX Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geary, N. Estradiol and appetite. Appetite 2000, 35, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammacharoen, S.; Lutz, T.A.; Geary, N.; Asarian, L. Hindbrain administration of estradiol inhibits feeding and activates estrogen receptor-α-expressing cells in the nucleus tractus solitarius of ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Lo, C.M.; Tso, P.; Davidson, W.S.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Estradiol increases the anorectic effect of central apolipoprotein A-IV. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3163–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyala, A.; Zhang, C.; Bryant, D.N.; Kelly, M.J.; Ronnekleiv, O.K. PI3K signaling effects in hypothalamic neurons mediated by estrogen. J.Comp. Neurol. 2008, 506, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.Q.H.; Tso, P.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Estradiol stimulates apolipoprotein A-IV gene expression in the nucleus of the solitary tract through estrogen receptor-α. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tso, P.; Woods, S.C.; Sakai, R.R.; Davidson, W.S.; Liu, M. Hypothalamic Apolipoprotein A-IV Is Regulated by Leptin. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, M.; Hosoi, T.; Yoshii, M.; Ozawa, K. Leptin induced GRP78 expression through the PI3K-mTOR pathway in neuronal cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.R.; Skibicka, K.P.; Grill, H.J. Caudal brainstem processing is sufficient for behavioral, sympathetic, and parasympathetic responses driven by peripheral and hindbrain glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor stimulation. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 4059–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, R.C.; Slusser, P.G.; Stone, S. Glucoreceptors controlling feeding and blood glucose: Location in the hindbrain. Science 1981, 213, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, D.Q.; Tso, P.; Jandacek, R.J.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Apolipoprotein E reduces food intake via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hypothalamus. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 105, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Y.; Tso, P.; Wang, D.Q.-H.; Davidson, W.S.; Woods, S.C.; Liu, M. Silencing steroid receptor coactivator-1 in the nucleus of the solitary tract reduces estrogenic effects on feeding and apolipoprotein A-IV expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, M.; Howles, P.; Tso, P. ApoA-IV improves insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake in mouse adipocytes via PI3K-Akt Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santollo, J.; Wiley, M.D.; Eckel, L.A. Acute activation of ER α decreases food intake, meal size, and body weight in ovariectomized rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R2194–R2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswender, K.D.; Morton, G.J.; Stearns, W.H.; Rhodes, C.J.; Myers, M.G., Jr.; Schwartz, M.W. Intracellular signalling. Key enzyme in leptin-induced anorexia. Nature 2001, 413, 794–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelling, R.W.; Morton, G.J.; Morrison, C.D.; Niswender, K.D.; Myers, M.G.; Rhodes, C.J.; Schwartz, M.W.; Myers, M.G., Jr.; Rhodes, C.J.; Schwartz, M.W. Insulin action in the brain contributes to glucose lowering during insulin treatment of diabetes. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asarian, L.; Geary, N. Sex differences in the physiology of eating. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, N.; Lovejoy, L. Sex differences in energy metabolism, obesity and eating behavior. In Sex on the Brain: From Genes to Behavior; Becker, J., Ed.; Oxford Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 253–274. [Google Scholar]
- Asarian, L.; Geary, N. Cyclic estradiol treatment normalizes body weight and restores physiological patterns of spontaneous feeding and sexual receptivity in ovariectomized rats. Horm. Behav. 2002, 42, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, L.A. Estradiol: A rhythmic, inhibitory, indirect control of meal size. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 82, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asarian, L.; Geary, N. Estradiol enhances cholecystokinin-dependent lipid-induced satiation and activates estrogen receptor-α-expressing cells in the nucleus tractus solitarius of ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5656–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shughrue, P.J.; Lane, M.V.; Merchenthaler, I. Comparative distribution of estrogen receptor-α and -β mRNA in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 388, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Fukagawa, K.; Sakata, T.; Tso, P. Suppression of food intake by apolipoprotein A-IV is mediated through the central nervous system in rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1830–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Doi, T.; Shen, L.; Woods, S.C.; Seeley, R.J.; Zheng, S.; Jackman, A.; Tso, P. Intestinal satiety protein apolipoprotein AIV is synthesized and regulated in rat hypothalamus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp Physiol. 2001, 280, R1382–R1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.R.; Clegg, D.J.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Barton, M. Obesity, insulin resistance and diabetes: Sex differences and role of oestrogen receptors. Acta Physiol. 2011, 203, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Makela, S.; Treuter, E.; Tujague, M.; Thomsen, J.; Andersson, G.; Enmark, E.; Pettersson, K.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1535–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lösel, R.; Wehling, M. Nongenomic actions of steroid hormones. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Diz-Chaves, Y.; Perez-Martin, M.; Darnaudéry, M. Estradiol, insulin-like growth factor-I and brain aging. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brinton, R.D. Estrogen regulation of glucose metabolism and mitochondrial function: Therapeutic implications for prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ali, A.; Ramirez, V.D. Steroids conjugated to bovine serum albumin as tools to demonstrate specific steroid neuronal membrane binding sites. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 1996, 21, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Barton, M. The G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrtačnik, P.; Ostanek, B.; Mencej-Bedrač, S.; Marc, J. The many faces of estrogen signaling. Biochem. Med. 2014, 24, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, I.; Shin, S.; Kim, M.; Kwon, S.; Oh, S.R.; Ahn, Y.S.; Kim, C.H. GPR30 mediates anorectic estrogen-induced STAT3 signaling in the hypothalamus. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.E.; Carstens, E.J.; Irani, B.G.; Gent, L.M.; Hahner, L.M.; Clegg, D.J. Sexually dimorphic role of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) in modulating energy homeostasis. Horm. Behav. 2014, 66, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Hu, C.; Brigman, J.L.; Zhu, G.; Hathaway, H.J.; Prossnitz, E.R. GPER Deficiency in Male Mice Results in Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia, and a Proinflammatory State. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4136–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjen, G.G. Nervenkitt: Notes on the history of the concept of neuroglia. Glia 1988, 1, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, J.G.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Bains, J.S.; Brown, C.H.; Stern, J.E. Glial Regulation of Neuronal Function: From Synapse to Systems Physiology. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micevych, P.; Bondar, G.; Kuo, J. Estrogen actions on neuroendocrine glia. Neuroendocrinology 2010, 91, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, J.; Karolczak, M.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; Beyer, C. Estrogen receptor-α is associated with the plasma membrane of astrocytes and coupled to the MAP/Src-kinase pathway. Glia 2005, 50, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaban, V.V.; Lakhter, A.J.; Micevych, P. A membrane estrogen receptor mediates intracellular calcium release in astrocytes. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 3788–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Pearson, K.J.; Xiong, Y.; Lo, C.M.; Tso, P.; Woods, S.C.; Davidson, W.S.; Liu, M. Characterization of apolipoprotein A-IV in brain areas involved in energy homeostasis. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 95, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehler, P.S.; Brown, C. Anorexia nervosa-Medical complications. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Shen, L.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.Q.-H.; Tso, P. Estradiol Enhances Anorectic Effect of Apolipoprotein A-IV through ERα-PI3K Pathway in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius. Genes 2020, 11, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121494
Liu M, Shen L, Xu M, Wang DQ-H, Tso P. Estradiol Enhances Anorectic Effect of Apolipoprotein A-IV through ERα-PI3K Pathway in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius. Genes. 2020; 11(12):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121494
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Min, Ling Shen, Meifeng Xu, David Q.-H. Wang, and Patrick Tso. 2020. "Estradiol Enhances Anorectic Effect of Apolipoprotein A-IV through ERα-PI3K Pathway in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius" Genes 11, no. 12: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121494
APA StyleLiu, M., Shen, L., Xu, M., Wang, D. Q.-H., & Tso, P. (2020). Estradiol Enhances Anorectic Effect of Apolipoprotein A-IV through ERα-PI3K Pathway in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius. Genes, 11(12), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11121494





