Genetic Transformation and siRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing for Aphid Resistance in Tomato
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
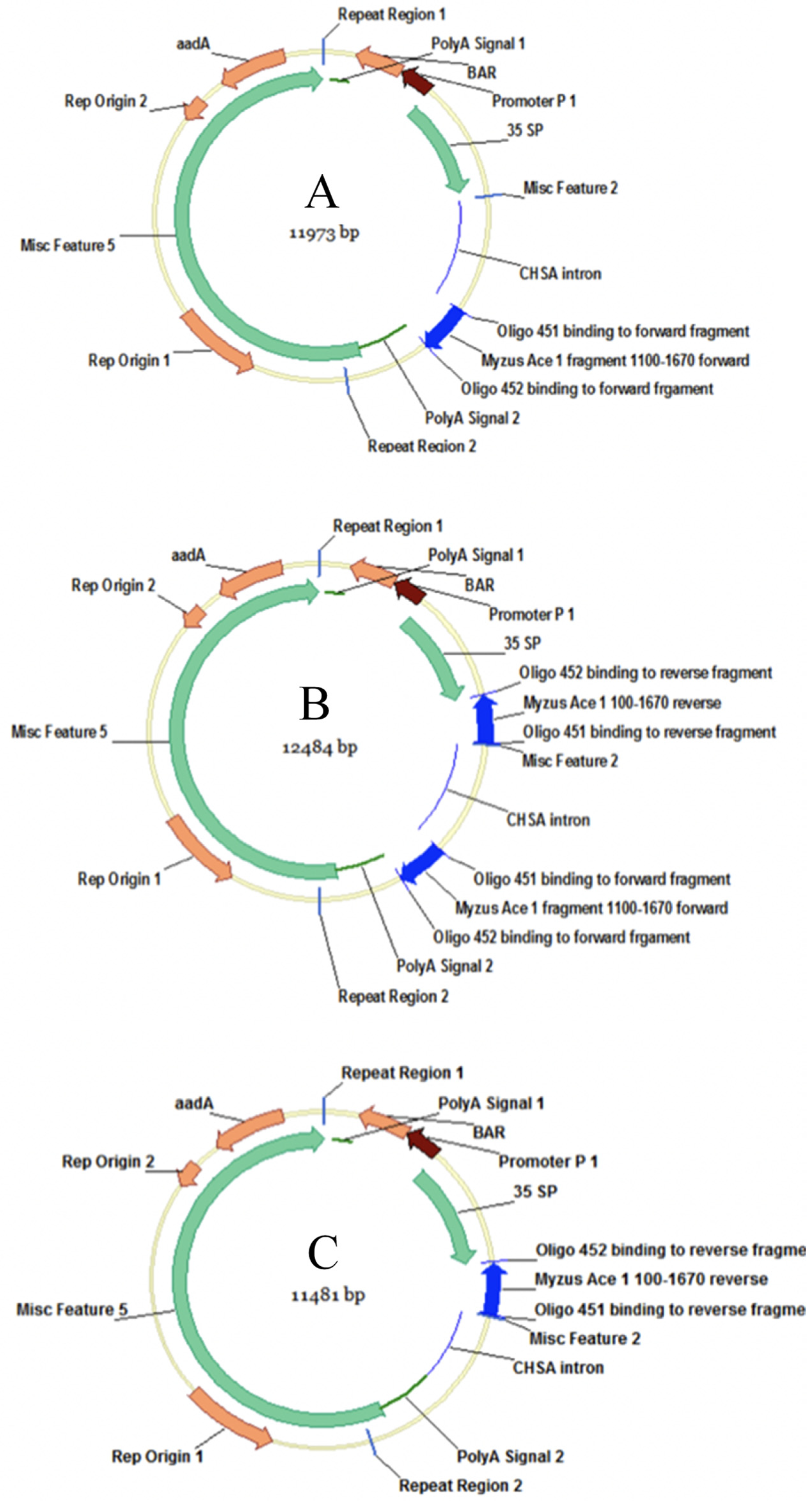
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Construct
2.2. Electroporation (Transformation) and Selection of Positive Colonies
2.3. Plant Materials and Explants Preparation
2.4. Co-Cultivation of CL Explants with Agrobacterium
2.5. Selection and Regeneration of Plantlets
2.6. Rooting and Establishment of Transgenic Plants
2.7. Characterization of Transgenic Plants by PCR Analysis
2.8. Characterization of Transgenic Plants by Northern Blotting
2.9. qRT-PCR Analysis of Ace 1 Expression in Aphids Fed on Transgenic Plants
2.10. Aphid Challenge Assay
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
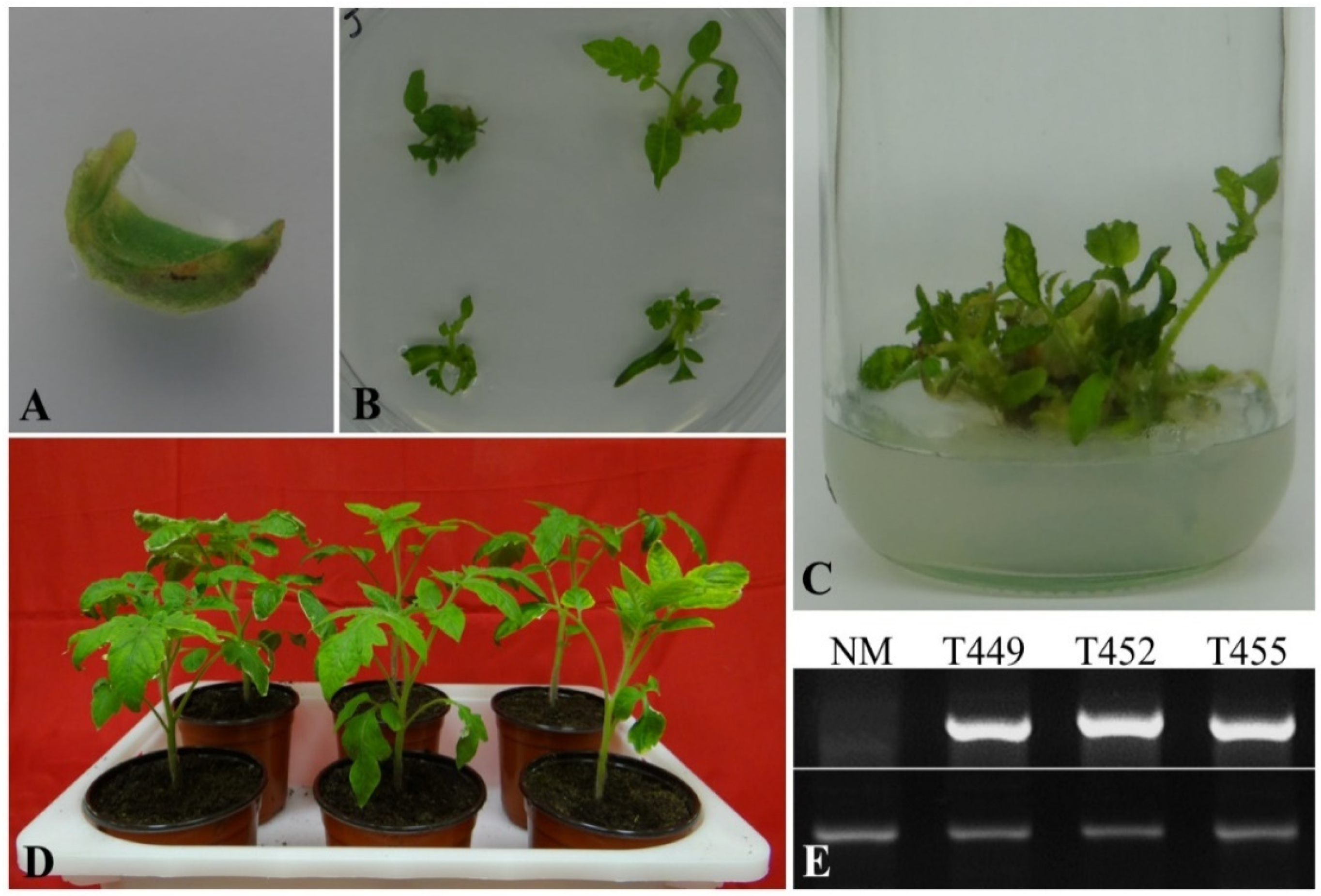
3.1. Generation of Transgenic Plants and PCR Confirmation
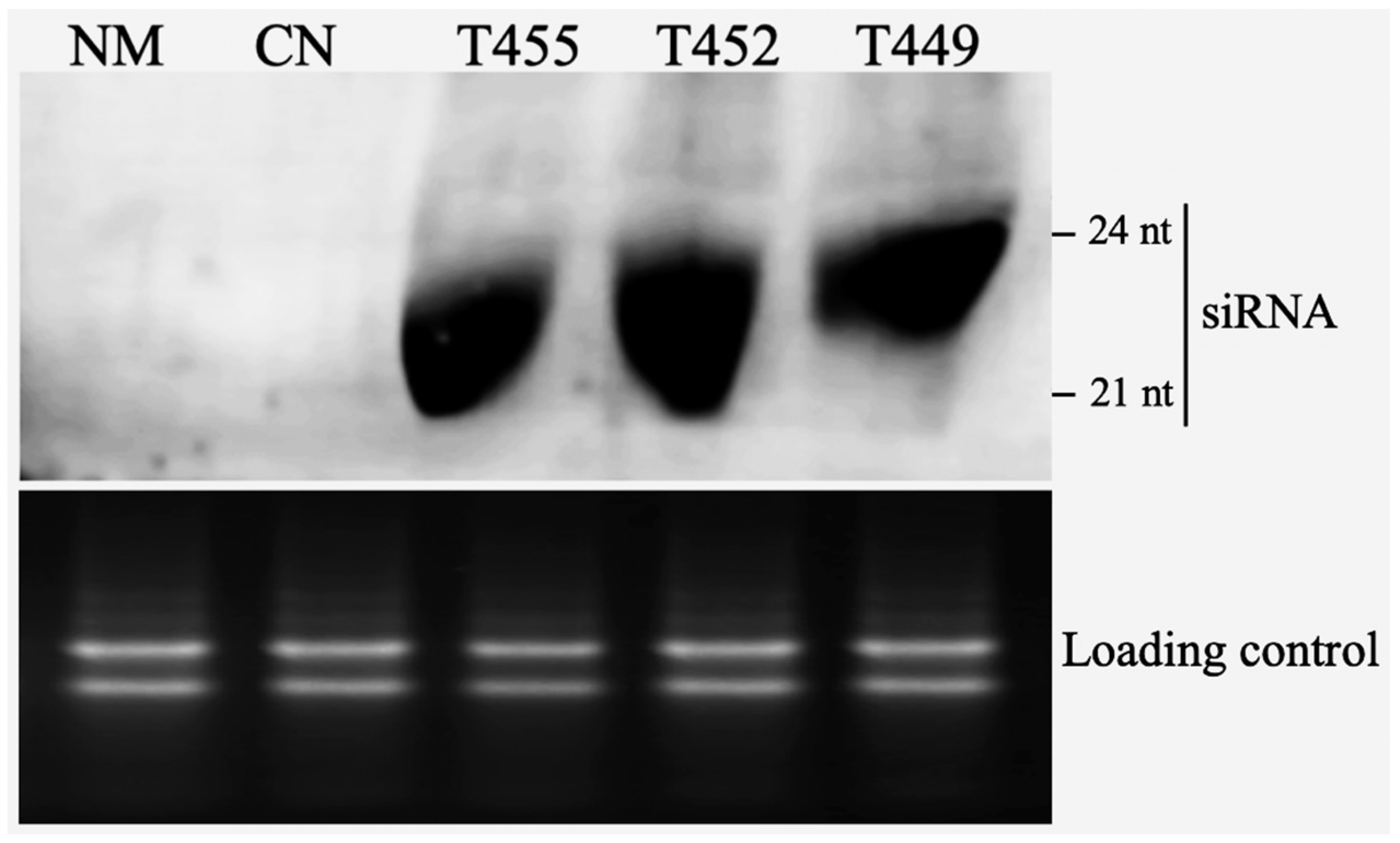
3.2. Northern Blotting of Transgenic Plants
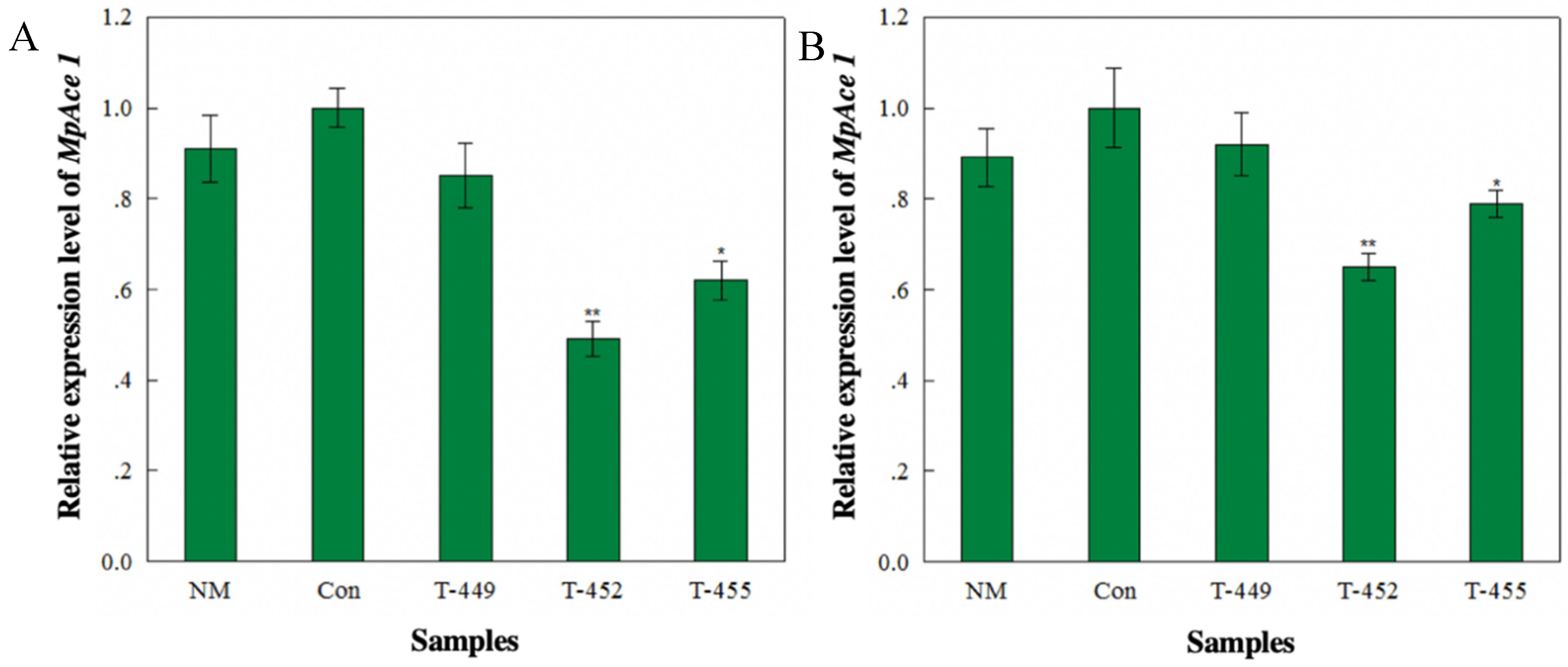
3.3. Transcriptional Analysis of Aphids Feeding on Transgenic Tomato Plants
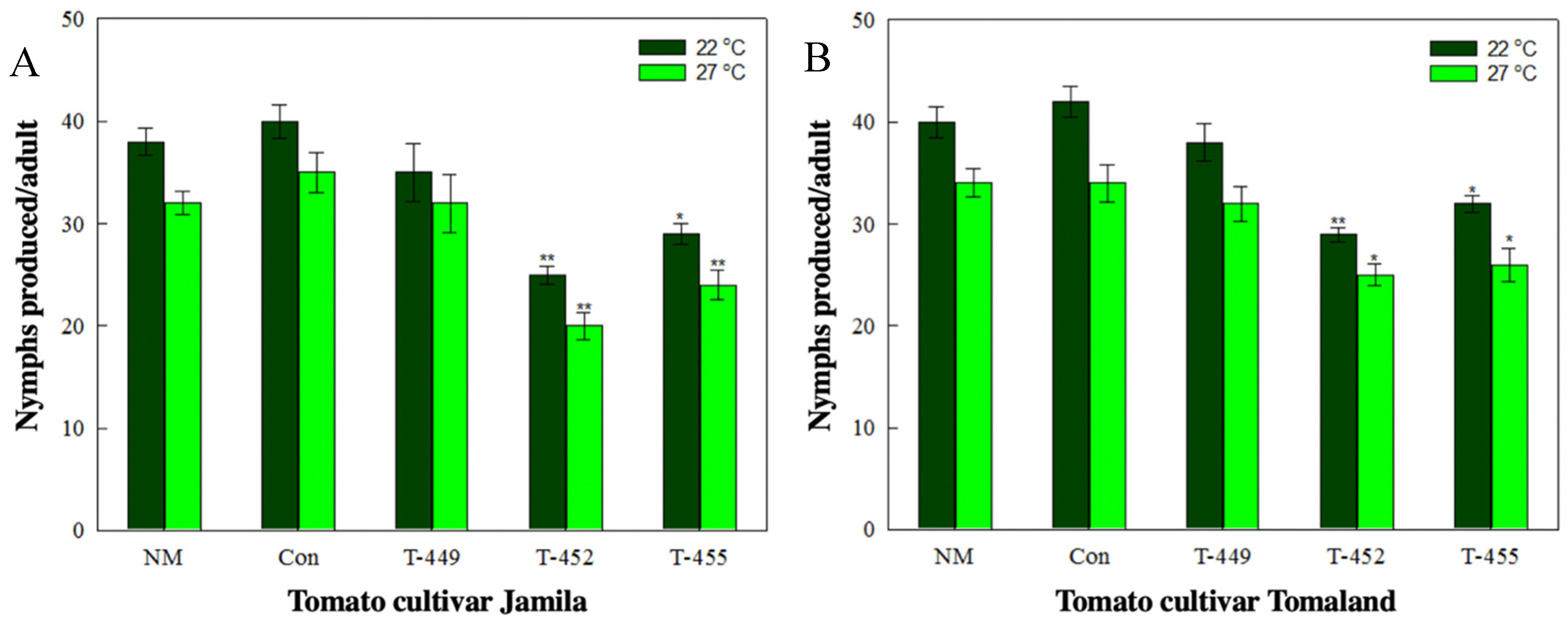
3.4. Aphid Resistance Against Transgenic Tomatoes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alatar, A.A.; Faisal, M.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Canto, T.; Saquib, Q.; Javed, S.B.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. Efficient and reproducible in vitro regeneration of Solanum lycopersicum and assessment genetic uniformity using flow cytometry and SPAR methods. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenhout, S.A.; Ammar, E.-D.; Whitfield, A.E.; Redinbaugh, M.G. Insect Vector Interactions with Persistently Transmitted Viruses. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2008, 46, 327–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, P.J.; Cheng, Y.; Cassell, J.L.; Thompson, G.A. Gene expression profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana in compatible plant-aphid interactions. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 51, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Emden, H.F. Plant resistance to Myzus persicae induced by a plant regulator and measured by aphid relative growth rate. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1969, 12, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeshima, T.; Kozaki, T.; Tomita, T.; Kono, Y. An amino acid substitution on the second acetylcholinesterase in the pirimicarb-resistant strains of the peach potato aphid, Myzus Persicae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, S.; Niedermeyer, J.; Fry, J.; Barnason, A.; Horsch, R.; Fraley, R. Leaf disc transformation of cultivated tomato (L. esculentum) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep. 1986, 5, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, P.; Simons, G.; Jesse, T.; Wijbrandi, J.; Heinen, L.; Hogers, R.; Frijters, A.; Groenendijk, J.; Diergaarde, P.; Reijans, M.; et al. The tomato Mi-1 gene confers resistance to both root-knot nematodes and potato aphids. Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-On, A.; Wolf, D.; Wang, Y.; Faure, J.-E.; Pilowsky, M.; Zelcer, A. Transgenic resistance to cucumber mosaic virus in tomato: Blocking of long-distance movement of the virus in lines harboring a defective viral replicase gene. Phytopathology 1998, 88, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jia, L.; Goggin, F. The reliability of virus-induced gene silencing experiments using tobacco rattle virus in tomato is influenced by the size of the vector control. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.J.; Baulcombe, D.C. A Species of Small Antisense RNA in Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing in Plants. Science 1999, 286, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mette, M.F.; Aufsatz, W.; van der Winden, J.; Matzke, M.A.; Matzke, A.J. Transcriptional silencing and promoter methylation triggered by double-stranded RNA. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5194–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Soumaila Issa, M.; Cooper, A.M.W.; Zhu, K.Y. RNA interference: Applications and advances in insect toxicology and insect pest management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Guo, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, P.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. Host-Induced Gene Silencing: A Powerful Strategy to Control Diseases of Wheat and Barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitino, M.; Hogenhout, S.A. Aphid Protein Effectors Promote Aphid Colonization in a Plant Species-Specific Manner. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 26, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitino, M.; Coleman, A.D.; Maffei, M.E.; Ridout, C.J.; Hogenhout, S.A. Silencing of Aphid Genes by dsRNA Feeding from Plants. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Song, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Niu, L.; Chen, X.; Fang, R. Plant-Generated Artificial Small RNAs Mediated Aphid Resistance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Yang, X.; Jing, X.; Zhang, K.; Jander, G.; Douglas, A.E. RNA interference against gut osmoregulatory genes in phloem-feeding insects. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 79, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zeng, F. Plant-mediated RNAi of a gap gene-enhanced tobacco tolerance against the Myzus persicae. Transgenic Res. 2014, 23, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Bhattacharya, R.; Uniyal, P.L.; Singh, R.; Niranjan, R.S. Host Generated siRNAs Attenuate Expression of Serine Protease Gene in Myzus persicae. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, A.D.; Wouters, R.H.M.; Mugford, S.T.; Hogenhout, S.A. Persistence and transgenerational effect of plant-mediated RNAi in aphids. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 66, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Duan, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Z.; Xie, C.; Ni, Z.; Liang, R. Silencing of an aphid carboxylesterase gene by use of plant-mediated RNAi impairs Sitobion avenae tolerance of Phoxim insecticides. Transgenic Res. 2014, 23, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatef, E.; Will, T.; Koch, A.; Imani, J.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kogel, K.-H. Silencing the expression of the salivary sheath protein causes transgenerational feeding suppression in the aphid Sitobion avenae. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.; Zhao, J.-H.; Guo, H.-S. Trans-Kingdom RNA Silencing in Plant–Fungal Pathogen Interactions. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto-Pastor, A.; Santos, B.A.; Valli, A.A.; Summers, W.; Schornack, S.; Baulcombe, D.C. Enhanced resistance to bacterial and oomycete pathogens by short tandem target mimic RNAs in tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2755–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, T.; Aranda, M.A.; Fereres, A. Climate change effects on physiology and population processes of hosts and vectors that influence the spread of hemipteran-borne plant viruses. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, J.M.; Fernandez, J.M.; Sorge, J.A.; Huse, W.D. Lambda ZAP: A bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 7583–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerschen, A.; Napoli, C.A.; Jorgensen, R.A.; Müller, A.E. Effectiveness of RNA interference in transgenic plants. FEBS Lett. 2004, 566, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.J.; Uchii, S.; Watanabe, S.; Ezura, H. A highly efficient transformation protocol for Micro-Tom, a model cultivar for tomato functional genomics. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Kang, X.-P.; Xing, X.-J.; Xu, X.-Y.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, S.-W.; Xing, G.-M. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L. cv. Hezuo 908) with improved efficiency. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.J.; Raza, A.; Amin, I.; Scheffler, J.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Brown, J.K.; Mansoor, S. RNAi-mediated mortality of the whitefly through transgenic expression of double-stranded RNA homologous to acetylcholinesterase and ecdysone receptor in tobacco plants. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. RNA interference of two acetylcholinesterase genes in Plutella xylostella reveals their different functions. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 79, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, G.P.; Rajam, M.V. Silencing of acetylcholinesterase gene of Helicoverpa armigera by siRNA affects larval growth and its life cycle. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satar, S.; Kersting, U.; Uygun, N. Effect of temperature on population parameters of Aphis gossypii Glover and Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae) on pepper. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2008, 115, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chown, S.L.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Kristensen, T.N.; Angilletta, M.J., Jr.; Stenseth, N.C.; Pertoldi, C. Adapting to climate change: A perspective from evolutionary physiology. Clim. Res. 2010, 43, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauerfeind, S.S.; Fischer, K. Simulating climate change: Temperature extremes but not means diminish performance in a widespread butterfly. Popul. Ecol. 2014, 56, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.O.; Bennett, A.F.; Bozinovic, F.; Clarke, A.; Lardies, M.A.; Lucassen, M.; Pelster, B.; Schiemer, F.; Stillman, J.H. Trade-Offs in Thermal Adaptation: The Need for a Molecular to Ecological Integration. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2006, 79, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.A.; Radcliffe, E.B.; Ragsdale, D.W. Effects of High and Fluctuating Temperatures on Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, D.R.; Nasreen, A.; Moffat, C.E.; Clarke, P.; Roitberg, B.D. Effects of simulated heat waves on an experimental community of pepper plants, green peach aphids and two parasitoid species. Oikos 2012, 121, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, W.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Ma, C.-S. Night warming on hot days produces novel impacts on development, survival and reproduction in a small arthropod. J. Anim. Ecol. 2014, 83, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colinet, H.; Sinclair, B.J.; Vernon, P.; Renault, D. Insects in Fluctuating Thermal Environments. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaedi, B.; Andrew, N.R. The physiological consequences of varied heat exposure events in adult Myzus persicae: A single prolonged exposure compared to repeated shorter exposures. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Plasmid Constructs | Number of Explants Co-Cultivated | Mean Number of Explants Produce Shoots | Mean Transformation Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jamila | Tomaland | Jamila | Tomaland | ||
| T-449 | 100 | 45b | 40b | 45b | 40b |
| T-452 | 100 | 63a | 58a | 63a | 58a |
| T-455 | 100 | 52c | 49c | 52c | 49c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faisal, M.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Alatar, A.A.; Saquib, Q.; Alwathnani, H.A.; Canto, T. Genetic Transformation and siRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing for Aphid Resistance in Tomato. Agronomy 2019, 9, 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120893
Faisal M, Abdel-Salam EM, Alatar AA, Saquib Q, Alwathnani HA, Canto T. Genetic Transformation and siRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing for Aphid Resistance in Tomato. Agronomy. 2019; 9(12):893. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120893
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaisal, Mohammad, Eslam M. Abdel-Salam, Abdulrahman A. Alatar, Quaiser Saquib, Hend A. Alwathnani, and Tomas Canto. 2019. "Genetic Transformation and siRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing for Aphid Resistance in Tomato" Agronomy 9, no. 12: 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120893
APA StyleFaisal, M., Abdel-Salam, E. M., Alatar, A. A., Saquib, Q., Alwathnani, H. A., & Canto, T. (2019). Genetic Transformation and siRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing for Aphid Resistance in Tomato. Agronomy, 9(12), 893. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9120893







