Local T-Cell Dysregulation and Immune Checkpoint Expression in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Data Collection
2.2. HPV-DNA Genotyping
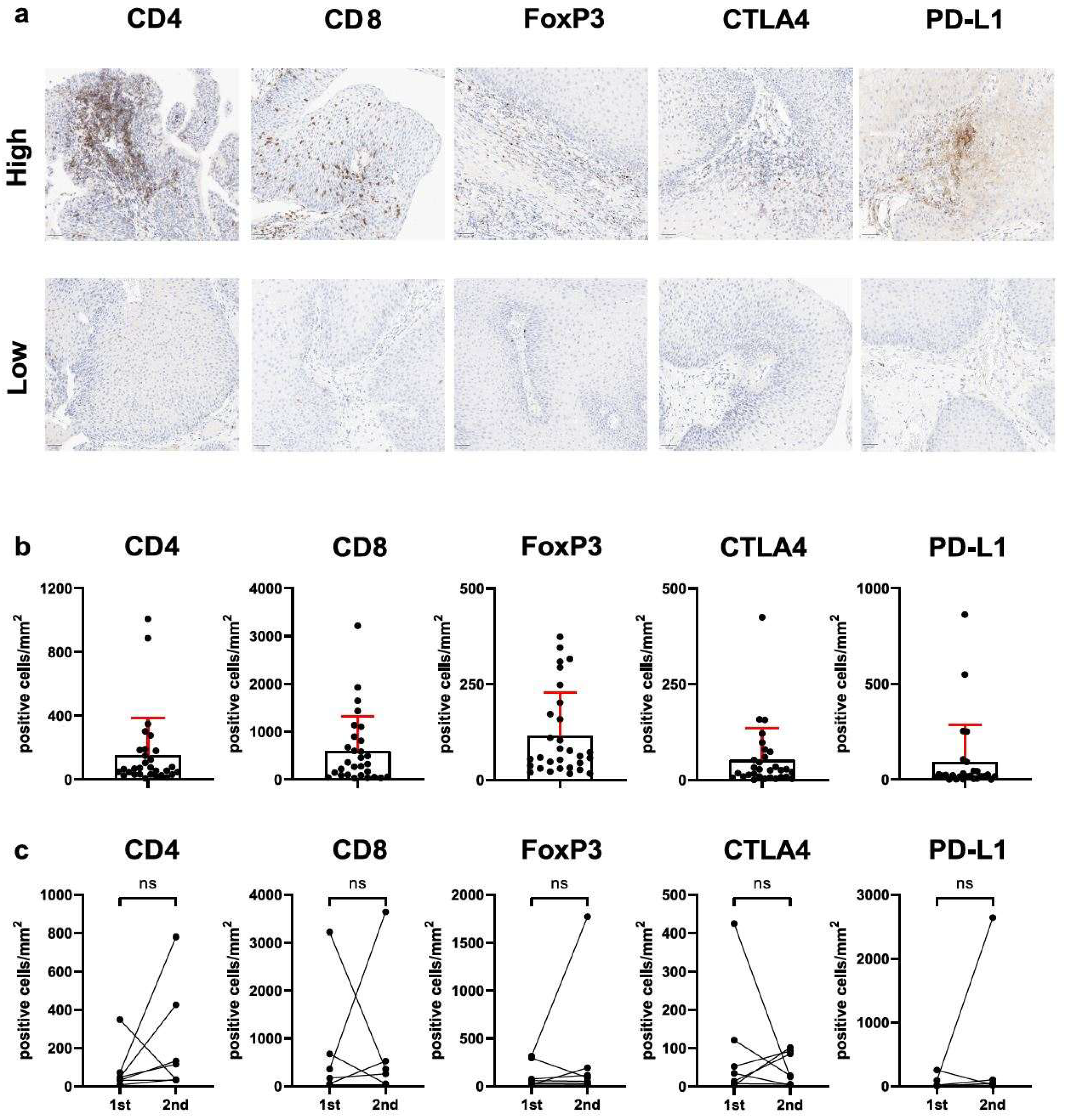
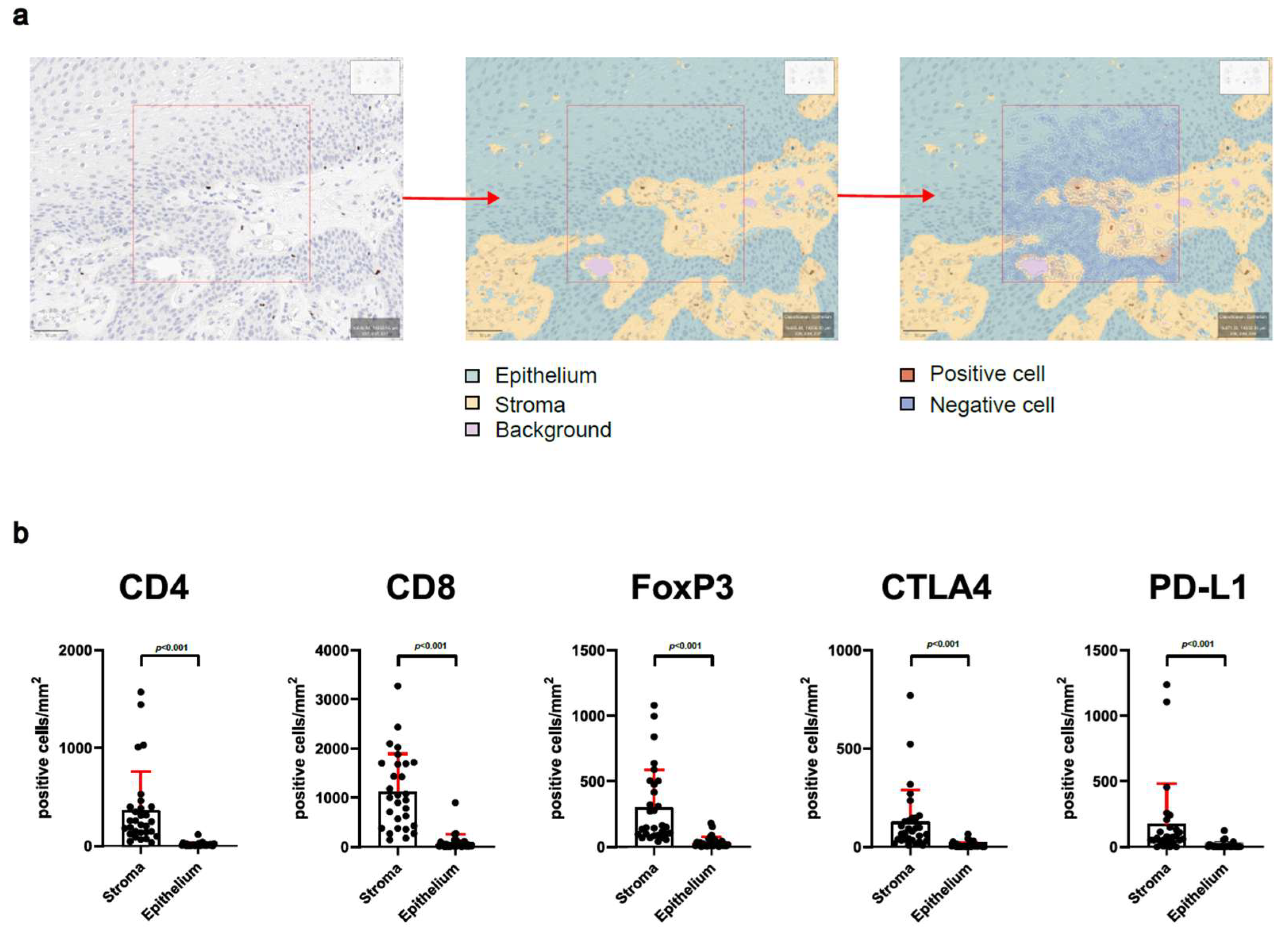
2.3. Immunohistochemistry and Digital Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. FOXP3+/CD4+ T-Cell Ratio (But Not Total T-Cell Infiltration or Immune Checkpoint Expression) Is Related to Clinical Disease Severity
3.2. Analysis of Stroma and Epithelium Reveals Special Distribution of Intralesional T-Cells
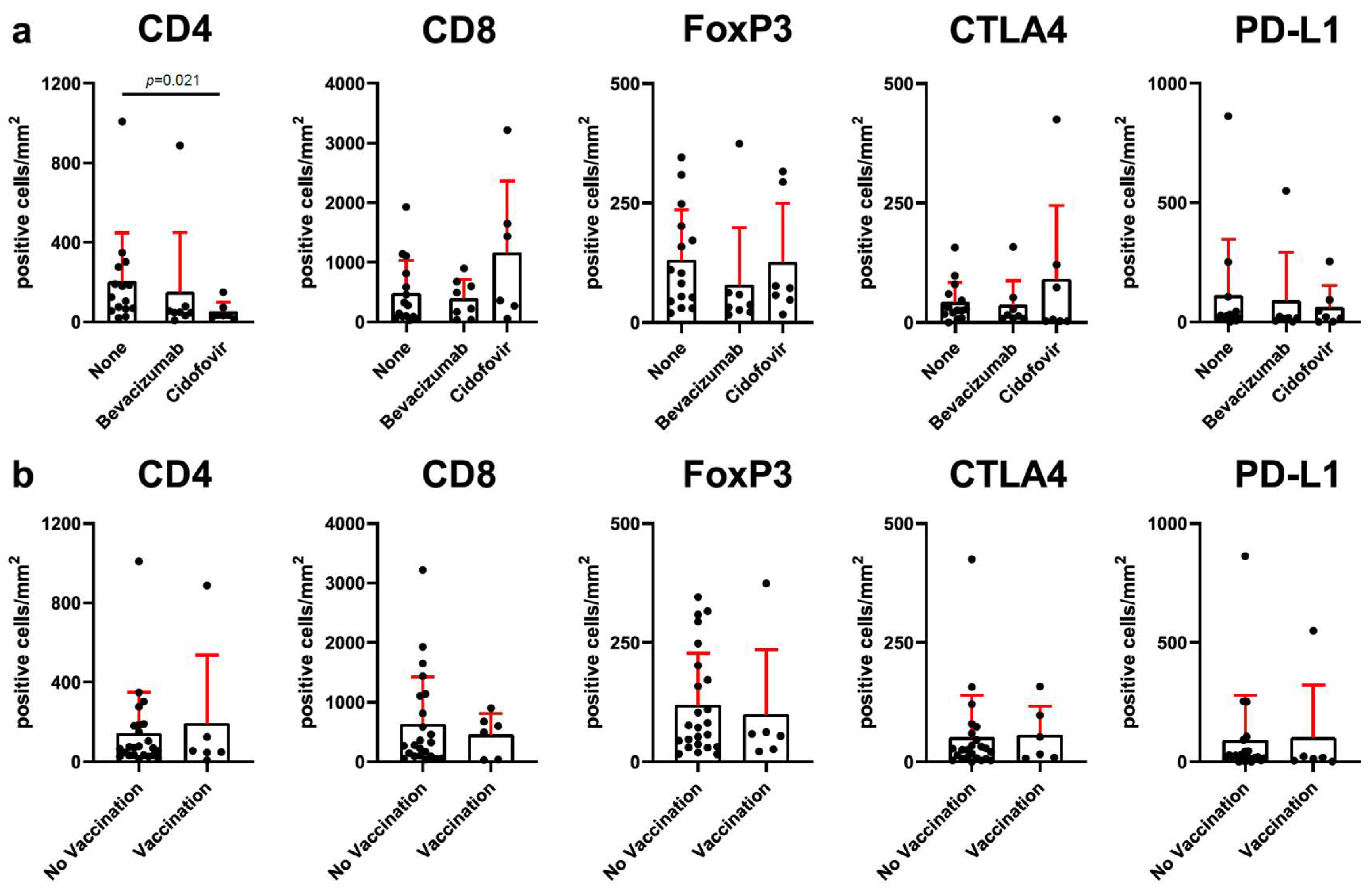
3.3. Adjuvant Therapy with Cidofovir Is Related to Reduced CD4+ T-Cell Infiltration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RRP | Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| CTLA4 | Cytotoxic lymphocyte antigen 4 |
| IFS | Intervention-free survival |
| HPV | Human papillomavirus |
| TIGIT | T-cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains |
| LAG3 | Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 |
| TIM3 | T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 |
| ICB | Immune checkpoint blockade |
| Tregs | Regulatory T-cells |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency viruses |
| IL-4 | Interleukin-4 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| Th1 | T helper type 1 |
References
- Stanley, M.A. Epithelial Cell Responses to Infection with Human Papillomavirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.; Derkay, C. Palliative Aspects of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 42, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seedat, R.Y.; Schall, R. Age of Diagnosis, Incidence and Prevalence of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis-A South African Perspective. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omland, T.; Akre, H.; Vãrdal, M.; Brøndbo, K. Epidemiological Aspects of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Population-Based Study. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Giorgi, M.R.M.; van den Heuvel, E.R.; Tjon Pian Gi, R.E.A.; Brunings, J.W.; Chirila, M.; Friedrich, G.; Golusinski, W.; Graupp, M.; Horcasitas Pous, R.A.; Ilmarinen, T.; et al. Age of Onset of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Distribution Analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2016, 41, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.; Erickson, E.; Koch, B.; Young, T.; Allen, D.; Kim, B.; deSilva, B.; Matrka, L. Smoking and Carcinoma Trends in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Patients. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatayli-Ozgursoy, S.; Bishop, J.A.; Hillel, A.; Akst, L.; Best, S.R.A. Risk Factors for Dysplasia in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in an Adult and Pediatric Population. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2016, 125, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkay, C.S.; Bluher, A.E. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: Update 2018. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 26, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Yang, P.C. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Pulmonary Involvement: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Respirology 2009, 14, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, P.A.; Ruiz, R.; Yoo, M.J.; Verma, A.; Ahmed, O.H.; Wang, B.; Dion, G.R.; Voigt, A.; Merati, A.; Rosen, C.A.; et al. Laryngeal Distribution of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis in a Previously Untreated Cohort. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Asai, R.; Makiyama, K. The Predominant Site of Pharyngeal Lesions in Patients with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol 2022, 279, 4461–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, P.A.; Kravietz, A.; Achlatis, E.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kidane, J.; Harrison, T.; Miller, J.; Drake, V.E.; Best, S.R.; et al. Prospective, Multi-Center Study of the Anatomic Distribution of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 2403–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonagura, V.R.; Hatam, L.J.; Rosenthal, D.W.; De Voti, J.A.; Lam, F.; Steinberg, B.M.; Abramson, A.L. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Complex Defect in Immune Responsiveness to Human Papillomavirus-6 and -11. APMIS 2010, 118, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devoti, J.; Hatam, L.; Lucs, A.; Afzal, A.; Abramson, A.; Steinberg, B.; Bonagura, V. Decreased Langerhans Cell Responses to IL-36γ: Altered Innate Immunity in Patients with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Greenberg, M.; Wentland, C.; Sepe, B.; Bowe, S.; Diercks, G.; Huynh, T.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Schlegel, R.; Kodack, D.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and CD8+ Infiltration Shows Heterogeneity in Juvenile Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 95, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, B.; Miller, J.; Kung, Y.J.; Wu, T.C.; Hung, C.F.; Roden, R.; Best, S.R. Profiling of VEGF Receptors and Immune Checkpoints in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Bishop, J.A.; Roden, R.B.S.; Allen, C.T.; Best, S.R.A. The PD-1 and PD-L1 Pathway in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, E27–E32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam, L.J.; DeVoti, J.A.; Rosenthal, D.W.; Lam, F.; Abramson, A.L.; Steinberg, B.M.; Bonagura, V.R. Immune Suppression in Premalignant Respiratory Papillomas: Enriched Functional CD4+Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells and PD-1/PD-L1/L2 Expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xi, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Pei, M.; Zhang, J.; Gui, J.; Ni, X. Restricted Recruitment of NK Cells with Impaired Function Is Caused by HPV-Driven Immunosuppressive Microenvironment of Papillomas in Aggressive Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Patients. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0094622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestas, S.A.; Shelly, S.; Soriano, R.M.; Klein, A. Trends in Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Treatment. Acta. Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2021, 72, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramov, T.; Vetckova, E.; Nikolova, M.; Valev, D.; Manolova, A.; Tafradgiiska, M.; Kostadinov, D.; Tchalacov, I. Therapeutic Approaches to the Treatment of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis of the Aerodigestive Tract (a Clinical Study). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2014, 28, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, M.; Nasrollahi, T.; Raskin, J.; Khan, S.; Alexander, R.E. Laryngotracheal Recurrent Papillomatosis: A Case Study and Survey of Surgical and Systemic Management. Ear Nose Throat. J. 2022, 101, 47S–51S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, N.K.; James, A.L. Antiviral Agents for the Treatment of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Systematic Review of the English-Language Literature. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 136, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, B.G.; Kashima, H.K.; Mounts, P.; Thurmond, L.; Chapman, S.; Buckley, S.; Wold, D. Long-Term Response of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis to Treatment with Lymphoblastoid Interferon Alfa-N1. Papilloma Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goon, P.; Sauzet, O.; Schuermann, M.; Oppel, F.; Shao, S.Y.; Scholtz, L.U.; Sudhoff, H.; Goerner, M. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP)-Meta-Analyses on the Use of the HPV Vaccine as Adjuvant Therapy. NPJ Vaccines 2023, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, K.; Reading, J.L.; Puttick, C.; Thakkar, K.; Abbosh, C.; Bentham, R.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Rosenthal, R.; Biswas, D.; Rowan, A.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Tumor- and T Cell-Intrinsic Mechanisms of Sensitization to Checkpoint Inhibition. Cell 2021, 184, 596-614.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Xie, H.; Lv, M.; Yang, Q.; Shuang, Z.; Gao, F.; Li, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, W. The Landscape of Objective Response Rate of Anti-PD-1/L1 Monotherapy across 31 Types of Cancer: A System Review and Novel Biomarker Investigating. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 2483–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.T.; Lee, S.; Norberg, S.M.; Kovalovsky, D.; Ye, H.; Clavijo, P.E.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Schlegel, R.; Schlom, J.; Strauss, J.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of PD-L1 Blockade in Patients with Aggressive Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creelan, B.C.; Ahmad, M.U.; Kaszuba, F.J.; Khalil, F.K.; Welsh, A.W.; Ozdemirli, M.; Grant, N.N.; Subramaniam, D.S. Clinical Activity of Nivolumab for Human Papilloma Virus-Related Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Oncologist 2019, 24, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open Source Software for Digital Pathology Image Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Orban, N. Infantile Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: Review of Adjuvant Therapies. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 958–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.M.; Hunt, P.W.; Critchfield, J.W.; McConnell, D.H.; Garcia, J.C.; Pollard, R.B.; Somsouk, M.; Deeks, S.G.; Shacklett, B.L. Increased Frequency of Regulatory T Cells Accompanies Increased Immune Activation in Rectal Mucosae of HIV-Positive Noncontrollers. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11422–11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, G.M.; Gallus, S.; Herrero, R.; Muñoz, N.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Vaccarella, S.; Anh, P.T.H.; Ferreccio, C.; Hieu, N.T.; Matos, E.; et al. Worldwide Distribution of Human Papillomavirus Types in Cytologically Normal Women in the International Agency for Research on Cancer HPV Prevalence Surveys: A Pooled Analysis. Lancet 2005, 366, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, P.J.L.; Gaspal, F.M.C.; Kim, M.Y. Two Sides of a Cellular Coin: CD4+CD3− Cells Regulate Memory Responses and Lymph-Node Organization. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quatrini, L.; Della Chiesa, M.; Sivori, S.; Mingari, M.C.; Pende, D.; Moretta, L. Human NK Cells, Their Receptors and Function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarz, P.; Bodnar, M.; Czech, J.; Mackiewicz–Nartowicz, H.; Sinkiewicz, A.; Szylberg, Ł.; Borowczak, J.; Rutkiewicz, P.; Zwierz, A.; Burduk, P. Assessment of Immunomodulation and Regulation of Cell Cycle in Epithelium and Stroma after Cidofovir Injection in Patients with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis—Pilot Study. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, H.; Atfeh, M. Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Intralesional Bevacizumab in the Treatment of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 186, 112138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clamp, P.J.; Saunders, M.W. Systematic Review of Intralesional Cidofovir Dosing Regimens in the Treatment of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, S.R.; Bock, J.M.; Fowler, N.B.; Raabe, E.H.; Klein, A.M.; Laetsch, T.W.; McClellan, K.; Rinkel, R.N.P.M.; Saba, N.F.; Sidell, D.R.; et al. A Consensus Statement on the Administration of Systemic Bevacizumab in Patients with Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 5041–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, R.J.; Rayle, C.; Joo, H.H.; Huang, E.Y.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Raabe, E.H.; Best, S.R. Systemic Bevacizumab for Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Single Institution’s Experience. Laryngoscope 2024, 134, 3253–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohl, M.P.; Rosen, C.A. Stabilization of Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis with Pembrolizumab Therapy: A Case Report. J. Voice 2023, 37, 637.e1–637.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotte, A. Combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1 Blockers for Treatment of Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.C.; Anang, N.A.A.S.; Sharma, R.; Andrews, M.C.; Reuben, A.; Levine, J.H.; Cogdill, A.P.; Mancuso, J.J.; Wargo, J.A.; Pe’er, D.; et al. Combination Anti–CTLA-4 plus Anti–PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade Utilizes Cellular Mechanisms Partially Distinct from Monotherapies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22699–22709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, A.; Kostine, M.; Barnetche, T.; Truchetet, M.E.; Schaeverbeke, T. Immune Related Adverse Events Associated with Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Y.; Salem, J.E.; Cohen, J.V.; Chandra, S.; Menzer, C.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S.; Das, S.; Beckermann, K.E.; Ha, L.; et al. Fatal Toxic Effects Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Carbone, D.P.; McKean, M.; Balaraman, R.; Shah, S.; Arrowsmith, E.; Peguero, J.A.; Joshi, R.; He, A.R.; Milillo, A.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of Target-Preserving Anti-CTLA-4 Antibody ONC-392 as Monotherapy in NSCLC Patients Who Progressed on PD(L)1-Targeted Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.S.; Selfridge, J.E.; Albany, C.; Taylor, M.H.; Mehmi, I.; Kwatra, V.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; de Souza, P.L.; Llorin-Sangalang, J.D.; Aysola, K.; et al. Phase 1 Study of BA3071, an Anti–CTLA-4 Conditionally Active Biologic, in Combination with Nivolumab in Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | RRP Cohort n = 30 (100%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 17 (57%) |
| Female | 13 (43%) | |
| Age | Median (range) | 32 (1–61) |
| Onset | Juvenile | 4 (13%) |
| Adult | 26 (87%) | |
| Surgical interventions | Median (range) | 3 (1–21) |
| Previous adjuvant treatment | Yes | 15 (50%) |
| No | 15 (50%) | |
| HPV vaccination | Yes | 6 (20%) |
| No | 24 (80%) | |
| Involvement of trachea | Yes | 2 (7%) |
| No | 28 (93%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eckel, H.N.C.; Lyu, S.I.; Faste, F.; Sharma, S.J.; Nobis, A.; Wuerdemann, N.; Ziogas, M.; Mayer, M.; Suchan, M.C.; Wennhold, K.; et al. Local T-Cell Dysregulation and Immune Checkpoint Expression in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Cells 2025, 14, 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130985
Eckel HNC, Lyu SI, Faste F, Sharma SJ, Nobis A, Wuerdemann N, Ziogas M, Mayer M, Suchan MC, Wennhold K, et al. Local T-Cell Dysregulation and Immune Checkpoint Expression in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Cells. 2025; 14(13):985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130985
Chicago/Turabian StyleEckel, Hans N. C., Su Ir Lyu, Frederik Faste, Shachi J. Sharma, Anne Nobis, Nora Wuerdemann, Maria Ziogas, Marcel Mayer, Malte C. Suchan, Kerstin Wennhold, and et al. 2025. "Local T-Cell Dysregulation and Immune Checkpoint Expression in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis" Cells 14, no. 13: 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130985
APA StyleEckel, H. N. C., Lyu, S. I., Faste, F., Sharma, S. J., Nobis, A., Wuerdemann, N., Ziogas, M., Mayer, M., Suchan, M. C., Wennhold, K., Garcia-Marquez, M. A., Thelen, M., Hagen, E., Eßer, J., Klasen, C., Siefer, O., Otte, M., Schloesser, H. A., Klussmann, J. P., ... Hansen, K. K. (2025). Local T-Cell Dysregulation and Immune Checkpoint Expression in Human Papillomavirus-Mediated Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Cells, 14(13), 985. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130985








