Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Compounds
2.3. Protein Extraction, Western Blotting and Antibodies
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. BrdU Assay
2.6. TUNEL Assay
2.7. RNA Silencing
2.8. Immunohistochemistry and Histological Examination
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
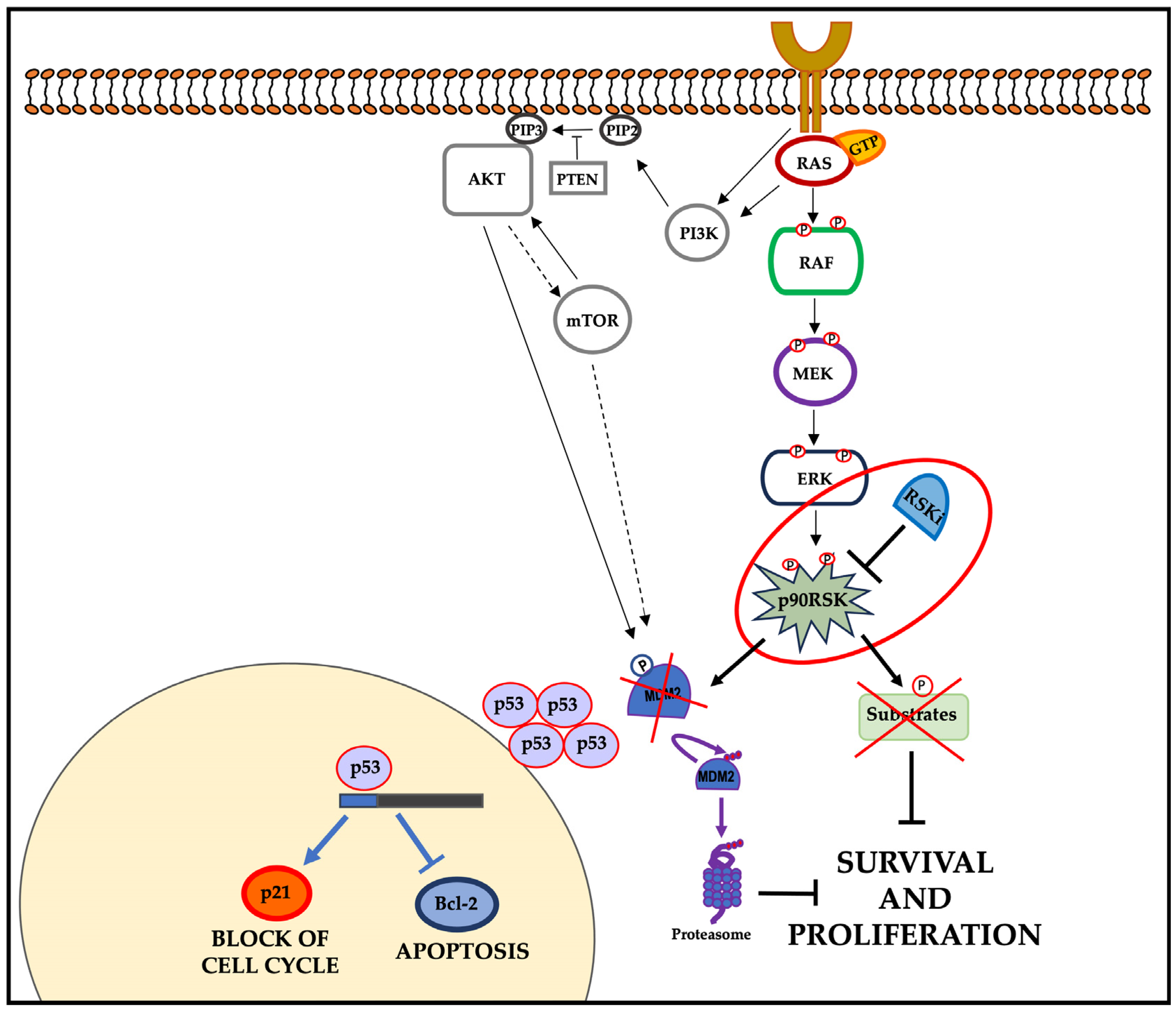
3.1. Inhibition of p90RSK Is Able to Increase p53 Level via Reduction in MDM2 Phosphorylation at Serine 166
3.2. In Tumor Cell Lines with Strongly Active p90RSK, MDM2-Mediated p53 Degradation Is Controlled by p90RSK
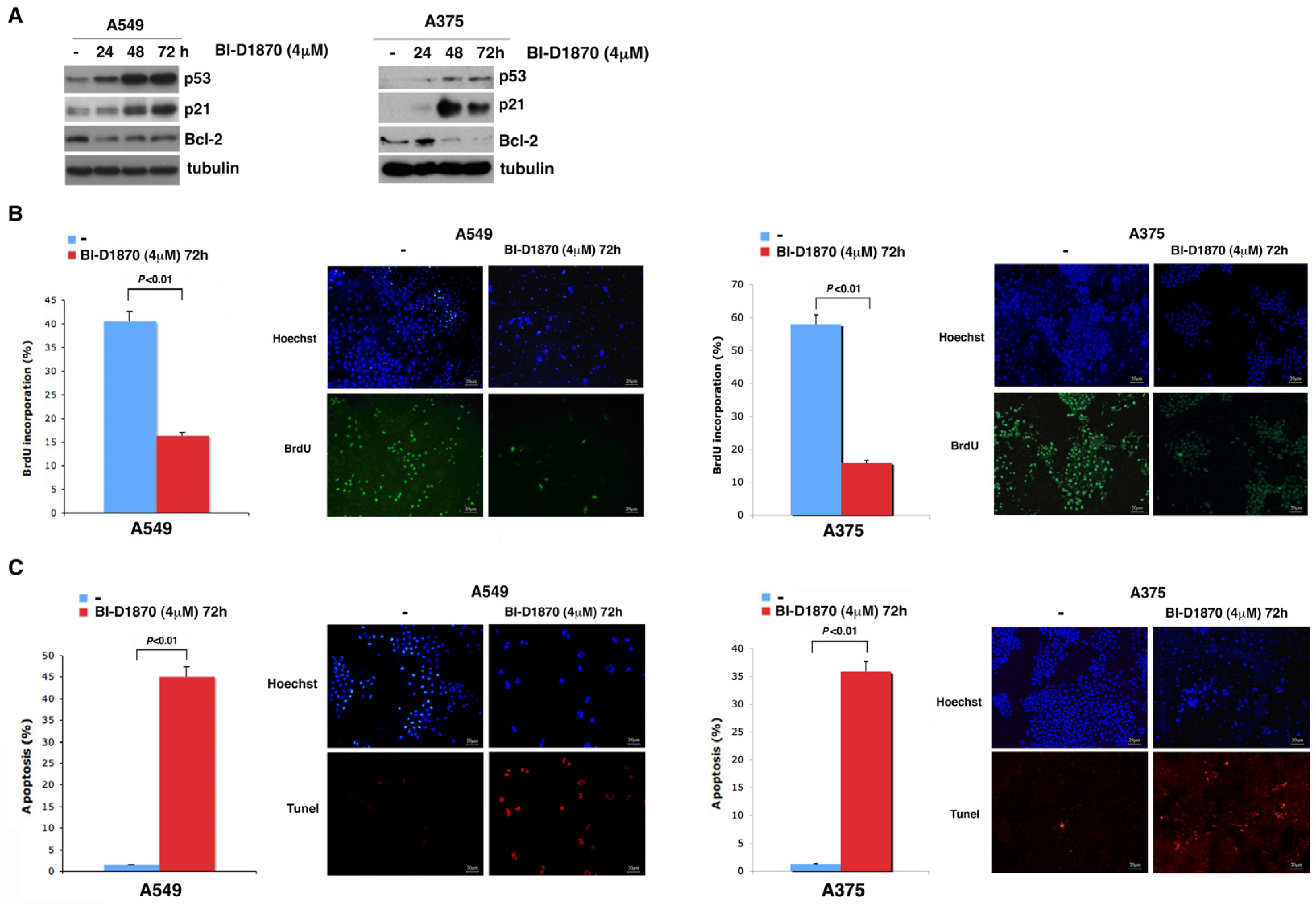
3.3. p90RSK Is Efficient at Regulating Proliferation in A549 and A375 Cell Lines
3.4. In A459 and A375 Cells, p90RSK Controls DNA Synthesis and Apoptosis through Regulation of p53
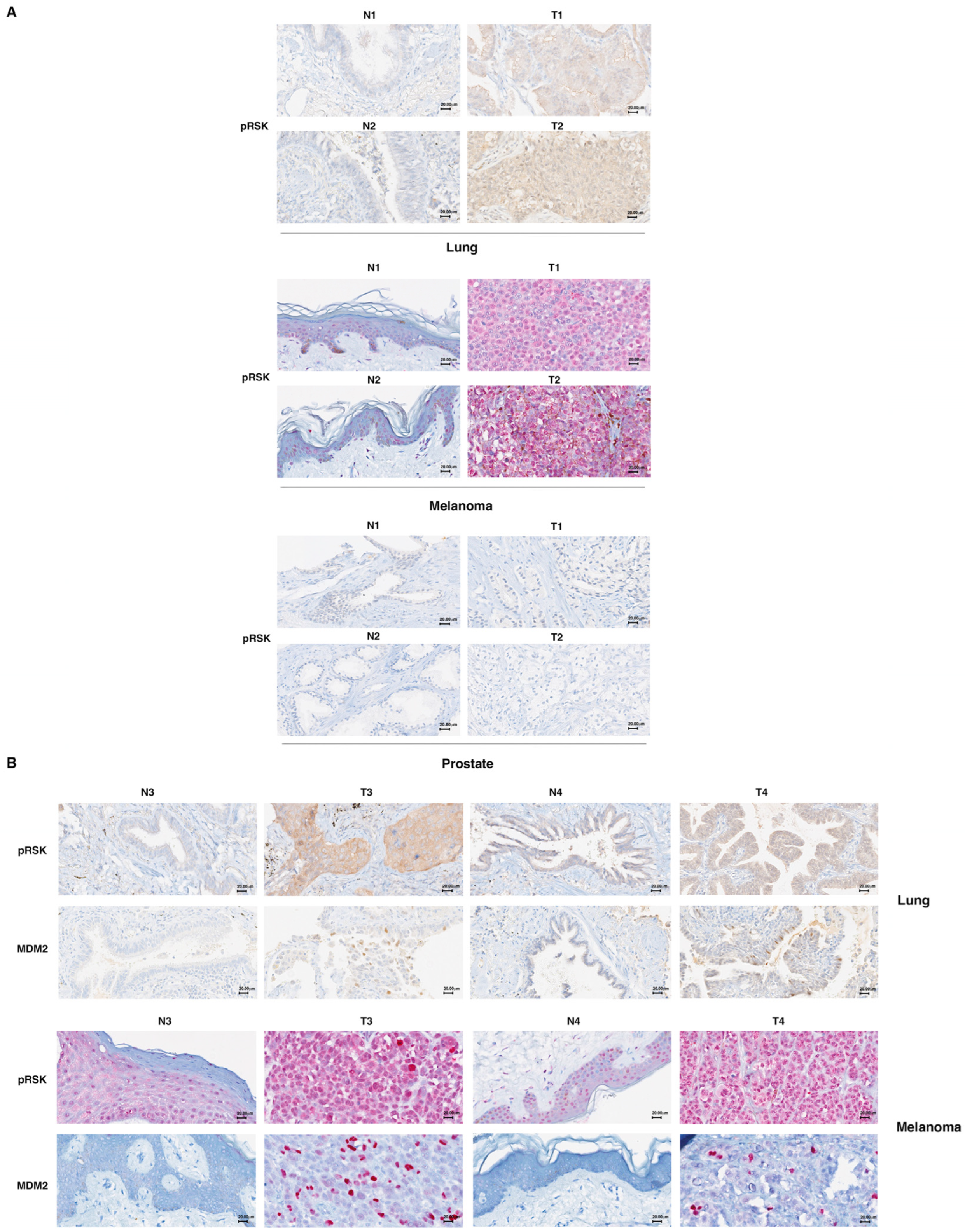
3.5. p90RSK Phosphorylation Is Correlated with Stabilization of MDM2 in Primary Lung Tumors and Melanomas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, S.; Seger, R. The Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: Multiple Substrates Regulate Diverse Cellular Functions. Growth Factors 2006, 24, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, R.; Chatani, Y.; Yamori, T.; Tsuruo, T.; Oka, H.; Yoshida, O.; Shimada, Y.; Ari-I, S.; Wada, H.; Fujimoto, J.; et al. Constitutive Activation of the 41-/43-KDa Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway in Human Tumors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.C.; Ng, C.; Schneider, A.M.; Ji, H.; Ying, H.; Wang, H.; DePinho, R.A.; Park, J. Il PAF-PAF-Mediated MAPK Signaling Hyperactivation via LAMTOR3 Induces Pancreatic Tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosten, M.; Sum, E.Y.M.; Lechuga, C.G.; Simón-Carrasco, L.; Jacob, H.K.C.; García-Medina, R.; Huang, S.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bernards, R.; Barbacid, M. Loss of P53 Induces Cell Proliferation via Ras-Independent Activation of the Raf/Mek/Erk Signaling Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15155–15160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Khoo, S.; Dang, A.; Witt, S.; Do, V.; Zhen, E.; Schaefer, E.M.; Cobb, M.H. Differential Regulation of Mitogen-Activated Protein/ERK Kinase (MEK)1 and MEK2 and Activation by a Ras-Independent Mechanism. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.T.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway in Cell Growth, Malignant Transformation and Drug Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.R. Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK Pathway for Cancer Therapy: From Mechanism to Clinical Studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, C.M.; Vijayendran, K.G.; Zipser, M.C.; Sawyer, A.M.; Niu, L.; Kim, J.J.; Hatton, C.; Chopra, R.; Oberholzer, P.A.; Karpova, M.B.; et al. MEK1 Mutations Confer Resistance to MEK and B-RAF Inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20411–20416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.; Ranieri, M.; Li, S.; Sahu, S.; Liu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Guidry, K.; Hu, H.; et al. Genome-Wide CRISPR Screens Identify Multiple Synthetic Lethal Targets That Enhance KRASG12C Inhibitor Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 4095–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Liu, S.; Rybkin, I.I.; Arbour, K.C.; Dilly, J.; Zhu, V.W.; Johnson, M.L.; Heist, R.S.; Patil, T.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Maria, A.; Na, N.; Paula, A.d.C.; Gorelick, A.N.; Hechtman, J.F.; Carson, J.; Lefkowitz, R.A.; Weigelt, B.; Taylor, B.S.; et al. V211D Mutation in MEK1 Causes Resistance to MEK Inhibitors in Colon Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadia, S.; Yarlagadda, N.; Awad, R.; Kundranda, M.; Niu, J.; Naraev, B.; Mina, L.; Dragovich, T.; Gimbel, M.; Mahmoud, F. Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors and Clinical Update of Us Food and Drug Administration-Approved Targeted Therapy in Advanced Melanoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 7095–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, E.M.; Ghandi, M.; Treacy, D.J.; Wagle, N.; Garraway, L.A. ERK Mutations Confer Resistance to Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7079–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frödin, M.; Gammeltoft, S. Role and Regulation of 90 KDa Ribosomal S6 Kinase (RSK) in Signal Transduction. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1999, 151, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, I.A.; Dalby, K.N.; Barry Caudwell, F.; Cohen, P.T.W.; Cohen, P. Comparison of the Specificities of P70 S6 Kinase and MAPKAP Kinase-1 Identifies a Relatively Specific Substrate for P70 S6 Kinase: The N-Terminal Kinase Domain of MAPKAP Kinase-1 Is Essential for Peptide Phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1995, 375, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Poteet-Smith, C.E.; Malarkey, K.; Sturgill, T.W. Identification of an Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) Docking Site in Ribosomal S6 Kinase, a Sequence Critical for Activation by ERK in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 2893–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.L.; Blenis, J. Evidence for Two Catalytically Active Kinase Domains in Pp90rsk. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, R.; Seckl, M.J.; Pardo, O.E. The P90 RSK Family Members: Common Functions and Isoform Specificity. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5301–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Roux, P.P. Regulation and Function of the RSK Family of Protein Kinases. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, R.; Mauri, F.A.; Taylor, H.; Derua, R.; Shia, A.; Gray, C.; Nicols, A.; Shiner, R.J.; Schofield, E.; Bates, P.A.; et al. An SiRNA Screen Identifies RSK1 as a Key Modulator of Lung Cancer Metastasis. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3513–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, D.; Cohen, M.S.; Taunton, J.; Patel, T.B. The PKARIalpha Subunit of Protein Kinase A Modulates the Activation of P90RSK1 and Its Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23670–23681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, A.P.; Corson, L.B.; Rossant, J.; Baker, J.C. Characterization of Mouse Rsk4 as an Inhibitor of Fibroblast Growth Factor-RAS-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 4255–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Romeo, Y.; Roux, P.P. Paving the Way for Targeting RSK in Cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.-P.; Mehic, D.; Bakiri, L.; Schilling, A.F.; Mandic, V.; Priemel, M.; Idarraga, M.H.; Reschke, M.O.; Hoffmann, O.; Amling, M.; et al. Essential Role of RSK2 in C-Fos–Dependent Osteosarcoma Development. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Elf, S.; Lythgoe, K.; Hitosugi, T.; Taunton, J.; Zhou, W.; Xiong, L.; Wang, D.; Muller, S.; Fan, S.; et al. P90 Ribosomal S6 Kinase 2 Promotes Invasion and Metastasis of Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Ramos, J.W. RSK Isoforms in Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6099–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, V.; Eichhorn, P.J.A.; García-García, C.; Ibrahim, Y.H.; Prudkin, L.; Sánchez, G.; Rodríguez, O.; Antón, P.; Parra, J.L.; Marlow, S.; et al. RSK3/4 Mediate Resistance to PI3K Pathway Inhibitors in Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, C.; Ullrich, A. PRKX, TTBK2 and RSK4 Expression Causes Sunitinib Resistance in Kidney Carcinoma- and Melanoma-Cell Lines. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E45–E55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. RSK Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents: Discovery, Optimization, and Challenges. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 251, 0223–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, L.D.; Elder, F.F.; Knuth, A.; Gagel, R.F. Cytogenetic characterization of three human and three rat medullary thyroid carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1995, 80, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Salzano, M.; De Falco, V.; Mian, C.; Barollo, S.; Secondo, A.; Bifulco, M.; Vitale, M. Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and its endogenous inhibitor α in medullary thyroid cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maietta, I.; Del Peschio, F.; Buonocore, P.; Viscusi, E.; Laudati, S.; Iannaci, G.; Minopoli, M.; Motti, M.L.; De Falco, V. P90RSK Regulates P53 Pathway by MDM2 Phosphorylation in Thyroid Tumors. Cancers 2023, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Tamaskovic, R.; Yang, Z.; Brazil, D.P.; Merlo, A.; Hess, D.; Hemmings, B.A. Stabilization of Mdm2 via Decreased Ubiquitination Is Mediated by Protein Kinase B/Akt-Dependent Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35510–35517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadja-Lamère, N.; Shum, M.; Déléris, P.; Roux, P.P.; Abe, J.; Marette, A. Insulin activates RSK (p90 ribosomal S6 kinase) to trigger a new negative feedback loop that regulates insulin signaling for glucose metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31165–31176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.B.; Lannigan, D.A. Therapeutic Targeting of P90 Ribosomal S6 Kinase. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1297292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugarolas, J.; Chandrasekaran, C.; Gordon, J.I.; Beach, D.; Jacks, T.; Hannon, G.J. Radiation-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest Compromised by P21 Deficiency. Nature 1995, 377, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemann, M.T.; Lowe, S.W. The P53-Bcl-2 Connection. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meevassana, J.; Mittrakulkij, C.; Toworrakul, P.; Saensuk, W.; Kamolratanakul, S.; Siritientong, T.; Ruangritchankul, K.; Kitkumthorn, N. Evaluation of P53 immunostaining in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Biomed. Rep. 2023, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon-Vargas, D.; Ronai, Z. p53-Mdm2--the affair that never ends. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyinka, A.; Nui, Y.; Cherlet, T.; Snell, L.; Watson, P.H.; Murphy, L.C. Activated Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Expression during Human Breast Tumorigenesis and Breast Cancer Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, C.; Zavala-Pompa, A.; Sequeira, J.H.; Shoji, M.; Sexton, D.G.; Cotsonis, G.; Cerimele, F.; Govindarajan, B.; Macaron, N.; Arbiser, J.L. Mitogen-Actived Protein Kinase Activation Is an Early Event in Melanoma Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3728–3733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, V.S.; Wang, H.Y.; Nuovo, G.J.; Malbon, C.C. Hyperexpression of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Human Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusciano, M.R.; Salzano, M.; Monaco, S.; Sapio, M.R.; Illario, M.; De Falco, V.; Santoro, M.; Campiglia, P.; Pastore, L.; Fenzi, G.; et al. The Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent kinase II is activated in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and mediates cell proliferation stimulated by RET/PTC. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brose, M.S.; Volpe, P.; Feldman, M.; Kumar, M.; Rishi, I.; Gerrero, R.; Einhorn, E.; Herlyn, M.; Minna, J.; Nicholson, A.; et al. BRAF and RAS Mutations in Human Lung Cancer and Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6997–7000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, H.; Bardelli, A.; Lengauer, C.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Velculescu, V.E. Tumorigenesis: RAF/RAS Oncogenes and Mismatch-Repair Status. Nature 2002, 418, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebbutt, N.; Pedersen, M.W.; Johns, T.G. Targeting the ERBB Family in Cancer: Couples Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Zhou, M.M. Structure and Regulation of MAPK Phosphatases. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. RAS Oncogenes: The First 30 Years. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.T.C.; Garnett, M.J.; Roe, S.M.; Lee, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Good, V.M.; Project, C.G.; Jones, C.M.; Marshall, C.J.; Springer, C.J.; et al. Mechanism of Activation of the RAF-ERK Signaling Pathway by Oncogenic Mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004, 116, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motti, M.L.; Minopoli, M.; Di Carluccio, G.; Ascierto, P.A.; Carriero, M.V. MicroRNAs as Key Players in Melanoma Cell Resistance to MAPK and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved Survival with Vemurafenib in Melanoma with BRAF V600E Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, G.; De Falco, V.; Salerno, P.; Jiang, Y.; Garbi, C.; Ugolini, C.; Miccoli, P.; Basolo, F.; Castellone, M.D.; Cirafici, A.M.; et al. BRAF is a therapeutic target in aggressive thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T. BRAF inhibitors and melanoma. Cancer J. 2011, 17, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Zhang, C.; Bollag, G.; Shokat, K.M.; Rosen, N. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 2010, 464, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartsough, E.; Shao, Y.; Aplin, A.E. Resistance to RAF Inhibitors Revisited. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Heynen, G.J.J.E.; Prahallad, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.; Blank, C.; Wesseling, J.; Willems, S.M.; et al. Reversible and Adaptive Resistance to BRAF(V600E) Inhibition in Melanoma. Nature 2014, 508, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Young, L.; Cavadas, M.; Owen, K.; Iorns, E.; Gunn, W.; Tan, F.; Lomax, J.; Perfito, N.; Errington, T. Registered Report: COT Drives Resistance to RAF Inhibition through MAP Kinase Pathway Reactivation. eLife 2016, 5, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Persaud, Y.; Janakiraman, M.; Kong, X.; Ng, C.; Moriceau, G.; Shi, H.; Atefi, M.; Titz, B.; Gabay, M.T.; et al. RAF Inhibitor Resistance Is Mediated by Dimerization of Aberrantly Spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature 2011, 480, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, S.R.; Theurillat, J.P.; Van Allen, E.; Wagle, N.; Hsiao, J.; Cowley, G.S.; Schadendorf, D.; Root, D.E.; Garraway, L.A. A Genome-Scale RNA Interference Screen Implicates NF1 Loss in Resistance to RAF Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, N.; Van Allen, E.M.; Treacy, D.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Rosenberg, M.; Goetz, E.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. MAP Kinase Pathway Alterations in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Patients with Acquired Resistance to Combined RAF/MEK Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratangelo, F.; Camerlingo, R.; Carriero, M.V.; Pirozzi, G.; Palmieri, G.; Gentilcore, G.; Ragone, C.; Minopoli, M.; Ascierto, P.A.; Motti, M.L. Effect of ABT-888 on the Apoptosis, Motility and Invasiveness of BRAFi-Resistant Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragone, C.; Minopoli, M.; Ingangi, V.; Botti, G.; Fratangelo, F.; Pessi, A.; Stoppelli, M.P.; Ascierto, P.A.; Ciliberto, G.; Motti, M.L.; et al. Targeting the Cross-Talk between Urokinase Receptor and Formyl Peptide Receptor Type 1 to Prevent Invasion and Trans-Endothelial Migration of Melanoma Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.J.L.; Robert, L.; Atefi, M.S.; Lassen, A.; Avarappatt, G.; Cerniglia, M.; Avramis, E.; Tsoi, J.; Foulad, D.; Graeber, T.G.; et al. Antitumor Activity of the ERK Inhibitor SCH722984 against BRAF Mutant, NRAS Mutant and Wild-Type Melanoma. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlino, M.S.; Todd, J.R.; Gowrishankar, K.; Mijatov, B.; Pupo, G.M.; Fung, C.; Snoyman, S.; Hersey, P.; Long, G.V.; Kefford, R.F.; et al. Differential Activity of MEK and ERK Inhibitors in BRAF Inhibitor Resistant Melanoma. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Cao, D.; Ren, Q.N.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhou, N.N.; Mai, S.J.; Feng, B.; Wang, H.Y. Combination Treatment With Inhibitors of ERK and Autophagy Enhances Antitumor Activity of Betulinic Acid in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer In Vivo and In Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 29, 684243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; Zalyte, E.; Rimkus, A.; Dapkus, D.; Noreika, R.; Urbonavicius, S. JNK, p38, ERK, and SGK1 Inhibitors in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschos, S.J.; Sullivan, R.J.; Hwu, W.J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Adjei, A.A.; Fong, P.C.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Tawbi, H.A.; Rubino, J.; Rush, T.S., 3rd; et al. Development of MK-8353, an orally administered ERK1/2 inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e92352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Cohen, J.V.; Tarantino, G.; Lian, C.G.; Liu, D.; Haq, R.; Hodi, F.S.; Lawrence, D.P.; Hurder, A.G.; Knoerzer, D.; et al. A Phase II Study of ERK Inhibition by Ulixertinib (BVD-523) in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathis, A.; Tolcher, A.W.; Wang, J.S.; Renouf, D.J.; Chen, L.C.; Suttner, L.H.; Freshwater, T.; Webber, A.L.; Nayak, T.; Siu, L.L. Results of an open-label phase 1b study of the ERK inhibitor MK-8353 plus the MEK inhibitor selumetinib in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2023, 41, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Pei, j.; Wang, A.; Shuai, W.; Feng, L.; Bu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Ouyang, L. Development of small molecule inhibitors of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2171–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maik-Rachline, G.; Hacohen-Lev-Ran, A.; Seger, R. Nuclear ERK: Mechanism of Translocation, Substrates, and Role in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Mathur, M.; Lan, J.; Costales, A.; Atallah, G.; Ramurthy, S.; Subramanian, S.; Setti, L.; Feucht, P.; Warne, B.; et al. Discovery of Potent and Selective RSK Inhibitors as Biological Probes. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6766–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwik, K.A.; Campbell, J.P.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Sandusky, Z.M.; Pasic, L.; Sowder, M.E.; Brenin, D.R.; Pietenpol, J.A.; O’Doherty, G.A.; et al. Development of a RSK inhibitor as a novel therapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting P53 in Context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, K.D.; Galbraith, M.D.; Andrysik, Z.; Espinosa, J.M. Mechanisms of Transcriptional Regulation by P53. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.B.; Schumacher, B. P53 in the DNA-Damage-Repair Process. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.J.; Vousden, K.H. P53 Mutations in Cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, V.J.N.; Eriksson, S.E.; Bianchi, J.; Wiman, K.G. Targeting Mutant P53 for Efficient Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; Ding, B.; Bains, C.P.; Wang, N.; Takeishi, Y.; Jalili, T.; King, G.L.; Walsh, R.A.; Yan, C.; Abe, J. Role of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (p90RSK) in reactive oxygen species and protein kinase C beta (PKC-beta)-mediated cardiac troponin I phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24135–24142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; McCormick, F. The Metabolic Landscape of RAS-Driven Cancers from biology to therapy. Nat Cancer. 2021, 2, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maietta, I.; Viscusi, E.; Laudati, S.; Iannaci, G.; D’Antonio, A.; Melillo, R.M.; Motti, M.L.; De Falco, V. Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13181546
Maietta I, Viscusi E, Laudati S, Iannaci G, D’Antonio A, Melillo RM, Motti ML, De Falco V. Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer. Cells. 2024; 13(18):1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13181546
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaietta, Immacolata, Eleonora Viscusi, Stefano Laudati, Giuseppe Iannaci, Antonio D’Antonio, Rosa Marina Melillo, Maria Letizia Motti, and Valentina De Falco. 2024. "Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer" Cells 13, no. 18: 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13181546
APA StyleMaietta, I., Viscusi, E., Laudati, S., Iannaci, G., D’Antonio, A., Melillo, R. M., Motti, M. L., & De Falco, V. (2024). Targeting the p90RSK/MDM2/p53 Pathway Is Effective in Blocking Tumors with Oncogenic Up-Regulation of the MAPK Pathway Such as Melanoma and Lung Cancer. Cells, 13(18), 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13181546









