Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Mechanisms and Recent Implications in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
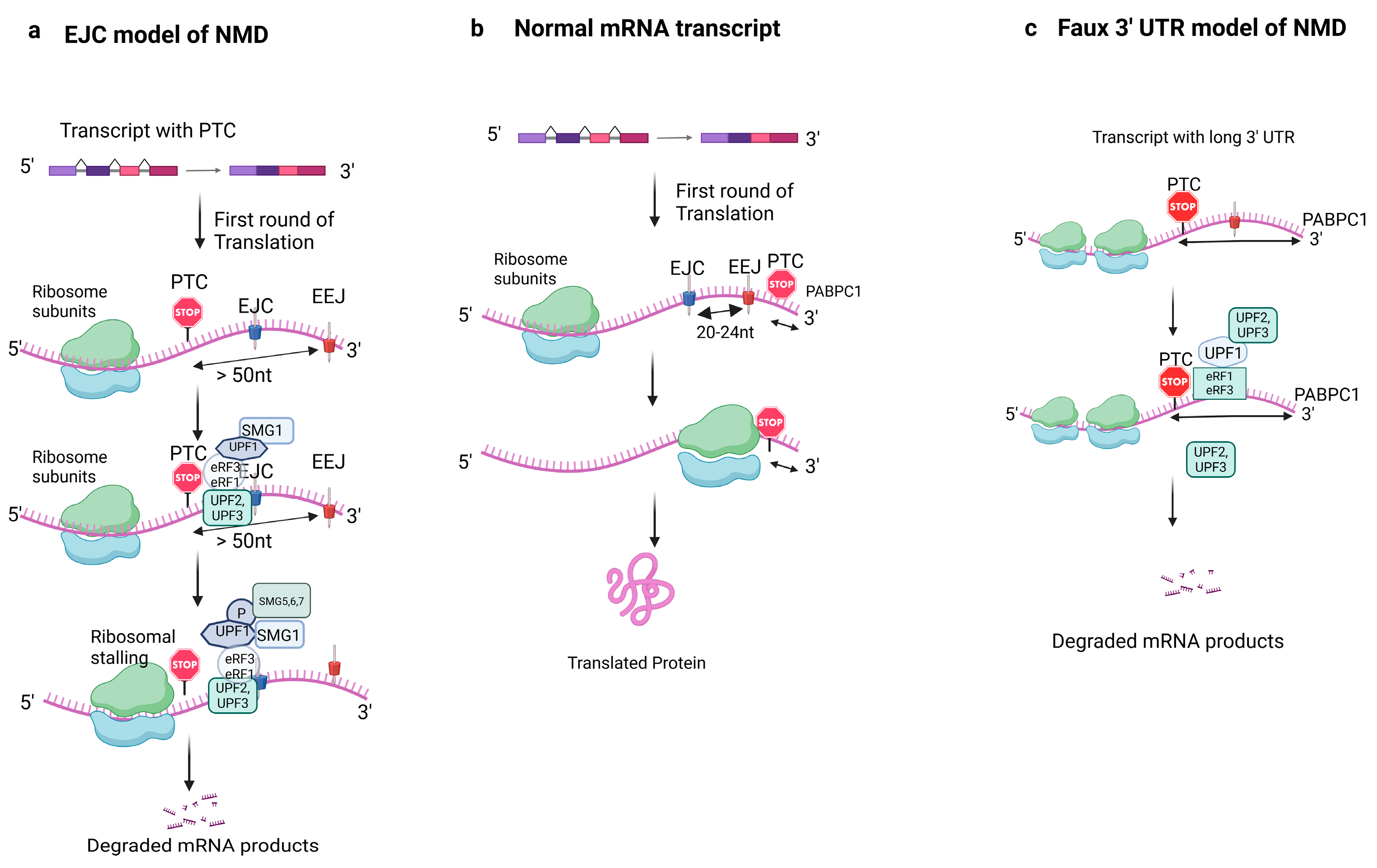
2. Mechanism of NMD and Key Players
2.1. Alternative NMD Mechanisms
2.2. Other Unclear Mechanisms of NMD
3. NMD in Physiological Processes
3.1. NMD and Regulation of Gene Expression
3.2. NMD and Development and Differentiation
3.3. NMD and Apoptosis
3.4. NMD and Autophagy
4. NMD Escape Mechanism
4.1. NMD Escape in Tumor Cells
4.2. NMD Escape and Its Role in Immunity
5. Inhibition of Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay
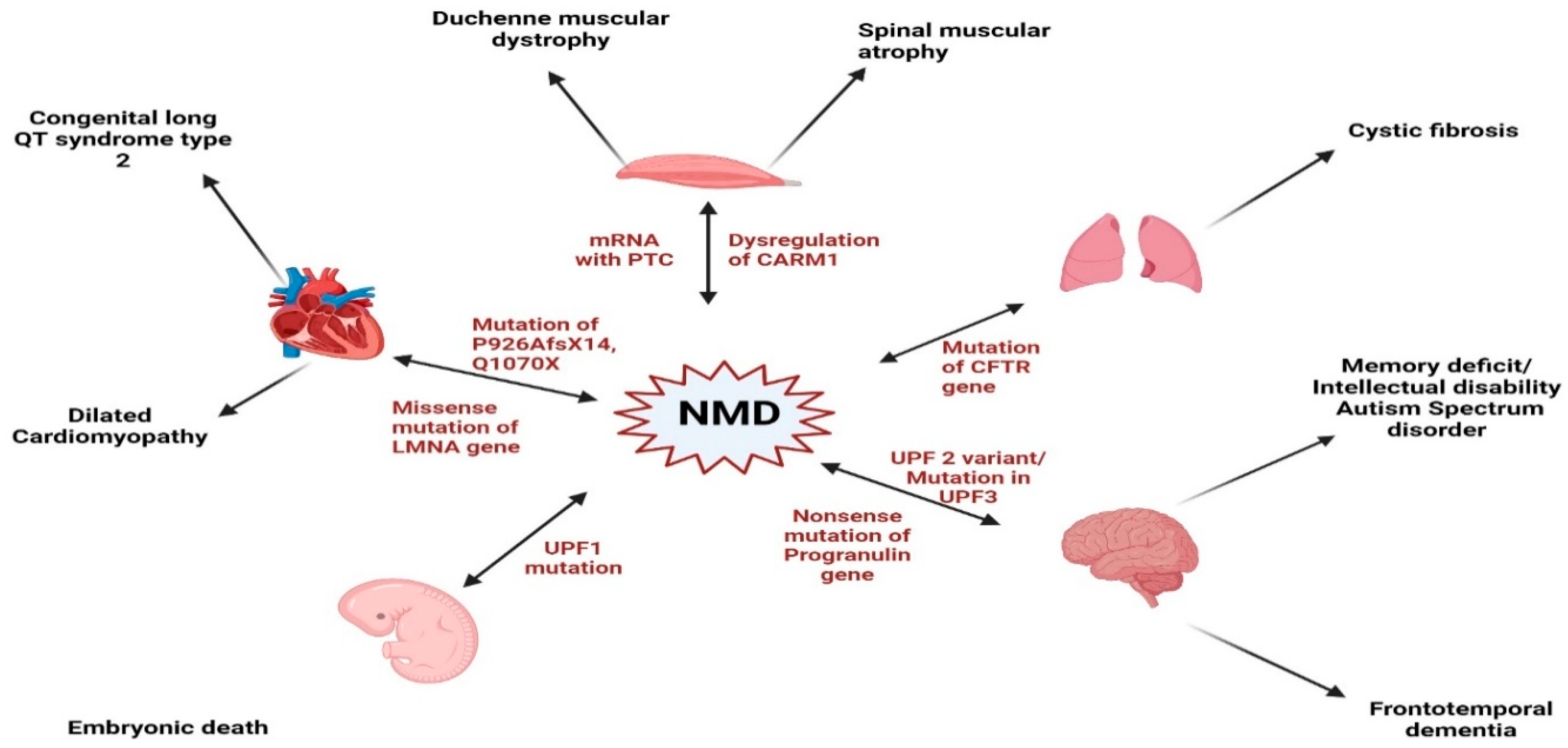
6. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay in Cardiovascular Disease Conditions
6.1. Cardiac Conduction Disease
6.2. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
6.3. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
7. Potentials of NMD in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease
8. Cross-Disease Insights into NMD: Implications for Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brogna, S.; Wen, J. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) mechanisms. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, L.; Schlossarek, S.; Willis, M.S.; Eschenhagen, T. The ubiquitin-proteasome system and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kervestin, S.; Jacobson, A. NMD: A multifaceted response to premature translational termination. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Jacobson, A. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Degradation of Defective Transcripts Is Only Part of the Story. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 339–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweingruber, C.; Rufener, S.C.; Zünd, D.; Yamashita, A.; Mühlemann, O. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay—Mechanisms of substrate mRNA recognition and degradation in mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2013, 1829, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, T.; Maquat, L.E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in humans at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Pearce, D.A. Nonsense-mediated decay in genetic disease: Friend or foe? Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2014, 762, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Qian, Y.; LaDuca, J.P.; Maquat, L.E. At least one intron is required for the nonsense-mediated decay of triosephosphate isomerase mRNA: A possible link between nuclear splicing and cytoplasmic translation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 5272–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Maquat, L.E. mRNA surveillance in mammalian cells: The relationship between introns and translation termination. RNA 2000, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hir, H.; Izaurralde, E.; Maquat, L.E.; Moore, M.J. The spliceosome deposits multiple proteins 20–24 nucleotides upstream of mRNA exon-exon junctions. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6860–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Singer, R.H. Cellular variability of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrani, N.; Ganesan, R.; Kervestin, S.; Mangus, D.A.; Ghosh, S.; Jacobson, A. A faux 3′-UTR promotes aberrant termination and triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature 2004, 432, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, F. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay at the crossroads of many cellular pathways. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, L. Making Sense of Inhibiting Nonsense in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2019, 139, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashima, I.; Yamashita, A.; Izumi, N.; Kataoka, N.; Morishita, R.; Hoshino, S.; Ohno, M.; Dreyfuss, G.; Ohno, S. Binding of a novel SMG-1-Upf1-eRF1-eRF3 complex (SURF) to the exon junction complex triggers Upf1 phosphorylation and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, T.; Yamashita, A.; Kashima, I.; Schell, T.; Anders, K.R.; Grimson, A.; Hachiya, T.; Hentze, M.W.; Anderson, P.; Ohno, S. Phosphorylation of hUPF1 induces formation of mRNA surveillance complexes containing hSMG-5 and hSMG-7. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, N.; Longman, D.; Cáceres, J.F. Mechanism and regulation of the nonsense-mediated decay pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, F. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay, a Finely Regulated Mechanism. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervestin, S.; Li, C.; Buckingham, R.; Jacobson, A. Testing the faux-UTR model for NMD: Analysis of Upf1p and Pab1p competition for binding to eRF3/Sup35p. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, Â.; Silva, A.L.; Pinto, J.; Ji, X.; Morgado, A.; Almeida, F.; Faustino, P.; Lavinha, J.; Liebhaber, S.A.; Romão, L. Nonsense Mutations in Close Proximity to the Initiation Codon Fail to Trigger Full Nonsense-mediated mRNA Decay. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32170–32180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, B.; Azzalin, C.M.; Hug, N.; Deplazes, A.; Peter, M.; Lingner, J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ebs1p is a putative ortholog of human Smg7 and promotes nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7688–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, J.P.B. The evolution and diversity of the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Brogna, S. Splicing-dependent NMD does not require the EJC in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.J.; Jacobson, A. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay maintains translational fidelity by limiting magnesium uptake. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1491–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Karousis, E.D.; Bourquin, J.; Bruggmann, R.; Mühlemann, O. Transcriptome-wide identification of NMD-targeted human mRNAs reveals extensive redundancy between SMG6- and SMG7-mediated degradation pathways. RNA 2017, 23, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mort, M.; Ivanov, D.; Cooper, D.N.; Chuzhanova, N.A. A meta-analysis of nonsense mutations causing human genetic disease. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickless, A.; Bailis, J.M.; You, Z. Control of gene expression through the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.T.; Sandberg, R.; Luo, S.; Khrebtukova, I.; Zhang, L.; Mayr, C.; Kingsmore, S.F.; Schroth, G.P.; Burge, C.B. Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 2008, 456, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weischenfeldt, J.; Waage, J.; Tian, G.; Zhao, J.; Damgaard, I.; Jakobsen, J.S.; Kristiansen, K.; Krogh, A.; Wang, J.; Porse, B.T. Mammalian tissues defective in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay display highly aberrant splicing patterns. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderlin, E.J.; Keenan, M.M.; Mense, M.; Revenko, A.S.; Monia, B.P.; Guo, S.; Huang, L. CFTR mRNAs with nonsense codons are degraded by the SMG6-mediated endonucleolytic decay pathway. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu-Yilik, G.; Amthor, B.; Gehring, N.H.; Bahri, S.; Paidassi, H.; Hentze, M.W.; Kulozik, A.E. Mechanism of escape from nonsense-mediated mRNA decay of human beta-globin transcripts with nonsense mutations in the first exon. RNA 2011, 17, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Moreno, J.F.; Romão, L. Perspective in Alternative Splicing Coupled to Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkopp, N.; Huntzinger, E.; Weiler, C.; Saulière, J.; Schmidt, S.; Sonawane, M.; Izaurralde, E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay effectors are essential for zebrafish embryonic development and survival. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3517–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shum, E.Y.; Jones, S.H.; Shao, A.; Chousal, J.N.; Krause, M.D.; Chan, W.K.; Lou, C.H.; Espinoza, J.L.; Song, H.W.; Phan, M.H.; et al. The Antagonistic Gene Paralogs Upf3a and Upf3b Govern Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay. Cell 2016, 165, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Pan, Q.; Reilly, P.T.; Elia, A.J.; McCracken, S.; Wakeham, A.C.; Itie-Youten, A.; Blencowe, B.J.; Mak, T.W. Smg1 is required for embryogenesis and regulates diverse genes via alternative splicing coupled to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12186–12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Shi, Y.; Wang, P.; Guachalla, L.M.; Sun, B.; Joerss, T.; Chen, Y.S.; Groth, M.; Krueger, A.; Platzer, M.; et al. Smg6/Est1 licenses embryonic stem cell differentiation via nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 1630–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, L.A.; Homan, C.C.; Jacob, R.; Barry, S.; Gecz, J. The UPF3B gene, implicated in intellectual disability, autism, ADHD and childhood onset schizophrenia regulates neural progenitor cell behaviour and neuronal outgrowth. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 4673–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.H.; Shao, A.; Shum, E.Y.; Espinoza, J.L.; Huang, L.; Karam, R.; Wilkinson, M.F. Posttranscriptional control of the stem cell and neurogenic programs by the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Kim, Y.K.; Woeller, C.F.; Tang, Y.; Maquat, L.E. SMD and NMD are competitive pathways that contribute to myogenesis: Effects on PAX3 and myogenin mRNAs. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatscher, T.; Boehm, V.; Gehring, N.H. Mechanism, factors, and physiological role of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 4523–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Furlan, A.; Gonzalez-Hilarion, S.; Leroy, C.; Gruenert, D.C.; Tulasne, D.; Lejeune, F. Caspases shutdown nonsense-mediated mRNA decay during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, M.W.; Maquat, L.E. The dharma of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in mammalian cells. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masse, I.; Molin, L.; Mouchiroud, L.; Vanhems, P.; Palladino, F.; Billaud, M.; Solari, F. A novel role for the SMG-1 kinase in lifespan and oxidative stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.; Romanow, W.J.; Geisen, C.; Otterness, D.M.; Mercurio, F.; Wang, H.G.; Dalton, W.S.; Abraham, R.T. A protective role for the human SMG-1 kinase against tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13174–13184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, R.; Lou, C.H.; Kroeger, H.; Huang, L.; Lin, J.H.; Wilkinson, M.F. The unfolded protein response is shaped by the NMD pathway. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, A.E.; Wilkinson, M. Stress and the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3509–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, M.W.; Maquat, L.E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA Decay and Cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 48, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zavadil, J.; Martin, L.; Parisi, F.; Friedman, E.; Levy, D.; Harding, H.; Ron, D.; Gardner, L.B. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated RNA decay by the tumor microenvironment promotes tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 3670–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Jeong, H.; Yu, S.-W. Autophagy as a decisive process for cell death. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlicka, K.; Kalathiya, U.; Alfaro, J. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Pathologies and the Potential for Novel Therapeutics. Cancers 2020, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengrod, J.; Martin, L.; Wang, D.; Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, P.; Dietz, H.C.; Gardner, L.B. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated RNA decay activates autophagy. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, K.; Yoshina, S.; Shen, X.; Han, J.; DeSantis, M.R.; Xiong, M.; Mitani, S.; Kaufman, R.J. RNA surveillance is required for endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8079–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyle, M.C.; Kolakada, D.; Cortazar, M.A.; Jagannathan, S. How to get away with nonsense: Mechanisms and consequences of escape from nonsense-mediated RNA decay. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2020, 11, e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasif, S.; Contu, L.; Mühlemann, O. Beyond quality control: The role of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) in regulating gene expression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 75, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasif, S.; Colombo, M.; Uldry, A.-C.; Schröder Markus, S.; de Brot, S.; Mühlemann, O. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay reduces the tumorigenicity of human fibrosarcoma cells. NAR Cancer 2023, 5, zcad048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, K.; Reading, J.L.; Lim, E.L.; Xu, H.; Liu, P.; Al-Bakir, M.; Wong, Y.N.S.; Rowan, A.; Funt, S.A.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Escape from nonsense-mediated decay associates with anti-tumor immunogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.D.; Burns, B.A.; Vandeventer, P.J.; Luna, P.N.; Shaw, C.A. Selection for or against escape from nonsense mediated decay is a novel signature for the detection of cancer genes. Cancer Genet. 2021, 258–259, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, A.d.; Jonchere, V.; Lagrange, A.; Bertrand, R.; Svrcek, M.; Marisa, L.; Buhard, O.; Greene, M.; Demidova, A.; Jia, J.; et al. Targeting nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiorno, R.; Colombo, M.P.; Lecis, D. Deciphering the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway to identify cancer cell vulnerabilities for effective cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, A.J.; Guna, A.; Galvez-Merchan, A.; Pal, A.; Esantsi, T.K.; Keys, H.R.; Frenkel, E.M.; Oania, R.; Weissman, J.S.; Voorhees, R.M. Coupled protein quality control during nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. J. Cell Sci. 2023, 136, jcs261216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeboom, R.G.H.; Vermeulen, M.; Lehner, B.; Supek, F. The impact of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay on genetic disease, gene editing and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehwinkel, J.; Raes, J.; Izaurralde, E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Target genes and functional diversification of effectors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2006, 31, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuki, F.; Yamashita, A.; Kashima, I.; Higuchi, I.; Osame, M.; Ohno, S. Specific inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay components, SMG-1 or Upf1, rescues the phenotype of Ullrich disease fibroblasts. Mol. Ther. 2006, 14, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, R.; Wilkinson, M. A conserved microRNA/NMD regulatory circuit controls gene expression. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, I.G.; Karam, R.; Huang, L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Lou, C.H.; Shum, E.Y.; Song, H.W.; Corbett, M.A.; Gifford, W.D.; Gecz, J.; et al. Identification of a microRNA that activates gene expression by repressing nonsense-mediated RNA decay. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, R.; Wengrod, J.; Gardner, L.B.; Wilkinson, M.F. Regulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Implications for physiology and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2013, 1829, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zong, R.; Wu, J.; Ren, Z. MicroRNA 4651 regulates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by targeting SMG9 mRNA. Gene 2019, 701, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z.; Ren, Z. MicroRNA 433 regulates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by targeting SMG5 mRNA. BMC Mol. Biol. 2016, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvanagiri, M.; Lewis, J.; Putzker, K.; Becker, J.P.; Leicht, S.; Krijgsveld, J.; Batra, R.; Turnwald, B.; Jovanovic, B.; Hauer, C.; et al. 5-azacytidine inhibits nonsense-mediated decay in a MYC-dependent fashion. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1593–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Su, R.C.; Zou, L.; Triggs-Raine, B.; Huang, S.; Xie, J. Increase of a group of PTC(+) transcripts by curcumin through inhibition of the NMD pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2015, 1849, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.; Katz, R.A.; Merkel, G.; Hittle, J.C.; Yen, T.J.; Skalka, A.M. Wortmannin potentiates integrase-mediated killing of lymphocytes and reduces the efficiency of stable transduction by retroviruses. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Yang, X.; Southwood, M.; Moore, S.; Crosby, A.; Upton, P.D.; Dunmore, B.J.; Morrell, N.W. Targeting translational read-through of premature termination mutations in BMPR2 with PTC124 for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Furic, L.; Desgroseillers, L.; Maquat, L.E. Mammalian Staufen1 recruits Upf1 to specific mRNA 3′UTRs so as to elicit mRNA decay. Cell 2005, 120, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kim, K.M.; Han, S.; Choe, J.; Park, S.G.; Choi, S.S.; Kim, Y.K. Staufen1-mediated mRNA decay functions in adipogenesis. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.Y.; Agrawal, I.; Tyan, S.H.; Sanford, E.; Chang, W.T.; Lim, K.; Ong, J.; Tan, B.S.Y.; Moe, A.A.K.; Yu, R.; et al. Dysfunction in nonsense-mediated decay, protein homeostasis, mitochondrial function, and brain connectivity in ALS-FUS mice with cognitive deficits. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, A.K.; Panigrahi, G.K.; Majumder, S.; Das, R.; Sahoo, A. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Physiological significance, mechanistic insights and future implications. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2024, 264, 155677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, R.; Anazi, S.; Ben-Omran, T.; Seidahmed, M.Z.; Caddle, L.B.; Palmer, K.; Ali, R.; Alshidi, T.; Hagos, S.; Goodwin, L.; et al. Mutations in SMG9, Encoding an Essential Component of Nonsense-Mediated Decay Machinery, Cause a Multiple Congenital Anomaly Syndrome in Humans and Mice. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 98, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuniga, G.; Levy, S.; Ramirez, P.; De Mange, J.; Gonzalez, E.; Gamez, M.; Frost, B. Tau-induced deficits in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay contribute to neurodegeneration. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Stupack, D.G.; Wilkinson, M.F. Nonsense-mediated RNA decay: An emerging modulator of malignancy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belew, A.T.; Meskauskas, A.; Musalgaonkar, S.; Advani, V.M.; Sulima, S.O.; Kasprzak, W.K.; Shapiro, B.A.; Dinman, J.D. Ribosomal frameshifting in the CCR5 mRNA is regulated by miRNAs and the NMD pathway. Nature 2014, 512, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Ohno, S.; Sonoda, K.; Fukuyama, M.; Makiyama, T.; Ozawa, T.; Horie, M. LMNA Missense Mutation Causes Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay and Severe Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkart, V.; Kowalski, K.; Disch, A.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; Lal, S.; Dos Remedios, C.; Perrot, A.; Zeug, A.; Ponimaskin, E.; Kosanke, M.; et al. Nonsense mediated decay factor UPF3B is associated with cMyBP-C haploinsufficiency in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2023, 185, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, C.; Zheng, S.; Yan, L.; Hedges, L.; Womack, B.; Fessel, J.; Cogan, J.; Austin, E.; Loyd, J.; West, J.; et al. Connectivity map analysis of nonsense-mediated decay-positive BMPR2-related hereditary pulmonary arterial hypertension provides insights into disease penetrance. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Ye, J.; Xu, R.X.; Shi, N.; Meng, X.M. TNNI3K is a novel mediator of myofilament function and phosphorylates cardiac troponin I. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Wu, K.; Liu, N.; Zhao, C.; Shi, X.; Liu, Q. Identification of a nonsense mutation in TNNI3K associated with cardiac conduction disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.T.; Sharifi, N.A.; Meyers, J.L.; Martinez-Murillo, F.; Dietz, H.C. Nonsense surveillance regulates expression of diverse classes of mammalian transcripts and mutes genomic noise. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignier, N.; Schlossarek, S.; Fraysse, B.; Mearini, G.; Krämer, E.; Pointu, H.; Mougenot, N.; Guiard, J.; Reimer, R.; Hohenberg, H.; et al. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and ubiquitin-proteasome system regulate cardiac myosin-binding protein C mutant levels in cardiomyopathic mice. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 239–248, Erratum in Circ. Res. 2015, 116, e25. https://doi.org/10.1161/RES.0000000000000047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarraga, I.G.; Zhang, L.; Stump, M.R.; Gong, Q.; Vincent, G.M.; Zhou, Z. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay caused by a frameshift mutation in a large kindred of type 2 long QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm 2011, 8, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Stump, M.R.; Zhou, Z. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by antisense morpholino oligonucleotides restores functional expression of hERG nonsense and frameshift mutations in long-QT syndrome. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 50, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatkin, D.; MacRae, C.; Sasaki, T.; Wolff, M.R.; Porcu, M.; Frenneaux, M.; Atherton, J.; Vidaillet, H.J., Jr.; Spudich, S.; De Girolami, U.; et al. Missense mutations in the rod domain of the lamin A/C gene as causes of dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction-system disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, S.K.; Bär, H.; Ehlermann, P.; Wälde, S.; Rutschow, D.; Zeller, R.; Ivandic, B.T.; Zentgraf, H.; Katus, H.A.; Herrmann, H.; et al. Incomplete nonsense-mediated decay of mutant lamin A/C mRNA provokes dilated cardiomyopathy and ventricular tachycardia. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Ha, C.; Shin, S.; Park, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, J.W. Enrichment of titin-truncating variants in exon 327 in dilated cardiomyopathy and its relevance to reduced nonsense-mediated mRNA decay efficiency. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1087359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Tao, L.; Lai, K.; Jiang, H.; Xiao, H. The TTN p. Tyr4418Ter mutation causes cardiomyopathy in human and mice. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharp, C.A.; Haywood, M.E.; Sbaizero, O.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Mestroni, L. The Giant Protein Titin’s Role in Cardiomyopathy: Genetic, Transcriptional, and Post-translational Modifications of TTN and Their Contribution to Cardiac Disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worman, H.J. Cell signaling abnormalities in cardiomyopathy caused by lamin A/C gene mutations. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, F.J.; Chen, S.C.; Garelick, M.G.; Dai, D.F.; Liao, C.Y.; Schreiber, K.H.; MacKay, V.L.; An, E.H.; Strong, R.; Ladiges, W.C.; et al. Rapamycin reverses elevated mTORC1 signaling in lamin A/C-deficient mice, rescues cardiac and skeletal muscle function, and extends survival. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 144ra103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlmann, L.; Kröger, I.; Vignier, N.; Schlossarek, S.; Krämer, E.; Coirault, C.; Sultan, K.R.; El-Armouche, A.; Winegrad, S.; Eschenhagen, T.; et al. Cardiac myosin-binding protein C is required for complete relaxation in intact myocytes. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolman, J.A.; Reith, S.; Uhl, K.; Bailey, S.; Gautel, M.; Jeschke, B.; Fischer, C.; Ochs, J.; McKenna, W.J.; Klues, H.; et al. A newly created splice donor site in exon 25 of the MyBP-C gene is responsible for inherited hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with incomplete disease penetrance. Circulation 2000, 101, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Maquat, L.E. Exploring the therapeutic potential of modulating nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. RNA 2025, 31, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, P.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.A. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay as a Mediator of Tumorigenesis. Genes 2023, 14, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wei, Z.; Nie, Y.; Chen, H.Z. Therapeutic potential of alternative splicing in cardiovascular diseases. eBioMedicine 2024, 101, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, G.; Fernandes, R.; García-Moreno, J.F.; Romão, L. Nonsense-mediated RNA decay and its bipolar function in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Li, P.; Mu, C.; Li, D.; Chen, K.; Liang, Z. UPF1 Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating SMURF2-Mediated Ubiquitination Degradation of FOXA2. Korean Circ. J. 2025, 55, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.W. Illuminating the Protective Role of UPF1 in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Korean Circ. J. 2025, 55, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Song, Y.; Tan, X. Deciphering HERG mutation in long QT syndrome type 2 using antisense oligonucleotide–mediated techniques: Lessons from cystic fibrosis. Heart Rhythm 2023, 20, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.; Cougot, N.; Mahuteau-Betzer, F.; Nguyen, C.H.; Grierson, D.S.; Bertrand, E.; Tazi, J.; Lejeune, F. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) by a new chemical molecule reveals the dynamic of NMD factors in P-bodies. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soret, J.; Bakkour, N.; Maire, S.; Durand, S.; Zekri, L.; Gabut, M.; Fic, W.; Divita, G.; Rivalle, C.; Dauzonne, D.; et al. Selective modification of alternative splicing by indole derivatives that target serine-arginine-rich protein splicing factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8764–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterholzner, L.; Izaurralde, E. SMG7 acts as a molecular link between mRNA surveillance and mRNA decay. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Grigoryan, A.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Breda, L.; Rivella, S.; Cardozo, T.; Gardner, L.B. Identification and characterization of small molecules that inhibit nonsense-mediated RNA decay and suppress nonsense p53 mutations. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3104–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, R.; Hiller, M.; Jiménez-Gracia, L.; van der Pal, Z.; Balog, J.; Adamzek, K.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; Spitali, P. Premature termination codons in the DMD gene cause reduced local mRNA synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16456–16464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, D.; Nawaz, U.; Corbett, M.; Espinoza, J.L.; Tatton-Brown, K.; Coman, D.; Wilkinson, M.F.; Gecz, J.; Jolly, L.A. A synonymous UPF3B variant causing a speech disorder implicates NMD as a regulator of neurodevelopmental disorder gene networks. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 2568–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrey, S.R.; Wilkinson, M.F. Nonsense-mediated RNA decay in the brain: Emerging modulator of neural development and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R.; Santos, J.X.; Martiniano, H.; Vilela, J.; Rasga, C.; Romão, L.; Vicente, A.M. Gene Variants Involved in Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay Suggest a Role in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Stoica, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, P.J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Buffington, S.A.; Huq, R.; Eissa, N.T.; Larsson, O.; Porse, B.T.; et al. Inhibition of Upf2-Dependent Nonsense-Mediated Decay Leads to Behavioral and Neurophysiological Abnormalities by Activating the Immune Response. Neuron 2019, 104, 665–679.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bufton, J.C.; Powers, K.T.; Szeto, J.A.; Toelzer, C.; Berger, I.; Schaffitzel, C. Structures of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors UPF3B and UPF3A in complex with UPF2 reveal molecular basis for competitive binding and for neurodevelopmental disorder-causing mutation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 5934–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaki, T.; Imamachi, N.; Pröschel, C.; Mitsutomi, S.; Nagao, R.; Akimitsu, N.; Maquat, L.E. Loss of the fragile X syndrome protein FMRP results in misregulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamelgarn, M.; Chen, J.; Kuang, L.; Jin, H.; Kasarskis, E.J.; Zhu, H. ALS mutations of FUS suppress protein translation and disrupt the regulation of nonsense-mediated decay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11904–E11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudikote, J.P.; Cascone, T.; Poteete, A.; Sitthideatphaiboon, P.; Wu, Q.; Morikawa, N.; Zhang, F.; Peng, S.; Tong, P.; Li, L.; et al. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated decay rescues p53β/γ isoform expression and activates the p53 pathway in MDM2-overexpressing and select p53-mutant cancers. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, R.; Dai, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yuan, J.; Tan, R. p53 contributes to cardiovascular diseases via mitochondria dysfunction: A new paradigm. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 846–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Geng, Y.; Feng, R.; Zhu, Q.; Miao, B.; Cao, J.; Fei, S. The Human RNA Surveillance Factor UPF1 Modulates Gastric Cancer Progression by Targeting Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2194–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwood, S.; Laselva, O.; Bily, T.M.I.; Brewer, R.A.; Rutherford, A.H.; Bear, C.E.; Ivakine, E.A. Allele-Specific Prevention of Nonsense-Mediated Decay in Cystic Fibrosis Using Homology-Independent Genome Editing. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar-Schwartz, A.; Cohen, Y.; Elhaj, A.; Ben-Hur, V.; Siegfried, Z.; Karni, R.; Dor, T. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay may improve stop codon read-through therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, L. Assessing the activity of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in lung cancer. BMC Med. Genomics 2017, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, F.; Huang, D.; Chi, Q.; Tang, N.L.S. Nonsense-Mediated Decay Targeted RNA (ntRNA): Proposal of a ntRNA-miRNA-lncRNA Triple Regulatory Network Usable as Biomarker of Prognostic Risk in Patients with Kidney Cancer. Genes 2022, 13, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wan, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhuo, Z.; Luo, X.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, F.; Tang, M.; Xiao, F. Evaluating the activity of nonsense-mediated RNA decay via Nanopore direct RNA sequencing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 621, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, F.O.; Hoque, M.M.; Majid, A.; Gbadegoye, J.O.; Raafat, A.; Lebeche, D. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Mechanisms and Recent Implications in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells 2025, 14, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161283
Hassan FO, Hoque MM, Majid A, Gbadegoye JO, Raafat A, Lebeche D. Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Mechanisms and Recent Implications in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells. 2025; 14(16):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161283
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Fasilat Oluwakemi, Md Monirul Hoque, Abdul Majid, Joy Olaoluwa Gbadegoye, Amr Raafat, and Djamel Lebeche. 2025. "Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Mechanisms and Recent Implications in Cardiovascular Diseases" Cells 14, no. 16: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161283
APA StyleHassan, F. O., Hoque, M. M., Majid, A., Gbadegoye, J. O., Raafat, A., & Lebeche, D. (2025). Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Mechanisms and Recent Implications in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cells, 14(16), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14161283








