Impact of Biochar on Physicochemical Properties of Haplic Luvisol Soil under Different Land Use: A Plot Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment
2.2. Soil and BioC Characterization
2.3. Analysis of BioC Influence on Soil Physicochemical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
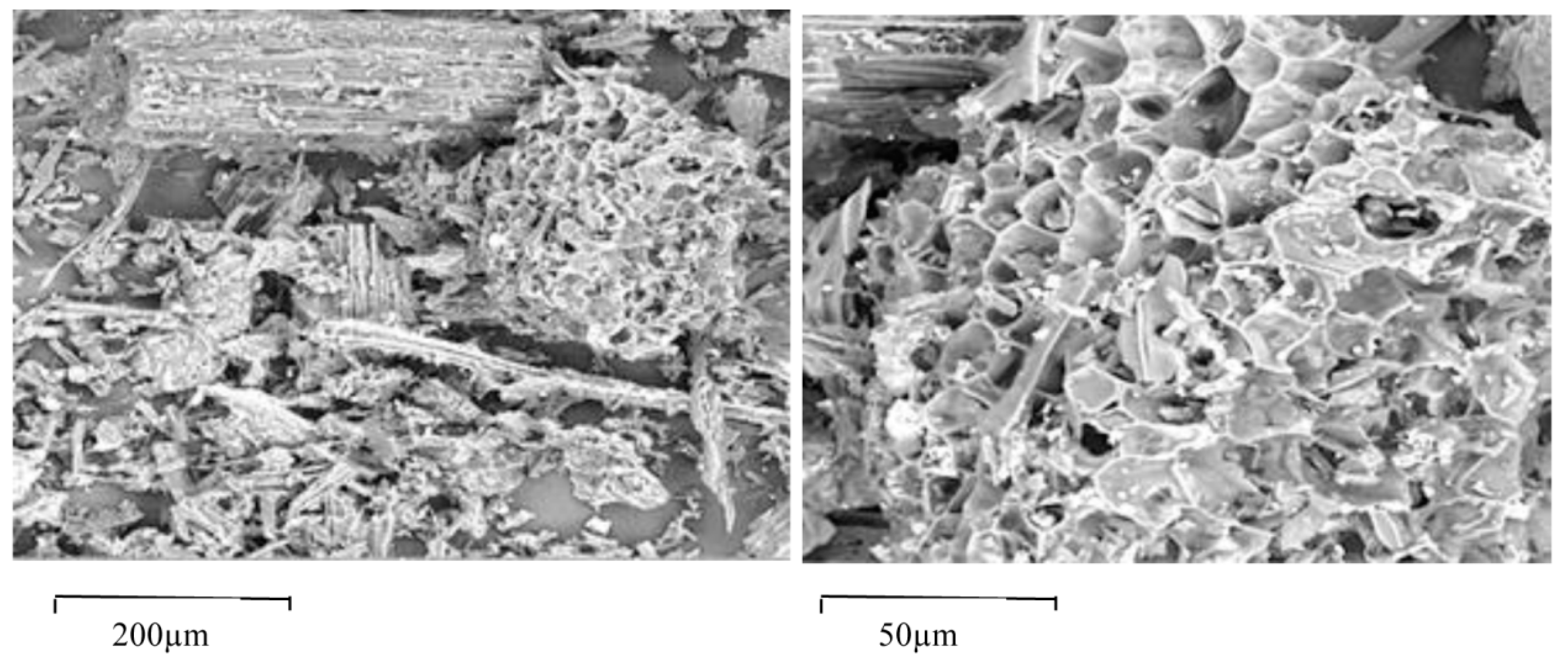
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Soils and BioC
3.2. The Effect of BioC Addition on Physicochemical Properties of the Soil under Fallow and Grassland
3.2.1. The Effect of BioC Addition on Soil Density
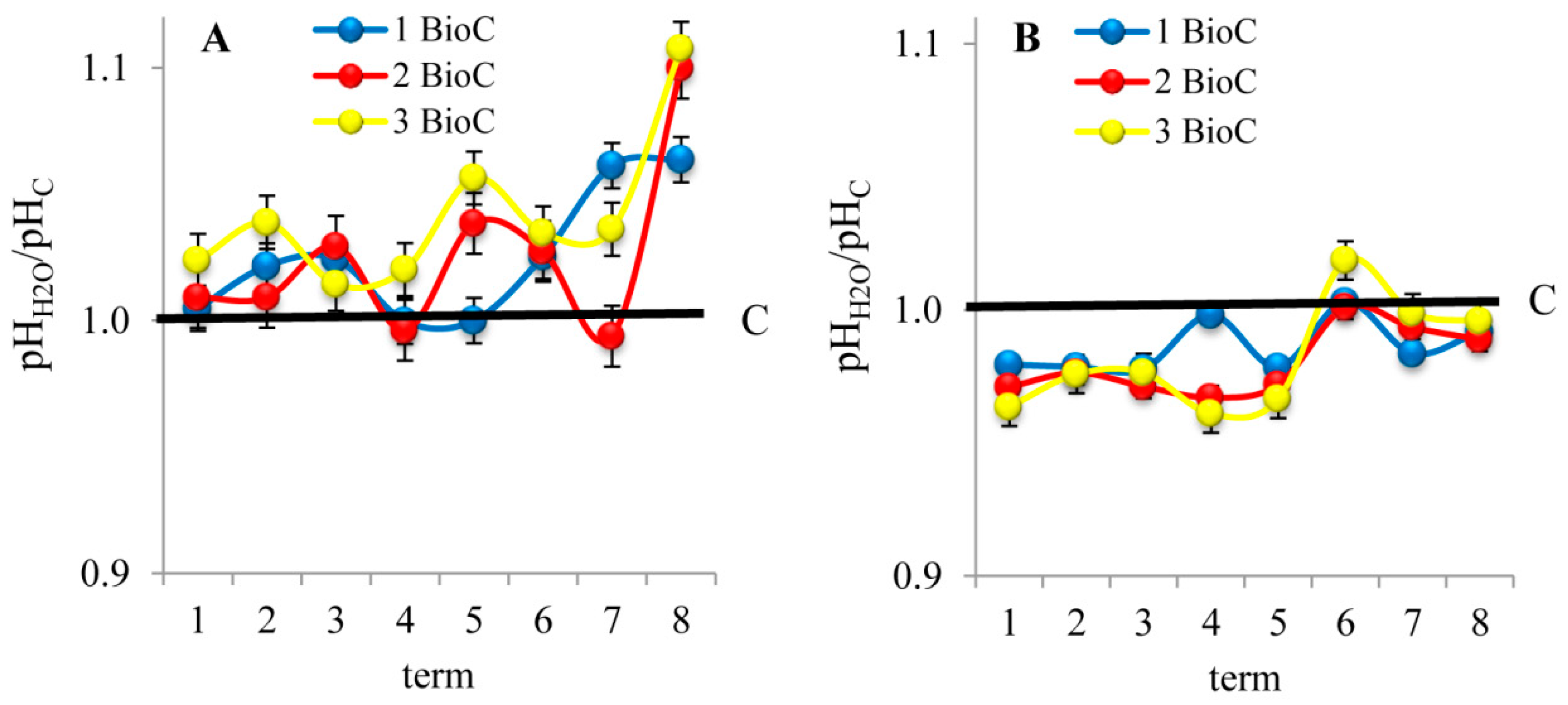
3.2.2. Effect of BioC Addition on Soil pH
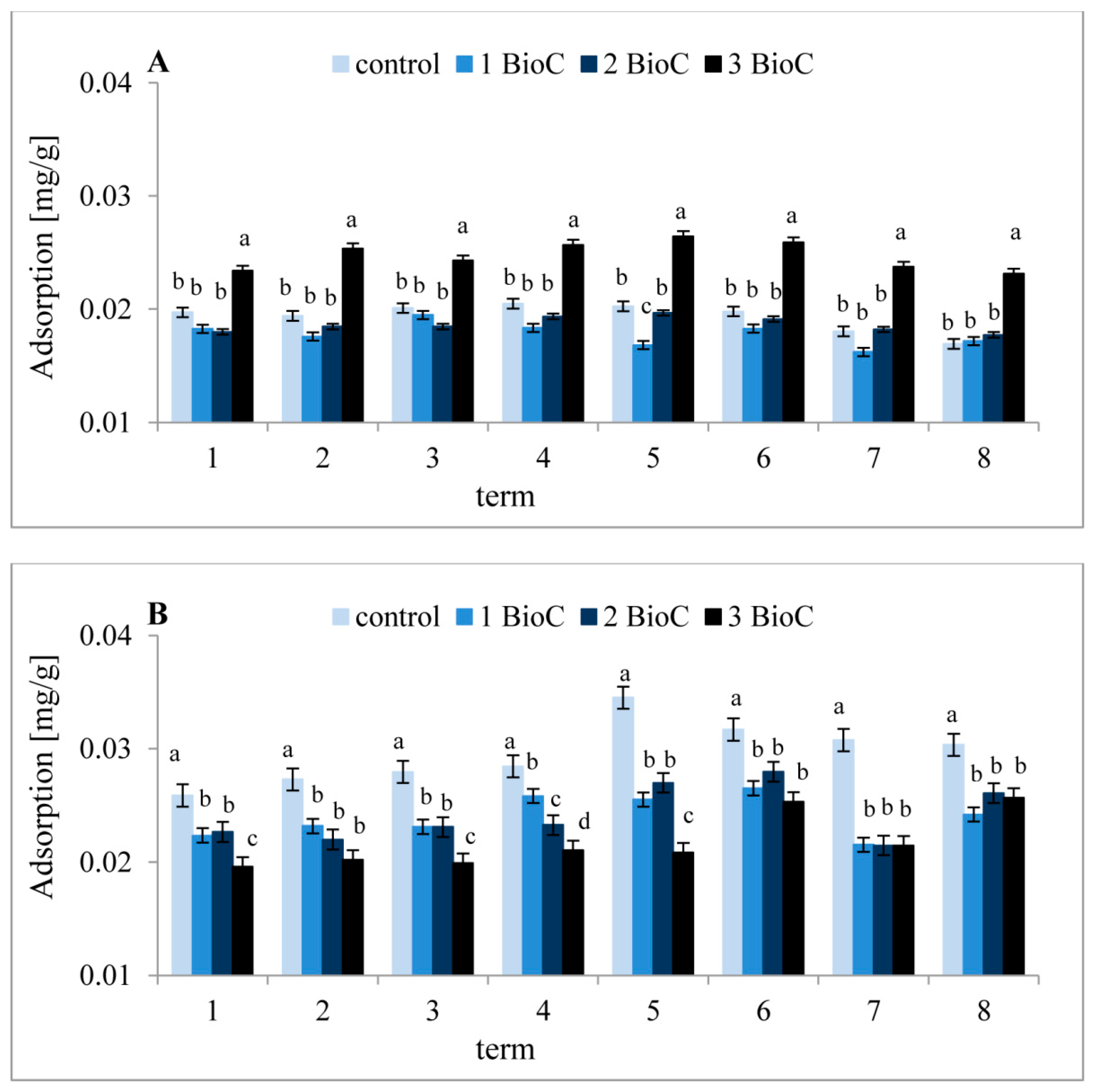
3.2.3. Effect of BioC Addition on Soil Surface Negative Charge
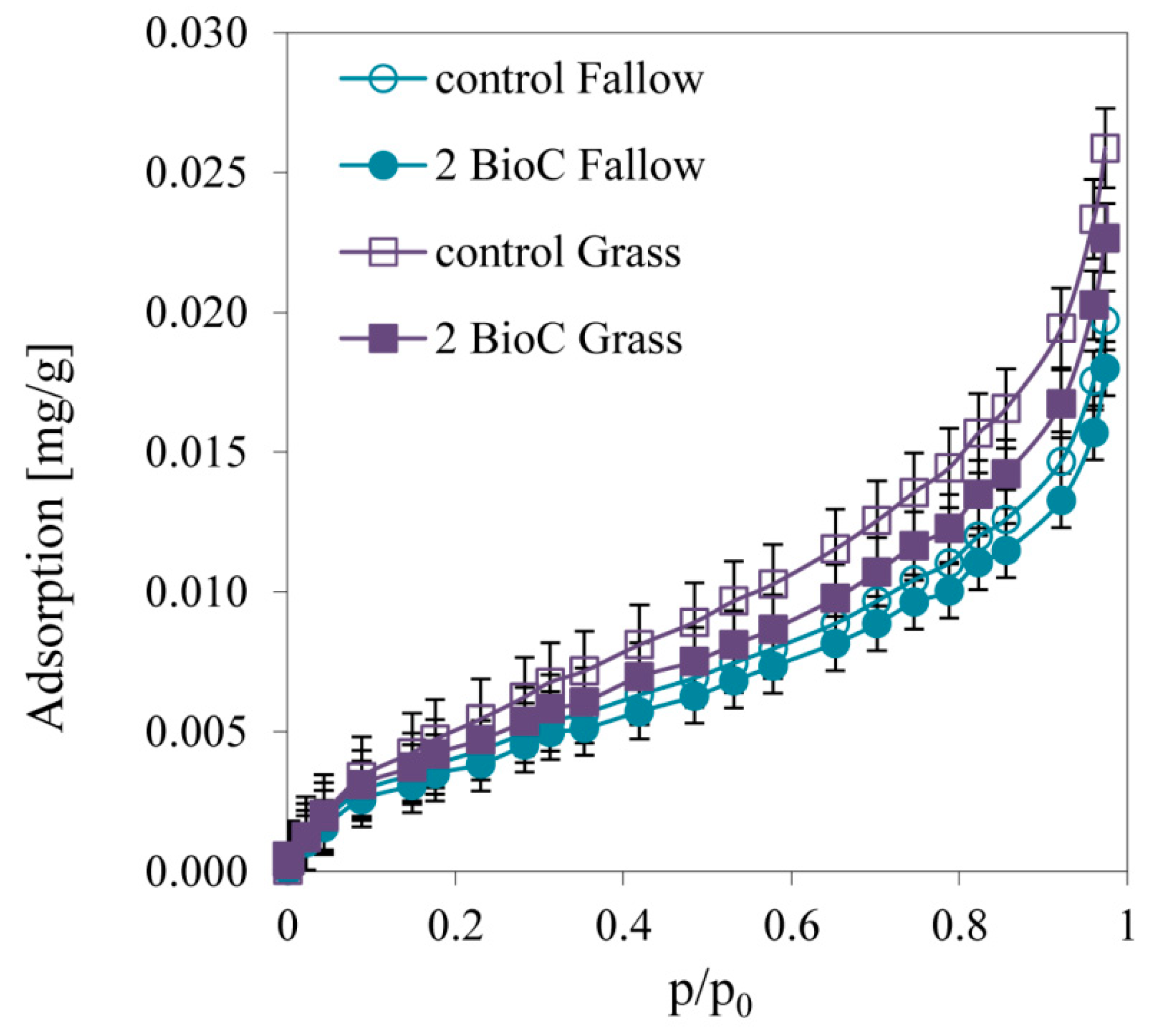
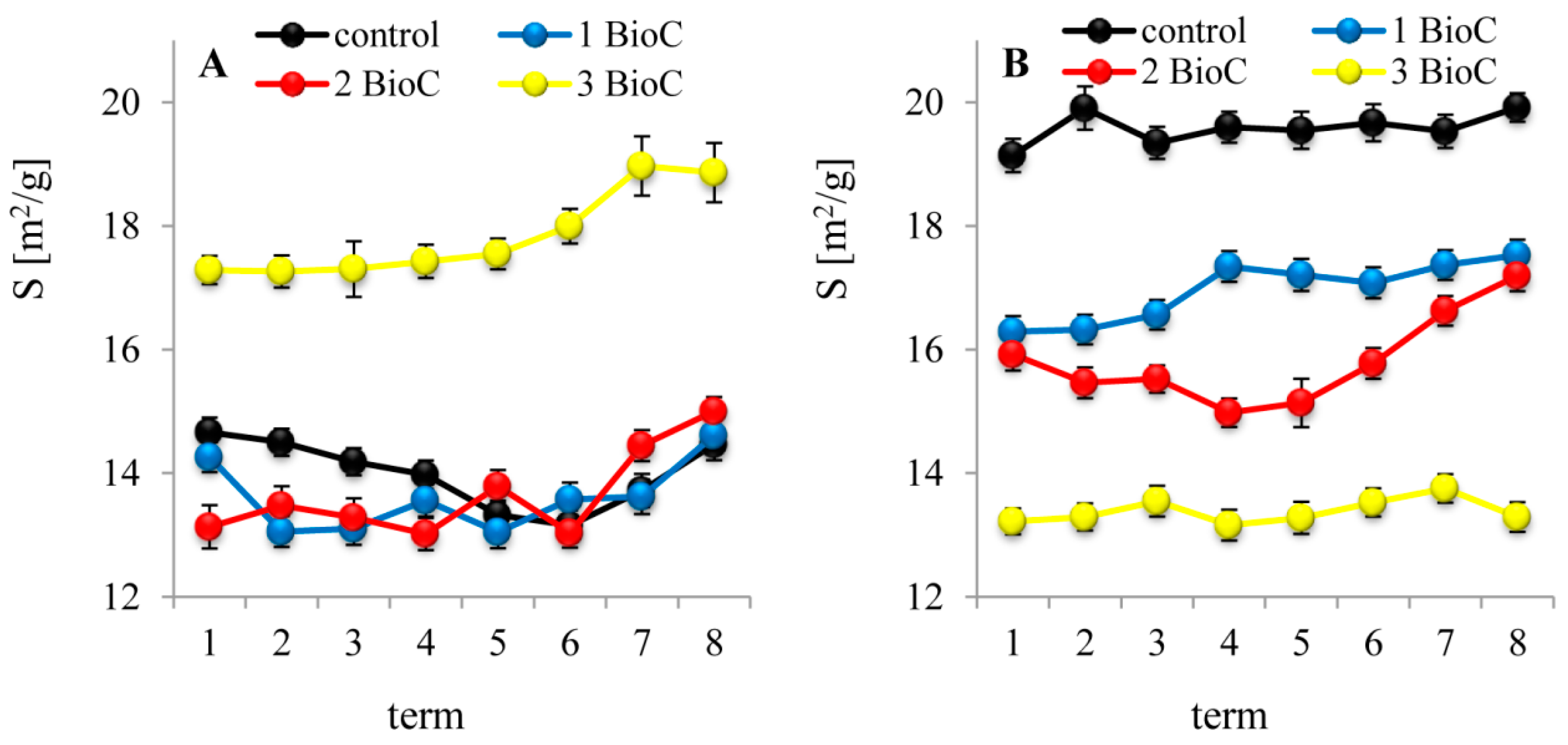
3.2.4. Effect of BioC Addition on Soil Surface Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Wu, C.; Gao, W. Effects of short-term fallow managements on soil microbial properties: A case study in China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, G. Secondary succession in a fallow central European wet grassland. Flora 2010, 205, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Wiedne, K.; Seeling, S.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Gerber, H. Biochar organic fertilizers from natural resources as substitute for mineral fertilizers. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, L. Potential benefits of biochar in agricultural soils: A review. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Ok, Y.S.; Award, Y.M.; Lee, S.S.; Sung, J.K.; Kautsospyros, A.; Moon, D.H. Impact of biochar application on upland agriculture: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, E.N. Impact of Biochar on Metal and Hydrophobic Organic Contaminats: A Tool for Environmental Remediation (An Overview). Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 2, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Uchimiya, M.; Chang, S.C.; Klasson, K.T. Screening biochars for heavy metal retention in soil: Role of oxygen functional groups. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Zimmerman, A.R. Effect of biochar amendment on sorption and leaching of nitrate, ammonium and phosphate in a sandy soil. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Sheng, G.; Chiou, G.T.; Xing, B. Compositions and sorptive properties of crop residue—Derived chars. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4649–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, W.H. Rice husk biochar for rice based cropping system in acid soil. The characteristics of rice husk biochar and its influence on the properties of acid sulphate soils and rice growth in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 2, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Sukaronto; Utomo, W.H.; Kusuma, Z.; Nugroho, W.H. Soil Fertility Status, Nutrient Uptake and Maize (Zea mays L.) Yield Following Biochar and Cattle Manure Application on Sandy Soils of Lombok, Indonesia. J. Trop. Agric. 2011, 49, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Jatav, H.S.; Jayant, H.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, V.; Chattopadhya, A.; Dhawal, S.K.; Singh, Y.V. Role of Biochar: In agriculture sector its implication and perspective. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2017, 5, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Nigussie, A.; Kissi, E.; Misganaw, M.; Ambaw, G. Effect of Biochar Application on Soil Properties and Nutrient Uptake of Lettuces (Lactuca sativa) Grown in Chromium Polluted Soils. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2012, 12, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Karami, A.; Homaee, M.; Afzalinia, S.; Ruhipour, H.; Basirat, S. Organic resource management: Impacts on soil aggregate stability and other soil physicochemical properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 148, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smebye, A.; Alling, V.; Vogt, R.D.; Gadmar, T.C.; Mulder, J.; Cornelissen, G.; Hale, S.E. Biochar amendment to soil changes dissolved organic matter content and composition. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, W.; Kookana, R.; Katayama, A. Characteristics of biochar and its application in remediation of contaminated soil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omondi, M.O.; Xia, X.; Nahayo, A.; Liu, X.; Karai, P.K.; Pan, G. Quantification of biochar effect on soil hydrological properties using meta-analysis of literature data. Geoderma 2016, 274, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco-Canqui, H. Biochar and soil physical properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Raghavan, V. Influence of wood—Derived biochar on the physico-mechanical and chemical characteristics of agricultural soils. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Bass, A.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Benefits of biochar, compost and biochar—Compost for soil quality, maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions in a tropical agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.G.I.D.; Moldrup, P.; Paradelo, M.; Elsgaard, L.; de Jonge, L.W. Effect of biochar on deispersibility of colloids in agricultural soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulak, M.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P.; Tomczyk, A. Influence of pH and grain size on physicochemical properties of biochar and released humic substances. Fuel 2019, 240, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gładki, J. Biochar as a chance for sustainable development. In On the Basis of the Work and Own Research of FLUID, 2nd ed.; Malec, K., Ed.; Apla Sp.J.: Sędziszów, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cybulak, M.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Hygroscopic moisture content of podzolic soil with biochar. Acta Agrophys. 2016, 23, 533–543. [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz, B.; Lipiec, J.; Łukowski, M.; Marczewski, W. The effect of biochar application on thermal properties and albedo of loess soil under grassland and fallow. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 164, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, J.; Honda, C.; Iseki, A. A new rapid and accurate method for the determination of carbon in soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1959, 5, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.K. Fuels and Combustion. In Thermal Power Plant: Design and Operation, 1st ed.; Elservier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 91–137. [Google Scholar]
- Boguta, P.; Sokołowska, Z. Interactions of humic acids with metals. Acta Agrophys. Monogr. 2013, 2, 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowska, Z.; Józefaciuk, G.; Bowanko, G. Adsorption of gases or vapors on solids. In Physical Chemistry of Soil Surface and Pore Properties; Józefaciuk, G., Sokołowska, Z., Hajnos, M., Eds.; Institute of Agrophysics, PAS: Lublin, Poland, 2004; pp. 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S. Adsorption, Surface area and Porosity, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Skic, K.; Boguta, P.; Sokołowska, Z. Analysis of the sorption properties of different soils using water vapour adsorption and potentiometric titration methods. Int. Agrophys. 2016, 30, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Józefaciuk, G. Effect of the size of aggregates on pore characteristics of minerals measured by mercury intrusion and water—Vapor desorption techniques. Clays Clay Miner. 2009, 57, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryżak, M.; Bartmiński, P.; Bieganowski, A. Methods for determination of particle size distribution of mineral soils. Acta Agrophys. Monogr. 2009, 4, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Rühlmann, J.; Körschens, M.; Graefe, J. A new approach to calculate the particle density of soils considering properties of the soil organic matter and the mineral matrix. Geoderma 2006, 130, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.E.; Chuang, V.J.; Masiello, C.A.; Gonnermann, H.; Gao, X.; Dugan, B.; Driver, L.E.; Panzacchi, P.; Zygourakis, K.; Davies, C.A. New approaches to measuring biochar density and porosity. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 66, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for environmental management: An introduction. In Biochar for Environmental Management, 2nd ed.; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Earthscan: London, UK, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeelnejad, L.; Shorafa, M.; Gorji, M.; Hosseini, S.M. Impacts of Woody Biochar Particle Size on Porosity and Hydraulic Conductivity of Biochar-Soil Mixtures: An Incubation Study. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2017, 48, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, J.; Williams, P.T.; Rand, B. Characterisation of biochar porosity from pyrolysis of biomass flax fibre. J. Energy Inst. 2013, 86, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanager, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, E.; Tuller, M.; Moldrup, P.; de Jonge, L.W. Effect of biochar and manure amendments on water vapor sorption in a sandy loam soil. Geoderma 2015, 243–244, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranagal, J.; Oleszczuk, P.; Tomaszewska–Krojańska, D.; Kraska, P.; Różyło, K. Effect of biochar application on the physical properties of Haplic Podzol. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 174, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, G.H. Soil pH, an early diagnostic tool: Its determination and interpretation. In History of Soil Science, 2nd ed.; Yaloon, D.H., Berkowicz, S., Eds.; Catena Verlag: Reiskirchen, Germany, 1997; Volume 29, pp. 177–210. [Google Scholar]
- Amoakwah, E.; Frimpong, K.A.; Okae-Anti, D.; Arthur, E. Soil water retention, air flow and pore structure characteristics after corn cob biochar application to a tropical sandy loam. Geoderma 2017, 307, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Thomas, S. Biochar Particle Size and Post—Pyrolysis Mechanical Processing Affect Soil pH, Water Retention Capacity and Plant Performance. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.; Khan, S.; Shah, Z. Soil respiration, pH and EC as influenced by biochar. Soil Environ. 2017, 36, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefaciuk, G.; Szatanik-Kloc, A. Soil Acidity and its Effect on Plants. Acta Agrophys. Monogr. 2002, 59, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nelissen, V.; Ruysschaert, G.; Manka’Abusi, D.; D’Hose, T.; De Beuf, K.; Al-Barri, B.; Cornelis, W.; Boeckx, P. Impact of a woody biochar on properties of a sandy loam soil and spring barley during a two-year field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 62, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, I.C.B.; Basilio, J.J.N.; Fernandes, L.A.; Colen, F.; Sampaio, R.A.; Frazao, L.A. Biochar from different residues on soil properties and common bean production. Sci. Agric. 2016, 74, 278–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Kopeć, M.; Losak, T. Effect of coapplication of poultry litter biochar and mineral fertilisers on soil quality and crop yield. Zemdirb. Agric. 2018, 105, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramirez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with biochar additions. Biol. Fert. Soils 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, K.E.; Brye, K.R.; Savin, M.C.; Longer, D.E. Biochar Source and Application Rate Effects on Soil Water Retention Determined Using Wetting Curves. Open J. Soil Sci. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aller, D.; Rathke, S.; Laird, D.; Cruse, R.; Hatfield, J. Impacts of fresh and aged biochars on plant available water and water use efficiency. Geoderma 2017, 307, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherejee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Hamdan, R.; Cooper, W.T. Physicochemical changes in pyrogenic organic matter (biochar) after 15 months of field aging. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.P.; Cowie, A.L. Long—Term influence of biochar on native organic carbon mineralisation in a low—Carbon clayey soil. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paetsch, L.; Mueller, C.W.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; von Lützow, M.; Girardin, C.; Rumpel, C. Effect of in-situ aged and fresh biochar on soil hydraulic conditions and microbial C use under drought conditions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Bradford, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, P.; Shang, J.; Li, B. Transport of biochar colloids in saturated porous media in the presence of humic substances or proteins. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theng, B.K.G.; Rostori, G.G.; Santi, C.A.; Percival, H.J. An improved method for determining the specific surface areas of topsols with varied organic matter, texture and clay mineral composition. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 50, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, P.; Bortolotti, V.; Fornasari, G.; Vannini, M. Evaluation of effect of soil organic matter on pores by 1H time—Domain magnetic resonance relaxometry and adsorption—Desorption of N2. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, G.; Feng, H.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Dyck, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Effects of straw and biochar amendments on aggregate stability, soil organic carbon and enzyme activities in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10108–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyvaluoma, J.; Hannula, M.; Arstila, K.; Wang, H.; Kulju, S.; Rasa, K. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on the hydrologically relevant porosity of willow biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 134, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boguta, P.; Sokołowska, Z.; Skic, K.; Tomczyk, A. Chemically engineered biochar—Effect of concentration and type of modifier on sorption and structural properties of biochar from wood waste. Fuel 2019, 256, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, W.J.; Jinag, H.; Chen, J.J.; Li, W.W.; Yu, H.Q. Modification of bio-char derived from fast pyrolysis of biomass and its application in removal of tetracyckline from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 21, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anovitz, L.M.; Cole, D.R. Characterization and analysis of porosity and pore structures. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2015, 80, 61–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heister, K. How accessible is the specific surface area of minerals? A comparative study with Al—Containig minerals as model susbtances. Geoderma 2016, 263, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, F.; Jeffery, S.; Bastos, A.C.; van der Velde, M.; Daifas, I. Biochar Application to Soils. A Critical Scientific Review of Effects on Soil Properties, Processes and Functions; European Commision: Luxembourg, 2010; pp. 1–162. [Google Scholar]
- Głąb, T.; Kulig, B. Effect of mulch and tillage system on soil porosity under wheat. Soil Till. Res. 2008, 99, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głąb, T.; Palmowska, J.; Zaleski, T.; Gondek, K. Effect of biochar application on soil hydrological properties and physical quality of sandy soil. Geoderma 2016, 281, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Ghosh, G.K. Soil hydro-physical Environment as Influences by Different Biochar Amendments. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2017, 8, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Zhang, R. Effects of biochars derived from different feedstocks and pyrolysis temperatures on soil physical and hydraulic properties. J. Soil Sediments 2013, 13, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.A.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta—Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material | d | Corg | A | pH (H2O) | pH (CaCl2) | Q | S | V | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g⋅cm−3) | (%) | (%) | (cmol⋅kg−1) | (m2⋅g−1) | (µl⋅g−1) | (nm) | |||
| Fallow | 2.61 | 0.98 | 97.3 | 6.21 | 5.52 | 5.90 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 9.20 |
| Grassland | 2.60 | 1.02 | 96.7 | 6.72 | 6.13 | 7.10 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 9.50 |
| Biochar | 1.46 | 15.4 | 43.2 | 8.25 | 7.21 | 107 | 69.9 | 45.8 | 5.16 |
| Fallow | |||||||
| Term | 0 kg ⋅m−2 | 1 kg ⋅m−2 | 2 kg ⋅m−2 | 3 kg ⋅m−2 | Min | Max | p |
| 1 | 25.86 ± 0.02 | 16.34 ± 0.03 | 16.58 ± 0.02 | 33.94 ± 0.02 | 3.94 | 6.58 | <0.05 |
| 8 | 43.52 ± 0.02 | 34.42 ± 0.03 | 18.06 ± 0.03 | 25.80 ± 0.01 | 3.52 | 8.06 | <0.05 |
| Grassland | |||||||
| Term | 0 kg ⋅m−2 | 1 kg ⋅m−2 | 2 kg ⋅m−2 | 3 kg ⋅m−2 | Min | Max | p |
| 1 | 17.20 ± 0.03 | 33.16 ± 0.02 | 26.82 ± 0.01 | 26.38 ± 0.01 | 3.16 | 7.20 | <0.05 |
| 8 | 35.96 ± 0.02 | 27.08 ± 0.03 | 36.42 ± 0.02 | 18.82 ± 0.02 | 5.96 | 8.82 | <0.05 |
| Fallow | |||||||
| Term | 0 kg ⋅m−2 | 1 kg ⋅m−2 | 2 kg ⋅m−2 | 3 kg ⋅m−2 | Min | Max | p |
| 1 | 213.55 ± 0.04d | 310.52 ± 0.02h | 310.89 ± 0.01h | 116.63 ± 0.02g | 10.52 | 16.63 | <0.05 |
| 2 | 213.48 ± 0.02d | 212.63 ± 0.02f | 213.44 ± 0.02e | 118.25 ± 0.02e | 12.63 | 18.25 | <0.05 |
| 3 | 313.05 ± 0.05e | 116.47 ± 0.06a | 312.12 ± 0.02g | 214.51 ± 0.01h | 12.12 | 16.47 | <0.05 |
| 4 | 213.95 ± 0.03c | 213.04 ± 0.03d | 213.38 ± 0.03f | 117.62 ± 0.02f | 13.04 | 17.62 | <0.05 |
| 5 | 312.74 ± 0.01f | 312.11 ± 0.01g | 214.07 ± 0.02d | 120.20 ± 0.02a | 12.11 | 20.20 | <0.05 |
| 6 | 214.31 ± 0.01b | 312.93 ± 0.02e | 214.34 ± 0.01c | 118.89 ± 0.01d | 12.93 | 18.89 | <0.05 |
| 7 | 313.05 ± 0.05e | 313.60 ± 0.01c | 215.39 ± 0.01a | 119.34 ± 0.01b | 13.05 | 19.34 | <0.05 |
| 8 | 215.11 ± 0.01a | 214.65 ± 0.01b | 215.08 ± 0.03b | 119.28 ± 0.01c | 14.65 | 19.28 | <0.05 |
| Min | 12.73 | 10.52 | 10.89 | 14.51 | |||
| Max | 15.11 | 16.47 | 15.39 | 20.20 | |||
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| Grassland | |||||||
| Term | 0 kg ⋅m−2 | 1 kg ⋅m−2 | 2 kg ⋅m−2 | 3 kg ⋅m−2 | Min | Max | p |
| 1 | 118.12 ± 0.04g | 216.14 ± 0.02f | 216.26 ± 0.04f | 313.97 ± 0.02g | 13.97 | 18.12 | <0.05 |
| 2 | 119.93 ± 0.03e | 217.47 ± 0.04e | 316.32 ± 0.03f | 415.14 ± 0.04e | 15.14 | 19.93 | <0.05 |
| 3 | 119.73 ± 0.03f | 215.01 ± 0.02g | 215.55 ± 0.03g | 214.27 ± 0.03f | 14.27 | 19.73 | <0.05 |
| 4 | 119.91 ± 0.01e | 218.15 ± 0.04d | 316.81 ± 0.01e | 415.14 ± 0.01e | 15.14 | 19.91 | <0.05 |
| 5 | 123.92 ± 0.03c | 218.66 ± 0.04c | 219.54 ± 0.04c | 315.85 ± 0.05d | 15.85 | 23.92 | <0.05 |
| 6 | 123.51 ± 0.01d | 220.17 ± 0.02b | 220.72 ± 0.03b | 319.54 ± 0.04b | 19.54 | 23.51 | <0.05 |
| 7 | 125.35 ± 0.05b | 218.13 ± 0.03d | 218.21 ± 0.02d | 218.35 ± 0.03c | 18.13 | 25.35 | <0.05 |
| 8 | 126.28 ± 0.10a | 222.98 ± 0.02a | 223.22 ± 0.03a | 222.93 ± 0.02a | 22.93 | 26.28 | <0.05 |
| Min | 18.12 | 15.01 | 15.55 | 13.97 | |||
| Max | 26.28 | 22.98 | 23.22 | 22.93 | |||
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| Fallow | |||||||
| Term | 0 kg ⋅m−2 | 1 kg ⋅m−2 | 2 kg ⋅m−2 | 3 kg ⋅m2 | Min | Max | p |
| 1 | 29.16 ± 0.04f | 111.14 ± 0.05c | 110.46 ± 0.05d | 28.62 ± 0.04g | 8.62 | 11.14 | <0.05 |
| 2 | 29.61 ± 0.02d | 110.23 ± 0.05d | 110.35 ± 0.06d | 29.70 ± 0.03d | 9.70 | 10.35 | <0.05 |
| 3 | 27.54 ± 0.05g | 27.55 ± 0.05f | 27.24 ± 0.03f | 19.18 ± 0.03e | 7.24 | 9.18 | <0.05 |
| 4 | 19.35 ± 0.05e | 19.89 ± 0.03e | 19.45 ± 0.06e | 28.92 ± 0.03f | 8.92 | 9.89 | <0.05 |
| 5 | 29.63 ± 0.04d | 45.46 ± 0.06h | 110.35 ± 0.05d | 37.06 ± 0.06h | 5.46 | 10.35 | <0.05 |
| 6 | 210.87 ± 0.06c | 111.49 ± 0.04b | 111.46 ± 0.04c | 210.65 ± 0.05c | 10.65 | 11.49 | <0.05 |
| 7 | 121.04 ± 0.05a | 36.02 ± 0.03g | 213.27 ± 0.04b | 214.05 ± 0.05b | 6.02 | 21.04 | <0.05 |
| 8 | 312.92 ± 0.12b | 213.69 ± 0.03a | 213.45 ± 0.05a | 114.31 ± 0.04a | 12.92 | 14.31 | <0.05 |
| Min | 7.54 | 5.46 | 7.24 | 7.06 | |||
| Max | 21.04 | 13.69 | 13.45 | 14.31 | |||
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
| Grassland | |||||||
| Term | 0 kg ⋅m−2 | 1 kg ⋅m−2 | 2 kg ⋅m−2 | 3 kg ⋅m−2 | Min | Max | p |
| 1 | 19.50 ± 0.03f | 19.74 ± 0.05f | 19.94 ± 0.05f | 19.54 ± 0.04g | 9.50 | 9.94 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 19.75 ± 0.05e | 19.92 ± 0.06e | 110.16 ± 0.06e | 110.15 ± 0.05e | 9.75 | 10.16 | 0.05 |
| 3 | 19.41 ± 0.04f | 28.65 ± 0.05h | 28.74 ± 0.04h | 19.59 ± 0.03fg | 8.65 | 9.59 | <0.05 |
| 4 | 28.91 ± 0.06g | 29.04 ± 0.04g | 19.73 ± 0.04g | 19.67 ± 0.04f | 8.91 | 9.73 | <0.05 |
| 5 | 210.55 ± 0.05d | 210.92 ± 0.03d | 210.85 ± 0.05d | 111.30 ± 0.03d | 10.55 | 11.30 | <0.05 |
| 6 | 210.83 ± 0.04c | 111.60 ± 0.03c | 111.34 ± 0.05c | 111.84 ± 0.04c | 10.83 | 11.84 | <0.05 |
| 7 | 114.84 ± 0.05a | 114.62 ± 0.04a | 114.21 ± 0.07a | 114.75 ± 0.05a | 14.21 | 14.84 | 0.05 |
| 8 | 114.20 ± 0.03b | 213.55 ± 0.05b | 213.63 ± 0.05b | 213.77 ± 0.03b | 13.55 | 14.20 | <0.05 |
| Min | 8.91 | 8.65 | 8.74 | 9.54 | |||
| Max | 14.84 | 14.62 | 14.21 | 14.75 | |||
| p | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cybulak, M.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Impact of Biochar on Physicochemical Properties of Haplic Luvisol Soil under Different Land Use: A Plot Experiment. Agronomy 2019, 9, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9090531
Cybulak M, Sokołowska Z, Boguta P. Impact of Biochar on Physicochemical Properties of Haplic Luvisol Soil under Different Land Use: A Plot Experiment. Agronomy. 2019; 9(9):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9090531
Chicago/Turabian StyleCybulak, Marta, Zofia Sokołowska, and Patrycja Boguta. 2019. "Impact of Biochar on Physicochemical Properties of Haplic Luvisol Soil under Different Land Use: A Plot Experiment" Agronomy 9, no. 9: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9090531
APA StyleCybulak, M., Sokołowska, Z., & Boguta, P. (2019). Impact of Biochar on Physicochemical Properties of Haplic Luvisol Soil under Different Land Use: A Plot Experiment. Agronomy, 9(9), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9090531






