Neuronal Damage in Murine Experimental Cerebral Malaria, Implications for Neuronal Repair and Sequelae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of Floating Brain Sections
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
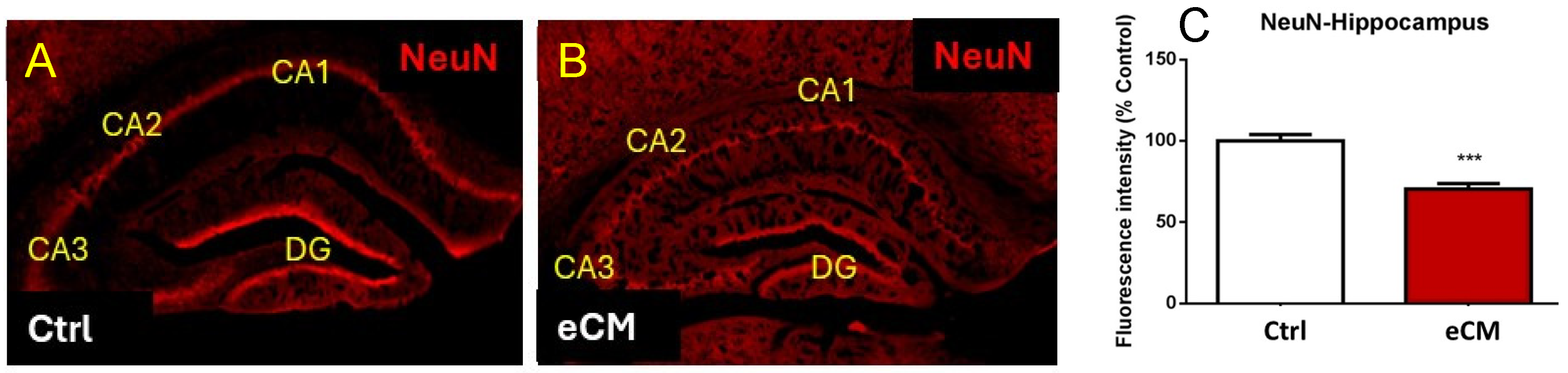
3.1. Neuronal Damage and Altered Morphology in eCM
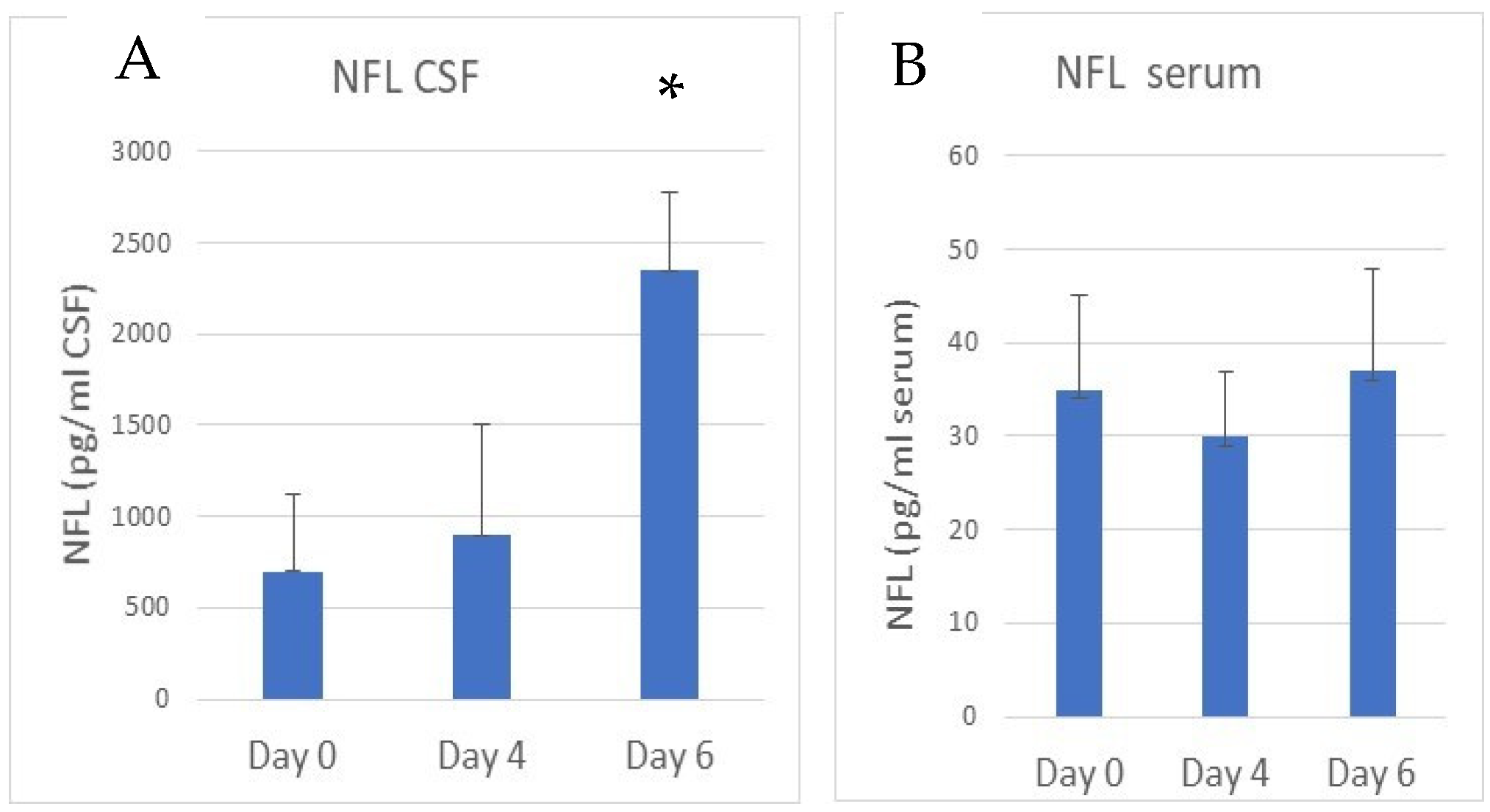
3.2. Increased NFL and Decreased MBP Immunostaining in the Hippocampus in eCM
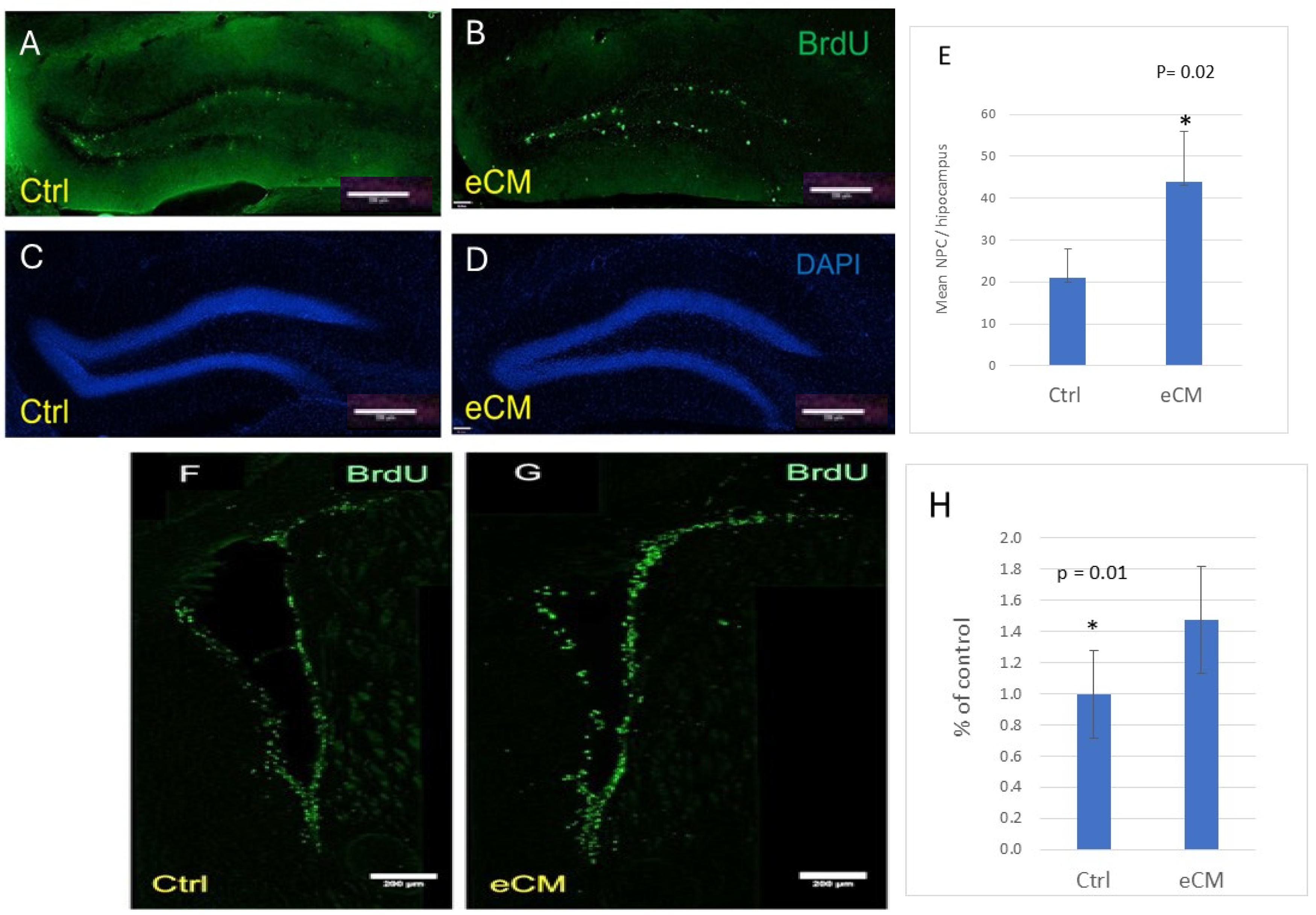
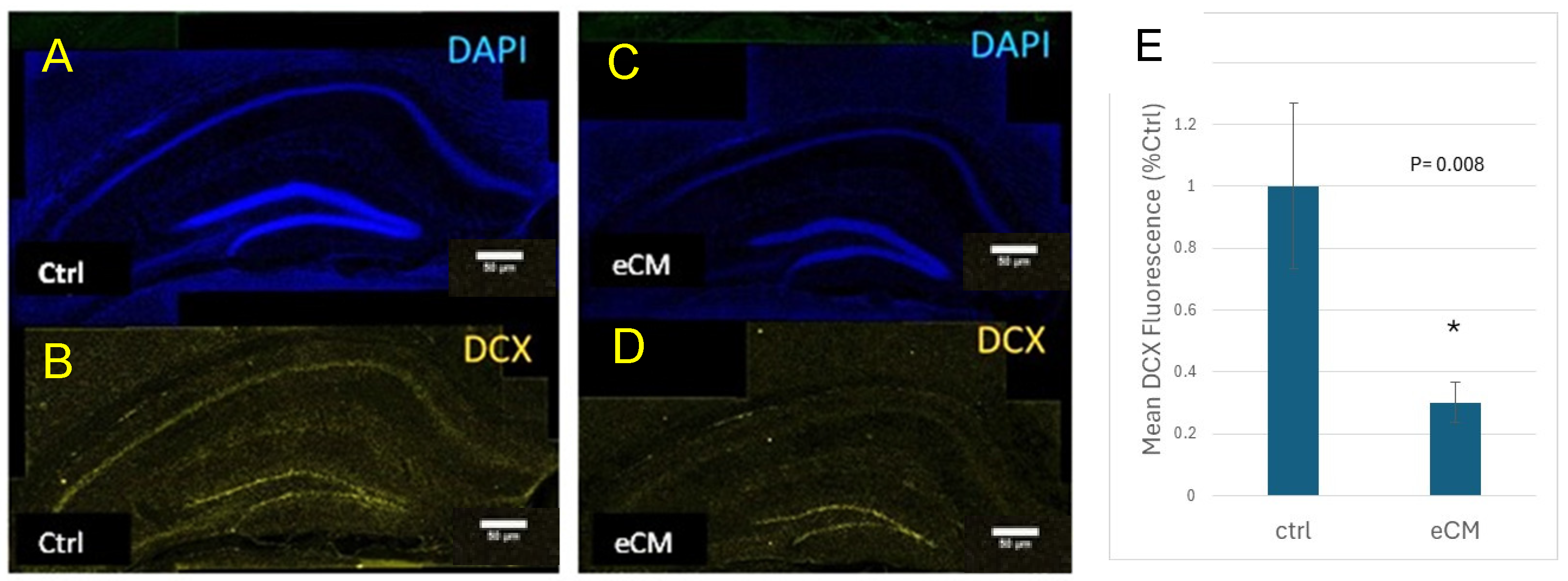
3.3. Decrease in Immature Neurons and Increased Neuroprogenitors in the Hippocampus During eCM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| eCM | experimental Cerebral Malaria |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DCX | Double Cortin |
| DG | Dentate Gyrus |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care Committee |
| NFL | neurofilament fragments |
| PbA | Plasmodium Berghei ANKA |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PFA | paraformaldehyde |
| PRBC | Plasmodium infected red blood cells |
References
- Weiss, D.J.; Lucas, T.C.D.; Nguyen, M.; Nandi, A.K.; Bisanzio, D.; Battle, K.E.; Cameron, E.; Twohig, K.A.; Pfeffer, D.A.; Rozier, J.A.; et al. Mapping the global prevalence, incidence, and mortality of Plasmodium falciparum, 2000–2017: A spatial and temporal modelling study. Lancet 2019, 394, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2024: Addressing Inequity in the Global Malaria Response; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; ISBN 978-92-4-010444-0. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.A.; Mung’ala-Odera, V.; Neville, B.G.; Murira, G.; Mturi, N.; Musumba, C.; Newton, C.R. Persistent neurocognitive impairments associated with severe falciparum malaria in Kenyan children. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Idro, R.; Carter, J.A.; Fegan, G.; Neville, B.G.; Newton, C.R. Risk factors for persisting neurological and cognitive impairments following cerebral malaria. Arch. Dis. Child. 2006, 91, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Idro, R.; Kakooza-Mwesige, A.; Balyejjussa, S.; Mirembe, G.; Mugasha, C.; Tugumisirize, J.; Byarugaba, J. Severe neurological sequelae and behaviour problems after cerebral malaria in Ugandan children. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- John, C.C.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Opoka, R.O.; Park, G.S.; Orchard, P.J.; Jurek, A.M.; Idro, R.; Byarugaba, J.; Boivin, M.J. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokine levels and cognitive impairment in cerebral malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Langfitt, J.T.; McDermott, M.P.; Brim, R.; Mboma, S.; Potchen, M.J.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Seydel, K.B.; Semrud-Clikeman, M.; Taylor, T.E. Neurodevelopmental Impairments 1 Year After Cerebral Malaria. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20181026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, M.; Carter, J.A.; Newton, C.R. The effect of Plasmodium falciparum on cognition: A systematic review. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbeck, G.L.; Beare, N.; Lewallen, S.; Glover, S.J.; Molyneux, M.E.; Kaplan, P.W.; Taylor, T.E. Identification of malaria retinopathy improves the specificity of the clinical diagnosis of cerebral malaria: Findings from a prospective cohort study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kariuki, S.M.; Abubakar, A.; Newton, C.R.; Kihara, M. Impairment of executive function in Kenyan children exposed to severe falciparum malaria with neurological involvement. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carter, J.A.; Murira, G.M.; Ross, A.J.; Mung’ala-Odera, V.; Newton, C.R. Speech and language sequelae of severe malaria in Kenyan children. Brain Inj. 2003, 17, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idro, R.; Marsh, K.; John, C.; Newton, C. Cerebral malaria: Mechanisms of brain injury and strategies for improved neurocognitive outcome. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangirana, P.; Menk, J.; John, C.C.; Boivin, M.J.; Hodges, J.S. The association between cognition and academic performance in Ugandan children surviving malaria with neurological involvement. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruiseñor-Escudero, H.; Familiar, I.; Nyakato, M.; Kutessa, A.; Namukooli, J.; Ssesanga, T.; Joyce, C.; Laughton, B.; Grab, J.; Chernoff, M.; et al. Building capacity in neurodevelopment assessment of children in sub-Saharan Africa: A quality assurance model to implement standardized neurodevelopment testing. Child. Neuropsychol. 2019, 25, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosa-Gonçalves, P.; Ribeiro-Gomes, F.L.; Daniel-Ribeiro, C.T. Malaria Related Neurocognitive Deficits and Behavioral Alterations. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 829413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ssemata, A.S.; Nakitende, A.J.; Kizito, S.; Thomas, M.R.; Islam, S.; Bangirana, P.; Nakasujja, N.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Tran, T.M.; et al. Association of severe malaria with cognitive and behavioural outcomes in low- and middle-income countries: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Malar. J. 2023, 22, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dorovini-Zis, K.; Schmidt, K.; Huynh, H.; Fu, W.; Whitten, R.O.; Milner, D.; Kamiza, S.; Molyneux, M.; Taylor, T.E. The neuropathology of fatal cerebral malaria in malawian children. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2146–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- White, N.J.; Warrell, D.A.; Looareesuwan, S.; Chanthavanich, P.; Phillips, R.E.; Pongpaew, P. Pathophysiological and prognostic significance of cerebrospinal-fluid lactate in cerebral malaria. Lancet 1985, 1, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacPherson, G.G.; Warrell, M.J.; White, N.J.; Looareesuwan, S.; Warrell, D.A. Human cerebral malaria. A quantitative ultrastructural analysis of parasitized erythrocyte sequestration. Am. J. Pathol. 1985, 119, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hempel, C.; Combes, V.; Hunt, N.H.; Kurtzhals, J.A.; Grau, G.E. CNS hypoxia is more pronounced in murine cerebral than noncerebral malaria and is reversed by erythropoietin. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beare, N.A.; Harding, S.P.; Taylor, T.E.; Lewallen, S.; Molyneux, M.E. Perfusion abnormalities in children with cerebral malaria and malarial retinopathy. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Medana, I.M.; Turner, G.D. Human cerebral malaria and the blood-brain barrier. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, J.; Dorovini-Zis, K.; Taylor, T.E.; Molyneux, M.E.; Beare, N.A.; Kamiza, S.; White, V.A. Correlation of hemorrhage, axonal damage, and blood-tissue barrier disruption in brain and retina of Malawian children with fatal cerebral malaria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Penet, M.F.; Viola, A.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Le Fur, Y.; Duhamel, G.; Kober, F.; Ibarrola, D.; Izquierdo, M.; Coltel, N.; Gharib, B.; et al. Imaging experimental cerebral malaria in vivo: Significant role of ischemic brain edema. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7352–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Seydel, K.B.; Kampondeni, S.D.; Valim, C.; Potchen, M.J.; Milner, D.A.; Muwalo, F.W.; Birbeck, G.L.; Bradley, W.G.; Fox, L.L.; Glover, S.J.; et al. Brain swelling and death in children with cerebral malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sahu, P.K.; Hoffmann, A.; Majhi, M.; Pattnaik, R.; Patterson, C.; Mahanta, K.C.; Mohanty, A.K.; Mohanty, R.R.; Joshi, S.; Mohanty, A.; et al. Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Reveals Different Courses of Disease in Pediatric and Adult Cerebral Malaria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e2387–e2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hunt, N.H.; Grau, G.E. Cytokines: Accelerators and brakes in the pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, A.L.; Lafferty, E.I.; Lovegrove, F.E.; Krudsood, S.; Tangpukdee, N.; Liles, W.C.; Kain, K.C. Whole blood angiopoietin-1 and -2 levels discriminate cerebral and severe (non-cerebral) malaria from uncomplicated malaria. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Conroy, A.L.; Hawkes, M.; McDonald, C.R.; Kim, H.; Higgins, S.J.; Barker, K.R.; Namasopo, S.; Opoka, R.O.; John, C.C.; Liles, W.C.; et al. Host Biomarkers Are Associated With Response to Therapy and Long-Term Mortality in Pediatric Severe Malaria. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lucchi, N.W.; Jain, V.; Wilson, N.O.; Singh, N.; Udhayakumar, V.; Stiles, J.K. Potential serological biomarkers of cerebral malaria. Dis. Markers 2011, 31, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jain, V.; Lucchi, N.W.; Wilson, N.O.; Blackstock, A.J.; Nagpal, A.C.; Joel, P.K.; Singh, M.P.; Udhayakumar, V.; Stiles, J.K.; Singh, N. Plasma levels of angiopoietin-1 and -2 predict cerebral malaria outcome in Central India. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stins, M.F.; Mtaja, A.; Mulendele, E.; Mwimbe, D.W.; Pinilla, G.; Mutengo, M.; Pardo, C.A.; Chipeta, J. Elevated brain derived neurotrophic factor in plasma and interleukin-6 levels in cerebrospinal fluid in meningitis compared to cerebral malaria. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 450, 120663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stins, M.F.; Mtaja, A.; Mulendele, E.; Mwimbe, D.; Pinilla-Monsalve, G.D.; Mutengo, M.; Pardo, C.A.; Chipeta, J. Inflammation and Elevated Osteopontin in Plasma and CSF in Cerebral Malaria Compared to Plasmodium-Negative Neurological Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hunt, N.H.; Grau, G.E.; Engwerda, C.; Barnum, S.R.; van der Heyde, H.; Hansen, D.S.; Schofield, L.; Golenser, J. Murine cerebral malaria: The whole story. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, P.K.; Duffy, F.J.; Dankwa, S.; Vishnyakova, M.; Majhi, M.; Pirpamer, L.; Vigdorovich, V.; Bage, J.; Maharana, S.; Mandala, W.; et al. Determinants of brain swelling in pediatric and adult cerebral malaria. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, H.; Tong, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Yan, B. Emotion Regulation of Hippocampus Using Real-Time fMRI Neurofeedback in Healthy Human. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bartsch, T.; Döhring, J.; Rohr, A.; Jansen, O.; Deuschl, G. CA1 neurons in the human hippocampus are critical for autobiographical memory, mental time travel, and autonoetic consciousness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17562–17567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Llorens-Martin, M.; Rabano, A.; Avila, J. The Ever-Changing Morphology of Hippocampal Granule Neurons in Physiology and Pathology. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cho, K.O.; Lybrand, Z.R.; Ito, N.; Brulet, R.; Tafacory, F.; Zhang, L.; Good, L.; Ure, K.; Kernie, S.G.; Birnbaum, S.G.; et al. Aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis contributes to epilepsy and associated cognitive decline. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Belarbi, K.; Arellano, C.; Ferguson, R.; Jopson, T.; Rosi, S. Chronic neuroinflammation impacts the recruitment of adult-born neurons into behaviorally relevant hippocampal networks. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Llorens-Martin, M.; Jurado-Arjona, J.; Fuster-Matanzo, A.; Hernandez, F.; Rabano, A.; Avila, J. Peripherally triggered and GSK-3beta-driven brain inflammation differentially skew adult hippocampal neurogenesis, behavioral pattern separation and microglial activation in response to ibuprofen. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Souza, J.B.; Riley, E.M. Cerebral malaria: The contribution of studies in animal models to our understanding of immunopathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.P.; Babu, P.P. NADPH Oxidase: A Possible Therapeutic Target for Cognitive Impairment in Experimental Cerebral Malaria. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 800–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Reznik, S.E.; Spray, D.C.; Weiss, L.M.; Tanowitz, H.B.; Gulinello, M.; Desruisseaux, M.S. Persistent cognitive and motor deficits after successful antimalarial treatment in murine cerebral malaria. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Akide Ndunge, O.B.; Shikani, H.J.; Dai, M.; Freeman, B.D.; Desruisseaux, M.S. Effects of anti-tau immunotherapy on reactive microgliosis, cerebral endotheliopathy, and cognitive function in an experimental model of cerebral malaria. J. Neurochem. 2023, 167, 441–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Stoltenburg-Didinger, G.; Neifer, S.; Bienzle, U.; Eling, W.M.; Kremsner, P.G. Selective damage of hippocampal neurons in murine cerebral malaria prevented by pentoxifylline. J. Neurol. Sci. 1993, 114, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strangward, P.; Haley, M.J.; Shaw, T.N.; Schwartz, J.M.; Greig, R.; Mironov, A.; de Souza, J.B.; Cruickshank, S.M.; Craig, A.G.; Milner, D.A., Jr.; et al. A quantitative brain map of experimental cerebral malaria pathology. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Langhorne, J.; Buffet, P.; Galinski, M.; Good, M.; Harty, J.; Leroy, D.; Mota, M.M.; Pasini, E.; Renia, L.; Riley, E.; et al. The relevance of non-human primate and rodent malaria models for humans. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barrera, V.; Haley, M.J.; Strangward, P.; Attree, E.; Kamiza, S.; Seydel, K.B.; Taylor, T.E.; Milner, D.A., Jr.; Craig, A.G.; Couper, K.N. Comparison of CD8(+) T Cell Accumulation in the Brain During Human and Murine Cerebral Malaria. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yanez, D.M.; Batchelder, J.; van der Heyde, H.C.; Manning, D.D.; Weidanz, W.P. Gamma delta T-cell function in pathogenesis of cerebral malaria in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gramaglia, I.; Velez, J.; Chang, Y.S.; Caparros-Wanderley, W.; Combes, V.; Grau, G.; Stins, M.F.; van der Heyde, H.C. Citrulline protects mice from experimental cerebral malaria by ameliorating hypoargininemia, urea cycle changes and vascular leak. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gramaglia, I.; Sobolewski, P.; Meays, D.; Contreras, R.; Nolan, J.P.; Frangos, J.A.; Intaglietta, M.; van der Heyde, H.C. Low nitric oxide bioavailability contributes to the genesis of experimental cerebral malaria. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramaglia, I.; Velez, J.; Combes, V.; Grau, G.E.; Wree, M.; van der Heyde, H.C. Platelets activate a pathogenic response to blood-stage Plasmodium infection but not a protective immune response. Blood 2017, 129, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, M.H.; Wang, T.; Jang, M.H.; Steiner, J.; Haughey, N.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H.; Nath, A.; Venkatesan, A. Rescue of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a mouse model of HIV neurologic disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Griffin, D.E. CSF changes during acute meningoencephalitis in mice caused by encephalomyocarditis virus. Ann. Neurol. 1981, 10, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weidanz, W.P.; LaFleur, G.; Brown, A.; Burns, J.M., Jr.; Gramaglia, I.; van der Heyde, H.C. Gammadelta T cells but not NK cells are essential for cell-mediated immunity against Plasmodium chabaudi malaria. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4331–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Medana, I.M.; Day, N.P.; Hien, T.T.; Mai, N.T.; Bethell, D.; Phu, N.H.; Farrar, J.; Esiri, M.M.; White, N.J.; Turner, G.D. Axonal injury in cerebral malaria. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Barro, C.; Zetterberg, H. Neurological symptoms and blood neurofilament light levels. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2021, 144, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wai, C.H.; Jin, J.; Cyrklaff, M.; Genoud, C.; Funaya, C.; Sattler, J.; Maceski, A.; Meier, S.; Heiland, S.; Lanzer, M.; et al. Neurofilament light chain plasma levels are associated with area of brain damage in experimental cerebral malaria. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Balanza, N.; Francis, C.K.; Crowley, V.M.; Weckman, A.M.; Zhong, K.; Baro, B.; Varo, R.; Bassat, Q.; Kain, K.C. Reply to Zayet et al. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 229, 296–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, D.; Gopinadhan, A.; Soto, A.; Bangirana, P.; Opoka, R.O.; Conroy, A.L.; Saykin, A.J.; Kawata, K.; John, C.C. Blood biomarkers of neuronal injury in paediatric cerebral malaria and severe malarial anaemia. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Datta, D.; Conroy, A.L.; Castelluccio, P.F.; Ssenkusu, J.M.; Park, G.S.; Opoka, R.O.; Bangirana, P.; Idro, R.; Saykin, A.J.; John, C.C. Elevated Cerebrospinal Fluid Tau Protein Concentrations on Admission Are Associated With Long-term Neurologic and Cognitive Impairment in Ugandan Children With Cerebral Malaria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leitner, D.F.; Stoute, J.A.; Landmesser, M.; Neely, E.; Connor, J.R. The HFE genotype and a formulated diet controlling for iron status attenuate experimental cerebral malaria in mice. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, C.; Hyttel, P.; Staalsø, T.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Kurtzhals, J.A. Erythropoietin treatment alleviates ultrastructural myelin changes induced by murine cerebral malaria. Malar. J. 2012, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Noël, A.; Zhou, L.; Foveau, B.; Sjöström, P.J.; LeBlanc, A.C. Differential susceptibility of striatal, hippocampal and cortical neurons to Caspase-6. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1319–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Medana, I.M.; Day, N.P.; Hien, T.T.; Mai, N.T.; Bethell, D.; Phu, N.H.; Turner, G.D.; Farrar, J.; White, N.J.; Esiri, M.M. Cerebral calpain in fatal falciparum malaria. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2007, 33, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villabona-Rueda, A.; Erice, C.; Pardo, C.A.; Stins, M.F. The Evolving Concept of the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB): From a Single Static Barrier to a Heterogeneous and Dynamic Relay Center. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szklarczyk, A.; Stins, M.; Milward, E.A.; Ryu, H.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Sullivan, D.; Conant, K. Glial activation and matrix metalloproteinase release in cerebral malaria. J. Neurovirol. 2007, 13, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochman, S.E.; Madaline, T.F.; Wassmer, S.C.; Mbale, E.; Choi, N.; Seydel, K.B.; Whitten, R.O.; Varughese, J.; Grau, G.E.; Kamiza, S.; et al. Fatal Pediatric Cerebral Malaria Is Associated with Intravascular Monocytes and Platelets That Are Increased with HIV Coinfection. MBio 2015, 6, e01390-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medana, I.M.; Idro, R.; Newton, C.R. Axonal and astrocyte injury markers in the cerebrospinal fluid of Kenyan children with severe malaria. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 258, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandala, W.L.; Msefula, C.L.; Gondwe, E.N.; Drayson, M.T.; Molyneux, M.E.; MacLennan, C.A. Cytokine Profiles in Malawian Children Presenting with Uncomplicated Malaria, Severe Malarial Anemia, and Cerebral Malaria. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00533-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tran, H.; Gupta, M.; Gupta, K. Targeting novel mechanisms of pain in sickle cell disease. Blood 2017, 130, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wassmer, S.C.; Moxon, C.A.; Taylor, T.; Grau, G.E.; Molyneux, M.E.; Craig, A.G. Vascular endothelial cells cultured from patients with cerebral or uncomplicated malaria exhibit differential reactivity to TNF. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bonaguidi, M.A.; Stadel, R.P.; Berg, D.A.; Sun, J.; Ming, G.L.; Song, H. Diversity of Neural Precursors in the Adult Mammalian Brain. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Satish Bollimpelli, V.; Kondapi, A.K. Differential sensitivity of immature and mature ventral mesencephalic neurons to rotenone induced neurotoxicity in vitro. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 30, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, B.; Mrowetz, H.; Kreutzer, C.; Rotheneichner, P.; Zaunmair, P.; Lange, S.; Coras, R.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Rivera, F.J.; Aigner, L. DCX(+) neuronal progenitors contribute to new oligodendrocytes during remyelination in the hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bennett, L.; Yang, M.; Enikolopov, G.; Iacovitti, L. Circumventricular organs: A novel site of neural stem cells in the adult brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2009, 41, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Miranda, A.S.; Brant, F.; Campos, A.C.; Vieira, L.B.; Rocha, N.P.; Cisalpino, D.; Binda, N.S.; Rodrigues, D.H.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Machado, F.S.; et al. Evidence for the contribution of adult neurogenesis and hippocampal cell death in experimental cerebral malaria cognitive outcome. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 920–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosun, M.; Semerci, F.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Heterogeneity of Stem Cells in the Hippocampus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1169, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Clavijo, L.; Martín-Suárez, S. The differential response to neuronal hyperexcitation and neuroinflammation of the hippocampal neurogenic niche. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1186256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Clark, D.J.; Bond, C.; Andrews, A.; Muller, D.J.; Sarkisian, A.; Opoka, R.O.; Idro, R.; Bangirana, P.; Witten, A.; Sausen, N.J.; et al. Admission Clinical and EEG Features Associated With Mortality and Long-term Neurologic and Cognitive Outcomes in Pediatric Cerebral Malaria. Neurology 2023, 101, e1307–e1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bangirana, P.; Opoka, R.O.; Boivin, M.J.; Idro, R.; Hodges, J.S.; John, C.C. Neurocognitive domains affected by cerebral malaria and severe malarial anemia in children. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2016, 46, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stins, M.F.; Gramaglia, I.; Velez, J.; Pardo, C.A.; van der Heyde, H. Neuronal Damage in Murine Experimental Cerebral Malaria, Implications for Neuronal Repair and Sequelae. Cells 2025, 14, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110807
Stins MF, Gramaglia I, Velez J, Pardo CA, van der Heyde H. Neuronal Damage in Murine Experimental Cerebral Malaria, Implications for Neuronal Repair and Sequelae. Cells. 2025; 14(11):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110807
Chicago/Turabian StyleStins, Monique F., Irene Gramaglia, Joyce Velez, Carlos A. Pardo, and Henri van der Heyde. 2025. "Neuronal Damage in Murine Experimental Cerebral Malaria, Implications for Neuronal Repair and Sequelae" Cells 14, no. 11: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110807
APA StyleStins, M. F., Gramaglia, I., Velez, J., Pardo, C. A., & van der Heyde, H. (2025). Neuronal Damage in Murine Experimental Cerebral Malaria, Implications for Neuronal Repair and Sequelae. Cells, 14(11), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110807






