Treated Wastewater Affects the Fertility and Geochemistry of Degraded Soil in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
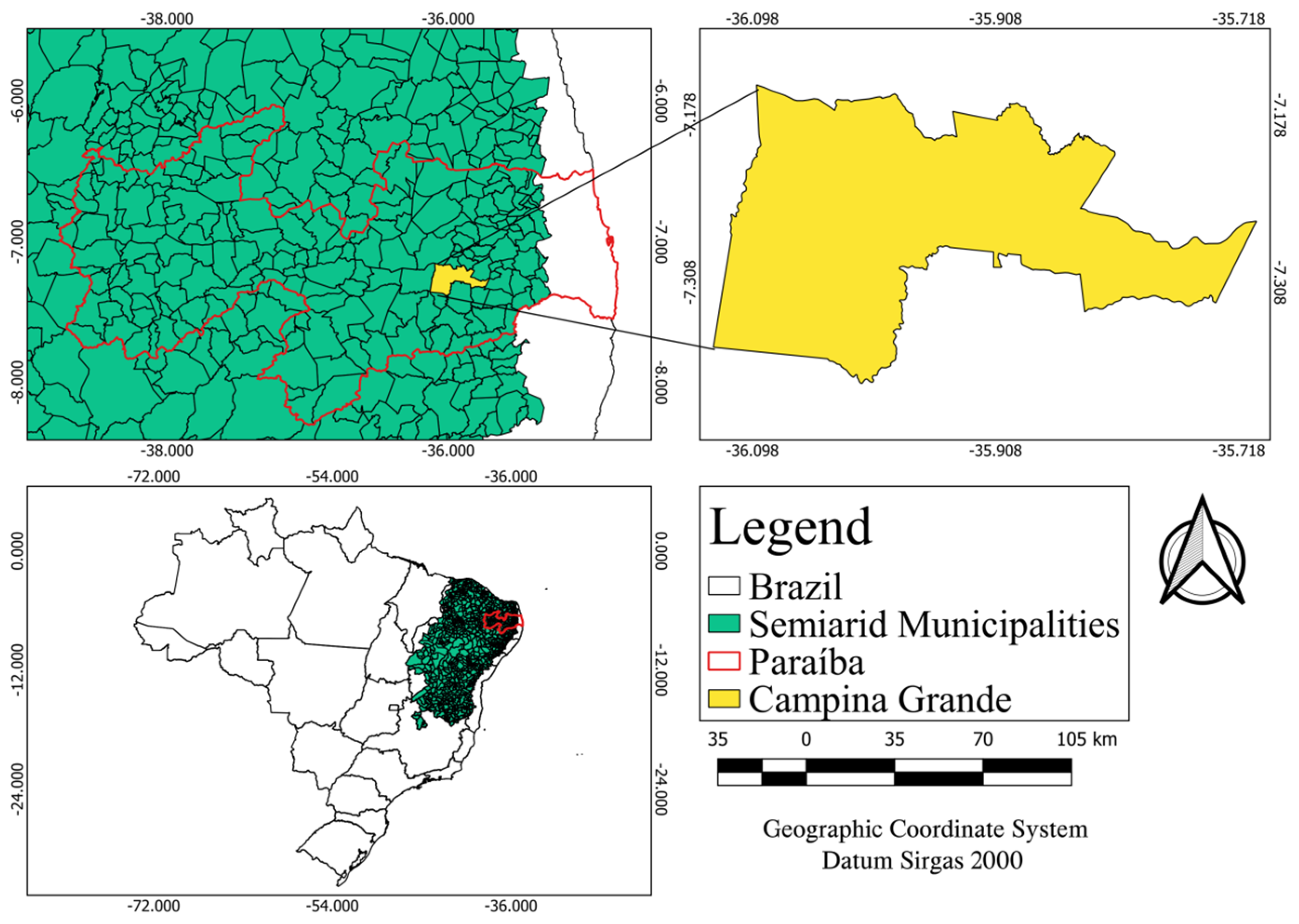
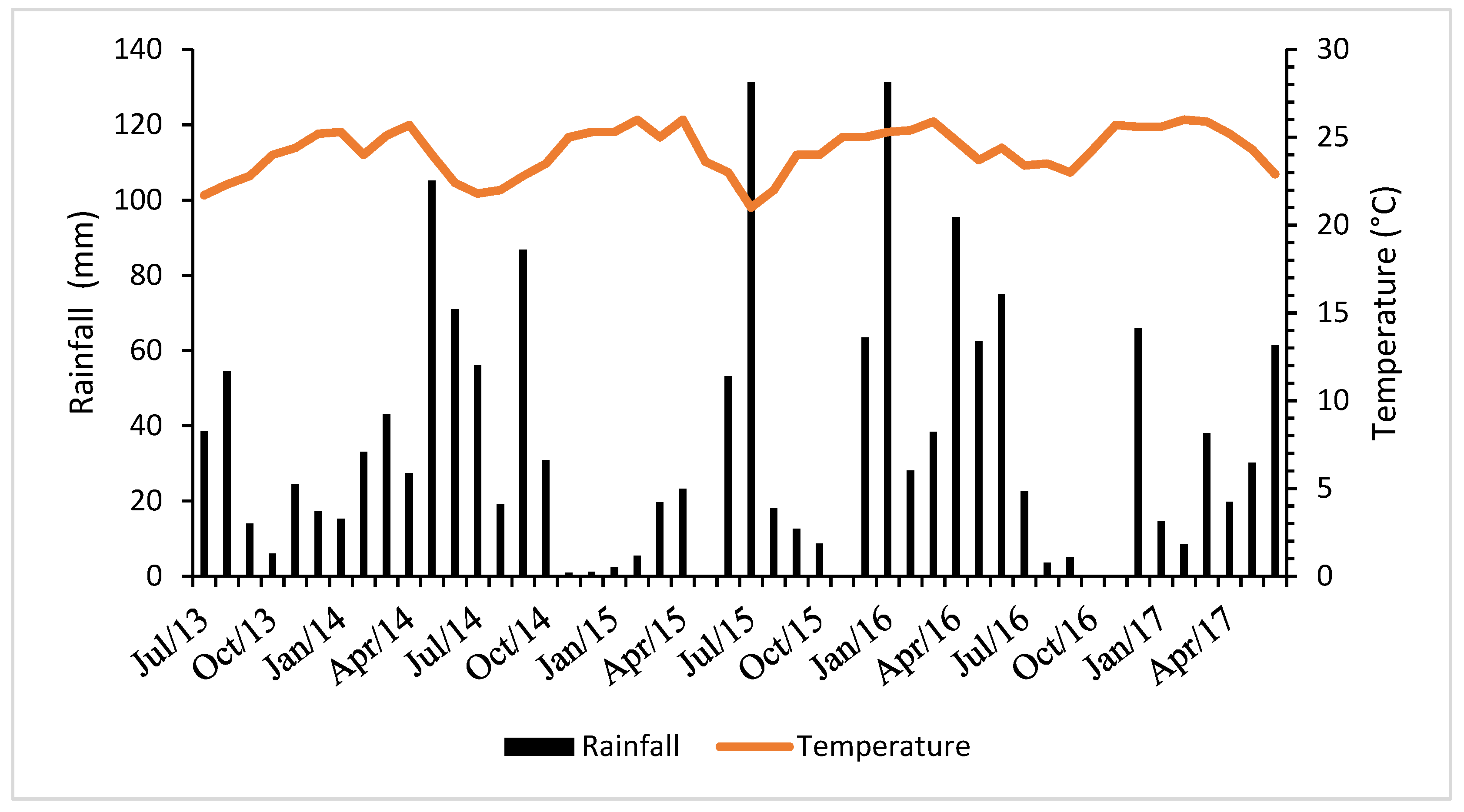
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Soil Characterization
2.3. Experimental Description
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.5. X-Ray Fluorescence
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Attributes
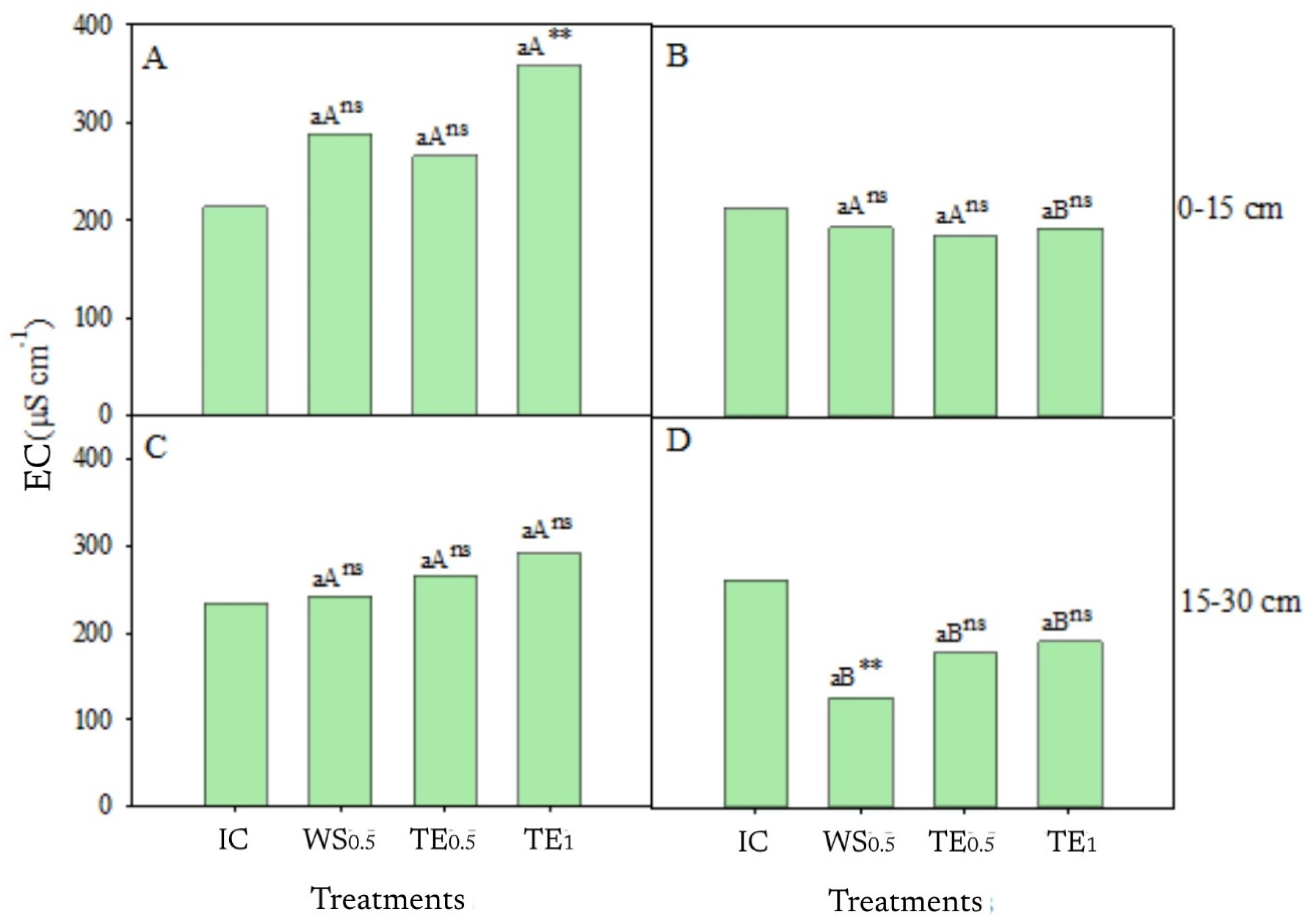
3.2. Electrical Conductivity and Na+ in the Exchange Complex
3.3. Soil Geochemistry
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Treated Wastewater on Soil Chemical Attributes
4.2. Soil Salinity and Sodicity
4.3. Tretated Wastewater and the Geochemical Environment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eni, I. Effects of land degradation on soil fertility: A case study of Calabar South, Nigeria. In Environmental Land Use Planning; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasella, J.; Vieira, R.M.S.P.; Barbosa, A.A.; Rodriguez, D.A.; Santana, M.d.O.; Sestini, M.F. Desertification trends in the Northeast of Brazil over the period 2000–2016. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, H.F.P.; Canassa, N.F.; Machado, C.C.C.; Tabarelli, M. Human disturbance is the major driver of vegetation changes in the Caatinga dry forest region. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.F.; Rodrigues, R.Z.d.S.; Heiskanen, J.; Abera, T.A.; Gasparetto, S.C.; Biase, A.G.; Ballester, M.V.R.; de Moura, Y.M.; Piedade, S.M.d.S.; Silva, A.K.d.O.; et al. Evaluating the temporal patterns of land use and precipitation under desertification in the semi-arid region of Brazil. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refati, D.C.; da Silva, J.L.B.; Macedo, R.S.; Lima, R.d.C.C.; da Silva, M.V.; Pandorfi, H.; Silva, P.C.; de Oliveira-Júnior, J.F. Influence of drought and anthropogenic pressures on land use and land cover change in the brazilian semiarid region. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 126, 104362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H. Understanding the rapid increase in drought stress and its connections with climate desertification since the early 1990s over the Brazilian semi-arid region. J. Arid Environ. 2024, 222, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Mohammadi, A.; Hejna, A.; Majtacz, J.; Esmaeili, A.; Habibzadeh, S.; Saeb, M.R.; Badawi, M.; Lima, E.C.; Mąkinia, J. Wastewater reuse in agriculture: Prospects and challenges. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalasmeh, A.A.; Alghzawi, M.Z.; Gharaibeh, M.A.; Mohawesh, O. Assessment of the effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil properties and on the performance of infiltration models. Water 2022, 14, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, R.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Hai, C.; Xie, Y. Assessment of the quality indices of soils irrigated by groundwater in a typical semi-arid steppe ecoregion. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Jain, A.; Kolton, M.; Pathak, A. Impacts of long-term irrigation of municipally-treated wastewater to the soil microbial and nutrient properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 959, 178143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M. Use of treated sewage or wastewater as an irrigation water for agricultural purposes- Environmental, health, and economic impacts. Total Environ. Res. Themes 2023, 6, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfanssi, S.; Ouazzani, N.; Mandi, L. Soil properties and agro-physiological responses of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) irrigated by treated domestic wastewater. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 202, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V.; Voicu, G. Water Scarcity and Wastewater Reuse in Crop Irrigation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Muscolo, A.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, W. Sustainable use and management of non-conventional water resources for rehabilitation of marginal lands in arid and semiarid environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael-Kordatou, I.; Michael, C.; Duan, X.; He, X.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Mills, M.A.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Dissolved effluent organic matter: Characteristics and potential implications in wastewater treatment and reuse applications. Water Res. 2015, 77, 213–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.L.; Souza, R.F.D.S.; Fraga, V.d.S.; Medeiros, S.d.S. Effects of Treated Wastewater on Soil Recovery in Degraded Semiarid Region. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2019, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametov, A.; Kondrashev, S.; Zvyagin, G.; Spitsov, D. Treated livestock wastewater influence on soil quality and possibilities of crop irrigation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2766–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoude, L.A.; Kamaleddine, F.; Said, R.B.; Mohtar, R.H.; Dbaibo, R.; Yanni, S.F. Treated wastewater reuse and its impact on soil properties and potato and corn growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 958, 178130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtouh, J.; Mohtar, R.; Assi, A.; Schwab, P.; Jantrania, A.; Deng, Y.; Munster, C. Impact of brackish groundwater and treated wastewater on soil chemical and mineralogical properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.C.P.D.; Gloaguen, T.V.; Gonçalves, R.A.B.; Santos, D.L.; Couto, C.F. Soil chemistry after irrigation with treated wastewater in semiarid climate. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2016, 40, e0140664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qadir, M.; Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Jiménez, B.; Siebe, C.; Siemens, J.; Hanjra, M.A. Environmental risks and cost-effective risk management in wastewater usesystems. In Wastewater: EconomicAsset in an Urbanizing World; Drechsel, P., Qadir, M., Wichelns, D., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Oubane, M.; Khadra, A.; Ezzari, A.; Kouisni, L.; Hafidi, M. Heavy metal accumulation and genotoxic effect of long-term wastewater irrigated peri-urban agricultural soils in semiarid climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickin, S.K.; Schuster-Wallace, C.J.; Qadir, M.; Pizzacalla, K. A review of health risks and pathways for exposure to wastewater use in agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoemena, K.I.; Rowshon, K.M.D.; Binti, C.M.H. Advances in utilization of wastewater in agricultural practice: A technical note. Irrig. Drainage 2020, 69, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgallal, M.; Fletcher, L.; Evans, B. Assessment of potential risks associated with chemicals in wastewater used for irrigation in arid and semiarid zones: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, K.K.; Soni, R.; Jamal, Q.M.S.; Tripathi, P.; Lal, J.A.; Jha, N.K.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, V.; Ruokolainen, J. Wastewater treatment and reuse: A review of its applications and health implications. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.; Ferreira-Neto, M.; Fernandes, C.S.; Dias, N.S.; Medeiros, J.F.; Brito, R.F.; Silva Sá, F.V. The effect of domestic sewage effluent and planting density on growth and yield of prickly pear cactus in the semiarid region of Brazil. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 185, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, F.O.; Vasconcelos, E.S.A.G.; Macedo, R.S.; Moro, L.; Araujo Neto, R.N.; Lira, E.C.; Bakker, A.P.; Araujo, J.S. Agricultural reuse on soil fertility at different times of year in semiarid region, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Gestão Ambient. Sustentabilidade 2023, 10, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.A.; Montenegro, A.A.A.; Lima, J.L.M.P.; Silva, T.G.F.; Pedrosa, E.M.R.; Almeida, T.A.B. Coupling water resources and agricultural practices for Sorghum in a semiarid environment. Water 2021, 13, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto, A.N.; Nascimento, J.J.V.R.; Medeiros, E.P. Changes in chemical attributes of a Fluvent cultivated with castor bean and irrigated with wastewater. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambiental. 2013, 17, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, S.; Churchman, J.; Rengasamy, P. Possible effects of irrigation with wastewater on the clay mineralogy of some Australian clayey soils: Laboratory study. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchouna, L.; Merdy, P.; Raynaud, M.; Pfeifer, H.; Lucas, Y. Effects of long-term irrigation with treated wastewater. Part I: Evolution of soil physico-chemical properties. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Samadi, A. Soil quality response to long-term wastewater irrigation in inceptisols from a semi-arid environment. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 91, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oort, F.; Thiry, M.; Foy, E.; Fujisaki, K.; Delarue, G.; Dairon, R.; Jongmans, T. Impacts of one century of wastewater discharge on soil transformation through ferrolysis and related metal pollutant distributions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.D.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrão, B.A.; Morais, F.D.; Mascarenhas, J.D.C.; Miranda, J.L.F.D.; Souza Junior, L.C.D.; Mendes, V.A. Projeto Cadastro de Fontes de Abastecimento por Água Subterrânea, Estado de Paraíba: Diagnóstico do Município de Campina Grande; CPRM: Recife, Brasil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- CPRM—Serviço Geológico do Brasil. Geologia e Recursos Minerais do Estado da Paraíba, 1st ed.; Santos, E.D., Ferreira, C.A., Silva, J.M.F., Jr., Eds.; CPRM: Recife, Brasil, 2002; 234p. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, M.C.C.; Queiroz, S.B. Reclassificação dos perfis descritos no Levantamento Exploratório-Reconhecimento de solos do estado da Paraíba. Rev. Biol. Ciências Terra 2006, 6, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jacomine, P.K.T.; Ribeiro, M.R.; Montenegro, J.O.; Silva, A.P.; Melo Filho, H.F.R. Levantamento Exploratório e de Reconhecimento dos Solos do Estado da Paraíba; Boletins DPFS-EPE-MA, 15—Pedologia, 8; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base For Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System For Naming Soils And Creating Legends For Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022; 234p. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Donagemma, G.K.; Fontana, A.; Teixeira, W.G. Manual of Soil Analysis Methods, 3rd ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brasil, 2017; 573p. [Google Scholar]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.D.; Santos, H.G.; Ker, J.C.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Shimizu, S.H. Manual de Descrição e Coleta de Solo No Campo, 7th ed.; Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo: Viçosa, Brasil, 2015; 102p. [Google Scholar]
- Yeomans, J.C.; Bremner, J.M. A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1988, 19, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis: A Advanced Course, 2nd ed.; UW-Madison Libraries Parallel Press: Madison, WI, USA, 2005; 930p. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, D.F. SISVAR: Um programa para análises e ensino de estatística. Rev. Symp. 2008, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Alvares, V.V.H.; Novaes, R.F.; Barros, N.F.; Cantarutti, R.B.E.; Lopes, A.S. Interpretação dos resultados das análises de solos. In Recomendação Para o Uso de Corretivos e Fertilizantes em Minas Gerais; Ribeiro, A.C., Guimarães, P.T.G., Alvarez, V.H., Eds.; Comissão de Fertilidade do Solo do Estado de Minas Gerais: Viçosa, Brasil, 1999; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, H.G.; Jacomine, P.K.T.; Anjos, L.H.C.; Oliveira, V.A.; Lumbreras, J.F.; Coelho, M.R.; Almeida, J.A.; Araújo Filho, J.C.; Oliveira, J.B.; Cunha, T.J.F. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos, 5th ed.; Revista e Ampliada; Embrapa: Brasília, Brasil, 2018; pp. 1–590. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, J.C.; Tomazi, M. Sistema Radicular de Plantas e Qualidade do Solo; Agropecuária Oeste-Comunicado Técnico (INFOTECA-E); Embrapa: Brasília, Brasil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Poustie, A.; Yang, Y.; Verburg, P.; Pagilla, K.; Hanigan, D. Reclaimed wastewater as a viable water source for agricultural irrigation: A review of food crop growth inhibition and promotion in the context of environmental change. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro Junior, C.R.; Pereira, M.G.; Filho, J.d.S.O.; Beutler, S.J. Can topography affect the restoration of soil properties after deforestation in a semiarid ecosystem? J. Arid Environ. 2019, 162, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Arif, M.S.; Yasmeen, T.; Riaz, M.; Rizwan, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Ali, S.; Riaz, M.A.; Sarosh, M. Seasonal variations of soil phosphorus and associated fertility indicators in wastewater-irrigated urban aridisol. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrover, M.; Moyà, G.; Vadell, J. Seasonal and depth variation of soil chemical and biological properties in alfalfa crops irrigated with treated wastewater and saline groundwater. Geoderma 2017, 286, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Ganjegunte, G.; Niu, G.; Ulery, A.; Flynn, R.; Enciso, J.M.; Meki, M.N.; Kiniry, J.R. Effects of treated urban wastewater irrigation on bioenergy sorghum and soil quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, K.; Schmidhalter, U. Characterisation of soil texture variability using the apparent soil electrical conductivity at a highly variable site. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 39, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, S.; Puskacova, A.; Ruzickova, I.; Wanner, J. Treated wastewater reuse for irrigation: Pros and cons. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Management and Rehabilitation of Saltaffected Soils. 2000. Available online: http://www.fao.org/AG/aGL/agll/spush/topic4.htm (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Queiroz, J.E.; Gonçalves, A.C.A.; Souto, J.S.; Folegatti, M.V. Avaliação e monitoramento da salinidade do solo. In Manejo Da Salinidade Na Agricultura: Estudo Básico e Aplicados; Gheyi, H.R., Dias, N.S., Lacerda, C.F., Eds.; INCT Sal: Fortaleza, Brasil, 2010; 472p. [Google Scholar]
- Muyen, Z.; Moore, G.A.; Wrigley, R.J. Soil salinity and sodicity effects of wastewater irrigation in South East Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Andiloro, S.; Tamburino, V.; Zimbone, S.M. Short-term effects of olive mill wastewater application on the hydrological and physico-chemical properties of a loamy soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedbabis, S.; Rouina, B.B.; Boukhris, M.; Ferrara, G. Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil chemical properties and infiltration rate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.E.S.; Santos, J.C.B.; Corrêa, M.M.; Nascimento, A.F.; Schulze, S.M.B.B.; Ferreira, T.O.; Araújo Filho, J.C.; Souza Júnior, V.S. Mineralogy and genesis of Planosols under a semi-arid climate, Borborema Plateau, NE Brazil. Catena 2020, 184, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.V.d.M.W.; de Sousa, J.E.S.; dos Santos, J.C.B.; Filho, J.C.d.A.; Corrêa, M.M.; Sousa, M.G.; Fracetto, F.J.C.; Fracetto, G.G.M.; Araujo, J.K.S.; Freire, G.A.P.; et al. Weathering of gneiss saprolites and formation under semiarid climate (NE Brazil). J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 123, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, E.R.G.; Santos, J.C.B.; Araújo Filho, J.C.; Schulze, S.M.B.B.; Corrêa, M.M.; Ferreira, T.O.; Sousa, J.E.S.; Souza Júnior, V.S. Parent rock–pedogenesis relationship: How the weathering of metamorphic rocks influences the genesis of Planosols and Luvisols under a semiarid climate in NE Brazil. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.B.; Oliveira, C.S.; Le Pera, E.; Sartor, L.R.; Corrêa, M.M.; Silva, A.H.N.; Muller, C.R.; Santos, R.A.; Azevedo, A.C. Saprolithology applied to pedology: Integrated study of soil and saprolite derived from crystalline rocks to better understand properties of whole regoliths along a climate gradient (NE Brazil). Geoderma 2022, 409, 115602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, S.L.R.; Donato, P.E.R.; Silva, J.A.; Rodrigues, M.G.V. Diagnóstico nutricional e recomendação de adubação para a cactus pear ‘Gigante’. Inf. Agropecuário 2017, 38, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.C.B.; Le Pera, E.; Oliveira, C.S.; Souza Júnior, V.S.; Pedron, F.A.; Corrêa, M.M.; Azevedo, A.C. Impact of weathering on REE distribution in soil-saprolite profiles developed on orthogneisses in Borborema Province, NE Brazil. Geoderma 2019, 347, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.B.; Le Pera, E.; Souza Júnior, V.S.; Corrêa, M.M.; Azevedo, A.C. Gneiss saprolite weathering and soil genesis along an east-west regolith sequence (NE Brazil). Catena 2017, 150, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bétard, F.; Caner, L.; Gunnell, Y.; Bourgeon, G. Illite neoformation in plagioclase during weathering: Evidence from semi-arid Northeast Brazil. Geoderma 2009, 152, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.A.; Paquet, H.; Begonha, A. Weathering of granites in a temperate climate (NW Portugal): Granitic saprolites and arenization. Catena 2002, 49, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, W.R.; Romero, R.E.; Souza Júnior, V.S.; Cooper, M.; Sartor, L.R.; Partiti, C.S.M.; Jorge, F.O.; Cohen, R.; Jesus, S.L.; Ferreira, T.O. Effects of slope orientation on pedogenesis of altimontane soils from the Brazilian semi-arid region (Baturité massif, Ceará). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3731–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Samadi, A.; Khoda Verdiloo, H. Impact of long-term wastewater irrigation on variability of soil attributes along a landscape in semi-arid region of Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Felix, V.J. Recuperação de Solo Degradado Utilizando Água Residuária Tratada em Sistema Agroflorestal No Semiárido; Tese (2023); PPG em Ciência do Solo; Universidade Federal da Paraíba: Areia, Brasil, 2023; 89p. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Unit | Water | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply | Residual | ||
| pH | - | 7.5 | 8.3 |
| EC | dS m−1 | 0.79 | 1.35 |
| TOC | mg L−1 | 1.72 | 3.7 |
| N | mg L−1 | 0.28 | 26.3 |
| NH4+ | mg L−1 | - | 22.3 |
| NO3− | mg L−1 | - | 4.5 |
| P | mg L−1 | 1.68 | 14 |
| PO43− | mg L−1 | - | 9.4 |
| K+ | mg L−1 | 5.4 | 27.6 |
| Ca2+ | mg L−1 | 11.2 | 24.5 |
| Mg2+ | mg L−1 | 6.4 | 10.7 |
| SO43− | mg L−1 | - | 51.9 |
| Na+ | mg L−1 | 9.1 | 22.3 |
| Cl− | mg L−1 | 178 | 270 |
| Trea. | pH 1:2.5 | C | P | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | Al3+ | H+Al | EB | CEC | ECEC | BS | AS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ---------------------------------------------------cmolc kg−1------------------------------------------------------- | --------%------ | ||||||||||
| Initial condition | ||||||||||||||
| 0–15 | 6.07 | 7.6 | 8.14 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 3.29 | 0.74 | 4.0 | 0.84 | 19.05 | 12.45 |
| 15–30 | 6.37 | 5.3 | 4.07 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 2.87 | 0.64 | 3.5 | 0.74 | 18.60 | 16.04 |
| After two years of irrigation | ||||||||||||||
| 0–15 cm soil layer | ||||||||||||||
| WS0.5 | 5.94 aA ns | 9.4 aA ns | 6.3 aA ns | 2.84 aA ** | 1.11 aA ns | 0.52 aA * | 0.08 aA ** | 0.11 aA ns | 2.45 aA ** | 4.55 aA ** | 7.00 aA ** | 4.66 aA ** | 66 bA ** | 2.51 aB ** |
| TE0.5 | 5.85 aA ns | 9.7 aA ns | 6.8 aA ns | 2.87 aA ** | 1.59 aA * | 0.52 aA * | 0.09 aA ** | 0.11 aA ns | 2.93 aA ** | 4.56 aA ** | 7.20 aA ** | 4.67 aA ** | 61 bA ** | 2.58 aA ** |
| TE1 | 6.02 aA ns | 10.9 aA ns | 9.5 aA ns | 2.88 aA ** | 2.13 aA ** | 0.92 aA ** | 0.11 aA ** | 0.10 aB ns | 2.32 aA ** | 6.04 aA ** | 8.36 aA ** | 6.14 aA ** | 71 aA ** | 1.78 aB ** |
| 15–30 cm soil layer | ||||||||||||||
| WS0.5 | 5.89 aA * | 8.1 aA ns | 7.2 aA * | 3.03 aA ** | 1.05 aA ns | 0.56 aA ns | 0.12 aA ** | 0.10 aA ns | 2.48 aA ** | 4.76 aA ** | 7.24 aA ** | 4.86 aA ** | 68 abA ** | 2.19 aA ** |
| TE0.5 | 5.79 aA * | 11.5 aA * | 6.2 aA ns | 2.74 aA ** | 1.40 aA * | 0.77 aA ** | 0.11 aA ** | 0.13 aA ns | 3.23 aA ns | 4.61 aA ** | 7.84 aA ** | 4.75 aA ** | 58 bA ** | 3.26 aA ** |
| TE1 | 5.89 aA * | 10.3 aA ns | 7.4 aA * | 3.14 aA ** | 2.00 aA ** | 0.82 aA ** | 0.12 aA ** | 0.10 aA ns | 2.08 aA ** | 6.08 aA ** | 8.16 aA ** | 6.18 aA ** | 73 aA ** | 1.83 aB ** |
| After two years the end of irrigation | ||||||||||||||
| 0–15 cm soil layer | ||||||||||||||
| WS0.5 | 5.72 aA ns | 7.9 aA ns | 7.9 aA ns | 1.62 aB ** | 1.06 aA ns | 0.37 aA ns | 0.10 aA ** | 0.14 aA ns | 3.05 aA ns | 3.12 aA ** | 6.17 aA * | 3.26 aA ** | 51 aB ** | 5.26 aA ** |
| TE0.5 | 5.62 aA * | 10.9 aA ns | 8.1 aA ns | 1.70 aB ** | 1.05 aA ns | 0.40 aA ns | 0.09 aA ** | 0.13 aA ns | 3.29 aA ns | 3.24 aA ** | 6.53 aA ** | 3.37 aA ** | 50 aA ** | 4.45 aA ** |
| TE1 | 5.65 aA ns | 9.6 aA ns | 9.8 aA ns | 1.61 aB ** | 1.09 aA ns | 0.40 aB ns | 0.10 aA ** | 0.19 aA * | 3.23 aA ns | 3.20 aB ** | 6.43 aB * | 3.39 aB ** | 48 aB ** | 6.71 aA ** |
| 15–30 cm soil layer | ||||||||||||||
| WS0.5 | 6.02 aA ns | 5.7 aA ns | 2.5 aB ns | 1.36 aB ** | 1.66 aA * | 0.34 aA ns | 0.09 aA * | 0.10 aA ns | 2.29 aA ns | 3.45 aA ** | 5.74 aA * | 3.55 aA ** | 59 aA ** | 3.30 aA ** |
| TE0.5 | 6.03 aA ns | 7.1 aA ns | 4.0 aA ns | 1.29 aB ** | 1.21 aA ns | 0.55 aA * | 0.10 aA ** | 0.14 aA ns | 2.00 aB ns | 3.15 aA ** | 5.15 aB ns | 3.28 aB ** | 61 aA ** | 4.81 aA ** |
| TE1 | 6.08 aA ns | 6.2 aA ns | 3.1 aB ns | 1.39 aB ** | 1.61 aA * | 0.60 aA * | 0.11 aA ** | 0.13 aA ns | 2.38 aA ns | 3.71 aB ** | 6.09 aB ** | 3.84 aB ** | 57 aB ** | 5.00 aA ** |
| Treatment | Irrigation Depth | Ca | Mg | Na | K | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mm | ---------------------- kg ha−1 ---------------------- | |||||
| WS0.5 | 53 | 5.91 | 3.38 | 4.80 | 2.85 | 0.9 |
| TE0.5 | 53 | 12.94 | 5.65 | 11.77 | 14.57 | 7.39 |
| TE1 | 76 | 18.62 | 8.13 | 16.95 | 20.98 | 10.64 |
| Period | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Cl | SO3 | K2O | CaO | MnO | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| --------------------------------------%--------------------------------------- | |||||||||
| Sand | |||||||||
| IC | 70.99 | 18.93 | 3.21 | 2.81 | 1.73 | 1.48 | 0.54 | - | - |
| With Effluent | 72.33 | 17.60 | 3.67 | 2.53 | 1.32 | 1.45 | 0.52 | - | - |
| No Effluent | 71.99 | 18.51 | 1.81 | 3.17 | 2.18 | 1.47 | 0.47 | - | - |
| Silt | |||||||||
| IC | 65.96 | 16.55 | 6.59 | 1.10 | 0.89 | 2.54 | 1.13 | 0.11 | 3.10 |
| With Effluent | 29.17 | 17.56 | 5.11 | 2.90 | 3.97 | 5.47 | 4.40 | 0.18 | 20.00 |
| No Effluent | 53.07 | 17.14 | 6.38 | 2.14 | 1.92 | 3.99 | 2.30 | 0.12 | 6.00 |
| Clay | |||||||||
| IC | 42.46 | 32.54 | 8.76 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 1.63 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 7.40 |
| With Effluent | 42.72 | 29.86 | 7.44 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 1.90 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 7.00 |
| No Effluent | 47.81 | 18.37 | 20.06 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 6.39 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 2.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felix, V.J.L.; de Sousa Medeiros, S.; Macedo, R.S.; Sousa, C.d.S.; da Silva Souza, R.F.; da Silva Fraga, V.; Bakker, A.P.; Santos, R.V.d.; de Oliveira Dias, B.; Campos, M.C.C. Treated Wastewater Affects the Fertility and Geochemistry of Degraded Soil in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. Agronomy 2025, 15, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030721
Felix VJL, de Sousa Medeiros S, Macedo RS, Sousa CdS, da Silva Souza RF, da Silva Fraga V, Bakker AP, Santos RVd, de Oliveira Dias B, Campos MCC. Treated Wastewater Affects the Fertility and Geochemistry of Degraded Soil in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030721
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelix, Victor Junior Lima, Salomão de Sousa Medeiros, Rodrigo Santana Macedo, Cristiano dos Santos Sousa, Renato Francisco da Silva Souza, Vânia da Silva Fraga, Alexandre Pereira Bakker, Robson Vinício dos Santos, Bruno de Oliveira Dias, and Milton César Costa Campos. 2025. "Treated Wastewater Affects the Fertility and Geochemistry of Degraded Soil in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030721
APA StyleFelix, V. J. L., de Sousa Medeiros, S., Macedo, R. S., Sousa, C. d. S., da Silva Souza, R. F., da Silva Fraga, V., Bakker, A. P., Santos, R. V. d., de Oliveira Dias, B., & Campos, M. C. C. (2025). Treated Wastewater Affects the Fertility and Geochemistry of Degraded Soil in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region. Agronomy, 15(3), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030721








