Protein Signature Differentiating Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determined Using a Human Isogenic Cell Line Model and Protein Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. iPMN and iMDSC In Vitro Induction
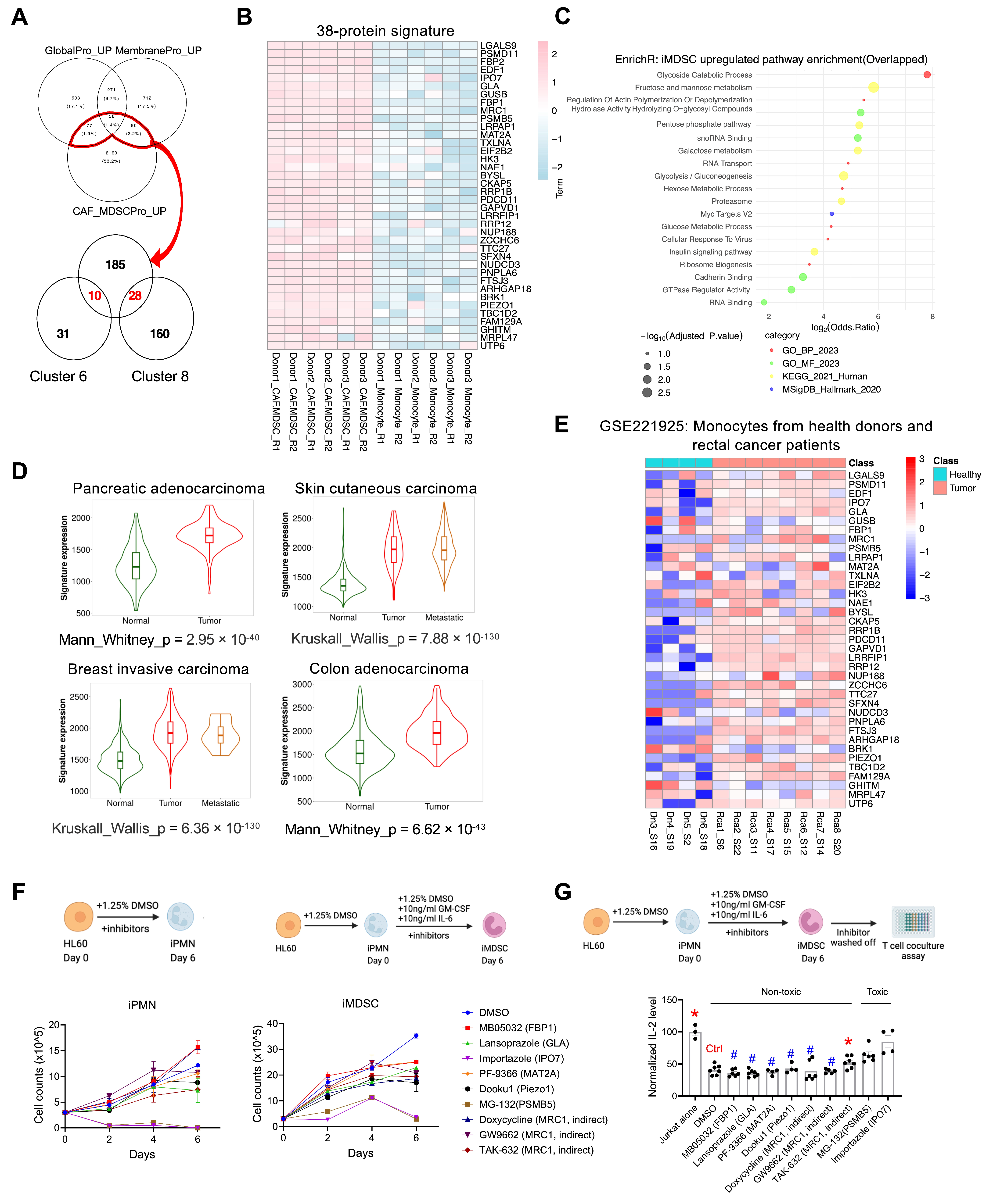
2.3. Jurkat Interleukin-2 (IL-2) Measurement to Evaluate Immunosuppression
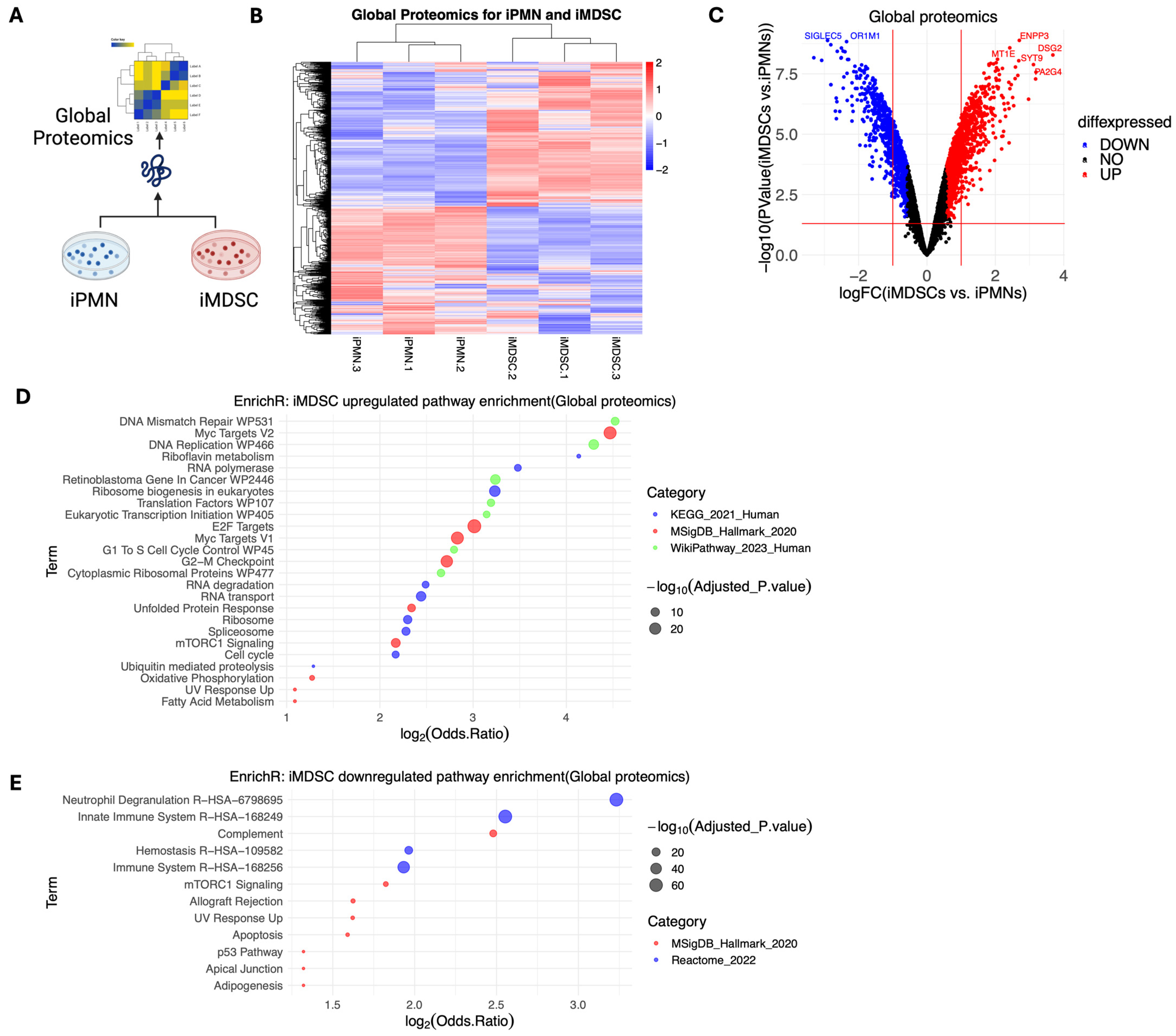
2.4. Global Proteomics
2.5. Membrane Proteomics
2.6. Differential Expression Analysis for Proteomics
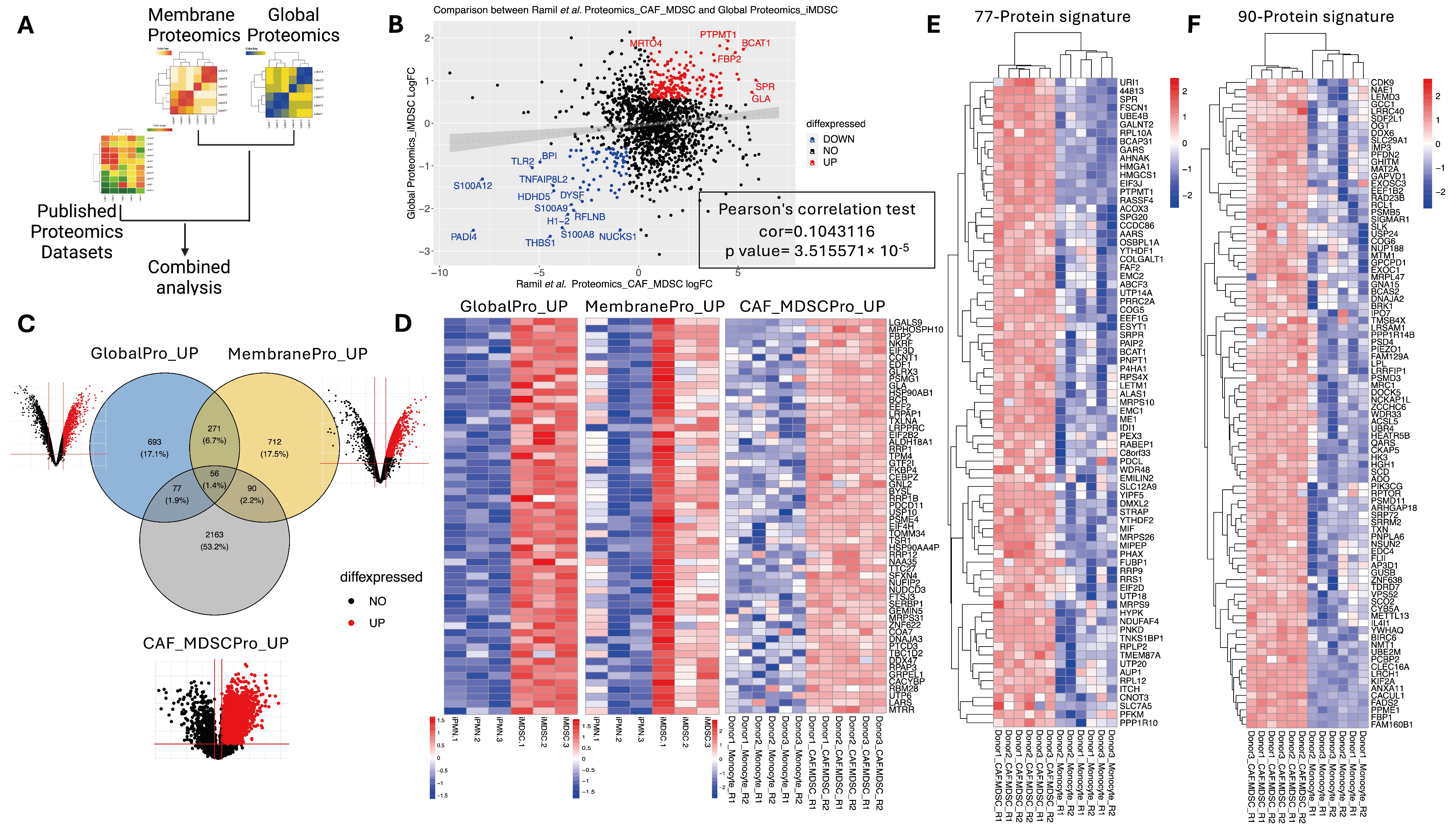
2.7. Comparative Analysis of Published Datasets and the Dataset from Our Study
3. Results
3.1. Confirming the iPMN/iMDSC Model and the Suppression of T Cells by iMDSC
3.2. Global Proteomic Profiling of iPMNs and iMDSCs
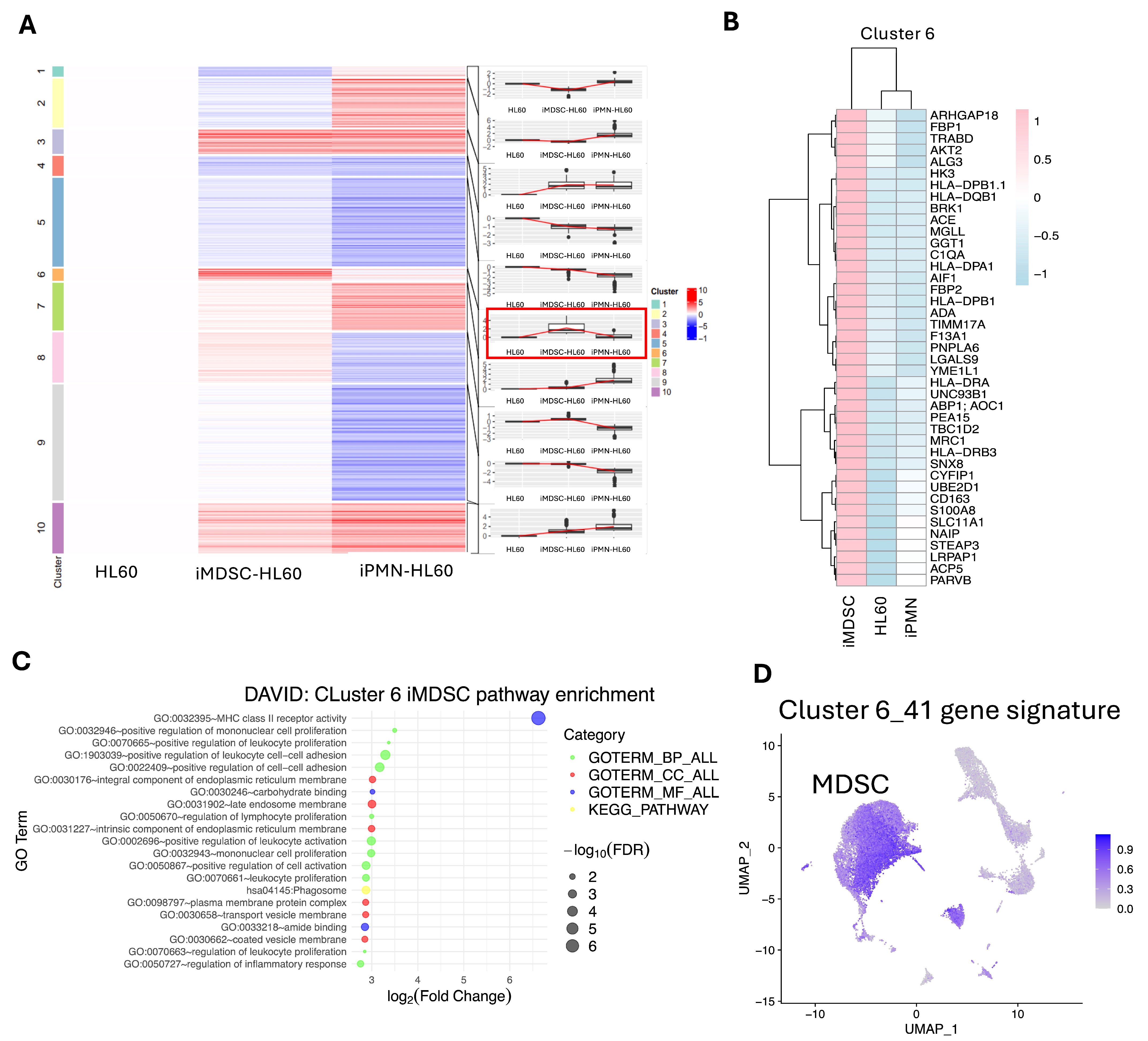
3.3. Membrane Proteomic Profiling of HL60, iPMN, and iMDSC
3.4. A 41-Protein Signature High in iMDSC but Low in iPMN and HL60
3.5. Integration of Global and Membrane Proteomics to Find Shared Proteins
3.6. Consistently Upregulated MDSC-Associated Proteins across Datasets
3.7. A 38-Protein MDSC Signature Based on Overlap Analysis, Functional Assessment, and Clinical Association
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, P.; Allison, J.P. The Future of Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Science 2015, 348, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Horner, J.W.; Paul, E.; Shang, X.; Troncoso, P.; Deng, P.; Jiang, S.; Chang, Q.; Spring, D.J.; Sharma, P.; et al. Effective Combinatorial Immunotherapy for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Nature 2017, 543, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Murphy, S.; Lu, X. Cancer-Cell-Intrinsic Mechanisms Regulate MDSCs through Cytokine Networks. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 375, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Ou, X.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shu, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as Immunosuppressive Regulators and Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groth, C.; Hu, X.; Weber, R.; Fleming, V.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Immunosuppression Mediated by Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs) during Tumour Progression. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veglia, F.; Sanseviero, E.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Era of Increasing Myeloid Cell Diversity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, M.; Lu, X. Targeting and Exploitation of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils to Enhance Immunotherapy and Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condamine, T.; Dominguez, G.A.; Youn, J.I.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Mony, S.; Alicea-Torres, K.; Tcyganov, E.; Hashimoto, A.; Nefedova, Y.; Lin, C.; et al. Lectin-Type Oxidized LDL Receptor-1 Distinguishes Population of Human Polymorphonuclear Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer Patients. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, aaf8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes-McAlister, J.; Gadjeva, M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantitative Proteomics of Murine-Derived Neutrophils. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2019, 126, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva, N.A.; Barlock, B.J.; Guha, P.; Ghosh, C.C.; Trebino, C.E.; Camberg, J.L.; Katz, S.C.; Rowley, D.C. Proteomic Signatures of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells from Liver and Lung Metastases Reveal Functional Divergence and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomazella, G.G.; da Silva, I.; Laure, H.J.; Rosa, J.C.; Chammas, R.; Wiker, H.G.; de Souza, G.A.; Greene, L.J. Proteomic Analysis of Total Cellular Proteins of Human Neutrophils. Proteome Sci. 2009, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Mozo, P.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Martinez-Pinna, R.; Blanco-Colio, L.M.; Lopez, J.A.; Camafeita, E.; Meilhac, O.; Michel, J.B.; Aparicio, C.; De Ceniga, M.V.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils Identifies Catalase as a Novel Biomarker of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Potential Implication of Oxidative Stress in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Progression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 3011–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtari, M.; Curtis, B.; Waller, E.K. Autoimmune Neutropenia in Adults. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergenfelz, C.; Larsson, A.-M.; von Stedingk, K.; Gruvberger-Saal, S.; Aaltonen, K.; Jansson, S.; Jernström, H.; Janols, H.; Wullt, M.; Bredberg, A.; et al. Systemic Monocytic-MDSCs Are Generated from Monocytes and Correlate with Disease Progression in Breast Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jethwaney, D.; Rafiqul, M.R.; Leidal, K.G.; de Bernabe, D.B.V.; Campbell, K.P.; Nauseef, W.M.; Gibson, B.W. Proteomic Analysis of Plasma Membrane and Secretory Vesicles from Human Neutrophils. Proteome Sci. 2007, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, G.D. The HL60 Cell Line: A Model System for Studying Human Myeloid Cell Differentiation. Br. J. Cancer 1988, 58, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler, H.P.; Golde, D.W. Human Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines: A Review. Blood 1980, 56, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubiani, O.; Ciancarelli, M.; Rapino, M.; Di Primio, R. Dimethyl Sulfoxide Induces Programmed Cell Death and Reversible G1 Arrest in the Cell Cycle of Human Lymphoid Pre-T Cell Line. Immunol. Lett. 1996, 50, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.; Leport, M.; Szilagyi, C.; Allen, J.M.; Bertrand, C.; Lagente, V. DMSO-Treated HL60 Cells: A Model of Neutrophil-like Cells Mainly Expressing PDE4B Subtype. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Zanier, R.; Degrassi, F. Reversible G1 Arrest by Dimethyl Sulfoxide as a New Method to Synchronize Chinese Hamster Cells. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wilt, E.; Lu, X. Human Isogenic Cell Line Models for Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, Y.; Kato, T.; Ito, H.; Kurota, Y.; Yamagishi, A.; Sakurai, T.; Araki, A.; Nara, H.; Tsuchiya, N.; Asao, H. The Pattern of GPI-80 Expression Is a Useful Marker for Unusual Myeloid Maturation in Peripheral Blood. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 186, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushach, I.; Zlotnik, A. Biological Role of Granulocyte Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) and Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (M-CSF) on Cells of the Myeloid Lineage. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gan, D.; Chang, W.; Peng, X.; Sung, E.S.; Gilbert, K.; et al. Neutrophils Resist Ferroptosis and Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis through Aconitate Decarboxylase 1. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1688–1703.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Tanikawa, T.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Wan, S.; Wei, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Endow Stem-like Qualities to Breast Cancer Cells through IL6/STAT3 and NO/NOTCH Cross-Talk Signaling. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Ye, Y.; Liu, P.; Yu, W.; Wei, F.; Ren, X.; Yu, J. Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling Pathway Promotes Immunosuppressive Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells via Suppression of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 in Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Jiang, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Fu, T.; Lu, T.; Song, L.; Ying, W.; et al. A Fast Workflow for Identification and Quantification of Proteomes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2013, 12, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bai, J.; Bandla, C.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Prakash, A.; Frericks-Zipper, A.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE Database Resources in 2022: A Hub for Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics Evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D543–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma Powers Differential Expression Analyses for RNA-Sequencing and Microarray Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and Collaborative HTML5 Gene List Enrichment Analysis Tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Functional Annotation of Gene Lists (2021 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and Integrative Analysis of Large Gene Lists Using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savardekar, H.; Allen, C.; Jeon, H.; Li, J.; Quiroga, D.; Schwarz, E.; Wu, R.C.; Zelinskas, S.; Lapurga, G.; Abreo, A.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis of Patient Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and the Response to Inhibition of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase. Mol. Cancer Res. 2023, 22, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramil, C.P.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, P.; Cronin, A.; Cabral, L.; Yin, Z.; Hai, J.; Wang, H.; Ruprecht, B.; Jia, Y.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Induced Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Inhibit T-Cell Function. Oncoimmunology 2024, 13, 2300882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larionova, I.; Patysheva, M.; Iamshchikov, P.; Kazakova, E.; Kazakova, A.; Rakina, M.; Grigoryeva, E.; Tarasova, A.; Afanasiev, S.; Bezgodova, N.; et al. PFKFB3 Overexpression in Monocytes of Patients with Colon but Not Rectal Cancer Programs Pro-Tumor Macrophages and Is Indicative for Higher Risk of Tumor Relapse. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1080501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, Á.; Győrffy, B. TNMplot.Com: A Web Tool for the Comparison of Gene Expression in Normal, Tumor and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Okoro, C.; Foell, D.; Freeze, H.H.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Srikrishna, G. Proinflammatory S100 Proteins Regulate the Accumulation of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, A.; Ponnazhagan, S. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as a Novel Target for the Control of Osteolytic Bone Disease. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e24064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, S.; Villasboas, J.; Shi, J.; Bothun, C.; Kim, H.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Ansell, S.M. Mass Cytometry Identifies a Novel Signature for Myeloid-Derived Suppressor-Cells in Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia. Blood 2019, 134, 3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Jin, Y.; Wen, X.-M.; Ma, J.-C.; Tang, L.-J.; Mao, Z.-W.; Qian, J.; Lin, J. The M2 Macrophage Marker CD206: A Novel Prognostic Indicator for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1683347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhu, X.-D.; Ao, J.-Y.; Ye, B.-G.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Chai, Z.-T.; Wang, C.-H.; Shi, W.-K.; Cao, M.-Q.; Li, X.-L.; et al. Colony-Stimulating Factor-1-Induced AIF1 Expression in Tumor-Associated Macrophages Enhances the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1333213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Kawasaki, T.; Zhou, H.; Okuzaki, D.; Okada, N.; Tachibana, M. Targeting GGT1 Eliminates the Tumor-Promoting Effect and Enhanced Immunosuppressive Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Caused by G-CSF. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 873792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, S.; Nelson, A.; Youn, J.; Cheng, P.; Quiceno, D.; Gabrilovich, D.I. Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cells Regulate Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer via Retrograde MHC Class II Signaling. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.-L.; Chen, W.-W.; Su, Y.-C.; Su, Y.-W.; Chuang, T.-H.; Hsu, S.-C.; Huang, L.-R. Glycolysis Regulates the Expansion of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Tumor-Bearing Hosts through Prevention of ROS-Mediated Apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemińska, I.; Węglarczyk, K.; Walczak, M.; Czerwińska, A.; Pach, R.; Rubinkiewicz, M.; Szczepanik, A.; Siedlar, M.; Baran, J. Mo-MDSCs Are Pivotal Players in Colorectal Cancer and May Be Associated with Tumor Recurrence after Surgery. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 17, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyagarajan, A.; Alshehri, M.S.A.; Miller, K.L.R.; Sherwin, C.M.; Travers, J.B.; Sahu, R.P. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Pancreatic Cancer: Implications in Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers 2019, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y. MDSCs in Breast Cancer: An Important Enabler of Tumor Progression and an Emerging Therapeutic Target. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1199273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomela, K.; Pietrzak, B.; Galus, Ł.; Mackiewicz, J.; Schmidt, M.; Mackiewicz, A.A.; Kaczmarek, M. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) in Melanoma Patients Treated with Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy. Cells 2023, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, X. High-Expression of Galactosidase Alpha Is Correlated with Poor Prognosis and Immune Infiltration in Low-Grade Glioma. J. Cancer 2023, 14, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Yang, B.K. Increased Nuclear Transporter Importin 7 Contributes to the Tumor Growth and Correlates with CD8 T Cell Infiltration in Cervical Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 732786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Xuan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Lan, C. Pancreatic Cancer Progression Is Regulated by IPO7/P53/LncRNA MALAT1/MiR-129-5p Positive Feedback Loop. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wan, P.; Hu, Y.; Kun, L.; Hu, Y.R.; Yang, X.; Ma, M. Activation of MAT2A-RIP1 Signaling Axis Reprograms Monocytes in Gastric Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aykut, B.; Chen, R.; Kim, J.I.; Wu, D.; Shadaloey, S.A.A.; Abengozar, R.; Preiss, P.; Saxena, A.; Pushalkar, S.; Leinwand, J.; et al. Targeting Piezo1 Unleashes Innate Immunity against Cancer and Infectious Disease. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabb5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Hsu, H.P.; Cho, C.Y.; Yen, M.C.; Weng, T.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Hung, Y.H.; Lee, K.T.; Hung, J.H.; et al. PSMB5 Plays a Dual Role in Cancer Development and Immunosuppression. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 2103–2120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rashidian, M.; LaFleur, M.W.; Verschoor, V.L.; Dongre, A.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Kolifrath, S.; Aref, A.R.; Lau, C.J.; Paweletz, C.P.; et al. Immuno-PET Identifies the Myeloid Compartment as a Key Contributor to the Outcome of the Antitumor Response under PD-1 Blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16971–16980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Jhong, J.-H.; Chen, Q.; Huang, K.-Y.; Strittmatter, K.; Kreuzer, J.; DeRan, M.; Wu, X.; Lee, T.-Y.; Slavov, N.; et al. Global Characterization of Macrophage Polarization Mechanisms and Identification of M2-Type Polarization Inhibitors. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Huang, M.; Cui, D.; Xie, J. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell: A Crucial Player in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1021612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorhoi, A.; Glaría, E.; Garcia-Tellez, T.; Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Zelinskyy, G.; Favier, B.; Singh, A.; Ehrchen, J.; Gujer, C.; Münz, C.; et al. MDSCs in Infectious Diseases: Regulation, Roles, and Readjustment. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liang, M.; Wang, X.; Gan, D.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Wan, J.; Feng, S.; et al. Protein Signature Differentiating Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determined Using a Human Isogenic Cell Line Model and Protein Profiling. Cells 2024, 13, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100795
Zhang Y, Hu J, Zhang X, Liang M, Wang X, Gan D, Li J, Lu X, Wan J, Feng S, et al. Protein Signature Differentiating Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determined Using a Human Isogenic Cell Line Model and Protein Profiling. Cells. 2024; 13(10):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100795
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuting, Jin Hu, Xiashiyao Zhang, Minzhi Liang, Xuechun Wang, Dailin Gan, Jun Li, Xuemin Lu, Jun Wan, Shan Feng, and et al. 2024. "Protein Signature Differentiating Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determined Using a Human Isogenic Cell Line Model and Protein Profiling" Cells 13, no. 10: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100795
APA StyleZhang, Y., Hu, J., Zhang, X., Liang, M., Wang, X., Gan, D., Li, J., Lu, X., Wan, J., Feng, S., & Lu, X. (2024). Protein Signature Differentiating Neutrophils and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Determined Using a Human Isogenic Cell Line Model and Protein Profiling. Cells, 13(10), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100795







