The Antinociceptive Effects and Sex-Specific Neurotransmitter Modulation of Metformin in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Treatment and Assessment Strategy
2.4. Assessment of the Pain Threshold
2.4.1. Von Frey Test (vFt)
2.4.2. Hot Plate Test
2.5. Assessment of Motor Behavior
2.5.1. Open Field Test (OFT)
2.5.2. Rotarod Test
2.6. Measurement of Depressive-like Behavior
2.6.1. Splash Test (ST)
2.6.2. Forced Swimming Test (FST)
2.6.3. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
2.7. Tissue Harvesting and Processing
2.7.1. Histopathological Analysis
2.7.2. Biochemical Analysis
2.7.3. Measurement of Serotonin and Norepinephrine Levels
2.7.4. Measurement of Glutamic Acid Levels
2.7.5. Measurement of TNF-α and IL-1β Levels
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
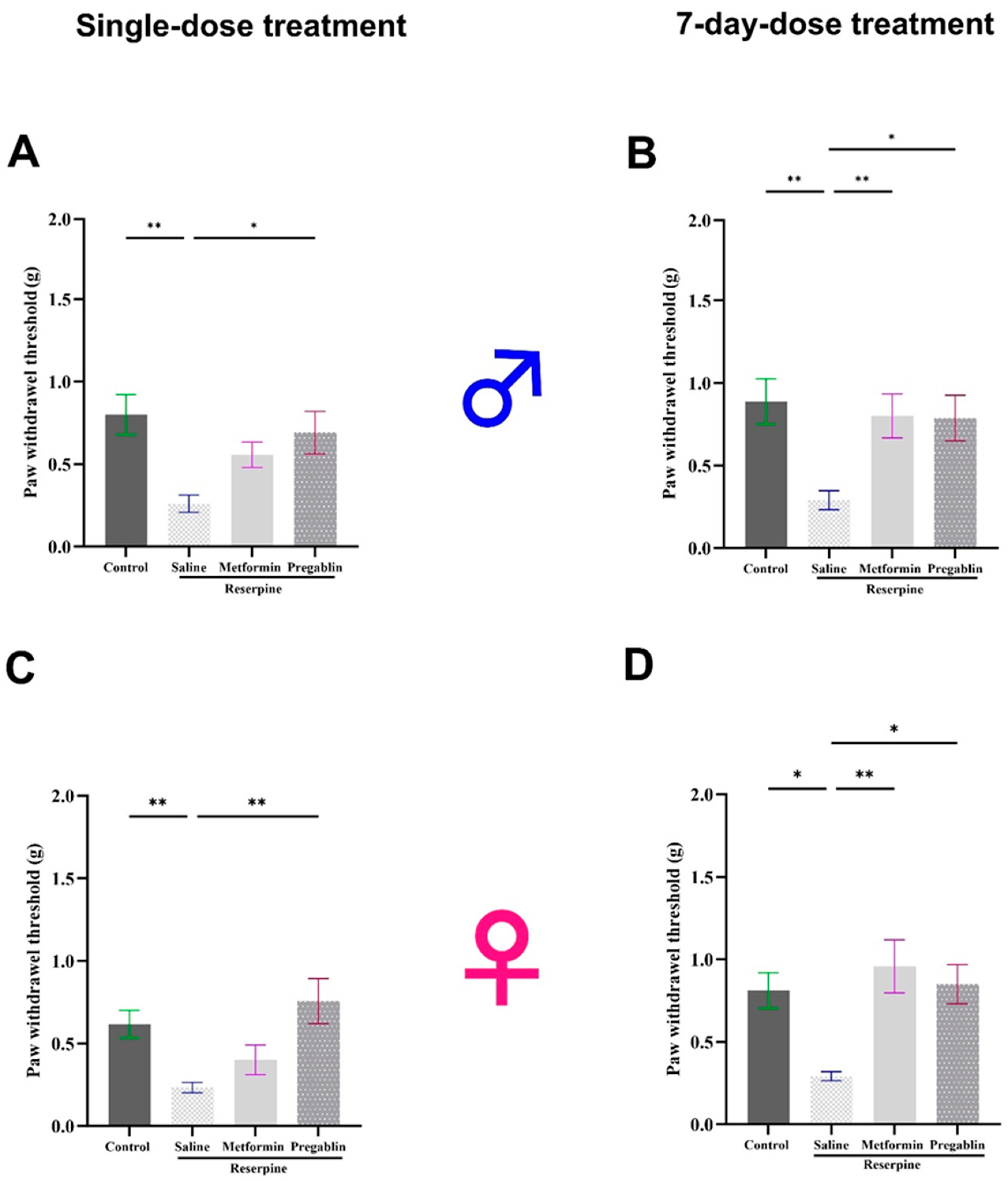
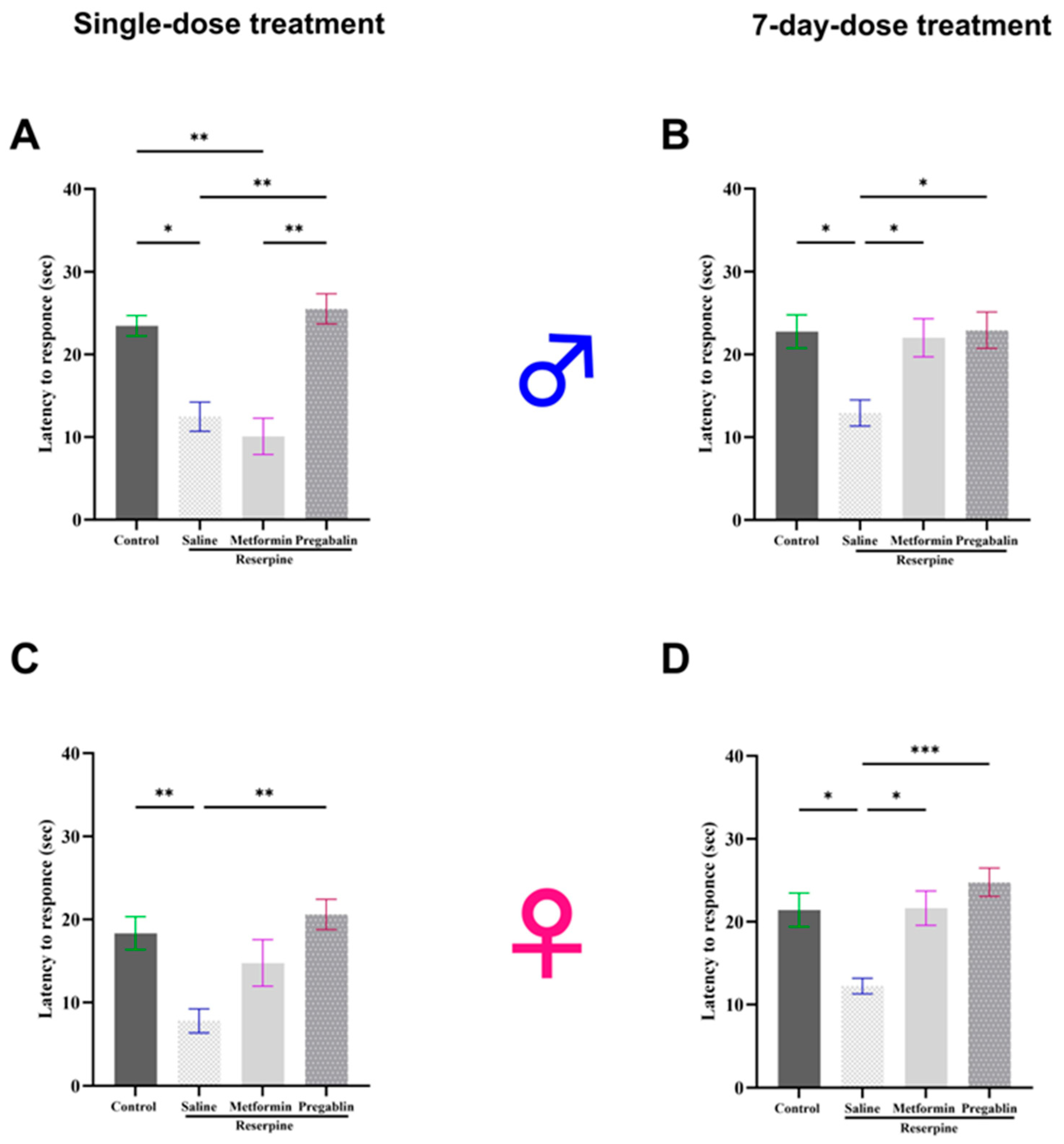
3.1. Metformin Treatment Reversed Reserpine-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hypersensitivity in Male and Female Mice After 7 Days of Treatment
3.2. Metformin Treatment Reversed Motor Defects in Male Mice Only
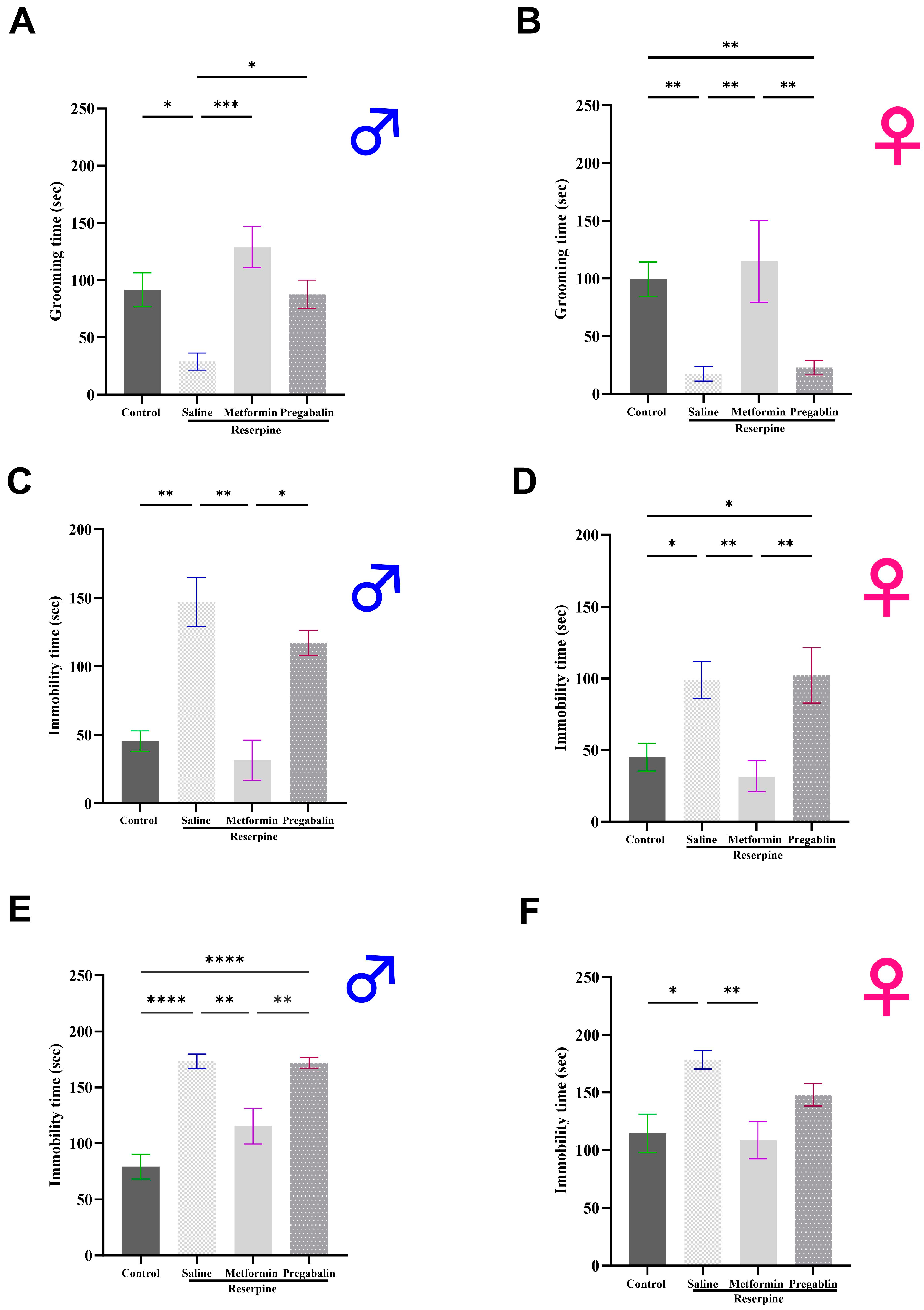
3.3. Metformin Demonstrated Antidepressant-Like Effects in Male and Female Mice
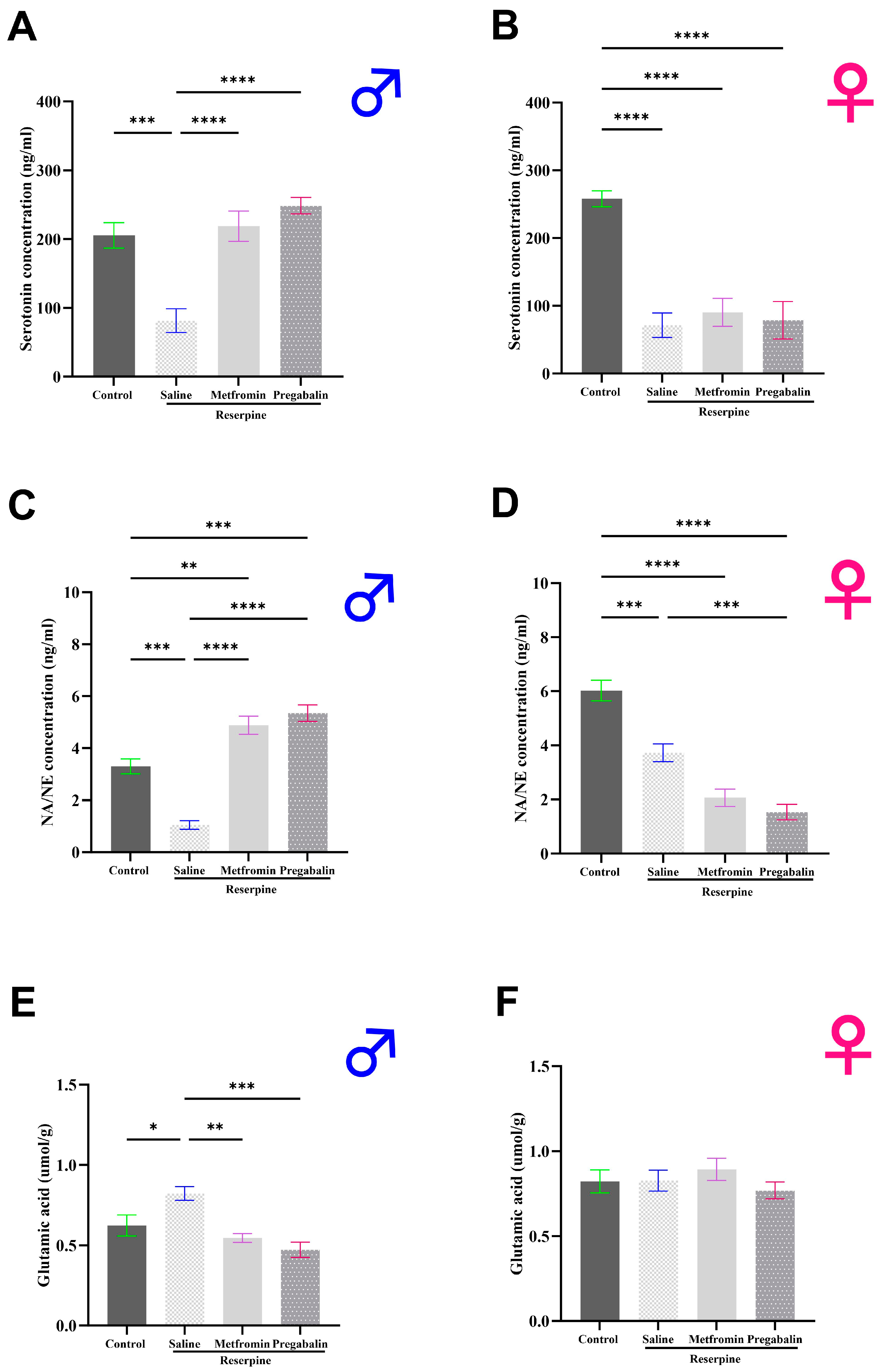
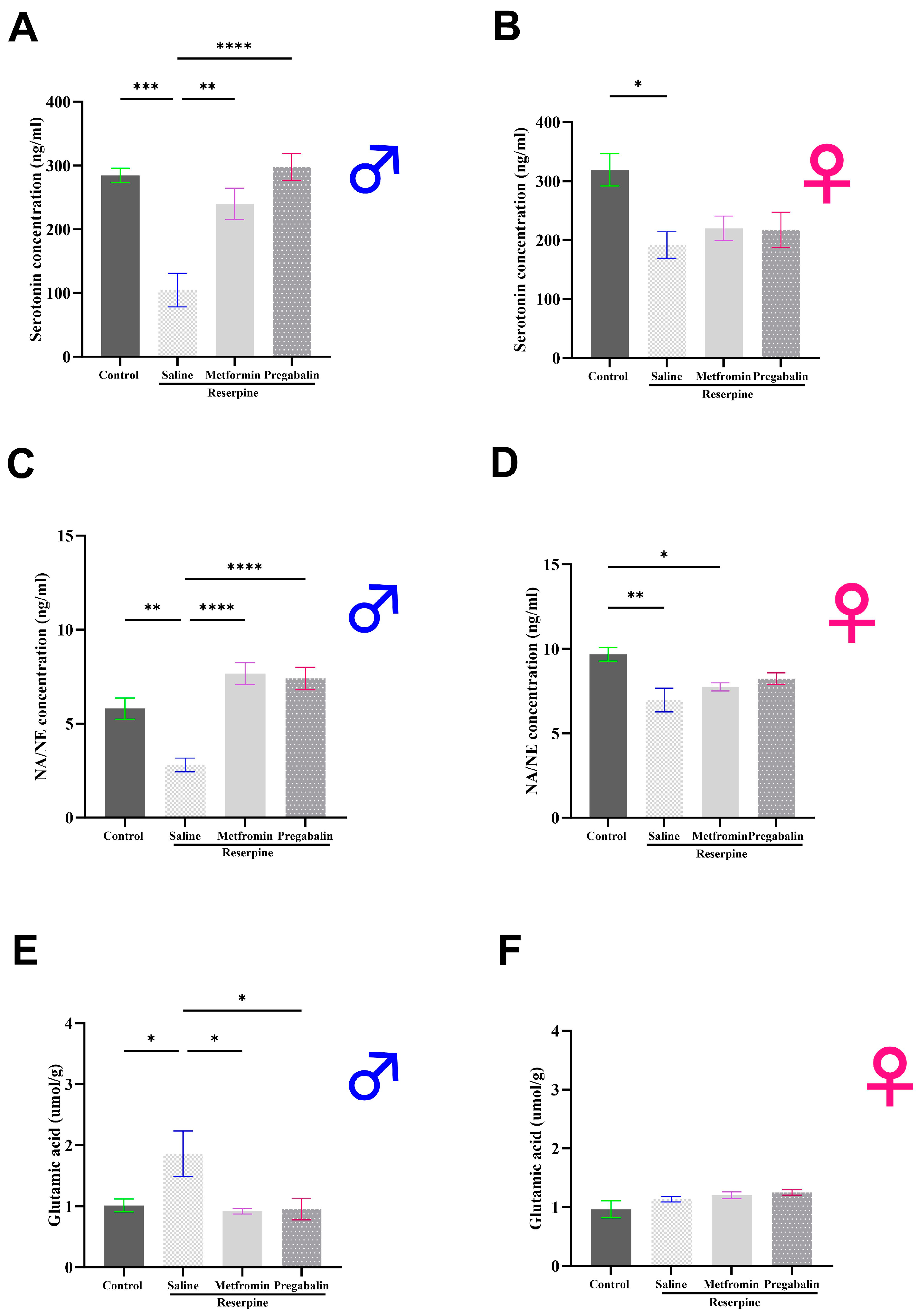
3.4. Metformin Modulated Neurotransmitter Levels in the Brain and Spinal Cord of Male Mice, but Not Females
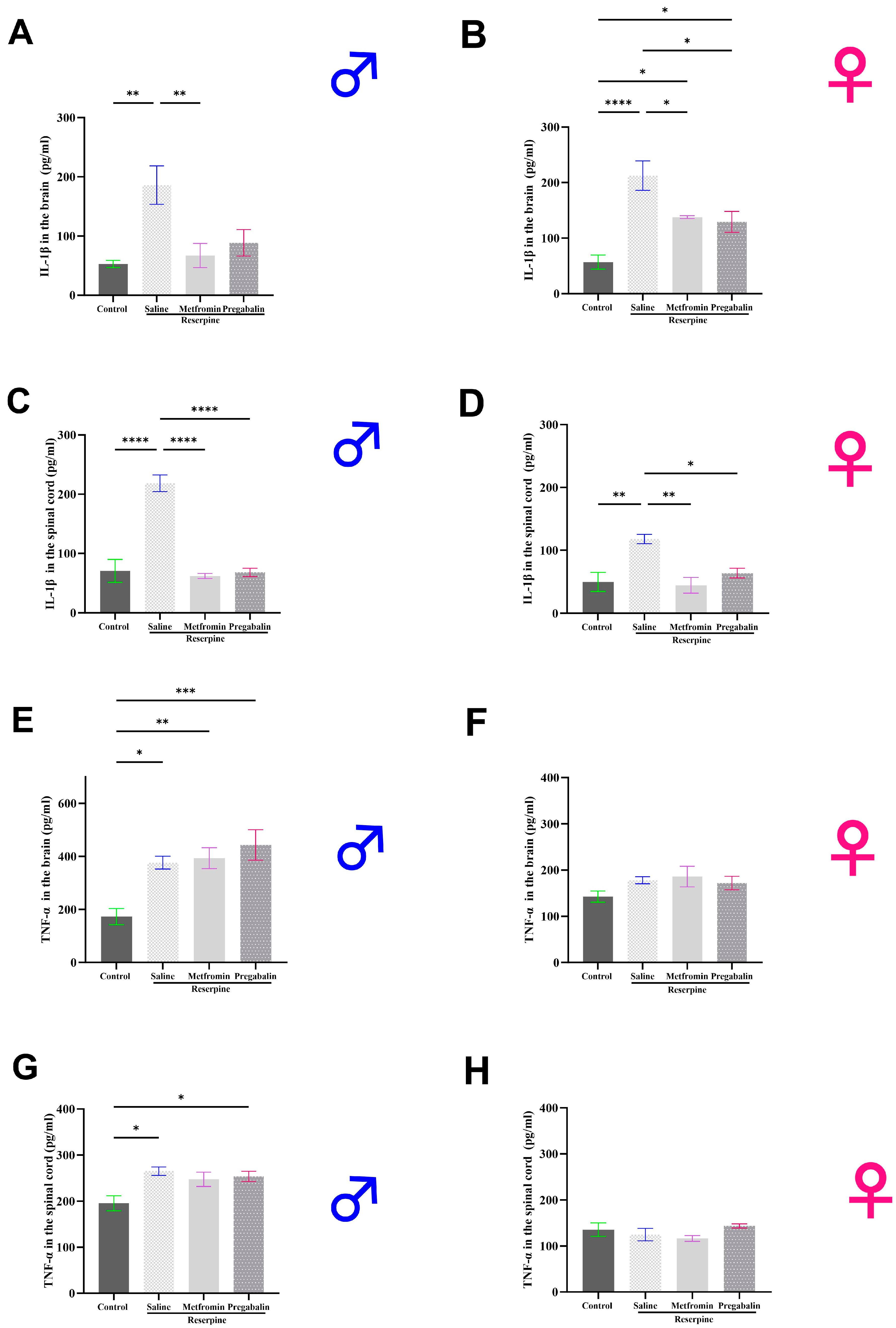
3.5. Metformin Modulated IL-1β Levels in the Brain and Spinal Cord of Both Male and Female Mice
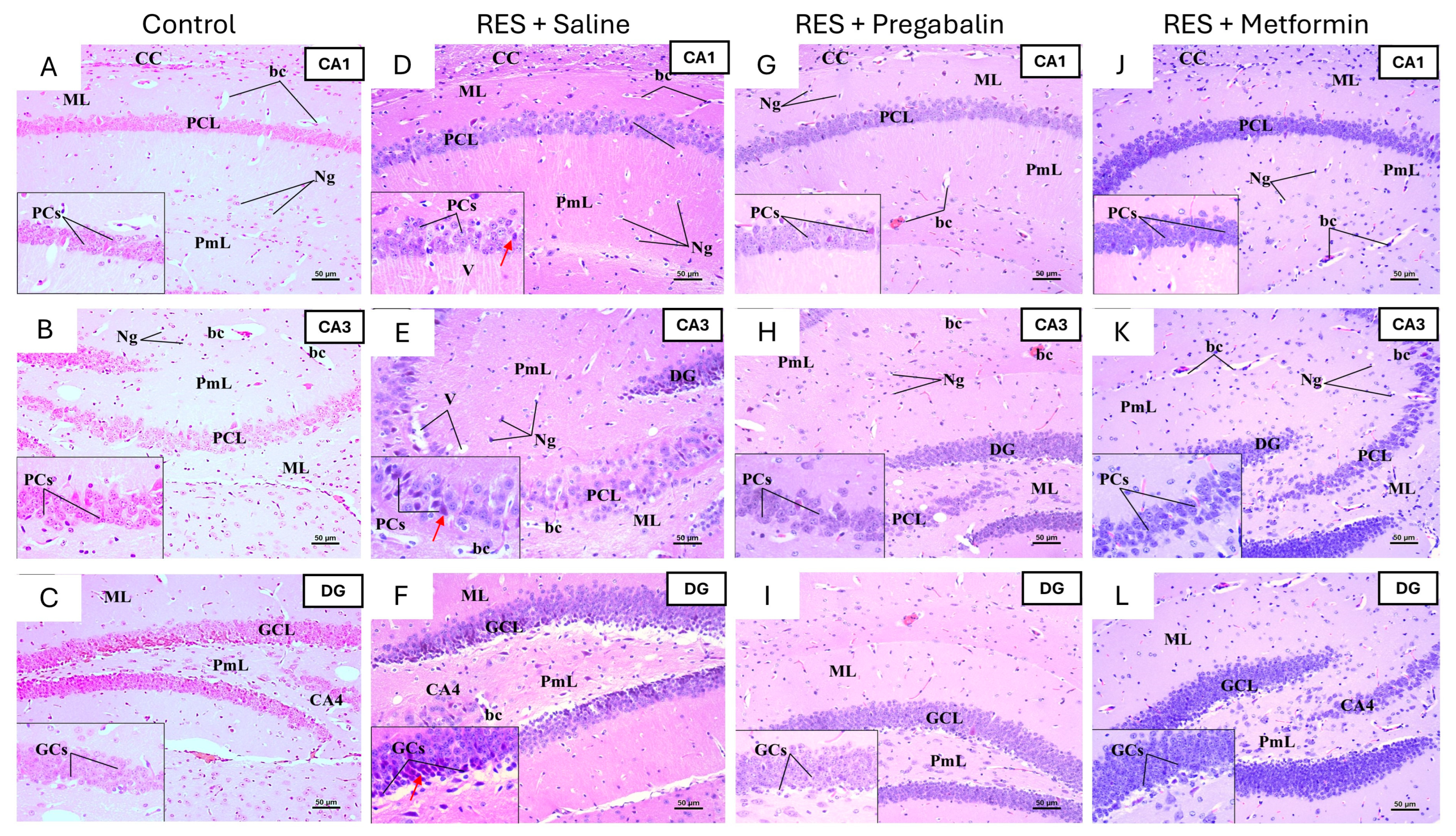
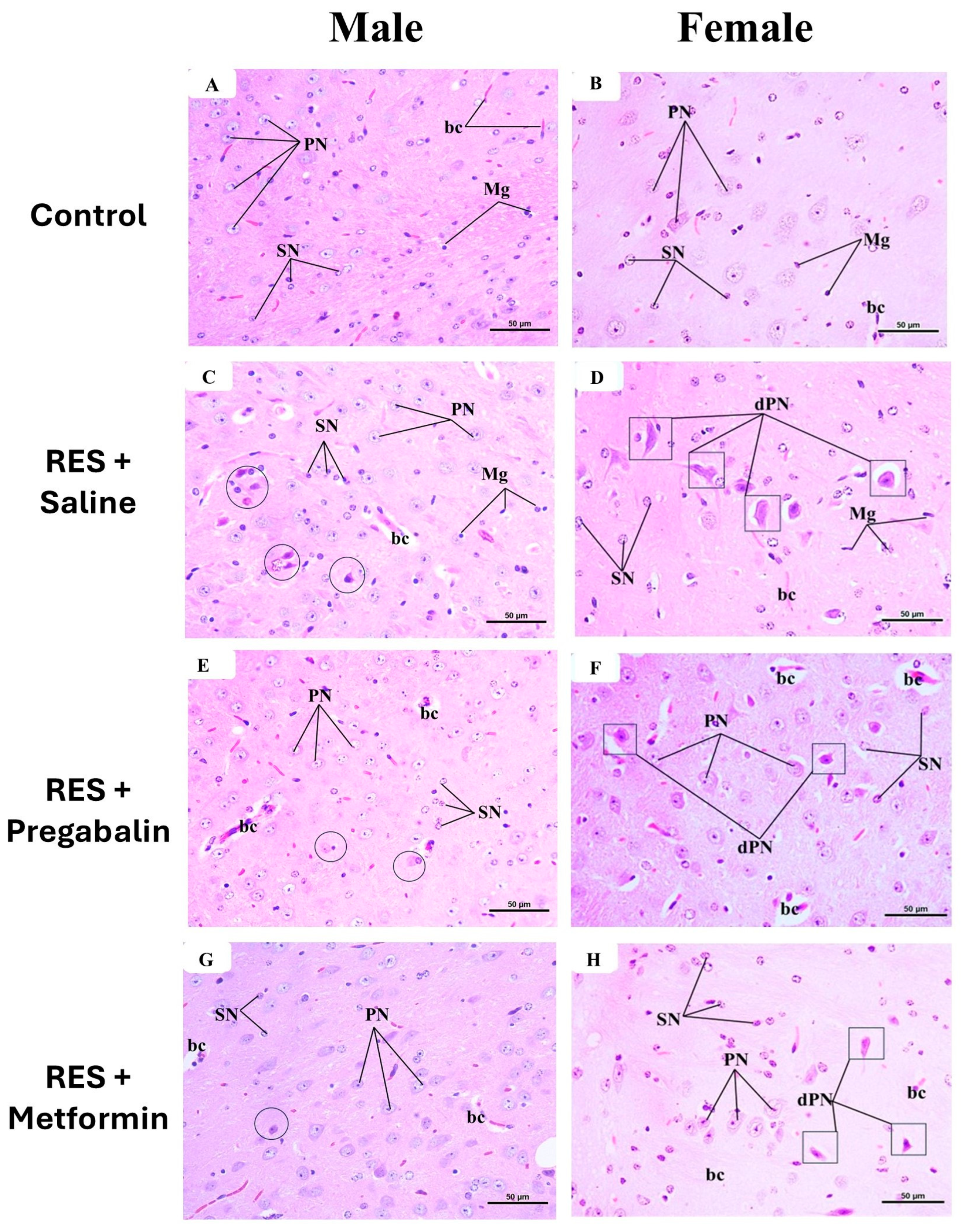
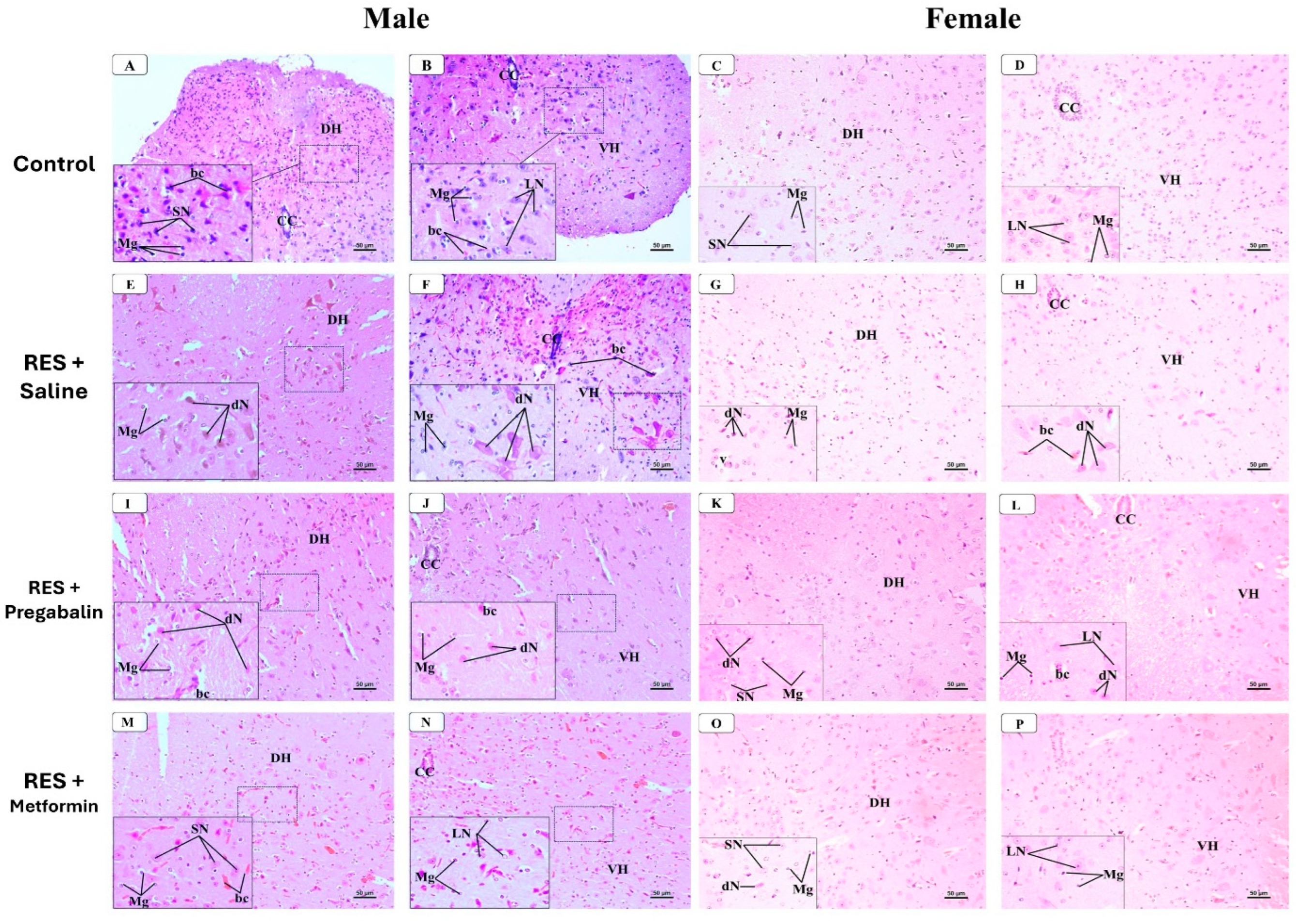
3.6. Metformin Alleviated Reserpine Induced-Histopathological Changes in the Hippocampus, Thalamus, and Spinal Cord
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Giorgi, V.; Marotto, D.; Atzeni, F. Fibromyalgia: An update on clinical characteristics, aetiopathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queiroz, L.P. Worldwide Epidemiology of Fibromyalgia. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Impellizzeri, D. Fibromyalgia: Pathogenesis, Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Treatment Options Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trucharte, A.; Leon, L.; Castillo-Parra, G.; Magán, I.; Freites, D.; Redondo, M. Emotional regulation processes: Influence on pain and disability in fibromyalgia patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Inanici, F.F.; Yunus, M.B. History of fibromyalgia: Past to present. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2004, 8, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutra, R.C.; Martins, C.P.; Paes, R.S.; Baldasso, G.M.; Ferrarini, E.G.; Scussel, R.; Zaccaron, R.P.; Machado-De-Ávila, R.A.; Silveira, P.C.L. Pramipexole, a dopamine D3/D2 receptor-preferring agonist, attenuates reserpine-induced fibromyalgia-like model in mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomares, F.B.; Roy, S.; Funck, T.; Feier, N.A.; Thiel, A.; Fitzcharles, M.-A.; Schweinhardt, P. Upregulation of cortical GABAA receptor concentration in fibromyalgia. Pain 2019, 161, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Schweinhardt, P. Dysfunctional Neurotransmitter Systems in Fibromyalgia, Their Role in Central Stress Circuitry and Pharmacological Actions on These Systems. Pain Res. Treat. 2011, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.; Kwong, W.J.; Armstrong, H.; Behling, M.; Niemira, J.; Lang, K. Analysis of Real World Dosing Patterns for the 3 FDA-Approved Medications in the Treatment of Fibromyalgia. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2018, 11, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Häuser, W.; Walitt, B.; Fitzcharles, M.-A.; Sommer, C. Review of pharmacological therapies in fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissardo, J.P.; Caprara, A.L.F. Pregabalin-associated movement disorders: A literature review. Brain Circ. 2020, 6, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.K.; Baidya, D.K.; Agarwal, A.; Khanna, P. Pregabalin in acute and chronic pain. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 27, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, M.; Jacobsen, H.B.; Andersson, S.; Stubhaug, A. Cognitive Effects of Perioperative Pregabalin. Anesthesiology 2019, 130, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kim, S.; Ko, Y.-J.; Park, B.-J. Duloxetine and cardiovascular adverse events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 124, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccardi, F.; Khunti, K.; Marx, N.; Davies, M.J. First-line treatment for type 2 diabetes: Is it too early to abandon metformin? Lancet 2020, 396, 1705–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Flores, G.D.C.; Guzmán-Priego, C.G.; Parra-Flores, L.I.; Murbartián, J.; Torres-López, J.E.; Granados-Soto, V. Metformin: A Prospective Alternative for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 558474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Kroin, J.S.; Moric, M.; McCarthy, R.J.; Buvanendran, A. Early Treatment With Metformin in a Mice Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Reduces Pain and Edema. Anesthesia Analg. 2020, 130, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, K.E.; Szabo-Pardi, T.; Wentworth, E.; McDougal, T.A.; Dussor, G.; Burton, M.D.; Price, T.J. The antidiabetic drug metformin prevents and reverses neuropathic pain and spinal cord microglial activation in male but not female mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullón, P.; Alcocer-Gómez, E.; Carrión, A.M.; Marín-Aguilar, F.; Garrido-Maraver, J.; Román-Malo, L.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; Culic, O.; Ryffel, B.; Apetoh, L.; et al. AMPK Phosphorylation Modulates Pain by Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer-Gómez, E.; Garrido-Maraver, J.; Bullón, P.; Marín-Aguilar, F.; Cotán, D.; Carrión, A.M.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Sánchez-Alcazar, J.A.; Battino, M.; et al. Metformin and caloric restriction induce an AMPK-dependent restoration of mitochondrial dysfunction in fibroblasts from Fibromyalgia patients. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivavedi, N.; Kumar, M.; Tej, G.N.V.C.; Nayak, P.K. Metformin and ascorbic acid combination therapy ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus and comorbid depression in rats. Brain Res. 2017, 1674, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristou, S.; Papanas, N. Reduction of Depression in Diabetes: A New Pleiotropic Action of Metformin? Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.E.; Abdel-Rahman, R.F.; Mahmoud, S.S.; Khattab, M.M.; Safar, M.M. Metformin and trimetazidine ameliorate diabetes-induced cognitive impediment in status epileptic rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 104, 106893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathkhor, A.J.; Ibraheem, N.M. Prevalence and Impact of obesity on fibromyalgia syndrome and its allied symptoms. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2023, 12, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, Y.; Oe, T.; Aoki, T.; Matsuoka, N. Biogenic amine depletion causes chronic muscular pain and tactile allodynia accompanied by depression: A putative animal model of fibromyalgia. Pain 2009, 146, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Kaur, A.; Singh, A.P.; Bhatti, R. Daphnetin, a natural coumarin averts reserpine-induced fibromyalgia in mice: Modulation of MAO-A. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AboTaleb, H.; Hindi, E.A.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Alturkistani, H.A.; Halawani, M.M.; Al-Thepyani, M.A.; Alghamdi, B.S. Evaluation of reserpine-induced fibromyalgia in mice: A comparative behavioral, neurochemical, and histological assessment of two doses. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusco, I.; Justino, A.B.; Silva, C.R.; Fischer, S.; Cunha, T.M.; Scussel, R.; Machado-De-Ávila, R.A.; Ferreira, J.; Oliveira, S.M. Kinins and their B1 and B2 receptors are involved in fibromyalgia-like pain symptoms in mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Cano, R.; Boivin, B.; Bullock, D.; Cornelissen, L.; Andrews, N.; Costigan, M. Up–Down Reader: An Open Source Program for Efficiently Processing 50% von Frey Thresholds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.L.; Hansen, R.B.; Storm, M.A.; Olesen, J.; Hansen, T.F.; Ossipov, M.; Izarzugaza, J.M.G.; Porreca, F.; Kristensen, D.M. Von Frey testing revisited: Provision of an online algorithm for improved accuracy of 50% thresholds. Eur. J. Pain 2019, 24, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.P.; Sperotto, N.D.; Maciel, I.S.; Leite, C.E.; Souza, A.H.; Campos, M.M. Effects of D-series resolvins on behavioral and neurochemical changes in a fibromyalgia-like model in mice. Neuropharmacology 2014, 86, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunskaar, S.; Berge, O.-G.; Hole, K. A modified hot-plate test sensitivie to mild analgesics. Behav. Brain Res. 1986, 21, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałat, K.; Furgała-Wojas, A. Serotonergic Neurotransmission System Modulator, Vortioxetine, and Dopaminergic D2/D3 Receptor Agonist, Ropinirole, Attenuate Fibromyalgia-Like Symptoms in Mice. Molecules 2021, 26, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dvorakova, L.S.; Vetter, I. Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, H.A.A.; Alghamdi, B.S. Neuroprotective Effects of Melatonin during Demyelination and Remyelination Stages in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 70, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarifi, A.; Alsalem, M.; Mustafa, A. Effects of intraplantar administration of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) on rotarod performance in mice. Scand. J. Pain 2019, 19, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagnino, A.P.A.; da Silva, R.B.M.; Chagastelles, P.C.; Pereira, T.C.B.; Venturin, G.T.; Greggio, S.; da Costa, J.C.; Bogo, M.R.; Campos, M.M. Nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor modulates painful and fatigue symptoms in a mouse model of fibromyalgia. Pain 2019, 160, 1383–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, S.S.; Camargo, E.A.; DeSantana, J.M.; Araújo, A.A.S.; Menezes, P.P.; Lucca-Júnior, W.; Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.C.; Bonjardim, L.R.; Quintans-Júnior, L. Linalool and linalool complexed in β-cyclodextrin produce anti-hyperalgesic activity and increase Fos protein expression in animal model for fibromyalgia. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 2014, 387, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serretti, A. Anhedonia and Depressive Disorders. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2023, 21, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The Forced Swim Test as a Model of Depressive-like Behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e52587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałat, K.; Siwek, A.; Starowicz, G.; Librowski, T.; Nowak, G.; Drabik, U.; Gajdosz, R.; Popik, P. Antidepressant-like effects of ketamine, norketamine and dehydronorketamine in forced swim test: Role of activity at NMDA receptor. Neuropharmacology 2015, 99, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mombereau, C.; Vassout, A. The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: Review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 571–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, G.K.; Hindi, E.A.; Zayed, M.A.; El-Aziz, G.S.A.; Alturkistani, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.F.; Al-Thepyani, M.A.; Bakhlgi, R.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Ashraf, G.M.; et al. The Impact of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depression on Spatial, Recognition and Reference Memory Tasks in Mice: Behavioral and Histological Study. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Benzo, R.P.; O Whipple, M.; McAllister, S.J.; Erwin, P.J.; Saligan, L.N. Beyond pain in fibromyalgia: Insights into the symptom of fatigue. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Marsá, M.; Palomares, N.; Morón, M.D.; Tajima, K.; Fuentes, M.E.; López-Ibor, J.J.; Carrasco, J.L. Psychological Factors Affecting Response to Antidepressant Drugs in Fibromyalgia. Psychosomatics 2011, 52, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.T.; Moore, B.J. Pregabalin for the treatment of fibromyalgia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2012, 13, 1527–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, E.S.; Becker, G.; Fialho, M.F.P.; Oliveira, S.M. Animal models of fibromyalgia: What is the best choice? Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 230, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W.-X.; Lu, K.; Pan, H.; Wang, T.; Oh, C.-D.; Yi, D.; Huang, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.S.; Braga, A.V.; Rodrigues, F.F.; Morais, M.I.; Dutra, M.M.; Batista, C.R.; Melo, I.S.; Costa, S.O.; Goulart, F.A.; Coelho, M.M.; et al. Metformin antinociceptive effect in models of nociceptive and neuropathic pain is partially mediated by activation of opioidergic mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, M.D.; Tillu, D.V.; Mazhar, K.; Mejia, G.L.; Asiedu, M.N.; Inyang, K.; Hughes, T.; Lian, B.; Dussor, G.; Price, T.J. Pharmacological activation of AMPK inhibits incision-evoked mechanical hypersensitivity and the development of hyperalgesic priming in mice. Neuroscience 2017, 359, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecikoza, U.; Tomić, M.; Nastić, K.; Micov, A.; Stepanović-Petrović, R. Synergism between metformin and analgesics/vitamin B12 in a model of painful diabetic neuropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Khoutorsky, A.; Sorge, R.E.; Yan, J.; Asiedu, M.N.; Valdez, A.; Ghosh, S.; Dussor, G.; Mogil, J.S.; Sonenberg, N.; et al. mTORC1 inhibition induces pain via IRS-1-dependent feedback activation of ERK. Pain 2013, 154, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Asiedu, M.N.; Tillu, D.V.; Sanoja, R.; Yan, J.; Lark, A.; Khoutorsky, A.; Johnson, J.; A Peebles, K.; Lepow, T.; et al. Targeting Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) in Preclinical Models Reveals a Potential Mechanism for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Mol. Pain 2011, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jîtcă, G.; Gáll, Z.; E Vari, C.; E Ősz, B.; Tero-Vescan, A.; Groșan, A.; Dogaru, M.T. Beneficial effects of metformin on haloperidol-induced motor deficits in rats. A behavioral assessment. Acta Marisiensis-Ser. Medica 2021, 67, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadernezhad, N.; Khalaj, L.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Mirmasoumi, M.; Ashabi, G. Metformin pretreatment enhanced learning and memory in cerebral forebrain ischaemia: The role of the AMPK/BDNF/P70SK signalling pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.; Silva, N.; Golden, S.H.; Rajala, U.; Timonen, M.; Stahl, D.; Ismail, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Association Between Depression and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troubat, R.; Barone, P.; Leman, S.; Desmidt, T.; Cressant, A.; Atanasova, B.; Brizard, B.; El Hage, W.; Surget, A.; Belzung, C.; et al. Neuroinflammation and depression: A review. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 53, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.M.; Crofford, L.J.; Martin, S.A.; Young, J.P.; Sharma, U. The Effect of Anxiety and Depression on Improvements in Pain in a Randomized, Controlled Trial of Pregabalin for Treatment of Fibromyalgia. Pain Med. 2007, 8, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- White, K.P.; Nielson, W.R.; Harth, M.; Ostbye, T.; Speechley, M. Chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain with or without fibromyalgia: Psychological distress in a representative community adult sample. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 588–594. [Google Scholar]
- Clauw, D.J.; Arnold, L.M.; McCarberg, B.H. The Science of Fibromyalgia. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmeules, J.A.; Cedraschi, C.; Rapiti, E.; Baumgartner, E.; Finckh, A.; Cohen, P.; Dayer, P.; Vischer, T.L. Neurophysiologic evidence for a central sensitization in patients with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnigenis, M.N.; Barland, P. Fibromyalgia syndrome and serotonin. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2001, 19, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Fürst, S. Transmitters involved in antinociception in the spinal cord. Brain Res. Bull. 1999, 48, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertovaara, A. Noradrenergic pain modulation. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 80, 53–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendroud, S.; Fitzgerald, L.A.; Murray, I.V.; Hanna, A. Physiology, Nociceptive Pathways; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’mahony, L.F.; Srivastava, A.; Mehta, P.; Ciurtin, C. Is fibromyalgia associated with a unique cytokine profile? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2602–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Chen, H. Metformin: A Novel Weapon Against Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 622262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.-C.; Lin, L.-X.; Hu, X.-F.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.-P.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Hu, L.; Liu, W.-T.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Shu, Y.; et al. AMPK activation attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation and IL-1β expression. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Feng, Y.; Tang, H. Metformin Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Expression and Regulates Inflammatory Microenvironment to Delay the Progression of Colorectal Cancer. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, R.F.; Laird, A.R.; Ramage, A.E.; Parkinson, A.L.; Lewis, J.; Clauw, D.J.; Williams, D.A.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Farrell, M.J.; Eickhoff, S.B.; et al. Structural Brain Anomalies and Chronic Pain: A Quantitative Meta-Analysis of Gray Matter Volume. J. Pain 2013, 14, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; Mohamed, H.K.; Kotb, H.I. Reactive Astrogliosis in an Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia: Effect of Dexmedetomidine. Cells Tissues Organs 2018, 205, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emad, Y.; Ragab, Y.; Zeinhom, F.; El-Khouly, G.; Abou-Zeid, A.; Rasker, J.J. Hippocampus dysfunction may explain symptoms of fibromyalgia syndrome. A study with single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCrae, C.S.; O’shea, A.M.; Boissoneault, J.; Vatthauer, K.; Robinson, M.; Staud, R.; Perlstein, W.M.; Craggs, J.G.; Center, G.M.R.V.A.M. Fibromyalgia patients have reduced hippocampal volume compared with healthy controls. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Arenas, G.; Pulido, G.; Treviño, S.; Vázquez-Roque, R.; Flores, G.; Moran, C.; Handal-Silva, A.; Guevara, J.; Venegas, B.; Díaz, A. Effects of metformin on recognition memory and hippocampal neuroplasticity in rats with metabolic syndrome. Synapse 2020, 74, e22153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, W.H.; Nunes, A.K.; França, M.E.R.; Santos, L.A.; Lós, D.B.; Rocha, S.W.; Barbosa, K.P.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Peixoto, C.A. Effects of metformin on inflammation and short-term memory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1644, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Lv, Z. Metformin improves cognitive impairment in diabetic mice induced by a combination of streptozotocin and isoflurane anesthesia. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 10982–10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarini, E.G.; Gonçalves, E.C.D.; Menegasso, J.F.; Rabelo, B.D.; Felipetti, F.A.; Dutra, R.C. Exercise Reduces Pain and Deleterious Histological Effects in Fibromyalgia-like Model. Neuroscience 2021, 465, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.J. Neuronal circuitry for pain processing in the dorsal horn. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, S.S.; Koochekpour, S. Glutamate, Glutamate Receptors, and Downstream Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Li, L.; Kandhare, A.D.; Mukherjee-Kandhare, A.A.; Bodhankar, S.L. Attenuation of reserpine-induced fibromyalgia via ROS and serotonergic pathway modulation by fisetin, a plant flavonoid polyphenol. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Giacomini, K.M. Transporters Involved in Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Treatment Response. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urakami, Y.; Okuda, M.; Saito, H.; Inui, K.-I. Hormonal regulation of organic cation transporter OCT2 expression in rat kidney. FEBS Lett. 2000, 473, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnouti, Y.; Petrick, J.S.; Klaassen, C.D. Tissue distribution and ontogeny of organic cation transporters in mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 34, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, F.; Vacca, V.; Tofanicchio, J.; Strimpakos, G.; Giacovazzo, G.; Pavone, F.; Coccurello, R.; Marinelli, S. Sex Differences in Neuropathy: The Paradigmatic Case of MetFormin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, C.; Pavlidi, P.; Sakelliadou, D.-G.; Grammatikopoulou, T.; Kokras, N. Sex Differences in Blood–Brain Barrier Transport of Psychotropic Drugs. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 844916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, V.; Demori, I.; Browne, C.J.; Deblieck, C.; Burlando, B. Fibromyalgia in Pregnancy: Neuro-Endocrine Fluctuations Provide Insight into Pathophysiology and Neuromodulation Treatment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AboTaleb, H.A.; Alturkistani, H.A.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Hindi, E.A.; Halawani, M.M.; Al-Thepyani, M.A.; Alghamdi, B.S. The Antinociceptive Effects and Sex-Specific Neurotransmitter Modulation of Metformin in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Cells 2024, 13, 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13231986
AboTaleb HA, Alturkistani HA, Abd El-Aziz GS, Hindi EA, Halawani MM, Al-Thepyani MA, Alghamdi BS. The Antinociceptive Effects and Sex-Specific Neurotransmitter Modulation of Metformin in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Cells. 2024; 13(23):1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13231986
Chicago/Turabian StyleAboTaleb, Hanin Abdulbaset, Hani A. Alturkistani, Gamal S. Abd El-Aziz, Emad A. Hindi, Mervat M. Halawani, Mona Ali Al-Thepyani, and Badrah S. Alghamdi. 2024. "The Antinociceptive Effects and Sex-Specific Neurotransmitter Modulation of Metformin in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia" Cells 13, no. 23: 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13231986
APA StyleAboTaleb, H. A., Alturkistani, H. A., Abd El-Aziz, G. S., Hindi, E. A., Halawani, M. M., Al-Thepyani, M. A., & Alghamdi, B. S. (2024). The Antinociceptive Effects and Sex-Specific Neurotransmitter Modulation of Metformin in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Cells, 13(23), 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13231986





