PARG Mutation Uncovers Critical Structural Determinant for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Hydrolysis and Chromatin Regulation in Embryonic Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Cells
- Cell culturing and transfection of ESCs
- Molecular cloning and generation of Parg-mutated ESCs with CRISPR/Cas9
- ELISA
- Western blotting
- Immunofluorescence staining
- Analysis of confocal images
- Flow cytometry analysis
- Protein modeling
- Transgenic Drosophila melanogaster line generation and crossing.
- Statistics
3. Results
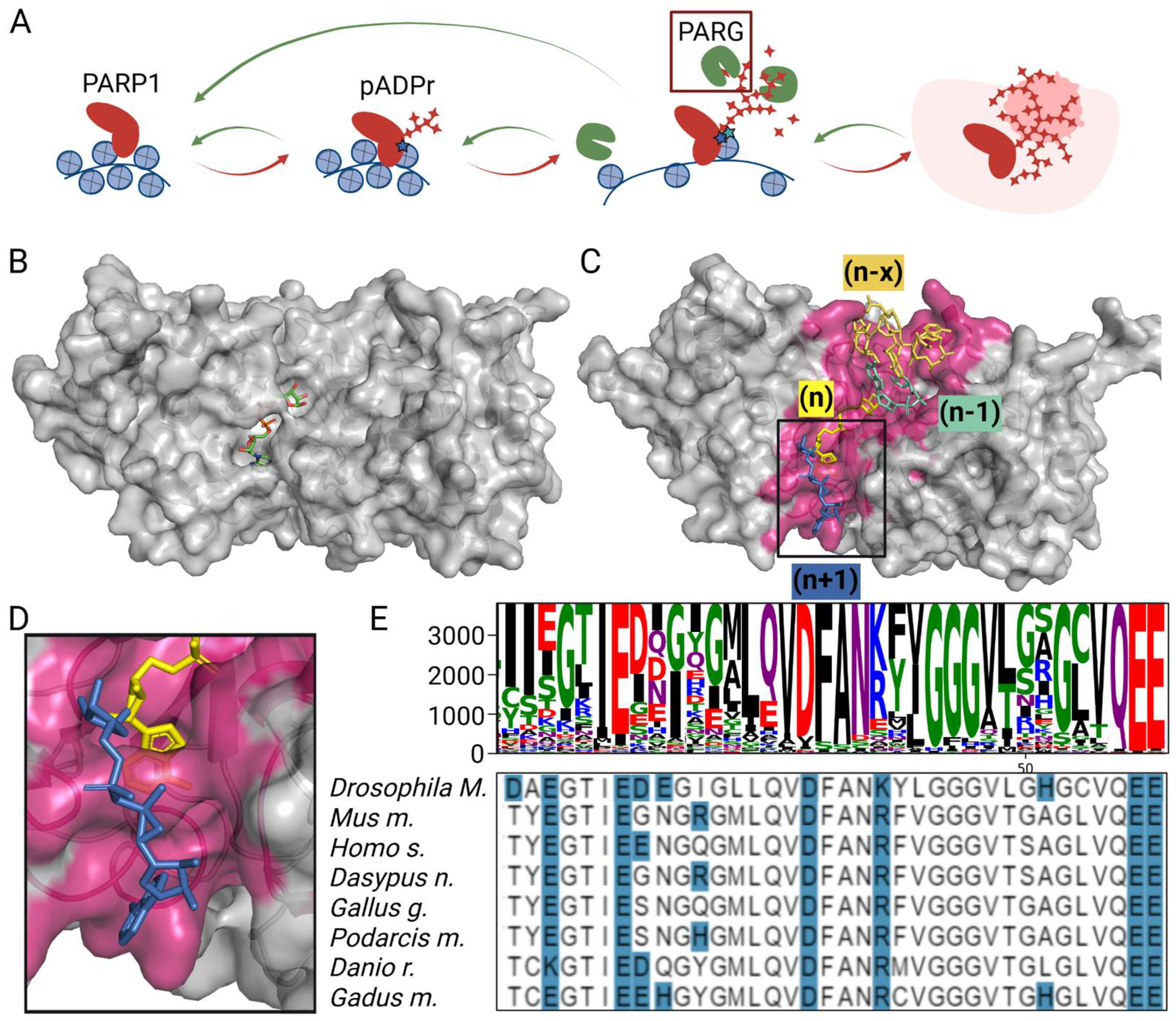
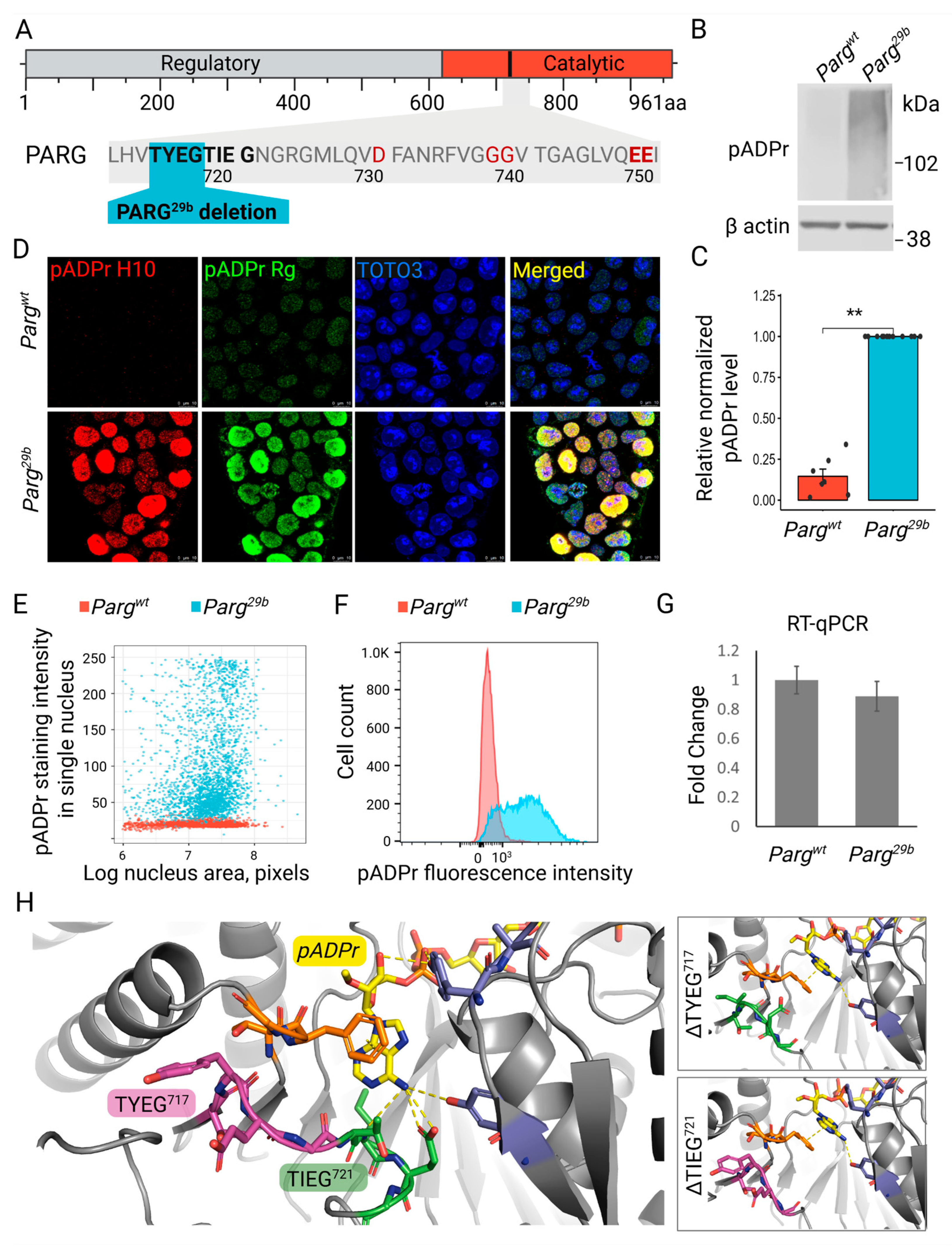
3.1. Critical Loop in PARG Catalytic Domain Regulates Poly(ADP-Ribose) Processing
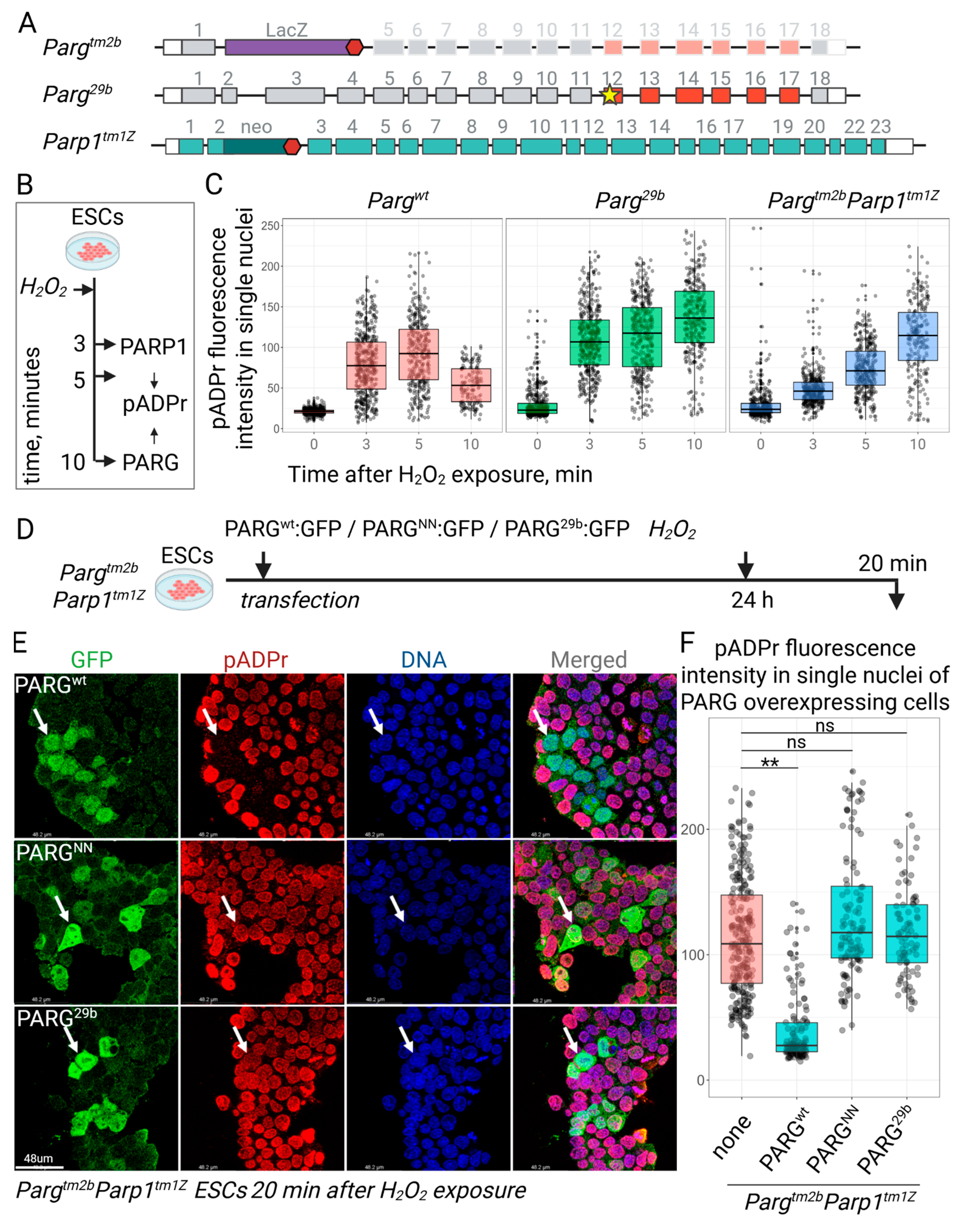
3.2. The Novel Mutation in Parg Locus Completely Impairs pADPr Catabolism in ESCs
3.3. ESC Proliferation and Survival Are Maintained in the Absence of Functional Parg
3.4. PARG29b Mutation Abolishes pADPr Hydrolysis In Vivo and Developmental Progression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| pADPr | Poly(ADP-ribose) |
| mADPr | Mono(ADP-ribose) |
| oADPr | Oligo(ADP-ribose) |
| PARP | Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase |
| PARG | Poly(ADP-ribose) Glycohydrolase |
| ESC(s) | Embryonic Stem Cell(s) |
| WT | Wild-Type |
| KO | Knockout |
References
- Amé, J.-C.; Spenlehauer, C.; de Murcia, G. The PARP Superfamily: Review Articles. Bioessays 2004, 26, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpova, Y.; Johnson, S.J.; Bordet, G.; Guo, D.; Ghatak, A.; Markov, D.A.; Tulin, A.V. Upregulation of PARG in Prostate Cancer Cells Suppresses Their Malignant Behavior and Downregulates Tumor-Promoting Genes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordet, G.; Kotova, E.; Tulin, A.V. Poly(ADP-Ribosyl)Ating Pathway Regulates Development from Stem Cell Niche to Longevity Control. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmeyer, M.; Neelsen, K.J.; Teloni, F.; Pozdnyakova, I.; Pellegrino, S.; Grøfte, M.; Rask, M.-B.D.; Streicher, W.; Jungmichel, S.; Nielsen, M.L.; et al. Liquid Demixing of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Is Seeded by Poly(ADP-Ribose). Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemasova, E.E.; Lavrik, O.I. Poly(ADP-Ribose) in Condensates: The PARtnership of Phase Separation and Site-Specific Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasovich, M.; Leung, A.K.L. PARPs and ADP-Ribosylation: Deciphering the Complexity with Molecular Tools. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 1552–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Gonzalez, R.; Jacobson, M.K. Characterization of Polymers of Adenosine Diphosphate Ribose Generated in Vitro and in Vivo. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 3218–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkauskaite, E.; Brassington, A.; Tan, E.S.; Warwicker, J.; Dunstan, M.S.; Banos, B.; Lafite, P.; Ahel, M.; Mitchison, T.J.; Ahel, I.; et al. Visualization of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Bound to PARG Reveals Inherent Balance between Exo- and Endo-Glycohydrolase Activities. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordet, G.; Bamgbose, G.; Tulin, A.V. Poly(ADP-Ribosyl)Ating Enzymes Coordinate Changes in the Expression of Metabolic Genes with Developmental Progression. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-K.; Kiefer, J.R.; Ho, C.M.W.; Stegeman, R.A.; Classen, S.; Tainer, J.A.; Ellenberger, T. Structure of Mammalian Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase Reveals a Flexible Tyrosine Clasp as a Substrate-Binding Element. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, D.; Dunstan, M.S.; Barkauskaite, E.; Weston, R.; Lafite, P.; Dixon, N.; Ahel, M.; Leys, D.; Ahel, I. The Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of a Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase. Nature 2011, 477, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Hu, X.; Sheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Theoretical Study on the Degradation of ADP-Ribose Polymer Catalyzed by Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2013, 42, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.N.; Koh, D.W.; Jacobson, M.K.; Oliveira, M.A. Identification of Three Critical Acidic Residues of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase Involved in Catalysis: Determining the PARG Catalytic Domain. Biochem. J. 2005, 388, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, J.A.; Bennett, N.; Brassington, C.; Durant, S.T.; Hassall, G.; Holdgate, G.; McAlister, M.; Nissink, J.W.M.; Truman, C.; Watson, M. Structures of the Human Poly (ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase Catalytic Domain Confirm Catalytic Mechanism and Explain Inhibition by ADP-HPD Derivatives. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, M.J.; Brichacek, M.; Barkauskaite, E.; Ariza, A.; Ahel, I.; Hergenrother, P.J. Synthesis of Dimeric ADP-Ribose and Its Structure with Human Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3558–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, Y.; Tulin, A.V. Adaptive Genetic Mechanisms in Mammalian Parp1 Locus. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2024, 14, jkae165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulas, C.; Kalkan, T.; von Meyenn, F.; Leitch, H.G.; Nichols, J.; Smith, A. Defined Conditions for Propagation and Manipulation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Development 2019, 146, dev173146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, C.; Kadekar, S.; Pijuan-Galitó, S.; Annerén, C. Fast and Efficient Transfection of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Using Non-Viral Reagents. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2016, 12, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.E.; Canver, M.C.; Orkin, S.H. Generation of Genomic Deletions in Mammalian Cell Lines via CRISPR/Cas9. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 95, e52118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adikusuma, F.; Pfitzner, C.; Thomas, P.Q. Versatile Single-Step-Assembly CRISPR/Cas9 Vectors for Dual gRNA Expression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, U.; Weigert, M.; Broaddus, C.; Myers, G. Cell Detection with Star-Convex Polygons. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11071, pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Pécot, T.; Cuitiño, M.C.; Johnson, R.H.; Timmers, C.; Leone, G. Deep Learning Tools and Modeling to Estimate the Temporal Expression of Cell Cycle Proteins from 2D Still Images. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discovery, C.; Boitreaud, J.; Dent, J.; McPartlon, M.; Meier, J.; Reis, V.; Rogozhnikov, A.; Wu, K. Chai-1: Decoding the Molecular Interactions of Life. bioRxiv 2024. [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate Prediction of Protein Structures and Interactions Using a Three-Track Neural Network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gagné, J.-P.; Poirier, G.G.; Xu, W. Crystallographic and Biochemical Analysis of the Mouse Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hanai, S.; Kanai, M.; Ohashi, S.; Okamoto, K.; Yamada, M.; Takahashi, H.; Miwa, M. Loss of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase Causes Progressive Neurodegeneration in Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunstan, M.S.; Barkauskaite, E.; Lafite, P.; Knezevic, C.E.; Brassington, A.; Ahel, M.; Hergenrother, P.J.; Leys, D.; Ahel, I. Structure and Mechanism of a Canonical Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.W.; Lawler, A.M.; Poitras, M.F.; Sasaki, M.; Wattler, S.; Nehls, M.C.; Stoger, T.; Poirier, G.G.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Failure to Degrade Poly(ADP-Ribose) Causes Increased Sensitivity to Cytotoxicity and Early Embryonic Lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17699–17704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotova, E.; Jarnik, M.; Tulin, A.V. Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 Is Required for Protein Localization to Cajal Body. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.A.; Panzeter, P.L.; Collinge, M.A.; Althaus, F.R. Endoglycosidic Cleavage of Branched Polymers by Poly(ADP-Ribose) Glycohydrolase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 220, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, P.; Buch-Larsen, S.C.; Suyari, O.; Smith, R.; Suskiewicz, M.J.; Schützenhofer, K.; Ariza, A.; Rack, J.G.M.; Nielsen, M.L.; Ahel, I. Serine ADP-Ribosylation in Drosophila Provides Insights into the Evolution of Reversible ADP-Ribosylation Signalling. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number | Sequence |
|---|---|
| 1 | GGCAAACGGATCCCACACAG |
| 2 | AGAATGGTGAGCGAACTGCA |
| 3 | GGAACAAAACTTGTACCCTG |
| 4 | TGCGATTCTGAAATACAATG |
| 5 | TCACTGTGGTCATCAGTGTG |
| 6 | TCCTTTAGTATCCATCCAAG |
| 7 | TCGGCACCAACATCTGACAA |
| 8 | GATTTATCAAGATTTAGCTG |
| 9 | CAAATGGAGGCGAATCACCT |
| 10 | TCAGGTACTTGAAGAAGCAG |
| 11 | TGTTTGAAGGACGTTCATCA |
| 12 | ACGCTTACACGTCACTTACG |
| 13 | TCATTCTGTCACGATGTCAC |
| 14 | AAGTGAGCCTGAGTCACCAA |
| 15 | GTAAATGTCACCAATCCTGT |
| 16 | TGGAGGTGGTGTGACTGGTG |
| 17 | TGTTTCACGGCTGTTCACTG |
| 18 | GAACAGTACAGTGAATACAC |
| 19 | CGATTGGCAGCGGCGCTGCA |
| 20 | TCTCAGGCACAAACTGATCG |
| 21 | TTTCAGAAGGAACTCCAGGA |
| 22 | ACCACAGCCCCAGTTTCCCG |
| 23 | TGCACACTTTCCTTACCGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karpova, Y.; Piatz, S.; Bordet, G.; Tulin, A.V. PARG Mutation Uncovers Critical Structural Determinant for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Hydrolysis and Chromatin Regulation in Embryonic Stem Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141049
Karpova Y, Piatz S, Bordet G, Tulin AV. PARG Mutation Uncovers Critical Structural Determinant for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Hydrolysis and Chromatin Regulation in Embryonic Stem Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(14):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141049
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarpova, Yaroslava, Sara Piatz, Guillaume Bordet, and Alexei V. Tulin. 2025. "PARG Mutation Uncovers Critical Structural Determinant for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Hydrolysis and Chromatin Regulation in Embryonic Stem Cells" Cells 14, no. 14: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141049
APA StyleKarpova, Y., Piatz, S., Bordet, G., & Tulin, A. V. (2025). PARG Mutation Uncovers Critical Structural Determinant for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Hydrolysis and Chromatin Regulation in Embryonic Stem Cells. Cells, 14(14), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141049








