Abstract
Cognitive impairment is a major healthcare challenge worldwide, with vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) being its second leading cause after Alzheimer’s disease. VCI is a heterogeneous group of cognitive disorders resulting from various vascular pathologies. Therefore, it is particularly difficult to determine its underlying cause and exact molecular basis. Nevertheless, the current understanding of the pathophysiological processes underlying VCI has changed and evolved in the last decades. The aim of this narrative review is to summarize the current state of knowledge on VCI pathogenesis and to analyze the potential role of the gut microbiota in this process, considering the most recent scientific reports and in accordance with the current understanding of these processes. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, which results in impaired blood supply, i.e., oxygen and nutrient deficiency, is the main underlying mechanism of VCI. Furthermore, chronic cerebral hypoperfusion triggers a cascade of molecular changes, starting with an energy imbalance, leading to glutamate excitotoxicity, acidotoxicity, and oxidative stress. Also, all of the above provoke the activation of microglia and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that recruit systemic immune cells and lead to their infiltration into the central nervous system, resulting in neuroinflammation. Blood–brain barrier dysfunction may occur at various stages of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, ultimately increasing its permeability and allowing potentially toxic substances to enter the brain parenchyma. Gut microbiota and their metabolites, which have been identified in numerous inflammatory conditions, may also influence the pathophysiological processes of VCI.
1. Introduction
As the global population continues to age, cognitive impairment is becoming a major healthcare challenge worldwide [1], and vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) is thought to be the second most common cause of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease [2]. Currently, VCI is a growing area of concern that requires greater attention in policy, healthcare, and research [3]. The prevalence of VCI may still be underestimated, as it shows considerable geographical variation. It ranges from approximately 20% of all dementia cases in Europe and North America to up to 30% in Asia and developing countries [4]. Hence, genetic predispositions, socioeconomic deprivation, and unhealthy lifestyle factors are well-established contributors that can increase the risk of developing dementia [5]. Individuals with lower socioeconomic status not only exhibit significantly higher risk of dementia [6], but also have an elevated prevalence of cardio-cerebrovascular diseases, which are among the greatest risk factors for VCI [7]. Additionally, the incidence of VCI rises with age, contributing significantly to the rising global prevalence of dementia, which is expected to nearly triple by 2050 [8].
VCI is a progressive disorder without a registered causal treatment; however, there are some preventive options affecting traditional risk factors for the disease [9]. In addition, no specific biomarker has been established to date, so earlier diagnostic tools are needed [9]. Typical clinical manifestations of VCI involve problems with reasoning, planning, judgment, and cognitive decline, particularly in executive function, which may be accompanied by gait disturbances [10]. However, VCI encompasses a broad spectrum of cognitive deficits, ranging from milder forms, such as vascular mild cognitive impairment (VaMCI), to more severe conditions like vascular dementia (VaD) [11]. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke–Canadian Stroke Network, the term VCI applies to cognitive deficits resulting from or related to underlying vascular factors, regardless of whether the pathogenesis of the vascular lesion is ischemic or hemorrhagic [12]. Therefore, the classification of VCI is complex and often ambiguous. The Vascular Impairment of Cognition Classification Consensus Study (VICCCS) has identified four basic subtypes of dementia: post-stroke dementia, multi-infarct (cortical) dementia, subcortical ischemic VCI, and mixed dementias, which encompass varying combinations of two or more etiologic cognitive deficits [13]. The presence of vascular abnormalities, leading to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and subsequent hypoxia, is a common feature of these pathologies. According to Rajeev et al., chronic cerebral hypoperfusion appears to be a critical underlying mechanism that integrates various factors, resulting in ischemia-induced neuronal damage [14]. Thus, the central nervous system (CNS) is particularly sensitive to disruptions in blood supply, and normal perfusion is essential for maintaining neuronal activity. Neuronal function and survival, as well as the structural and functional integrity of the brain, are critically dependent on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients [15]. Therefore, chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and ischemia are associated with omnidirectional changes within the CNS, promoting oxidative stress, inflammatory processes, and subsequent neuronal damage. Together, these pathological changes contribute to the development of VCI (summarized in Table 1 and Figure 1) [16]. Finally, given the extensive research on the gut microbiota in various inflammation-mediated conditions, it is important to consider its potential role in the development of VCI. Recognizing the fact that the comprehension of pathological processes underlying VCI has evolved in the last decades, this narrative review aims to summarize the current understanding of the pathogenesis of VCI, focusing on the key role of blood–brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction, oxidative stress, and immunological processes in the pathophysiology of the disease. Furthermore, the potential influence of the gut microbiota on the development of VCI will be explored. To date, the vast majority of papers have focused on detailed descriptions of separated processes, without providing a coherent synthesis of all these elements, particularly the link between the gut microbiota and the description of disease pathophysiology.

Table 1.
Molecular mechanisms underlying vascular cognitive impairment, their clinical manifestations, and potential therapeutic implications.
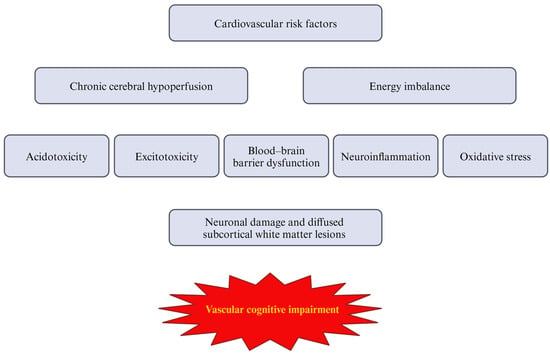
Figure 1.
The sequence of vascular cognitive impairment pathophysiology.
2. Materials and Methods
To conduct a comprehensive analysis of the topic, a thorough search of the relevant literature was undertaken using the PubMed and Google Scholar databases, covering studies from their inception to 23 September 2024. Both experimental and clinical studies were included. Titles and abstracts were screened for key terms such as ‘vascular cognitive impairment’, ‘vascular dementia’, ‘molecular mechanism’, ‘molecular basis’, and ‘gut microbiota’. To ensure thorough coverage, relevant references from the identified articles were also manually reviewed by the authors.
3. Molecular Basis of Vascular Cognitive Impairment
VCI comprises a heterogeneous group of cognitive deficits resulting from various vascular pathologies. It can result from a widespread acute ischemic stroke affecting strategic areas of the brain, such as the frontal cortex, or from multiple cortical infarcts causing direct damage to cerebral tissue [17]. On the other hand, diffuse subcortical ischemic damage associated with cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is also a common cause of VCI. This is why it is so difficult not only to classify these pathologies, but also to understand their molecular mechanisms [13]. Yet, it is known that chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and thromboembolic events, which reduce cerebral blood flow and induce hypoxia, cause oxidative stress and inflammation in the nervous system [18]. The molecular mechanisms underlying the consequences of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion are summarized in Figure 2.
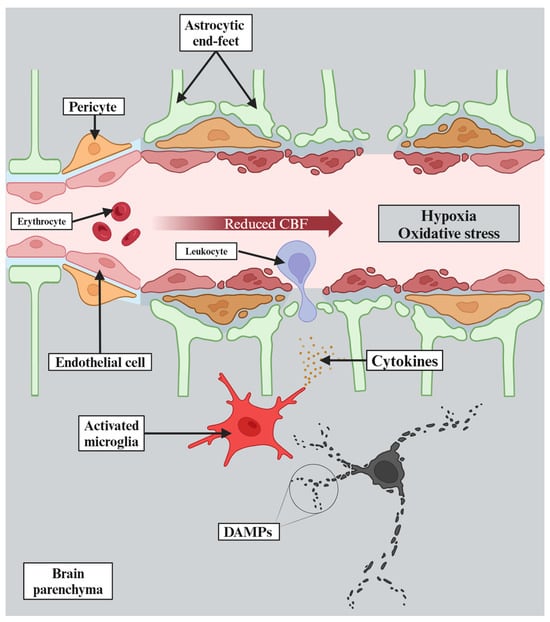
Figure 2.
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion leads to reduced cerebral blood flow (CBF), which then causes hypoxia. Moreover, hypoxia results in rapid depletion of adenosine triphosphate that triggers excitotoxicity and acidotoxicity. The pathophysiological changes described above lead to oxidative stress and further cellular damage. Thereafter, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are released, triggering activation of microglia, which consequently release pro-inflammatory cytokines that exacerbate neuroinflammation. Finally, all of this causes endothelial dysfunction resulting in blood–brain barrier dysfunction and further deterioration of the whole process.
3.1. Energy Imbalance, Excitotoxicity, and Acidotoxicity
Although the brain accounts for less than 2% of total body weight, it requires over 20% of the body’s energy supply [19]. Hence, it is not surprising that a blood flow of at least 50 mL/100 g/min is required to provide an adequate supply of both glucose and oxygen [20]. Consequently, it is relatively easy to induce damage through chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Under hypoxic–ischemic conditions, neurons, which derive their energy primarily from aerobic glucose metabolism, rapidly become depleted of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This condition impairs the function of ATP-dependent ion pumps, including ATP-dependent sodium–potassium pumps (Na+/K+-ATPases), which are responsible for maintaining the resting potential of cells [14]. As a result, potassium ions (K+) flow out of the cell while sodium ions (Na+) flow in the opposite direction, leading to anoxic depolarization of not only neurons but also of glial cells. This results in an electrochemical imbalance and the opening of voltage-gated calcium (Ca2+) channels in the presynaptic membrane, causing an excessive influx of Ca2+ ions that cannot be efficiently removed from the cell [20]. The elevated intracellular Ca2+ levels, in turn, induce an unrestricted release of glutamate, the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS, into the synaptic cleft [20,21].
Also, ATP deficiency impairs glutamate transporters, resulting in insufficient reuptake of glutamate by astrocytes [20]. A study by Ketheeswaranathan et al. using a mouse model of ischemic stroke induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion demonstrated that the mRNA expression of glial cell glutamate transporters was significantly reduced in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of ischemic stroke mice compared to the control group [22]. Combined, these factors cause an energy imbalance that leads to excessive glutamate accumulation in the synaptic cleft, ultimately inducing a state of excitotoxicity within the CNS [23].
Excitotoxicity, in general, refers to cell death caused by the overactivity of excitatory amino acids. In the case of neuronal excitotoxicity, it is specifically glutamate-induced neuronal damage. Through its interaction with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, glutamate may trigger an additional influx of Ca2+ ions into neurons, causing further release of glutamate [24]. The interaction of glutamate with certain alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isooxazole-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors, long thought to be impermeable to calcium, may also increase intracellular Ca2+ concentration. In addition, the expression of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors may be increased in pathological conditions. Since AMPA receptors are permeable to zinc cations, which induce mitochondrial damage, their role in excitotoxicity should not be underestimated [25]. Studies also report glutamate-independent pathways of Ca2+ influx, such as the melastatin subfamily of transient receptor potential channels or acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) [26]. Given that hypoxia favors anaerobic glucose metabolism, it ultimately leads to the reduction of pyruvate to lactate anions, which is accompanied by the production of protons (H+) causing acidosis [27]. Over the years, various theories have been proposed as to how acidosis causes neural damage. The current understanding of acidotoxicity emphasizes the role of ASICs, which are activated by a decrease in extracellular pH, enabling the influx of Ca2+ ions into neurons [27,28]. Additionally, proton-activated chloride (Cl−) channels also trigger Cl− influx into neurons [27]. The disruption of ion balance, leading to the accumulation of Na+, Cl−, and Ca2+ ions in neurons, is accompanied by an osmotic influx of water, resulting in cytotoxic edema and ultimately oncosis [29,30]. Another potential mechanism of Ca2+ influx-driven cell death may be that of the activation of catabolic enzymes, such as endonuclease and calpain, leading to apoptosis or necrosis depending on the metabolic state of the neuron [20,31].
3.2. Oxidative Stress
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), or free radicals, are formed during oxidative phosphorylation in the inner mitochondrial membrane, a process essential for the survival and function of all cell types [32]. ROS, including superoxide anions, peroxide, hydroxyl radicals, and singlet oxygen, contribute to various physiological processes such as cellular communication, modulation of gene expression, and immune response [33]. However, excessive ROS production, beyond the neutralizing capacity of the CNS antioxidant defenses, can lead to oxidative damage, including extensive lipid peroxidation, but also to protein and DNA damage. This phenomenon is known as oxidative stress and has been linked to numerous neurodegenerative disorders [32]. Even though the hypothesis that ROS may be involved in the aging process dates back to the 1950s, for many years, little was known about the molecular basis of this association [34]. In fact, the level of oxidative stress is still difficult to measure directly due to the short lifespan and rapid reactivity of ROS. Therefore, studies often use proxies, mainly the products of lipid peroxidation and damaged proteins or DNA [35]. Given that the CNS is mainly composed of lipid-rich tissues and that fatty acids are particularly susceptible to peroxidation, oxidative stress is naturally associated with neurological diseases, including AD and VCI [36].
A study by Gustaw-Rothenberg et al. revealed elevated markers of oxidative stress, including malondialdehyde (MDA), a product of lipid peroxidation, in both AD and VaD groups, compared to healthy controls. Also, patients with VaD had significantly higher plasma concentrations of oxidative stress markers than those with AD [37]. Based on animal studies, oxidative stress is considered a key component of ischemic brain injury [38], a finding further confirmed by Kelly et al. Their study reported elevated levels of F2-isoprostanes (F2IPs), another lipid peroxidation marker, in early stroke patients compared to controls, which correlated with plasma matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) levels in all stroke patients [39]. Thus, metalloproteinases may be responsible for the proteolytic dysfunction of the BBB and the white matter hyperintensities characteristic of VCI [40].
Furthermore, recent studies have shown that the levels of antioxidants may decrease during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion [38]. As mentioned above, chronic cerebral hypoperfusion leads to Ca2+ imbalance, which subsequently causes an overproduction of ROS in various pathways, including those involving the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (Nox) family and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) [14]. Based on animal model studies, Nox might be a key contributor to chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced oxidative stress and cognitive dysfunction [38]. For instance, a study conducted by Choi et al. in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, induced by bilateral common carotid artery ligation (two-vessel occlusion, 2VO), showed increased MDA levels and increased Nox1 expression in the hippocampi of 2VO rats. The study also demonstrated that Nox1 inhibition by apocynin significantly reduced superoxide production and oxidative DNA damage, as assessed by 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine immunoreactivity. Additionally, the neuronal loss in the CA1 hippocampal subfield, observed in 2VO rats, was significantly reduced following apocynin administration. Furthermore, apocynin treatment resulted in shorter mean session latencies and fewer search errors in spatial memory tests compared to the 2VO group [41].
NO-mediated vasodilation is another mechanism affected by oxidative stress. Since superoxide reacts with NO much faster than it can be neutralized by superoxide dismutases (SODs), the availability of NO produced by endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) is reduced. Thus, oxidative stress not only impairs endothelial function, leading to reduced cerebral blood flow, but it also disrupts neuronal signaling and neurogenesis, ultimately contributing to VCI [42]. Furthermore, ROS are produced not only during hypoxia; reperfusion and reoxygenation can also trigger their extensive release [33,43]. During hypoxia, electrons with reduction potential accumulate in the mitochondria. Upon the restoration of oxygenation, excess electrons can escape from the mitochondrial electron transport chain and interact with oxygen molecules to generate ROS [43].
Finally, oxidative stress contributes to inflammation, causing further damage. ROS can also cause intracellular damage starting in the mitochondria. Subsequent mitochondrial dysfunction results in the release of mitochondrial-derived damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), typically ROS-modified mitochondrial DNA and proteins [43]. Mitochondrial-derived DAMPs can activate the endogenous pathway of neuroinflammation through the NLRP3 inflammasome, causing activation of pro-caspase-1 and subsequent release of interleukin (IL)–18 and IL–1β. Also, extracellular mitochondrial-derived DAMPs activate a toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9)-dependent inflammatory cascade in other glial cells [44]. This creates a self-perpetuating vicious cycle that further accelerates neurodegeneration [43].
3.3. Neuroinflammation
The CNS has long been considered an immune-privileged area [45]. However, this concept has changed dramatically since the early days of pioneering neuroimmunological research [46]. The current understanding of CNS–immune interactions has not only revealed communication between the CNS and the peripheral immune system, but it has also identified the presence of a functional meningeal lymphatic system within the CNS [47]. Therefore, neuroinflammation, which can be defined as an immune response in the CNS, is not a spatially separated process as peripheral leukocytes can infiltrate the CNS, drawn in by secreted cytokines [48]. However, neuroinflammation is mainly regulated by microglia, CNS-residing immune cells, which originate from macrophage precursors [48]. Neuroinflammation itself is a complex process that contributes to both ischemic brain injury and also brain tissue regeneration [20]. While the classification of neurological disorders includes certain conditions categorized as inflammatory, e.g., multiple sclerosis, recent studies suggest that inflammation is associated with other diseases not traditionally considered neuroinflammatory, including Alzheimer’s disease [49].
A meta-analysis conducted by Custodero et al. demonstrated that serum or plasma IL–6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–α levels were significantly elevated in patients with VaD compared to healthy controls, but only IL–6 levels differed significantly between VaD and AD patients. C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were not significantly altered in patients with VaD compared to controls [50]. Additionally, serum IL–6 concentration is associated with white matter hyperintensities, the hallmark of VCI, as demonstrated by Kumiko Nagai et al. [51]. Furthermore, a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study by Yuge Xia et al. demonstrated an association between VaD and seven circulating cytokines, including IL–7, IL–17, and interferon gamma (IFN)–γ [52]. Therefore, it seems reasonable to consider neuroinflammatory components as integral to the VCI pathophysiology [16,53].
Furthermore, studies using a rat model of CCH, 2VO, have highlighted the activation of both astrocytes and microglia in response to hypoxia and ischemia [54]. Based on histopathologic examination of brain tissue from five patients with VaD, Rosenberg et al. suggest that microglia-/macrophage-induced damage may be associated with the progressive form of VaD [40]. Microglia are the first line of immune response within the CNS, recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and DAMPs [55]. As described above, during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, damaged cells release cellular debris, including fragments such as mitochondrial DNA, and act as DAMPs that activate microglia [44].
In general, microglia adopt two phenotypic states: pro-inflammatory (M1) and anti-inflammatory (M2). Activation by DAMPs through TLR4 induces the M1 phenotype [56]. A study in hypoxic neonatal rats revealed increased post-hypoxia TLR4 immunofluorescence and expression. Furthermore, TLR4 activation caused a significant increase in TNF–α and IL–1β expression, which was suppressed by TLR4 neutralization with a hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α antibody prior to exposure to hypoxia [57]. However, hypoxia itself causes upregulation of HIF-1α, which is a nuclear transcription factor that activates nuclear factor (NF)-κB [16]. NF-κB is considered to be one of major mediators of the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF–α, IL–1β, and IL–6 [58]. The release of these cytokines can lead to cell death and neuronal loss, which exacerbate inflammation in the nervous system and can manifest clinically as cognitive decline [43]. Additionally, microglia can produce adhesion molecules and chemokines [14]. IL–1β and TNF–α have also been shown to influence BBB permeability [59]. This cascade causes the recruitment of leukocytes and facilitates their infiltration into the CNS [14,20]. These leukocytes secrete further pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMPs [20], which are also produced and released by microglia [16]. Not only do MMPs cause damage to the extracellular matrix, but they also proteolyze the cerebrovascular basement membrane and tight junctions (TJs), thereby dysregulating BBB integrity [60]. Thus, the above processes contribute to both neurodegeneration and further exacerbation of inflammation.
3.4. Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction
The BBB, together with the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier at the choroid plexus and the arachnoid barrier, is a key component of the system that isolates the CNS from the peripheral systemic circulation. The BBB is a selectively permeable structure that separates the systemic blood circulation from the brain parenchyma and controls the influx of both nutrients and potentially toxic substances, as well as the outflow of CNS-derived metabolites. The BBB is not a homogeneous structure, as its composition and permeability vary depending on the specific region of the CNS it encloses [61]. It is composed of endothelial cells interconnected by TJs, together with pericytes and astrocyte end-feet that collectively regulate barrier integrity and function [62].
Recent studies have identified the dysregulation of the BBB in various pathological conditions, including cognitive disorders [63]. BBB dysfunction has also been observed in animal models of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion [64]. For instance, Ueno et al. conducted a study using a 2VO rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion to evaluate BBB permeability. They used horseradish peroxidase (HRP), an exogenous tracer often used to assess BBB integrity. Their findings demonstrated that chronic cerebral hypoperfusion increased BBB permeability, as indicated by the presence of HRP in the brain parenchyma, a phenomenon absent in the control group [65]. Similar results have been reported in clinical studies. Wallin et al. showed that patients with VaD exhibited significantly increased cerebrospinal fluid to serum albumin ratios compared to the control group, indicating compromised BBB integrity. They also suggest that the observed alterations in BBB permeability are more likely a consequence of underlying vascular dysfunction rather than a direct effect of stroke episodes [66].
In support of this theory, several traditional cardiovascular risk factors, including hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, and smoking, are known to induce endothelial dysfunction. This results in decreased levels of vasodilators, such as nitric oxide (NO), and increased production of endothelium-derived vasoconstricting factors [67]. Hence, these pathologies could disrupt the regulation of cerebral blood flow, potentially leading to hypoperfusion and subsequent hypoxia [68]. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion could affect the expression of TJs in endothelial cells, resulting in increased BBB permeability. Also, NMDA receptors are present on various brain cell types, including BBB endothelial cells. During chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced excitotoxicity, prolonged activation of NMDA receptors on endothelial cells initiates a cascade similar to that observed in neurons, ultimately contributing to the disruption of BBB integrity. The increased permeability of the BBB allows infiltration by immune cells, which exacerbate BBB dysfunction by promoting OS and neuroinflammatory processes [23].
4. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Vascular Cognitive Impairment
The role of the microbiota has been widely studied since its discovery, with the gut microbiota being of particular interest to neuroscientists. This attention has increased even further with the discovery of the gut–brain axis and the recognition of these bidirectional interactions in health and disease [69]. The healthy intestinal microbiota is predominantly composed of two phyla, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, which together account for 90% of all bacteria. The Firmicutes phylum consists of over 200 genera, 95% of which are Clostridium genera. The Bacteroidetes phylum, on the contrary, consists mainly of Bacteroides and Prevotella genera [70]. Dysbiosis, which is an imbalance in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, is often associated with inflammatory disorders [71,72].
Dysbiosis has also been shown to occur in the course of cognitive impairment [73]. Unfortunately, most of the studies analyzing the effect of gut microbiota on cognitive performance were conducted in patients with dementia in general or focused on patients with Alzheimer’s disease. For instance, a study by Kan et al. demonstrated diminished amounts of the Ruminococcus, Butyricimonas, and Oxalobacter genera in MCI patients compared to controls. These genera could discriminate MCI patients from the controls and were linked to attention and executive function. However, according to this study, there was no significant difference in alpha and beta diversity between the two groups [74]. In contrast, Vogt et al. identified changes in bacterial abundance in the gut microbiota of AD patients, including a decrease in Firmicutes and an increase in Bacteroidetes phyla, and a decrease in the Bifidobacterium genus [75]. There is also growing evidence that the gut microbiota may influence the development of VCI [76]. In a study by Fongang et al., the Barnesiella intestinihominis bacterium was associated with markers indicating greater progression of CSVD, one of the subtypes of VCI. In contrast, the abundance of Pseudobutyrivibrio and Ruminococcus genera was associated with decreased markers of CSVD [77].
Furthermore, the role of gut microbiota has been highlighted in the pathogenesis of hypertension [78], diabetes mellitus [79], cholesterol metabolism disorders, and atherosclerosis [80], which are traditional cardiovascular risk factors that may contribute to VCI [81]. Finally, the microbiota–gut–brain axis has been implicated in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion [82]. A study conducted in an animal model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion revealed that 2VO rats exhibited elevated levels of Bacteroidetes and Verrucomicrobia genera and a decreased abundance of Firmicutes and Tenericutes. In addition, a quantitative analysis of short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacteria, including the Prevotellaceae family and the Bifidobacterium genus, showed their lower levels in the 2VO group [82]. SCFAs, such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, are primary metabolites synthesized in the colon by the gut microbiota through the fermentation of dietary fiber. They are thought to be pivotal in the gut–brain axis crosstalk, as they have anti-inflammatory properties, increase BBB integrity, and enhance neurogenesis [83]. Additionally, research conducted in the 2VO-induced chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model showed that intraperitoneal butyrate administration improved cognitive function, as measured by spatial learning and memory tests [84]. Another gut microbiota-derived metabolite, trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is a proatherogenic and prothrombotic factor, implicated in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disorders [85]. A study by Deng et al. showed that the administration of TMAO aggravates VCI in 2VO rats. In addition, TMAO activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, which activates pro-caspase-1, and decreases the expression of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1). Therefore, TMAO is thought to exacerbate oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and ultimately apoptosis [86]. However, human-based research is needed to determine the exact impact of gut microbiota and their metabolites on VCI. All the multidirectional effects of gut microbiota on VCI are summarized in Figure 3. The gut microbiota is not only related to the pathophysiology of VCI, but also associated with its coexistence with celiac disease [87]. A majority of studies pertaining to celiac disease highlighted the significance of intestinal dysbiosis in the course of the disease [88]. Additionally, a study by Pennisi et al. using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation revealed that patients with celiac disease had enhanced intracortical facilitation [89]. According to Bella et al., patients with VCI also had enhanced intracortical facilitation at baseline assessment; however, it showed a trend to decrease during a follow-up of approximately 2 years, compared with control group [90]. Therefore, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation would be a useful diagnostic tool in both celiac disease and VCI. Finally, diet might influence cognitive functions directly or by affecting gut microbiota [91]. According to Jennings et al., some diet components, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can improve cognitive functions [92]. Diets rich in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids increase SCFA production and the amount of SCFA-producing bacteria, subsequently exerting an anti-inflammatory effect [93]. Moreover, Pennisi et al. indicated that daily mocha coffee and red wine consumption might be synergistically associated with global cognition and mood status in patients with VaMCI [94].
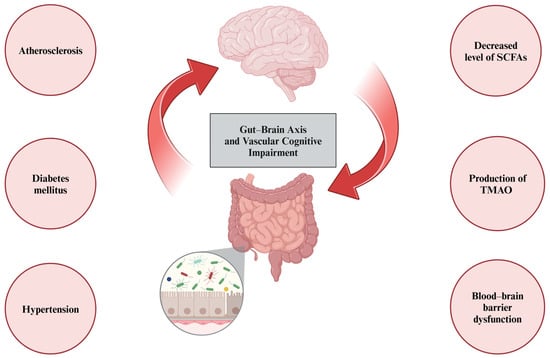
Figure 3.
Gut microbiota may influence vascular cognitive impairment omnidirectionally. First, its role has been established in traditional vascular risk factors, such as atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, or hypertension. Second, dysbiosis leads to reduced levels of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and elevated levels of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), leading to blood–brain barrier dysfunction and chronic low-grade inflammatory processes.
5. Limitations and Future Research Directions
This article addresses a broad and complex topic. Additionally, little is still known about the exact sequence of pathological changes in the course of VCI, as many studies focus on a particular element of disease pathophysiology rather than the process as a whole. Also, we are aware that a still relatively small research base of studies analyzing the role of gut microbiota in VCI pathogenesis is a limitation of our paper. Moreover, huge prospective longitudinal studies describing changes in the gut microbiota with the progression of the disorder are lacking, and, to date, there have been no multicenter, randomized clinical trials evaluating the targeting of the gut microbiota as a treatment option for VCI. Therefore, clinical studies are needed to determine this relationship and, potentially, to implement a causal treatment for this progressive disorder. Also, research directly linking the molecular basis of disease to clinical practice is warranted [95], as there is still no specific biomarker for VCI [9].
6. Conclusions
Although VCI is becoming a major healthcare problem worldwide, little is still known about its pathophysiology. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion is its main driver, which subsequently triggers a whole cascade of molecular changes, including an energy imbalance, leading to glutamate excitotoxicity, acidotoxicity, and oxidative stress. All of the above trigger the activation of microglia and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that recruit systemic immune cells and lead to their infiltration into the central nervous system, resulting in neuroinflammation. BBB dysfunction also plays a critical role in the pathological process. However, it is difficult to determine whether it is the first element of the cascade or an effect that further exacerbates neuroinflammation. In particular, little is known about the role of gut microbiota in VCI development and progression. Given that there is no pharmacological treatment for VCI to date [96], targeting gut microbiota is a novel and promising future option for clinicians, thus underscoring the translational nature of the research analyzing these interrelationships.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.O. and A.G.; data curation, P.O.; writing—original draft preparation, P.O.; writing—review and editing, P.O. and A.G.; visualization, P.O.; supervision, A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
All figures were created with Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence of Dementia in 2019 and Forecasted Prevalence in 2050: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang Wong, E.; Chang Chui, H. Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2022, 28, 750–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethemiotaki, I. Global Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases by Gender and Age during 2010–2019. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2024, 8, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, F.J.; Ikram, M.A. Epidemiology of Vascular Dementia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Pan, A.; Liu, G. Associations of Socioeconomic Status and Healthy Lifestyle with Incident Early-Onset and Late-Onset Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023, 4, e693–e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-N.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Li, Y.-Z.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.-T.; Wu, B.-S.; Tan, L.; Dong, Q.; Pan, A.; et al. Socioeconomic Status, Lifestyle and Risk of Incident Dementia: A Prospective Cohort Study of 276730 Participants. Geroscience 2023, 46, 2265–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.W.; Bae, S.; Kim, M.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Heo, S.-J.; Kim, M.; Lee, O.-H.; Kim, Y.; Im, E.; Uhm, J.-S.; et al. Socioeconomic Disparities and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study. J. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 04210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, F.J.; Ikram, M.A. Epidemiology of Dementia: The Burden on Society, the Challenges for Research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1750, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hainsworth, A.H.; Elahi, F.M.; Corriveau, R.A. An Introduction to Therapeutic Approaches to Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Cereb. Circ. Cogn. Behav. 2021, 2, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesbroek, J.M.; Biessels, G.J. Diagnosing Vascular Cognitive Impairment: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, P.; Kalaria, R.; O’Brien, J.; Skoog, I.; Alladi, S.; Black, S.E.; Blacker, D.; Blazer, D.G.; Chen, C.; Chui, H.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Vascular Cognitive Disorders. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2014, 28, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachinski, V.; Iadecola, C.; Petersen, R.C.; Breteler, M.M.; Nyenhuis, D.L.; Black, S.E.; Powers, W.J.; DeCarli, C.; Merino, J.G.; Kalaria, R.N.; et al. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke–Canadian Stroke Network Vascular Cognitive Impairment Harmonization Standards. Stroke 2006, 37, 2220–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrobot, O.A.; O’Brien, J.; Black, S.; Chen, C.; DeCarli, C.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Ford, G.A.; Kalaria, R.N.; Pantoni, L.; Pasquier, F.; et al. The Vascular Impairment of Cognition Classification Consensus Study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, V.; Chai, Y.L.; Poh, L.; Selvaraji, S.; Fann, D.Y.; Jo, D.-G.; De Silva, T.M.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V.; et al. Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion: A Critical Feature in Unravelling the Etiology of Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukandala, G.; Tynan, R.; Lanigan, S.; O’Connor, J. The Effects of Hypoxia and Inflammation on Synaptic Signaling in the CNS. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Ji, X.; Liu, J. Neuroinflammation in Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Current Evidence, Advances, and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Flier, W.M.; Skoog, I.; Schneider, J.A.; Pantoni, L.; Mok, V.; Chen, C.L.H.; Scheltens, P. Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, P.; Chopp, M.; Chen, J. Models and Mechanisms of Vascular Dementia. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 272, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifat, A.E.; Nozohouri, S.; Archie, S.R.; Chowdhury, E.A.; Abbruscato, T.J. Brain Energy Metabolism in Ischemic Stroke: Effects of Smoking and Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, D.Y.-W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Manzanero, S.; Chunduri, P.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathogenesis of Acute Stroke and the Role of Inflammasomes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 941–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov Kirdajova, D.; Kriska, J.; Tureckova, J.; Anderova, M. Ischemia-Triggered Glutamate Excitotoxicity From the Perspective of Glial Cells. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketheeswaranathan, P.; Turner, N.A.; Spary, E.J.; Batten, T.F.C.; McColl, B.W.; Saha, S. Changes in Glutamate Transporter Expression in Mouse Forebrain Areas Following Focal Ischemia. Brain Res. 2011, 1418, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeev, V.; Fann, D.Y.; Dinh, Q.N.; Kim, H.A.; De Silva, T.M.; Lai, M.K.P.; Chen, C.L.-H.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathophysiology of Blood Brain Barrier Dysfunction during Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1639–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Z. Molecular Mechanisms of Excitotoxicity and Their Relevance to Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ma, Y.-Y. Calcium Permeable-AMPA Receptors and Excitotoxicity in Neurological Disorders. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 711564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Inoue, K.; Si, H.; Xiong, Z. Calcium-Permeable Ion Channels Involved in Glutamate Receptor-Independent Ischemic Brain Injury. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M Tóth, O.; Menyhárt, Á.; Frank, R.; Hantosi, D.; Farkas, E.; Bari, F. Tissue Acidosis Associated with Ischemic Stroke to Guide Neuroprotective Drug Delivery. Biology 2020, 9, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.; Xiong, Z. Acidotoxicity in Brain Ischaemia. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayata, C.; Ropper, A.H. Ischaemic Brain Oedema. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2002, 9, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majno, G.; Joris, I. Apoptosis, Oncosis, and Necrosis. An Overview of Cell Death. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 146, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mongin, A.A. Disruption of Ionic and Cell Volume Homeostasis in Cerebral Ischemia: The Perfect Storm. Pathophysiology 2007, 14, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S. Oxidative Stress and the Central Nervous System. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, S. Targeting Oxidative Stress for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke: Upstream and Downstream Therapeutic Strategies. Brain Circ. 2016, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemma, C.; Vila, J.; Bachstetter, A.; Bickford, P.C. Oxidative Stress and the Aging Brain: From Theory to Prevention; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 0849338182. [Google Scholar]
- Katerji, M.; Filippova, M.; Duerksen-Hughes, P. Approaches and Methods to Measure Oxidative Stress in Clinical Samples: Research Applications in the Cancer Field. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 504678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, M.; Luca, A.; Calandra, C. The Role of Oxidative Damage in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 504678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustaw-Rothenberg, K.; Kowalczuk, K.; Stryjecka-Zimmer, M. Lipids’ Peroxidation Markers in Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2010, 10, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.-Q.; Wang, X.-R.; Xiao, L.-Y.; Tu, J.-F.; Zhu, W.; He, T.; Liu, C.-Z. Molecular Mechanisms of Vascular Dementia: What Can Be Learned from Animal Models of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion? Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 3670–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Morrow, J.D.; Ning, M.; Koroshetz, W.; Lo, E.H.; Terry, E.; Milne, G.L.; Hubbard, J.; Lee, H.; Stevenson, E.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G.A.; Sullivan, N.; Esiri, M.M. White Matter Damage Is Associated With Matrix Metalloproteinases in Vascular Dementia. Stroke 2001, 32, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Seo, J.-H.; Kim, H.Y.; Shin, C.Y.; Han, J.-S.; Han, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, J. NADPH Oxidase 1, a Novel Molecular Source of ROS in Hippocampal Neuronal Death in Vascular Dementia. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 21, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrissobolis, S.; Faraci, F.M. The Role of Oxidative Stress and NADPH Oxidase in Cerebrovascular Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmytriv, T.R.; Duve, K.V.; Storey, K.B.; Lushchak, V.I. Vicious Cycle of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Pathophysiology of Chronic Vascular Encephalopathy. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1443604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Liu, N.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Y. Mitochondrial-Derived Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Amplify Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, M.J.; Doose, J.M.; Melchior, B.; Schmid, C.D.; Ploix, C.C. CNS Immune Privilege: Hiding in Plain Sight. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 213, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, N.; Das, B.K. CNS: Not an Immunoprivilaged Site Anymore but a Virtual Secondary Lymphoid Organ. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 37, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Harris, T.H.; Kipnis, J. Revisiting the Mechanisms of CNS Immune Privilege. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The Devil Is in the Details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degan, D.; Ornello, R.; Tiseo, C.; Carolei, A.; Sacco, S.; Pistoia, F. The Role of Inflammation in Neurological Disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1485–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodero, C.; Ciavarella, A.; Panza, F.; Gnocchi, D.; Lenato, G.M.; Lee, J.; Mazzocca, A.; Sabbà, C.; Solfrizzi, V. Role of Inflammatory Markers in the Diagnosis of Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1373–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Kozaki, K.; Sonohara, K.; Akishita, M.; Toba, K. Relationship between Interleukin-6 and Cerebral Deep White Matter and Periventricular Hyperintensity in Elderly Women. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2011, 11, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, X.; Sun, R. Circulating Cytokines and Vascular Dementia: A Bi-Directional Mendelian Randomization Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 189, 112394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipollini, V.; Troili, F.; Giubilei, F. Emerging Biomarkers in Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: From Pathophysiological Pathways to Clinical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, E.; Luiten, P.G.M.; Bari, F. Permanent, Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion in the Rat: A Model for Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 54, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.M.; Rodríguez, J.; Giambartolomei, G.H. Microglia at the Crossroads of Pathogen-Induced Neuroinflammation. ASN Neuro 2022, 14, 175909142211045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, M.; Gerner, S.T.; Doeppner, T.R. The Dual Role of Microglia in Ischemic Stroke and Its Modulation via Extracellular Vesicles and Stem Cells. Neuroprotection 2024, 2, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Kan, E.M.; Lu, J.; Hao, A.; Dheen, S.T.; Kaur, C.; Ling, E.-A. Toll-like Receptor 4 Mediates Microglial Activation and Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Neonatal Rat Brain Following Hypoxia: Role of TLR4 in Hypoxic Microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-ΚB: A Key Role in Inflammatory Diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versele, R.; Sevin, E.; Gosselet, F.; Fenart, L.; Candela, P. TNF-α and IL-1β Modulate Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Decrease Amyloid-β Peptide Efflux in a Human Blood-Brain Barrier Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempe, R.G.; Hartz, A.M.; Bauer, B. Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Brain and Blood–Brain Barrier: Versatile Breakers and Makers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1481–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, I.; Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; Suciu, M.; Hermenean, A.; Krizbai, I.A. Heterogeneity of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1143544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.A.; Bell, R.D.; Zlokovic, B. V Central Nervous System Pericytes in Health and Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.A.; Banks, W.A. Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction as a Cause and Consequence of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Chiba, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Murakami, R.; Fujihara, R.; Kawauchi, M.; Miyanaka, H.; Nakagawa, T. Blood-brain Barrier Damage in Vascular Dementia. Neuropathology 2016, 36, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Tomimoto, H.; Akiguchi, I.; Wakita, H.; Sakamoto, H. Blood–Brain Barrier Disruption in White Matter Lesions in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002, 22, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, A.; Blennow, K.; Fredman, P.; Gottfries, C.G.; Karlsson, I.; Svenner-holm, L. Blood Brain Barrier Function in Vascular Dementia. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 81, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, H.A.R.; Carr, C.S.; Al Suwaidi, J. Endothelial Dysfunction: Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Therapy, and Outcome. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, P.; Tarantini, S.; Csiszar, A.; Ungvari, Z. Functional Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Mechanisms and Consequences of Cerebral Autoregulatory Dysfunction, Endothelial Impairment, and Neurovascular Uncoupling in Aging. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H1–H20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carding, S.; Verbeke, K.; Vipond, D.T.; Corfe, B.M.; Owen, L.J. Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiota in Disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasarello, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Communication of Gut Microbiota and Brain via Immune and Neuroendocrine Signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuc, M.; Misiak, B.; Pawłowski, M.; Stańczykiewicz, B.; Zabłocka, A.; Szcześniak, D.; Pałęga, A.; Rymaszewska, J. Gut Microbiota in Dementia. Critical Review of Novel Findings and Their Potential Application. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 104, 110039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chao, Y.-P.; Lai, Y.-J.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Chuang, Y.-F. Altered Gut Microbiota in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Case-Control Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1162057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, K.; HuangFu, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, B. Vascular Cognitive Impairment and the Gut Microbiota. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fongang, B.; Satizabal, C.; Kautz, T.F.; Wadop, Y.N.; Muhammad, J.A.S.; Vasquez, E.; Mathews, J.; Gireud-Goss, M.; Saklad, A.R.; Himali, J.; et al. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden Is Associated with Decreased Abundance of Gut Barnesiella Intestinihominis Bacterium in the Framingham Heart Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Zheng, T.; Meric, G.; Marques, F.Z. The Gut Microbiome and Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadagopan, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Begg, M.; Tarhuni, M.; Fotso, M.; Gonzalez, N.A.; Sanivarapu, R.R.; Osman, U.; Latha Kumar, A.; Mohammed, L. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Diabetes and Therapeutics Targeting Leaky Gut: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e41559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourakis, M.; Mayer, G.; Rousseau, G. The Role of Gut Microbiota on Cholesterol Metabolism in Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, P.B. Risk Factors for Vascular Dementia and Alzheimer Disease. Stroke 2004, 35, 2620–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Su, J.; Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Weng, R.; Ni, W.; Gu, Y. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Participates in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion by Disrupting the Metabolism of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Microbiome 2022, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Du, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, J. β-Hydroxybutyrate Improves Cognitive Impairment Caused by Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via Amelioration of Neuroinflammation and Blood-Brain Barrier Damage. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 193, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-K.; Chen, C.-C.; Liu, P.-Y.; Panyod, S.; Liao, B.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Kao, H.-L.; Kuo, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chiu, T.H.T.; et al. Identification of TMAO-Producer Phenotype and Host–Diet–Gut Dysbiosis by Carnitine Challenge Test in Human and Germ-Free Mice. Gut 2019, 68, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zou, J.; Hong, Y.; Peng, Q.; Fu, X.; Duan, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Higher Circulating Trimethylamine N-Oxide Aggravates Cognitive Impairment Probably via Downregulating Hippocampal SIRT1 in Vascular Dementia Rats. Cells 2022, 11, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, G.; Bella, R.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, G.; Ferri, R.; Pennisi, M. Cognitive Impairment and Celiac Disease: Is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation a Trait d’Union between Gut and Brain? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenit, M.; Olivares, M.; Codoñer-Franch, P.; Sanz, Y. Intestinal Microbiota and Celiac Disease: Cause, Consequence or Co-Evolution? Nutrients 2015, 7, 6900–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, G.; Lanza, G.; Giuffrida, S.; Vinciguerra, L.; Puglisi, V.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, M.; D’Agate, C.C.; Naso, P.; Aprile, G.; et al. Excitability of the Motor Cortex in De Novo Patients with Celiac Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bella, R.; Ferri, R.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; Pennisi, M.; Puglisi, V.; Vinciguerra, L.; Spampinato, C.; Mazza, T.; Malaguarnera, G.; et al. TMS Follow-up Study in Patients with Vascular Cognitive Impairment-No Dementia. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 534, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młynarska, E.; Jakubowska, P.; Frąk, W.; Gajewska, A.; Sornowska, J.; Skwira, S.; Wasiak, J.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Associations of Microbiota and Nutrition with Cognitive Impairment in Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, A.; Cunnane, S.C.; Minihane, A.M. Can Nutrition Support Healthy Cognitive Ageing and Reduce Dementia Risk? BMJ 2020, 369, m2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Interplay between Gut Microbiota and Diet in Cardio-Metabolic Health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1897212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.; Cantone, M.; Cappellani, F.; Concerto, C.; Ferri, R.; Godos, J.; Grosso, G.; Lanza, G.; Rodolico, A.; Torrisi, G.; et al. Combined Effect of Red Wine and Mocha Pot Coffee in Mild Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 194, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinciguerra, L.; Lanza, G.; Puglisi, V.; Fisicaro, F.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Cantone, M. Update on the Neurobiology of Vascular Cognitive Impairment: From Lab to Clinic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battle, C.E.; Abdul-Rahim, A.H.; Shenkin, S.D.; Hewitt, J.; Quinn, T.J. Cholinesterase Inhibitors for Vascular Dementia and Other Vascular Cognitive Impairments: A Network Meta-Analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD013306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).