Phosphate Fertilizer Effects on Microbial Resource Limitations in Wheat Cropland: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Soil EEAs and EES
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities (EEA) and Stoichiometries (EES)
3.2. Indicators of Microbial Resource Limitation
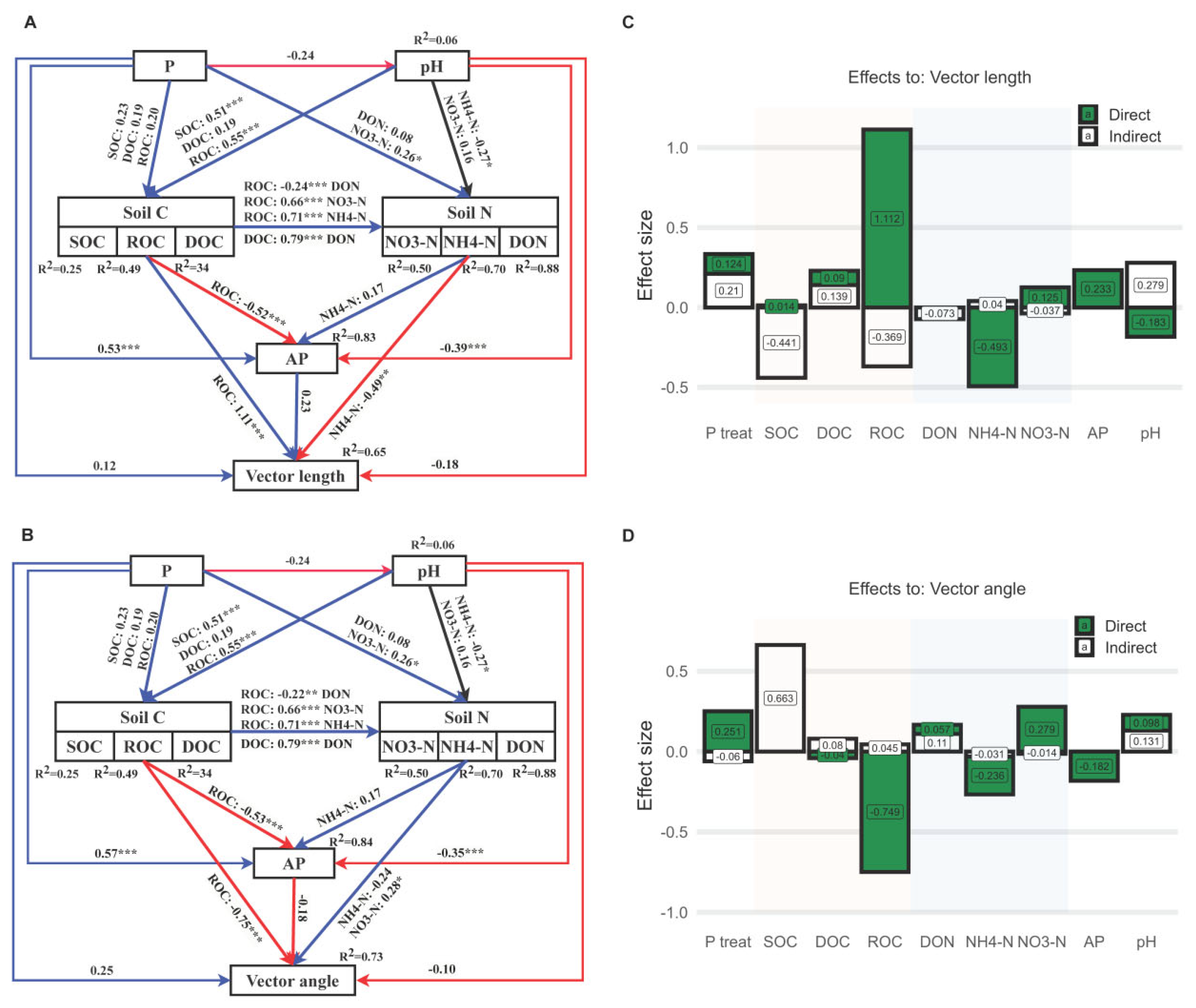
3.3. Linkages Between Enzyme Stoichiometry and Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of P Addition on Soil Enzyme Activities and Stoichiometry
4.2. Factors Determining Microbial Metabolic Limitations in the Wheat Field
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEA | Extracellular enzyme activity |
| EES | Extracellular enzymatic stoichiometry |
| BG | Soil β-glucosidase |
| LAP | Leucine aminopeptidse |
| NAG | Soil N-acetyl-b-glucosaminidase |
| AKP | Soil alkaline phosphatase |
| C | Carbon |
| N | Nitrogen |
| P | Phosphorus |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| DOC | Soil dissolved organic carbon |
| ROC | Soil readily oxidizable organic carbon |
| DON | Dissolved organic nitrogen |
| TN | Soil total nitrogen |
| AP | Soil available phosphorus |
| AN | Soil available nitrogen |
| NH4+-N | Soil ammonia nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Soil nitrate nitrogen |
References
- Cui, J.; Zhu, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Ai, C.; He, P.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, P. Effect of high soil C/N ratio and nitrogen limitation caused by the long-term combined organic-inorganic fertilization on the soil microbial community structure and its dominated SOC decomposition. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, E.; Luo, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lu, X.; Jiang, L.; Luo, X.; Wen, D. Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Cai, S.; Sulaiman, A.A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Rengel, Z.; Zhang, D. Dynamics of root–microbe interactions governing crop phosphorus acquisition after straw amendment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 181, 109039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.C.M.; Galindo, F.S.; Gazola, R.P.D.; Dupas, E.; Rosa, P.A.L.; Mortinho, E.S.; Filho, M.C.M.T. Corn Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency Response to Phosphorus Rates Associated with Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, D.; Wang, M.; Müeller, T.; Zou, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W. Phosphorus fertilizer management for high yields in intensive winter wheat-summer maize rotation system: Integrating phosphorus budget and soil available phosphorus. Field Crops Res. 2024, 313, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Livi, K.J. Underassessed phosphorus fixation mechanisms in soil sand fraction. Geoderma 2013, 192, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Bing, H.; Sun, H.; Wang, J. Leaching disturbed the altitudinal distribution of soil organic phosphorus in subalpine coniferous forests on Mt. Gongga, SW China. Geoderma 2018, 326, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xiao, W. The global positive effect of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 176, 108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Ruan, H. Phosphorus additions imbalance terrestrial ecosystem C:N:P stoichiometry. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 7353–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achat, D.L.; Augusto, L.; Gallet-Budynek, A.; Loustau, D. Future challenges in coupled C–N–P cycle models for terrestrial ecosystems under global change: A review. Biogeochemistry 2016, 131, 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, E.; Wen, D.; Jiang, L.; Luo, X.; Kuang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, C.; Allen, K.T.; He, X.; Huang, X.; et al. Latitudinal patterns of terrestrial phosphorus limitation over the globe. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, F.; Xia, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Dong, J.; Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Che, R.; et al. Meta-analysis of the impacts of phosphorus addition on soil microbes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, L.; Hu, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Wei, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Huang, C. The amounts and ratio of nitrogen and phosphorus addition drive the rate of litter decomposition in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, F.; Li, Q.; Solanki, M.K.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.-X.; Dong, D.-F. Soil phosphorus transformation and plant uptake driven by phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1383813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, B.; Zeng, H. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects the unique habitat of karst tiankeng and helps to alleviate the P-limitation of soil microbes. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Canarini, A.; Zhang, W.; Lang, M.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Richter, A.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Microbial life-history strategies mediate microbial carbon pump efficacy in response to N management depending on stoichiometry of microbial demand. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Peng, S.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. New insights into the patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry in soil and sediment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.; Weintraub, M.N.; Moorhead, D. Estimating microbial carbon use efficiency in soil: Isotope-based and enzyme-based methods measure fundamentally different aspects of microbial resource use. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 169, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Qu, T.; Xue, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; An, S. Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry and microbial non-homeostatic regulation depend on relative resource availability during litter decomposition. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Wu, D. Land conversion from cropland to grassland alleviates climate warming effects on nutrient limitation: Evidence from soil enzymatic activity and stoichiometry. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Guo, X.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fang, L. Stoichiometric models of microbial metabolic limitation in soil systems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Rinkes, Z.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Weintraub, M.N. Dynamic relationships between microbial biomass, respiration, inorganic nutrients and enzyme activities: Informing enzyme-based decomposition models. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Q.; Li, G.; Liu, G.; Geissen, V.; Ritsema, C.J.; Xue, S. Impact of nitrogen addition on plant-soil-enzyme C–N–P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bing, H.; Moorhead, D.L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ye, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals widespread soil phosphorus limitation to microbial metabolism across Chinese forests. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guan, P.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, D. Stronger microbial nutrient limitations in subsoil along the precipitation gradient of agroecosystem: Insights from soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1137172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xin, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, X.; Yang, W.; Zhu, A. Microbial community alteration driven by labile organic carbon enhances phosphorus availability under different tillage regimes. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 3707–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, T.; Li, Z. Temporal variation of microbial nutrient limitation in citrus plantations: Insights from soil enzyme stoichiometry. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Moorhead, D.L.; Cui, Y.; Wanek, W.; Li, S.; Wang, C. Exogenous nitrogen input skews estimates of microbial nitrogen use efficiency by ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Ecol. Process. 2023, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Duan, Y.; Yao, B.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W. Soil extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects microbial metabolic limitations in different desert types of northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Prażuch, W.; Ilek, A. Vertical variations in enzymatic activity and C:N:P stoichiometry in forest soils under the influence of different tree species. Eur. J. For. Res. 2024, 14, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bing, H.; Fang, L.; Jiang, M.; Shen, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reveals the carbon and phosphorus limitations of microbial metabolisms in the rhizosphere and bulk soils in alpine ecosystems. Plant Soil 2019, 458, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C. Fencing as an effective approach for restoration of alpine meadows: Evidence from nutrient limitation of soil microbes. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Herath, S.; Peng, X. Phosphorus addition increases microbial necromass by increasing N availability in China: A meta-analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 190, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.H.; Huang, C.B.; Wang, K.B.; Liu, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Hai, X.Y.; Shangguan, Z.P. Drivers of soil microbial metabolic limitation changes along a vegetation restoration gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zou, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, H.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X. Phosphorus Application Decreased Copper Concentration but Not Iron in Maize Grain. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Lin, J.; Jiang, L.; Huang, B.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M.-K.; Ge, H.; Huang, Y. Impacts of collapsing gullies on the dynamics of soil organic carbon in the red soil hilly region of southeast China. CATENA 2020, 190, 104547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-G.; Zhou, X.-B.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Cheng, X. Moss C, N, P and K stoichiometry and their relationships are related to soil nutrients and environment in a temperate desert of central Asia. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 16, rtac070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-j.; Li, Y.-g.; Zhou, X.-b.; Yin, B.-f.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.-m. Moss patch size as a factor profoundly influencing soil nutrient characteristics and multifunctionality of temperate desert in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Müller, T.; Lakshmanan, P.; Liu, Y.; Liang, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Soil phosphorus availability and fractionation in response to different phosphorus sources in alkaline and acid soils: A short-term incubation study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.K.; Porazinska, D.; Concienne, B.L.; Darcy, J.L.; King, A.J.; Nemergut, D.R. Biogeochemical Stoichiometry Reveals P and N Limitation Across the Post-glacial Landscape of Denali National Park, Alaska. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 1164–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhu, W.; Cui, D.; Mao, L.; Liao, J. Extension of the glmm.hp package to zero-inflated generalized linear mixed models and multiple regression. J. Plant Ecol. 2023, 16, rtad038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S.; Freckleton, R. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling inr for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 7, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Crowther, T.W.; Vinay, N.; Luo, Z.; Yu, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Nutrient limitation of soil organic carbon stocks under straw return. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, W.W.; Johnson, J.M.F.; Karlen, D.L.; Lightle, D.T. Corn Stover to Sustain Soil Organic Carbon Further Constrains Biomass Supply. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1665–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Xiu, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D. Soil bacterial community composition is altered more by soil nutrient availability than pH following long-term nutrient addition in a temperate steppe. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1455891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashian-Victoroff, C.; Yanai, R.D.; Horton, T.R.; Lamit, L.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus additions affect fruiting of ectomycorrhizal fungi in a temperate hardwood forest. Fungal Ecol. 2025, 73, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Sun, L.; Xia, Z.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yu, W. Phosphorus limitation regulates the responses of microbial carbon metabolism to long-term combined additions of nitrogen and phosphorus in a cropland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 200, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.; Cui, Y.; Sinsabaugh, R.; Schimel, J. Interpreting patterns of ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 180, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinger, C.; Rousk, J.; Sandén, H. Can enzymatic stoichiometry be used to determine growth-limiting nutrients for microorganisms?—A critical assessment in two subtropical soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklein, A.R.; Houlton, B.Z. Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol. 2011, 193, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Wen, Y.; Ma, J.; Macdonald, A.; Hill, P.W.; Chadwick, D.R.; Wu, L.; Jones, D.L. Long-term farmyard manure application affects soil organic phosphorus cycling: A combined metagenomic and 33P/14C labelling study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphorus mineralization can be driven by microbial need for carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, S.; Yu, G. Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailike, A.; Liang, Y.; Fu, R.; Hao, H.; Wang, R.; Peng, N.; Li, S.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, W.; et al. Impact of organic carbon composition on bacterial taxa assembly upon phosphorus addition in organic and mineral soil layers of a Robinia pseudoaccacia plantation. Pedosphere 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mentler, A.; Rosinger, C.; Wriessnig, K.; Bruhn, N.; Bernardini, L.G.; Bieber, M.; Huber, S.; Bodner, G. Labile not stable SOC fractions constitute the manageable drivers of soil health advances in carbon farming. Geoderma 2024, 449, 116991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Razavi, B.S.; Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Ge, T. C/P stoichiometry of dying rice root defines the spatial distribution and dynamics of enzyme activities in root-detritusphere. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Manzoni, S.; Moorhead, D.L.; Richter, A. Carbon use efficiency of microbial communities: Stoichiometry, methodology and modelling. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Massart, S. Nitrogen fertilization affected microbial carbon use efficiency and microbial resource limitations via root exudates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 174933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, R.J.; Mokolobate, M.S. Amelioration of Al toxicity and P deficiency in acid soils by additions of organic residues: A critical review of the phenomenon and the mechanisms involved. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 59, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Trofymow, J.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Porporato, A. Stoichiometric controls on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing litter. Ecol. Monogr. 2010, 80, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, E.; Condron, L.M.; Oberson, A.; Sinaj, S.; Fardeau, J.C. Processes Governing Phosphorus Availability in Temperate Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

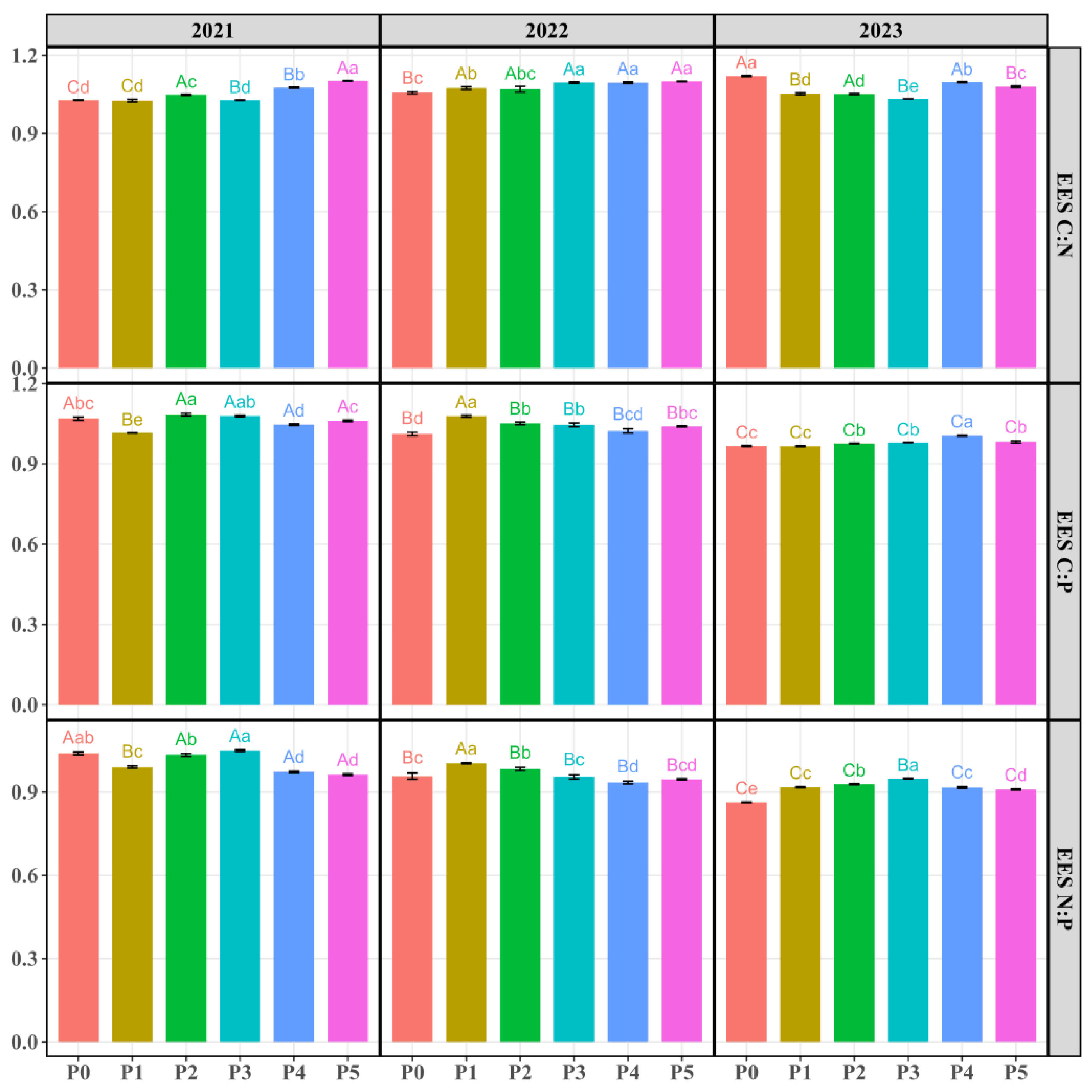
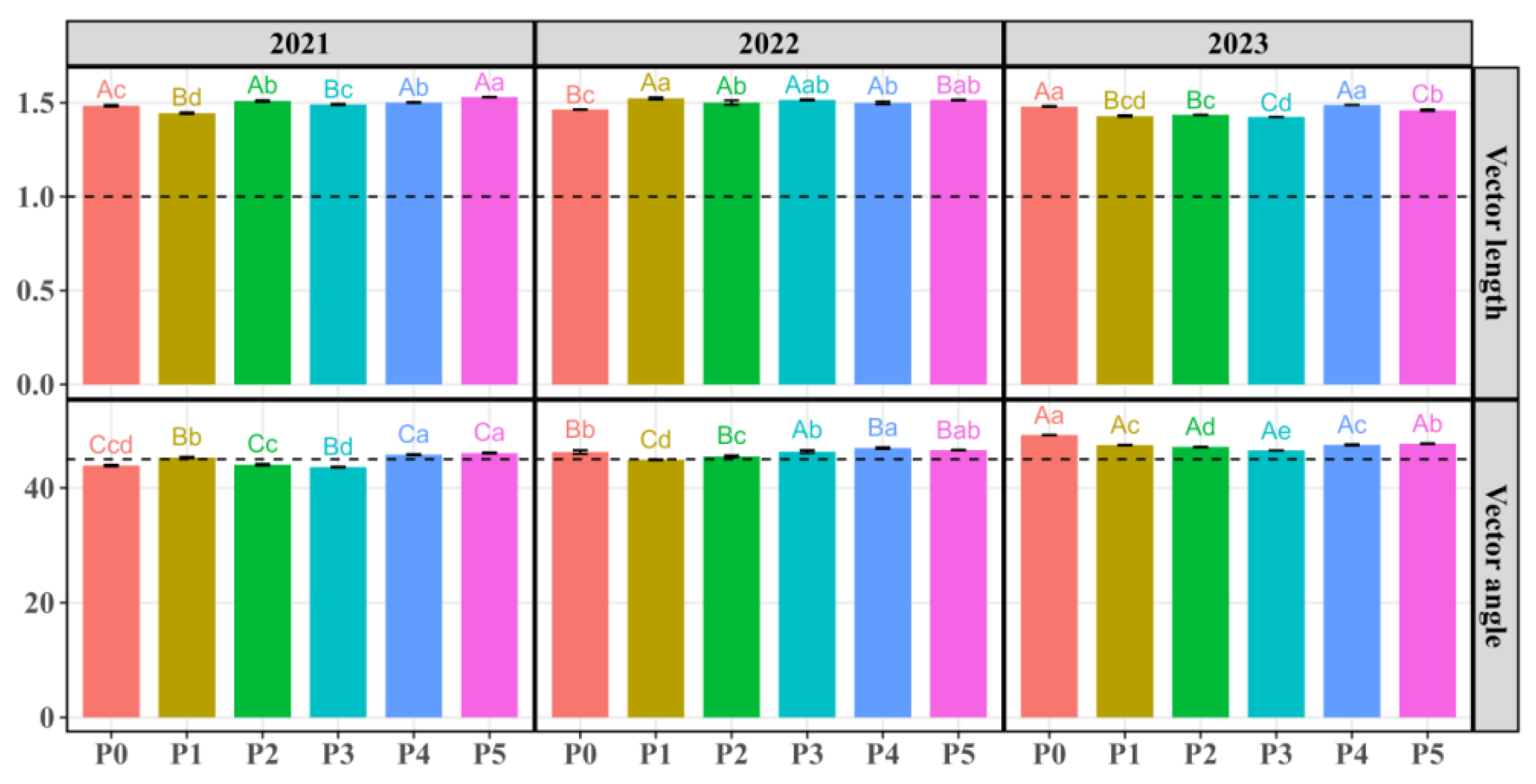
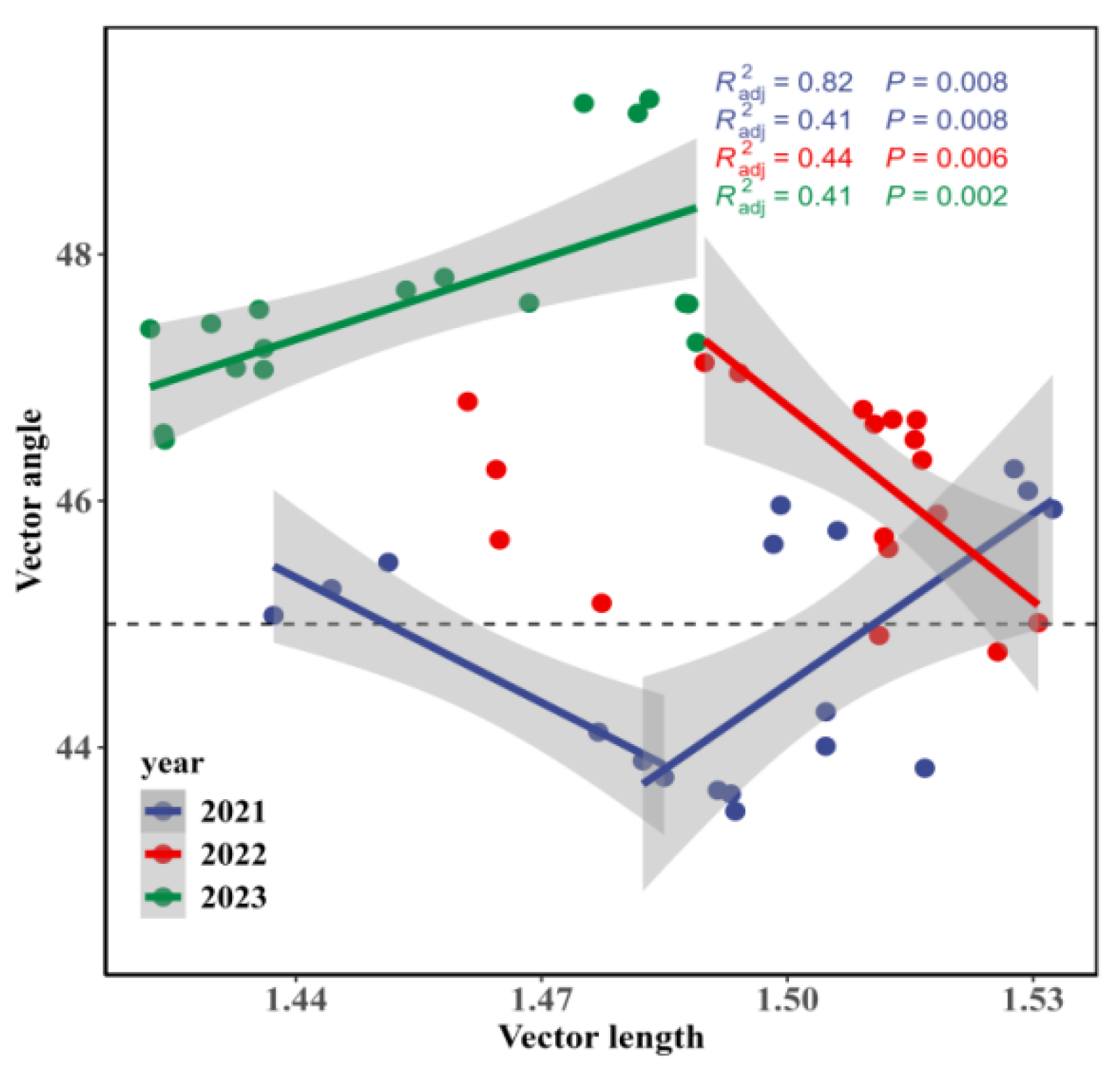
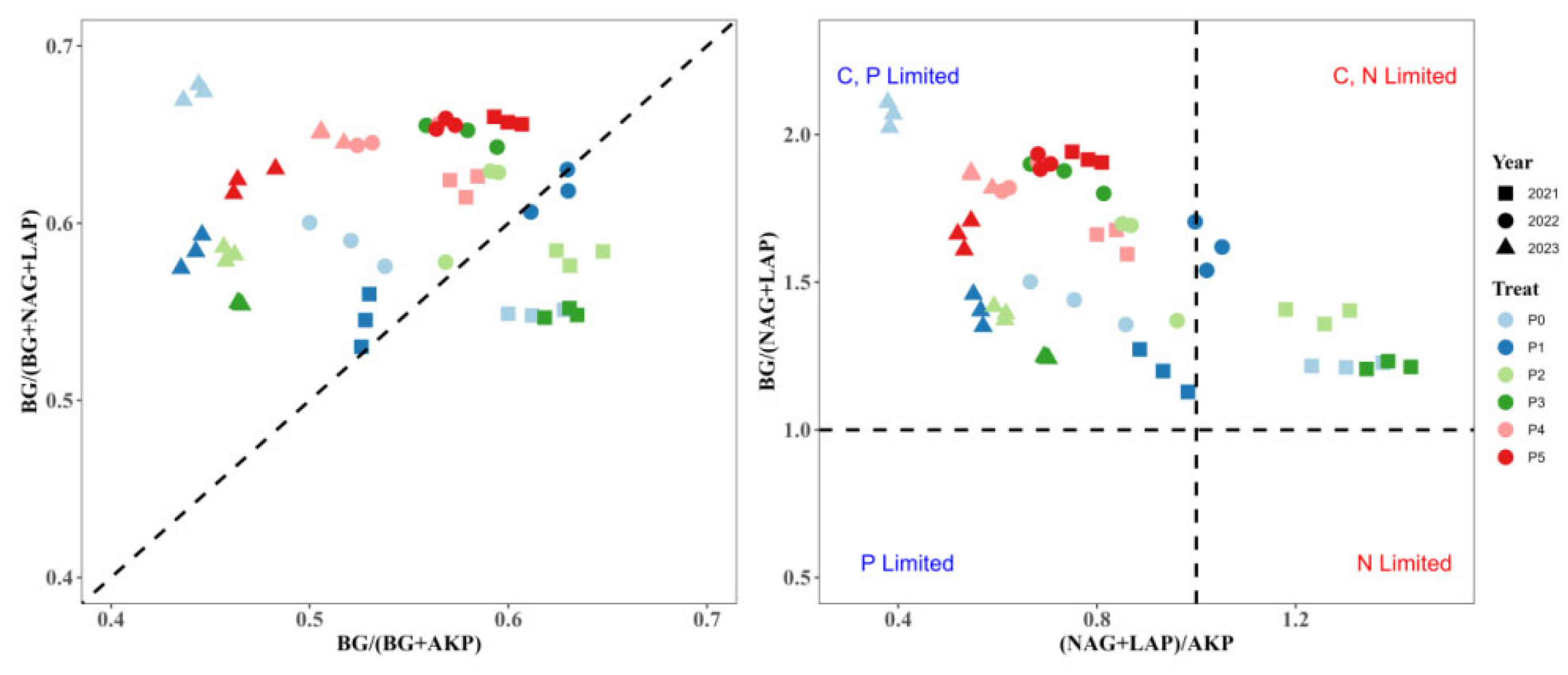

| Year | P Addition | Year × P Addition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| BG | 393.149 | <0.001 | 45.405 | <0.001 | 40.857 | <0.001 |
| NAG | 261.681 | <0.001 | 154.309 | <0.001 | 90.466 | <0.001 |
| LAP | 2428.113 | <0.001 | 435.115 | <0.001 | 152.35 | <0.001 |
| AKP | 281.441 | <0.001 | 12.795 | <0.001 | 36.115 | <0.001 |
| EEA C:N | 103.565 | <0.001 | 76.405 | <0.001 | 45.428 | <0.001 |
| EEA C:P | 636.292 | <0.001 | 12.364 | <0.001 | 35.017 | <0.001 |
| EEA N:P | 660.401 | <0.001 | 58.581 | <0.001 | 41.482 | <0.001 |
| Vector length | 222.292 | <0.001 | 29.275 | <0.001 | 39.138 | <0.001 |
| Vector angle | 670.689 | <0.001 | 58.82 | <0.001 | 41.858 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Y. Phosphate Fertilizer Effects on Microbial Resource Limitations in Wheat Cropland: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Agronomy 2025, 15, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030731
Li Y, Cheng Y, Wang F, Liu X, Huang W, Shen C, Zhang Y. Phosphate Fertilizer Effects on Microbial Resource Limitations in Wheat Cropland: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030731
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yonggang, Yanan Cheng, Fei Wang, Xing Liu, Wenwen Huang, Changwei Shen, and Ying Zhang. 2025. "Phosphate Fertilizer Effects on Microbial Resource Limitations in Wheat Cropland: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030731
APA StyleLi, Y., Cheng, Y., Wang, F., Liu, X., Huang, W., Shen, C., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Phosphate Fertilizer Effects on Microbial Resource Limitations in Wheat Cropland: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Agronomy, 15(3), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030731






