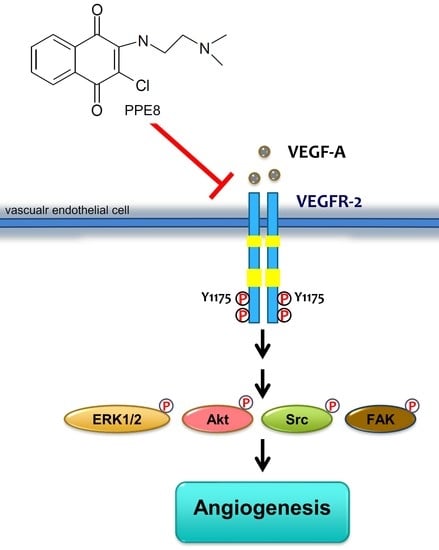
Suppressing VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 Signaling Contributes to the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of PPE8, a Novel Naphthoquinone-Based Compound
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of PPE8
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. MTT Assay
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.6. Cell Migration Assay
2.7. Cell Invasion Assay
2.8. Tube Formation Assay
2.9. Animals
2.10. Rat Aortic Ring Sprouting Assay
2.11. In Vivo Matrigel Plug Angiogenesis Assay
2.12. Mouse Xenograft Model
2.13. Immunohistochemically Analysis
2.14. Immunoblotting
2.15. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PPE8, a Novel Naphthoquinone-Based Compound Reduced Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of VEGF-A-Stimulated HUVECs
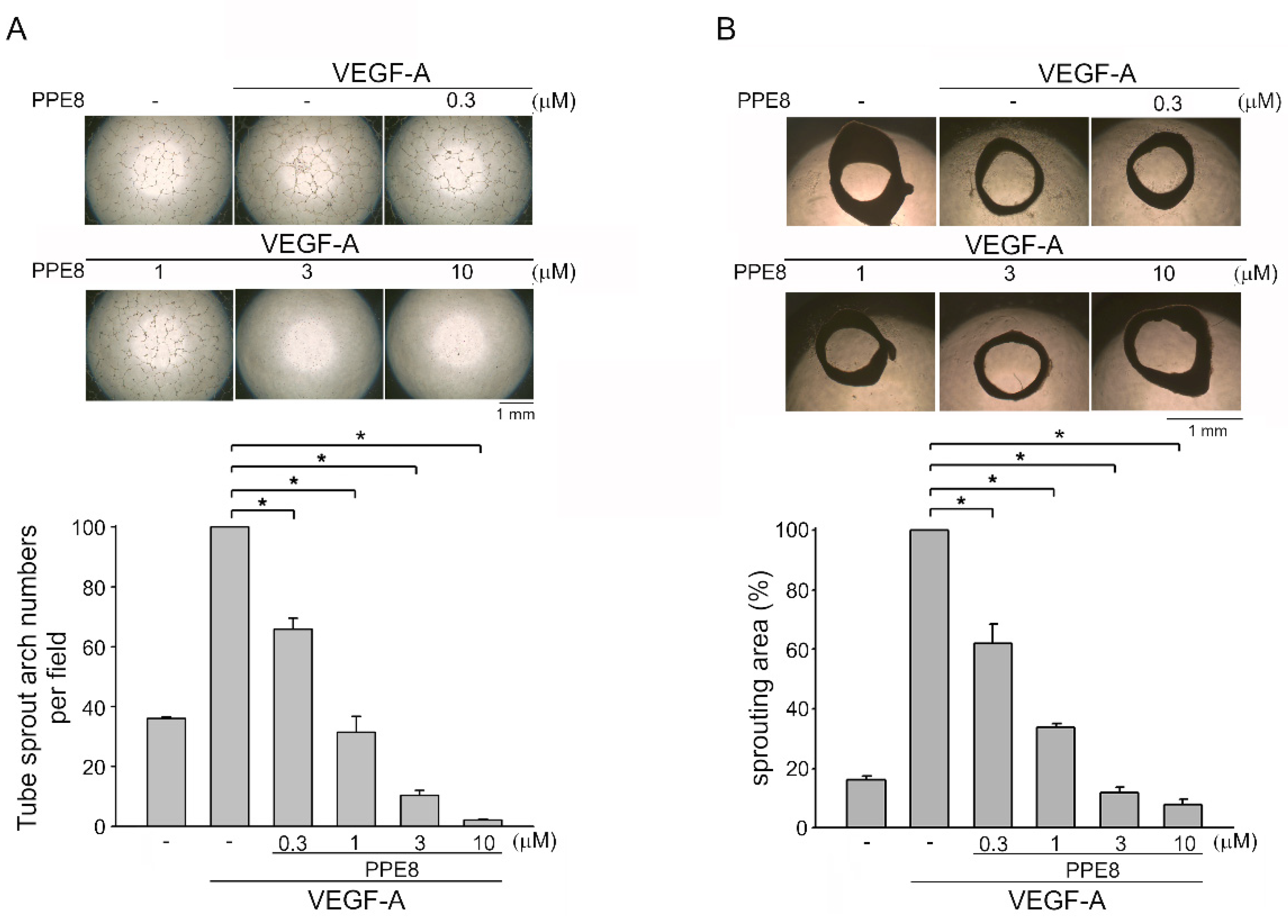
3.2. PPE8 Attenuated VEGF-A-elicited Tubular Formation of HUVECs and Microvessel Sprouting
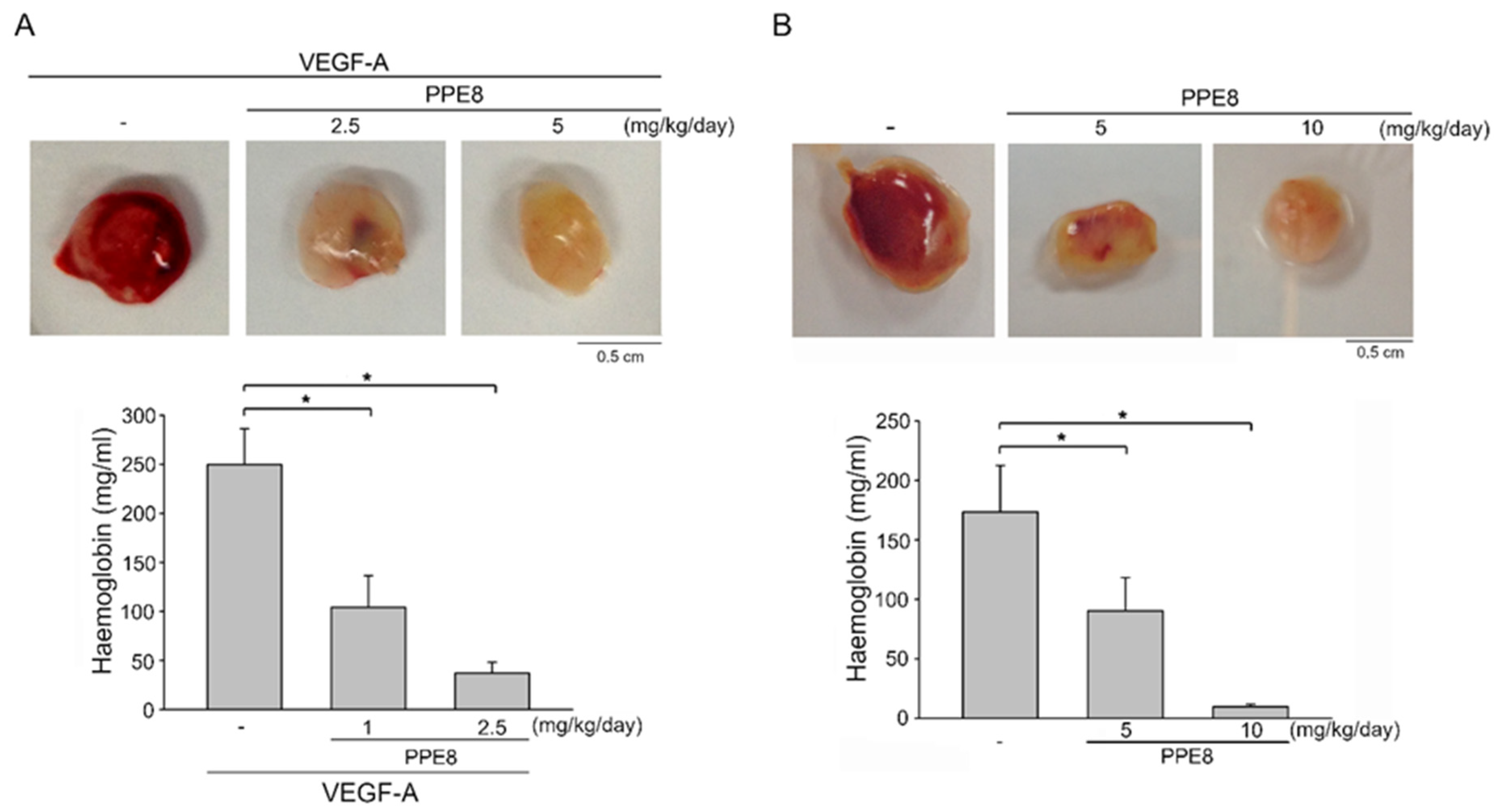
3.3. PPE8 Attenuated VEGF-A- or Tumor-Cell-Induced Angiogenesis In Vivo
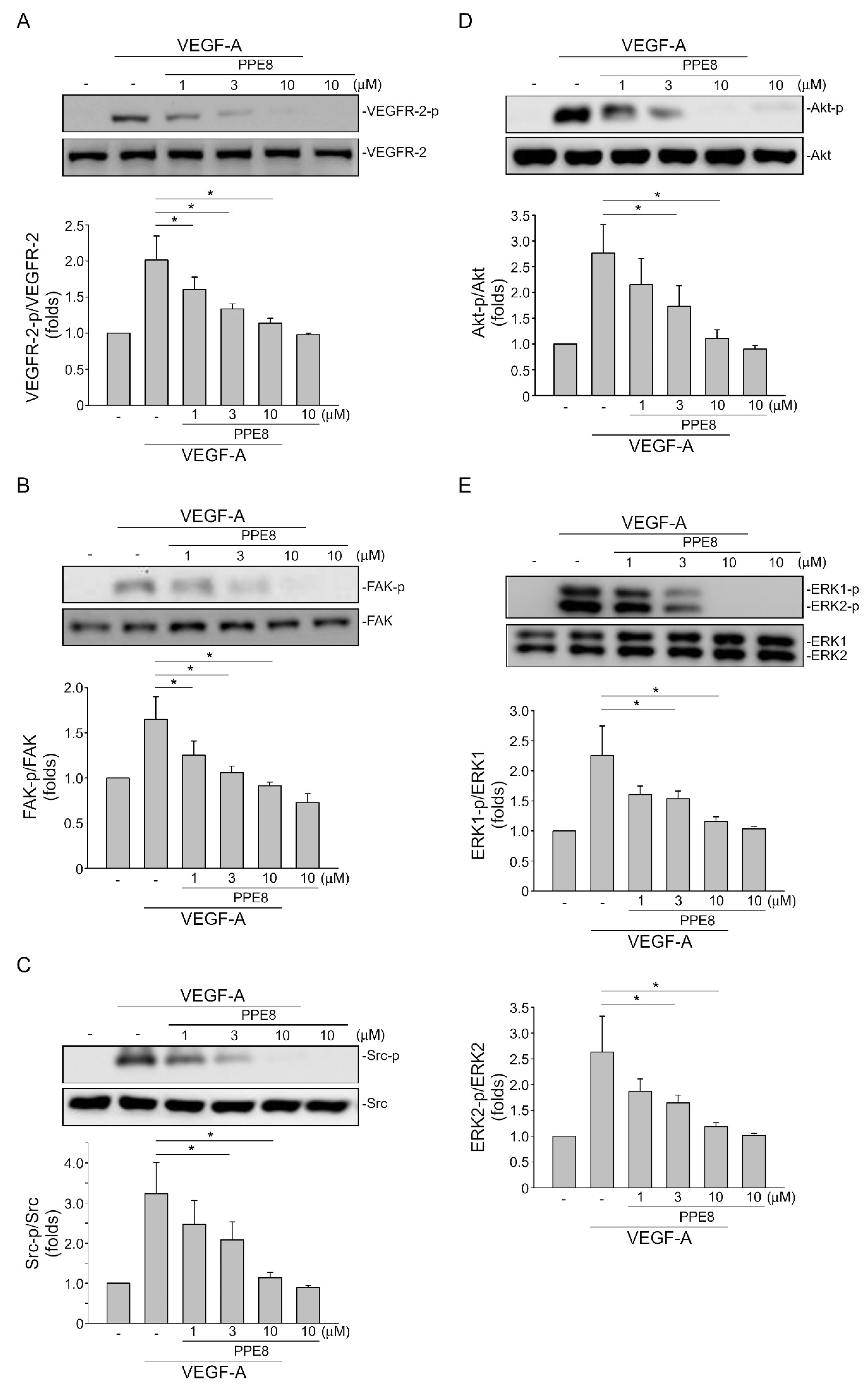
3.4. PPE8 Reduced Endothelial VEGF-A-VEGFR-2 Signaling
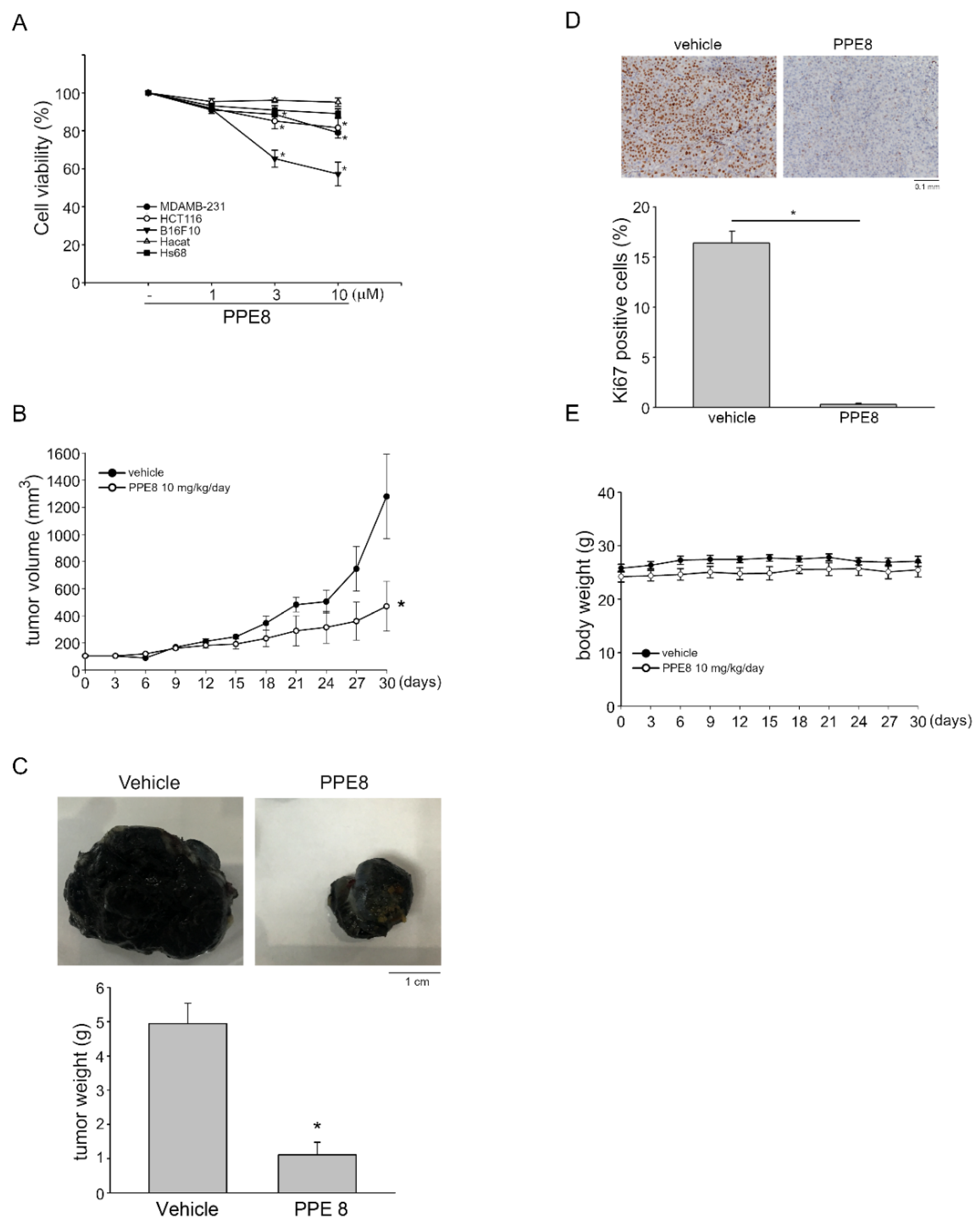
3.5. PPE8 Attenuated Melanoma Growth In Vivo
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribatti, D. The Discovery of Tumor Angiogenesis Factors: A Historical Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1464, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.D.; Seano, G.; Jain, R.K. Normalizing Function of Tumor Vessels: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges. Annu Rev. Physiol 2019, 81, 505–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, B. Targeting VEGF/VEGFR to Modulate Antitumor Immunity. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.; Zhao, W.; Ye, B.; Chen, D. Combination of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Brain Metastases From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021, 11, 67313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresmini, D.; Guida, M. Neoangiogenesis in Melanoma: An Issue in Biology and Systemic Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. Anti-angiogenic Agents in Combination With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Promising Strategy for Cancer Treatment. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Yang, H.; Chon, H.J.; Kim, C. Combination of anti-angiogenic therapy and immune checkpoint blockade normalizes vascular-immune crosstalk to potentiate cancer immunity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Dimberg, Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eelen, G.; Treps, L.; Li, X.; Carmeliet, P. Basic and Therapeutic Aspects of Angiogenesis Updated. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinathan, G.; Milagre, C.; Pearce, O.M.; Reynolds, L.E.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.; Leinster, D.A.; Zhong, H.; Hollingsworh, R.E.; Thompson, R.; Whiteford, J.R.; et al. Interleukin-6 Stimulates Defective Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3098–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeulen, P.B.; van Golen, K.L.; Dirix, L.Y. Angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, growth pattern, and tumor emboli in inflammatory breast cancer: A review of the current knowledge. Cancer 2010, 116, 2748–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Soumya, S.J.; Arya, P.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R. VEGF-A/VEGFR2 signaling network in endothelial cells relevant to angiogenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2016, 10, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Bove, A.M.; Simone, G.; Ma, B. Molecular Bases of VEGFR-2-Mediated Physiological Function and Pathological Role. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 599281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor as a target for anticancer therapy. Oncologist 2004, 9, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvetti, L.; Pilotto, S.; Carbognin, L.; Ferrara, R.; Caccese, M.; Tortora, G.; Bria, E. The coming of ramucirumab in the landscape of anti-angiogenic drugs: Potential clinical and translational perspectives. Expert Opin Biol. 2015, 15, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.M.; Tulpule, A.; Quinn, D.I.; Gorospe, G., 3rd; Smith, D.L.; Hornor, L.; Boswell, W.D.; Espina, B.M.; Groshen, S.G.; Masood, R.; et al. Phase I study of antisense oligonucleotide against vascular endothelial growth factor: Decrease in plasma vascular endothelial growth factor with potential clinical efficacy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, N.; Martin, J.; Ruan, Q.; Rafique, A.; Rosconi, M.P.; Shi, E.; Pyles, E.A.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Stahl, N.; Wiegand, S.J. Binding and neutralization of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and related ligands by VEGF Trap, ranibizumab and bevacizumab. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, M.E.; Endicott, J.A.; Johnson, L.N. Protein kinase inhibitors: Insights into drug design from structure. Science 2004, 303, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abd, A.M.; Alamoudi, A.J.; Abdel-Naim, A.B.; Neamatallah, T.A.; Ashour, O.M. Anti-angiogenic agents for the treatment of solid tumors: Potential pathways, therapy and current strategies—A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, N.S.; Mahran, M.A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel naphthoquinone derivatives as potential anticancer and antimicrobial agents. Boll. Chim. Farm. 2004, 143, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaan, Y.M.; Das, J.R.; Bakare, O.; Enwerem, N.M.; Berhe, S.; Beyene, D.; Williams, V.; Zhou, Y.; Copeland, Y.L., Jr. Biological evaluation of 2,3-dichloro-5,8-dimethoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone as an anti-breast cancer agent. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Vasanth Kumar, S.; Wahab, H.A. Molecular docking, synthesis, and biological evaluation of naphthoquinone as potential novel scaffold for H5N1 neuraminidase inhibition. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, V.K.; Yadav, D.B.; Singh, R.V.; Vaish, M.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Shukla, P.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives as antibacterial and antiviral agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3463–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Lo, C.Y.; Gwo, Z.H.; Lin, H.J.; Chen, L.G.; Kuo, C.D.; Wu, J.Y. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Lipophilic 1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives against Human Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2015, 20, 11994–12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mladenka, P.; Macakova, K.; Krcmova, L.K.; Javorska, L.; Mrstna, K.; Carazo, A.; Protti, M.; Remiao, F.; Novakova, L.; OEMONOM Researchers Collaborators. Vitamin K—Sources, physiological role, kinetics, deficiency, detection, therapeutic use, and toxicity. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 677–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.P. Anti-cancer activities of 1,4-naphthoquinones: A QSAR study. Anticancer Agents. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, C.E.; Dantas, R.F.; Ferreira, S.B.; Gomes, L.P.; Silva, F.P., Jr. The diverse mechanisms and anticancer potential of naphthoquinones. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, E.S.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Iranshahy, M.; Asili, J.; Kretschmer, N.; Shakeri, A.; Sahebkar, A. Naphthoquinone Derivatives Isolated from Plants: Recent Advances in Biological Activity. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2019–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, J.C.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, T.J.; Tseng, C.H.; Sung, P.J.; Lee, H.Z.; Bao, B.Y.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lu, T.L. Naphthoquinone derivative PPE8 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in p53 null H1299 cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 2015, 453679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murota, H.; Shinya, T.; Nishiuchi, A.; Sakanaka, M.; Toda, K.I.; Ogata, T.; Hayama, N.; Kimachi, T.; Takahashi, S. Inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth by a novel 1,4-naphthoquinone derivative. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, J.C.; Chung, C.L.; Huang, T.F.; Chang, T.C.; Chen, K.C.; Gao, G.Y.; Hsu, M.J.; Huang, S.W. A novel 2-aminobenzimidazole-based compound Jzu 17 exhibits anti-angiogenesis effects by targeting VEGFR-2 signalling. Br. J. Pharm. 2019, 176, 4034–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. Br. J. Pharm. 2020, 177, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.F.; Huang, S.W.; Hsu, Y.F.; Yu, M.C.; Ou, G.; Huang, W.J.; Hsu, M.J. WMJ-8-B, a novel hydroxamate derivative, induces MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell death via the SHP-1-STAT3-survivin cascade. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 174, 2941–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.W.; Lien, J.C.; Kuo, S.C.; Huang, T.F. PPemd26, an anthraquinone derivative, suppresses angiogenesis via inhibiting VEGFR2 signalling. Br. J. Pharm. 2014, 171, 5728–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apte, R.S.; Chen, D.S.; Ferrara, N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell 2019, 176, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazzazi, H.; Isenberg, J.S.; Popel, A.S. Inhibition of VEGFR2 Activation and Its Downstream Signaling to ERK1/2 and Calcium by Thrombospondin-1 (TSP1): In silico Investigation. Front Physiol. 2017, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, C.; Mazzone, M.; Jonckx, B.; Carmeliet, P. FLT1 and its ligands VEGFB and PlGF: Drug targets for anti-angiogenic therapy? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevs, J.; Fakler, J.; Eisele, S.; Medinger, M.; Bing, G.; Esser, N.; Marme, D.; Unger, C. Antiangiogenic potency of various chemotherapeutic drugs for metronomic chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.; Hess, K.; Jardim, D.L.F.; Gagliato, D.D.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Falchook, G.; Fu, S.Q.; Janku, F.; Naing, A.; Piha-Paul, S.; et al. Synergy Between VEGF/VEGFR Inhibitors and Chemotherapy Agents in the Phase I Clinic. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5956–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahma, O.E.; Hodi, F.S. The Intersection between Tumor Angiogenesis and Immune Suppression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5449–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Shen, L. Extracellular vesicle-mediated regulation of tumor angiogenesis- implications for anti-angiogenesis therapy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemali, S.; Farajnia, S.; Barzegar, A.; Rahmati-Yamchi, M.; Baghban, R.; Rahbarnia, L.; Nodeh, H.R.Y. New Developments in Anti-Angiogenic Therapy of Cancer, Review and Update. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Najjar, N.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Ketola, R.A.; Vuorela, P.; Urtti, A.; Vuorela, H. The chemical and biological activities of quinones: Overview and implications in analytical detection. Phytochem. Rev. 2011, 10, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayashima, T.; Mori, M.; Yoshida, H.; Mizushina, Y.; Matsubara, K. 1,4-Naphthoquinone is a potent inhibitor of human cancer cell growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2009, 278, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Pal, K.; Elkhanany, A.; Dutta, S.; Cao, Y.; Mondal, G.; Iyer, S.; Somasundaram, V.; Couch, F.J.; Shridhar, V.; et al. Plumbagin inhibits tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motzer, R.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.Y.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grunwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Kopyltsov, E.; Mendez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Clear Trial Investigators. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Li, A.; Yi, M.; Yu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, K. Recent advances on anti-angiogenesis receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Hematol Oncol. 2019, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, W. The Emerging Regulation of VEGFR-2 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2015, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beenken, A.; Mohammadi, M. The FGF family: Biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrae, J.; Gallini, R.; Betsholtz, C. Role of platelet-derived growth factors in physiology and medicine. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1276–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giavazzi, R.; Sennino, B.; Coltrini, D.; Garofalo, A.; Dossi, R.; Ronca, R.; Tosatti, M.P.; Presta, M. Distinct role of fibroblast growth factor-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor on tumor growth and angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Luna Martins, D.; Borges, A.A.; NADA, E.S.; Faria, J.V.; Hoelz, L.V.B.; de Souza, H.; Bello, M.L.; Boechat, N.; Ferreira, V.F.; Faria, R.X. P2 × 7 receptor inhibition by 2-amino-3-aryl-1,4-naphthoquinones. Bioorg Chem. 2020, 104, 104278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badolato, M.; Carullo, G.; Caroleo, M.C.; Cione, E.; Aiello, F.; Manetti, F. Discovery of 1,4-Naphthoquinones as a New Class of Antiproliferative Agents Targeting GPR55. Acs. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munni, Y.A.; Ali, M.C.; Selsi, N.J.; Sultana, M.; Hossen, M.; Bipasha, T.H.; Rahman, M.; Uddin, M.N.; Hosen, S.M.Z.; Dash, R. Molecular simulation studies to reveal the binding mechanisms of shikonin derivatives inhibiting VEGFR-2 kinase. Comput Biol. Chem. 2021, 90, 107414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, F.; Simons, M. Modulation of VEGF receptor 2 signaling by protein phosphatases. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.F.; Hsu, Y.F.; Chiu, P.T.; Huang, W.J.; Huang, S.W.; Ou, G.; Sheu, J.R.; Hsu, M.J. WMJ-S-001, a novel aliphatic hydroxamate derivative, exhibits anti-angiogenic activities via Src-homology-2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vestweber, D. Vascular Endothelial Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Regulates Endothelial Function. Physiology 2021, 36, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, V.; Hudson, L.; Fay, J.; Richards, C.E.; Jahns, H.; Verreault, M.; Bielle, F.; Idbaih, A.; Lamfers, M.L.M.; Hopkins, A.M.; et al. Transcriptional CDK inhibitors, CYC065 and THZ1 promote Bim-dependent apoptosis in primary and recurrent GBM through cell cycle arrest and Mcl-1 downregulation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, F.; Duranyildiz, D.; Oguz, H.; Camlica, H.; Yasasever, V.; Topuz, E. Circulating serum levels of angiogenic factors and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1 and 2 in melanoma patients. Melanoma Res. 2006, 16, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, T.R.; Fulford, A.D.; Nedderman, D.M.; Umberger, T.S.; Hozak, R.R.; Joshi, A.; Melemed, S.A.; Benjamin, L.E.; Plowman, G.D.; Schade, A.E.; et al. Tumor Cell Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 Is an Adverse Prognostic Factor in Patients with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Lung. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacal, P.M.; Ruffini, F.; Pagani, E.; D’Atri, S. An autocrine loop directed by the vascular endothelial growth factor promotes invasiveness of human melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.G.; Zhou, H.B.; Neelakantan, D.; Hughes, C.J.; Hsu, J.Y.; Srinivasan, R.R.; Lewis, M.T.; Ford, H.L. VEGF-C mediates tumor growth and metastasis through promoting EMT-epithelial breast cancer cell crosstalk. Oncogene 2021, 40, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, M.P.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Al-Sarraf, N.; Gray, S.G. VEGF-mediated cell survival in non-small-cell lung cancer: Implications for epigenetic targeting of VEGF receptors as a therapeutic approach. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.M.; Xu, L.Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y. Effects of autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in non-small cell lung cancer cell line A549. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamerlik, P.; Lathia, J.D.; Rasmussen, R.; Wu, Q.L.; Bartkova, J.; Lee, M.; Moudry, P.; Bartek, J.; Fischer, W.; Lukas, J.; et al. Autocrine VEGF-VEGFR2-Neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, M.-J.; Chen, H.-K.; Lien, J.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, S.-W. Suppressing VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 Signaling Contributes to the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of PPE8, a Novel Naphthoquinone-Based Compound. Cells 2022, 11, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132114
Hsu M-J, Chen H-K, Lien J-C, Huang Y-H, Huang S-W. Suppressing VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 Signaling Contributes to the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of PPE8, a Novel Naphthoquinone-Based Compound. Cells. 2022; 11(13):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132114
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Ming-Jen, Han-Kun Chen, Jin-Cherng Lien, Yu-Han Huang, and Shiu-Wen Huang. 2022. "Suppressing VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 Signaling Contributes to the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of PPE8, a Novel Naphthoquinone-Based Compound" Cells 11, no. 13: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132114
APA StyleHsu, M.-J., Chen, H.-K., Lien, J.-C., Huang, Y.-H., & Huang, S.-W. (2022). Suppressing VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 Signaling Contributes to the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of PPE8, a Novel Naphthoquinone-Based Compound. Cells, 11(13), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132114