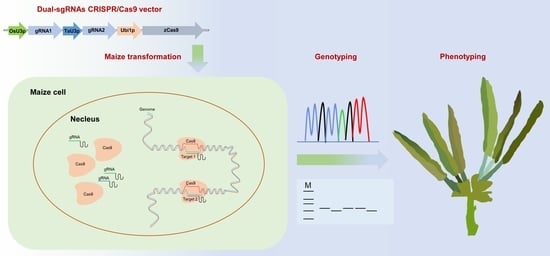
Use of CRISPR/Cas9-Based Gene Editing to Simultaneously Mutate Multiple Homologous Genes Required for Pollen Development and Male Fertility in Maize
Abstract
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, T.; Fang, C.; Hou, Q.; Wu, S.; Xie, K.; An, X.; Wan, X. Use of CRISPR/Cas9-Based Gene Editing to Simultaneously Mutate Multiple Homologous Genes Required for Pollen Development and Male Fertility in Maize. Cells 2022, 11, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030439
Liu X, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Yan T, Fang C, Hou Q, Wu S, Xie K, An X, Wan X. Use of CRISPR/Cas9-Based Gene Editing to Simultaneously Mutate Multiple Homologous Genes Required for Pollen Development and Male Fertility in Maize. Cells. 2022; 11(3):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030439
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinze, Shaowei Zhang, Yilin Jiang, Tingwei Yan, Chaowei Fang, Quancan Hou, Suowei Wu, Ke Xie, Xueli An, and Xiangyuan Wan. 2022. "Use of CRISPR/Cas9-Based Gene Editing to Simultaneously Mutate Multiple Homologous Genes Required for Pollen Development and Male Fertility in Maize" Cells 11, no. 3: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030439
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, S., Jiang, Y., Yan, T., Fang, C., Hou, Q., Wu, S., Xie, K., An, X., & Wan, X. (2022). Use of CRISPR/Cas9-Based Gene Editing to Simultaneously Mutate Multiple Homologous Genes Required for Pollen Development and Male Fertility in Maize. Cells, 11(3), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030439