YOLOv9s-Pear: A Lightweight YOLOv9s-Based Improved Model for Young Red Pear Small-Target Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
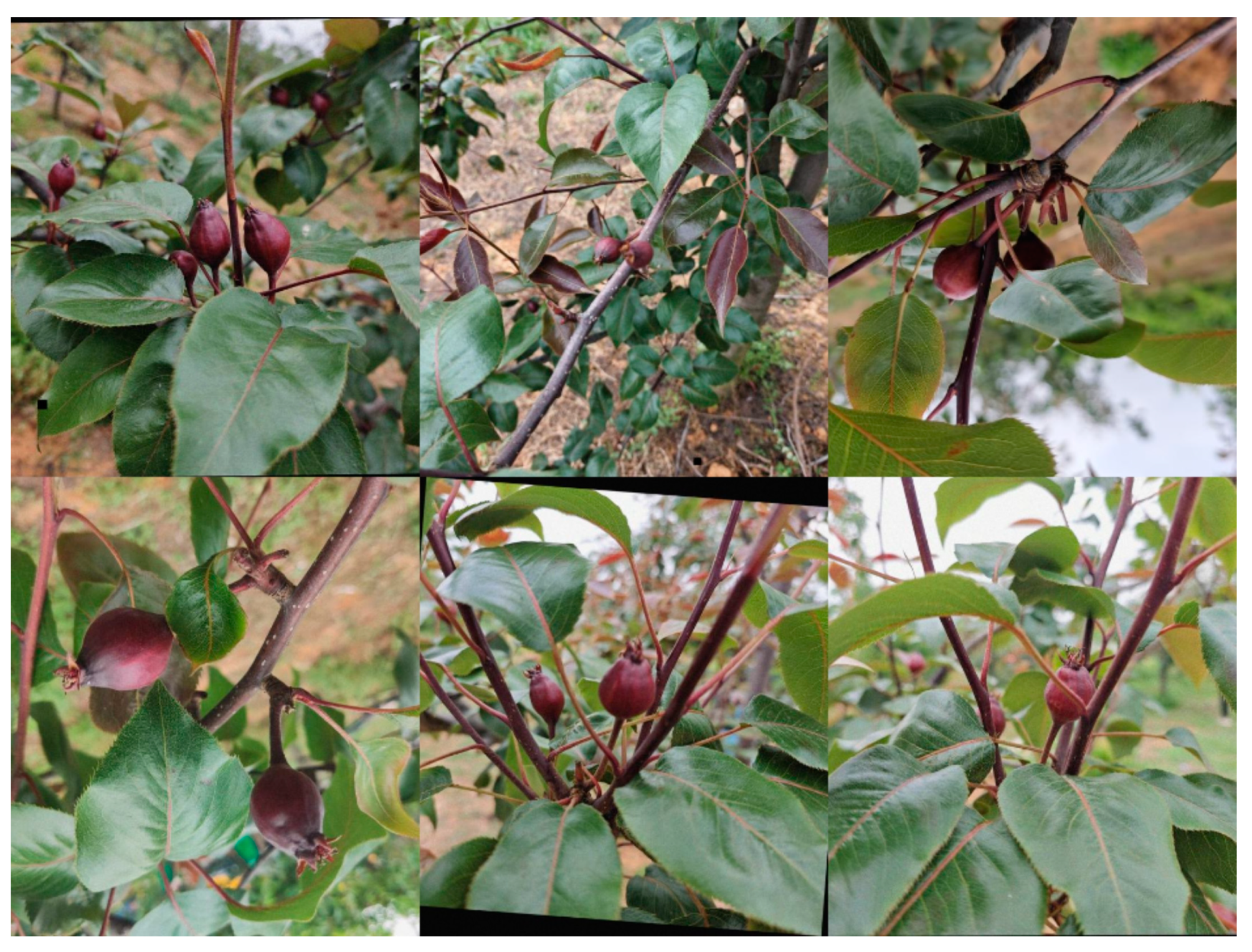
2.1. Dataset Construction
2.2. Construction of the Young Red Pear Recognition Model
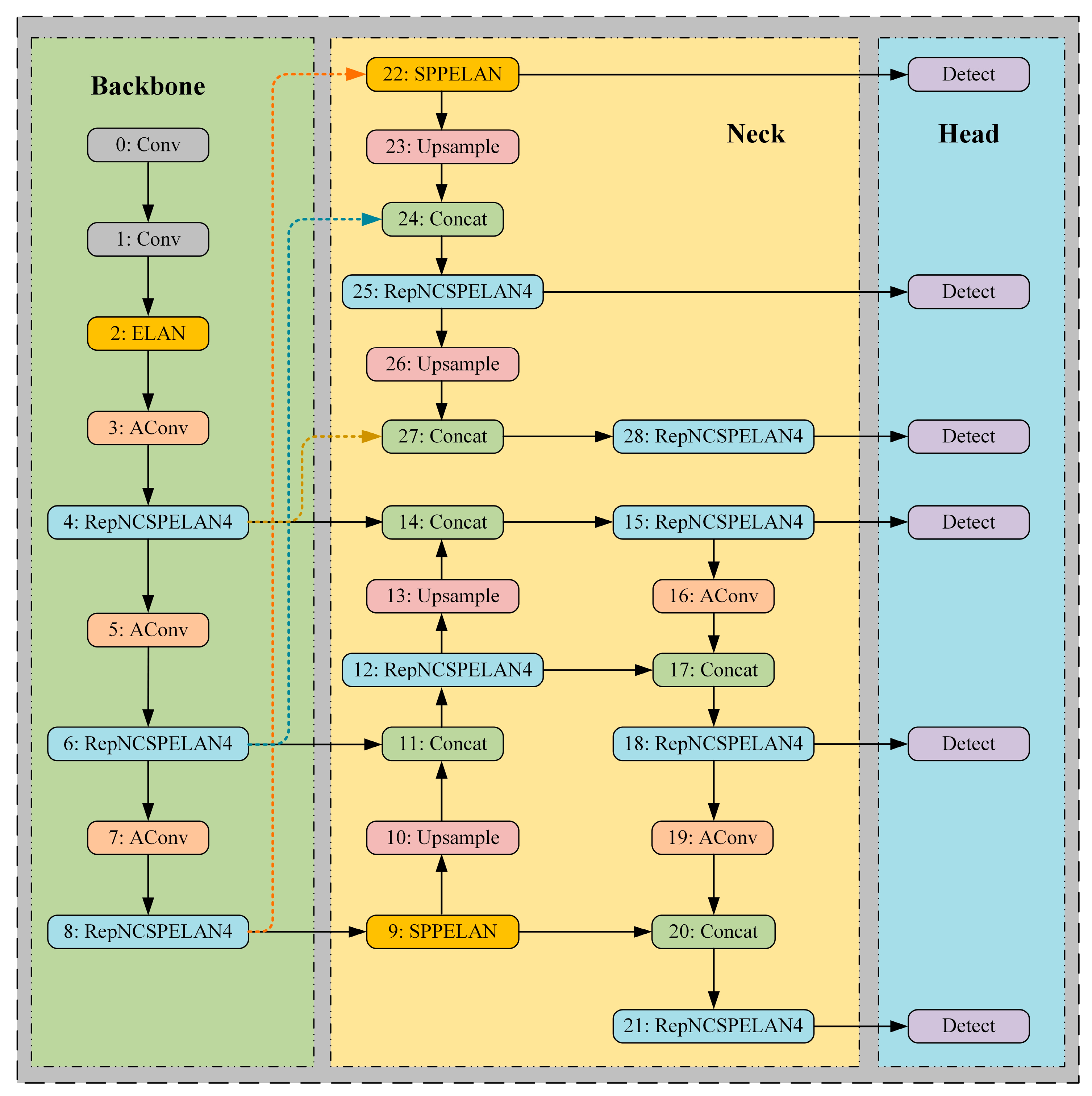
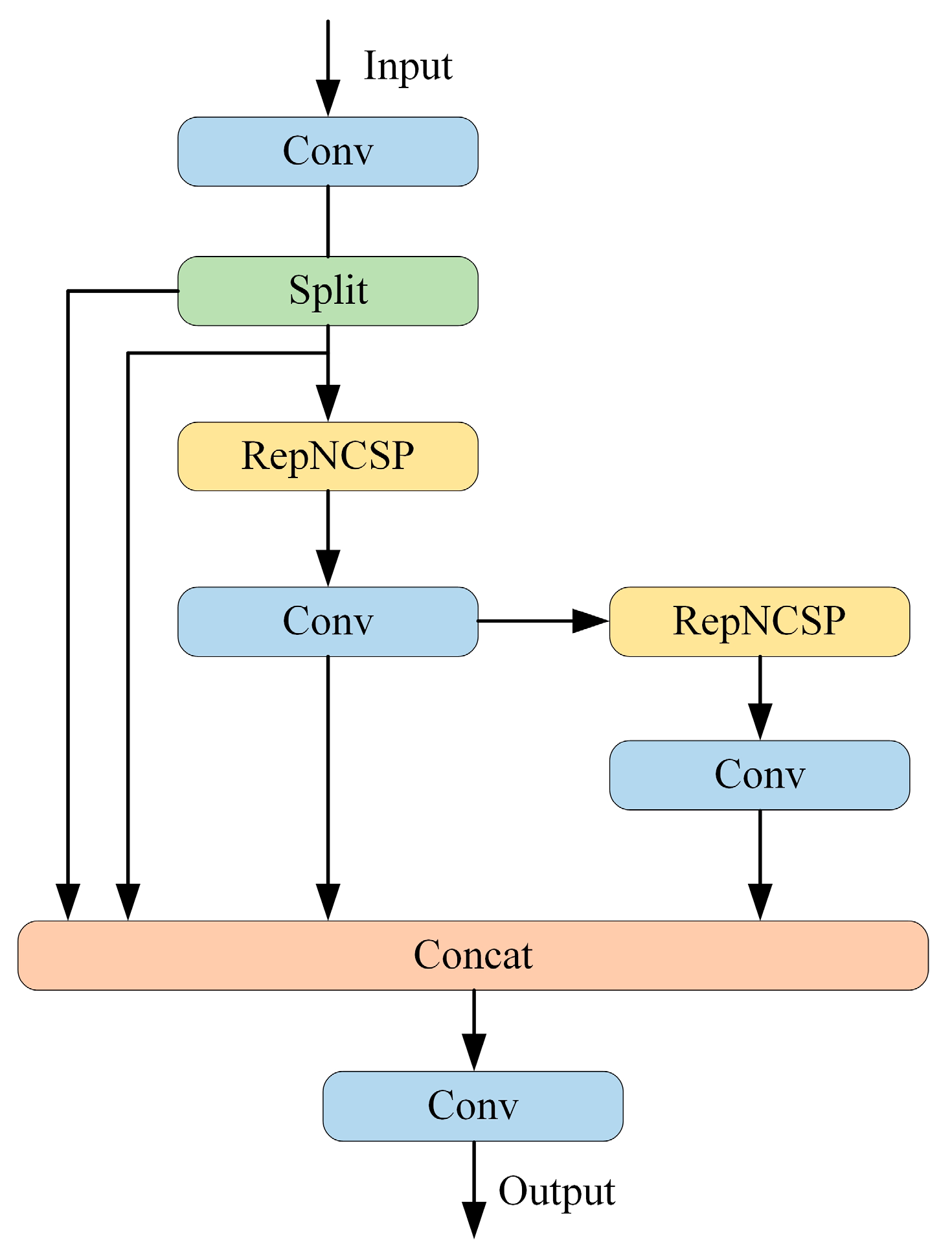
2.2.1. Analysis of the Original YOLOv9s Network Structure
2.2.2. Construction of the C2fUIBELAN4 Module
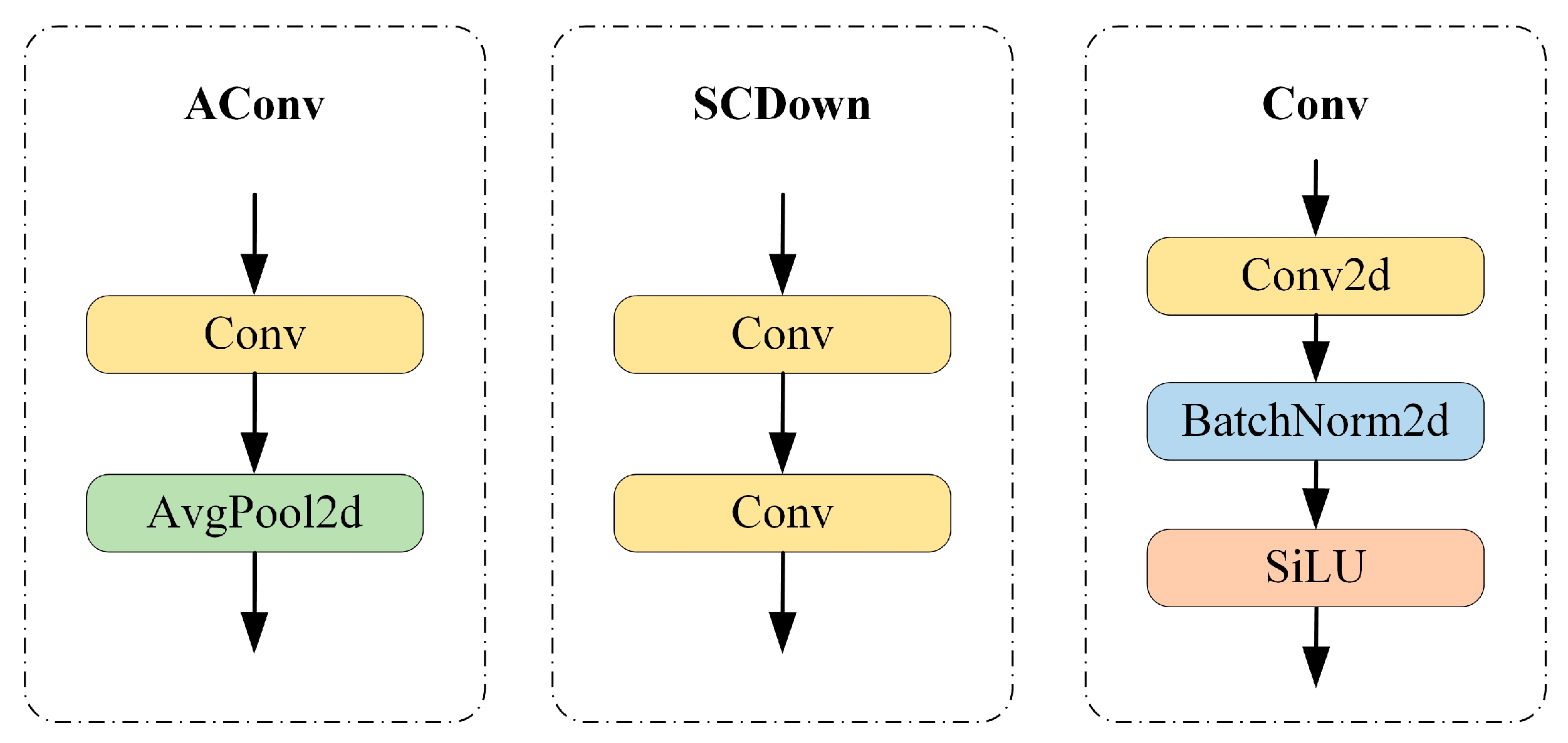
2.2.3. SCDown Module
2.2.4. Improvement of the Detection Head
2.2.5. Young Red Pear Recognition Model
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.2. Ablation Experiments
3.3. Comparison of Different Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The introduction of SCDown, C2FUIBELAN, and v10detect modules all contributed to improving the model’s detection performance, with the v10detect module having the most significant impact on accuracy improvement and the C2FUIBELAN module being the most effective in reducing the model’s parameter count and computational resource consumption.
- The combination of improvement strategies significantly enhanced the detection performance of the YOLOv9s model. When applying the SCDown, C2FUIBELAN, and v10detect modules together, the model’s performance further improved. The YOLOv9s-Pear model achieved P = 0.971, R = 0.970, mAP50 = 0.991, and mAP50-95 = 0.848.
- Compared to the SSD-ResNet18, RTDETR-ResNet18, YOLOv5s, YOLOv6s, YOLOv8s, and YOLOv9s models, the YOLOv9s-Pear model demonstrated superior performance, achieving higher precision while maintaining lower parameter counts and computational complexity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onishi, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kurita, H.; Fukao, T.; Arihara, H.; Iwai, A. An automated fruit harvesting robot by using deep learning. Robomech J. 2019, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, L.T.; Nguyen, P.T.; Di Sipio, C.; Di Ruscio, D. Automated fruit recognition using EfficientNet and MixNet. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 171, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gené-Mola, J.; Ferrer-Ferrer, M.; Gregorio, E.; Blok, P.M.; Hemming, J.; Morros, J.-R.; Rosell-Polo, J.R.; Vilaplana, V.; Ruiz-Hidalgo, J. Looking behind occlusions: A study on amodal segmentation for robust on-tree apple fruit size estimation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Qing, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; Yuwen, X.; Qu, M. YOLO-Peach: A High-Performance Lightweight YOLOv8s-Based Model for Accurate Recognition and Enumeration of Peach Seedling Fruits. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukunda, C.B.; Duque-Lazo, J.; González-Ferreiro, E.; Thaden, H.; Kleinn, C. Ensemble classification of individual Pinus crowns from multispectral satellite imagery and airborne LiDAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 65, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Song, H. Fusion of the YOLOv4 network model and visual attention mechanism to detect low-quality young apples in a complex environment. Precis. Agric. 2022, 23, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorj, U.-O.; Lee, M.; Yun, S.-S. An yield estimation in citrus orchards via fruit detection and counting using image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 140, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Fang, W.; Sun, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Li, G.; Li, R.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Q. A novel apple fruit detection and counting methodology based on deep learning and trunk tracking in modern orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacrés, J.; Viscaino, M.; Delpiano, J.; Vougioukas, S.; Cheein, F.A. Apple orchard production estimation using deep learning strategies: A comparison of tracking-by-detection algorithms. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 204, 107513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.R.; Jalal, A.S. Apple disease classification using color, texture and shape features from images. Signal Image Video Process. 2016, 10, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Fan, X.; Suo, X. Appearance quality classification method of Huangguan pear under complex background based on instance segmentation and semantic segmentation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 914829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, N.; Srinivasan, K.; Pravin Kumar, S.; Rukkumani, V.; Ramya, R. Fruit classification using traditional machine learning and deep learning approach. In Proceedings of the Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing: ICCVBIC 2019, Coimbatore, India, 25–26 September 2019; pp. 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Guo, W.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ninomiya, S. On plant detection of intact tomato fruits using image analysis and machine learning methods. Sensors 2014, 14, 12191–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archana, R.; Jeevaraj, P.E. Deep learning models for digital image processing: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargoti, S.; Underwood, J.P. Image segmentation for fruit detection and yield estimation in apple orchards. J. Field Robot. 2017, 34, 1039–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, V.K.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, B.; Mohan, S.; Khan, A.A. Detection of apple plant diseases using leaf images through convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 2022, 11, 6594–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, R.; Chen, N.; Yuan, H. A detection algorithm for cherry fruits based on the improved YOLO-v4 model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 13895–13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Yu, D.; Liu, S.; Shu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. A review of plant phenotypic image recognition technology based on deep learning. Electronics 2021, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Hu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, R. Fruit Target Detection Based on BCo-YOLOv5 Model. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 8457173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, S.; Ning, J. An improved YOLO algorithm for detecting flowers and fruits on strawberry seedlings. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 237, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzia, V.; Khaliq, A.; Salvetti, F.; Chiaberge, M. Real-time apple detection system using embedded systems with hardware accelerators: An edge AI application. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 9102–9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhou, W.; Na, L. High-precision object detection network for automate pear picking. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, J.L.; de Oliveira Neto, J.; Badue, C.; Oliveira-Santos, T.; de Souza, A.F. Yolo-papaya: A papaya fruit disease detector and classifier using cnns and convolutional block attention modules. Electronics 2023, 12, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, L.; Ruan, C.; Jia, W. FBoT-Net: Focal bottleneck transformer network for small green apple detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, B.; Xue, J. YOLO-P: An efficient method for pear fast detection in complex orchard picking environment. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1089454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Xia, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, F.; Yun, L. EL-YOLO: An efficient and lightweight low-altitude aerial objects detector for onboard applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 256, 124848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, S.A.; Castro, L.; Moreira, G.; Dos Santos, F.N.; Cunha, M.; Dias, J.; Moreira, A.P. Evaluating the single-shot multibox detector and YOLO deep learning models for the detection of tomatoes in a greenhouse. Sensors 2021, 21, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- An, R.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, G. GC-YOLOv9: Innovative smart city traffic monitoring solution. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 106, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X. MTP-YOLO: You only look once based maritime tiny person detector for emergency rescue. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.-T.; Mui, K.C.; Thien, N.N.; Tien, P.P. Automating Tomato Ripeness Classification and Counting with YOLOv9. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 1892–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Liu, F. IDP-YOLOV9: Improvement of Object Detection Model in Severe Weather Scenarios from Drone Perspective. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhan, S.; Cao, G.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X. C2f-Enhanced YOLOv5 for Lightweight Concrete Surface Crack Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Advances in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, Wuhan, China, 18–20 November 2023; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Ma, K.; Wang, Z.; Shi, P. YOLOv7-CSAW for maritime target detection. Front. Neurorobotics 2023, 17, 1210470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Leichner, C.; Delakis, M.; Fornoni, M.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, W.; Banbury, C.; Ye, C.; Akin, B. MobileNetV4-Universal Models for the Mobile Ecosystem. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10518. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M. YOLOv5, YOLOv8 and YOLOv10: The Go-To Detectors for Real-time Vision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.02988. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan Geetha, A.; Alif, M.A.R.; Hussain, M.; Allen, P. Comparative Analysis of YOLOv8 and YOLOv10 in Vehicle Detection: Performance Metrics and Model Efficacy. Vehicles 2024, 6, 1364–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Number | SCDown | C2FUIBELAN | v10detect | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | 0.948 | 0.923 | 0.970 | 0.747 |
| 2 | √ | - | - | 0.964 | 0.911 | 0.977 | 0.764 |
| 3 | - | √ | - | 0.954 | 0.911 | 0.970 | 0.751 |
| 4 | - | - | √ | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.989 | 0.833 |
| 5 | √ | √ | - | 0.964 | 0.971 | 0.991 | 0.834 |
| 6 | √ | √ | √ | 0.971 | 0.970 | 0.991 | 0.848 |
| Model | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD-ResNet18 | 0.942 | 0.937 | 0.979 | 0.748 |
| RTDETR-ResNet18 | 0.957 | 0.897 | 0.976 | 0.752 |
| YOLOv5s | 0.938 | 0.936 | 0.978 | 0.743 |
| YOLOv6s | 0.945 | 0.942 | 0.979 | 0.773 |
| YOLOv8s | 0.949 | 0.938 | 0.979 | 0.752 |
| YOLOv9s | 0.948 | 0.923 | 0.970 | 0.747 |
| YOLOv9s-Pear | 0.971 | 0.970 | 0.991 | 0.848 |
| Model | Preprocess Time (ms) | Inference Time (ms) | Postprocess Time (ms) | Total Computational Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD-ResNet18 | 0.8 | 15.6 | 1.1 | 17.5 |
| RTDETR-ResNet18 | 0.5 | 40.5 | 0.2 | 41.2 |
| YOLOv5s | 0.8 | 10.4 | 1.9 | 13.1 |
| YOLOv6s | 0.8 | 11.4 | 1.0 | 13.2 |
| YOLOv8s | 0.8 | 11.2 | 0.8 | 12.8 |
| YOLOv9s | 0.8 | 15.1 | 0.7 | 16.6 |
| YOLOv9s-Pear | 0.3 | 11.6 | 0.2 | 12.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Duan, Z.; Qing, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; Yuwen, X. YOLOv9s-Pear: A Lightweight YOLOv9s-Based Improved Model for Young Red Pear Small-Target Recognition. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092086
Shi Y, Duan Z, Qing S, Zhao L, Wang F, Yuwen X. YOLOv9s-Pear: A Lightweight YOLOv9s-Based Improved Model for Young Red Pear Small-Target Recognition. Agronomy. 2024; 14(9):2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092086
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yi, Zhen Duan, Shunhao Qing, Long Zhao, Fei Wang, and Xingcan Yuwen. 2024. "YOLOv9s-Pear: A Lightweight YOLOv9s-Based Improved Model for Young Red Pear Small-Target Recognition" Agronomy 14, no. 9: 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092086
APA StyleShi, Y., Duan, Z., Qing, S., Zhao, L., Wang, F., & Yuwen, X. (2024). YOLOv9s-Pear: A Lightweight YOLOv9s-Based Improved Model for Young Red Pear Small-Target Recognition. Agronomy, 14(9), 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14092086







