VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptor Heterozygosity Confers Distinct Biological Properties to BV2 Microglial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Generation of VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− BV2 Microglial Cell Lines
2.3. RNA Interference and Transfection of BV2 Microglial Cells
2.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Immunocytochemistry
2.7. Nitric Oxide (Griess Assay)
2.8. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Staining (Flow Cytometry)
2.9. Real-Time Assessment of Cell Motility (Wound Healing Assay)
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Validation of VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptor Heterozygosity in BV2 Microglia
3.2. VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− BV2 Microglial Cell Lines Exhibit Increased Inflammatory Profiles
3.3. VPAC1 and VPAC2 Haploinsufficiency Differentially Affects the Survivability of BV2 Microglial Cells
3.4. VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− BV2 Microglia Show Opposite Baseline Activation of the Unfolded Protein Response
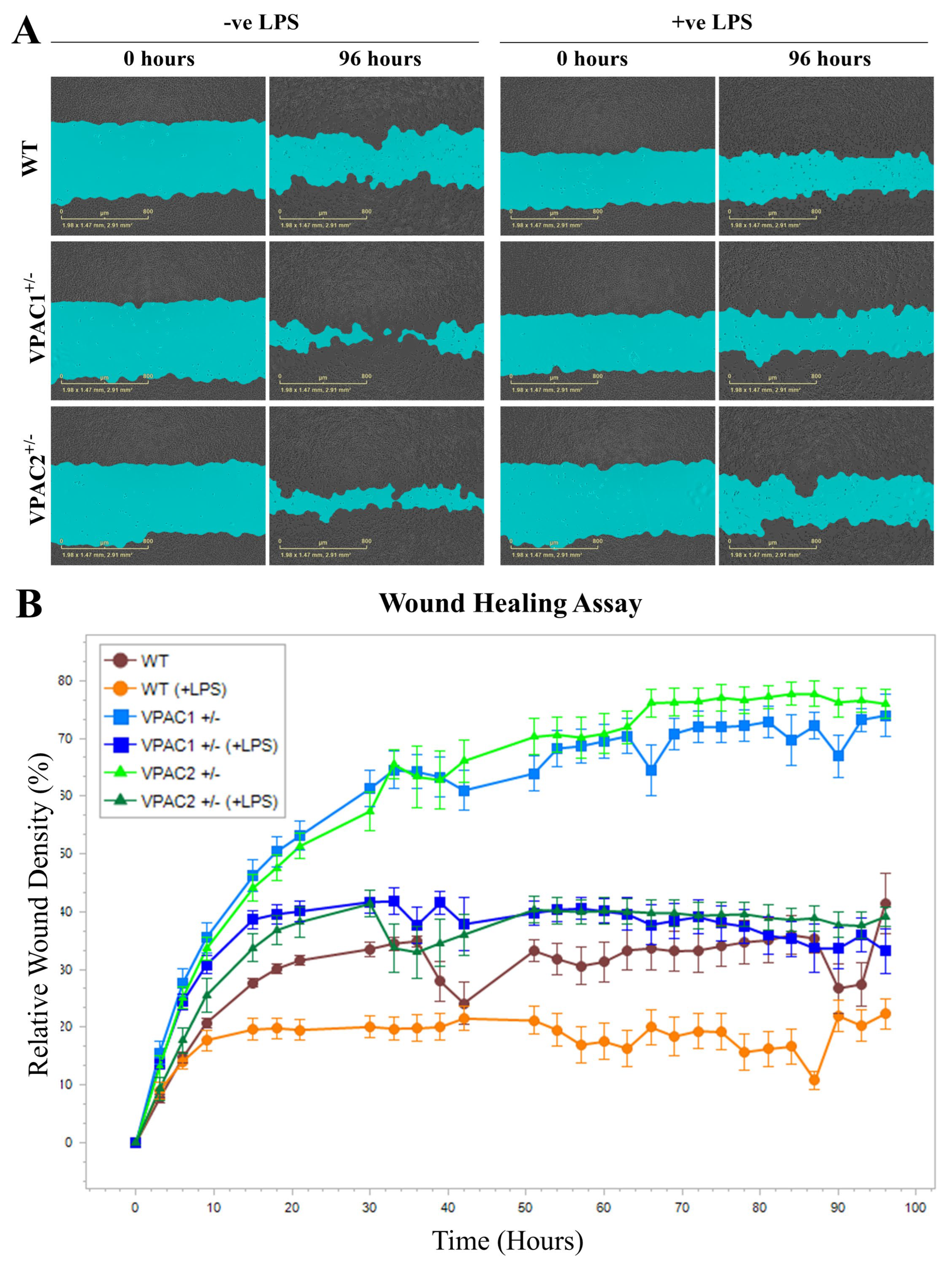
3.5. Increased Baseline Mobility of VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− BV2 Microglia
3.6. Partial Deletion of VPAC1 and VPAC2 Enhances Pro-Inflammatory Gene Expression in BV2 Microglia
3.7. VPAC2+/− Microglia Release Increased NO in Response to a Lipopolysaccharide Challenge
3.8. VPAC1 Heterozygosity Renders BV2 Cells More Susceptible to LPS-Induced Apoptosis
3.9. VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− Microglia Display Opposite UPR Activation Patterns upon LPS Challenge
3.10. Lipopolysaccharide Treatment Reduces BV2 Microglia Cell Motility Irrespective of Genotype
4. Discussion
4.1. Defining Two Haploinsufficient Genotypes and the Essential Role of VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptors in BV2 Microglial Homeostasis
4.2. VPAC Receptors and Their Role in the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR)
4.3. Differential Baseline UPR Activation in VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− Cells
4.4. Divergent LPS-Induced UPR Dysregulation in VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− Cells
4.5. Cell Motility and Inflammatory Responses in VPAC1+/− and VPAC2+/− Cells
4.6. Study Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. 2), 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidpour, A.; Morgun, A.V.; Boitsova, E.B.; Malinovskaya, N.A.; Martynova, G.P.; Khilazheva, E.D.; Kopylevich, N.V.; Gertsog, G.E.; Salmina, A.B. Neuroinflammation and Infection: Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Dysfunction of Neurovascular Unit. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Basic mechanisms of neurodegeneration: A critical update. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 457–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochocka, M.; Diniz, B.S.; Leszek, J. Inflammatory Response in the CNS: Friend or Foe? Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8071–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelobaba, I.; Savic, D.; Lavrnja, I. Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroinflammation: The Overview of Current and Prospective Therapies. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 693–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; El Khoury, J.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.S.; Koh, S.-H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wofford, K.L.; Loane, D.J.; Cullen, D.K. Acute drivers of neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury. Neural. Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvineau, A.; Ceraudo, E.; Tan, Y.V.; Nicole, P.; Laburthe, M. The VPAC1 receptor: Structure and function of a class B GPCR prototype. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, T.; Nakamachi, T.; Shioda, S. Discovery of PACAP and its receptors in the brain. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejda, A.; Sokolowska, P.; Nowak, J.Z. Neuroprotective potential of three neuropeptides PACAP, VIP and PHI. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soles-Tarres, I.; Cabezas-Llobet, N.; Vaudry, D.; Xifro, X. Protective Effects of Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide and Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Against Cognitive Decline in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, L.; Finlayson, K. VPAC and PAC receptors: From ligands to function. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 294–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaudry, D.; Falluel-Morel, A.; Bourgault, S.; Basille, M.; Burel, D.; Wurtz, O.; Fournier, A.; Chow, B.K.; Hashimoto, H.; Galas, L.; et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors: 20 years after the discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 283–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, M.; Miyakawa, H.; Wada, K.; Furuta, A. Activation of the VIP/VPAC2 system induces reactive astrocytosis associated with increased expression of glutamate transporters. Brain Res. 2011, 1383, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, G.; Leggio, G.M.; Marzagalli, R.; Al-Badri, G.; Drago, F.; Castorina, A. Identification of Dysregulated microRNA Networks in Schwann Cell-Like Cultures Exposed to Immune Challenge: Potential Crosstalk with the Protective VIP/PACAP Neuropeptide System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castorina, A.; Scuderi, S.; D’Amico, A.G.; Drago, F.; D’Agata, V. PACAP and VIP increase the expression of myelin-related proteins in rat schwannoma cells: Involvement of PAC1/VPAC2 receptor-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmar, A.J.; Fahrenkrug, J.; Gozes, I.; Laburthe, M.; May, V.; Pisegna, J.R.; Vaudry, D.; Vaudry, H.; Waschek, J.A.; Said, S.I. Pharmacology and functions of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide: IUPHAR review 1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduna, T.; Lelievre, V. Neuropeptides shaping the central nervous system development: Spatiotemporal actions of VIP and PACAP through complementary signaling pathways. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvineau, A.; Laburthe, M. VPAC receptors: Structure, molecular pharmacology and interaction with accessory proteins. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Farooqi, N.; O’Brien, K.; Gran, B. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, C.; Jayaram, B.; Becquet, L.; Wang, Y.; O’Dorisio, M.S.; Waschek, J.A.; Tan, Y.-V. VPAC1 receptor (Vipr1)-deficient mice exhibit ameliorated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, with specific deficits in the effector stage. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.V.; Abad, C.; Wang, Y.; Lopez, R.; Waschek, J. VPAC2 (vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor type 2) receptor deficient mice develop exacerbated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with increased Th1/Th17 and reduced Th2/Treg responses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 44, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpa, A.; Bento, M.; Caulino-Rocha, A.; Pawlak, S.; Cunha-Reis, D. Opposing reduced VPAC(1) and enhanced VPAC(2) VIP receptors in the hippocampus of the Li(2+)-pilocarpine rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 158, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.B.; Nobuta, H.; Abad, C.; Lee, S.K.; Bala, N.; Zhu, C.; Richter, F.; Chesselet, M.F.; Waschek, J.A. PACAP deficiency sensitizes nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons to paraquat-induced damage and modulates central and peripheral inflammatory activation in mice. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deczkowska, A.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Weiner, A.; Colonna, M.; Schwartz, M.; Amit, I. Disease-Associated Microglia: A Universal Immune Sensor of Neurodegeneration. Cell 2018, 173, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goursaud, S.; Focant, M.C.; Berger, J.V.; Nizet, Y.; Maloteaux, J.M.; Hermans, E. The VPAC2 agonist peptide histidine isoleucine (PHI) up-regulates glutamate transport in the corpus callosum of a rat model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (hSOD1G93A) by inhibiting caspase-3 mediated inactivation of GLT-1a. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3674–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunia, J.; Niaz, A.; Mandwie, M.; Thomas Broome, S.; Keay, K.A.; Waschek, J.A.; Al-Badri, G.; Castorina, A. PACAP and VIP Modulate LPS-Induced Microglial Activation and Trigger Distinct Phenotypic Changes in Murine BV2 Microglial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas Broome, S.; Fisher, T.; Faiz, A.; Keay, K.A.; Musumeci, G.; Al-Badri, G.; Castorina, A. Assessing the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Anxiolytic Drug Buspirone Using CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglial Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castorina, A.; D’Amico, A.; Scuderi, S.; Leggio, G.; Drago, F.; D’Agata, V. Dopamine D3 receptor deletion increases tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) activity in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 2013, 250, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, J.H.; Ko, H.M.; Suk, K.; Park, E.J.; Choi, D.K. Genome-wide inspection of chromosomal aberrations in microglia BV-2 cells by array-based comparative genomic hybridization. BioChip J. 2009, 3, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Blasi, E.; Barluzzi, R.; Bocchini, V.; Mazzolla, R.; Bistoni, F. Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 27, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, R.; Yeu, Y.; Tyler Piazza, J.; Tan, Z.; Rene Clemenceau, J.; Wu, X.; Barrett, Q.; Herbert, J.; Mathews, D.H.; Kim, J.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9-based mutagenesis frequently provokes on-target mRNA misregulation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Jonakait, G.M.; Ganea, D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit chemokine production in activated microglia. Glia 2002, 39, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, K.; Imai, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Kohsaka, S. Microglia/macrophage-specific protein Iba1 binds to fimbrin and enhances its actin-bundling activity. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Brough, D. Understanding the mechanism of IL-1beta secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: The good, the bad, and the inflamed. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ohgidani, M.; Hata, N.; Inamine, S.; Sagata, N.; Shirouzu, N.; Mukae, N.; Suzuki, S.O.; Hamasaki, H.; Hatae, R.; et al. CD206 Expression in Induced Microglia-Like Cells From Peripheral Blood as a Surrogate Biomarker for the Specific Immune Microenvironment of Neurosurgical Diseases Including Glioma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 670131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withana, M.; Castorina, A. Potential Crosstalk between the PACAP/VIP Neuropeptide System and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Relevance to Multiple Sclerosis Pathophysiology. Cells 2023, 12, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.; Agartz, I.; Ögren, S.O.; Patrone, C.; Lundberg, M. PACAP Protects Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Neurotoxic Effect of Ketamine Associated with Decreased Apoptosis, ER Stress and mTOR Pathway Activation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, A.; Kambe, Y.; Inoue, K.; Tatsukawa, H.; Kurihara, T.; Griffin, M.; Kojima, S.; Miyata, A. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type 1 receptor (PAC1) gene is suppressed by transglutaminase 2 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 32720–32730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Cai, J.; Yan, S.; Huang, Z.; He, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; et al. Phosphorylation at Ser(724) of the ER stress sensor IRE1α governs its activation state and limits ER stress-induced hepatosteatosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, L.N.; Abiraman, K.; Plyler, E.S.; Sprenkle, N.T.; Gibson, S.A.; McFarland, B.C.; Rajbhandari, R.; Rowse, A.L.; Benveniste, E.N.; Meares, G.P. Attenuation of PKR-like ER Kinase (PERK) Signaling Selectively Controls Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-induced Inflammation Without Compromising Immunological Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 15830–15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lively, S.; Schlichter, L.C. The microglial activation state regulates migration and roles of matrix-dissolving enzymes for invasion. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, D.J.; Choi, H.B.; Hines, R.M.; Phillips, A.G.; MacVicar, B.A. Prevention of LPS-induced microglia activation, cytokine production and sickness behavior with TLR4 receptor interfering peptides. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Nance, E.; Alnasser, Y.; Kannan, R.; Kannan, S. Microglial migration and interactions with dendrimer nanoparticles are altered in the presence of neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castorina, A.; Scheller, J.; Keay, K.A.; Marzagalli, R.; Rose-John, S.; Campbell, I.L. Increased Expression of the Neuropeptides PACAP/VIP in the Brain of Mice with CNS Targeted Production of IL-6 Is Mediated in Part by Trans-Signalling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, R.; Sivasathiaseelan, H.; Khan, D.; Zaben, M.; Gray, W. Microglial VPAC1R mediates a novel mechanism of neuroimmune-modulation of hippocampal precursor cells via IL-4 release. Glia 2014, 62, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castorina, A.; Tiralongo, A.; Giunta, S.; Carnazza, M.L.; Rasi, G.; D’Agata, V. PACAP and VIP prevent apoptosis in schwannoma cells. Brain Res. 2008, 1241, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Kontarakis, Z.; Gerri, C.; Nolte, H.; Hölper, S.; Krüger, M.; Stainier, D.Y. Genetic compensation induced by deleterious mutations but not gene knockdowns. Nature 2015, 524, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Brolosy, M.A.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Genetic compensation: A phenomenon in search of mechanisms. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, A.H.; Ziebell, F.; Joberty, G.; Zinn, N.; Mueller, W.F.; Clauder-Münster, S.; Eberhard, D.; Fälth Savitski, M.; Grandi, P.; Jakob, P.; et al. Biological plasticity rescues target activity in CRISPR knock outs. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, I.; Jeandriens, J.; Couvineau, A.; Sanmukh, S.; Latek, D. Signal Transduction by VIP and PACAP Receptors. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Piper, S.J.; Zhao, P.; Miller, L.J.; Wootten, D.; Sexton, P.M. Targeting VIP and PACAP Receptor Signaling: New Insights into Designing Drugs for the PACAP Subfamily of Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Weissman, A.M. The Unfolded Protein Response, Degradation from Endoplasmic Reticulum and Cancer. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Lourie, R.; Das, I.; Chen, A.C.; McGuckin, M.A. The interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza, A.; Carlesso, A.; Chintha, C.; Creedican, S.; Doultsinos, D.; Leuzzi, B.; Luis, A.; McCarthy, N.; Montibeller, L.; More, S.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling—From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 241–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panganiban, R.A.; Park, H.R.; Sun, M.; Shumyatcher, M.; Himes, B.E.; Lu, Q. Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies suppressors of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13384–13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, I.; Leroy, K.; Gaspard, N.; Brion, J.-P.; Robberecht, P. Cell surface targeting of VPAC1 receptors: Evidence for implication of a quality control system and the proteasome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storka, A.; Burian, B.; Führlinger, G.; Clive, B.; Sun, T.; Crevenna, R.; Gsur, A.; Mosgöller, W.; Wolzt, M. VPAC1 receptor expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a human endotoxemia model. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Turner, M.J.; DeLay, M.L.; Klenk, E.I.; Sowders, D.P.; Colbert, R.A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response are linked to synergistic IFN-beta induction via X-box binding protein 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z. New insights into the roles of CHOP-induced apoptosis in ER stress. Acta. Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadomari, S.; Mori, M. Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.W.; Bahader, G.A.; Albassan, M.; Shah, Z.A. The ER chaperone, BIP protects Microglia from ER stress-mediated Apoptosis in Hyperglycemia. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 169, 105573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Martín, H.; Gavilán, E.; Parrado, C.; Burguillos, M.A.; Daza, P.; Ruano, D. Distinct UPR and Autophagic Functions Define Cell-Specific Responses to Proteotoxic Stress in Microglial and Neuronal Cell Lines. Cells 2024, 13, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Jang, H.J.; Hwang, D.H. Toll-like receptor 4-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to impairment of vasodilator action of insulin. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E767–E776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
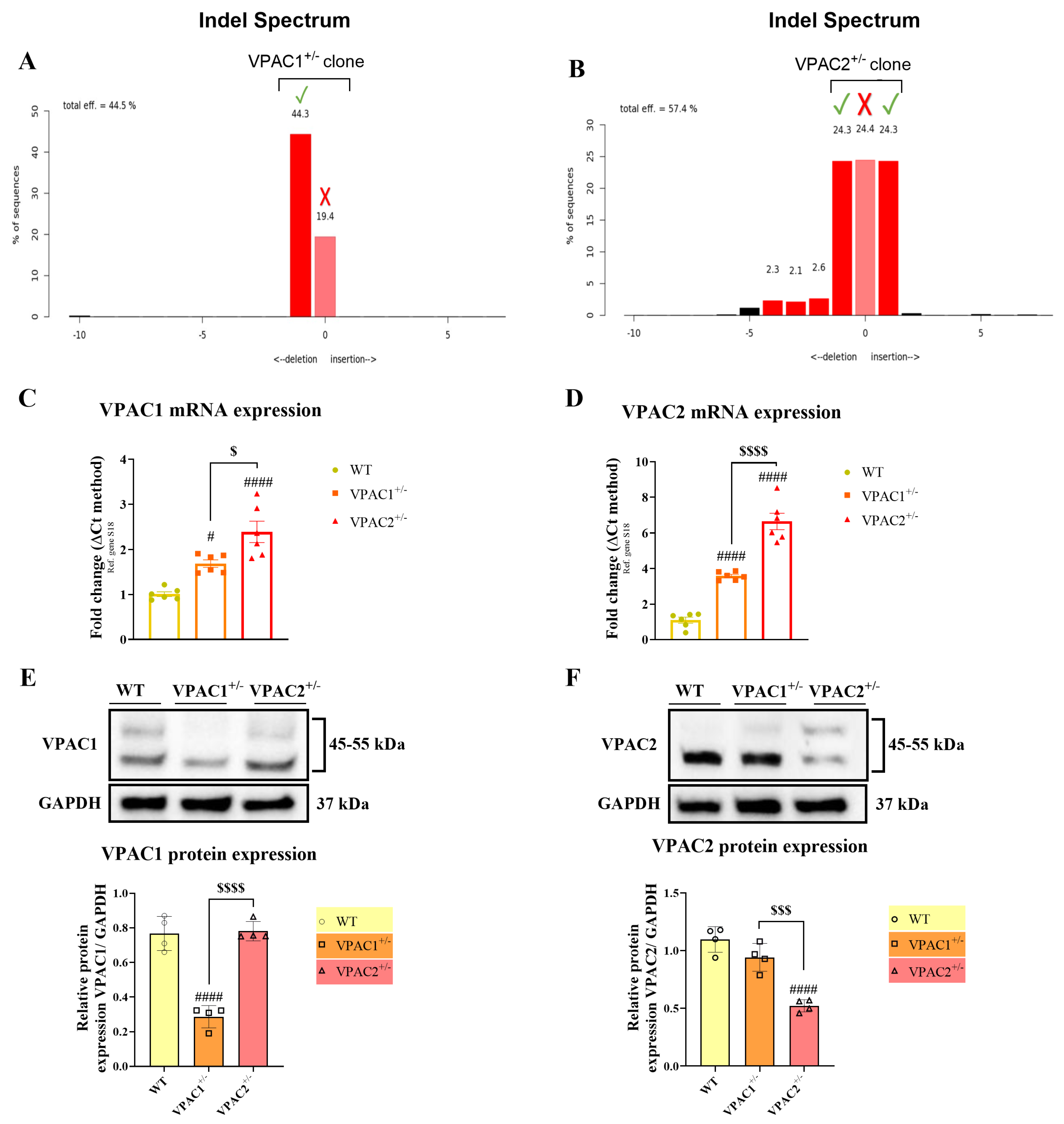
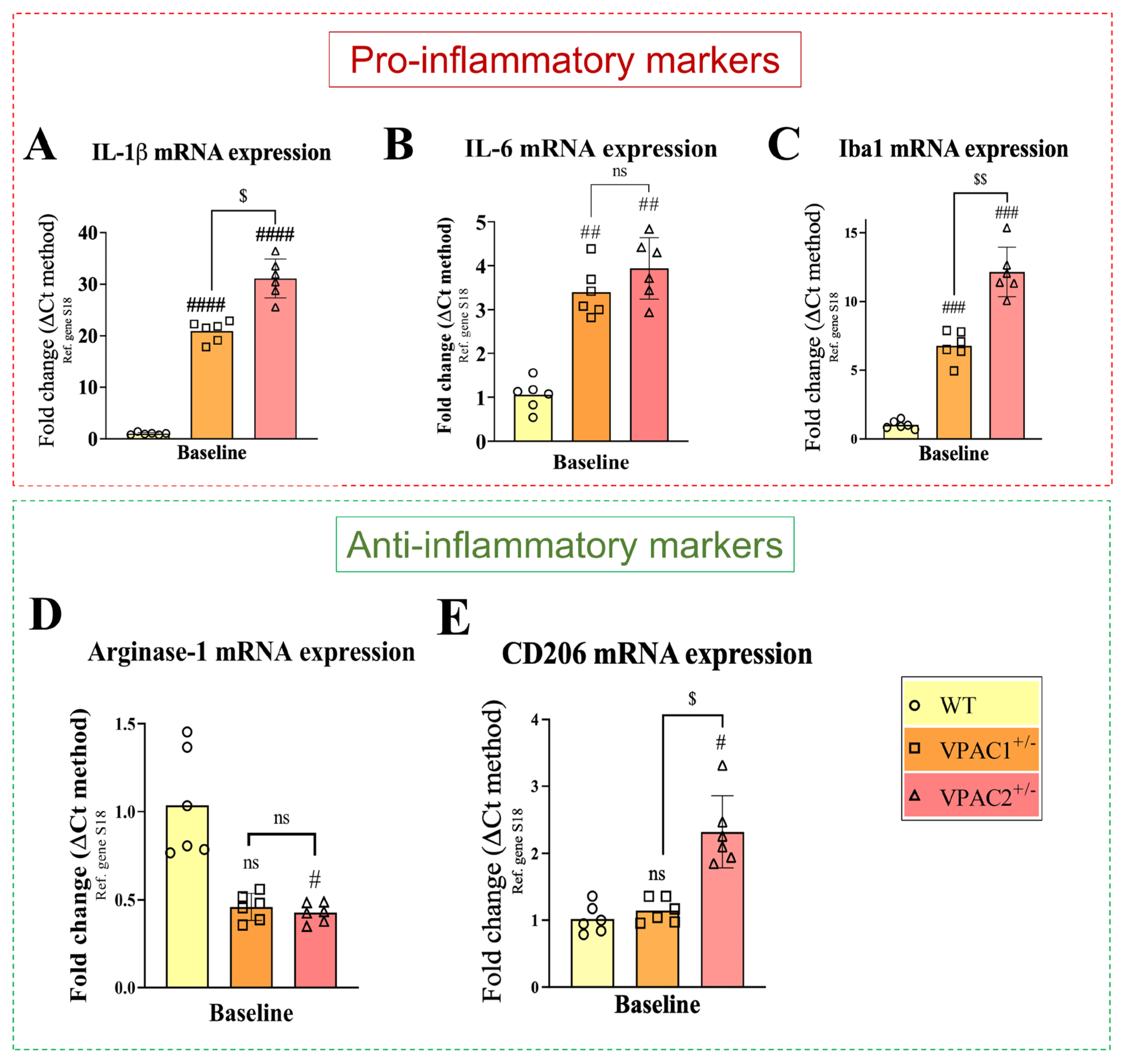
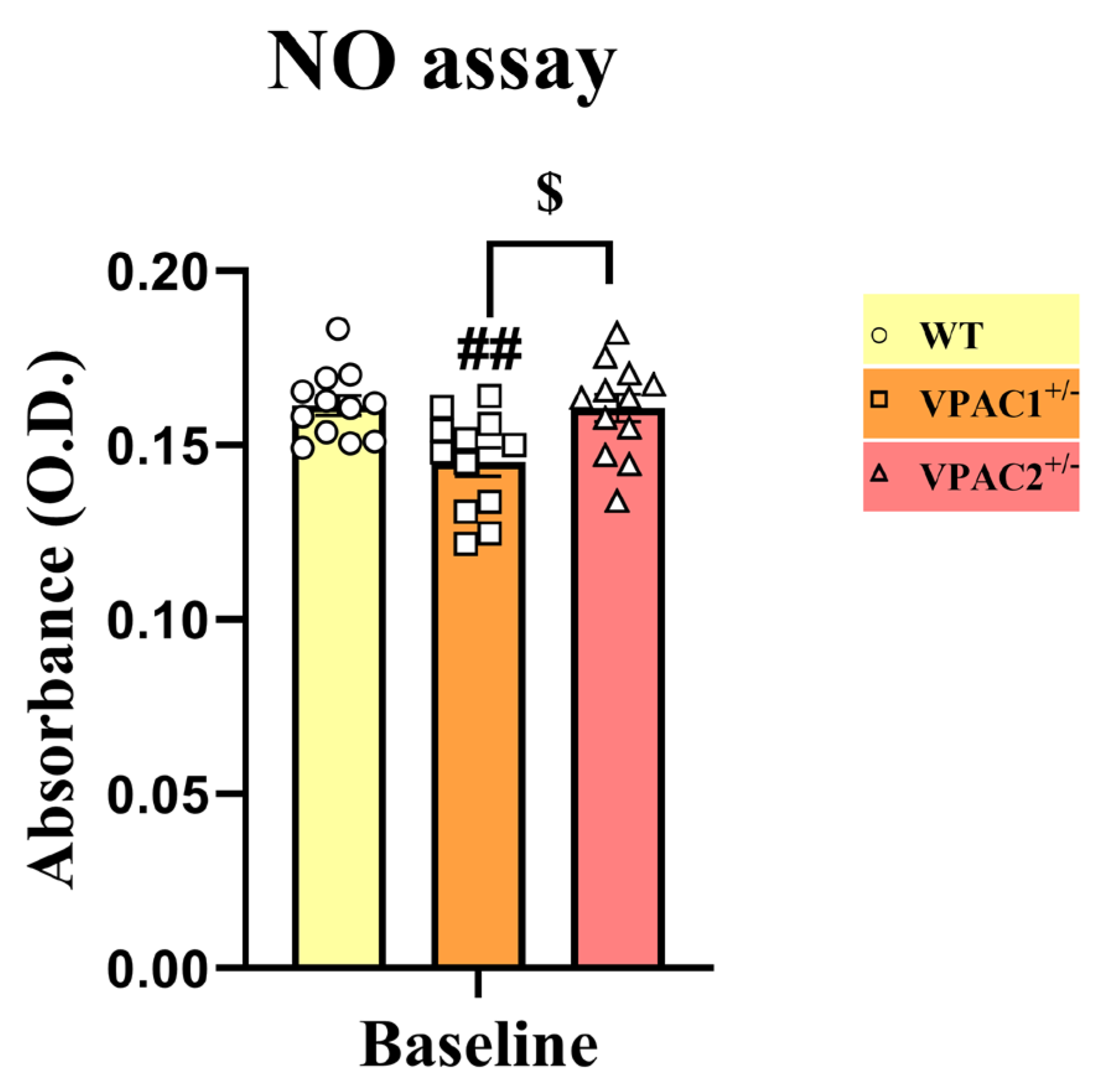




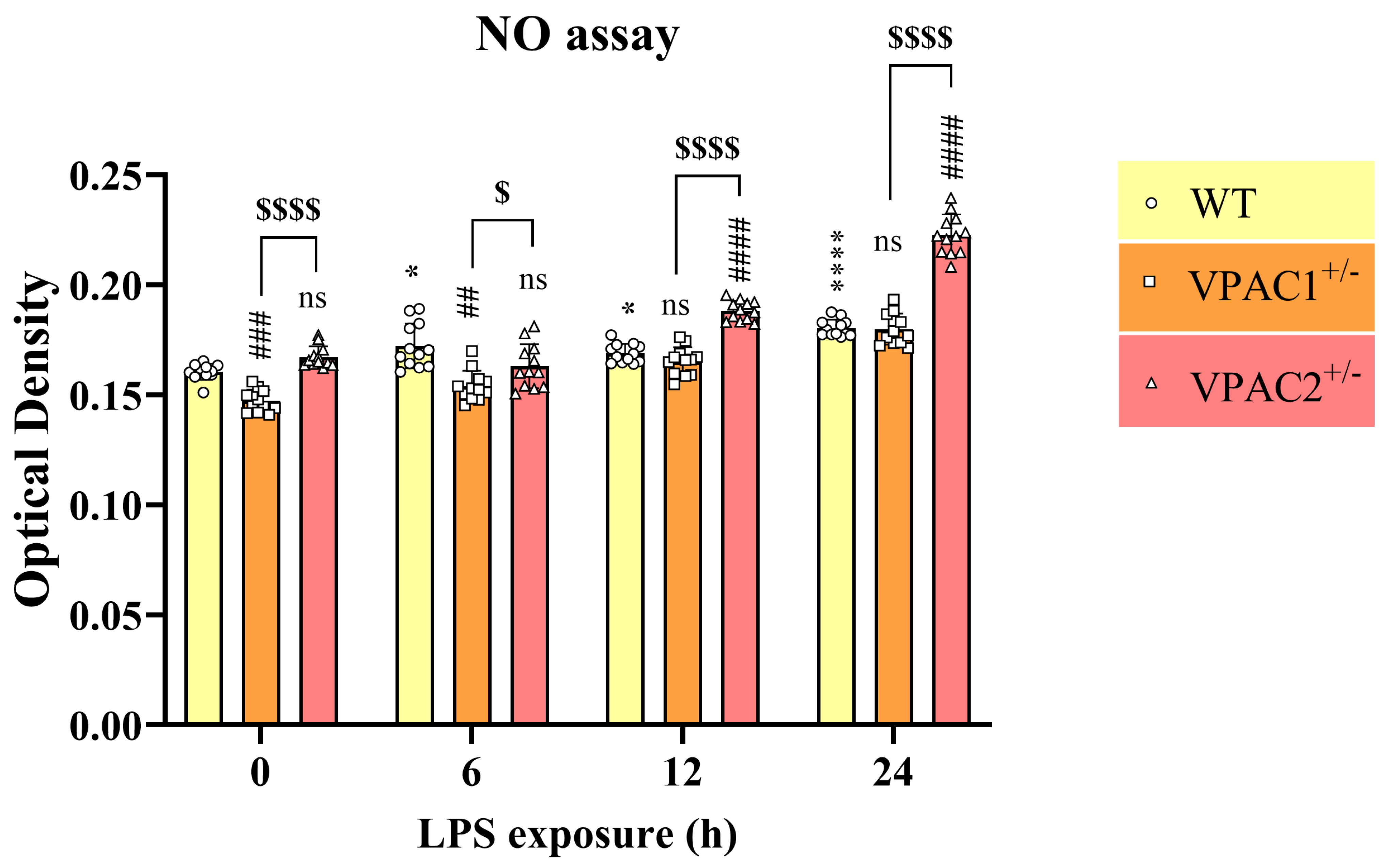


| Gene Reference Sequence | Forward (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | Location (Chromosome: Range) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse (3′-5′) | |||
| Mouse VIPR1 (NC_000075.7) | (CACC)GTGCCAGCACGCAGAGCCAGC | 83.9 | 9: 121471943–121471962 |
| (AAAC)GCTGGCTCTGCGTGCTGGCAC | 80.5 | ||
| Mouse VIPR2 (NC_000078.7) | (CACC)GAGAGCTGCTAAGCAGCCAAA | 74.5 | 12: 116043718–116043737 |
| (AAAC)TTTGGCTGCTTAGCAGCTCTC | 68.5 |
| Gene Reference Sequence | Forward (5′-3′) | Location | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse (3′-5′) | ||||
| Mouse VIPR1 (NC_000075.7) | CCTGGAGCTGTGCCTCATAG | 19 | 64.9 | 840 |
| TCTCAGAGGAGGTGACCAGG | 839 | 64.6 | ||
| Mouse VIPR2 (NC_000078.7) | CACACCCACAGCCACTAAGA | 96 | 63.9 | 991 |
| ACCATGACGGAGGCACAAAT | 1067 | 66.6 |
| Gene Reference (Accession Number) | Forward (5′-3′) | Location | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse (3′-5′) | ||||
| Mouse VIPR1 (NC_000075.7) | CACAGACCCCGTAGGCG | 45 | 65.6 | 677 |
| GGTCTAAGGTAGAGCAAGCCC | 701 | 62.9 | ||
| Mouse VIPR2 (NC_000078.7) | GAAAGGTGAAGCGTTGGATCT | 267 | 64.3 | 601 |
| CAGAAACCTGAAGTCCCATTTTCC | 844 | 67.5 |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (3′-5′) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIPR1 | CCCTCTGTTTGGAGTTCACTAT | TACGACGAGTTCAAAGACCATT | 88 |
| VIPR2 | ATTTCATAGATGCGTGTGGCTA | TGCTTCCTGTTGTAAGAGACAT | 126 |
| IL-1β | GCTACCTGTGTCTTTCCCGT | CATCTCGGAGCCTGTAGTGC | 164 |
| IL-6 | CCCCAATTTCCAATGCTCTCC | CGCACTAGGTTTGCCGAGTA | 141 |
| Iba1 | ACGTTCAGCTACTCTGACTTTC | GTTGGCCTCTTGTGTTCTTTG | 107 |
| Arg1 | ACAAGACAGGGCTCCTTTCAG | TTAAAGCCACTGCCGTGTTC | 105 |
| CD206 | AGTGATGGTTCTCCCGTTTC | ACCTTTCAGCTCACCACAAT | 90 |
| ATF4 | CCTCAGACAGTGAACCCAAT | AATGCTCTGGAGTGGAAGAC | 127 |
| DDIT3 | GCTCTCCAGATTCCAGTCAG | CTCCTTCTCCTTCATGCGTT | 131 |
| TLR4 | ATCATGGCACTGTTCTTCTCC | ACTTTGCTGAGTTTCTGATCCA | 107 |
| S18 | CCCTGAGAAGTTCCAGCACA | GGTGAGGTCGATGTCTGCTT | 145 |
| Antibody | Source | Catalogue Number | Predicted Molecular Weight | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPAC1 | Merck Life Science | SAB4503084 | 51 kDa | 1:1000 |
| VPAC2 | Abcam | ab28624 | 52 kDa | 1:1000 |
| Phospho-IRE1α (Ser724) | Merck Life Science | ZRB1072 | 110 kDa | 1:2500 |
| PERK | GeneTex | GTX129275 | 120 kDa | 1:2000 |
| GAPDH | Bio-Rad | VPA00187 | 37 kDa | 1:1000 |
| Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) (Secondary) | Abcam | ab6721 | - | 1:10,000 |
| Antibody | Source | Catalogue Number | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phospho-IRE1α (Ser724) | Merck Life Science | ZRB1072 | 1:500 |
| Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1) | Merck Life Science | SAB2702364 | 1:250 |
| Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H&L) (TRITC) | Abcam | ab6718 | 1:2500 |
| Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H&L) (FITC) | Abcam | ab6785 | 1:2500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.Y.R.; Jansen, M.I.; Marzagalli, R.; Musumeci, G.; D’Agata, V.; Castorina, A. VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptor Heterozygosity Confers Distinct Biological Properties to BV2 Microglial Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110769
Song XYR, Jansen MI, Marzagalli R, Musumeci G, D’Agata V, Castorina A. VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptor Heterozygosity Confers Distinct Biological Properties to BV2 Microglial Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(11):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110769
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xin Ying Rachel, Margo Iris Jansen, Rubina Marzagalli, Giuseppe Musumeci, Velia D’Agata, and Alessandro Castorina. 2025. "VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptor Heterozygosity Confers Distinct Biological Properties to BV2 Microglial Cells" Cells 14, no. 11: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110769
APA StyleSong, X. Y. R., Jansen, M. I., Marzagalli, R., Musumeci, G., D’Agata, V., & Castorina, A. (2025). VPAC1 and VPAC2 Receptor Heterozygosity Confers Distinct Biological Properties to BV2 Microglial Cells. Cells, 14(11), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110769










