Microbially Mediated Carbon Regulation by Straw Mulching in Rainfed Maize Rhizosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Crops and Nutrient Management
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.3.1. Soil Sampling
2.3.2. Determination of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3.3. Determination of Soil Enzymatic Activities
2.3.4. Soil Carbon Fractions Analyses
2.4. Determination of Microbial Community
Soil DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.5. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
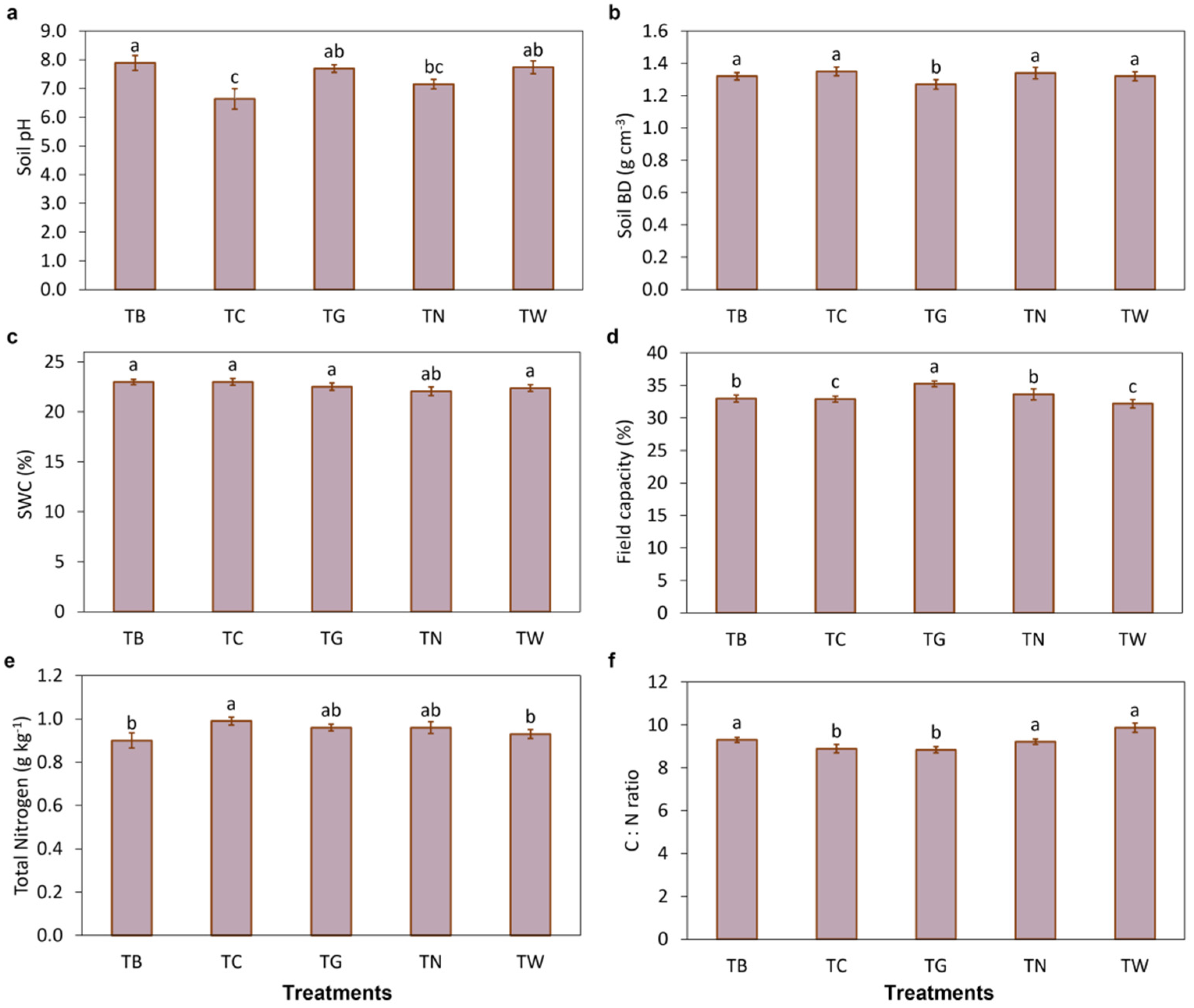
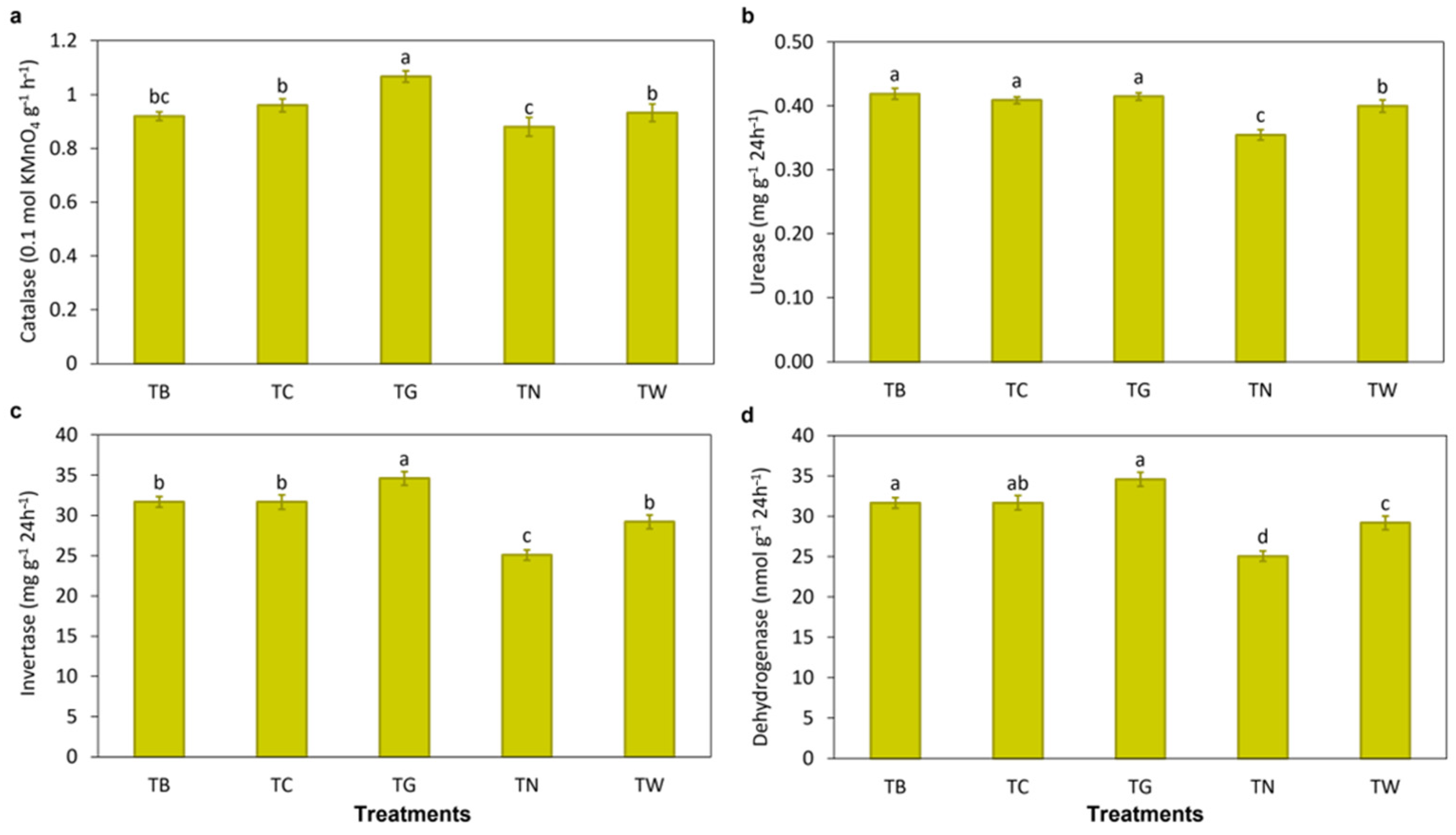
3.1. Effects of Mulching Practices on Soil Characteristics and Enzymatic Activities
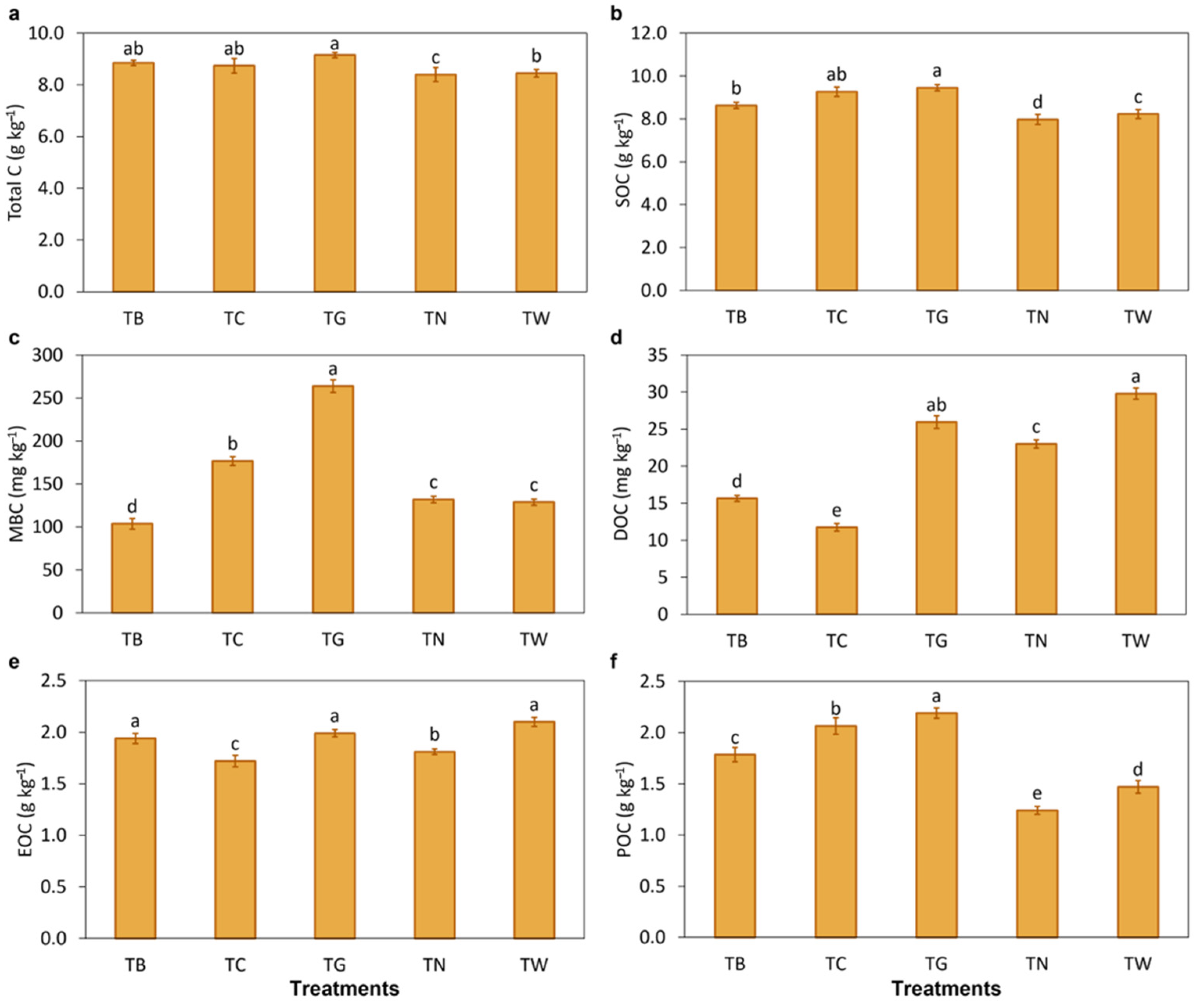
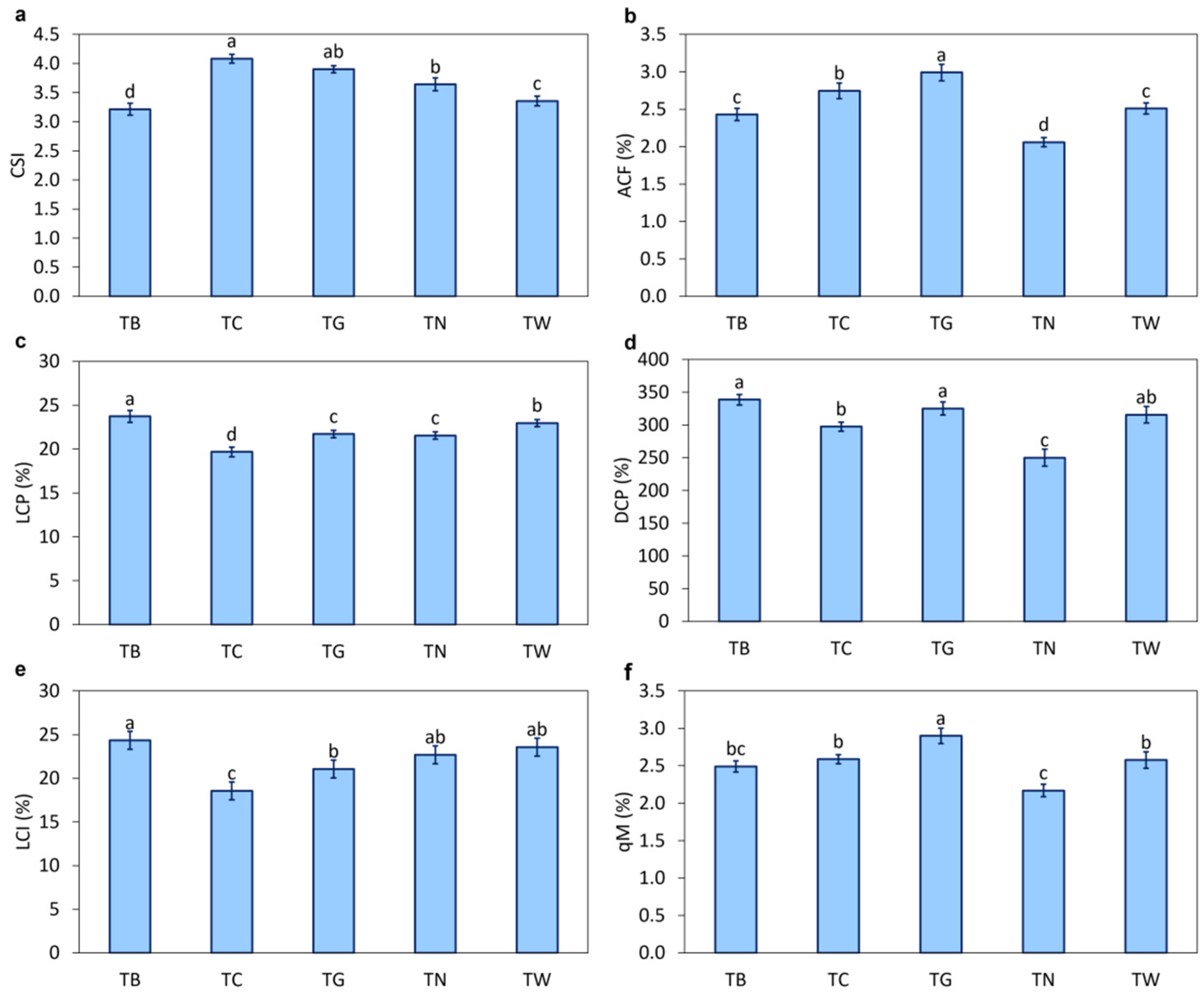
3.2. Effects of Mulching Practices on Soil Carbon Fractions
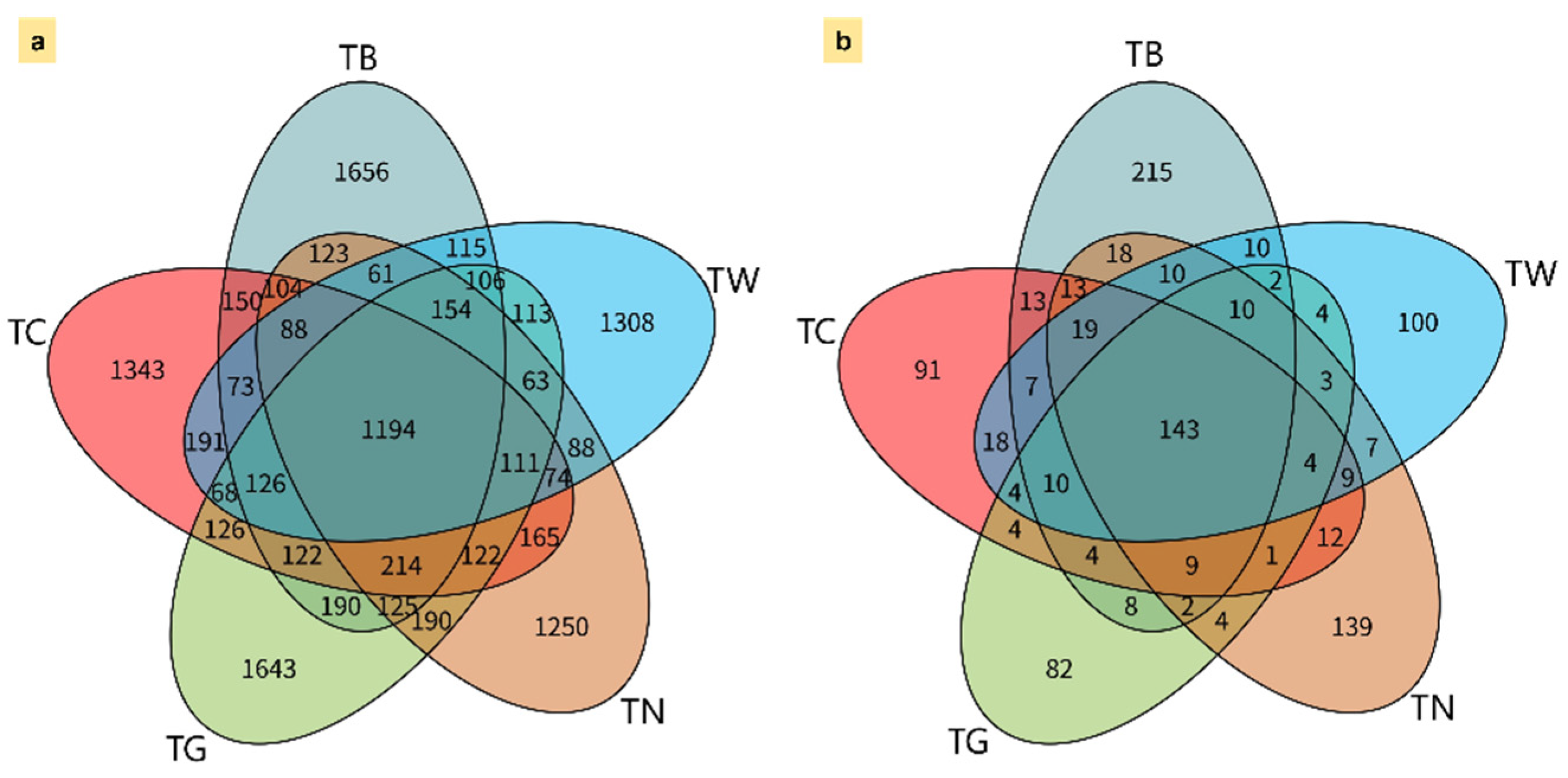
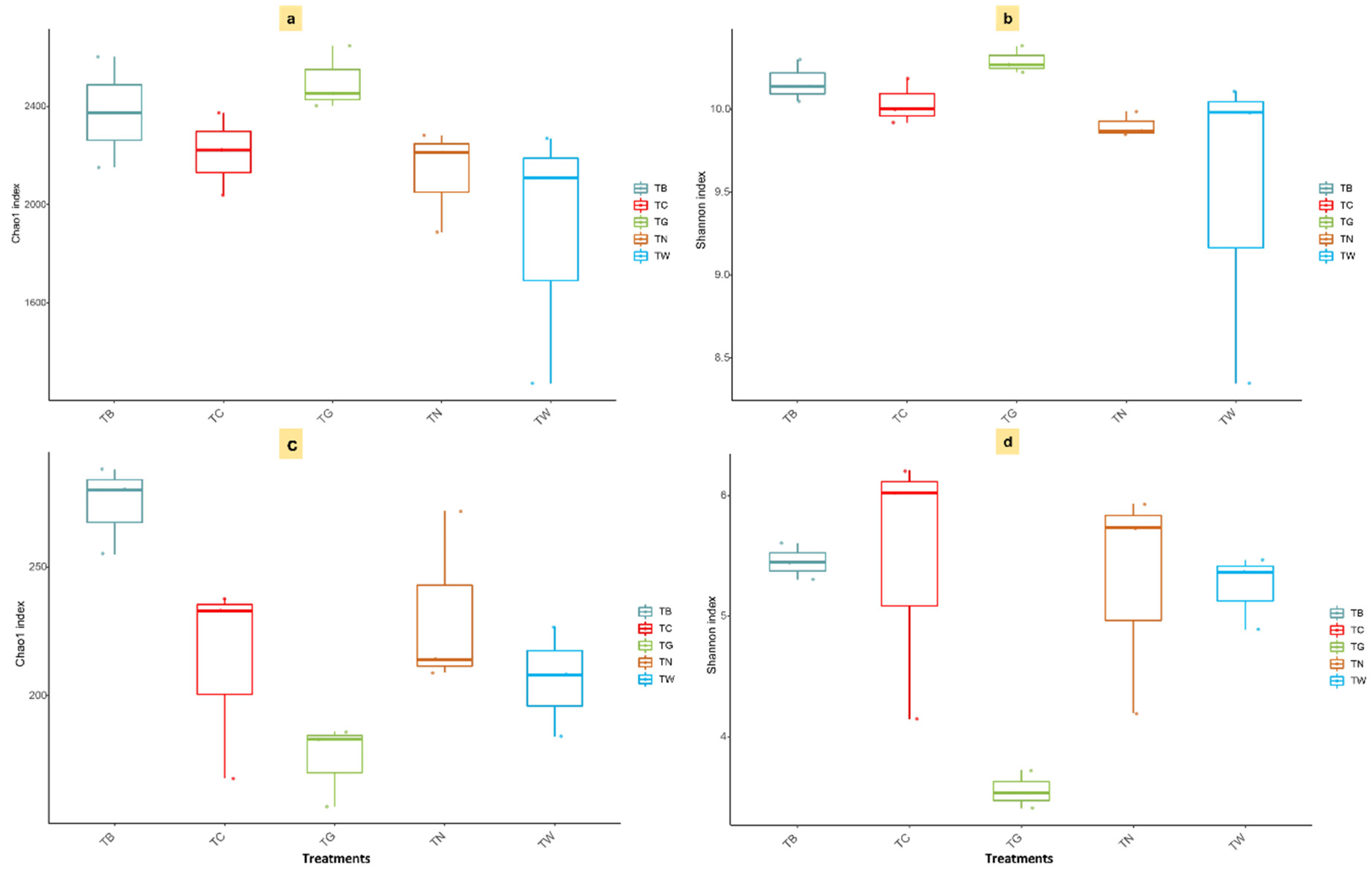
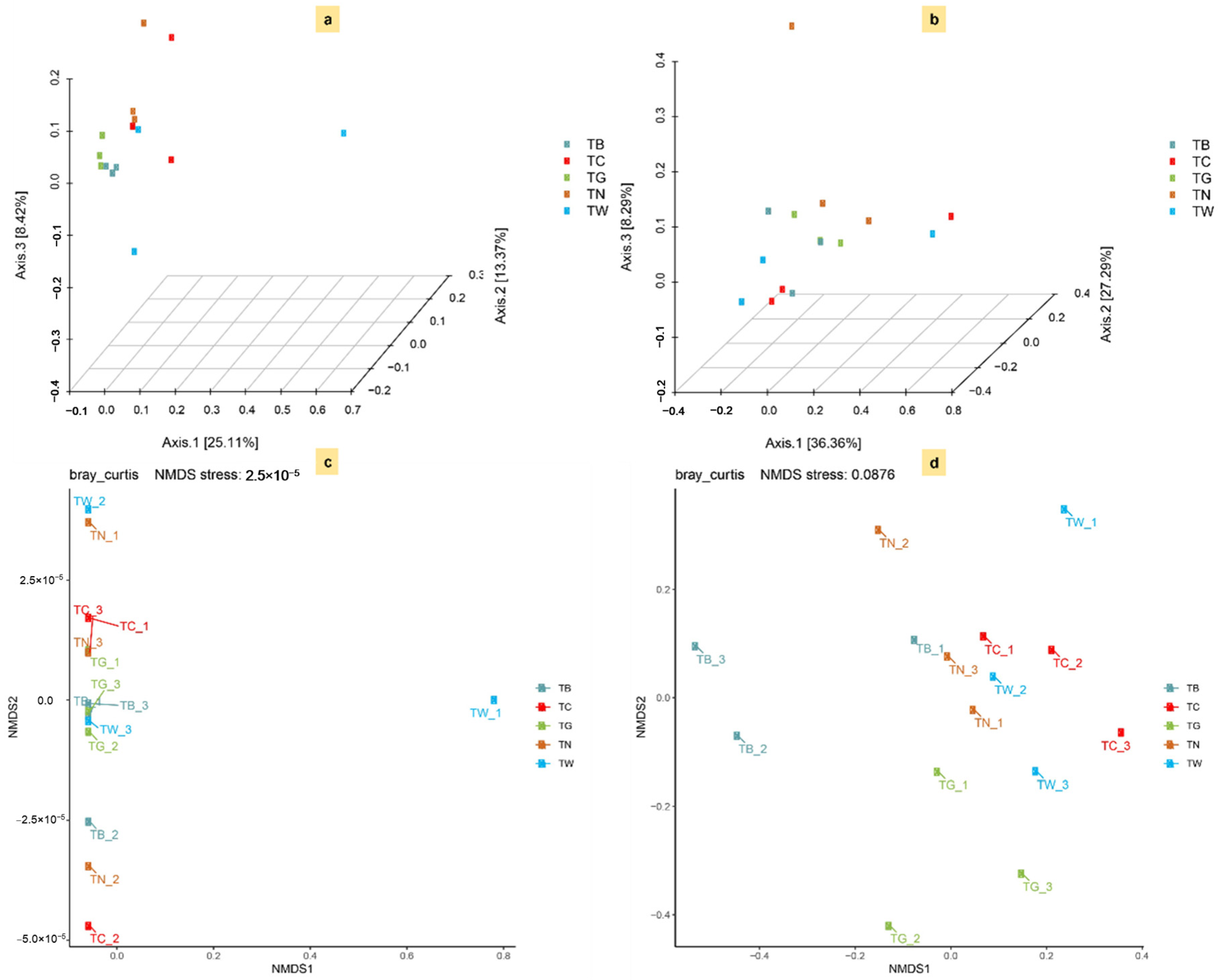
3.3. Microbial α and β-Diversity in Response to Mulching Practices
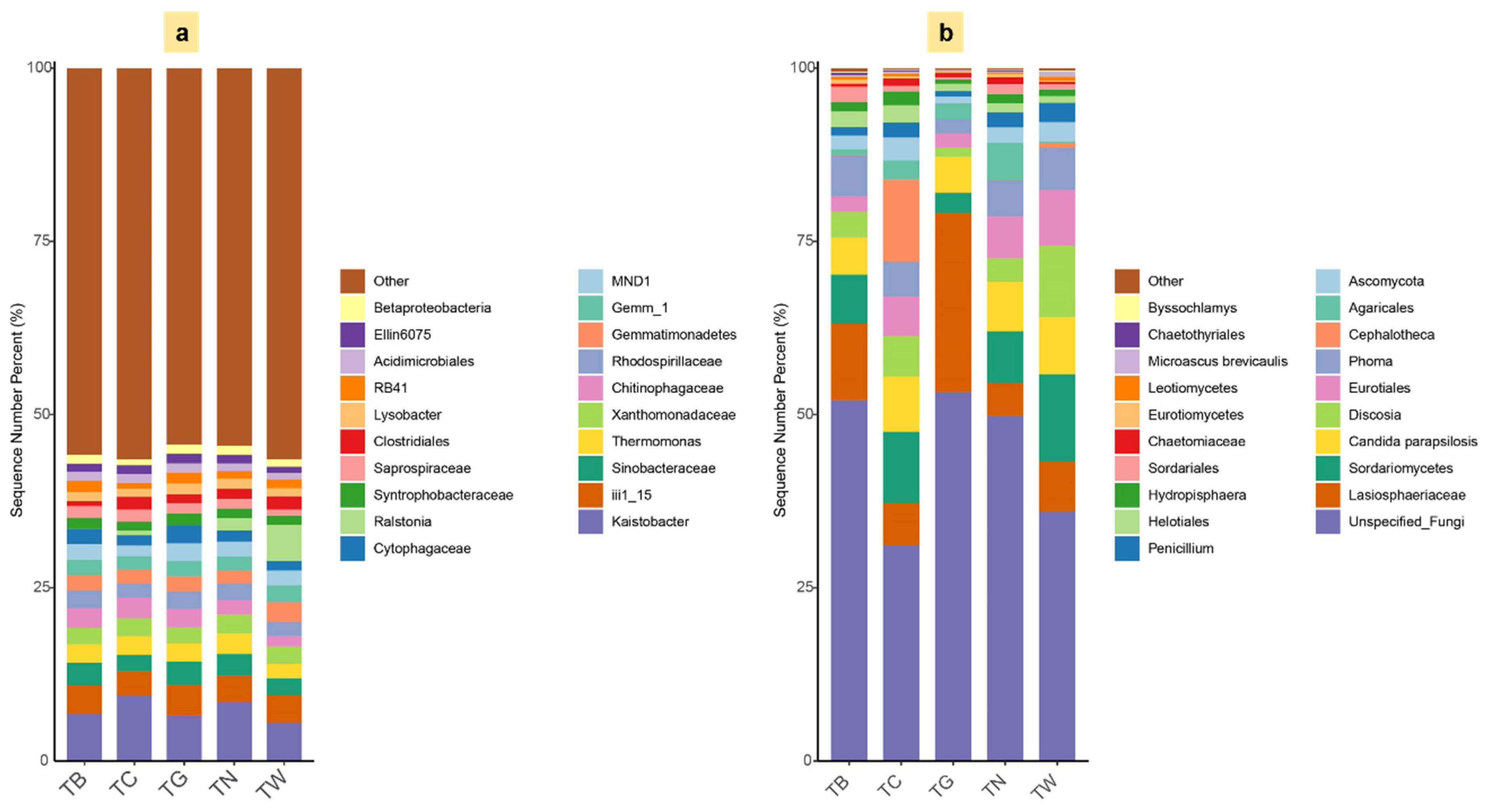
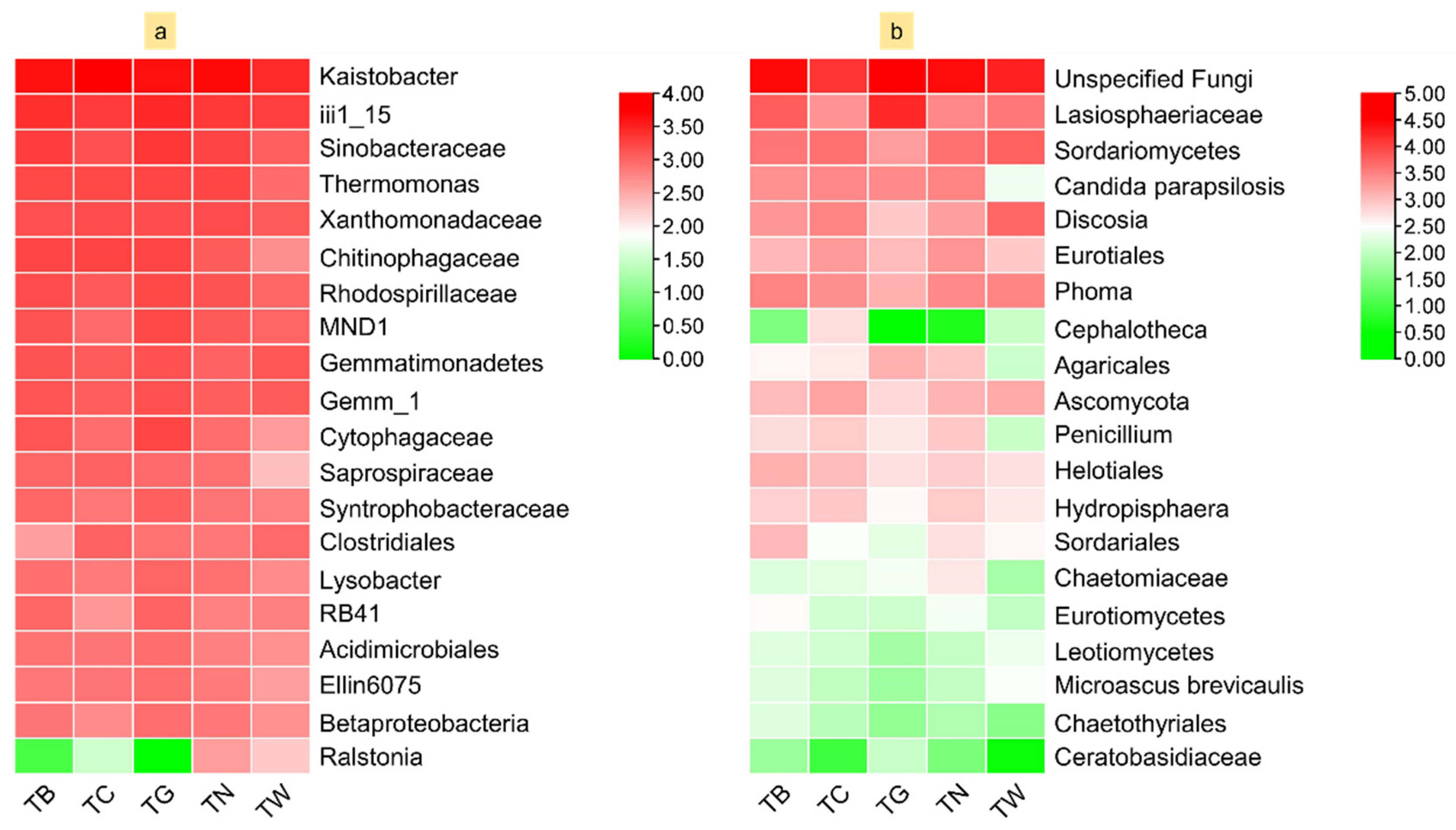
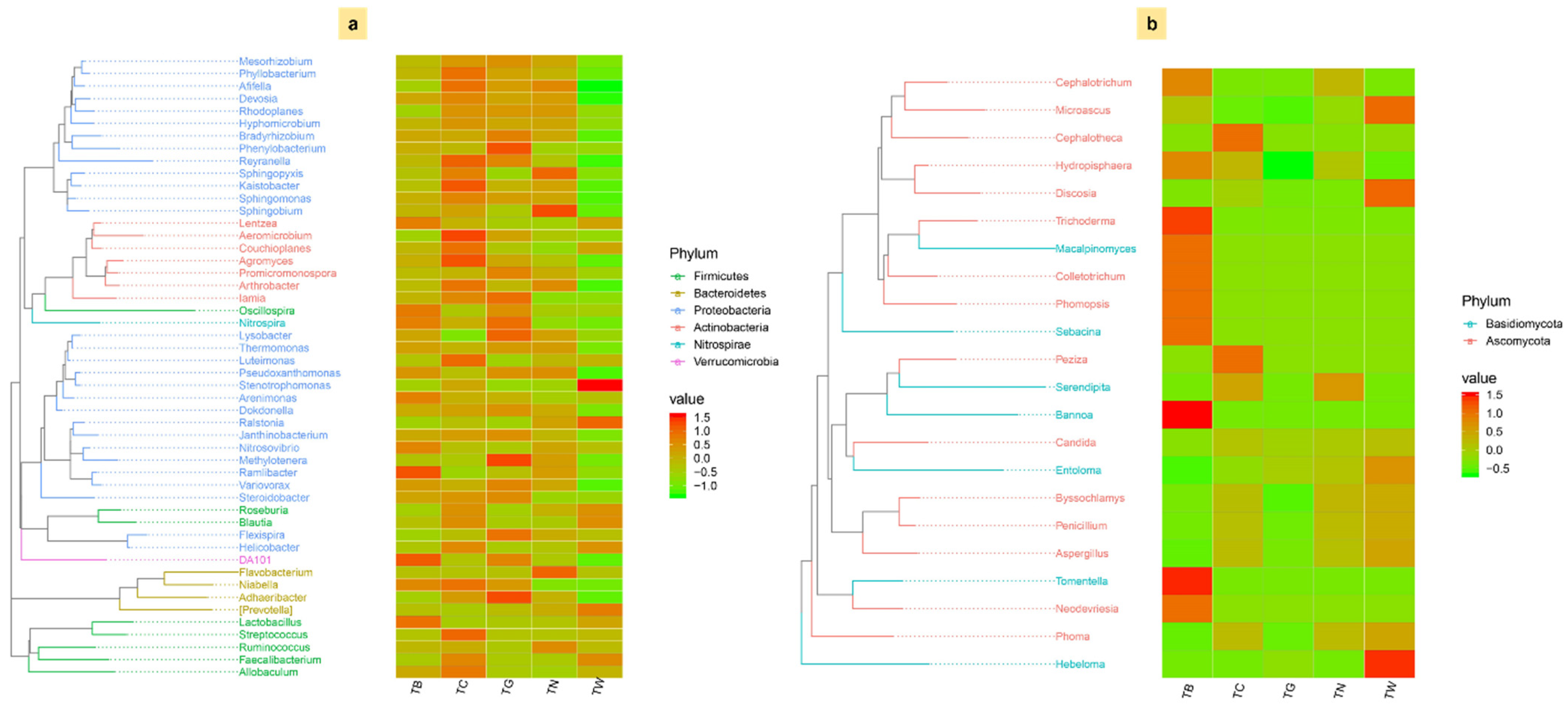
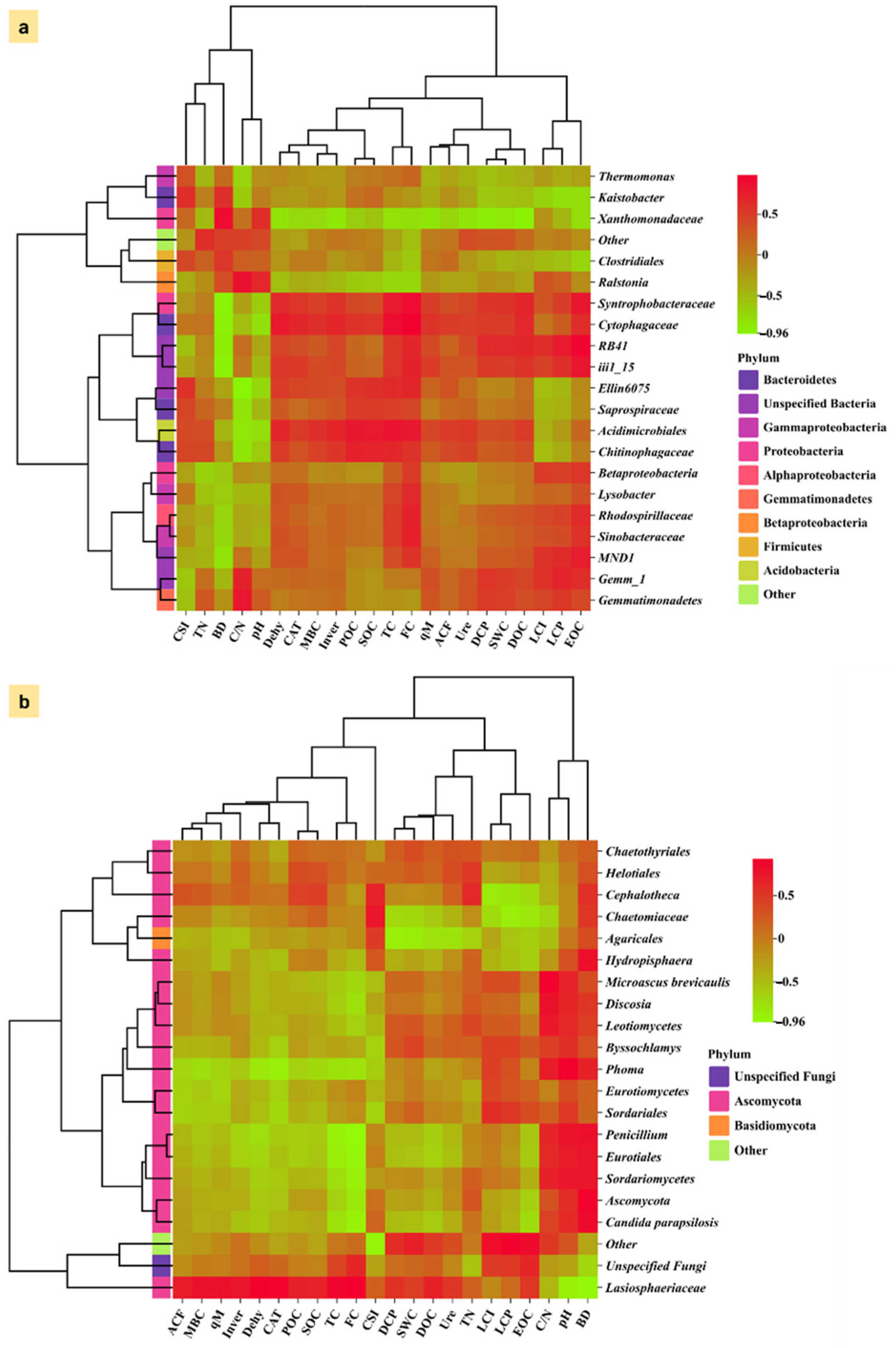
3.4. Composition of Microbial Diversity Under Different Mulching Practices
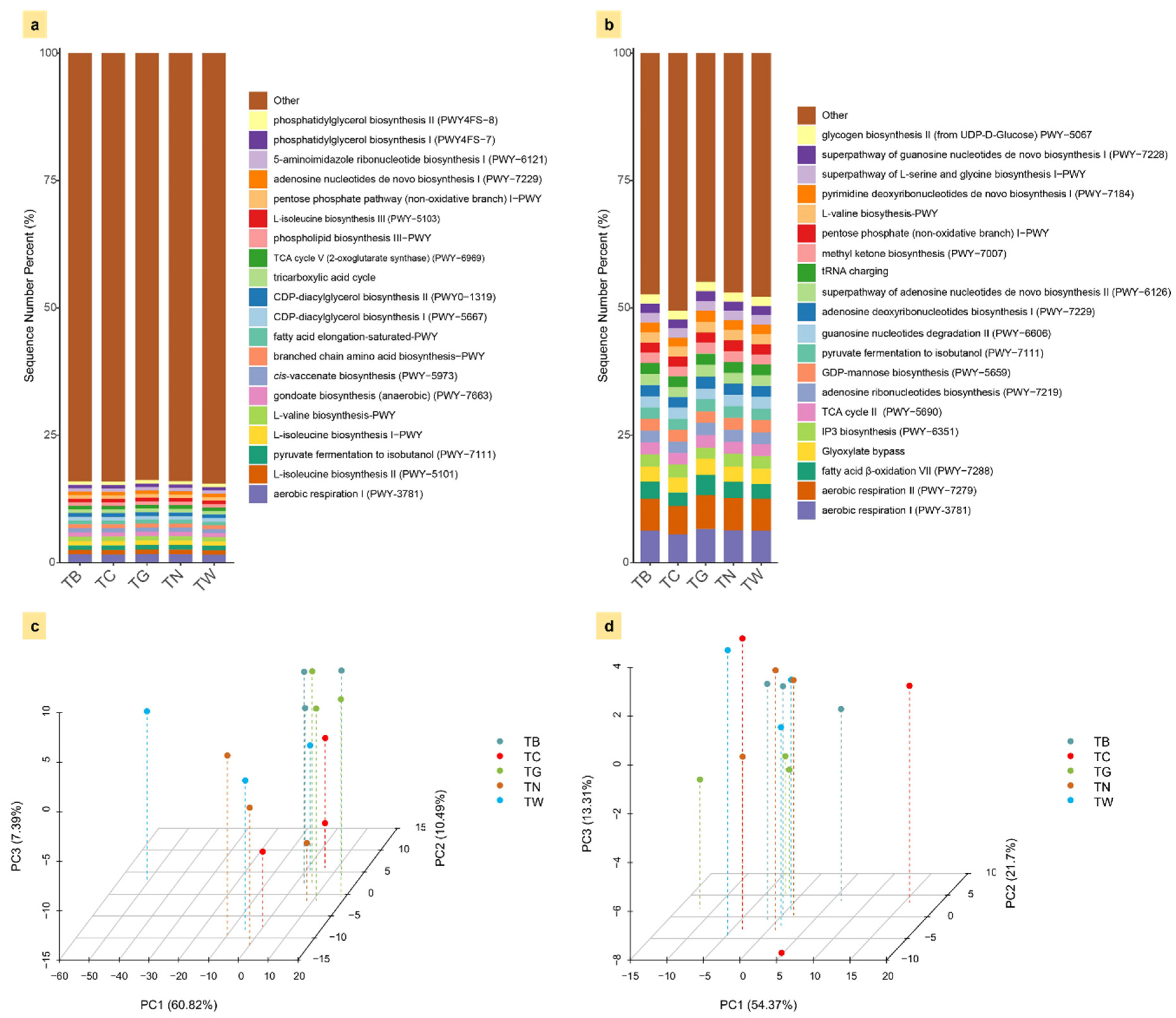
3.5. Functional Prediction of Soil Microbial Communities
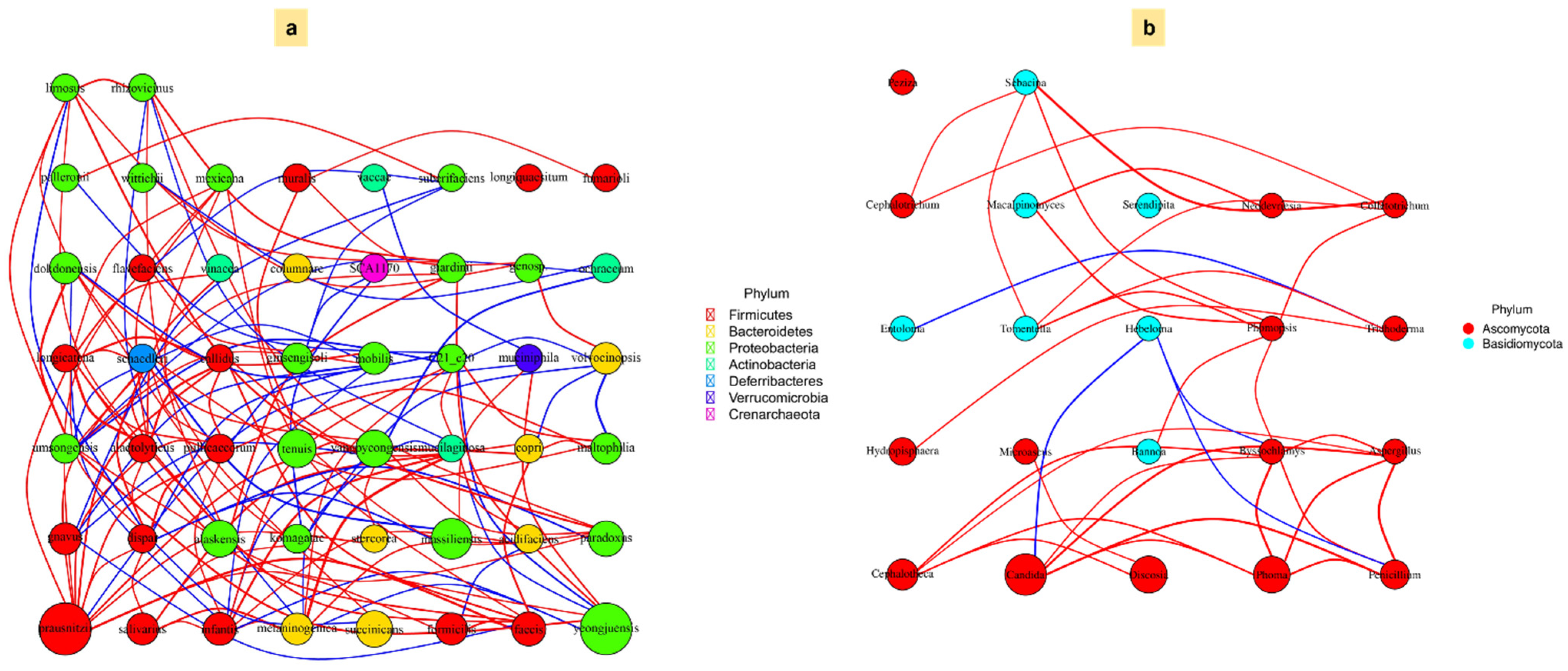
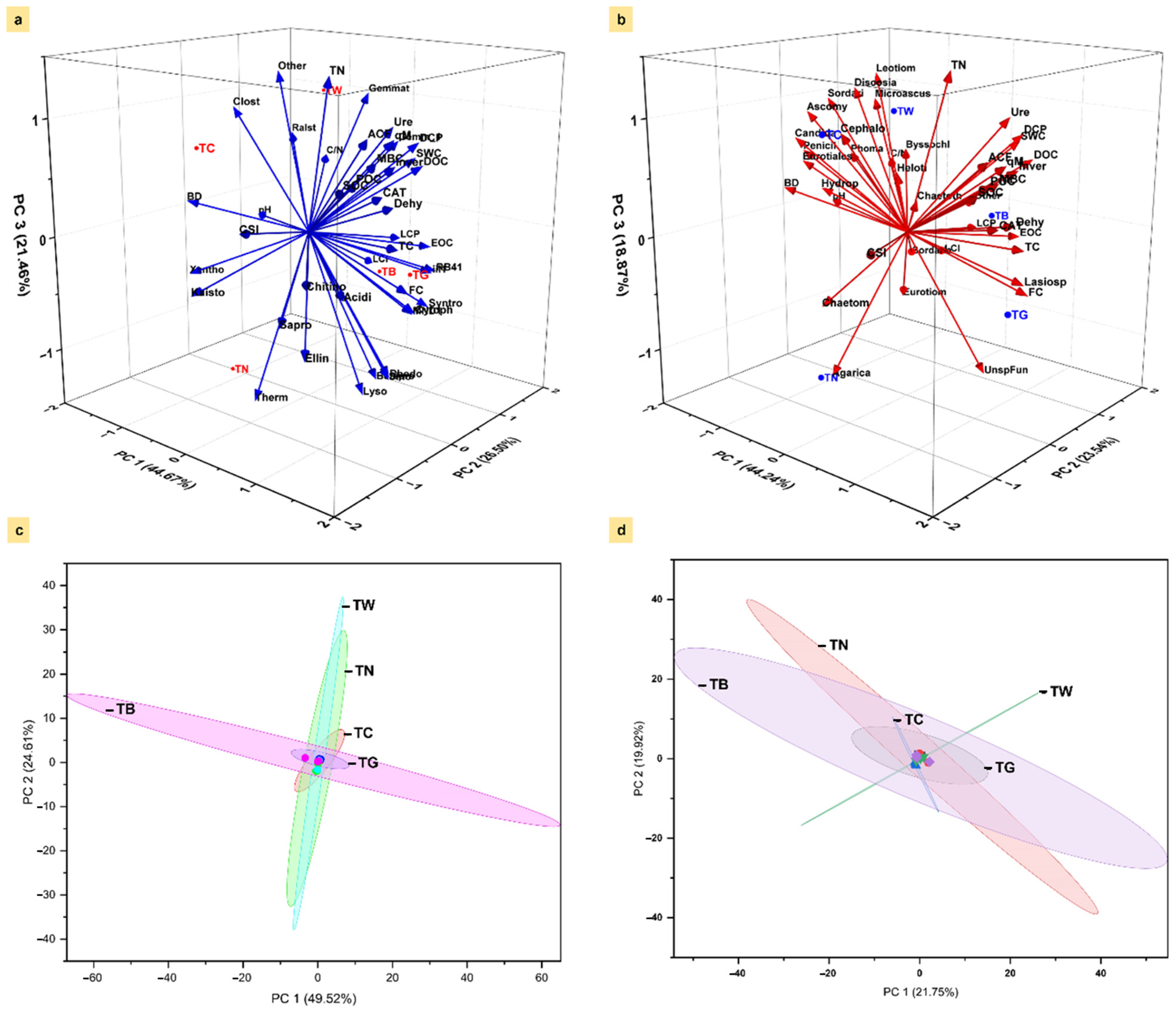
3.6. Association Between Microbial Community and Carbon Fractions Under Mulching Practices
4. Discussion
4.1. Mulching Practices Improved Soil Properties and Enzymatic Activities
4.2. Mulching Practices Regulated Soil Organic Carbon Fractions
4.3. Soil Microbial Community Structure and Composition Under Mulching Practices
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Li, L.; Coulter, J.A.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Z.; Cai, L.; Carberry, P.; Whitbread, A. Conservation tillage increases yield and precipitation use efficiency of wheat on the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balwinder, S.; Eberbach, P.L.; Humphreys, E.; Kukal, S.S. The effect of rice straw mulch on evapotranspiration, transpiration and soil evaporation of irrigated wheat in Punjab, India. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satishkumar, N.; Tevari, P.; Singh, A. A study on constraints faced by farmers in adapting to climate change in rainfed agriculture. J. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 44, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Siddique, K.H.; Turner, N.C.; Li, X.G.; Niu, J.Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Chai, Q. Ridge-furrow mulching systems—An innovative technique for boosting crop productivity in semiarid rain-fed environments. Adv. Agron. 2013, 118, 429–476. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Turner, N.C.; Gong, Y.H.; Li, F.M.; Fang, C.; Ge, L.J.; Ye, J.S. Benefits and limitations to straw-and plastic-film mulch on maize yield and water use efficiency: A meta-analysis across hydrothermal gradients. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 99, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Chai, S.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheng, H.; Chang, L.; Huang, C.; Li, R.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; et al. Maize straw strip mulching as a replacement for plastic film mulching in maize production in a semiarid region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, G.; Dou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Khan, A.A. Plastic mulch increases dryland wheat yield and water-use productivity, while straw mulch increases soil water storage. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 3174–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Sainju, U.M.; Zhao, F.; Liu, W. Soil microbial community and carbon and nitrogen fractions responses to mulching under winter wheat. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 139, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Ros, G.H.; Furtak, K.; Iqbal, H.M.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Soil carbon sequestration–An interplay between soil microbial community and soil organic matter dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Niu, L.; You, Y.; Cui, S.; Chen, C.; Li, Z. Effects of conservation tillage and straw mulching on crop yield, water use efficiency, carbon sequestration and economic benefits in the Loess Plateau region of China: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 238, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cheng, X.; He, X.; Bei, Q.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, K.; Tian, X.; Duan, M.; et al. Effects of bio-mulching on wheat soil microbial community and carbon utilization efficiency in southwest China. Catena 2022, 214, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Lu, N.; Liu, X.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, Q. Consecutive Biochar Application Alters Soil Enzyme Activities in the Winter Wheat–Growing Season. Soil Sci. 2014, 179, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Duan, Y.; Wang, G.L.; Wang, A.Q.; Shao, G.Z.; Meng, X.H.; Hu, H.Y.; Zhang, D.M. Straw alters the soil organic carbon composition and microbial community under different tillage practices in a meadow soil in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Huang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, D.; Haider, S.; Song, J.; Moreira, B.R.D.A.; Ren, G.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; et al. Impact of straw-biochar amendments on microbial activity and soil carbon dynamics in wheat-maize system. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.R. Bulk density. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Properties, Including Statistics of Measurement and Sampling; The American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; Volume 9, pp. 374–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, D.S. Determination of microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in soil. In Advances in Nitrogen Cycling in Agricultural Systems; Wilson, J.R., Ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1988; pp. 368–386. [Google Scholar]
- Cadle, S.H.; Groblicki, P.J. An evaluation of methods for the determination of organic and elemental carbon in particulate samples. In Particulate Carbon: Atmospheric Life Cycle; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zha, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Smith, P.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Evaluating indices of soil organic carbon stability. A case study for forest restoration projects near Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.R.; Islam, K.R.; Stine, M.A.; Gruver, J.B.; Samson-Liebig, S.E. Estimating active carbon for soil quality assessment: A simplified method for laboratory and field use. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 2003, 18, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.H.; Domsch, K.H. Application of eco-physiological quotients (qCO2 and qD) on microbial biomasses from soils of different cropping histories. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Gil, J. Effects of mulching on soil physical properties and runoff under semi-arid conditions in southern Spain. Catena 2010, 81, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.H.H.; Kristiansen, P.; Marschner, P. Influence of mulch C/N ratio and decomposition stage on plant N uptake and N availability in soil with or without wheat straw. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; Jiang, G. Effects of straw mulching thickness on the soil health in a temperate organic vineyard. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Response of soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities to long-term reclamation of coastal saline soil, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dang, P.; Qin, X.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Siddique, K.H. Straw incorporation with ridge–furrow plastic film mulch alters soil fungal community and increases maize yield in a semiarid region of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.; Li, B. Effects of conservation tillage on soil enzyme activities of global cultivated land: A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Soil structure and organic carbon relationships following 10 years of wheat straw management in no-till. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 95, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Mu, L.; Shao, L. Linking macroaggregation to soil microbial community and organic carbon accumulation under different tillage and residue managements. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Hu, G.; Shao, S.; He, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Dynamic contribution of microbial residues to soil organic matter accumulation influenced by maize straw mulching. Geoderma 2019, 333, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Ding, R.; Wang, J.; Nie, J. Changes in soil characteristics and maize yield under straw returning system in dryland farming. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qin, R.; Shi, X.; Wei, H.; Sun, G.; Li, F.M.; Zhang, F. The effects of plastic film mulching and straw mulching on licorice root yield and soil organic carbon content in a dryland farming. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Ma, Q.; Liao, J.; Wang, D.; Guan, Q.; Jones, D.L. Organic mulching promotes soil organic carbon accumulation to deep soil layer in an urban plantation forest. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Pang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Li, Y. Buried straw layer plus plastic mulching improves soil organic carbon fractions in an arid saline soil from Northwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Feng, H. Effects of straw mulching and plastic film mulching on improving soil organic carbon and nitrogen fractions, crop yield and water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, R.R.; Roshanthan, T.; Gnanavelrajah, N.; Karunaratne, S.B. Organic carbon fractions, aggregate stability, and available nutrients in soil and their interrelationships in tropical cropping systems: A case study. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z.; Song, Z.; Cooper, J.M.; Zhao, B. Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil organic carbon stocks as affected by long-term organic and mineral fertilization regimes in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wright, A.L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Long-term tillage effects on the distribution patterns of microbial biomass and activities within soil aggregates. Catena 2011, 87, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, F. Molecular structure of dissolved organic carbon in a sandy soil receiving contrasting quality organic residues. Geoderma 2023, 440, 116720. [Google Scholar]
- Olk, D.C. A chemical fractionation for structure–function relations of soil organic matter in nutrient cycling. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering fungal: Bacterial dominance in soils–methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Awasthi, M.K.; Yang, J.; Duan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z. Mulching practices alter the bacterial-fungal community and network in favor of soil quality in a semiarid orchard system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yu, S.; Zhang, L.; Dong, K.; Feng, B. Mulching practices manipulate the microbial community diversity and network of root associated compartments in the Loess Plateau. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fan, J.; Fu, W.; Niu, X.; Yang, Q.; Hao, M. Changes in soil microbial community and co-occurrence network after long-term no-tillage and mulching in dryland farming. Plant Soil 2024, 495, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.U.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H. Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Knight, R. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rui, J.; Mao, Y.; Yannarell, A.; Mackie, R. Dynamics of the bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere of a maize cultivar. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanomi, G.; Lorito, M.; Vinale, F.; Woo, S.L. Organic amendments, beneficial microbes, and soil microbiota: Toward a unified framework for disease suppression. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Ruiz, L.V.; Vas-co-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A.; et al. Global diversity and geography of soil fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Ken-nedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Si, P.; Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Influence of film mulching on soil microbial community in a rainfed region of northeastern China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, T. Characteristics of the soil microbial community structure under long-term chemical fertilizer application in yellow soil paddy fields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the park grass experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyadarshan, A.; Naik, S.K.; Dhakar, M.K.; Purakayastha, T.J.; Mahanta, D.; Choudhary, M.; Mali, S.S.; Kumar, R.; Dash, A.K.; Das, A.; et al. Soil Carbon Dynamics and Soil Quality Index Under Different Agricultural Production Systems in Rain-Fed Ecosystems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 3003–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; Yao, S.-H.; Cao, X.-Y.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Olk, D.C.; Mao, J.-D.; Zhang, B. Structural evidence for soil organic matter turnover following glucose addition and microbial controls over soil carbon change at different horizons of a Mollisol. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 119, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; He, B.; Dong, B.; Zhang, G. Film mulched ridge–furrow tillage improves the quality and fertility of dryland agricultural soil by enhancing soil organic carbon and nutrient stratification. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 292, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.; Jin, J.; Wang, G.; Tang, C.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X. The fate of soybean residue-carbon links to changes of bacterial community composition in Mollisols differing in soil organic carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 109, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kong, J.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Cai, Z.; Huang, X. Relationships of decomposability and C/N ratio in different types of organic matter with suppression of Fusarium oxysporum and microbial communities during reductive soil disinfestation. Biol. Control. 2016, 101, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Kan, Z.-R.; Liu, P.; Qi, J.-Y.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, H.-L. Residue management induced changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen under different tillage practices in the North China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Si, M.; Fan, B.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Precipitation Determines the Spatial Variability of Vegetation and Topsoil Organic Carbon Densities of Alpine Grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecosystems 2025, 28, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Traits | Shapiro–Wilk Test * | Levene Test ** | Non-Parametric Test *** | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | p-Value | F | p-Value | F | p-Value | |
| Soil pH | 0.8001 | 0.0037 | 2.689 | 0.093 | 2.75 | 0.0886 |
| Soil water content | 0.9526 | 0.5670 | 3.678 | 0.043 | 6.06 | 0.0097 |
| Bulk density | 0.9879 | 0.9979 | 5.088 | 0.017 | 2.21 | 0.1410 |
| Field capacity | 0.9518 | 0.5530 | 2.528 | 0.107 | 1.23 | 0.3583 |
| Catalase activity | 0.8222 | 0.0072 | 8.575 | 0.003 | 27.5 | 0.0000 |
| Urease activity | 0.8613 | 0.0252 | 1.905 | 0.186 | 3.06 | 0.0692 |
| Invertase activity | 0.9715 | 0.8798 | 0.487 | 0.745 | 16.9 | 0.0002 |
| Sucrase activity | 0.9164 | 0.1699 | 2.236 | 0.138 | 5.29 | 0.0149 |
| Total carbon | 0.8899 | 0.0668 | 7.403 | 0.005 | 9.85 | 0.0017 |
| Total nitrogen | 0.9247 | 0.2271 | 2.909 | 0.078 | 1.68 | 0.2296 |
| C/N ratio | 0.9723 | 0.8899 | 2.371 | 0.122 | 4.95 | 0.0184 |
| Soil organic carbon | 0.9355 | 0.3295 | 0.191 | 0.938 | 25.9 | 0.0000 |
| Dissolved organic carbon | 0.9542 | 0.5936 | 0.322 | 0.857 | 8.21 | 0.0033 |
| Microbial biomass carbon | 0.9568 | 0.6372 | 0.609 | 0.665 | 27.5 | 0.0000 |
| Easily oxidizable carbon | 0.8915 | 0.0707 | 1.019 | 0.443 | 33.7 | 0.0000 |
| Particulate organic carbon | 0.9128 | 0.1497 | 0.274 | 0.888 | 43.2 | 0.0000 |
| Active carbon fraction | 0.9690 | 0.8428 | 0.225 | 0.936 | 33.7 | 0.0000 |
| Carbon stability index | 0.9414 | 0.4006 | 0.214 | 0.925 | 43.2 | 0.0000 |
| Dissolved carbon proportion | 0.9102 | 0.1366 | 0.262 | 0.929 | 16.6 | 0.0002 |
| Labile carbon index | 0.9279 | 0.2534 | 0.205 | 0.917 | 43.2 | 0.0000 |
| Labile carbon proportion | 0.9803 | 0.9717 | 0.206 | 0.929 | 23.1 | 0.0000 |
| Microbial quotient | 0.9765 | 0.9400 | 0.233 | 0.936 | 12.9 | 0.0006 |
| Microbial Traits | SS | MS | F. Model | R2 | Pr (>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Abundance | 0.509122 | 0.127280 | 1.433911 | 0.364500 | 0.001 |
| Fungal Abundance | 0.901839 | 0.225459 | 1.839710 | 0.423924 | 0.030 |
| Bacterial Functions | 0.037435 | 0.009358 | 1.615283 | 0.392508 | 0.078 |
| Fungal Functions | 0.034990 | 0.008747 | 1.730844 | 0.409101 | 0.121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, L.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Zhou, Y. Microbially Mediated Carbon Regulation by Straw Mulching in Rainfed Maize Rhizosphere. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061412
Pang L, Wu H, Lu J, Zheng H, Wang X, Mumtaz MZ, Zhou Y. Microbially Mediated Carbon Regulation by Straw Mulching in Rainfed Maize Rhizosphere. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061412
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Lei, Haimei Wu, Jianlong Lu, Haofei Zheng, Xiaohua Wang, Muhammad Zahid Mumtaz, and Yanli Zhou. 2025. "Microbially Mediated Carbon Regulation by Straw Mulching in Rainfed Maize Rhizosphere" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061412
APA StylePang, L., Wu, H., Lu, J., Zheng, H., Wang, X., Mumtaz, M. Z., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Microbially Mediated Carbon Regulation by Straw Mulching in Rainfed Maize Rhizosphere. Agronomy, 15(6), 1412. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061412






