The Influence of Interleukin 6 Knockout on Age-Related Degenerative Changes in the Cerebellar Cortex of Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Histology
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. TUNEL Method
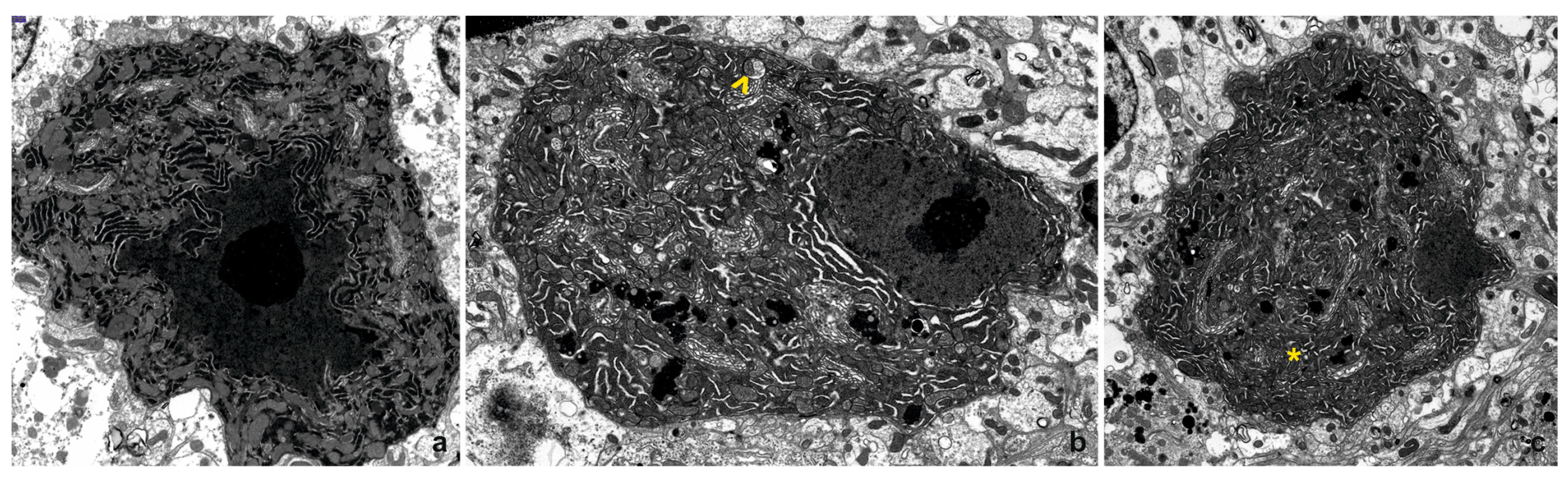
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of the Mouse Cerebellar Cortex
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
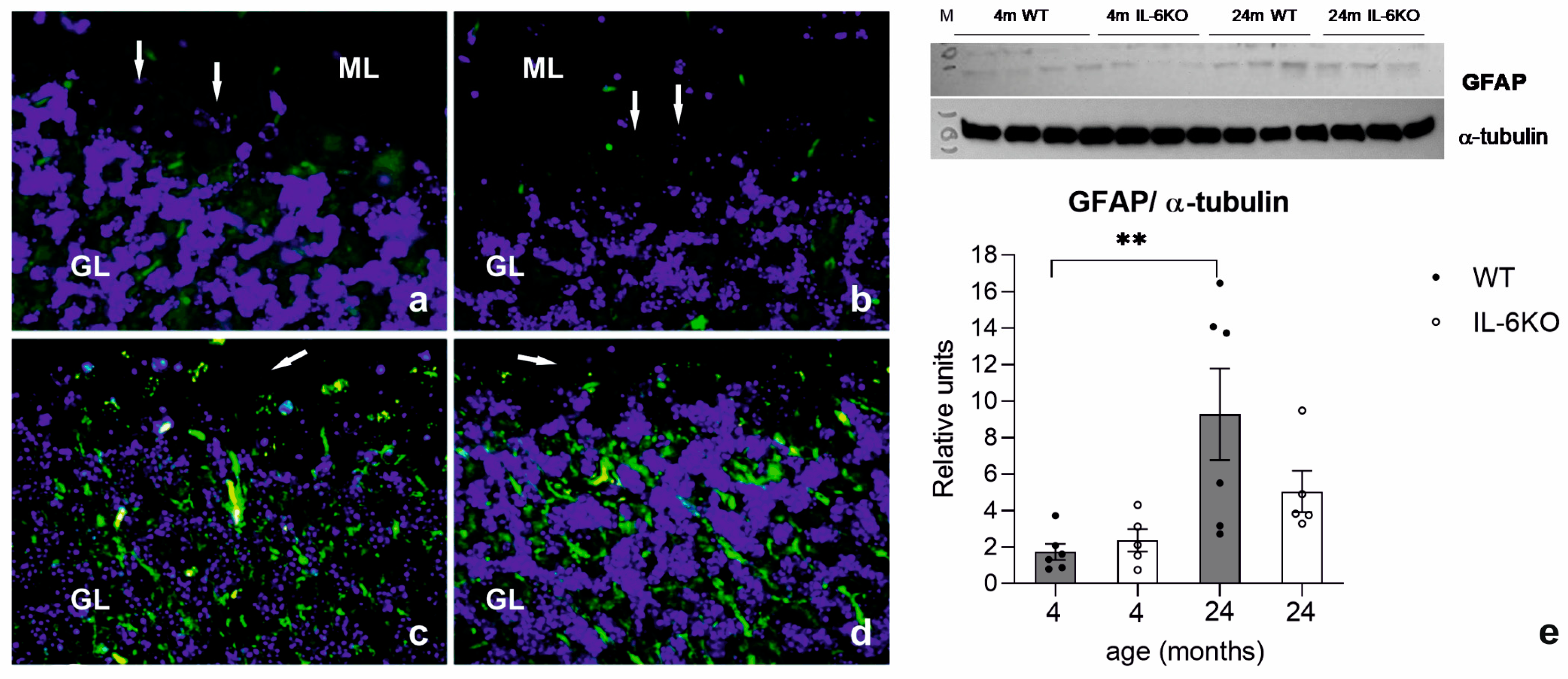
3.3. Expression of Glial Cell Response Marker GFAP
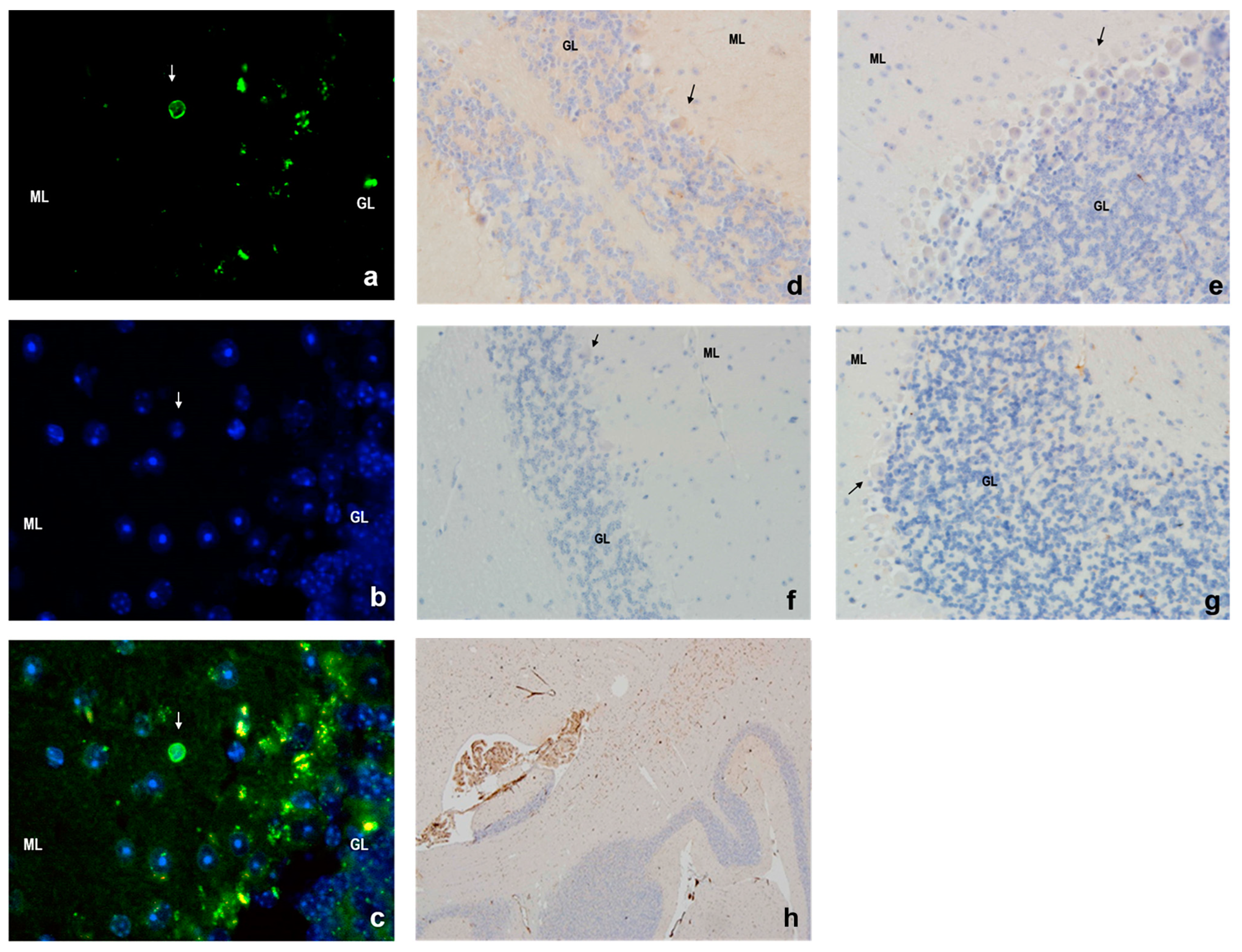
3.4. Apoptosis in Mouse Cerebellar Cortex
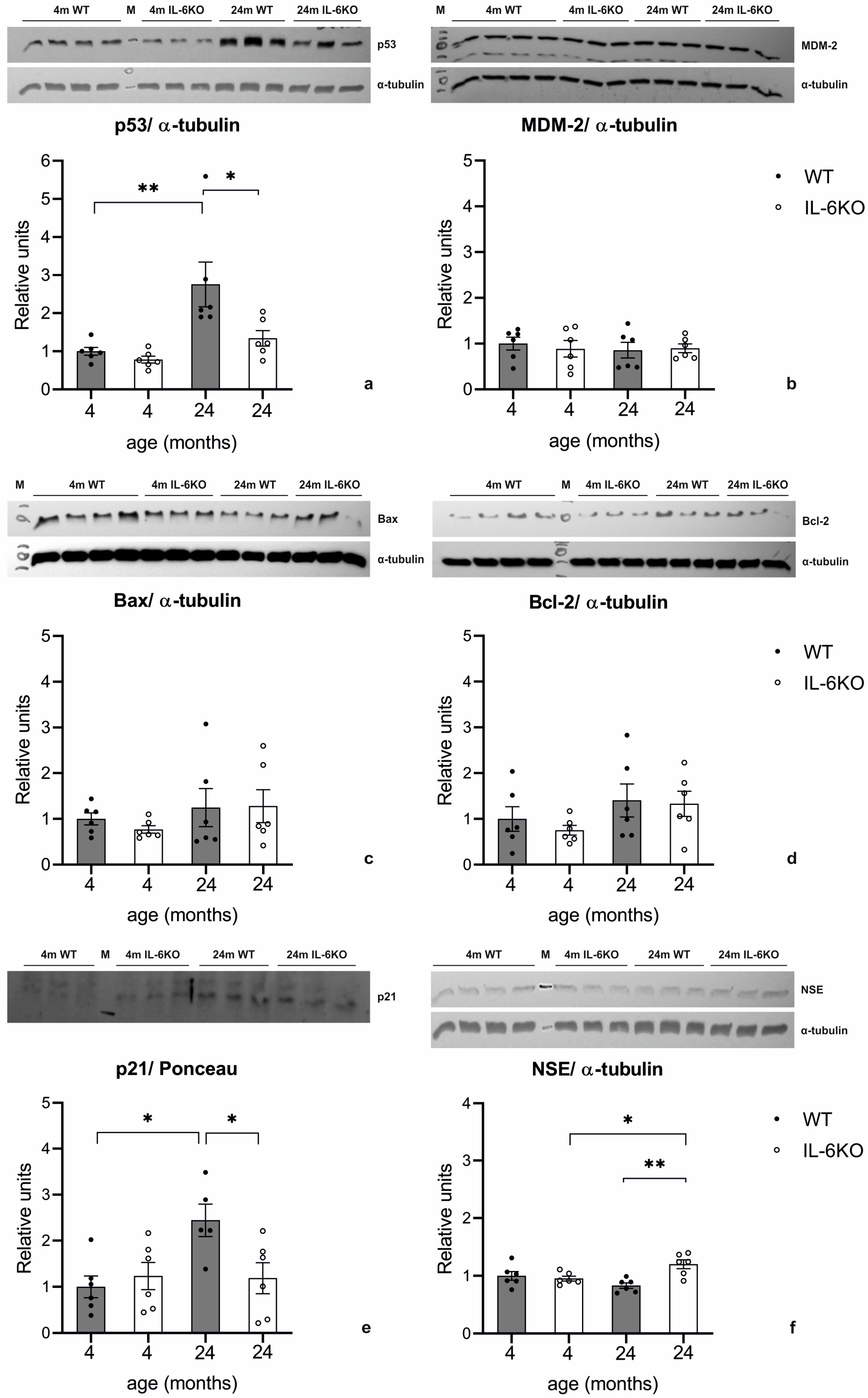
3.5. Expression of p53, MDM-2, Bax, Bcl-2, p21, and NSE in Mouse Cerebellar Cortex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DDR | DNA Damage Response |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein |
| GR | Granular Layer |
| H+E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| KO | Knockout |
| ML | Molecular Layer |
| NSE | Neuron-Specific Enolase |
| PC | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| RER | Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| RT | Room Temperature |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-marker Nick-End Labeling |
| WT | Wild-Type |
References
- Erta, M.; Quintana, A.; Hidalgo, J. Interleukin-6, a major cytokine in the central nervous system. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruol, D.L. IL-6 regulation of synaptic function in the CNS. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.K.; King, J.S. Localization of gp130 in the developing and adult mouse cerebellum. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2000, 19, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.E.; Campbell, I.L.; Gruol, D.L. Altered physiology of Purkinje neurons in cerebellar slices from transgenic mice with chronic central nervous system expression of interleukin-6. Neuroscience 1999, 89, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadient, R.A.; Otten, U. Expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) mRNAs in rat brain during postnatal development. Brain Res. 1994, 637, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVine, S.M.; Brown, D.C. IL-6 and TNFalpha expression in brains of twitcher, quaking and normal mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 73, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.L.; Hofer, M.J.; Pagenstecher, A. Transgenic models for cytokine-induced neurological disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahwiler, B.H.; Mamoon, A.M.; Tobias, C.A. Spontaneous bioelectric activity of cultured cerebellar Purkinje cells during exposure to agents which prevent synaptic transmission. Brain Res. 1973, 53, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinas, R.; Sugimori, M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J. Physiol. 1980, 305, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruol, D.L.; Nelson, T.E. Purkinje neuron physiology is altered by the inflammatory factor interleukin-6. Cerebellum 2005, 4, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershler, W.B. Interleukin-6: A cytokine for gerontologists. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1993, 41, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummer, K.K.; Zeidler, M.; Kalpachidou, T.; Kress, M. Role of IL-6 in the regulation of neuronal development, survival and function. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, F.A.; Carvalho, L.R.; Grinberg, L.T.; Farfel, J.M.; Ferretti, R.E.; Leite, R.E.; Jacob Filho, W.; Lent, R.; Herculano-Houzel, S. Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, M.J. The cerebellum in thought and action: A fronto-cerebellar aging hypothesis. New Ideas Psychol. 2004, 22, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilber, P.; Caston, J. Motor skills and motor learning in Lurcher mutant mice during aging. Neuroscience 2001, 102, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattay, V.S.; Fera, F.; Tessitore, A.; Hariri, A.R.; Das, S.; Callicott, J.H.; Weinberger, D.R. Neurophysiological correlates of age-related changes in human motor function. Neurology 2002, 58, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniwaki, T.; Okayama, A.; Yoshiura, T.; Togao, O.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamasaki, T.; Ogata, K.; Shigeto, H.; Ohyagi, Y.; Kira, J.; et al. Age-related alterations of the functional interactions within the basal ganglia and cerebellar motor loops in vivo. Neuroimage 2007, 36, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Pan, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, F.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Qin, C. Interleukin-6 deficiency reduces neuroinflammation by inhibiting the STAT3-cGAS-STING pathway in Alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Espinal, M.; Blasco-Agell, L.; Fernandez-Carasa, I.; Andres-Benito, P.; di Domenico, A.; Richaud-Patin, Y.; Baruffi, V.; Marruecos, L.; Espinosa, L.; Garrido, A.; et al. Blocking IL-6 signaling prevents astrocyte-induced neurodegeneration in an iPSC-based model of Parkinson’s disease. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e163359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, R.; Gamage, R.; Munch, G.; Gyengesi, E. The effect of aging and chronic microglia activation on the morphology and numbers of the cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 751, 135807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrina, M.L.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocytes in the aging brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccia, A.; Elledge, S.J. The DNA damage response: Making it safe to play with knives. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, J.P.; Gu, W. Modes of p53 regulation. Cell 2009, 137, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korwek, Z.; Alster, O. The role of the DNA damage response in apoptosis and cell senescence. Postep. Biochem. 2014, 60, 248–262. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, W. The complexity of p53-mediated metabolic regulation in tumor suppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 4–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonda, T.A.; Taranta, A.; Kaminski, K.A.; Dziemidowicz, M.; Litvinovich, S.; Kozuch, M.; Bialuk, I.; Chyczewski, L.; Winnicka, M.M. CCN1 expression in interleukin-6 deficient mouse kidney in experimental model of heart failure. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2013, 51, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, R.; Ikari, K.; Hayashi, M.; Tamai, K.; Tagawa, K. Age-related changes in the Purkinje’s cells in the rat cerebellar cortex: A quantitative electron microscopic study. Folia Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn. 1984, 38, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.B.; Gundersen, H.J.; Pakkenberg, B. Aging of the human cerebellum: A stereological study. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 466, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.A.; Henrique, R.M.; Rocha, E.; Marini-Abreu, M.M.; Oliveira, M.H.; Silva, M.W. Age-related changes in the volume of somata and organelles of cerebellar granule cells. Neurobiol. Aging 1998, 19, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattoretti, P.; Bertoni-Freddari, C.; Caselli, U.; Paoloni, R.; Meier-Ruge, W. Morphologic changes in cerebellar mitochondria during aging. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 1996, 18, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ojaimi, J.; Masters, C.L.; Opeskin, K.; McKelvie, P.; Byrne, E. Mitochondrial respiratory chain activity in the human brain as a function of age. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1999, 111, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamna, H. Heme, iron, and the mitochondrial decay of ageing. Ageing Res. Rev. 2004, 3, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidadavolu, L.S.; Cosarderelioglu, C.; Merino Gomez, A.; Wu, Y.; Bopp, T.; Zhang, C.; Nguyen, T.; Marx-Rattner, R.; Yang, H.; Antonescu, C.; et al. Interleukin-6 Drives Mitochondrial Dysregulation and Accelerates Physical Decline: Insights from an Inducible Humanized IL-6 Knock-In Mouse Model. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2023, 78, 1740–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, A.; Lopez-Lengowski, K.; Roffman, J.L.; Karmacharya, R. Distinct effects of interleukin-6 and interferon-gamma on differentiating human cortical neurons. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 103, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.A.; Henrique, R.M.; Rocha, E.; Silva, M.W.; Oliveira, M.H. Quantitative age-changes in endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus of cerebellar granule cells. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlugos, C.A. Analyses of smooth endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellar parallel fibers in aging, ethanol-fed rats. Alcohol 2005, 35, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.A.; Rocha, E.; Marini-Abreu, M.M. Heterogeneity and death of Purkinje cells of rat neocerebellum (Crus I and Crus II): Hypothetic mechanisms based on qualitative and quantitative microscopical data. J. Hirnforsch. 1994, 35, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Hua, T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, X. Age-related changes of structures in cerebellar cortex of cat. J. Biosci. 2006, 31, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.M.; Murphy, K.J.; Deighan, B.F.; O’Reilly, J.A.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; Cowley, T.R.; Gonzalez-Reyes, R.E.; Lynch, M.A. The impact of glial activation in the aging brain. Aging Dis. 2010, 1, 262–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bialuk, I.; Cieslinska, M.; Kowalczuk, O.; Bonda, T.A.; Niklinski, J.; Winnicka, M.M. IL-6 deficiency attenuates p53 protein accumulation in aged male mouse hippocampus. Biogerontology 2020, 21, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Morgan, J.I.; Pecot, M.; Soumare, A.; Osborne, A.; Soares, H.D. Regenerating motor neurons express Nna1, a novel ATP/GTP-binding protein related to zinc carboxypeptidases. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyuhou, S.; Kato, N.; Gemba, H. Emergence of endoplasmic reticulum stress and activated microglia in Purkinje cell degeneration mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 396, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Morgan, J.I. The Purkinje cell degeneration (pcd) mouse: An unexpected molecular link between neuronal degeneration and regeneration. Brain Res. 2007, 1140, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, L.; Neal, J.T.; Miles, M.; Martinez, R.A.; Smith, A.C.; Sopher, B.L.; La Spada, A.R. The Purkinje cell degeneration 5J mutation is a single amino acid insertion that destabilizes Nna1 protein. Mamm. Genome 2006, 17, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Horton, A.; Bravin, M.; DeJager, P.L.; Selimi, F.; Heintz, N. A novel protein complex linking the delta 2 glutamate receptor and autophagy: Implications for neurodegeneration in lurcher mice. Neuron 2002, 35, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, C.T. To die or not to die: DNA repair in neurons. Mutat. Res. 2005, 577, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laposa, R.R.; Huang, E.J.; Cleaver, J.E. Increased apoptosis, p53 up-regulation, and cerebellar neuronal degeneration in repair-deficient Cockayne syndrome mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurk, D.; Wang, C.; Miwa, S.; Maddick, M.; Korolchuk, V.; Tsolou, A.; Gonos, E.S.; Thrasivoulou, C.; Saffrey, M.J.; Cameron, K.; et al. Postmitotic neurons develop a p21-dependent senescence-like phenotype driven by a DNA damage response. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawge, G.; Khatik, G.L. p53 regulated senescence mechanism and role of its modulators in age-related disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 190, 114651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Uechi, T.; Kenmochi, N. Guarding the ’translation apparatus’: Defective ribosome biogenesis and the p53 signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 2, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cieślińska, M.W.; Bialuk, I.; Dziemidowicz, M.; Szynaka, B.; Reszeć-Giełażyn, J.; Winnicka, M.M.; Bonda, T.A. The Influence of Interleukin 6 Knockout on Age-Related Degenerative Changes in the Cerebellar Cortex of Mice. Cells 2025, 14, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070532
Cieślińska MW, Bialuk I, Dziemidowicz M, Szynaka B, Reszeć-Giełażyn J, Winnicka MM, Bonda TA. The Influence of Interleukin 6 Knockout on Age-Related Degenerative Changes in the Cerebellar Cortex of Mice. Cells. 2025; 14(7):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070532
Chicago/Turabian StyleCieślińska, Magdalena Wiktoria, Izabela Bialuk, Magdalena Dziemidowicz, Beata Szynaka, Joanna Reszeć-Giełażyn, Maria Małgorzata Winnicka, and Tomasz Andrzej Bonda. 2025. "The Influence of Interleukin 6 Knockout on Age-Related Degenerative Changes in the Cerebellar Cortex of Mice" Cells 14, no. 7: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070532
APA StyleCieślińska, M. W., Bialuk, I., Dziemidowicz, M., Szynaka, B., Reszeć-Giełażyn, J., Winnicka, M. M., & Bonda, T. A. (2025). The Influence of Interleukin 6 Knockout on Age-Related Degenerative Changes in the Cerebellar Cortex of Mice. Cells, 14(7), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070532





