LncRNA LOC610012 Inhibits Canine Mammary Tumor Activity via the PTGS2/EP3 and GSK3β Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies
2.2. Clinical Sample Collection and Cell Culture
2.3. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
2.4. Overexpression of LncRNA LOC610012 in Cells
2.5. Overexpression and Knockdown of PTGS2
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Wound-Healing Assay
2.8. Transwell Assay
2.9. In Vivo Tumorigenicity Assay
2.10. Colony Formation Assay
2.11. Intracellular ROS Detection
2.12. RNA-Seq Analysis of Downstream Genes
2.13. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.14. Western Blot Analysis
2.15. Electron Microscopy for Mitochondrial Morphology
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
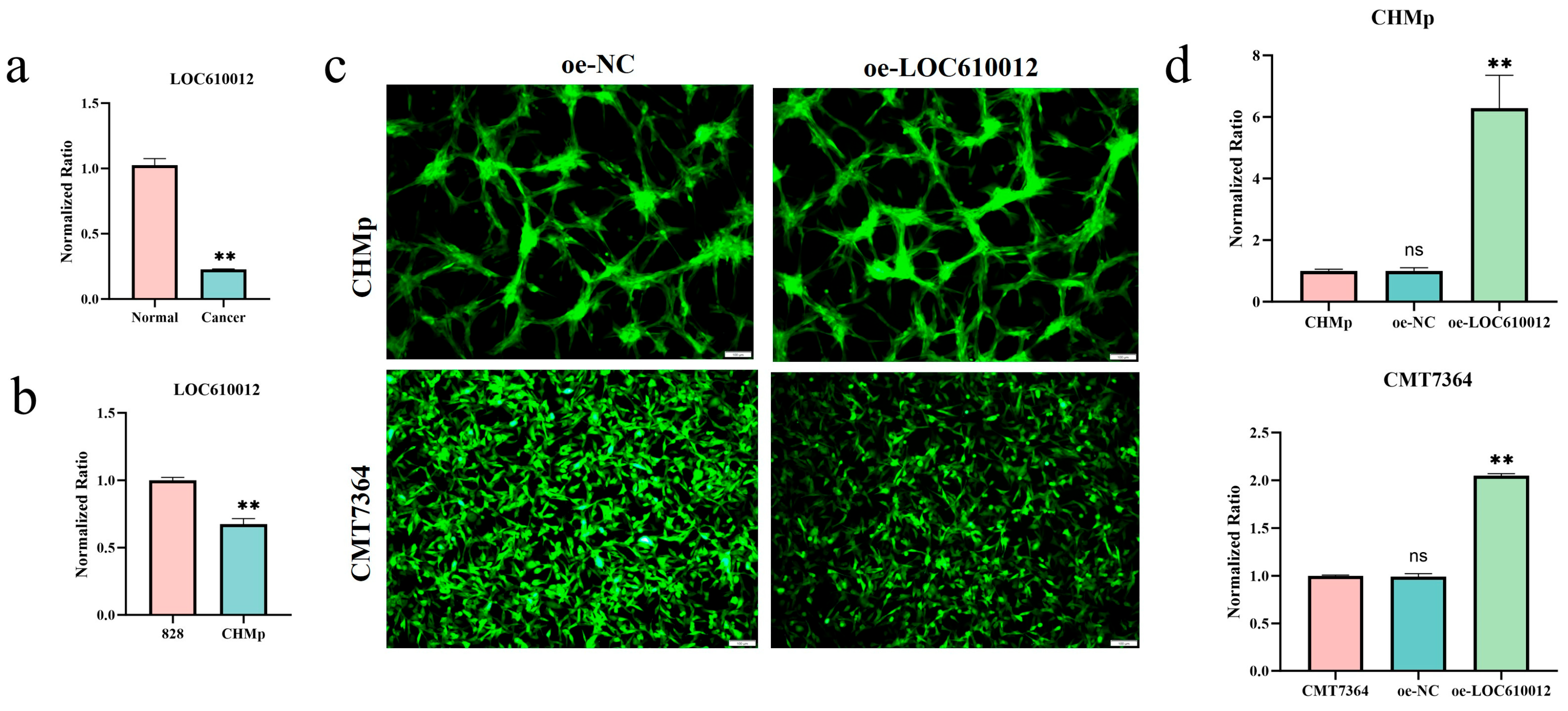
3.1. LOC610012 Is Downregulated in CMT Tissues and Cells
3.2. LOC610012 Inhibits CMT Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Tumorigenicity In Vitro and In Vivo
3.3. RNA-Seq Identifies PTGS2 as a Key Downstream Target of LOC610012
3.4. LOC610012 Downregulates PTGS2 to Inhibit EP3 and Promote GSK-3β Phosphorylation
3.5. LOC610012 Induces ROS Accumulation
3.6. PTGS2 Overexpression Partially Rescues LOC610012-Mediated ROS Accumulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMT | Canine mammary tumor |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CTCs | Circulating tumor cells |
| GSK-3 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HDACI | Histone deacetylase inhibitor |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| lncRNAs | Long non-coding RNAs |
| MRCC | Mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time quantitative PCR |
References
- Vazquez, E.; Lipovka, Y.; Cervantes-Arias, A.; Garibay-Escobar, A.; Haby, M.M.; Queiroga, F.L.; Velazquez, C. Canine Mammary Cancer: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Animals 2023, 13, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.H.; Du, C.T.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, R.L.; Tang, X.Y.; Xie, G.H. Epidemiological Investigation of Canine Mammary Tumors in Mainland China between 2017 and 2021. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 843390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.; da Costa, R.M.G.; Dias, F.; Gama, A.; Gaspar, V.M.; Mano, J.F.; Oliveira, P.A.; Medeiros, R. Exploring the Role of Micrornas as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Canine Mammary Tumors. Geroscience 2024, 46, 6641–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.M.; Moore, A.S.; Frimberger, A.E. Surgical Treatment of Mammary Carcinomas in Dogs with or without Postoperative Chemotherapy. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2016, 14, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.A.; Lopes, C.C.; Ribeiro, J.R.; Martins, L.R.; Santos, J.C.; Amorim, I.F.; Gärtner, F.; Matos, A.J. Identification of Prognostic Factors in Canine Mammary Malignant Tumours: A Multivariable Survival Study. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.M.G.; Dos Santos, T.R.; Silva, M.J.B. Identifying the Risk Factors for Malignant Mammary Tumors in Dogs: A Retrospective Study. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.I.; Silva-Carvalho, R.; Prada, J.; Pinto, C.; Gregório, H.; Lobo, L.; Pires, I.; Queiroga, F.L. Tgfbeta in Malignant Canine Mammary Tumors: Relation with Angiogenesis, Immunologic Markers and Prognostic Role. Vet. Q. 2024, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, M.C.; Daulagala, A.C.; Kourtidis, A. Lnccation: Lncrna Localization and Function. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202009045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene Regulation by Long Non-Coding Rnas and Its Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Jia, K. Lncrna Expression Profiles in Canine Mammary Tumors Identify Lnc34977 as a Promoter of Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Canine Mammary Tumor Cells. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascione, L.; Giudice, L.; Ferraresso, S.; Marconato, L.; Giannuzzi, D.; Napoli, S.; Bertoni, F.; Giugno, R.; Aresu, L. Long Non-Coding Rnas as Molecular Signatures for Canine B-Cell Lymphoma Characterization. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhou, J.; Diao, H. Long Non-Coding Rna as a Potential Biomarker for Canine Tumors. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husna, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Chen, H.W.; Hasan, M.N.; Nakagawa, T.; Miura, N. Long Non-Coding Rna and Transfer Rna-Derived Small Fragments in Exosomes Are Potential Biomarkers for Canine Oral Melanoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, E.; Hu, M.; Ge, R.; Tong, D.; Fan, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Lncrna-42060 Regulates Tamoxifen Sensitivity and Tumor Development Via Regulating the Mir-204-5p/Sox4 Axis in Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 654694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, L.; Fan, J.; Li, L. Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis Based on 10 Case-Control Studies. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14 (Suppl. S1), S105–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Sharma-Walia, N. Crosstalk between Osteoprotegerin (Opg), Fatty Acid Synthase (Fasn) and, Cycloxygenase-2 (Cox-2) in Breast Cancer: Implications in Carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenberg, A.J.; Lippman, S.M.; Mann, J.R.; Subbaramaiah, K.; DuBois, R.N. Cyclooxygenase-2 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: Pharmacologic Targets for Chemoprevention. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurram, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Cui, H.; Du, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Celecoxib Conjugated Fluorescent Probe for Identification and Discrimination of Cyclooxygenase-2 Enzyme in Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5187–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Li, B.; He, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, F. Lncrna Hulc Promotes the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Stabilizing Cox-2 Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embi, N.; Rylatt, D.B.; Cohen, P. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 from Rabbit Skeletal Muscle. Eur. J. Biochem. 1980, 107, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, J.A.; Dale, T.C. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3: A Key Regulator of Cellular Fate. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1930–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodgett, J.R. Molecular Cloning and Expression of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3/Factor A. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souder, D.C.; Anderson, R.M. An Expanding Gsk3 Network: Implications for Aging Research. Geroscience 2019, 41, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, K.; Poria, D.K.; Sehareen, S.W.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Tang, W.; McKennett, L.; Padmanaban, V.; Czarra, K.; Ewald, A.J.; Ueno, N.T.; et al. Stabilization of E-Cadherin Adhesions by Cox-2/Gsk3β Signaling Is a Targetable Pathway in Metastatic Breast Cancer. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e156057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, C.; Liu, S.; Trachootham, D.; Huang, P. Targeting Ros in Cancer: Rationale and Strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 583–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Wu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Z.; Han, X.; Qin, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. The Pi3k/Akt/Gsk-3β/Ros/Eif2b Pathway Promotes Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis Via Suppression of Nk Cell Cytotoxicity and Tumor Cell Susceptibility. Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Bai, H.; Cui, W.; Guo, W.; Feng, D.; et al. Adiponectin Peptide Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Nlrp3 Inflammasome Activation after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Ampk/Gsk-3β. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, 113302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.T.; Lin, J.F.; Li, T.; Li, J.J.; Xu, R.H.; Ju, H.Q. Lncrna-Mediated Posttranslational Modifications and Reprogramming of Energy Metabolism in Cancer. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre, F.; Colantoni, A.; Helmer-Citterich, M. Revealing Protein–Lncrna Interaction. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 17, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Shaath, H.; Elkord, E.; Alajez, N.M. Long Non-Coding Rna (Lncrna) Transcriptional Landscape in Breast Cancer Identifies Linc01614 as Non-Favorable Prognostic Biomarker Regulated by Tgfβ and Focal Adhesion Kinase (Fak) Signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, F. The Role of Lncrna-Regulated Autophagy in Aki. BioFactors 2023, 49, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Ou, X.; Sun, K.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Zhao, Z.; He, Y.; Peng, J.; Xu, J. M6a Modification–Mediated Lncrna Tp53tg1 Inhibits Gastric Cancer Progression by Regulating Cip2a Stability. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 4135–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Z.; Cheng, T.T.; He, Q.J.; Lei, Z.Y.; Chi, J.; Tang, Z.; Liao, Q.X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, L.S.; Cui, S.Z. Linc01133 as Cerna Inhibits Gastric Cancer Progression by Sponging Mir-106a-3p to Regulate Apc Expression and the Wnt/Β-Catenin Pathway. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.L.; Chipman, J.G.; Robertson, D.L.; Erikson, R.L.; Simmons, D.L. Expression of a Mitogen-Responsive Gene Encoding Prostaglandin Synthase Is Regulated by Messenger-Rna Splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2692–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famaey, J.P. In Vitro and in Vivo Pharmacological Evidence of Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition by Nimesulide: An Overview. Inflamm. Res. 1997, 46, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Goradel, N.; Najafi, M.; Salehi, E.; Farhood, B.; Mortezaee, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 in Cancer: A Review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 5683–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, N.; Sun, D.; Lan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Feng, L.; Zhang, B.; Jin, L.; et al. Andrographolide Inhibits Breast Cancer through Suppressing Cox-2 Expression and Angiogenesis Via Inactivation of P300 Signaling and Vegf Pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tober, K.L.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Maruyama, T.; Oberyszyn, T.M. Possible Cross-Regulation of the E Prostanoid Receptors. Mol. Carcinog. 2007, 46, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Xie, S.; Ma, L.; Nie, D. Mpges-1/Pge2 Promotes the Growth of T-All Cells in Vitro and in Vivo by Regulating the Expression of Mtdh Via the Ep3/Camp/Pka/Creb Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, R.; Carpino, G.; Petrungaro, S.; Mammola, C.L.; Tomaipitinca, L.; Filippini, A.; Facchiano, A.; Ziparo, E.; Giampietri, C. Multifaceted Roles of Gsk-3 in Cancer and Autophagy-Related Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4629495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.P.; Stavropoulou, A.V.; Lam, E.W.; Charles Coombes, R.; Vigushin, D.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin A induces ubiquitin-dependent cyclin D1 degradation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Zou, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J. Curcumin Ameliorates Ckd-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress through Inhibiting Gsk-3β Activity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias-Rizk, T.; El Hajj, J.; Segal-Bendirdjian, E.; Hilal, G. The Long Non Coding Rna H19 as a Biomarker for Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Lebanese Women. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primers Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| LncRNA LOC610012 (forward) | TGGCAGCGTCTGTAACTGAA |
| LncRNA LOC610012 (reverse) | AGGGCAACTTTACTGGGAACA |
| PTGS2 (forward) | GCGGGAGCATAACAGAGTGT |
| PTGS2 (reverse) | GCTCGTCTGGAATAACCGCT |
| EGR1 (forward) | GCCACCACATACTCTTCCGT |
| EGR1 (reverse) | TTGTCATGTCCGAAAGCCCT |
| NR4A2 (forward) | GTATGGGTCCTCGCCTCAAG |
| NR4A2 (reverse) | AGCCTGTGCTGTAGTTGTCC |
| STEAP1 (forward) | AGGAGACACCAGAGTGCTGA |
| STEAP1 (reverse) | AAGCTCGGCAGGACAATCAA |
| DUSP6 (forward) | GTTGGAGGAGTTCGGCATCA |
| DUSP6 (reverse) | GACACCACAGTTTTTGCCCC |
| LRRC75A (forward) | CAAGCGATCCCCAAAACAGG |
| LRRC75A (reverse) | GTCTGAACCGCACCTACAGT |
| CCL24 (forward) | CTGCACTGGGTCCAGAAGTT |
| CCL24 (reverse) | AAGCTTGGGGCATCTCTGC |
| IL11 (forward) | AGCCGCTCTCTTCTTGTGTC |
| IL11 (reverse) | TTCCCTCGTGTAAGGCACAG |
| GAPDH (forward) | TGACACCCACTCTTCCACCTTC |
| GAPDH (reverse) | CGGTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCA |
| siRNA Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| si-PTGS2 | Sense | GCUUUAGGCUGAAGCCCUATT |
| Antisense | UAGGGCUUCAGCCUAAAGCTT | |
| si-NC | Sense | UUCUUCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| Antisense | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, W.; Qiu, C. LncRNA LOC610012 Inhibits Canine Mammary Tumor Activity via the PTGS2/EP3 and GSK3β Signaling Pathways. Cells 2025, 14, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130974
Zhang B, He L, Wang X, Liu W, Li Y, Wang Y, Feng H, Li W, Qiu C. LncRNA LOC610012 Inhibits Canine Mammary Tumor Activity via the PTGS2/EP3 and GSK3β Signaling Pathways. Cells. 2025; 14(13):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130974
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bohan, Lixin He, Xiao Wang, Wenjing Liu, Yuxin Li, Yinan Wang, Huili Feng, Wenxuan Li, and Changwei Qiu. 2025. "LncRNA LOC610012 Inhibits Canine Mammary Tumor Activity via the PTGS2/EP3 and GSK3β Signaling Pathways" Cells 14, no. 13: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130974
APA StyleZhang, B., He, L., Wang, X., Liu, W., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Feng, H., Li, W., & Qiu, C. (2025). LncRNA LOC610012 Inhibits Canine Mammary Tumor Activity via the PTGS2/EP3 and GSK3β Signaling Pathways. Cells, 14(13), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130974







