A Comparative Review of Cytokines and Cytokine Targeting in Sepsis: From Humans to Horses
Abstract
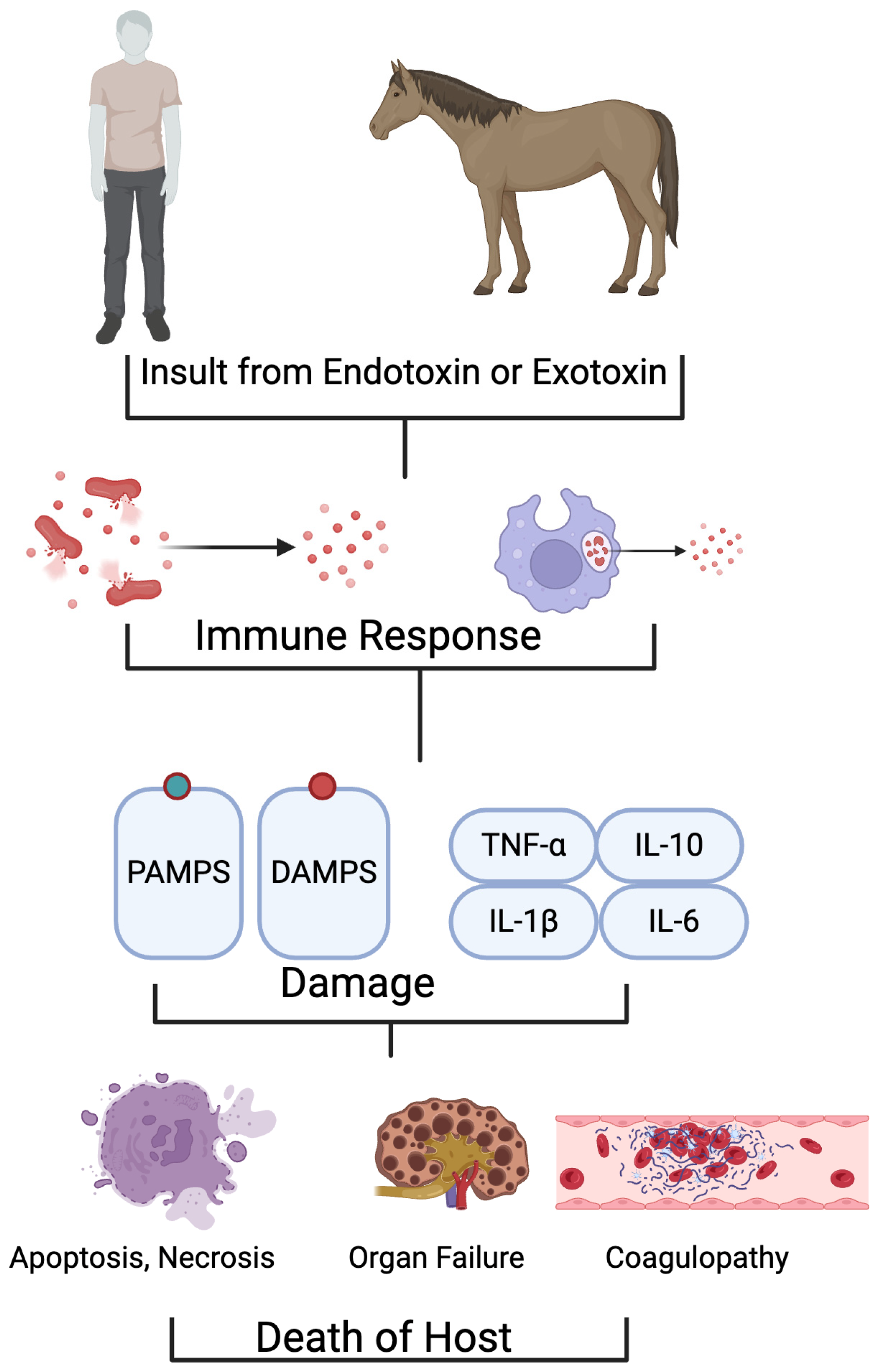
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of Sepsis and Cytokines Roles
2.1. Cytokines
2.2. IL-6
2.3. IL-1β
2.4. TNF-α
2.5. IL-10
3. Cytokine Targeting as a Treatment for Sepsis
3.1. Monoclonal Antibody Treatment
3.2. Cytokine Antagonist
3.3. Cytokine Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| CD | Cellular Differentiation Molecule |
| IL | Interleukin |
| SIRS | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| mAb | Monoclonal Antibody |
References
- Blangy-Letheule, A.; Vergnaud, A.; Dupas, T.; Rozec, B.; Lauzier, B.; Leroux, A.A. Spontaneous Sepsis in Adult Horses: From Veterinary to Human Medicine Perspectives. Cells 2023, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.H.; Chan, D.L.; Pinheiro, D.; Armitage-Chan, E.; Garden, O.A. The immunopathology of sepsis: Pathogen recognition, systemic inflammation, the compensatory anti-inflammatory response, and regulatory T cells. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 457–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prest, J.; Nguyen, T.; Rajah, T.; Prest, A.B.; Sathananthan, M.; Jeganathan, N. Sepsis-Related Mortality Rates and Trends Based on Site of Infection. Crit. Care Explor. 2022, 4, e0775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, C.; Reichert, F.; Cassini, A.; Horner, R.; Harder, T.; Markwart, R.; Tröndle, M.; Savova, Y.; Kissoon, N.; Schlattmann, P.; et al. Global incidence and mortality of neonatal sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S. A review of equine sepsis. Equine Vet. Educ. 2015, 27, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheats, M.K. A Comparative Review of Equine SIRS, Sepsis, and Neutrophils. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 1992, 20, 864–874. [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.F.; Kwong, G.P.; Lambert, J.; Massie, S.; Lockhart, S. Prognostic Value and Development of a Scoring System in Horses With Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, W.; Bernhagen, J.; Bucala, R. Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets—An updated view. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 165974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Yu, M.; Chai, Y. Pathological alteration and therapeutic implications of sepsis-induced immune cell apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qu, M.; Li, W.; Wu, D.; Cata, J.P.; Miao, C. Neutrophil, neutrophil extracellular traps and endothelial cell dysfunction in sepsis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gårdlund, B.; Sjölin, J.; Nilsson, A.; Roll, M.; Wickerts, C.J.; Wretlind, B. Plasma levels of cytokines in primary septic shock in humans: Correlation with disease severity. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharamti, A.; Samara, O.; Monzon, A.; Scherger, S.; DeSanto, K.; Sillau, S.; Franco-Paredes, C.; Henao-Martínez, A.; Shapiro, L. Association between cytokine levels, sepsis severity and clinical outcomes in sepsis: A quantitative systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, S. The cytokine storm and factors determining the sequence and severity of organ dysfunction in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Historical insights into cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37 (Suppl. 1), S34–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, E.K.; Hobbs, K.J.; McKinney-Aguirre, C.A.; Gonzalez, L.M. Biomarkers of Intestinal Injury in Colic. Animals 2023, 13, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Gauldie, J.; Cox, G.; Baumann, H.; Jordana, M.; Lei, X.F.; Achong, M.K. IL-6 is an antiinflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molano Franco, D.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Roqué, I.F.M.; Montero Oleas, N.G.; Nuvials, X.; Zamora, J. Plasma interleukin-6 concentration for the diagnosis of sepsis in critically ill adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 4, Cd011811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivas, M.C.; Villamarin Guerrero, H.F.; Tascon, A.J.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A. Plasma interleukin-6 levels correlate with survival in patients with bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.D.; Moore, J.N.; Crowe, N.; Moldawer, L.L. Effect of experimentally induced endotoxemia on serum interleukin-6 activity in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 53, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.H.; Collatos, C. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 activity and endotoxin concentration in peritoneal fluid and blood of horses with acute abdominal disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1999, 13, 457–464. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorka, C.E.; Scoggin, K.E.; Ali, H.E.; Loux, S.C.; Dini, P.; Troedsson, M.H.T.; Ball, B.A. Interleukin-6 pathobiology in equine placental infection. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 85, e13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.; Siwinska, N.; Elzinga, S.; Barker, V.; Stefaniak, T.; Schanbacher, B.; Place, N.; Niedzwiedz, A.; Adams, A. Effects of equine metabolic syndrome on inflammation and acute-phase markers in horses. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2020, 72, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-L.; Shi, F.-D.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Song, Y.; Wu, Z.-S.; Shi, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, K.-Z.; et al. Interleukin-1β Protection Against Experimental Sepsis in Mice. Inflammation 2021, 44, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemon, J.K.; Miller, M.R.; Weiser, J.N. Sensing of interleukin-1 cytokines during Streptococcus pneumoniae colonization contributes to macrophage recruitment and bacterial clearance. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3204–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Sousa, M.; Medrano, L.M.; Liu, P.; Almansa, R.; Fernández-Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Sánchez, E.; Rico, L.; Heredia-Rodríguez, M.; Gómez-Pesquera, E.; Tamayo, E.; et al. IL-1B rs16944 polymorphism is related to septic shock and death. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 47, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, A.Q.; Gu, W.; Wang, J.; Feng, K.; Qin, L.; Ying, C.; Zhu, P.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Jiang, J.X. Clinical relevance of IL-1beta promoter polymorphisms (-1470, -511, and -31) in patients with major trauma. Shock 2010, 33, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, E.M.; Frank, N. Effects of continuous or intermittent lipopolysaccharide administration for 48 hours on the systemic inflammatory response in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagnetti, C.; Mariella, J.; Pirrone, A.; Cinotti, S.; Mari, G.; Peli, A. Expression of interleukin-1β, interleukin-8, and interferon-γ in blood samples obtained from healthy and sick neonatal foals. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.-I.; Lee, A.-H.; Shin, H.-Y.; Song, H.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, C.E.; Markowitz, N.P.; Saravolatz, L.D. The role of tumor necrosis factor in sepsis. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1992, 62 Pt 2, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharamti, A.A.; Samara, O.; Monzon, A.; Montalbano, G.; Scherger, S.; DeSanto, K.; Chastain, D.B.; Sillau, S.; Montoya, J.G.; Franco-Paredes, C.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokines levels in sepsis and healthy volunteers, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha associated sepsis mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2022, 158, 156006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigato, O.; Ujvari, S.; Castelo, A.; Salomão, R. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and sepsis: Evidence for a role in host defense. Infection 1996, 24, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies-Gow, N.J.; Wray, H.; Bailey, S.R.; Harris, P.A.; Elliott, J. The effect of tumour necrosis factor-α and insulin on equine digital blood vessel function in vitro. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamer, H.G.; El-Ashker, M.R.; Nour, E.M.; Wafa, E.W.; Youssef, M.A. Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Equine: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2017, 50, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.D.; Moore, J.N.; Crowe, N. Serum tumor necrosis factor activity in horses with colic attributable to gastrointestinal tract disease. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1991, 52, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.B.; Beckmann, N.; Salyer, C.E.; Hanschen, M.; Crisologo, P.A.; Caldwell, C.C. Potential Targets to Mitigate Trauma- or Sepsis-Induced Immune Suppression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 622601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, P.M.; Elbim, C.; Marie, J.C.; Chiandotto, M.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; El-Benna, J. Anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 on human neutrophil respiratory burst involves inhibition of GM-CSF-induced p47PHOX phosphorylation through a decrease in ERK1/2 activity. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Heureux, M.; Kashiouris, M.; Fowler, A.; Fisher, B. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN IL-10 AND MORTALITY IN SEPSIS-INDUCED ARDS. Chest 2020, 158 (Suppl. 4), A621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Magdesian, K.G.; Mapes, S.; Leutenegger, C.M. Expression of molecular markers in blood of neonatal foals with sepsis. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbian, N.; Abutbul, A.; El-Amore, R.; Eliaz, R.; Beeri, R.; Reicher, B.; Mevorach, D. Apoptotic cell therapy for cytokine storm associated with acute severe sepsis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.V.; Piscoya, A.; Pasupuleti, V.; Phan, M.T.; Julakanti, S.; Khen, P.; Roman, Y.M.; Carranza-Tamayo, C.O.; Escobedo, A.A.; White, C.M. Beneficial and Harmful Effects of Monoclonal Antibodies for the Treatment and Prophylaxis of COVID-19: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 1349–1361.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acchione, M.; Kwon, H.; Jochheim, C.M.; Atkins, W.M. Impact of linker and conjugation chemistry on antigen binding, Fc receptor binding and thermal stability of model antibody-drug conjugates. mAbs 2012, 4, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargile, J.L.; MacKay, R.J.; Dankert, J.R.; Skelley, L. Effect of treatment with a monoclonal antibody against equine tumor necrosis factor (TNF) on clinical, hematologic, and circulating TNF responses of miniature horses given endotoxin. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargile, J.L.; MacKay, R.J.; Dankert, J.R.; Skelley, L. Effects of tumor necrosis factor blockade on interleukin 6, lactate, thromboxane, and prostacyclin responses in miniature horses given endotoxin. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langreder, N.; Schäckermann, D.; Meier, D.; Becker, M.; Schubert, M.; Dübel, S.; Reinard, T.; Figge-Wegener, S.; Roßbach, K.; Bäumer, W.; et al. Development of an inhibiting antibody against equine interleukin 5 to treat insect bite hypersensitivity of horses. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahavi, D.; Weiner, L. Monoclonal Antibodies in Cancer Therapy. Antibodies 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, F.W.; Thomas, M.; Arnold, D.; Palmer, T.; Moran, E.; Mentzer, A.J.; Maskell, N.; Baillie, K.; Summers, C.; Hingorani, A.; et al. Therapeutic potential of IL6R blockade for the treatment of sepsis and sepsis-related death: A Mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsabani, M.; Abrams, S.T.; Cheng, Z.; Morton, B.; Lane, S.; Alosaimi, S.; Yu, W.; Wang, G.; Toh, C.H. Reduction of NETosis by targeting CXCR1/2 reduces thrombosis, lung injury, and mortality in experimental human and murine sepsis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 128, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasarzik, J.; Lischer, C.J.; Ehrle, A.; Estrada, R.; Rettig, M.; Klaus, C.; Einspanier, R.; Bondzio, A. Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist and Interleukin-1 Beta Levels in Equine Synovial Fluid of Normal and Osteoarthritic Joints: Influence of Anatomic Joint Location and Repeated Arthrocentesis. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 42, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesecke, S.; Stecher, S.S.; Gross, S.; Felix, S.B.; Nierhaus, A. Extracorporeal cytokine elimination as rescue therapy in refractory septic shock: A prospective single-center study. J. Artif. Organs 2017, 20, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terayama, T.; Yamakawa, K.; Umemura, Y.; Aihara, M.; Fujimi, S. Polymyxin B Hemoperfusion for Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surg. Infect. 2017, 18, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocho, T.; Mori, H.; Islam, M.; Maruchi, Y.; Takenaka, N.; Tomino, A.; Tsuda, M.; Kano, H.; Takeyama, N.; Islam, M. Removal of Circulating Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Components with an Immobilized Polymyxin B Filter: A Preliminary Study. Shock 2020, 54, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, A.; Waalders, N.J.B.; van Lier, D.P.T.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. CytoSorb hemoperfusion markedly attenuates circulating cytokine concentrations during systemic inflammation in humans in vivo. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Träger, K.; Skrabal, C.; Fischer, G.; Schroeder, J.; Marenski, L.; Liebold, A.; Reinelt, H.; Datzmann, T. Hemoadsorption treatment with CytoSorb(®) in patients with extracorporeal life support therapy: A case series. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 43, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H. Hemoadsorption in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients requiring venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A systematic review. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, N.Y.; Gromova, E.G.; Kuznetsova, L.S.; Sitdikova, S.M.; Kiselevskii, M.V. Dynamics of elimination of bacterial endotoxins and cytokines from the blood of tumor patients with sepsis in hemoperfusion using carbon adsorbents. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 151, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, K.; Davis, J.; Cooper, B.; Ueda, Y.; Burke, M.; Sheats, M. Hemadsorption extracorporeal therapy removes cytokines ex vivo in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 85, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, K.J.; Le Sueur, A.N.V.; Burke, M.J.; Cooper, B.L.; Sheats, M.K.; Ueda, Y. Feasibility of hemoperfusion using extracorporeal therapy in the horse. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1414426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, K.J.; Le Sueur, A.N.V.; Hallowell, K.; Martin, E.; Sheats, M.K.; Ueda, Y. Use of extracorporeal hemoperfusion therapy in an adult horse with Clostridioides difficile colitis and severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honore, P.M.; Hoste, E.; Molnár, Z.; Jacobs, R.; Joannes-Boyau, O.; Malbrain, M.; Forni, L.G. Cytokine removal in human septic shock: Where are we and where are we going? Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjo, A.; Molnar, Z.; Zádori, N.; Gede, N.; Erőss, B.; Szakó, L.; Kiss, T.; Márton, Z.; Malbrain, M.L.N.G.; Szuldrzynski, K.; et al. Dosing of Extracorporeal Cytokine Removal In Septic Shock (DECRISS): Protocol of a prospective, randomised, adaptive, multicentre clinical trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e050464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Cytokine | Author/Year | Paper | Major Finding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | IL-1β | Jimenez-Sousa, 2017 | IL-1B rs16944 polymorphism is related to septic shock and death | Frequency of septic shock higher in patients with IL-1β rs16944 genotype. |
| TNF-α | Debets, 1989 | Plasma tumor necrosis factor and mortality in critically ill septic patients | Sepsis is accompanied by detectable circulating TNF in 25% of the cases, and for these patients mortality is twice that for comparable TNF-negative patients. | |
| Human | TNF-α, IL-1 | Damas, 1989 | Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 serum levels during severe sepsis in humans | There was a correlation between the TNF alpha level and sepsis severity score as well as with mortality. In contrast, IL-1 beta serum levels were only slightly increased and were not correlated with severity or mortality. |
| Human | IL-6, IL-10 | Kellum, 2007 | Understanding the Inflammatory Cytokine Response in Pneumonia and Sepsis Results of the Genetic and Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Study | Highest risk of death was with combined high levels of IL-6 and IL-10. |
| Human | IL-10 | Sherry RM, 1996 | Interleukin-10 is associated with the development of sepsis in trauma patients | Plasma IL-10 concentrations were associated with development of hypotension and sepsis. |
| Human | IL-6 | Vivas, 2021 | Plasma interleukin-6 levels correlate with survival in patients with bacterial sepsis and septic shock | Patients who developed septic shock maintained high concentrations of IL-6 and had lower survival to those that maintained low IL-6 concentrations. |
| Human | IL-6, IL-10 | Zhang, 2022 | Evaluating IL-6 and IL-10 as rapid diagnostic tools for Gram-negative bacteria and as disease severity predictors in pediatric sepsis patients in the intensive care unit | IL-6 and IL-10 are comparably effective in discriminating Gram+ or Gram- sepsis in pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) patients. |
| Human | IL-1β, IL-6, | Mera, 2011 | Multiplex cytokine profiling in patients with sepsis | IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, interferon-γ, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor-α exhibited persistent increases in non-survivors. |
| Human | IL-6, IL-10 | Pin-Wu, 2009 | Serial cytokine levels in patients with severe sepsis | IL-6 and IL-10 were the key cytokines in the pathogenesis of severe sepsis. IL-6 was comparatively more associated with septic shock and IL-10 was comparatively more associated with mortality. |
| Equine | TNF-α | Morris, 1991 | Tumor necrosis factor activity in serum from neonatal foals with presumed septicemia | Increased serum TNF-a is associated with disease severity in septic foals. |
| Equine | TNF-α | MacKay, 1991 | Tumor necrosis factor activity in the circulation of horses given endotoxin | TNF activity is elevated in horses with experimental endotoxemia and is associated with clinical signs. |
| Equine | TNF-α | Morris, 1991 | Serum tumor necrosis factor activity in horses with colic attributable to gastrointestinal tract disease | Possible association between colic and serum TNF activity in horses and that high mortality may be associated with horses with markedly increased serum TNF activity. |
| Equine | IL-10, TNF-α, IL-1β | Pusterla, 2006 | Expression of molecular markers in blood of neonatal foals with sepsis | Cytokine profiles in septic foals may suggest an immunosuppressive state. |
| Equine | TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-10 | Anderson, 2020 | Depletion of pulmonary intravascular macrophages rescues inflammation-induced delayed neutrophil apoptosis in horses | Apoptosis was delayed in horses with elevated TNF-a in SIRS. |
| Equine | IL-1β, IL-8, IFN-g | Castagnetti, 2011 | Expression of interleukin-1β, interleukin-8, and interferon-γ in blood samples obtained from healthy and sick neonatal foals | Evaluation of IL-1β expression in sick neonatal foals can help identify those with sepsis. |
| Equine | IL-6, IL-10 | Burton, 2009 | Serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-10 concentrations in normal and septic neonatal foal | Serum IL-6: IL-10 ratio is likely to provide a valuable prognosticator for neonatal septicemia. |
| Cytokine | Cell Types | Function in Sepsis | Therapies that Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | Macrophages, Monocytes | Apoptosis, Cell Proliferation, Differentiation | Steroids, Hemoperfusion, Monoclonal Antibodies |
| IL-6 | T-cells, Macrophages, Endothelial Cells | Apoptosis, Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, Cytokine Production | Steroids, Hemoperfusion, Monoclonal Antibodies, Cytokine Antagonist |
| TNF- α | Macrophages,CD4 T-Cells, NK Cells | Cell Proliferation, Cytokine Production, Apoptosis, Tumor Necrosis | Steroids, Hemoperfusion, Monoclonal Antibodies, Cytokine Antagonist |
| IL-10 | Th2 Cells, B-Cells, Monocytes | Inhibition of Inflammatory Cytokines | Steroids, Hemoperfusion, No Other Approved Therapy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hobbs, K.J.; Bayless, R.; Sheats, M.K. A Comparative Review of Cytokines and Cytokine Targeting in Sepsis: From Humans to Horses. Cells 2024, 13, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171489
Hobbs KJ, Bayless R, Sheats MK. A Comparative Review of Cytokines and Cytokine Targeting in Sepsis: From Humans to Horses. Cells. 2024; 13(17):1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171489
Chicago/Turabian StyleHobbs, Kallie J., Rosemary Bayless, and M. Katie Sheats. 2024. "A Comparative Review of Cytokines and Cytokine Targeting in Sepsis: From Humans to Horses" Cells 13, no. 17: 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171489
APA StyleHobbs, K. J., Bayless, R., & Sheats, M. K. (2024). A Comparative Review of Cytokines and Cytokine Targeting in Sepsis: From Humans to Horses. Cells, 13(17), 1489. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171489








