Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MIR143 Contribute to Protection against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) in Caucasian Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.3. miRSNP Selection and iPlex Primer Design
2.4. Primary Multiplex PCR
2.5. MALDI-TOF MS and Data Analysis
2.6. In-Vitro Culture of Cell Lines and Primary Lymphocytes
2.7. Validation of Genotyping by MassARRAY® and Genotyping of Cell Lines and Healthy Controls by Sanger Sequencing
2.8. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and q-PCR
2.9. Protein Detection by Western Blot
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. NHL-GWAS Replication Dataset
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Association of MIR143 SNPs and NHL Risk
3.2. Replication of Summary Statistics in a Large EUROPEAN NHL GWAS Meta-Analysis
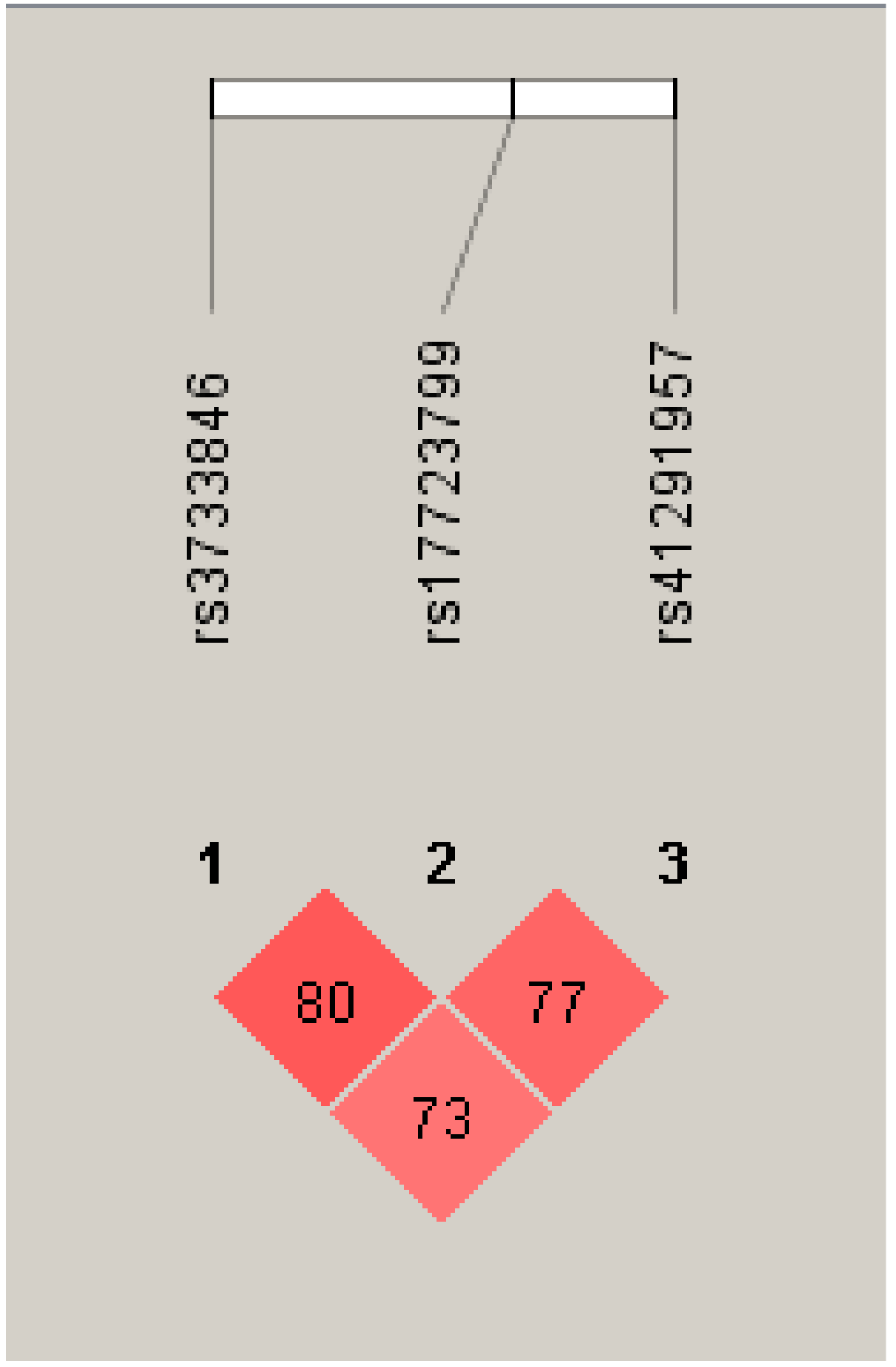
3.3. Haplotype Analysis of MIR143 SNPs in LD on Chromosome 5
3.4. Genotyping of rs17723799 (C>T) in Cell Lines and Healthy Control Samples
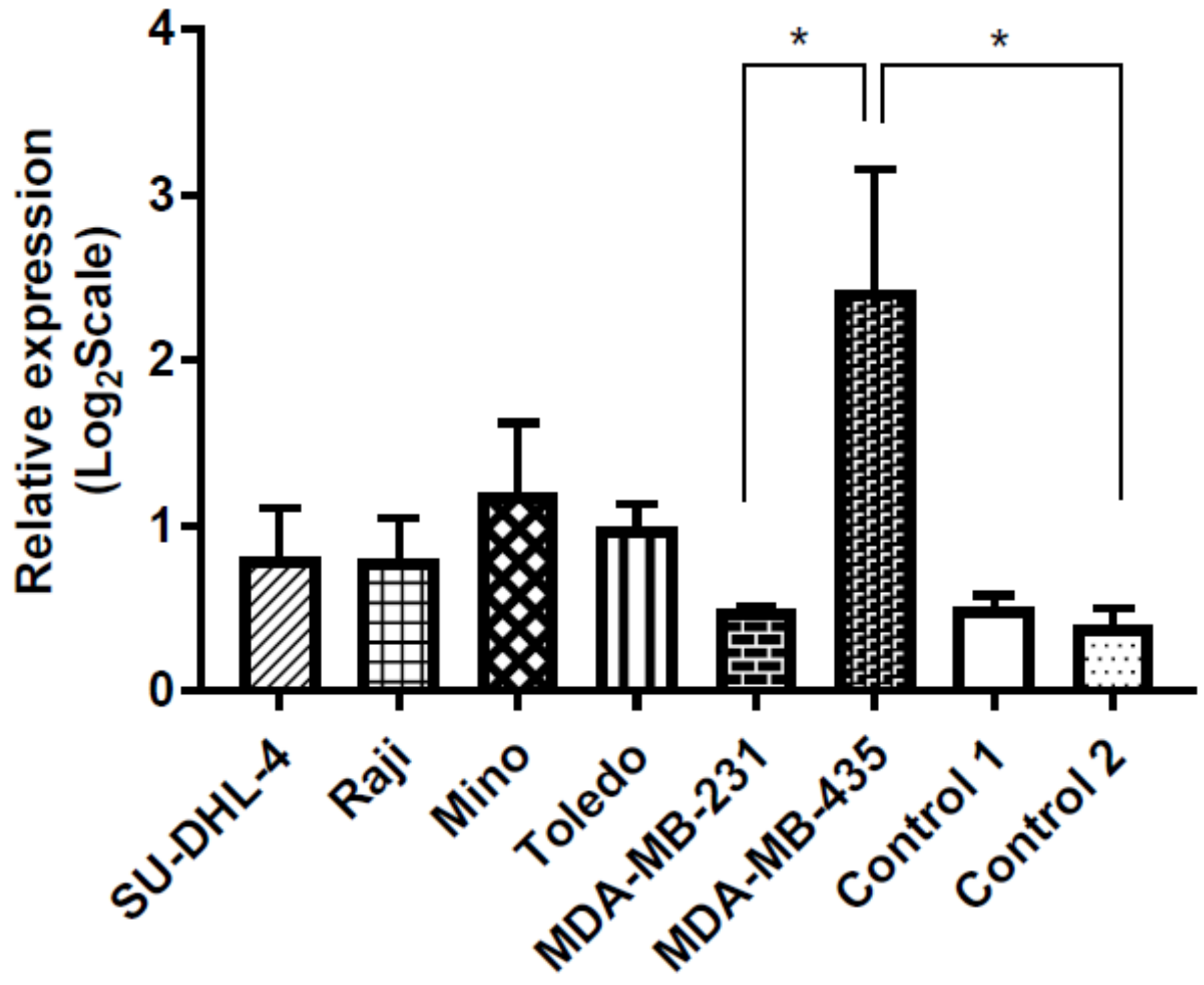
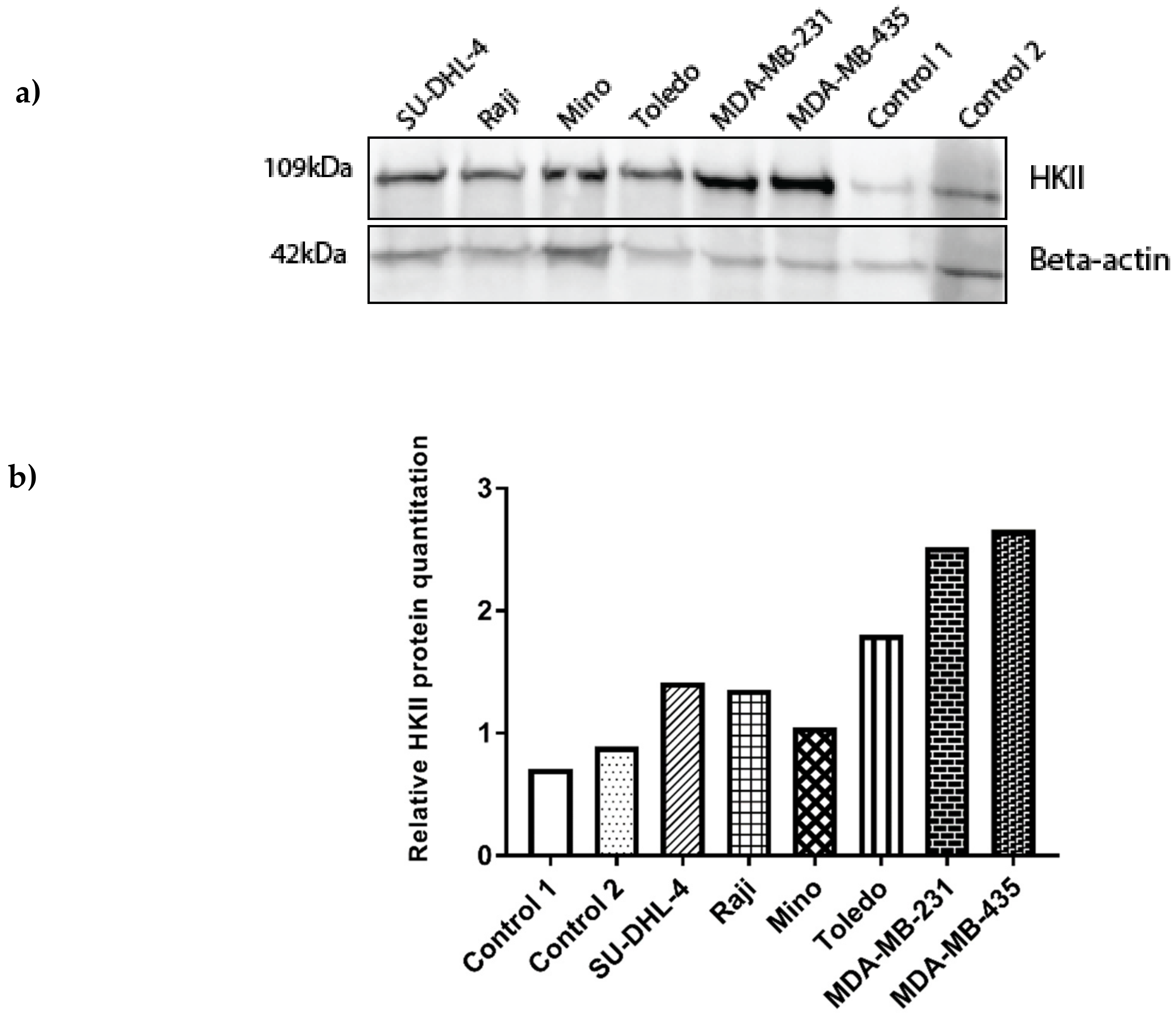
3.5. miR-143 Target Gene HKII Expression in Cancer Cell Lines and Healthy Control Lymphocytes
3.5.1. HKII Gene Expression Is Increased in NHL Compared to Healthy Controls
3.5.2. Increased HKII Gene Expression May Be Associated with the MIR143 rs17723799 TT Genotype
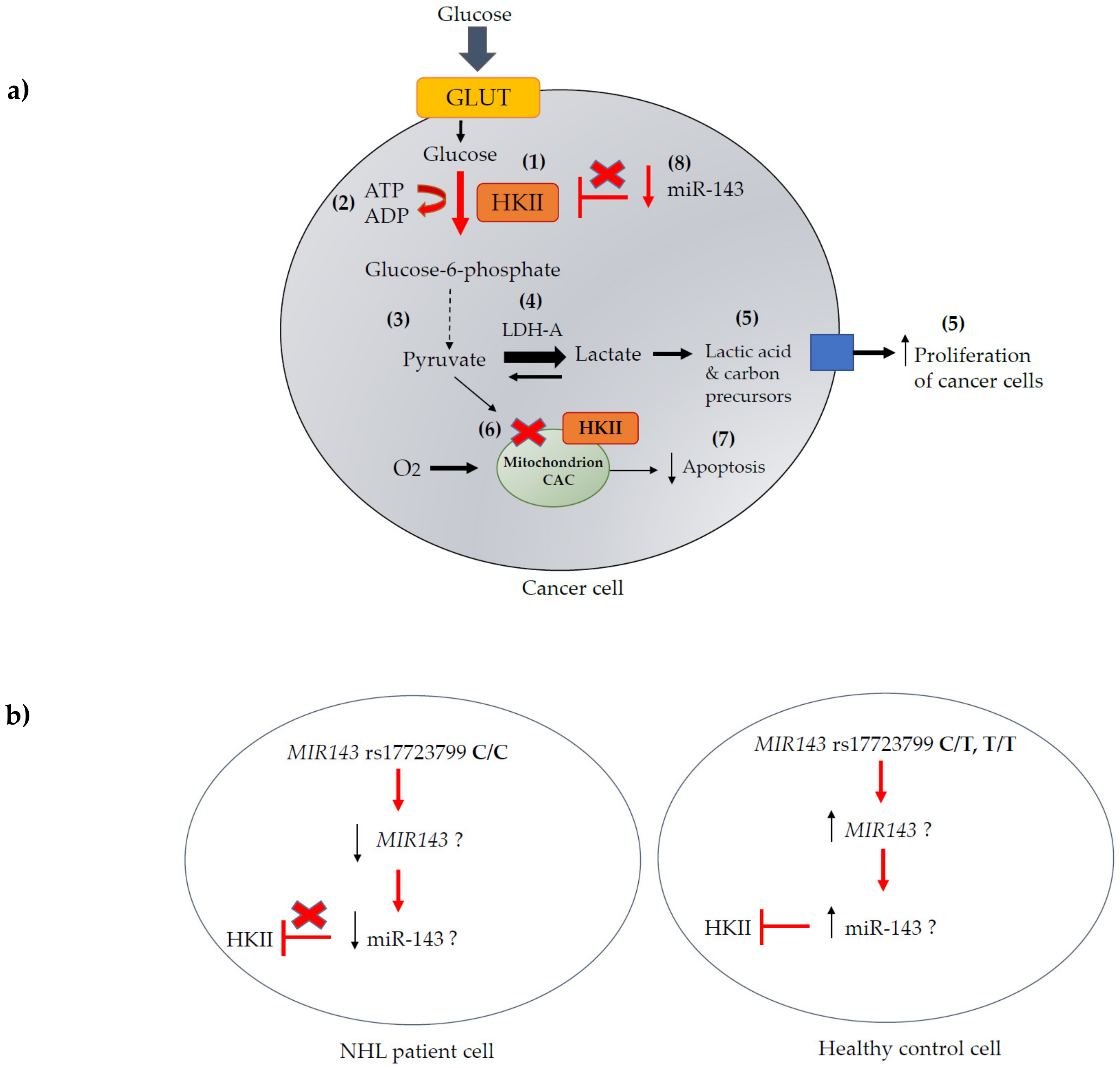
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skrabek, P.; Turner, D.; Seftel, M. Epidemiology of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Transfus. Apheresis Sci. 2013, 49, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2018. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/ (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- Lymphoma Coalition Europe. Available online: https://www.lymphomacoalition.org/europe (accessed on 15 November 2018).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare 2017. Cancer in Australia 2017 Cancer Series No. 101. Cat. No. CAN 100. Canberra: AIHW. Available online: www.aihw.gov.au (accessed on 23 September 2018).
- Yadav, C.; Ahmad, A.; D’Souza, B.; Agarwal, A.; Nandini, M.; Ashok Prabhu, K.; D’Souza, V. Serum Lactate Dehydrogenase in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: A Prognostic Indicator. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 31, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehle, A.; Hoefig, K.P.; Repsilber, D.; Thorns, C.; Ziepert, M.; Wesche, K.O.; Thiere, M.; Loeffler, M.; Klapper, W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. MicroRNA signatures characterize diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and follicular lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Chi, J.; Taylor, S.; Tramonti, D.; Ballabio, E.; Palazzo, S.; Saunders, N.J.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Expression of microRNAs in diffuse large B cell lymphoma is associated with immunophenotype, survival and transformation from follicular lymphoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2003, 13, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, G.C.; Singh, J.; Barik, S. MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Mol. Cell. Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salzman, D.W.; Weidhaas, J.B. SNPing cancer in the bud: MicroRNA and microRNA-target site polymorphisms as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, B.R. Transcription and Processing of Human microRNA Precursors. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treiber, T.; Treiber, N.; Meister, G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 107, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannini, I.; Fanini, F.; Fabbri, M. Emerging roles of microRNAs in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 48, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, P.S.; Venkatesh, T.; Tsutsumi, R. In silico analysis of polymorphisms in microRNAs that target genes affecting aerobic glycolysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, M.; Zhou, D.; Zhi, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. MSDD: A manually curated database of experimentally supported associations among miRNAs, SNPs and human diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D181–D185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, H.-M.; Wang, K.; Hu, T.; Shan, G.; Sun, J.; Guo, A.-Y. Genome-wide identification of SNPs in microRNA genes and the SNP effects on microRNA target binding and biogenesis. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Xi, Z.; Liu, R.; Yin, W.; Sui, Z.; Ren, B.; Miller, H.; Gong, Q.; Liu, C. The Function of MicroRNAs in B-Cell Development, Lymphoma, and Their Potential in Clinical Practice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk, A. MicroRNA polymorphisms as markers of risk, prognosis and treatment response in hematological malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 93, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, G.; Sutherland, H.; Haupt, L.; Griffiths, L. Dysregulated MicroRNA Expression Profiles and Potential Cellular, Circulating and Polymorphic Biomarkers in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Genes 2016, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaitheesvaran, B.; Xu, J.; Yee, J.; Q.-Y., L.; Go, V.L.; Xiao, G.G.; Lee, W.N. The Warburg effect: A balance of flux analysis. Metab. Off. J. Metab. Soc. 2015, 11, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.; Agnihotri, S.; Micallef, J.; Mukherjee, J.; Sabha, N.; Cairns, R.; Hawkins, C.; Guha, A. Hexokinase 2 is a key mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human glioblastoma multiforme. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.J.; Singh, A.; Xue, K.; Mavis, C.; Barth, M.; Yanamadala, V.; Lenz, P.; Grau, M.; Lenz, G.; Czucman, M.S.; et al. Up-regulation of hexokinase II contributes to rituximab-chemotherapy resistance and is a clinically relevant target for therapeutic development. Oncotarget 2017, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akins, N.S.; Nielson, T.C.; Le, H.V. Inhibition of Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis: An Emerging Drug Discovery Approach to Combat Cancer. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, D.; Fitzgerald, D.; Shreeve, S.M.; Hua, E.; Bronder, J.L.; Weil, R.J.; Davis, S.; Stark, A.M.; Merino, M.J.; Kurek, R.; et al. Analyses of resected human brain metastases of breast cancer reveal the association between up-regulation of hexokinase 2 and poor prognosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, S.; Schulze, A. Glycolysis Back in the Limelight: Systemic Targeting of HK2 Blocks Tumor Growth. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, M.; Darekar, S.; Klein, G.; Kashuba, E. Different Mechanisms of Regulation of the Warburg Effect in Lymphoblastoid and Burkitt Lymphoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, K.; Jaber, S.; Nahid, M.; Underwood, K.; Beheshti, A.; Landon, A.; Bhandary, B.; Bastian, P.; Evens, A.M.; Haley, J.; et al. Role of hypoxia in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma: Metabolic repression and selective translation of HK2 facilitates development of DLBCL. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowska, E.; Wojtala, M.; Gajewska, A.; Soszyński, M.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Effect of 3-bromopyruvate acid on the redox equilibrium in non-invasive MCF-7 and invasive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J. Bioenergy Biomembr. 2016, 48, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacon-Cortes, D.; Smith, R.A.; Haupt, L.M.; Lea, R.A.; Youl, P.H.; Griffiths, L.R. Genetic association analysis of miRNA SNPs implicates MIR145 in breast cancer susceptibility. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyaya, A.; Smith, R.A.; Chacon-Cortes, D.; Revêchon, G.; Bellis, C.; Lea, R.A.; Haupt, L.M.; Chambers, S.K.; Youl, P.H.; Griffiths, L.R. Association of the microRNA-Single Nucleotide Polymorphism rs2910164 in miR146a with sporadic breast cancer susceptibility: A case control study. Gene 2016, 576, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacon-Cortes, D.; Haupt, L.M.; Lea, R.A.; Griffiths, L.R. Comparison of genomic DNA extraction techniques from whole blood samples: A time, cost and quality evaluation study. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 5961–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com.
- Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Barrett, J.C.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2004, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Niu, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, D. A functional polymorphism in microRNA-196a2 is associated with increased susceptibility to non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3279–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerhan, J.R.; Berndt, S.I.; Vijai, J.; Ghesquières, H.; McKay, J.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, Z.; Yeager, M.; Conde, L.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, G.; Wang, S. A Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism of miR-196a2T>C rs11614913 Is Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Chinese Population. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2016, 20, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham-Gregory, E.C.; Thapa, D.R.; Martinson, J.; Duggal, P.; Penugonda, S.; Bream, J.H.; Chang, P.-Y.; Dandekar, S.; Chang, S.-C.; Detels, R.; et al. MicroRNA-related polymorphisms and non-Hodgkin lymphoma susceptibility in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, A.; Liu, B.; Zhong, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Mei, H. rs11614913 polymorphism in miRNA-196a2 and cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1121–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Bai, P.; Jin, H.; Wang, T.; Song, C.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L. Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of miR-143/145 and risk of colorectal cancer. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Huang, Q.; Meng, D.; Huang, M.; Li, C.; Qin, T. A Functional rs353293 Polymorphism in the Promoter of miR-143/145 Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Bladder Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.; Xiao, T.; Fang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, F.; Gao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. MicroRNA-143 (miR-143) Regulates Cancer Glycolysis via Targeting Hexokinase 2 Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 23227–23235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschiaroli, A.; Giacobbe, A.; Formosa, A.; Markert, E.K.; Bongiorno-Borbone, L.; Levine, A.J.; Candi, E.; D’Alessandro, A.; Zolla, L.; Finazzi Agrò, A.; et al. miR-143 regulates hexokinase 2 expression in cancer cells. Oncogene 2012, 32, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, H.W.; Hu, S.; Lu, M.H.; Liang, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, E.D.; et al. A novel miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. Embo J. 2012, 31, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinali, T.; Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Baradaran, B. Regulatory mechanisms of miR-145 expression and the importance of its function in cancer metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.-L.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Zheng, J.-F.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y. Altered miR-143 and miR-150 expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 4510–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, H.; Enokida, H.; Itesako, T.; Kojima, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Tatarano, S.; Chiyomaru, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Seki, N. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster targets hexokinase-2 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Ferreira, A.C.; Robaina, M.C.; de Rezende, L.M.M.; Severino, P.; Klumb, C.E. Histone deacetylase inhibitor prevents cell growth in Burkitt’s lymphoma by regulating PI3K/Akt pathways and leads to upregulation of miR-143, miR-145, and miR-101. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Wu, D.; Zhou, H. Overexpression of microRNA-143 inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carithers, L.J.; Ardlie, K.; Barcus, M.; Branton, P.A.; Britton, A.; Buia, S.A.; Compton, C.C.; DeLuca, D.S.; Peter-Demchok, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; et al. A Novel Approach to High-Quality Postmortem Tissue Procurement: The GTEx Project. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2015, 13, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bcndoye. Comparison of LDH Activity in Normal and Cancerous Cell Metabolism. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:LDH_activity-_normal_vs_canceous_cells.png (accessed on 9 November 2018).
| NHL Subtype | No. of Cases in the Cohort |
|---|---|
| FL | 95 |
| DLBCL | 88 |
| Other B-cell/NHL/unclassified | 79 |
| B-CLL | 16 |
| T-cell lymphoma | 7 |
| Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) | 6 |
| Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) | 4 |
| Mucosa-associated lymphoid tumour (MALT) | 3 |
| Burkitt’s lymphoma (BL) | 2 |
| Total | 300 |
| SNP | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | Accession ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs3733846 | TGTTTGCCTCCATCTCCTCT | CCTTCCCATGGAGCTTTGT | NC_000005.1 |
| rs41291957 | CAGGAAACACAGTTGTGAGG 1 | AGGAGAAGGGGTGTTAGAGG 1 | NC_000005.1 |
| rs17723799 | TGGTCATCCAATCAGCCACC | GGAAGGGACCCTGTCAACTG | NC_000005.1 |
| Chr | miRNA/Target Gene | SNP | A1 | A2 | MAF/NCHROBS | MAF 1000G | HWEUNAFF | OR | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E2F2 | rs2075993 | G | A | 0.5/862 | G = 0.3488/1747 | 0.2368 | 0.885 | 0.4535 | 1 |
| 1 | GEMIN3 3′-UTR | rs197412 | C | T | 0.4092/870 | C = 0.4744/2376 | 0.6013 | 0.8779 | 0.4301 | 1 |
| 2 | hsa-miR-155-3p | rs4672612 | A | G | 0.338/858 | A = 0.3878/1942 | 0.5476 | 1.095 | 0.6006 | 1 |
| 4 | TET2 | rs7670522 | A* | C | 0.4701/870 | C = 0.3600/1803 | 1.000 | 1.089 | 0.6041 | 1 |
| 4 | hsa-miR-4330/5100 | rs2647257 | T | A | 0.408/848 | T = 0.2386/1195 | 0.3732 | 0.9403 | 0.7094 | 1 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-224-5p | rs12719481 | G | A | 0.2719/868 | G = 0.3670/1838 | 1.000 | 1.072 | 0.7052 | 1 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-143 | rs3733846 | G | A | 0.1367/878 | G = 0.2063/1033 | 1.000 | 0.5646 | 0.012 | 0.467 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-143 | rs17723799 | T | C | 0.1129/868 | T = 0.1118/560 | 1.000 | 0.423 | 0.0004 | 0.015 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-143 | rs41291957 | A | G | 0.1412/878 | A = 0.1214/608 | 1.000 | 0.5624 | 0.008 | 0.326 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-145 | rs353291 | C | T | 0.4237/826 | C = 0.3608/1807 | 0.1473 | 1.204 | 0.2648 | 1 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-146-a | rs2910164 | C | G | 0.2204/862 | C = 0.2797/2881 | 0.5978 | 1.19 | 0.3908 | 1 |
| 5 | hsa-miR-218-2 | rs11134527 | A | G | 0.2189/868 | A = 0.3462/1734 | 0.7982 | 1.061 | 0.7635 | 1 |
| 6 | XPO5 | rs11077 | G | T | 0.4255/872 | G = 0.4036/2021 | 0.3862 | 0.9566 | 0.7869 | 1 |
| 6 | TAB2 | rs9485372 | A | G | 0.1965/850 | A = 0.2408/1206 | 1.000 | 0.844 | 0.4084 | 1 |
| 6 | ESR1, C6orf97 | rs2046210 | A | G | 0.3353/850 | A = 0.4121/2064 | 1.000 | 1.277 | 0.1659 | 1 |
| 8 | TP53 | rs896849 | G | A | 0.1501/866 | G = 0.2183/1093 | 0.4915 | 0.9369 | 0.7695 | 1 |
| 8 | CASC21 | rs13281615 | G | A | 0.4417/840 | G = 0.4912/2460 | 0.3853 | 0.7541 | 0.08388 | 1 |
| 8 | AGO2 | rs3864659 | C | A | 0.1023/860 | C = 0.1436/719 | 0.6026 | 1.147 | 0.6275 | 1 |
| 8 | AGO2 | rs4961280 | A | C | 0.1835/872 | A = 0.1490/746 | 0.7390 | 1.416 | 0.1075 | 1 |
| 9 | hsa-miR-101-2 | rs462480 | G | T | 0.3984/876 | G = 0.4451/2229 | 0.7246 | 1.001 | 0.9948 | 1 |
| 10 | hsa-miR-608 | rs4919510 | G | C | 0.1979/874 | G = 0.3638/1822 | 1.000 | 1.115 | 0.6034 | 1 |
| 10 | hsa-miR-202 | rs12355840 | C | T | 0.1368/848 | C = 0.3189/1597 | 0.6598 | 0.494 | 0.1049 | 1 |
| 11 | hsa-miR-210 | rs1062099 | C | G | 0.1701/876 | C = 0.1649/826 | 0.3067 | 1.29 | 0.2536 | 1 |
| 11 | LSP1 | rs3817198 | C | T | 0.3289/836 | C = 0.2155/1079 | 0.7152 | 0.7085 | 0.04181 | 1 |
| 11 | TMEM45, BARX2 | rs7107217 | A | C | 0.4883/858 | A = 0.4876/2442 | 0.5987 | 0.8992 | 0.514 | 1 |
| 12 | KRAS 3′-UTR | rs61764370 | C | A | 0.0962/852 | C = 0.0347/174 | 1.000 | 0.6795 | 0.1473 | 1 |
| 12 | hsa-miR-196-a2 | rs11614913 | T | C | 0.4205/880 | T = 0.333/1666 | 0.226 | 0.928 | 0.6501 | 1 |
| 12 | pre-miR-618 | rs2682818 | A | C | 0.1465/874 | A = 0.2424/1214 | 0.3061 | 1.115 | 0.6448 | 1 |
| 14 | HIF1A 3′-UTR | rs2057482 | T | C | 0.1250/856 | T = 0.2424/1214 | 0.6797 | 1.106 | 0.6831 | 1 |
| 14 | DICER1 | rs3742330 | G | A | 0.0878/854 | G = 0.1382/692 | 0.2499 | 1.261 | 0.4423 | 1 |
| 14 | DICER1 | rs1057035 | C | T | 0.3709/852 | C = 0.1723/863 | 0.854 | 0.8726 | 0.4174 | 1 |
| 16 | TOX3 | rs8051542 | T | C | 0.4322/856 | T = 0.3133/1569 | 1.000 | 0.7698 | 0.1095 | 1 |
| 16 | TOX3 | rs3803662 | A | G | 0.2207/852 | A = 0.4403/2205 | 1.000 | 0.9065 | 0.6119 | 1 |
| 18 | hsa-miR-143-5p | rs4987859 | T | C | 0.0631/856 | T = 0.0477/239 | 0.597 | 0.744 | 0.3466 | 1 |
| 18 | hsa-miR-27-a-5p | rs4987852 | C | T | 0.0667/854 | C = 0.0190/95 | 0.4495 | 1.081 | 0.811 | 1 |
| 18 | hsa-miR-27-a-5p | rs1016860 | T | C | 0.1175/868 | T = 0.1166/584 | 1.000 | 0.8423 | 0.4808 | 1 |
| 21 | hsa-miR-155 HG | rs987195 | G | C | 0.0917/840 | G = 0.1472/737 | 0.361 | 0.6702 | 0.1265 | 1 |
| 21 | hsa-miR-155 | rs12482371 | C | T | 0.1632/858 | C = 0.4151/2079 | 0.5662 | 0.7506 | 0.1748 | 1 |
| X | hsa-miR-221/222 | rs34678647 | T | G | 0.0375/667 | T = 0.1423/537 | 0.1782 | 0.433 | 0.05456 | 1 |
| Chr | Gene | SNP | A1 | Model | OR (CI 95%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | MIR143 | rs3733846 | G | Additive | 0.54 (0.34–0.87) | 0.010 |
| 5 | MIR143 | rs41291957 | A | Additive | 0.61 (0.39–0.94) | 0.024 |
| 5 | MIR143 | rs17723799 | T | Additive | 0.61 (0.26–0.71) | 0.0009 |
| rs17723799 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allele | Genotype | |||||||
| C (%) | T (%) | p-Value | C/C (%) | C/T (%) | T/T (%) | p-Value | HWE | |
| Controls | 234 (84.8) | 42 (15.2) | 0.013 | 99 (71.7) 244 (82.4) | 36 (26.1) 48 (16.2) | 3 (2.2) 4 (1.4) | 0.039 | 1.000 0.311 |
| Cases | 536 (90.5) | 56 (9.5) | ||||||
| MAF | 770 (88.7) | 98 (11.3) | ||||||
| 1000G (%) | 88.8 | 11.2 | ||||||
| gnomAD (%) | 86.9 | 13.1 | ||||||
| rs3733846 | ||||||||
| Allele | Genotype | |||||||
| A (%) | G (%) | p-Value | A/A (%) | A/G (%) | G/G (%) | p-Value | HWE | |
| Controls | 231 (83) | 47 (17) | 0.057 | 96 (69) 232 (77) | 39 (28) 63 (21) | 4 (3) 5 (2) | 0.167 | 1.000 0.785 |
| Cases | 527 (88) | 73 (12) | ||||||
| MAF (%) | 758 (86.3) | 120 (13.7) | ||||||
| 1000G (%) | 79.4 | 20.6 | ||||||
| gnomAD (%) | 84.4 | 15.6 | ||||||
| rs41291957 | ||||||||
| Allele | Genotype | |||||||
| G (%) | A (%) | p-Value | G/G (%) | G/A (%) | A/A (%) | p-Value | HWE | |
| Controls | 229 (82.4) | 49 (17.6) | 0.043 | 94 (67.6) 233 (77.7) | 41 (29.5) 59 (19.7) | 4 (2.9) 8 (2.6) | 0.070 | 1.000 0.106 |
| Cases | 525 (87.5) | 75 (12.5) | ||||||
| MAF (%) | 754 (85.9) | 124 (14.1) | ||||||
| 1000G (%) | 87.9 | 12.1 | ||||||
| gnomAD (%) | 84 | 16 | ||||||
| Model | Genotype | Controls (%) | Cases (%) | χ2 | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allelic | T vs. C | 39/459 | 36/178 | 12.84 | - | 0.0003 |
| Additive | - | - | - | 0.43 (0.26–0.71) | 0.0009 | |
| Co-dominant | CC | 97 (71.9) | 243 (82.4) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| CT | 35 (25.9) | 48 (16.3) | 0.55 (0.33–0.91) | |||
| TT | 3 (2.2) | 4 (1.4) | 0.47 (0.10–2.23) | 0.051 | ||
| Dominant | CC | 97 (71.9) | 243 (82.4) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| CT–TT | 38 (28.1) | 52 (17.6) | 0.54 (0.33–0.88) | 0.015 | ||
| Recessive | CC–CT | 132 (97.8) | 291 (98.6) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| TT | 3 (2.2) | 4 (1.4) | 0.53 (0.11–2.52) | 0.438 | ||
| Over-dominant | CC–TT | 100 (74.1) | 247 (83.7) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| CT | 35 (25.9) | 48 (16.3) | 0.56 (0.33–0.92) | 0.024 | ||
| Log-additive | - | 135 (31.4) | 295 (68.6) | 0.58 (0.38–0.90) | 0.017 |
| SNP | Location (GRChg38) | rs3733846 | rs12659504 | rs878008 | rs17723799 | rs41291957 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3733846 | 149,425,059 | - | 1.000/1.000 | 1.000/1.000 | 1.000/1.000 | 0.721/0.941 |
| rs12659504 | 149,425,442 | - | - | 1.000/1.000 | 1.000/1.000 | 0.721/0.942 |
| rs878008 | 149,425,488 | - | - | - | 1.000/1.000 | 0.721/0.942 |
| rs17723799 | 149,427,514 | - | - | - | - | 0.999/0.999 |
| rs41291957 | 149,428,827 | - | - | - | - | - |
| SNP | Chr | Location (GRChg38) | Group | Controls | Cases | Effect Allele | EAF Controls | EAF Cases | OR | CI (95%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs12659504 | 5 | 149,425,442 | NCI | 6221 | 2661 | G | 0.1502 | 0.1359 | 0.93 | 0.84–1.02 | 0.120 |
| rs12659504 | 5 | 149,425,442 | GELA | 525 | 548 | G | 0.1418 | 0.125 | 0.90 | 0.70–1.15 | 0.392 |
| rs12659504 | 5 | 149,425,442 | MAYO_DLBCL | 171 | 392 | G | 0.173 | 0.1569 | 0.79 | 0.54–1.14 | 0.211 |
| rs12659504 | 5 | 149,425,442 | SF | 747 | 254 | G | 0.133 | 0.1205 | 0.89 | 0.66–1.21 | 0.456 |
| rs12659504 | 5 | 149,425,442 | Meta-analysis | 7664 | 3855 | 0.91 | 0.84–0.99 | 0.033 | |||
| rs878008 | 5 | 149,425,488 | NCI | 6221 | 2661 | C | 0.1501 | 0.1362 | 0.93 | 0.84–1.02 | 0.132 |
| rs878008 | 5 | 149,425,488 | GELA | 524 | 548 | C | 0.1396 | 0.1242 | 0.91 | 0.71–1.16 | 0.445 |
| rs878008 | 5 | 149,425,488 | MAYO_DLBCL | 172 | 392 | C | 0.172 | 0.1548 | 0.78 | 0.53–1.13 | 0.188 |
| rs878008 | 5 | 149,425,488 | SF | 747 | 253 | C | 0.1307 | 0.1199 | 0.90 | 0.66–1.23 | 0.516 |
| rs878008 | 5 | 149,425,488 | Meta-analysis | 7664 | 3854 | 0.92 | 0.84–1.00 | 0.041 |
| Haplotype | rs3733846 | rs41291957 | rs17723799 | Frequencies Cases | Frequencies Controls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | A | C | 0.03608 | 0.03255 |
| 2 | A | A | T | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| 3 | A | G | C | 0.81643 | 0.79232 |
| 4 | A | G | T | 0.02582 | 0.00517 |
| 5 | G | A | C | 0.02159 | - |
| 6 | G | A | T | 0.06733 | 0.14260 |
| 7 | G | G | C | 0.03092 | 0.02067 |
| 8 | G | G | T | 0.00182 | 0.00670 |
| Haplotype | rs3733846 | rs41291957 | rs17723799 | Haplotype Frequencies | OR (CI 95%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | G | C | 0.80883 | 0.90 (0.43–1.90) | 0.7799 |
| 2 | A | G | T | 0.01898 | 6.34 (0.60–67.07) | 0.1246 |
| 3 | G | A | C | 0.01461 | Inf (Inf-Inf) | 0.0000 |
| 4 | G | A | T | 0.09137 | 0.42 (0.18–1.00) | 0.0495 |
| 5 | G | G | C | 0.02762 | 1.22 (0.38–3.88) | 0.7370 |
| rare | * | * | * | 0.00359 | 0.12 (0.00–2.95) | 0.1920 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bradshaw, G.; Haupt, L.M.; Aquino, E.M.; Lea, R.A.; Sutherland, H.G.; Griffiths, L.R. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MIR143 Contribute to Protection against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) in Caucasian Populations. Genes 2019, 10, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030185
Bradshaw G, Haupt LM, Aquino EM, Lea RA, Sutherland HG, Griffiths LR. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MIR143 Contribute to Protection against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) in Caucasian Populations. Genes. 2019; 10(3):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030185
Chicago/Turabian StyleBradshaw, Gabrielle, Larisa M. Haupt, Eunise M. Aquino, Rodney A. Lea, Heidi G. Sutherland, and Lyn R. Griffiths. 2019. "Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MIR143 Contribute to Protection against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) in Caucasian Populations" Genes 10, no. 3: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030185
APA StyleBradshaw, G., Haupt, L. M., Aquino, E. M., Lea, R. A., Sutherland, H. G., & Griffiths, L. R. (2019). Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MIR143 Contribute to Protection against Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) in Caucasian Populations. Genes, 10(3), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030185






