Abstract
Infection with canine heartworm (Dirofilaria immitis), spread via mosquito vectors, causes coughing, asthma, pneumonia, and bronchitis in humans and other animals. The disease is especially severe and often fatal in dogs and represents a serious threat to public health worldwide. Cysteine protease inhibitors (CPIs), also known as cystatins, are major immunomodulators of the host immune response during nematode infections. Herein, we cloned and expressed the cystatin Di-CPI from D. immitis. Sequence analysis revealed two specific cystatin-like domains, a Q-x-V-x-G motif, and a SND motif. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that Di-CPI is a member of the second subgroup of nematode type II cystatins. Probing of D. immitis total proteins with anti-rDi-CPI polyclonal antibody revealed a weak signal, and immunofluorescence-based histochemical analysis showed that native Di-CPI is mainly localized in the cuticle of male and female worms and the gut of male worms. Treatment of canine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs) with recombinant Di-CPI induced a Th2-type immune response characterized by high expression of the anti-inflammatory factor interleukin-10. Proliferation assays showed that Di-CPI inhibits the proliferation of canine PMBCs by 15%. Together, the results indicate that Di-CPI might be related to cellular hyporesponsiveness in dirofilariasis and may help D. immitis to evade the host immune system.
1. Introduction
The filarial nematode Dirofilaria immitis, also known as canine heartworm, mainly occurs in tropical and temperate regions throughout the world, and causes canine and feline cardiopulmonary dirofilariasis as well as human pulmonary dirofilariasis [1]. Females of mosquito species in the Culicidae family, such as Culex, Aedes, Anopheles, and Culiseta, are the main vectors of D. immitis [2]. Dogs are the most suitable definitive host, which serves as a reservoir. A typical symptom in dogs is a persistent, chronic, and unproductive cough which is aggravated by exercise, and in most cases is accompanied by dyspnea and/or stress tachypnea [3,4]. However, as incidental hosts of D. immitis, feline cardiopulmonary dirofilariasis and human pulmonary dirofilariasis are habitually misdiagnosed due to the asymptomatic nature of these diseases [1,5].
Inflammation is the main consequence of this disease [6,7], and arteries are affected initially, followed by the lung parenchyma and right heart chamber [1]. Given that D. immitis worms are continuously exposed to the host immune system, and yet can achieve a lifespan of years, they must engage in various immune evasion strategies [8]. During short-term immune evasion, infective larvae avoid host immune responses by releasing surface antigens, whereas in long-term immune evasion, pre-adult and adult worms mask their surface by adsorbing different host molecules and cells [9,10].
Cystatins are native, reversible, tight-binding inhibitors of members of the papain (C1) and legumain (C13) families of cysteine proteases (see the MEROPS database; http://merops.sanger.ac.uk). Based on primary sequence homology, the presence or absence of disulfide bonds, and physiological localization, cystatins are assigned to three subfamilies: stefins (type I cystatins), cystatins (type II cystatins), and kininogens (type III cystatins) [11]. Initially, cystatins were characterized as inhibitors of endogenous cysteine proteases that block the active site through noncovalent binding of a highly conserved Q-x-V-x-G motif [12,13,14]. However, alternative functions for cystatins have since been proposed, including immunoregulation, and this has been investigated for nematode cystatins [11,15,16,17]. For instance, the cystatin cysteine protease inhibitor (CPI)-2 from Brugia malayi potentially interferes with antigen processing and presentation by inhibiting host proteases [18,19]. In addition, filarial cystatins hold promise for treating allergic and inflammatory diseases [16,17,20,21,22,23] by regulating cytokine production in different regulatory cell types, including upregulation of interleukin (IL)-10 [17,20,21,23,24,25,26,27] and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α [24] and downregulation of IL-4 [20], IL-5, and IL-13 [21]. The main target cell type of cystatins are monocytes/macrophages, both in vitro and in vivo [15,24,25,28].
Although studies on some filarial nematode cystatins have been reported, D. immitis proteins remain poorly understood. The aims of the present study were (i) to express and characterize cystatin Di-CPI from D. immitis (ii), determine the immunogenicity of Di-CPI and investigate its tissue distribution in female and male parasites, and (iii) examine the role of Di-CPI in the immune system of D. immitis through in vitro cell assays.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
Two female 8-week-old New Zealand white rabbits (3.0−3.5 kg) were obtained from Dashuo Laboratory Animal Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). All animals were housed and fed as previously reported [29].
2.2. Parasites and Sera
Adult D. immitis worms were obtained from an adult dog that died suddenly, and D. immitis serum was isolated from a naturally infected 2-year-old dog (10 kg) diagnosed by PCR in a veterinary hospital in Sichuan province, Chengdu, China. Negative serum was obtained from a healthy 3-month-old dog (4 kg), also from a veterinary hospital in Sichuan province, Chengdu, China.
2.3. Cloning and Expression of Di-CPI and Di-TIM
Total RNA was extracted from adult mixed-sex D. immitis worms using an RNA extraction kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) and transcribed into cDNA using a first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Scientific, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The full length coding sequence of Di-CPI was amplified from D. immitis cDNA using the primers 5′-CCGGAATTCGTCACCGGTATTATGGAA-3′ (forward, EcoRI site underlined) and 5′-CCGCTCGAGAATCTCTTATTCATGGTAGTACTTT-3′ (reverse, XhoI site underlined), designed based on our assembled and annotated D. immitis transcriptome [30], and ligated into the pET-32a (+) expression vector (Novagen, NJ, USA). The resulting recombinant plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells (Invitrogen, Carsbad, CA, USA). The gene encoding the control protein triosephosphate isomerase of D. immitis (Di-TIM) was cloned and expressed as above using the primers 5′-CGCGGATCCATGTCGCGAAAATTTCTTGT-3′ (forward, BamHI site underlined) and 5′-CCCAAGCTTTTAATCACGTGCATGAATAATTT-3′ (reverse, HindIII site underlined). Recombinant proteins were expressed following induction with 1 mM isopropyl β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) for 6 h, and then purified by Ni2+ affinity chromatography (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). EndoTrap columns were used to remove endotoxin according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Bioendo, Xiamen, China). Final endotoxin concentrations were measured by Limulus amoebocyte lysate tests (Bioendo, Xiamen, China). The average endotoxin concentration for rDi-CPI was 0.025 endotoxin units (EU) per application, and for rDi-TIM, it was 0.05 EU per application. The protein concentration after endotoxin removal was measured using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, MA, USA). Purified recombinant CPI (2 mg/mL) and TIM (1 mg/mL) (with endotoxin removed) were stored at −80°C until needed.
2.4. Molecular Characterisation of Di-CPI
The open reading frame (ORF) tool ORFfinder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/) was used to analyze the Di-CPI ORF and deduce the amino acid sequence, and the SignalP 4.1 Server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) was used to predict the signal sequence of Di-CPI. Molecular weight, isoelectric point, and conserved domains were predicted using ExPASy online software tools (https://www.expasy.org/). In addition, the secondary structure of Di-CPI was predicted using YASPIN secondary structure prediction (http://www.ibi.vu.nl/programs/yaspinwww/). Based on similarity, multiple sequence alignment was performed using ClustalX version 2 [31] and a phylogenetic tree was constructed by the maximum likelihood (ML) method using MEGA 6.0 software [32].
2.5. Preparation of Polyclonal Antibody Against rDi-CPI
Polyclonal antibody against rDi-CPI was produced essentially as previously reported using two female New Zealand rabbits [29]. Briefly, before immunization, rabbit sera were collected to serve as negative controls, and each rabbit was then immunized subcutaneously with 200 μg of rDi-CPI emulsified with an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant (Sigma, CA, USA), followed by two boosters every two weeks using the same route and dose, but with Freund’s incomplete adjuvant. At two weeks after the third immunization, sera were collected and purified using HiTrap Protein A affinity chromatography (Bio-Rad), and the resulting IgG was stored at −80°C until needed.
2.6. Western Blotting and Immunochemical Analysis
For immunoblot analysis, D. immitis total proteins were obtained using a mammalian protein extraction kit (CWBIO, Beijing, China). Purified rDi-CPI and total proteins were separated by 12% sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane. The rest of the Western blotting procedure was performed as described previously [33].
For immunohistochemistry studies, D. immitis sections were incubated with a 1/100 dilution of rabbit anti-rDi-CPI serum overnight at 4 °C, and then incubated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody (1:100 dilution in 1% Evans Blue; Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX, USA) as described previously [30]. Finally, sections were analyzed with a fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
2.7. Cell Isolation and Culturing
For isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from the blood of a healthy dog, density gradient centrifugation was performed using the Ficoll–Hypaque method (Solarbio, Beijing, China), and samples were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Isolated PBMCs were resuspended in RPMI 1640 (Hyclone, CA, USA) containing 10% fetal calf serum (PAA, Germany), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 mg/mL streptomycin, and 20 mmoL/L L-glutamine (Biochrom, Germany), and counted with a Cell Counting Chamber (Qiujing, Shanghai, China).
2.8. Proliferation Assay
PBMCs (3.5 × 105/well) were stimulated with 5 μg/mL phytohemagglutinin (PHA) (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and 2 μg/mL IL-2 (Peprotech, CT, USA), and incubated with rDi-CPI (1 μg/mL, 2 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL) or rDi-TIM (5 μg/mL) for 48 h, then incubated with Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (Dojindo, Kyushu, Japan) (10 μL/well) for 4 h. Samples for each group were repeated in triplicate wells. Proliferative responses were analyzed and the optical density at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, MA, USA).
2.9. Cytokine Analysis
Canine-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antibody pairs for IL-4, IL-10, IL-12, TNF-α, and IFN-γ (Zhuocai, Shanghai, China) were used according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to determine cytokine levels in cell culture supernatants of PBMCs. Briefly, PBMCs were isolated by density gradient centrifugation and cultured (3.5 × 105 cells/well) in 96-well flat-bottom plates at 37 °C for 6, 24, 48, or 72 h in the presence of 5 μg/mL rDi-CPI or 5 μg/ml control protein (rDi-TIM). All samples were analyzed in triplicate.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Multiple groups were compared by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s tests, and pairs of groups were compared using Student’s t-tests or Mann–Whitney U-tests using SPSS version 20.0 (SPSS Inc., USA). Data are presented as mean values ± standard error of the mean (SEM), determined using Prism 6 (Graphpad Software Inc., CA, USA). Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
2.11. Ethics Statement
All animals were handled in strict accordance with the Animal Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China (released on 18 September 2009). All procedures were carried out in line with the Regulations for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Animal Ethics Committee of Sichuan Agricultural University (Ya’an, China; Approval No. 2015–028).
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Characterisation of Di-CPI
The full-length Di-CPI sequence was amplified from mixed-sex adult D. immitis cDNA samples and confirmed to be identical to the sequence obtained from the annotated D. immitis transcriptome [31]. The Di-CPI protein consists of 125 amino acid residues, has a predicted molecular weight of 14.5 kDa, and has a calculated isoelectric point (pI) of 5.45. An N-terminal signal sequence was not found. Sequence analysis revealed high sequence identity with orthologs from Onchocerca volvulus (85%), Brugia malayi (82%), Litomosoides sigmodontis (79%), Loa loa (75%), and Acanthocheilonema viteae (72%). Despite low overall sequence identity (20–30%) between Di-CPI and vertebrate type II cystatins (Mus musculus = 26%, Homo sapiens = 30%, Canis lupus familiaris = 25%), all the key structural features are conserved, including the conserved inhibitory domain signature Q-x-V-x-G associated with papain inhibition, the N-terminal glycine residue, the C-terminal PW motif, and a single disulfide bond. In addition, a SND motif associated with asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) inhibition was observed (Figure 1).
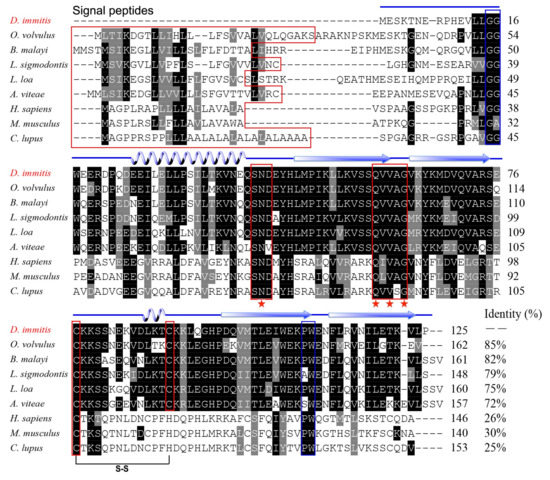
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of Dirofilaria immitis cysteine protease inhibitor (Di-CPI). Alignment of the deduced Di-CPI amino acid sequence with those of homologous proteins from nematodes (Onchocerca volvulus, AAA29423.1; Brugia malayi, AAD51086.1; Litomosoides sigmodontis, AAF35896.1; Loa loa, XP_003147913; Acanthocheilonema viteae, AAA87228.1) and mammals (Mus musculus, NP_034106.2; Human, AAH13083.1; Canine, XP_003639869.1) was performed using Clustal X software version 2 and shaded using BOXshade version 3.21. Predicted secondary structural elements, including
strands and helices, are shown above the alignment as arrows and loops,
respectively. The Q-x-V-x-G motif and SND motif are enclosed in red boxes. A conserved glycine residue in the N-terminal region and the PW hairpin loop in the C-terminal region are enclosed in the blue boxes. N-terminal signal peptides are enclosed in a red box.
To investigate the evolutionary history of Di-CPI, amino acid sequences of both mammalian and nematode cystatins were aligned and subjected to phylogenetic analysis using an ML tree (Figure 2). Combining the results of sequence analysis with phylogenetic analysis, Di-CPI appears to be a member of the second subgroup of nematode type II cystatins.
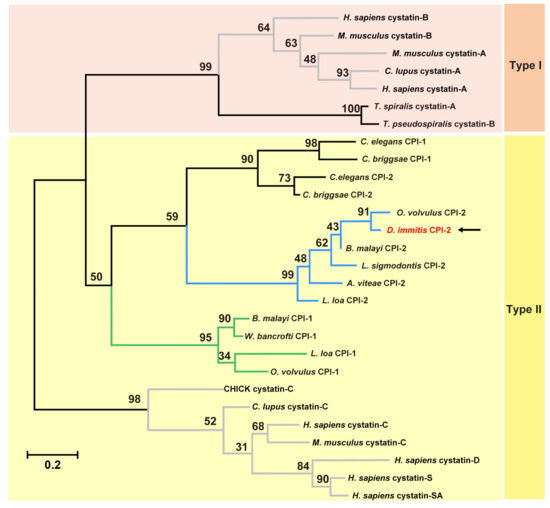
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationships between Di-CPI and homologous cystatins/CPIs. The tree was constructed from a multiple sequence alignment performed using Clustal W2 and plotted using MEGA 6.06. Amino acid sequences used in the tree, with their GenBank accession numbers, are as follows: Homo sapiens cystatin-B, NP_000091.1; Mus musculus cystatin-B, NP_001076014.1; Mus musculus cystatin-A, NP_005204.1; Canis lupus familiaris cystatin-A, SPO16019.1; Homo sapiens cystatin-A, NP_005204.1; Trichinella spiralis, KRY35881.1; Trichinella pseudospira, KRZ14801.1; Caenorhabditis elegans CPI-1, NP_500915.1; Caenorhabditis briggsae CPI-1, CAP25989.2; Caenorhabditis elegans CPI-2, AF068718.1; Caenorhabditis briggsae CPI-2, CAP29292.1; Onchocerca volvulus CPI-2, |P22085.2; Brugia malayi, AAD51086.1; Litomosoides sigmodontis, AAF35896.1; Acanthocheilonema viteae, AAA87228.1; Loa loa CPI-2, XP_003147913.1; Loa loa CPI-1, XP_003136654.1; Brugia malayi CPI-2, U80972.1; Wuchereria bancrofti, EJW82673.1; Onchocerca volvulus CPI-1, AF177194.1; CHICK, P01038.2; Canis lupus familiaris cystatin-C, XP_003639869.1; Homo sapiens cystatin-C, P01034.1; Homo sapiens cystatin-D, P28325.1; Homo sapiens cystatin-S, P01036.3; Homo sapiens cystatin- SA, P09228.1. Numbers indicate bootstrap values. The branches in grey and in black represent mammalian cystatins and nematode cystatins, respectively. In addition, the green and blue branches represent first subgroup of filarial cystatins and the second subgroup of filarial cystatins, respectively. The pink and yellow backgrounds represent type I and type II cystatins, respectively.
3.2. Expression and Characterisation of Di-CPI
The Di-CPI cDNA was successfully inserted into the pET32a (+) expression vector, and the protein was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) cells in soluble form. The recombinant protein was ~35 kDa, according to SDS-PAGE, and contains a ~20 kDa epitope tag (including Trx-tag, His-tag, and S-tag) fusion protein (Figure 3, lane 1). Purified protein was prepared for Western blotting and immunohistochemistry analyses (Figure 3, lane 2). Western blotting yielded a single band at ~35 kDa that was recognized by dog anti-D. immitis serum (Figure 3, lane 3). Additionally, a weak band at ~15 kDa was observed when total protein from D. immitis was probed with anti-rDi-CPI polyclonal antibody (Figure 3, lane 5), which corresponds to the predicted size of native Di-CPI.
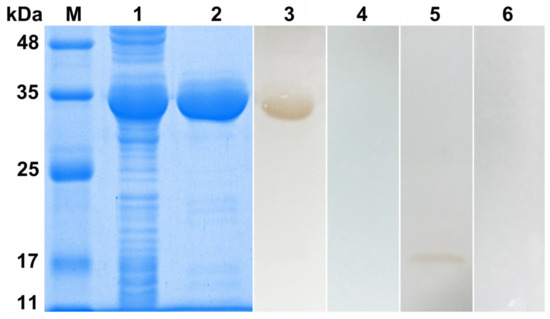
Figure 3.
Sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western blotting analysis of Di-CPI. M, molecular weight markers; Lane 1, IPTG-induced recombinant (r) Di-CPI in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3); Lane 2, purified rDi-CPI (6 μg); Lane 3, purified rDi-CPI probed with serum from a dog naturally infected with D. immitis (6 μg); Lane 4, purified rDi-CPI probed with naive dog serum; Lane 5, total protein from D. immitis probed with anti-rDi-CPI serum (20 μg); Lane 6, total protein from D. immitis probed with native (preimmune) rabbit serum (20 μg).
The distribution of Di-CPI in transverse sections of adult D. immitis worms was assessed by immunofluorescence using rabbit anti-rDi-CPI antibody. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that native Di-CPI was mainly distributed in cuticle of both male and female worms (Figure 4A,B), and a large amount of fluorescence was also observed in the gut of male worms (Figure 4B).
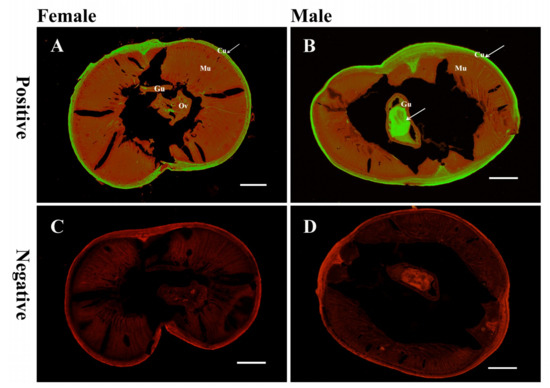
Figure 4.
Immunolocalization of native Di-CPI. Both adult female and male worms were probed. The location of native Di-CPI protein is indicated by green fluorescence. Sections (5 μm) were incubated with either rabbit anti-rDi-CPI IgG at 1:100 (A and B) or preimmune IgG at 1:100 (C and D), diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Arrows indicate a positive signal in the cuticle of female worms (A) and male worms (B) and the gut of male worms (B). No staining was observed for female or male worms using IgG purified from preimmune serum (C and D), confirming specific immunolabeling was achieved. Cu, cuticle; Gu, gut; Ov, ovary. Scale bars = 100 μm.
3.3. Inhibition of the Proliferation of Canine PBMCs by rDi-CPI
To determine whether Di-CPI is involved in host cellular responses, we firstly evaluated the effect of rDi-CPI on T-cell proliferation induced by IL-2 and PHA. At 48 h post-treatment, 5 μg/mL of rDi-CPI inhibited the proliferation of canine PBMCs by 15% (Figure 5, p < 0.01). Compared with the control protein, rDi-TIM, rDi-CPI significantly inhibited proliferation by 10% (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in T-cell proliferation among samples treated with 1 μg/mL, 2 μg/mL, or 5 μg/mL of rDi-CPI; one of the possible explanations for this is that the lowest amount of rDi-CPI was already above saturation.
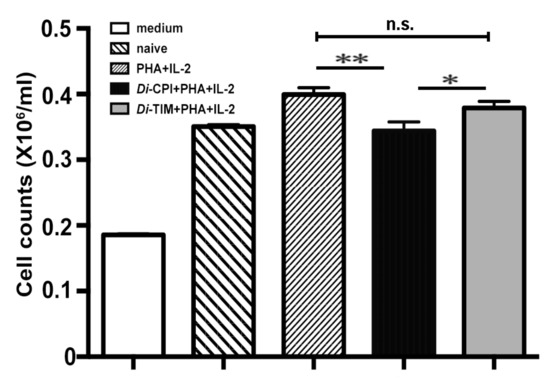
Figure 5.
Inhibition on the proliferation of canine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) by Di-CPI. Canine T cells were stimulated with PHA + IL-2, PHA + IL-2 + rDi-CPI, or PHA + IL-2 + rDi-TIM for 48 h as determined by CCK-8. Di-CPI inhibited the proliferation of canine T cells by 15% compared with naive controls and 10% compared with Di-TIM controls. Naive indicates no protein was added to wells. Data are mean ± SEM of 3 samples with triplicate wells; representative data from one of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) were determined by Student’s t-tests.
3.4. Cytokine Analysis
Based on our preliminary data, we hypothesized that inhibition of T-cell proliferation may be associated with the production of cytokines. In order to investigate Di-CPI-induced immune responses, we quantified the levels of both Type 1 T helper (Th1) and Type 2 T helper (Th2) cytokines in PBMCs. Following incubation for 6 h, rDi-CPI had induced the production of IL-10, and the peak in IL-10 production (Figure 6A, p < 0.01) was followed by a significant decrease of the production of IL-12 (Figure 6B, p < 0.01) and TNF-α (Figure 6C, p < 0.05) at 48 h. However, no significant production of IFN-γ and IL-4 was observed with rDi-CPI after 48 h compared with controls (Figure 6D,E).
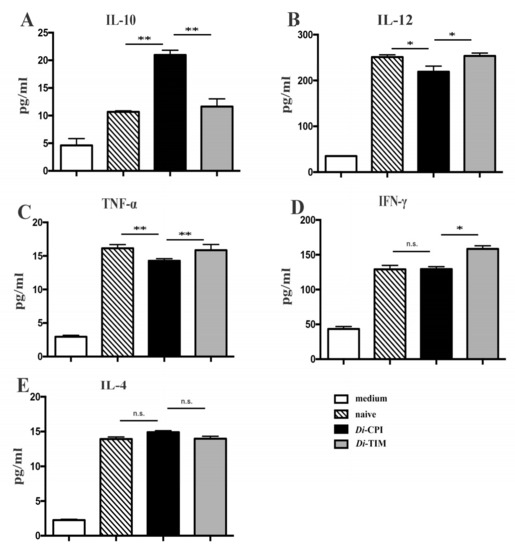
Figure 6.
Analysis of cytokines following inhibition of canine PBMCs by Di-CPI. Supernatants of canine PBMCs stimulated for 48 h were subjected to ELISA to measure the concentration of IL-10, IL-12, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-4. rDi-CPI treatment increased anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 (A), followed by significant decrease of the production of IL-12 (B) and TNF-α (C). IFN-γ (D) and IL-4 (E) showed no significant difference compared with controls. Naive indicates no protein was added to wells. Data are mean ± SEM of 3 samples with triplicate wells; representative data from one of three independent experiments. n.s., not significant. Statistically significant differences (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01) were determined by Mann–Whitney U-tests.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we cloned, expressed, and characterized Di-CPI from D. immitis based on the transcriptome sequence [30]. Based on both sequence similarity and phylogenetic analyses, Di-CPI is clearly a member of the cystatin superfamily and most likely a member of the second subgroup of type II nematode cystatins. Type II cystatins from nematodes fall into three subgroups, represented by Bm-CPI-1, Bm-CPI-2, and Bm-CPI-3 in B. malayi [34]; Ov-CPI-1 and Ov-CPI-2 in O. volvulus [24,35,36]; and Ce-CPI-1 and Ce-CPI-2 in C. elegans [18,37]. Among the three subgroups, the second subgroup that includes Bm-CPI-2 is perhaps the most intriguing. In addition to the classical inhibitory that blocks C1 papain-like proteases such as cathepsins B, L, and S, the second subgroup of filarial cystatins also possess a site resembling a feature in the vertebrate cystatin C protein that controls C13 legumain-like asparaginyl endopeptidase (AEP) [35,38,39]. The SND motif in mammalian cystatin C, which is also present in Bm-CPI-2, is associated with AEP inhibitory activity and suppresses the activity of mammalian AEP [18,19]. Intriguingly, sequence alignment revealed that Di-CPI has an SND motif, which is also present in other second subgroup filarial cystatins such as those from A. viteae [25], L. sigmodontis [40], and O. volvulus [36] (Figure 1). Hence, we speculate that Di-CPI may have the potential to block mammalian AEP activity, but further experiments are required to confirm this hypothesis.
To date, research on the location of native cystatin in D. immitis has not been reported. It is intriguing to note that this protein is expressed in the cuticle of both male and female adult D. immitis worms, and also in the gut of male worms. According to a previous study, both cystatin (Di-CPI) and triosephosphate isomerase (Di-TIM, or Di-TPI) are among the most abundant proteins secreted into a culture medium by D. immitis [41]; however, neither of these proteins have an apparent signal sequence. In recent studies, parasites have been shown to release exosome-like vesicles [42,43,44,45,46,47] which function as cell-to-cell effectors in the host–parasite interaction. Therefore, one of the possible explanations is that Di-CPI was released to the extracellular environment as the cargo of exosomes by fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane. Confirmation of this speculation requires further study. Adult D. immitis worms are believed to produce numerous proteins to mask their surface and thereby avoid host immune responses [10]. Similarly, surface-expressed CPIs might help D. immitis evade host immune responses. Bm-CPI-2 mRNA was detected throughout all developmental stages of the life cycle in the mosquito vector and mammalian hosts, indicating a positive role in parasite maintenance [19]. Additionally, a homologous gene product is highly expressed in the cuticle of molting larvae in O. volvulus [48]. In the present study, we only probed the distribution of Di-CPI in adult worms, and further investigation of expression levels during each developmental stage is clearly needed. We speculate that Di-CPI may not only be active in adult worms, but also larvae, and may be associated with maturation and molting in D. immitis, but further experiments are required for confirmation.
In the immunopathogenic mechanisms of D. immitis, a dual Th1/Th2 response was observed in BALA/c mice immunized with antigenic extracts from D. immitis adult worms (DiSA) [1,49]. The Th2-type anti-inflammatory response was stimulated mainly by D. immitis antigens, whereas the Th1-type proinflammatory response was stimulated by Wolbachia bacteria released from dying worms [49]. The Th2-type response was characterized by the high levels of IL-4 and IL-10 mRNAs, and IgG1 production was predominant in microfilaremic canine infections [50]. In the present work, we simultaneously measured the expression of IL-4 and IL-10 in Di-CPI-induced canine PBMCs and found that Di-CPI induced a Th2-type anti-inflammatory immune response characterized by high expression of IL-10. High levels of IL-10 are characteristic of filarial infections and are linked to hyporesponsiveness in lymphatic filariasis [25,51,52]. Furthermore, IL-10 induced by cystatins is reportedly effective against dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced intestinal inflammation [27], mucosal inflammation [53], and colitis [26]. In addition, Di-CPI also suppressed the Th1-type proinflammatory immune response by reducing the production of IL-12 and TNF-α. We also found that Di-CPI inhibited canine T-cell proliferation by 15%, and hypothesized that Di-CPI participates in immune evasion in canine heartworm disease. Evidence suggests that filarial cystatins are involved in immune interference, and they may be important immune evasion molecules [11,54,55,56]. For instance, A. viteae CPI-2 (Av17) directly inhibits the proliferation of murine T cells in vitro and induces the production of cytokine IL-10 [25]. Meanwhile, O. volvulus CPI-2, also known as OV-17 and onchocystatin, significantly inhibits human T-cell proliferation [28]. Thus, high expression of IL-10 induced by Di-CPI, together with effective inhibition of canine T-cell proliferation by Di-CPI, indicates that Di-CPI plays a positive role in immune evasion and may be an effective inhibitor of host inflammatory responses. It is worth noting that changes in cytokine levels varied from study to study [17,21,24,25,57]. In the present work, we observed numerically modest cytokine level changes; this is probably due to the different parasite cystatins and different host PBMCs, as PBMCs from different hosts may show varied responses to a specific parasite cystatin and vice versa.
5. Conclusions
In summary, we characterized the cystatin Di-CPI from D. immitis and observed high expression on the surface of male and female adult worms following immunolocalization analysis. Additionally, we demonstrated its immune regulation ability using ex vivo canine PBMCs. The findings show that Di-CPI inhibits canine T-cell proliferation and modulates inflammatory responses by inducing expression of IL-10 and reducing expression of IL-12 and TNF-α. Thus, Di-CPI may be an important immune evasion molecule and may play an important role in host–parasite interactions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.D. and J.X.; methodology, X.D. and Y.L.; sample preparation, H.S. and H.Z.; data curation, M.W. and B.J.; formal analysis, X.G. and Y.X.; writing and original draft preparation, X.D.; writing and review and editing, X.D., G.Y., and J.X.; supervision, G.Y.; and project administration, X.P. and W.L.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Chengdu Giant Panda Breeding Research Foundation (No. CFP2014-17). The funder had no role in study design, sample collection, data analysis, or preparation or publication of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the native English-speaking scientists of Elixigen Company (Hintington Beach, California) for editing our manuscript. We are grateful to Yu Li, Xiaoxiao Yin, and Weiwen Rui for their crucial suggestions and assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Simon, F.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Morchon, R.; Gonzalez-Miguel, J.; Mellado, I.; Carreton, E.; Montoya-Alonso, J.A. Human and animal dirofilariasis: The emergence of a zoonotic mosaic. Clin. Microbiol Rev. 2012, 25, 507–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockova, E.; Iglodyova, A.; Kocisova, A. Potential mosquito (Diptera:Culicidae) vector of Dirofilaria repens and Dirofilaria immitis in urban areas of Eastern Slovakia. Parasitol Res. 2015, 114, 4487–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, R.A. Influence of number of parasites and exercise on the severity of heartworm disease in dogs. Proc. Heartworm Symp. 1995, 113, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, H.; Ishihara, K.; Sasaki, Y. Canine dirofilarial hemoglobinuria: Changes in right heart hemodynamics and heartworm migration from pulmonary artery towards right atrium following β 1-blocker administration. J. Vet. Med. Sci 1987, 49, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón, F.; Lopez-Belmonte, J.; Marcos-Atxutegi, C.; Morchón García, R.; R Martín-Pacho, J. What is happening outside North America regarding human Dirofilariasis? Vet. Parasitol 2005, 133, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theis, J.H. Public health aspects of dirofilariasis in the United States. Vet. Parasitol 2005, 133, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón, F.; Kramer, L.H.; Román, A.; Blasini, W.; Morchón, R.; Marcos-Atxutegi, C.; Grandi, G.; Genchi, C. Immunopathology of Dirofilaria immitis infection. Vet. Res. Commun 2007, 31, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.W.; Genchi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Guerrero, J.; Venco, L.J.A.i.p. Heartworm disease in animals and humans. Adv. Parasit 2008, 66, 193–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kadipasaoglu, A.K.; Bilge, F.H. Partial characterization of the adsorbed protein layer on Dirofilaria immitis (Nematoda) cuticle. Parasitol Res. 1989, 75, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, F.H.; Kadipasaoglu, K.A.; Mccormick, C.M.; Baier, R.E. Surface characterization of the cuticle of Dirofilaria immitis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 1989, 23, 1027–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, S.; Lucius, R. Modulation of host immune responses by nematode cystatins. Int J. Parasitol 2003, 33, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Stoka, V.; Turk, D. Cystatins: Biochemical and structural properties, and medical relevance. Front. Biosci 2008, 13, 5780–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancela, M.; Corvo, I.; da Salva, E.; Teichmann, A.; Roche, L.; Diaz, A.; Tort, J.F.; Ferreira, H.B.; Zaha, A. Functional characterization of single-domain cystatin-like cysteine proteinase inhibitors expressed by the trematode Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1695–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nata; Kopitarjerala, A. The Role of Cysteine Proteinases and their Inhibitors in the Host-Pathogen Cross Talk. Curr Protein Pept Sc 2012, 13, 767–775. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, C.; Ziegler, T.; Figueiredo, A.S.; Rausch, S.; Hepworth, M.R.; Obsivac, N.; Sers, C.; Lang, R.; Hammerstein, P.; Lucius, R.; et al. A helminth immunomodulator exploits host signaling events to regulate cytokine production in macrophages. Plos Pathog 2011, 7, e1001248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhong, S. Modulation of dendritic cell function and immune response by cysteine protease inhibitor from murine nematode parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus. Immunology 2013, 138, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuijs, M.J.; Hartmann, S.; Selkirk, M.E.; Roberts, L.B.; Openshaw, P.J.; Schnoeller, C. The Helminth-Derived Immunomodulator AvCystatin Reduces Virus Enhanced Inflammation by Induction of Regulatory IL-10+ T Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.; Manoury, B.; Balic, A.; Watts, C.; Maizels, R.M. Bm-CPI-2, a cystatin from Brugia malayi nematode parasites, differs from Caenorhabditis elegans cystatins in a specific site mediating inhibition of the antigen-processing enzyme AEP. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 2005, 139, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoury, B.; Gregory, W.F.; Maizels, R.M.; Watts, C. Bm-CPI-2, a cystatin homolog secreted by the filarial parasite Brugia malayi, inhibits class II MHC-restricted antigen processing. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnoeller, C.; Rausch, S.; Pillai, S.; Avagyan, A.; Wittig, B.M.; Loddenkemper, C.; Hamann, A.; Hamelmann, E.; Lucius, R.; Hartmann, S. A Helminth Immunomodulator Reduces Allergic and Inflammatory Responses by Induction of IL-10-Producing Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilowicz-Luebert, E.; Steinfelder, S.; Kuhl, A.A.; Drozdenko, G.; Lucius, R.; Worm, M.; Hamelmann, E.; Hartmann, S. A nematode immunomodulator suppresses grass pollen-specific allergic responses by controlling excessive Th2 inflammation. Int. J. Parasitol 2013, 43, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, R.A.; Rausch, S.; Ebner, F.; Günzel, D.; Richter, J.F.; Hering, N.A.; Schulzke, J.-D.; Kühl, A.A.; Keles, A.; Janczyk, P.; et al. A Transgenic Probiotic Secreting a Parasite Immunomodulator for Site-Directed Treatment of Gut Inflammation. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, S.; Barrios, L.; Zakzuk, J.; Regino, R.; Ahumada, V.; Franco, L.; Ocampo, Y.; Caraballo, L. A recombinant cystatin from Ascaris lumbricoides attenuates inflammation of DSS-induced colitis. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönemeyer, A.; Lucius, R.; Sonnenburg, B.; Brattig, N.; Sabat, R.; Schilling, K.; Bradley, J.; Hartmann, S. Modulation of Human T Cell Responses and Macrophage Functions by Onchocystatin, a Secreted Protein of the Filarial Nematode Onchocerca volvulus. J. Immunol 2001, 167, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Kyewski, B.; Sonnenburg, B.; Lucius, R. A filarial cysteine protease inhibitor down-regulates T cell proliferation and enhances interleukin-10 production. Eur. J. Immunol 1997, 27, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, V.; Amdare, N.; Tarnekar, A.; Goswami, K.; Reddy, M.V.R. Brugia malayi cystatin therapeutically ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J. Digest Dis. 2016, 16, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.S.; Kyoung, C.M.; Kyung, P.M.; Kang, S.A.; Na, B.K.; Cheol, A.S.; Dong-Hee, K.; Yu, H.S. Parasitic Helminth Cystatin Inhibits DSS-Induced Intestinal Inflammation Via IL-10+F4/80+ Macrophage Recruitment. Korean J. Parasitol 2011, 49, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- 28 Schierack, P.; Lucius, R.; Sonnenburg, B.; Schilling, K.; Hartmann, S. Parasite-Specific Immunomodulatory Functions of Filarial Cystatin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2422–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Wang, T.; Peng, X.; Yang, G. Cloning and characterization of a novel sigma-like glutathione S-transferase from the giant panda parasitic nematode, Baylisascaris schroederi. Parasite Vector 2015, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Lan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Rong, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, W.; Nie, H.; Yue, X. Novel Insights into the Transcriptome of Dirofilaria immitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41639. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Blackshields, G.; Np, B.; Chenna, R.; Pa, M.G.; Mcwilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Im, W.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. ClustalW and ClustalX version 2. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, X.; He, M.; Ren, Y.; Shen, N.; Li, C.; He, R.; Xie, Y.; Gu, X.; Jing, B. Identification of a novel PYP-1 gene in Sarcoptes scabiei and its potential as a serodiagnostic candidate by indirect-ELISA. Parasitology 2017, 145, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, W.F.; Maizels, R.M. Cystatins from filarial parasites: Evolution, adaptation and function in the host-parasite relationship. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustigman, S.; Brotman, B.; Huima, T.; Prince, A.M. Characterization of an Onchocerca volvulus cDNA clone encoding a genus specific antigen present in infective larvae and adult worms. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1991, 45, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustigman, S.; Brotman, B.; Huima, T.; Prince, A.M.; Mckerrow, J.H. Molecular cloning and characterization of onchocystatin, a cysteine proteinase inhibitor of Onchocerca volvulus. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17339–17346. [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi, S.; Zhang, J.; Oksov, Y.; Ji, Q.; Lustigman, S. The Caenorhabditis elegans CPI-2a cystatin-like inhibitor has an essential regulatory role during oogenesis and fertilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28415–28429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Fernandez, M.; Barrett, A.J.; Gerhartz, B.; Dando, P.M.; Ni, J.; Abrahamson, M. Inhibition of mammalian legumain by some cystatins is due to a novel second reactive site. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19195–19203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopitar-Jerala, N. The role of cystatins in cells of the immune system. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6295–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, A.W.; Schulz-Key, H.; Soboslay, P.T.; Taylor, D.W.; Maclennan, K.; Hoffmann, W.H. Litomosoides sigmodontis cystatin acts as an immunomodulator during experimental filariasis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, J.; Satti, M.; Moreno, Y.; Madrill, N.; Whitten, D.; Headley, S.A.; Agnew, D.; Geary, T.; Mackenzie, C.J.P. First analysis of the secretome of the canine heartworm, Dirofilaria immitis. Parasite Vector 2012, 5, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twu, O.; de Miguel, N.; Lustig, G.; Stevens, G.C.; Vashisht, A.A.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Johnson, P.J.J.P.p. Trichomonas vaginalis exosomes deliver cargo to host cells and mediate host: Parasite interactions. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, A.; Trelis, M.; Cortés, A.; Sotillo, J.; Cantalapiedra, F.; Minguez, M.T.; Valero, M.L.; Del Pino, M.M.S.; Muñoz-Antoli, C.; Toledo, R.J.P.o. Extracellular vesicles from parasitic helminths contain specific excretory/secretory proteins and are internalized in intestinal host cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, D.; Trelis, M.; Montaner, S.; Cantalapiedra, F.; Galiano, A.; Hackenberg, M.; Marcilla, A.J.J.o.p. Surface analysis of Dicrocoelium dendriticum. The molecular characterization of exosomes reveals the presence of miRNAs. J. Proteomics 2014, 105, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.M.; Clos, J.; de’Oliveira, C.C.; Shirvani, O.; Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.E.J.J.C.S. An exosome-based secretion pathway is responsible for protein export from Leishmania and communication with macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.H.; Coakley, G.; Simbari, F.; McSorley, H.J.; Quintana, J.F.; Le Bihan, T.; Kumar, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Lear, M.; Harcus, Y.J.N.c. Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, M.; Fraser, L.M.; Agbedanu, P.N.; Harischandra, H.; Moorhead, A.R.; Day, T.A.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Kimber, M.J.J.P.n.t.d. Release of small RNA-containing exosome-like vesicles from the human filarial parasite Brugia malayi. PLoS Neglected Trop D 2015, 9, e0004069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, I.L.; Barry, J.D. Temporal reiteration of a precise gene expression pattern during nematode development. Embo J. 1996, 15, 3633–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Atxutegi, C.; Kramer, L.H.; Fernandez, I.; Simoncini, L.; Genchi, M.; Prieto, G.; Simón, F. Th1 response in BALB/c mice immunized with Dirofilaria immitis soluble antigens: A possible role for Wolbachia? Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 112, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchón, R.; López-Belmonte, J.; Bazzocchi, C.; Grandi, G.; Kramer, L.; Simón, F.J.V.i. Dogs with patent Dirofilaria immitis infection have higher expression of circulating IL-4, IL-10 and iNOS mRNA than those with occult infection. Vet. Immunol. Immuno. 2007, 115, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.; Devaney, E. Interleukin-10 and Antigen-Presenting Cells Actively Suppress Th1 Cells in BALB/c Mice Infected with the Filarial Parasite Brugia pahangi. Infect. Immunol. 1999, 67, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Mahanty, S.; Mollis, S.N.; Ravichandran, M.; Abrams, J.S.; Kumaraswami, V.; Jayaraman, K.; Ottesen, E.A.; Nutman, T.B. High Levels of Spontaneous and Parasite Antigen-Driven Interieukin-10 Production Are Associated with Antigen-Specific Hyporesponsiveness in Human Lymphatic Filariasis. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 173, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, T.; Rausch, S.; Steinfelder, S.; Klotz, C.; Hepworth, M.R.; Kühl, A.A.; Burda, P.-C.; Lucius, R.; Hartmann, S. A Novel Regulatory Macrophage Induced by a Helminth Molecule Instructs IL-10 in CD4+ T Cells and Protects against Mucosal Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M.; Gomez-Escobar, N.; Gregory, W.F.; Murray, J.; Zang, X. Immune evasion genes from filarial nematodes. INT J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizels, R.M.; Blaxter, M.L.; Scott, A.L. Immunological genomics of Brugia malayi: Filarial genes implicated in immune evasion and protective immunity. Para. Immunol. 2001, 23, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vray, B.; Hartmann, S.; Hoebeke, J. Immunomodulatory properties of cystatins. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ju, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, C.; Man, S.; Ximei, Z.; Zhongkai, W.J.P.R. Cloning, expression and characterisation of a type II cystatin from Schistosoma japonicum, which could regulate macrophage activation. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3985–3992. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).