Galectin-3 Plays a Role in Neuroinflammation in the Visual Pathway in Experimental Optic Neuritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. EAE Induction
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Immunoblotting
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EAE Induces Inflammation in the Visual Pathway
3.2. Mice with MOG-Induced EAE Show Upregulation of Gal-3 in Microglia and Macrophages in the Visual Pathway
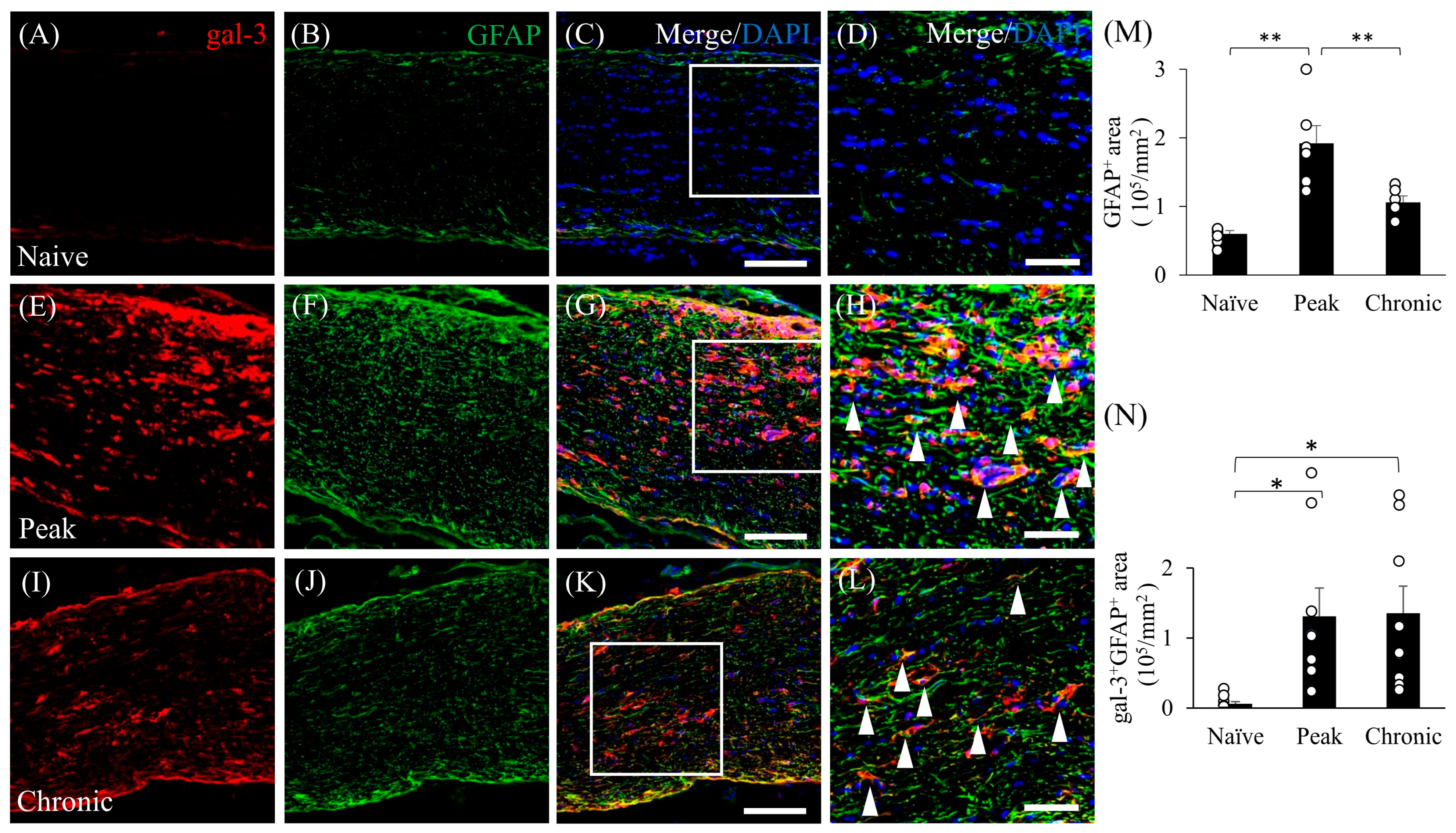
3.3. Astrocytic Expression of Gal-3 in the Optic Nerve during EAE
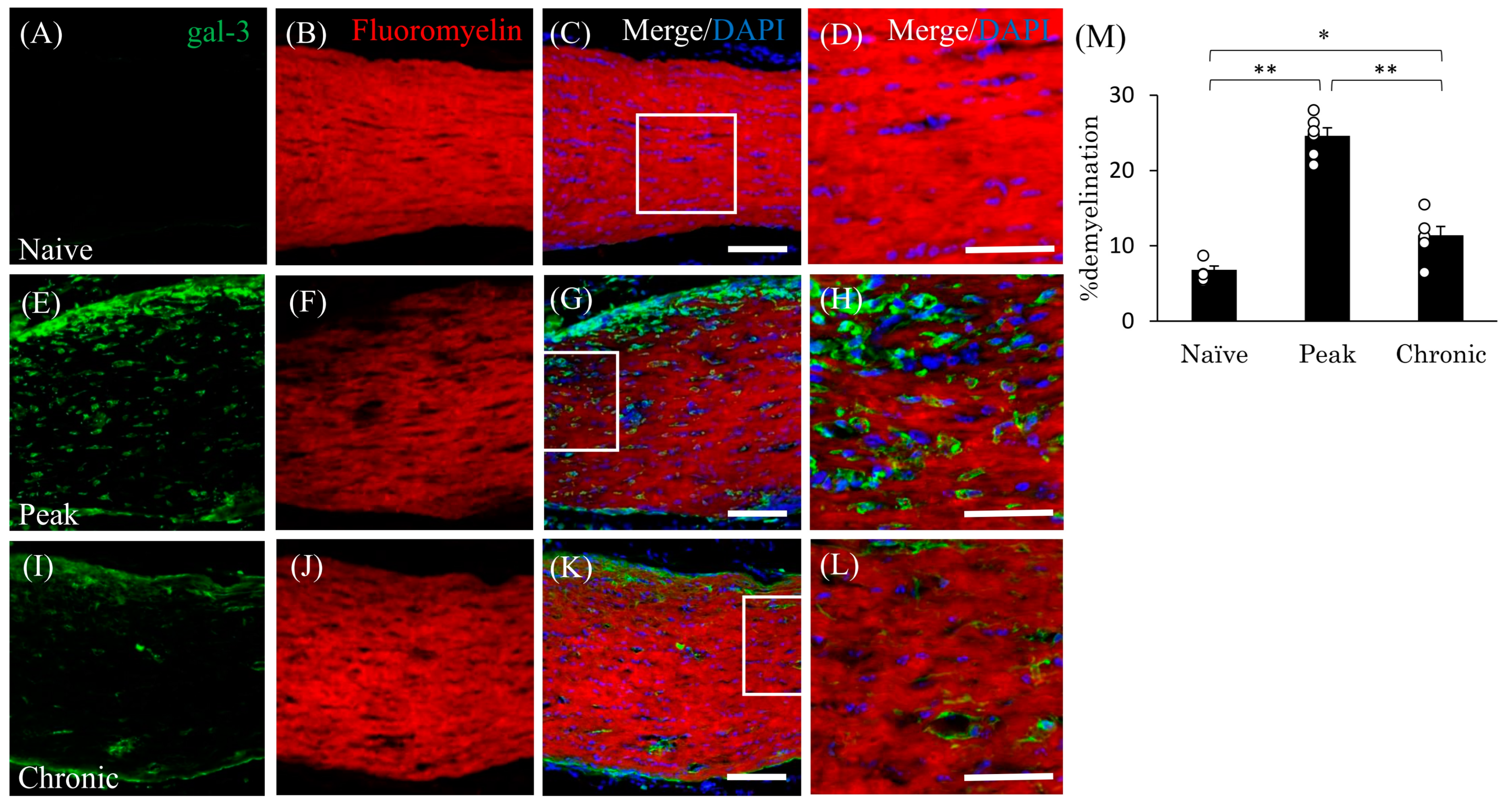
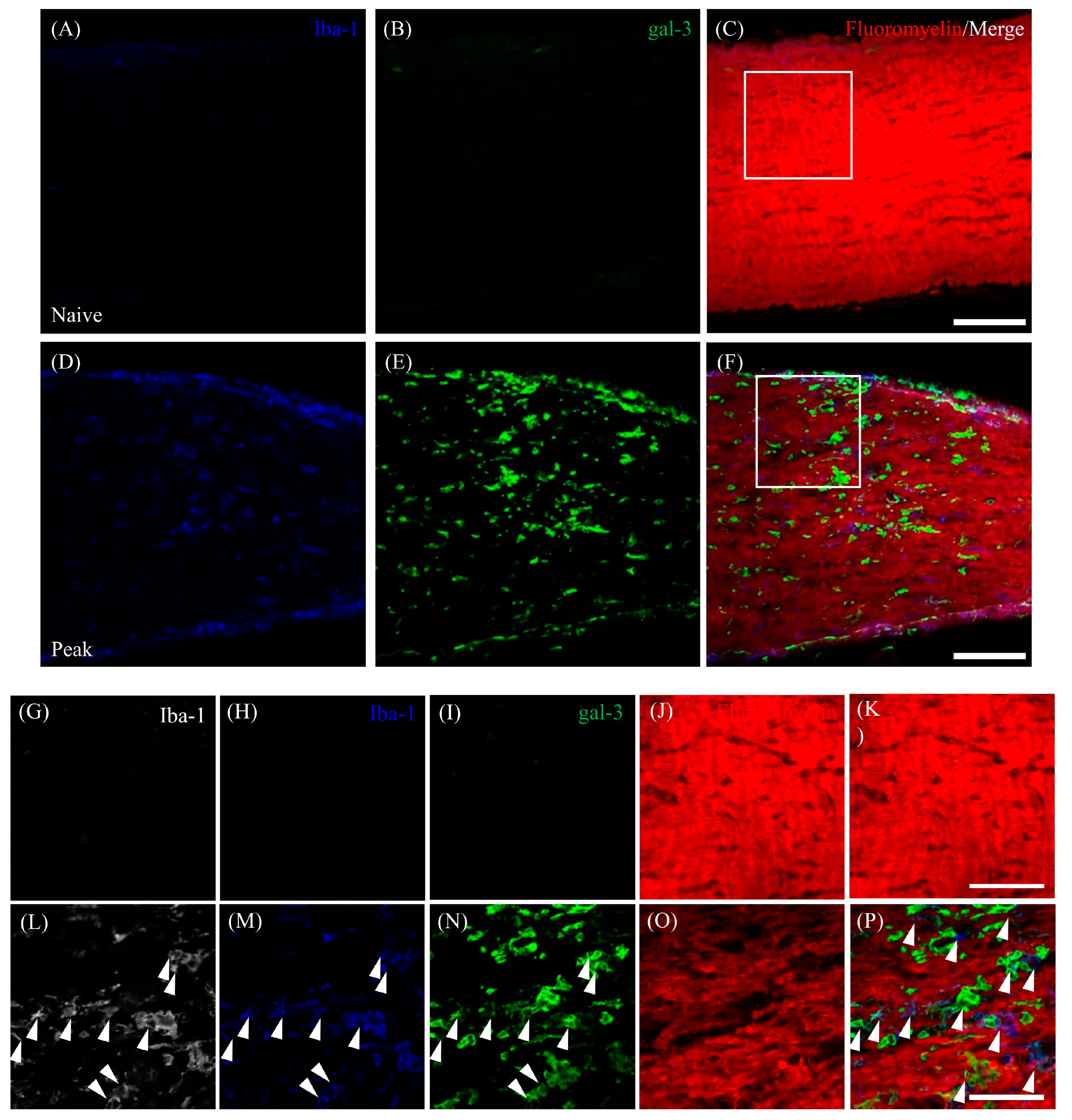
3.4. Accumulation of Gal-3+ Cells in the Demyelinating Lesions in EAE
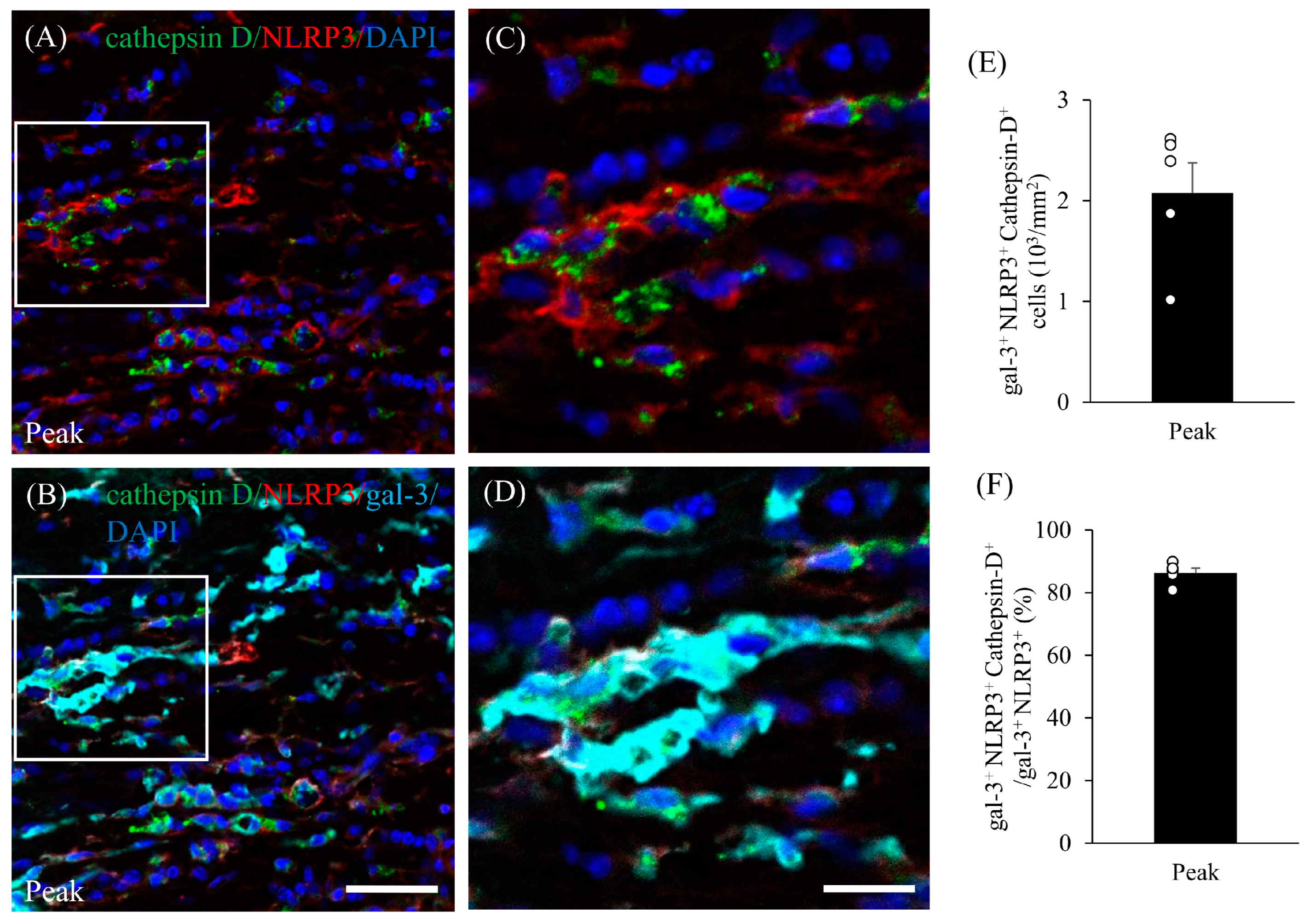
3.5. Expression of Gal-3 in Cathepsin D-Expressing Activated Microglia/Macrophages
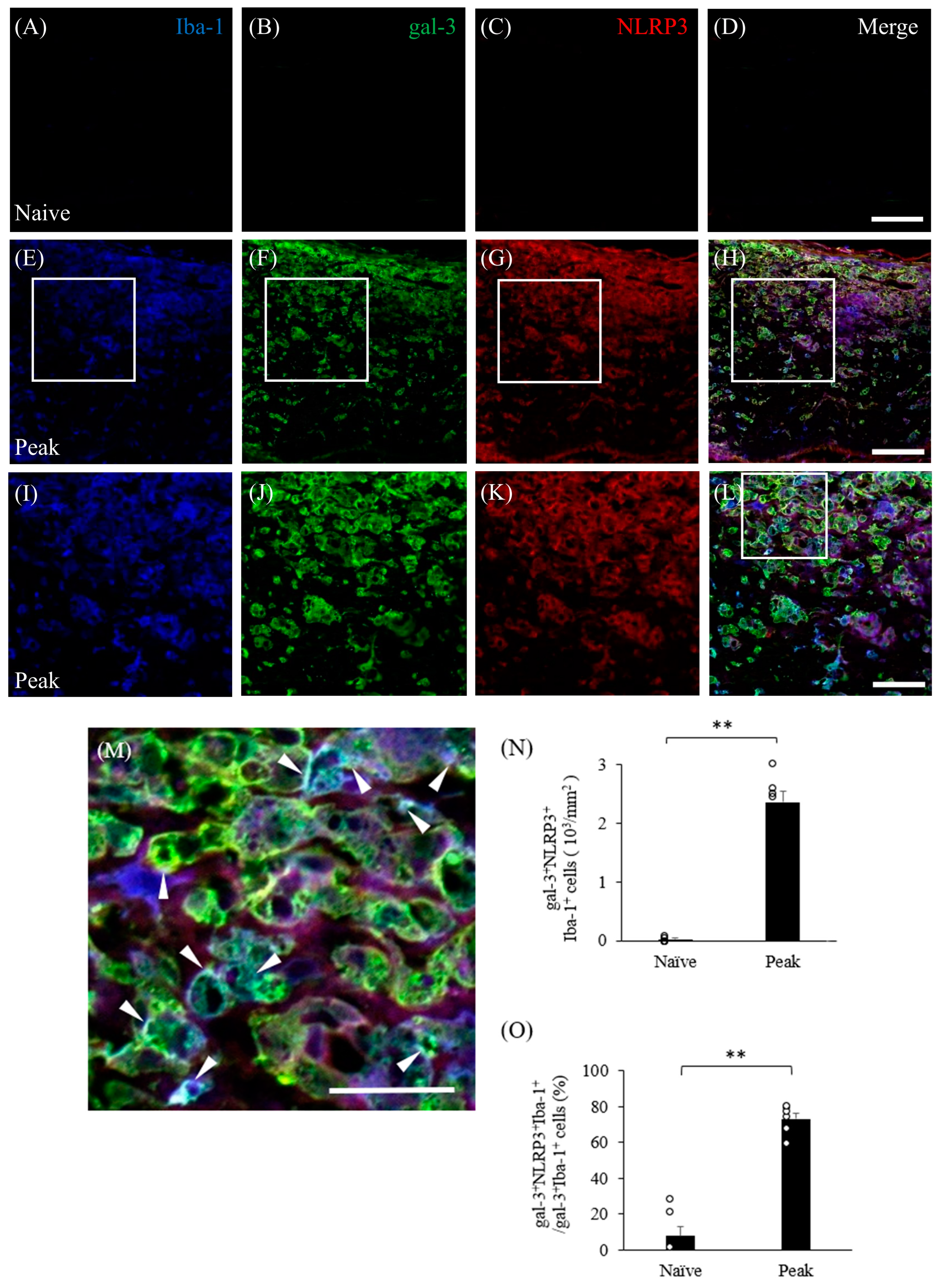
3.6. Inflammasome Activation Upregulates Gal-3 in Microglia/Macrophages in Mice with EAE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| EAE | experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| gal-3 | galectin-3 |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acid protein |
| Iba-1 | ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 |
| MBP | myelin basic protein |
| MOG | myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| NMO | neuromyelitis optica |
| ON | optic neuritis |
| OLs | oligodendrocytes |
| OPC | oligodendrocyte precursor cell |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PFA | paraformaldehyde |
References
- Noseworthy, J.H.; Lucchinetti, C.; Rodriguez, M.; Weinshenker, B.G. Multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, D.S.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Calabresi, P.A. Multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, R.W.; Cleary, P.A.; Anderson, M.M.; Keltner, J.L.; Shults, W.T.; Kaufman, D.I.; Buckley, E.G.; Corbett, J.J.; Kupersmith, M.J.; Miller, N.R.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of corticosteroids in the treatment of acute optic neuritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, N. Optic neuritis as an early sign of multiple sclerosis. Eye Brain 2016, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J. Optic Neuritis. Continuum 2019, 25, 1236–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bando, Y.; Geisler, J.G. Disease modifying mitochondrial uncouplers, MP101, and a slow release ProDrug, MP201, in models of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Nun, A.; Kaushansky, N.; Kawakami, N.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Berer, K.; Liblau, R.; Hohlfeld, R.; Wekerle, H. From classic to spontaneous and humanized models of multiple sclerosis: Impact on understanding pathogenesis and drug development. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 54, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Farooqi, N.; O’Brien, K.; Gran, B. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordano, C.; Ramos, C.; Arnow, S.; Cruz-Herranz, A.; Guglielmetti, C.; Iester, M.; Bandini, F. Inflammation in the anterior visual pathway in multiple sclerosis: What do the animal models teach us? Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redler, Y.; Levy, M. Rodent Models of Optic Neuritis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 580951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Dine, K.; Geisler, J.G.; Shindler, K.S. Mitochondrial Uncoupler Prodrug of 2,4-Dinitrophenol, MP201, Prevents Neuronal Damage and Preserves Vision in Experimental Optic Neuritis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 7180632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, T.A.; Dutt, M.; Shindler, K.S. Optic neuritis and retinal ganglion cell loss in a chronic murine model of multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2011, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Huang, Z.; Sun, S.L.; Kaplan, H.J.; Sun, D. Myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific T-cells induce severe optic neuritis in the C57BL/6 mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4060–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nio-Kobayashi, J.; Itabashi, T. Galectins and Their Ligand Glycoconjugates in the Central Nervous System Under Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 767330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, H.; Shimizu, F.; Kitagawa, T.; Yamanaka, N.; Akada, J.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Sano, Y.; Takeshita, Y.; Maeda, T.; Abe, M.; et al. Identification of galectin-3 as a possible antibody target for secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2017, 23, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itabashi, T.; Arima, Y.; Kamimura, D.; Higuchi, K.; Bando, Y.; Takahashi-Iwanaga, H.; Murakami, M.; Watanabe, M.; Iwanaga, T.; Nio-Kobayashi, J. Cell- and stage-specific localization of galectin-3, a β-galactoside-binding lectin, in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 118, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.R.; Al Rasebi, Z.; Mensah-Brown, E.; Shahin, A.; Xu, D.; Goodyear, C.S.; Fukada, S.Y.; Liu, F.T.; Liew, F.Y.; Lukic, M.L. Galectin-3 deficiency reduces the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, H.R.; Carvalho, J.N.A.; Abreu, C.A.; Mariano de Souza Aguiar Dos Santos, D.; Carvalho, J.R.; Marques, S.A.; da Costa Calaza, K.; Martinez, A.M.B. Lack of Galectin-3 attenuates neuroinflammation and protects the retina and optic nerve of diabetic mice. Brain Res. 2018, 1700, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, F.; Rotshenker, S. Galectin-3/MAC-2 in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 160, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotshenker, S.; Reichert, F.; Gitik, M.; Haklai, R.; Elad-Sfadia, G.; Kloog, Y. Galectin-3/MAC-2, Ras and PI3K activate complement receptor-3 and scavenger receptor-AI/II mediated myelin phagocytosis in microglia. Glia 2008, 56, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, Y.; Hagiwara, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Aburakawa, Y.; Kimura, T.; Murakami, C.; Ono, M.; Tanaka, T.; Jiang, Y.P.; et al. Kallikrein 6 secreted by oligodendrocytes regulates the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Glia 2018, 66, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bando, Y.; Nomura, T.; Bochimoto, H.; Murakami, K.; Tanaka, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, S. Abnormal morphology of myelin and axon pathology in murine models of multiple sclerosis. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 81, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettelli, E.; Pagany, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Linington, C.; Sobel, R.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific T cell receptor transgenic mice develop spontaneous autoimmune optic neuritis. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, C.; Takano, T.; Masumura, M.; Nakamura, R.; Koda, S.; Bochimoto, H.; Yoshida, S.; Bando, Y. Involvement of Degenerating 21.5 kDa Isoform of Myelin Basic Protein in the Pathogenesis of the Relapse in Murine Relapsing-Remitting Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and MS Autopsied Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balabanov, R.; Strand, K.; Goswami, R.; McMahon, E.; Begolka, W.; Miller, S.D.; Popko, B. Interferon-gamma-oligodendrocyte interactions in the regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanborg, R. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Methods Enzymol. 1988, 140, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca-Kelly, Z.; Nassrallah, M.; Uribe, J.; Khan, R.S.; Dine, K.; Dutt, M.; Shindler, K.S. Resveratrol neuroprotection in a chronic mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.W.; Liang, H.F.; Schmidt, R.E.; Cross, A.H.; Song, S.K. Selective vulnerability of cerebral white matter in a murine model of multiple sclerosis detected using diffusion tensor imaging. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 28, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciaguerra, L.; Flanagan, E.P. Updates in NMOSD and MOGAD Diagnosis and Treatment: A Tale of Two Central Nervous System Autoimmune Inflammatory Disorders. Neurol. Clin. 2023, 42, 77–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafler, D.A. Multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, H. Pathogenic mechanisms associated with different clinical courses of multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlinson, C.; Jenkins, S.; Thei, L.; Dallas, M.L.; Chen, R. Post-Ischaemic Immunological Response in the Brain: Targeting Microglia in Ischaemic Stroke Therapy. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volarevic, V.; Milovanovic, M.; Ljujic, B.; Pejnovic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Nilsson, U.; Leffler, H.; Lukic, M.L. Galectin-3 deficiency prevents concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1954–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baaklini, C.S.; Rawji, K.S.; Duncan, G.J.; Ho, M.F.S.; Plemel, J.R. Central Nervous System Remyelination: Roles of Glia and Innate Immune Cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, J.R.; Klegeris, A. Emerging roles of microglial cathepsins in neurodegenerative disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 139, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ock, J.; Kim, A.K.; Lee, H.W.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, D.R.; Park, J.Y.; Suk, K. Neurotoxicity of microglial cathepsin D revealed by secretome analysis. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mamun, A.; Wu, Y.; Monalisa, I.; Jia, C.; Zhou, K.; Munir, F.; Xiao, J. Role of pyroptosis in spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 28, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordt, E.A.; Polster, B.M. NADPH oxidase- and mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species in proinflammatory microglial activation: A bipartisan affair? Free Radical. Biol. Med. 2014, 76, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Activation and regulation of cellular inflammasomes: Gaps in our knowledge for central nervous system injury. J. Cerebral Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiao, L.; He, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Jiang, C.; Mei, G.; Yu, J.; Chen, H.; Yao, P.; et al. Quercetin Attenuates Atherosclerotic Inflammation by Inhibiting Galectin-3-NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Tomilov, A.; Olson, K.A.; Dehnad, A.; Fish, S.R.; Cortopassi, G.; Zhao, B.; et al. Galectin-3 regulates inflammasome activation in cholestatic liver injury. FASEB J. 2016, 12, 4202–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.Z.; Wei, W.; Ke, P.; Xu, Z.Q.; Zhou, J.X.; Liu, C. Activating cannabinoid receptor 2 alleviates pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via activation of autophagy and inhibiting NLRP 3 inflammasome. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Williams, K.L.; Gunn, M.D.; Shinohara, M.L. NLRP3 inflammasome induces chemotactic immune cell migration to the CNS in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10480–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidoni, C.; Follo, C.; Savino, M.; Melone, M.A.; Isidoro, C. The Role of Cathepsin D in the Pathogenesis of Human Neurodegenerative Disorders. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 845–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, R.A.; Murphey, C.; Ji, N.; Cardona, A.E.; Forsthuber, T.G. The kinetics of myelin antigen uptake by myeloid cells in the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5848–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawji, K.S.; Kappen, J.; Tang, W.; Teo, W.; Plemel, J.R.; Stys, P.K.; Yong, V.W. Deficient surveillance and phagocytic activity of myeloid cells within demyelinated lesions in aging mice visualized by ex vivo live multiphoton imaging. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 1973–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, D.; Sun, Z.; Yang, H.; Yin, Q. Galectin-3: A key player in microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.; Pasquini, L.A. Galectin-3-Mediated Glial Crosstalk Drives Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and (Re)myelination. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagno, K.E.; Mitchell, C.H. The P2X7 Receptor in Microglial Cells Modulates the Endolysosomal Axis, Autophagy and Phagocytosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 645244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lively, S.; Schlichter, L.C. Microglia responses to pro-inflammatory stimuli (LPS, IFNγ+TNFα) and reprogramming by resolving cytokines (IL-4, IL-10). Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, J.M.; Riparip, L.K.; Rosi, S. Call off the dog(ma): M1/M2 polarization is concurrent following traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirko, S.; Irmler, M.; Gascón, S.; Bek, S.; Schneider, S.; Dimou, L.; Obermann, J.; De Souza Paiva, D.; Poirier, F.; Beckers, J.; et al. Astrocyte reactivity after brain injury-: The role of galectins 1 and 3. Glia 2015, 63, 2340–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive astrocytes: Production, function and therapeutic potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skripuletz, T.; Hackstette, D.; Bauer, K.; Gudi, V.; Pul, R.; Voss, E.; Berger, K.; Kipp, M.; Baumgärtner, W.; Stangel, M. Astrocytes regulate myelin clearance through recruitment of microglia during cuprizone-induced demyelination. Brain 2013, 136 Pt 1, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.A.; Baer, A.S.; Lubec, G.; Hoeger, H.; Widhalm, G.; Kotter, M.R. Inhibition of oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation by myelin-associated proteins. Neurosurg. Focus 2008, 24, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plemel, J.R.; Manesh, S.B.; Sparling, J.S.; Tetzlaff, W. Myelin inhibits oligodendroglial maturation and regulates oligodendrocytic transcription factor expression. Glia 2013, 61, 1471–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotter, M.R.; Li, W.W.; Zhao, C.; Franklin, R.J. Myelin impairs CNS remyelination by inhibiting oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Funaki, M.; Nio-Kobayashi, J.; Suzuki, R.; Bando, Y. Galectin-3 Plays a Role in Neuroinflammation in the Visual Pathway in Experimental Optic Neuritis. Cells 2024, 13, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070612
Funaki M, Nio-Kobayashi J, Suzuki R, Bando Y. Galectin-3 Plays a Role in Neuroinflammation in the Visual Pathway in Experimental Optic Neuritis. Cells. 2024; 13(7):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070612
Chicago/Turabian StyleFunaki, Masako, Junko Nio-Kobayashi, Ryoji Suzuki, and Yoshio Bando. 2024. "Galectin-3 Plays a Role in Neuroinflammation in the Visual Pathway in Experimental Optic Neuritis" Cells 13, no. 7: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070612
APA StyleFunaki, M., Nio-Kobayashi, J., Suzuki, R., & Bando, Y. (2024). Galectin-3 Plays a Role in Neuroinflammation in the Visual Pathway in Experimental Optic Neuritis. Cells, 13(7), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070612





