Evaluation of the Usefulness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids Formed Using SphereRing® and the Lethal Damage Sensitivity to Synovial Fluid In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ADSC Collection and Ethics
2.2. Spheroid Formation Using SphereRing
2.3. Extraction of Total RNA from Cultured Cells
2.4. Transcriptome Analysis Using DNA Microarray
2.5. cDNA Synthesis and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
2.6. SF Collection and Measurement of Viable ADSCs
2.7. Comprehensive Cytokine Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Culture of ADSCs Using SphereRing
3.2. Pathological Specimens of the Spheroids
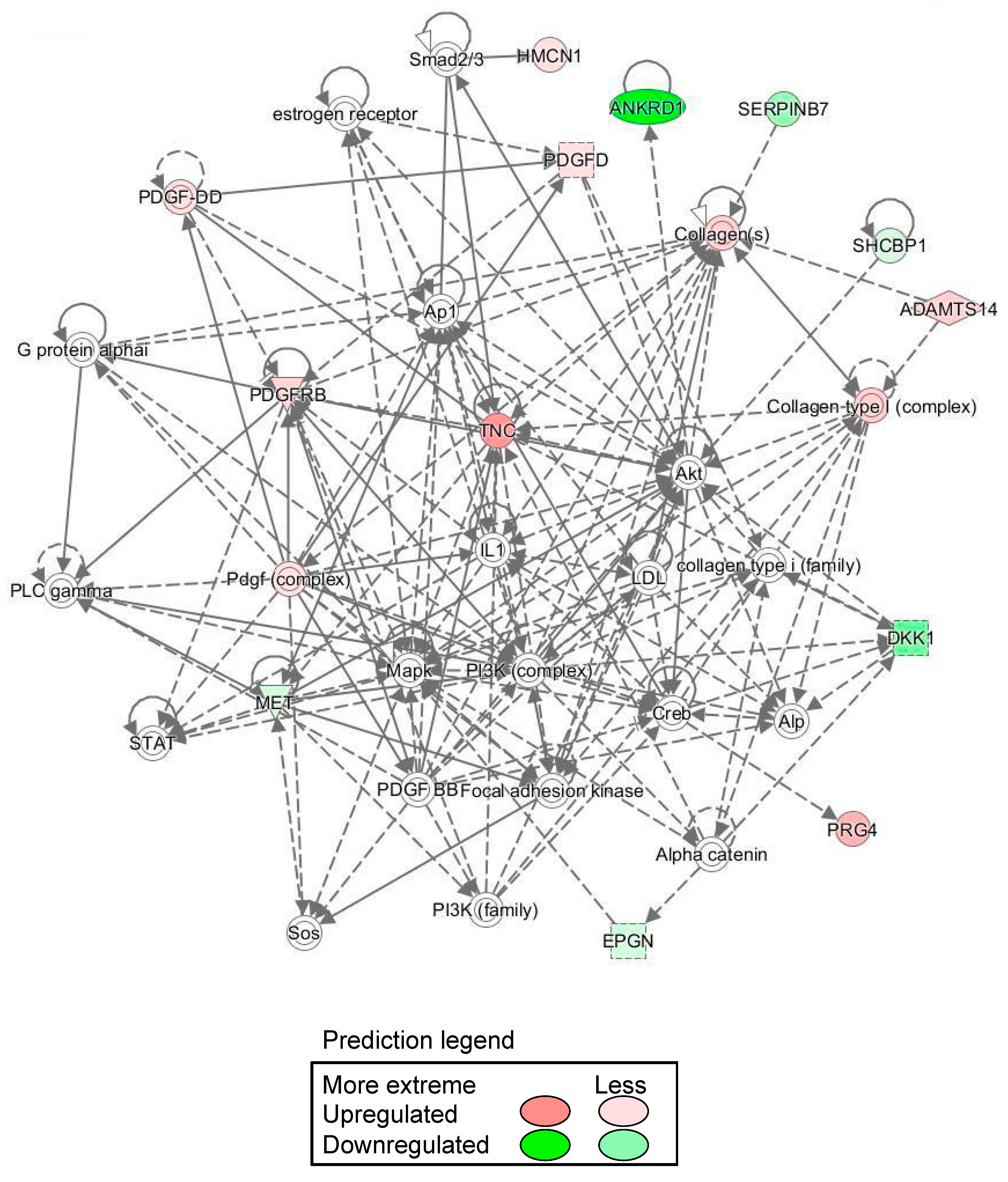
3.3. Transcriptome Analysis Using DNA Microarray
3.4. Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR
3.5. Comprehensive Cytokine Assay
3.6. Effect of SF on Cultured ADSCs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Primorac, D.; Molnar, V.; Rod, E.; Jeleč, Ž.; Čukelj, F.; Matišić, V.; Vrdoljak, T.; Hudetz, D.; Hajsok, H.; Borić, I. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Pathogenesis and State-Of-The-Art Non-Operative Therapeutic Considerations. Genes 2020, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Shen, B.; Ling, P.; Liu, S.; Xue, J.; Liu, F.; Shao, H.; Chen, J.; Ma, A.; Liu, X. Culture-expanded allogenic adipose tissue-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration in an experimental rat osteoarthritis model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baer, P.C.; Griesche, N.; Luttmann, W.; Schubert, R.; Luttmann, A.; Geiger, H. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro: Evaluation of an optimal expansion medium preserving stemness. Cytotherapy 2010, 12, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Hawker, G.A.; Laporte, A.; Croxford, R.; Coyte, P.C. The economic burden of disabling hip and knee osteoarthritis (OA) from the perspective of individuals living with this condition. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermans, J.; Koopmanschap, M.A.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; van Linge, J.H.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Reijman, M.; Burdorf, A. Productivity costs and medical costs among working patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safiri, S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; Smith, E.; Hill, C.; Bettampadi, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Hoy, D.; Ashrafi-Asgarabad, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990–2017: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangha, O. Epidemiology of rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brooks, P.M. Impact of osteoarthritis on individuals and society: How much disability? Social consequences and health economic implications. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2002, 14, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lories, R.J.; Monteagudo, S. Review Article: Is Wnt Signaling an Attractive Target for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis? Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orchard, J.; Moen, M.H. Has reimbursement for knee osteoarthritis treatments now reached ‘postfact’ status? Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1510–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Osani, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Arden, N.K.; Bennell, K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Kraus, V.B.; Lohmander, L.S.; Abbott, J.H.; Bhandari, M.; et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neuprez, A.; Neuprez, A.H.; Kaux, J.-F.; Kurth, W.; Daniel, C.; Thirion, T.; Huskin, J.-P.; Gillet, P.; Bruyère, O.; Reginster, J.-Y. Total joint replacement improves pain, functional quality of life, and health utilities in patients with late-stage knee and hip osteoarthritis for up to 5 years. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Martino, A.; Di Matteo, B.; Papio, T.; Tentoni, F.; Selleri, F.; Cenacchi, A.; Kon, E.; Filardo, G. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid Injections for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: Results at 5 Years of a Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Ha, C.-W.; Park, Y.-B.; Nam, E.; Lee, J.-E.; Lee, H.-J. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for clinical outcomes and cartilage repair in osteoarthritis of the knee: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2019, 139, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Noor, N.; Abdullah Nurul, A.; Ahmad Mohd Zain, M.; Wan Nor Aduni, W.; Azlan, M. Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Potential Treatments for Osteoarthritis. Cells 2021, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage Cells from Human Adipose Tissue: Implications for Cell-Based Therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Shimazu, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Pan, H.; Koike, C.; Yoshida, E.; Takagishi, K.; Kato, Y. Retention of Multilineage Differentiation Potential of Mesenchymal Cells during Proliferation in Response to FGF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 288, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mineda, K.; Feng, J.; Ishimine, H.; Takada, H.; Doi, K.; Kuno, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Kanayama, K.; Kato, H.; Mashiko, T.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Human Adipose-Derived Stem/Stromal Cell Microspheroids Prepared by Three-Dimensional Culture in Non-Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Gel. Steam Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, K.; Tsuboi, N.; Shimizu, A.; Katsuno, T.; Kim, H.; Saka, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Sado, Y.; Imai, E.; Matsuo, S.; et al. Serum-Starved Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Ameliorate Crescentic GN by Promoting Immunoregulatory Macrophages. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, N.; Hattori, M.; Ohtsuru, T.; Otsuji, M.; Lyman, S.; Shimomura, K.; Nakamura, N. Comparative Clinical Outcomes After Intra-articular Injection With Adipose-Derived Cultured Stem Cells or Noncultured Stromal Vascular Fraction for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.-G.; Jo, S.-B.; Kwon, O.-R.; Suh, D.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; Park, S.-H.; Choi, Y.-J. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injections Improve Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2013, 29, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Screpis, D.; Di Donato, S.L.; Bonetti, S.; Piovan, G.; Zorzi, C. Autologous micro-fragmented adipose tissue for the treatment of diffuse degenerative knee osteoarthritis: An update at 3 year follow-up. J. Exp. Orthop. 2018, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, N.; Yamakawa, M.; Shirata, T.; Kimura, T.; Kaneshima, H. Clinical results following intra-articular injection of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Regen. Ther. 2017, 6, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.H.; Chai, J.W.; Jeong, E.C.; Oh, S.; Shin, J.S.; Shim, H.; Yoon, K.S. Intra-articular Injection of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A 2-Year Follow-up Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 2774–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamo-Espinosa, J.M.; Mora, G.; Blanco, J.F.; Granero-Moltó, F.; Núñez-Córdoba, J.M.; López-Elío, S.; Andreu, E.J.; Sánchez-Guijo, F.; Aquerreta, J.D.; Bondía, J.M.; et al. Intra-articular injection of two different doses of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells versus hyaluronic acid in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Long-term follow up of a multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial (phase I/II). J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntyre, J.A.; Jones, I.; Han, B.; Vangsness, J.C.T. Intra-articular Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for the Human Joint: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 3550–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhang, S.H.; Lee, S.; Shin, J.-Y.; Lee, T.-J.; Kim, B.-S. Transplantation of Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells as Spheroids Enhances Vascularization. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarz, Z.; Tamama, K. Spheroid Culture of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 9176357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilroy, G.E.; Foster, S.J.; Wu, X.; Ruiz, J.; Sherwood, S.; Heifetz, A.; Ludlow, J.W.; Stricker, D.M.; Potiny, S.; Green, P.; et al. Cytokine profile of human adipose-derived stem cells: Expression of angiogenic, hematopoietic, and pro-inflammatory factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, H.; Okano, T.; Orita, K.; Mamoto, K.; Sobajima, S.; Iwaguro, H.; Nakamura, H. Local transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells has a significant therapeutic effect in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achilli, T.-M.; Meyer, J.; Morgan, J.R. Advances in the formation, use and understanding of multi-cellular spheroids. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zubillaga, V.; Alonso-Varona, A.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Salaberria, A.M.; Palomares, T. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Chondrospheroids Cultured in Hypoxia and a 3D Porous Chitosan/Chitin Nanocrystal Scaffold as a Platform for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B. The effects of spheroid formation of adipose-derived stem cells in a microgravity bioreactor on stemness properties and therapeutic potential. Biomaterials 2015, 41, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Young, T.-H. Short-Term Spheroid Formation Enhances the Regenerative Capacity of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Promoting Stemness, Angiogenesis, and Chemotaxis. Steam Cells Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Mineda, K.; Wu, S.-H.; Mashiko, T.; Doi, K.; Kuno, S.; Kinoshita, K.; Kanayama, K.; Asahi, R.; Sunaga, A.; et al. An injectable non-cross-linked hyaluronic-acid gel containing therapeutic spheroids of human adipose-derived stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korff, T.; Augustin, H.G. Integration of Endothelial Cells in Multicellular Spheroids Prevents Apoptosis and Induces Differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, N.-E.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, H. Spheroid Culture System Methods and Applications for Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; David, O.; Clejan, S.; Giordano, C.L.; Pappas-Lebeau, H.; Xu, L.; O’Connor, K.C. Spatial Composition of Prostate Cancer Spheroids in Mixed and Static Cultures. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, I.; Suzuki, I.; Morimura, T.; Sakai, Y. An Orbital Shaking Culture of Mammalian Cells in O-shaped Vessels to Produce Uniform Aggregates. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 143, e57922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragni, E.; Colombini, A.; Viganò, M.; Libonati, F.; Perucca Orfei, C.; Zagra, L.; de Girolamo, L. Cartilage Protective and Immunomodulatory Features of Osteoarthritis Synovial Fluid-Treated Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secreted Factors and Extracellular Vesicles-Embedded miRNAs. Cells 2021, 10, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, K.M.; O’Brien, T.D.; Pluhar, E.G.; Conzemius, M. Canine adipose-derived stromal cell viability following exposure to synovial fluid from osteoarthritic joints. Vet. Rec. Open 2015, 2, e000063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Truong, N.C.; Bui, K.H.-T.; Van Pham, P. Characterization of Senescence of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells After Long-Term Expansion. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1084, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Koya, T.; Togi, M.; Date, I.; Watanabe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kato, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishigaki, Y.; et al. Quality Verification with a Cluster−Controlled Manufacturing System to Generate Monocyte−Derived Dendritic Cells. Vaccines 2021, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Inoue, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Iida, Y.; Ishigaki, Y.; Miyazawa, K. High-salt diet promotes crystal deposition through hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rat model. Int. J. Urol. 2019, 26, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellgren, J.H.; Lawrence, J.S. Radiological Assessment of Osteo-Arthrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1957, 16, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Courtney, P.; Doherty, M. Joint aspiration and injection and synovial fluid analysis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 27, 137–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijs, M.J.C.; van Buul, G.M.; Lubberts, E.; Bos, P.K.; Verhaar, J.A.N.; Hoogduijn, M.J.; van Osch, G.J.V.M. Effect of Arthritic Synovial Fluids on the Expression of Immunomodulatory Factors by Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An Explorative in vitro Study. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durgin, B.G.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Gomez, D.; Karaoli, T.; Alencar, G.F.; Butcher, J.T.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Bendeck, M.P.; Isakson, B.E.; Owens, G.K.; et al. Smooth muscle cell-specific deletion of Col15a1 unexpectedly leads to impaired development of advanced atherosclerotic lesions. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2017, 312, H943–H958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, M.; Yoshida, T.; Sudo, A. Tenascin-C in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 577015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naot, D.; Bentley, J.; Macpherson, C.; Pitto, R.P.; Bava, U.; Choi, A.J.; Matthews, B.G.; Callon, K.E.; Gao, R.; Horne, A.; et al. Molecular characterisation of osteoblasts from bone obtained from people of Polynesian and European ancestry undergoing joint replacement surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, G.-I. Current status of regenerative medicine in osteoarthritis. Bone Jt. Res. 2021, 10, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Park, J.; Kim, J.; Im, G. Characterization of adipose-derived stromal/stem cell spheroids versus single-cell suspension in cell survival and arrest of osteoarthritis progression. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.-I. Perspective on Intra-articular Injection Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis Treatment. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cui, L.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Diels-Alder Cross-Linked, Washing-Free Hydrogel Films with Ordered Wrinkling Patterns for Multicellular Spheroid Generation. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3474–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, R.; Wu, F. MSC spheroids-loaded collagen hydrogels simultaneously promote neuronal differentiation and suppress inflammatory reaction through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Biomaterials 2021, 265, 120448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.H.; Bhang, S.H.; Shin, J.-Y.; Shin, J.; Kim, B.-S. Enhanced Cartilage Formation via Three-Dimensional Cell Engineering of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Chen, K.; Xiao, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, K. Evaluation of relationship between SPON1 gene and genetic susceptibility of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.B.; Chen, E.H.; Lynch, S.E. A review of the effects of insulin-like growth factor and platelet derived growth factor on in vivo cartilage healing and repair. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, T.; Fukai, A.; Mabuchi, A.; Ikeda, T.; Yano, F.; Ohba, S.; Nishida, N.; Akune, T.; Yoshimura, N.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of endochondral ossification by HIF-2α during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis development. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronemberger, G.S.; Dalmônico, G.M.L.; Rossi, A.; Leite, P.E.; Saraiva, A.M.; Beatrici, A.; Silva, K.R.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Baptista, L.S. Scaffold- and serum-free hypertrophic cartilage tissue engineering as an alternative approach for bone repair. Artif. Organs 2020, 44, E288–E299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhata, Y.; Kikuchi, Y.; Tomita, S.; Yoshimoto, K. Small spheroids of adipose-derived stem cells with time-dependent enhancement of IL-8 and VEGF-A secretion. Genes Cells 2016, 21, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Gene Symbol | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| GADPH | F | CAACGAATTTGGCTACAGCA | 195 |
| R | AGGGGTCTACATGGCAACTG | ||
| TNC-R | F | GGTACAGTGGGACAGCAGGT | 279 |
| R | GCCTGCCTTCAAGATTTCTG | ||
| COL15A1 | F | GCTTTGGCTTTTGAGTCCAG | 293 |
| R | AGGATGGAGTTGGAGGTGTG | ||
| ANGPTL2 | F | CTGGGCCTGGAGAACATTTA | 334 |
| R | CTCGGAACTCAGCCCAGTAG | ||
| KRT34 | F | GAGCTGACCCTCTGCAAGTC | 292 |
| R | GCTGCTCTGAGCTGGATACC | ||
| KRTAP2–3/2–4 | F | CTTGTCCTCCCTGAGCTACG | 292 |
| R | GGGACTGCACAGACACAGG |
| Molecular and Cellular Functions | ||
|---|---|---|
| GO term | p-value | #Molecules |
| Cellular Movement | 3.02 × 103–3.39 × 105 | 9 |
| Cell Morphology | 3.02 × 102–2.50 × 104 | 7 |
| Cellular Development | 2.19 × 102–2.50 × 104 | 15 |
| Cell Death and Survival | 2.69 × 102–1.70 × 103 | 7 |
| Cell-To-Cell Signaling and Interaction | 2.86 × 102–1.70 × 103 | 8 |
| Molecular and Cellular Functions | ||
|---|---|---|
| GO term | p-value | #Molecules |
| Cell Cycle | 4.32 × 103–6.55 × 107 | 18 |
| Cellular Assembly and Organization | 4.32 × 103–2.48 × 106 | 13 |
| DNA Replication, Recombination, and Repair | 4.71 × 103–2.48 × 106 | 6 |
| Cell Death and Survival | 5.65 × 103–3.80 × 106 | 16 |
| Cellular Movement | 5.46 × 103–5.00 × 106 | 13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuku, A.; Taki, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Kitajima, H.; Takaki, T.; Koya, T.; Tanida, I.; Nozaki, K.; Sunami, H.; Hirata, H.; et al. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids Formed Using SphereRing® and the Lethal Damage Sensitivity to Synovial Fluid In Vitro. Cells 2022, 11, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030337
Fuku A, Taki Y, Nakamura Y, Kitajima H, Takaki T, Koya T, Tanida I, Nozaki K, Sunami H, Hirata H, et al. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids Formed Using SphereRing® and the Lethal Damage Sensitivity to Synovial Fluid In Vitro. Cells. 2022; 11(3):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030337
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuku, Atsushi, Yasuhiko Taki, Yuka Nakamura, Hironori Kitajima, Takashi Takaki, Terutsugu Koya, Ikuhiro Tanida, Kaori Nozaki, Hiroshi Sunami, Hiroaki Hirata, and et al. 2022. "Evaluation of the Usefulness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids Formed Using SphereRing® and the Lethal Damage Sensitivity to Synovial Fluid In Vitro" Cells 11, no. 3: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030337
APA StyleFuku, A., Taki, Y., Nakamura, Y., Kitajima, H., Takaki, T., Koya, T., Tanida, I., Nozaki, K., Sunami, H., Hirata, H., Tachi, Y., Masauji, T., Yamamoto, N., Ishigaki, Y., Shimodaira, S., Shimizu, Y., Ichiseki, T., Kaneuji, A., Osawa, S., & Kawahara, N. (2022). Evaluation of the Usefulness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Spheroids Formed Using SphereRing® and the Lethal Damage Sensitivity to Synovial Fluid In Vitro. Cells, 11(3), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030337









