Functional Similarity and Difference among Bra-MIR319 Family in Plant Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
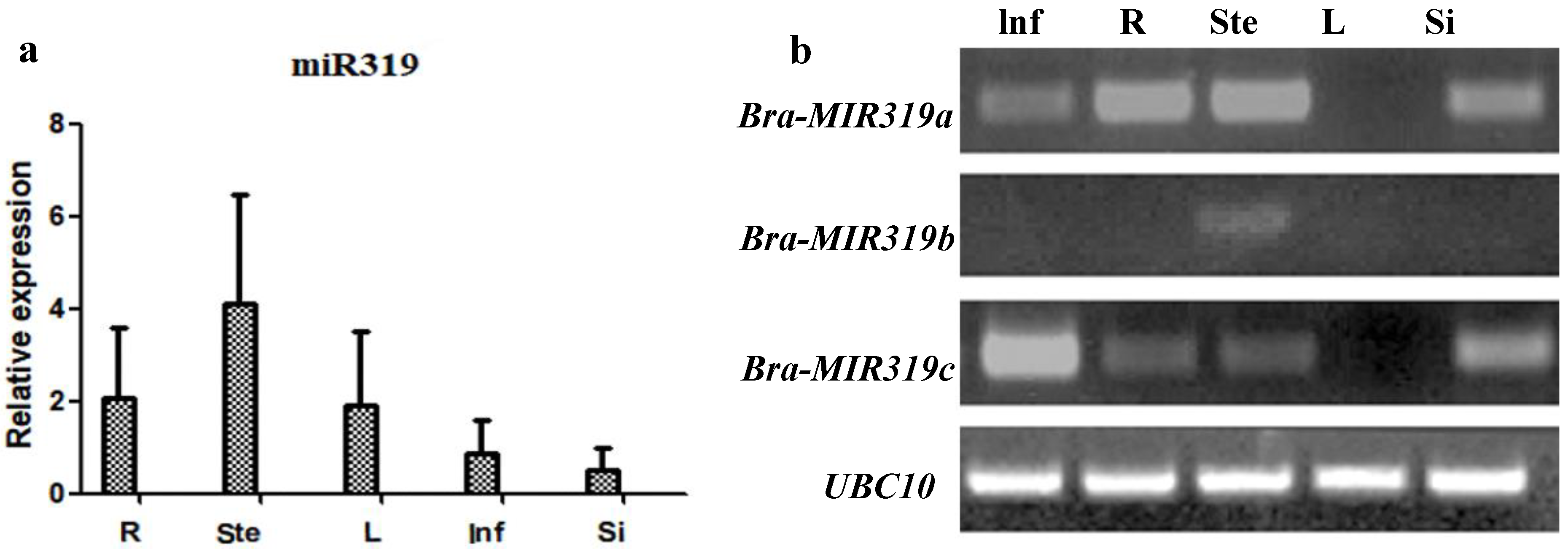
2.2. Expression Profile Analysis
2.3. Generation of Bra-MIR319-Overexpression Arabidopsis Lines
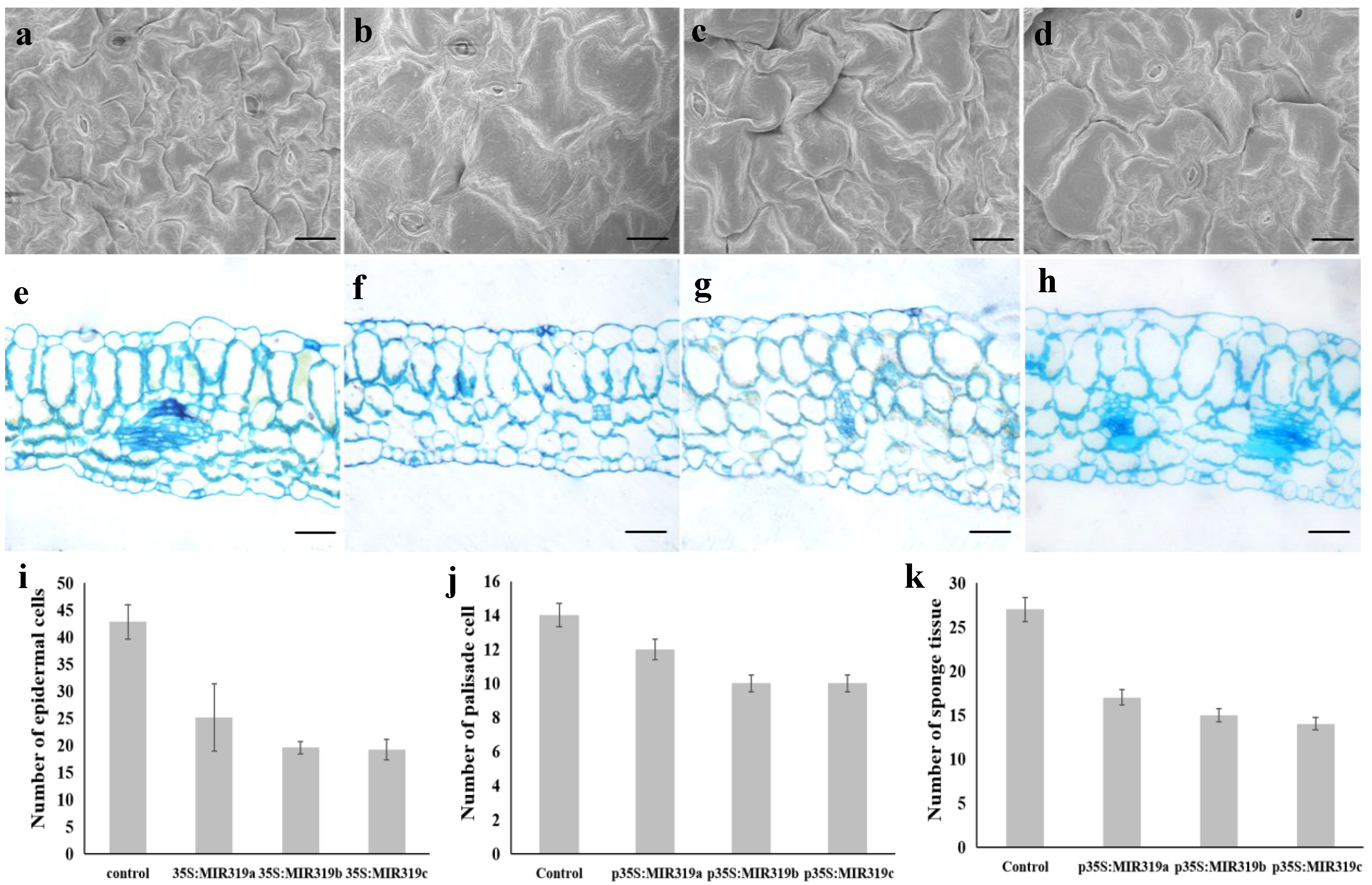
2.4. Morphological and Cytological Observation
2.5. Cleavage Site of miRNA Targets
2.6. Transient Expression in N. benthamiana
3. Results
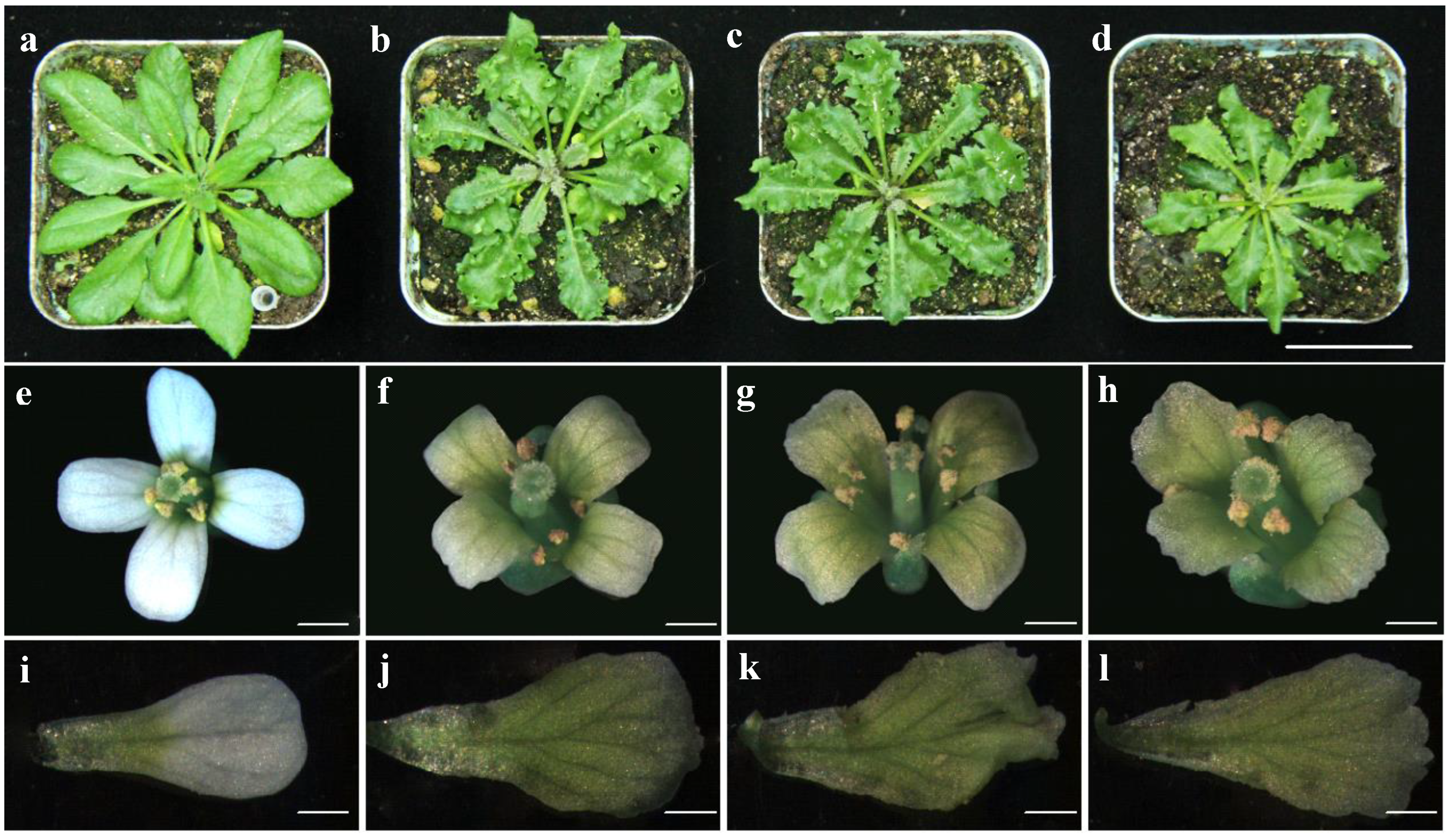
3.1. Bra-MIR319 Family Members Have Functional Similarity in Leaf and Petal Morphogenesis
3.2. Bra-MIR319 Family Members Overexpressing in Arabidopsis Can Inhibit Cell Division
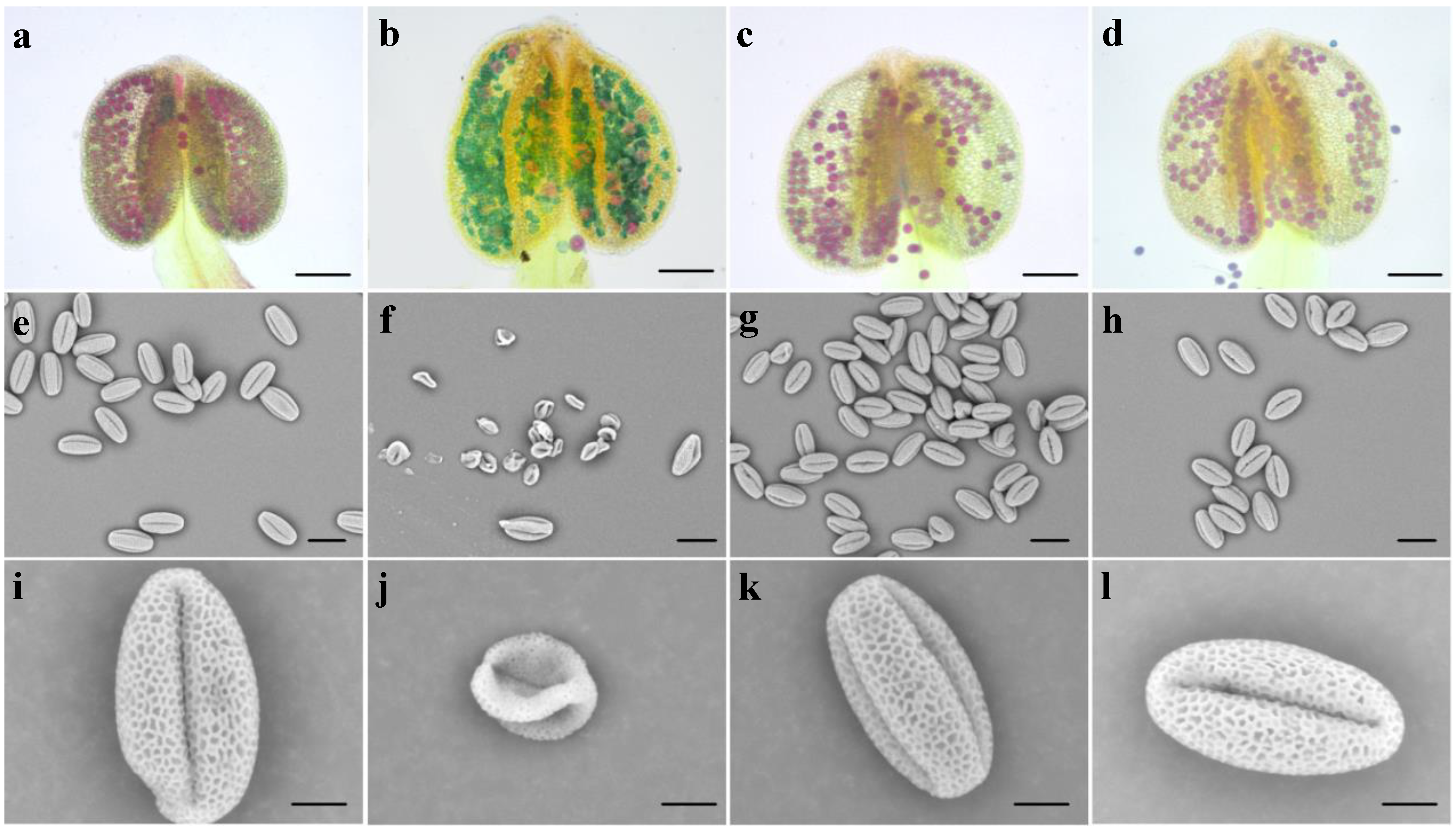
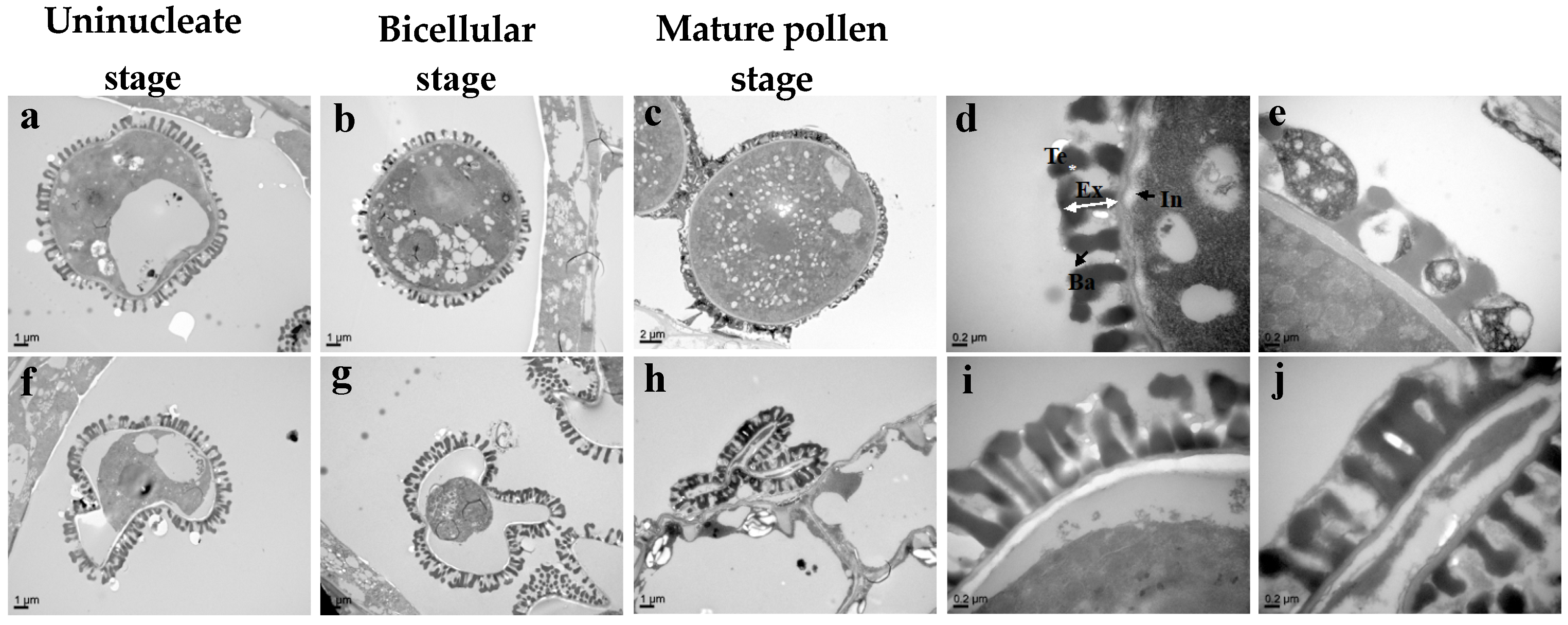
3.3. Bra-MIR319a Overexpressing in Arabidopsis Reduces Pollen Viability
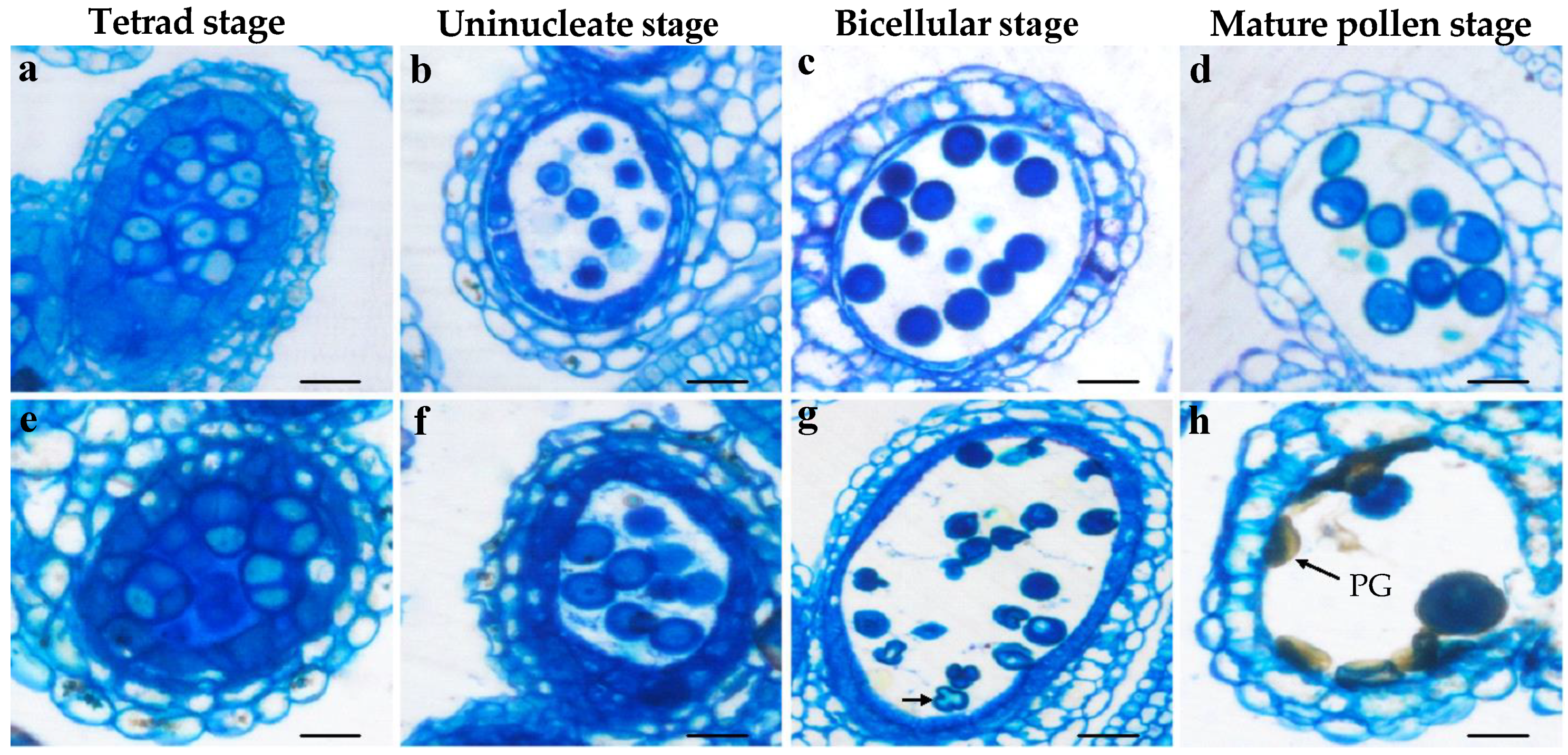
3.4. Bra-MIR319a Overexpressing in Arabidopsis Affects the Formation of Pollen Content and Intine
3.5. Bra-miR319a Can Target Homologs of MYB101
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones-Rhoades, M.; Bartel, D.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and Their Regulatory Roles in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Mao, L. Evolution of plant microRNA gene families. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Mao, Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Ji, Z. miRClassify: An advanced web server for miRNA family classification and annotation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 45, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.; SarkarDas, S.; Singh, A.; Gautam, V.; Kumar, P.; Majee, M.; Sarkar, A.K. Phylogenetic analysis reveals conservation and diversification of microRNA166 genes among diverse plant species. Genomics 2014, 103, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palatnik, J.F.; Allen, E.; Wu, X.; Schommer, C.; Schwab, R.; Carrington, J.; Weigel, D. Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature 2003, 425, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palatnik, J.F.; Wollmann, H.; Schommer, C.; Schwab, R.; Boisbouvier, J.; Rodriguez, R.; Warthmann, N.; Allen, E.; Dezulian, T.; Huson, D.; et al. Sequence and expression differences underlie functional specialization of arabidopsis microRNAs miR159 and miR319. Dev. Cell 2007, 13, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, T.; Sato, F.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Roles of miR319 and TCP transcription factors in leaf development. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresso, E.G.; Chorostecki, U.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F.; Schommer, C. Spatial control of gene expression by miR319-regulated TCP transcription factors in leaf development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schommer, C.; Debernardi, J.M.; Bresso, E.G.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F. Repression of cell proliferation by miR319-regulated TCP4. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant-Downton, R.; Le Trionnaire, G.; Schmid, R.; Rodriguez-Enriquez, J.; Hafidh, S.; Mehdi, S.; Twell, D.; Dickinson, H. MicroRNA and tasiRNA diversity in mature pollen of Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder, C.D.; Smith, L.B.; Teakle, G.R.; King, G.J. Contrasting genome organisation: Two regions of the Brassica oleracea genome compared with collinear regions of the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Genome 2001, 44, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wu, J.; Liang, J.; Schnable, J.C.; Yang, W.; Cheng, F.; Wang, X. Impacts of whole-genome triplication on MIRNA evolution in Brassica rapa. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 3085–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Das, S. Synteny and comparative analysis of miRNA retention, conservation, and structure across Brassicaceae reveals lineage-and sub-genome-specifc changes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, X.; Song, Y.; Du, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D. Adaptive evolution and functional innovation of Populus-specific recently evolved microRNAs. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez Montes, R.A.; De Fátima Rosas-Cárdenas, F.; De Paoli, E.; Accerbi, M.; Rymarquis, L.A.; Mahalingam, G.; Marsch-Martínez, N.; Meyers, B.C.; Green, P.J.; De Folter, S. Sample sequencing of vascular plants demonstrates widespread conservation and divergence of microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.W.; Shen, X.P.; Xiang, X.; Cao, J. Evolution of MIR159/319 genes in Brassica campestris and their function in pollen development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Henriques, R.; Lin, S.S.; Niu, Q.W.; Chua, N.H. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, F.; Qiu, L.; Wang, F.; Cao, J.; Huang, L. BcMF8, a putative arabinogalactan protein-encoding gene, contributes to pollen wall development, aperture formation and pollen tube growth in Brassica campestris. Annu. Bot. 2014, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Cao, J.; Huang, L. Comparative transcriptome analysis and ChIP-sequencing reveals stagespecific gene expression and regulation profiles associated with pollen wall formation in Brassica rapa. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 264–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Lal, M.; Das, S. Comparative genomics reveals origin of MIR159A-MIR159B paralogy, and complexities of PTGS interaction between miR159 and target GA-MYBs in Brassicaceae. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2019, 294, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Chauhan, C.; Das, S. Microsynteny analysis to understand evolution and impact of polyploidization on MIR319 family within Brassicaceae. Dev. Genes. Evol. 2018, 228, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warthmann, N.; Das, S.; Lanz, C.; Weigel, D. Comparative analysis of the MIR319a microRNA locus in Arabidopsis and related Brassicaceae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challa, K.R.; Aggarwal, P.; Nath, U. Activation of YUCCA5 by the Transcription Factor TCP4 Integrates Developmental and Environmental Signals to Promote Hypocotyl Elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2016, 28, 2117–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, B.C.; Nath, U.; Carpenter, R.; Coen, E.S. CINCINNATA controls both cell differentiation and growth in petal lobes and leaves of Antirrhinum. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schommer, C.; Palatnik, J.F.; Aggarwal, P.; Chételat, A.; Cubas, P.; Farmer, E.E.; Nath, U.; Weigel, D. Control of jasmonate biosynthesis and senescence by miR319 targets. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, E.C.; Oinam, G.S.; Yeung, S.S.; Harry, I. Anther, pollen and tapetum development in safflower, Carthamus tinctorius L. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2011, 24, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drakakaki, G.; Zabotina, O.; Delgado, I.; Robert, S.; Keegstra, K.; Raikhel, N. Arabidopsis reversibly glycosylated polypeptides 1 and 2 are essential for pollen development. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Tan, Z.M.; Zhu, L.; Niu, Q.K.; Zhou, J.J.; Li, M.; Chen, L.Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ye, D. MYB97, MYB101 and MYB120 function as male factors that control pollen tube-synergid interaction in Arabidopsis thaliana fertilization. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Liu, T.; Cao, J. Functional Similarity and Difference among Bra-MIR319 Family in Plant Development. Genes 2019, 10, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120952
Hu Z, Liu T, Cao J. Functional Similarity and Difference among Bra-MIR319 Family in Plant Development. Genes. 2019; 10(12):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120952
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ziwei, Tingting Liu, and Jiashu Cao. 2019. "Functional Similarity and Difference among Bra-MIR319 Family in Plant Development" Genes 10, no. 12: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120952
APA StyleHu, Z., Liu, T., & Cao, J. (2019). Functional Similarity and Difference among Bra-MIR319 Family in Plant Development. Genes, 10(12), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10120952




