Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Disulfide Isomerase Shapes T Cell Efficacy for Adoptive Cellular Therapy of Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. T Cell and Tumor Cell Culture
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Redox State Determination of Ero1α and PDI
2.5. RNA Analysis
2.6. FACS Staining and Analysis
2.7. Metabolic Assays
2.8. T Cell Transfers and Tumor Model
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PDI Inhibition Promotes Viability in Healthy T Cells
3.2. IL-15 Primed T Cells Express Diminished Terminal UPR and Oxidative Stress
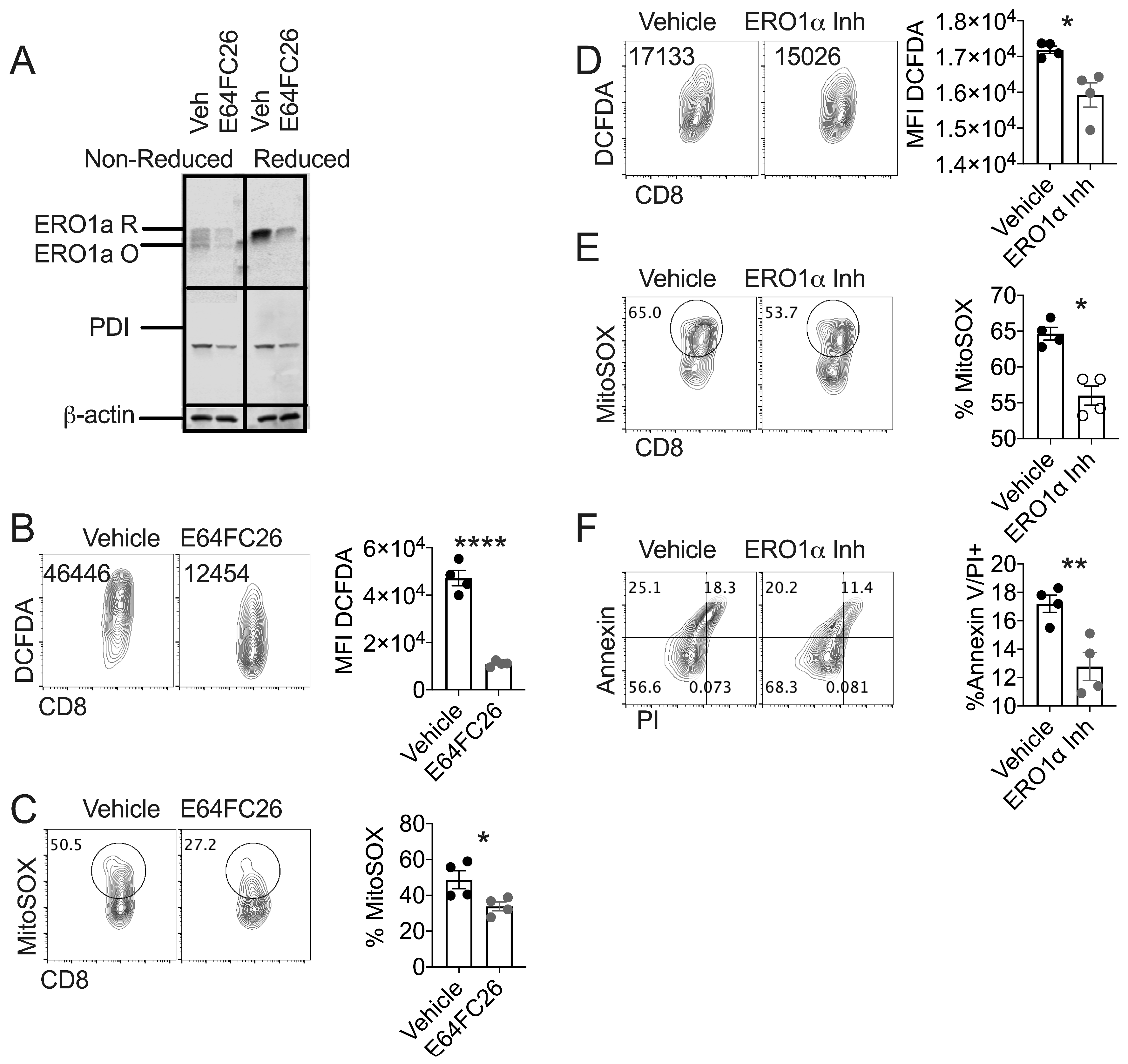
3.3. PDI Inhibition Diminishes Oxidative Stress in Healthy T Cells
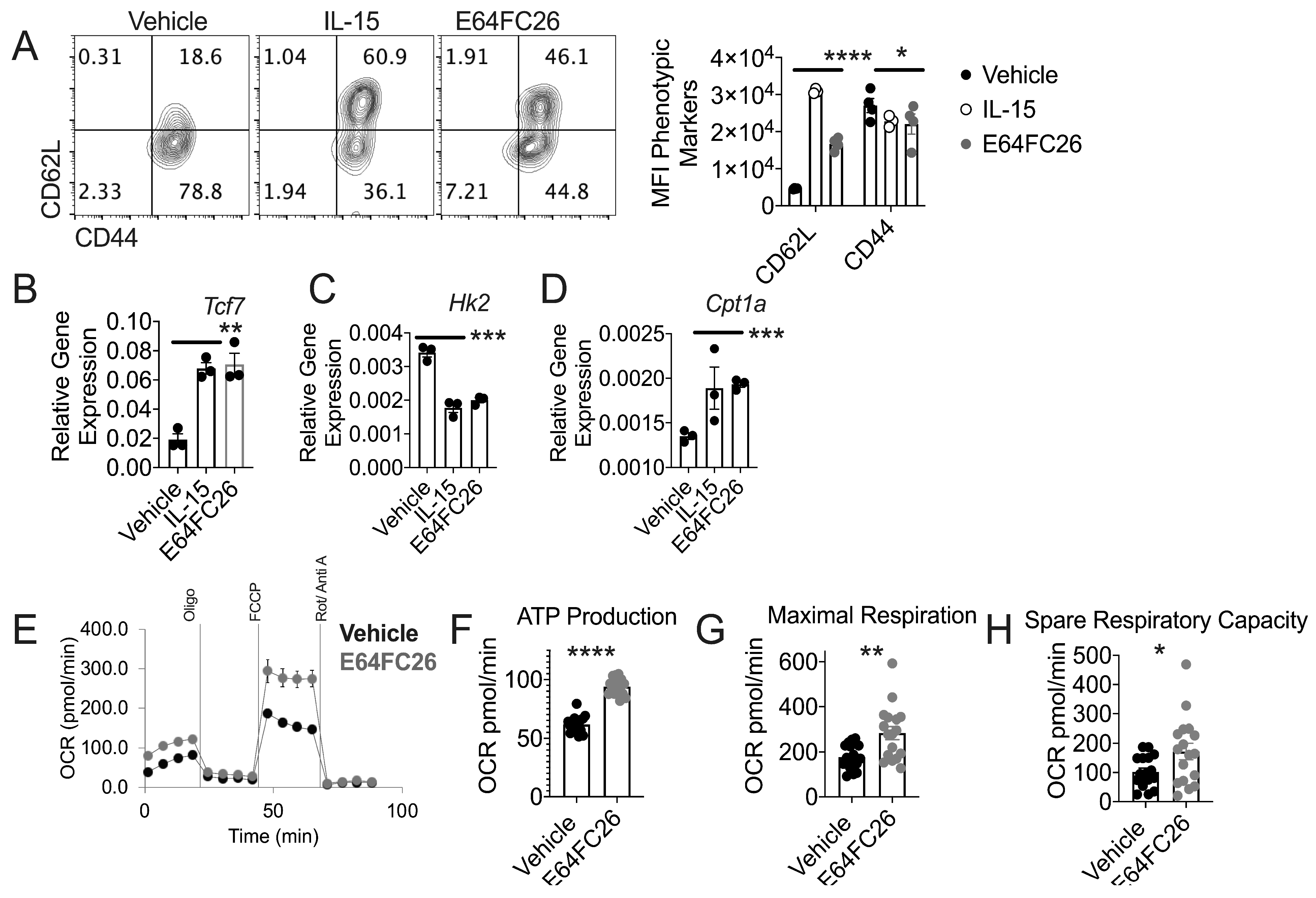
3.4. PDI Inhibition Promotes Traits Associated with T cell Tumor Control
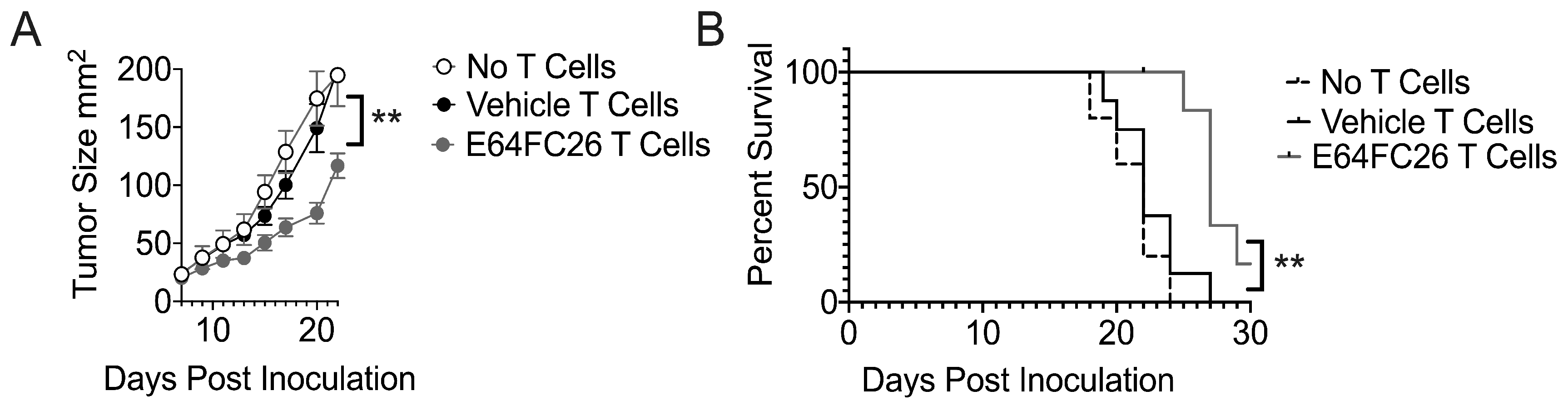
3.5. T Cells Treated with PDI Inhibition Promote Superior Tumor Control
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emens, L.A.; Middleton, G. The interplay of immunotherapy and chemotherapy: Harnessing potential synergies. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Hodi, F.S.; Kaufman, H.L.; Wigginton, J.M.; Wolchok, J.D. Combination immunotherapy: A road map. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urra, H.; Dufey, E.; Avril, T.; Chevet, E.; Hetz, C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the hallmarks of cancer. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, R.; Amaravadi, R.K. Targeting the unfolded protein response in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 120, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tameire, F.; Verginadis, I.I.; Leli, N.M.; Polte, C.; Conn, C.S.; Ojha, R.; Salas Salinas, C.; Chinga, F.; Monroy, A.M.; Fu, W.; et al. Atf4 couples myc-dependent translational activity to bioenergetic demands during tumour progression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, K.E.; Lawrence, K.A.; Essman, M.T.; Walton, Z.J.; Leddy, L.R.; Thaxton, J.E. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to mitochondrial exhaustion of cd8(+) t cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatolin, S.; Phillips, J.G.; Jha, B.K.; Govindgari, S.; Hu, J.; Grabowski, D.; Parker, Y.; Lindner, D.J.; Zhong, F.; Distelhorst, C.W.; et al. Novel protein disulfide isomerase inhibitor with anticancer activity in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3340–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.M.; Reyes, L.; Duncan, R.M.; Bian, H.; Reitz, A.B.; Manevich, Y.; McClure, J.J.; Champion, M.M.; Chou, C.J.; Sharik, M.E.; et al. Inhibitors of the protein disulfide isomerase family for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Moretti, A.I.; Martins Laurindo, F.R. Protein disulfide isomerases: Redox connections in and out of the endoplasmic reticulum. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 617, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurindo, F.R.; Pescatore, L.A.; Fernandes Dde, C. Protein disulfide isomerase in redox cell signaling and homeostasis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1954–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grek, C.; Townsend, D.M. Protein disulfide isomerase superfamily in disease and the regulation of apoptosis. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Dis. 2014, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Manevich, Y.; Tew, K.D.; Townsend, D.M. S-glutathionylation of protein disulfide isomerase regulates estrogen receptor alpha stability and function. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 273549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tew, K.D.; Townsend, D.M. Redox platforms in cancer drug discovery and development. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesarwani, P.; Al-Khami, A.A.; Scurti, G.; Thyagarajan, K.; Kaur, N.; Husain, S.; Fang, Q.; Naga, O.S.; Simms, P.; Beeson, G.; et al. Promoting thiol expression increases the durability of antitumor t-cell functions. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6036–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Kesarwani, P.; Thyagarajan, K.; Iamsawat, S.; Dalheim, A.; Nguyen, H.; Selvam, S.P.; Nasarre, P.; Scurti, G.; et al. Thioredoxin-1 improves the immunometabolic phenotype of antitumor t cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 9198–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaunay-Moisan, A.; Appenzeller-Herzog, C. The antioxidant machinery of the endoplasmic reticulum: Protection and signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 83, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, D.A.; Gannon, S.A.; Thorpe, C. Oxidative protein folding: From thiol-disulfide exchange reactions to the redox poise of the endoplasmic reticulum. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.M. S-glutathionylation: Indicator of cell stress and regulator of the unfolded protein response. Mol. Interv. 2007, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appenzeller-Herzog, C. Glutathione- and non-glutathione-based oxidant control in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Ron, D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaxton, J.E.; Wallace, C.; Riesenberg, B.; Zhang, Y.; Paulos, C.M.; Beeson, C.C.; Liu, B.; Li, Z. Modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress controls cd4(+) t-cell activation and antitumor function. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, K.; Morita, M.; Bederman, A.G.; Konieczny, B.T.; Kissick, H.T.; Sonenberg, N.; Ahmed, R. Translation is actively regulated during the differentiation of cd8(+) effector t cells. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Sankar, S.; Neamati, N. Protein disulfide isomerase: A promising target for cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Restifo, N.P. Pharmacologic induction of cd8+ t cell memory: Better living through chemistry. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 11ps12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restifo, N.P.; Gattinoni, L. Lineage relationship of effector and memory t cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berard, M.; Brandt, K.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Tough, D.F. Il-15 promotes the survival of naive and memory phenotype cd8+ t cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5018–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieri, N.; Camisa, B.; Cocchiarella, F.; Forcato, M.; Oliveira, G.; Provasi, E.; Bondanza, A.; Bordignon, C.; Peccatori, J.; Ciceri, F.; et al. Il-7 and il-15 instruct the generation of human memory stem t cells from naive precursors. Blood 2013, 121, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Back, S.H.; Hur, J.; Lin, Y.H.; Gildersleeve, R.; Shan, J.; Yuan, C.L.; Krokowski, D.; Wang, S.; Hatzoglou, M.; et al. Er-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bories, G.F.P.; Leitinger, N. Macrophage metabolism in atherosclerosis. Febs Lett. 2017, 591, 3042–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Novoa, I.; Lu, P.D.; Calfon, M.; Sadri, N.; Yun, C.; Popko, B.; Paules, R.; et al. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, E. Ero1: A protein disulfide oxidase and h2o2 producer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 83, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, J.D.; Chin, K.T.; Zito, E.; Zhang, Y.; Heldman, N.; Harding, H.P.; Fass, D.; Thorpe, C.; Ron, D. A small molecule inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum oxidation 1 (ero1) with selectively reversible thiol reactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20993–21003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Ji, Y.; Restifo, N.P. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in t-cell immunity and cancer immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res.: Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4695–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, I.; Schaeuble, K.; Chennupati, V.; Fuertes Marraco, S.A.; Calderon-Copete, S.; Pais Ferreira, D.; Carmona, S.J.; Scarpellino, L.; Gfeller, D.; Pradervand, S.; et al. Intratumoral tcf1(+)pd-1(+)cd8(+) t cells with stem-like properties promote tumor control in response to vaccination and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Immunity 2019, 50, 195–211.e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishton, R.J.; Sukumar, M.; Restifo, N.P. Metabolic regulation of t cell longevity and function in tumor immunotherapy. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, M.D.; Sowell, R.T.; Kaech, S.M.; Pearce, E.L. Metabolic instruction of immunity. Cell 2017, 169, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Qiu, J.; O’Sullivan, D.; Buck, M.D.; Noguchi, T.; Curtis, J.D.; Chen, Q.; Gindin, M.; Gubin, M.M.; van der Windt, G.J.; et al. Metabolic competition in the tumor microenvironment is a driver of cancer progression. Cell 2015, 162, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Windt, G.J.; Everts, B.; Chang, C.H.; Curtis, J.D.; Freitas, T.C.; Amiel, E.; Pearce, E.J.; Pearce, E.L. Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a critical regulator of cd8+ t cell memory development. Immunity 2012, 36, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Windt, G.J.; O’Sullivan, D.; Everts, B.; Huang, S.C.; Buck, M.D.; Curtis, J.D.; Chang, C.H.; Smith, A.M.; Ai, T.; Faubert, B.; et al. Cd8 memory t cells have a bioenergetic advantage that underlies their rapid recall ability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14336–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, S.J.; Abu-Elheiga, L.A. Fatty acid metabolism: Target for metabolic syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S138–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, C.J.; Knochelmann, H.M.; Smith, A.S.; Wyatt, M.M.; Rangel Rivera, G.O.; Arhontoulis, D.C.; Bartee, E.; Li, Z.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Paulos, C.M. Fueling cancer immunotherapy with common gamma chain cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurton, L.V.; Singh, H.; Najjar, A.M.; Switzer, K.C.; Mi, T.; Maiti, S.; Olivares, S.; Rabinovich, B.; Huls, H.; Forget, M.A.; et al. Tethered il-15 augments antitumor activity and promotes a stem-cell memory subset in tumor-specific t cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7788–E7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appenzeller-Herzog, C.; Riemer, J.; Zito, E.; Chin, K.T.; Ron, D.; Spiess, M.; Ellgaard, L. Disulphide production by ero1alpha-pdi relay is rapid and effectively regulated. Embo J. 2010, 29, 3318–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, S.J.; Yun, C.Y.; Oyadomari, S.; Novoa, I.; Zhang, Y.; Jungreis, R.; Nagata, K.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Chop induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 3066–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffel, M.J.; Scurti, G.; Simms, P.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Mehrotra, S.; Nishimura, M.I.; Voelkel-Johnson, C. Efficacy of adoptive t-cell therapy is improved by treatment with the antioxidant n-acetyl cysteine, which limits activation-induced t-cell death. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6006–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Grusdat, M.; Duncan, G.S.; Dostert, C.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; Cox, M.; Binsfeld, C.; Hao, Z.; Brustle, A.; Itsumi, M.; et al. Glutathione primes t cell metabolism for inflammation. Immunity 2017, 46, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Grusdat, M.; Duncan, G.S.; Dostert, C.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; Cox, M.; Binsfeld, C.; Hao, Z.; Brustle, A.; Itsumi, M.; et al. Glutathione primes t cell metabolism for inflammation. Immunity 2017, 46, 1089–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hurst, K.E.; Lawrence, K.A.; Reyes Angeles, L.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, J.; Townsend, D.M.; Dolloff, N.; Thaxton, J.E. Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Disulfide Isomerase Shapes T Cell Efficacy for Adoptive Cellular Therapy of Tumors. Cells 2019, 8, 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121514
Hurst KE, Lawrence KA, Reyes Angeles L, Ye Z, Zhang J, Townsend DM, Dolloff N, Thaxton JE. Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Disulfide Isomerase Shapes T Cell Efficacy for Adoptive Cellular Therapy of Tumors. Cells. 2019; 8(12):1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121514
Chicago/Turabian StyleHurst, Katie E., Kiley A. Lawrence, Lety Reyes Angeles, Zhiwei Ye, Jie Zhang, Danyelle M. Townsend, Nathan Dolloff, and Jessica E. Thaxton. 2019. "Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Disulfide Isomerase Shapes T Cell Efficacy for Adoptive Cellular Therapy of Tumors" Cells 8, no. 12: 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121514
APA StyleHurst, K. E., Lawrence, K. A., Reyes Angeles, L., Ye, Z., Zhang, J., Townsend, D. M., Dolloff, N., & Thaxton, J. E. (2019). Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein Disulfide Isomerase Shapes T Cell Efficacy for Adoptive Cellular Therapy of Tumors. Cells, 8(12), 1514. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121514





