Soil Erosion Characteristics of the Agricultural Terrace Induced by Heavy Rainfalls on Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
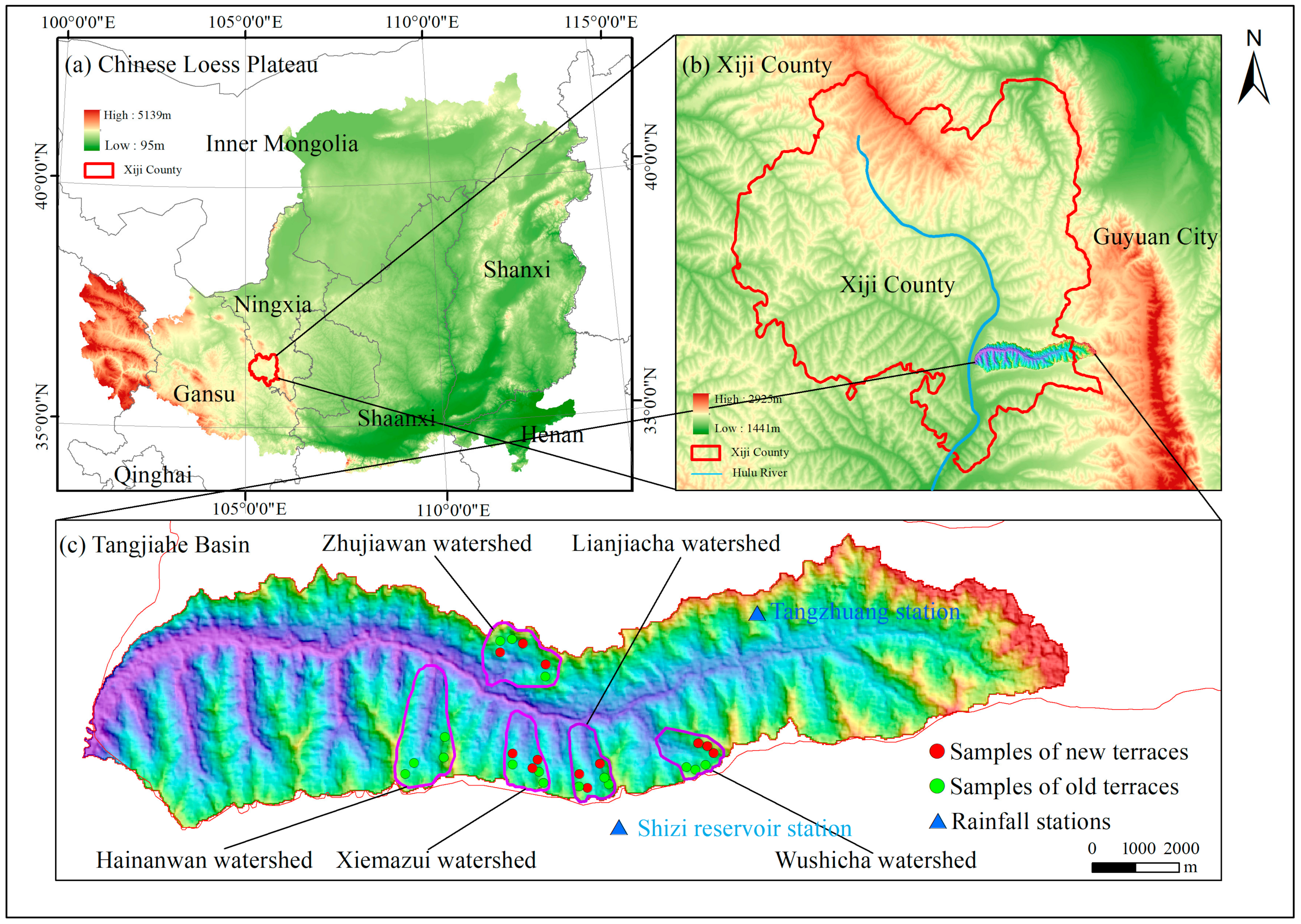
2.1. Study Area
2.2. The Heavy Rainfall Event
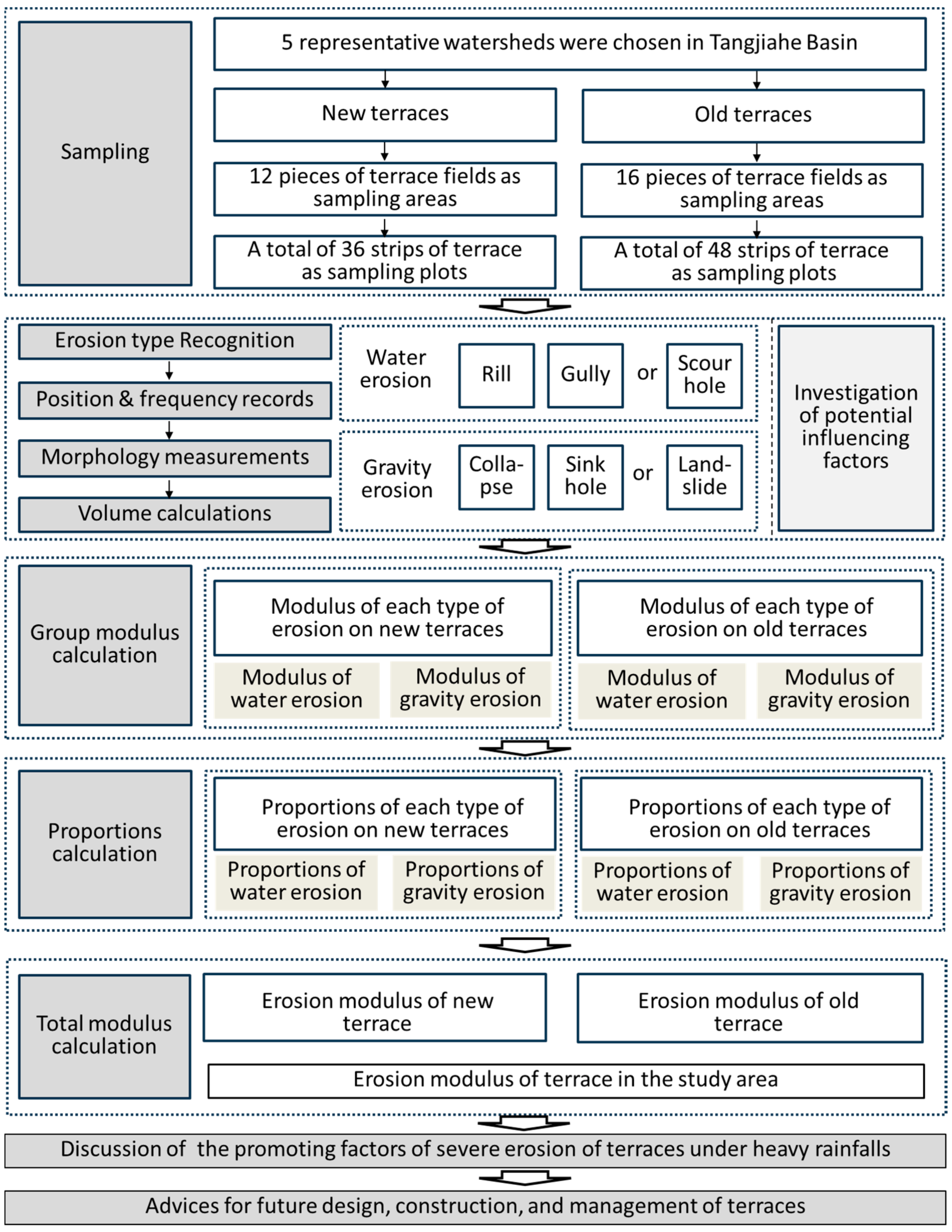
2.3. Investigation Methods
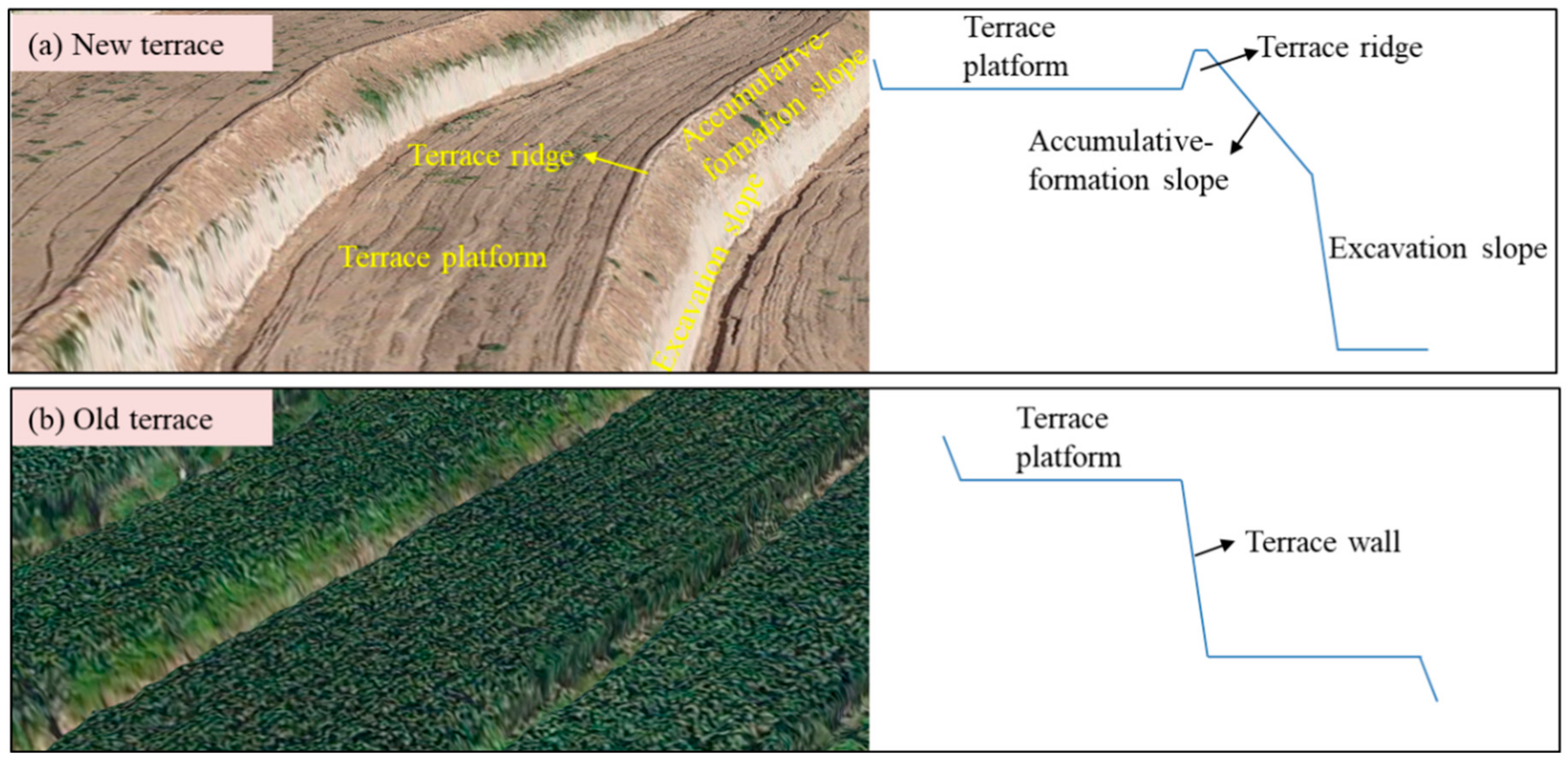
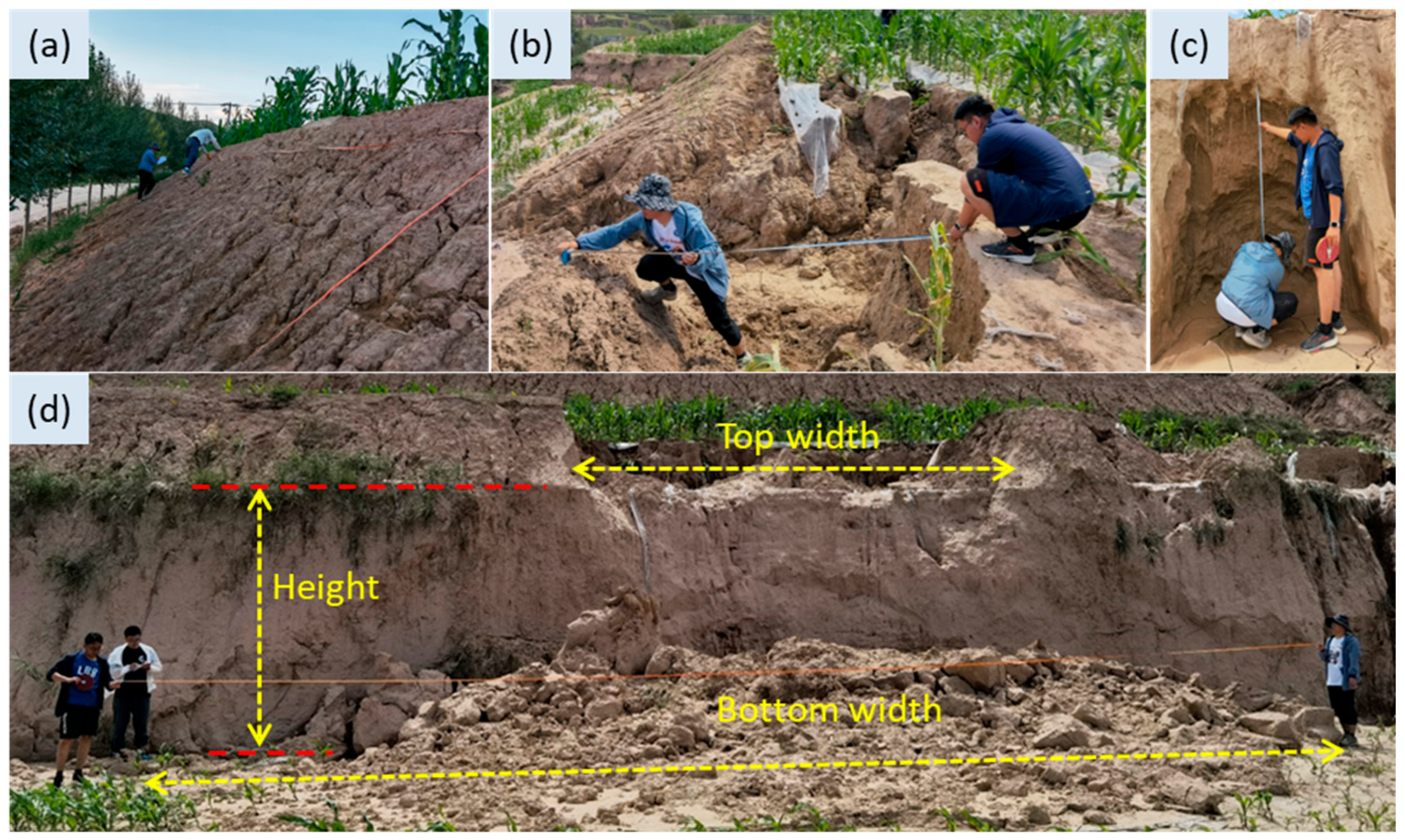
2.4. Eroison Types Recognition and Morphology Measurements
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
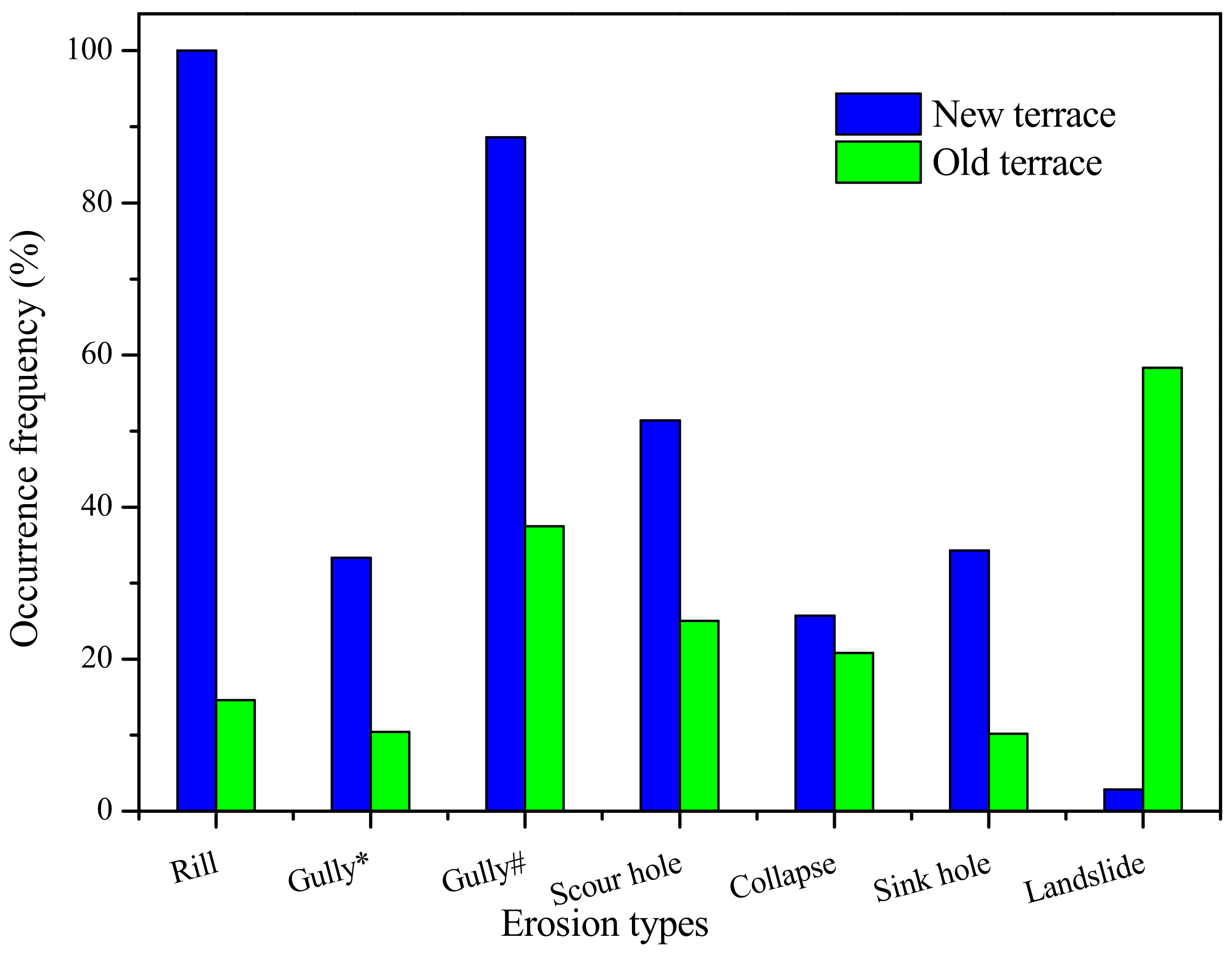
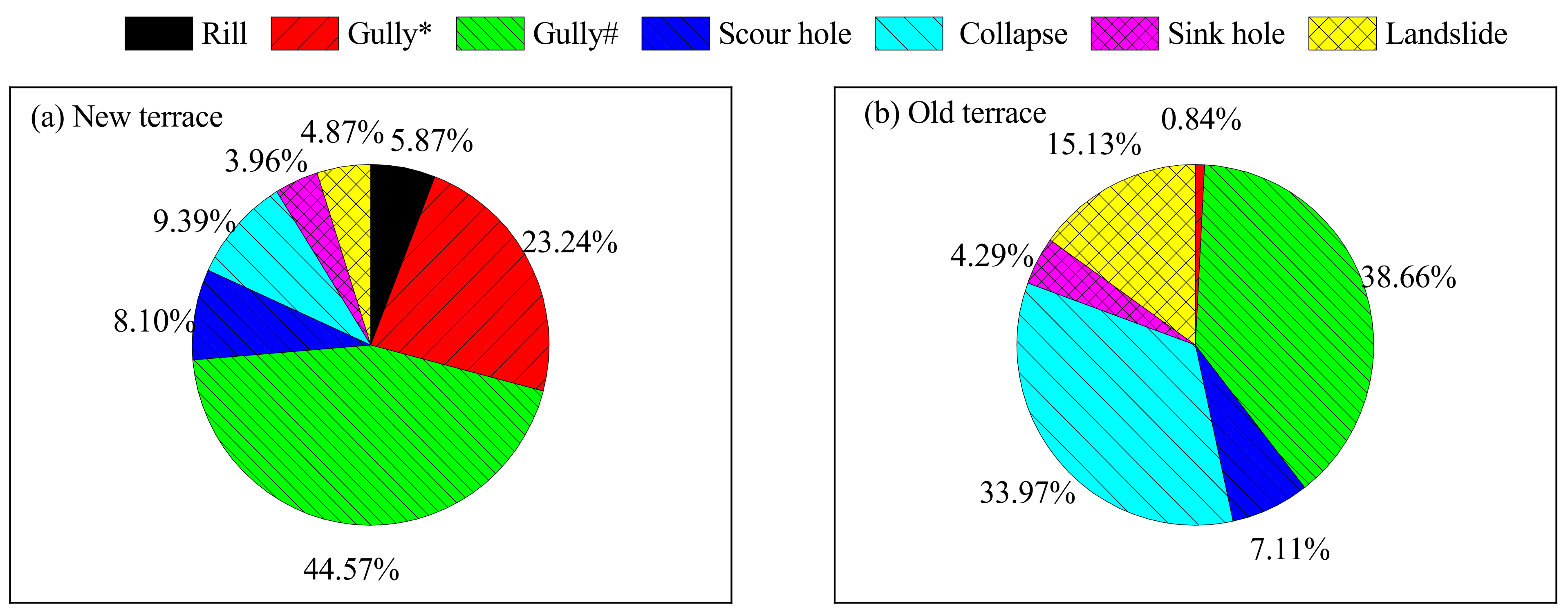
3.1. Terrace Erosion Types and Occurrence Frequencies
3.1.1. Water Erosion
3.1.2. Gravity Erosion
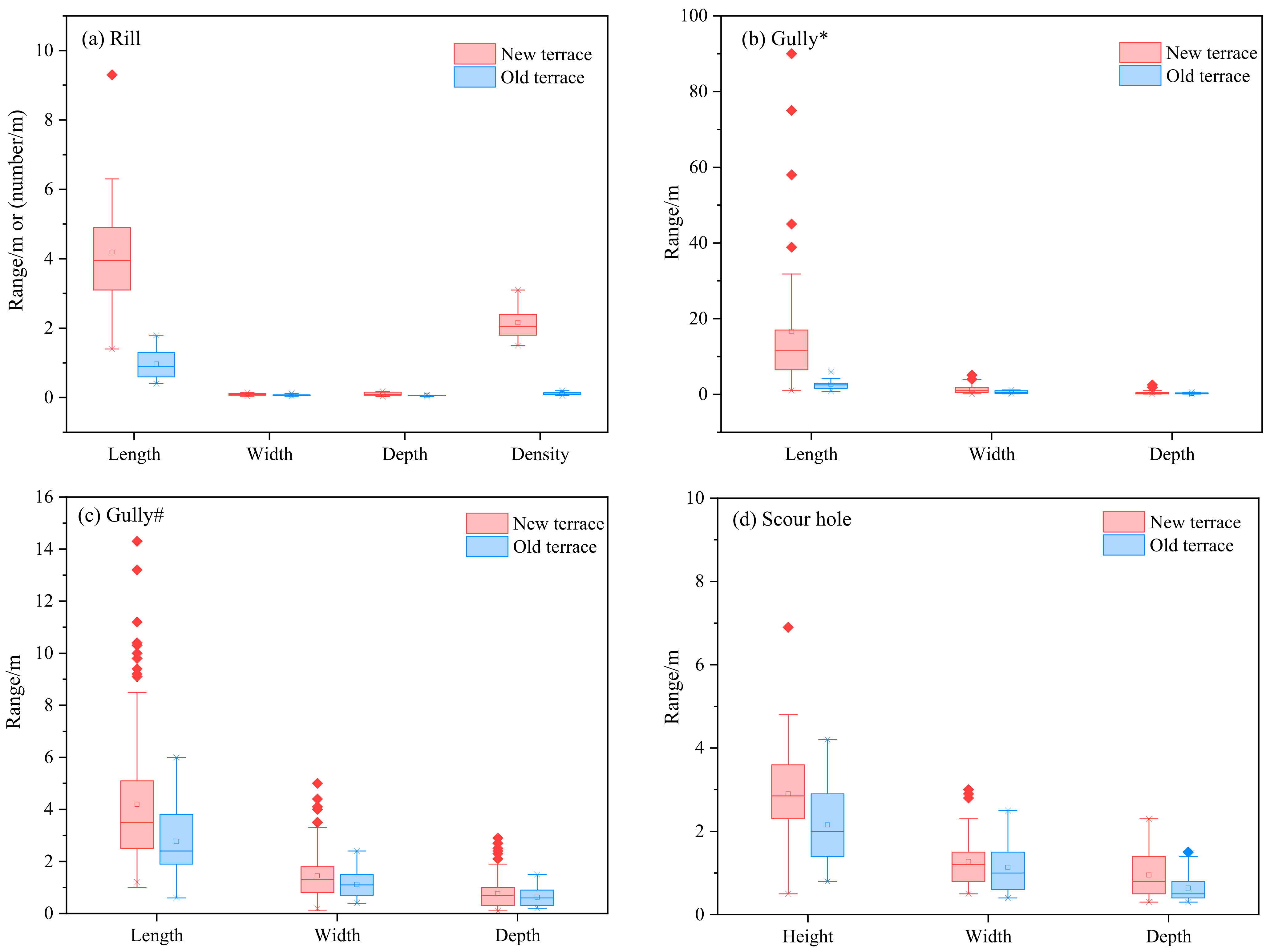
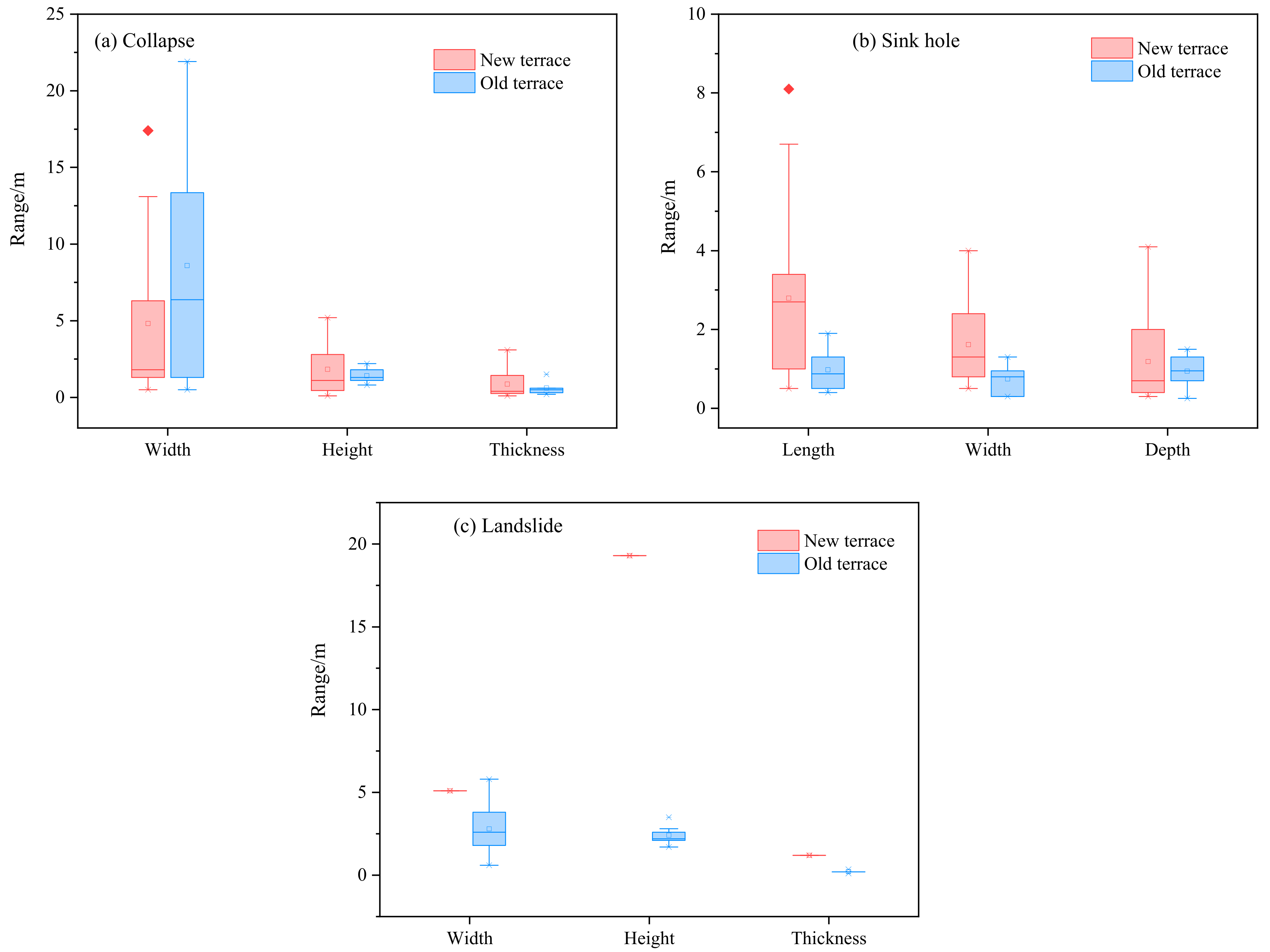
3.2. Terrace Erosion Morphology
3.2.1. Water Erosion Morphology
3.2.2. Gravity Erosion Morphology
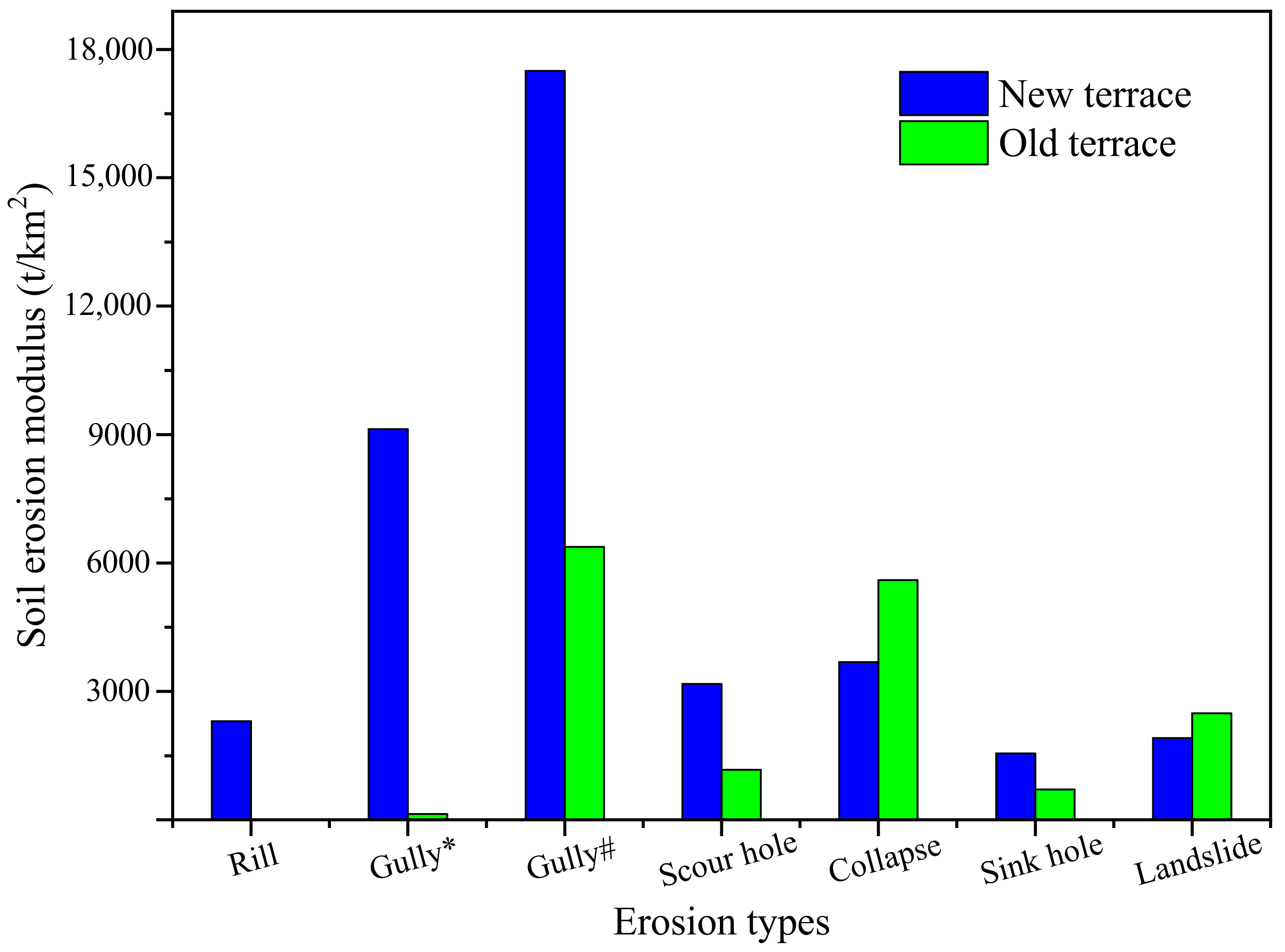
3.3. Erosion Modulus and Proportions of Each Erosion Type
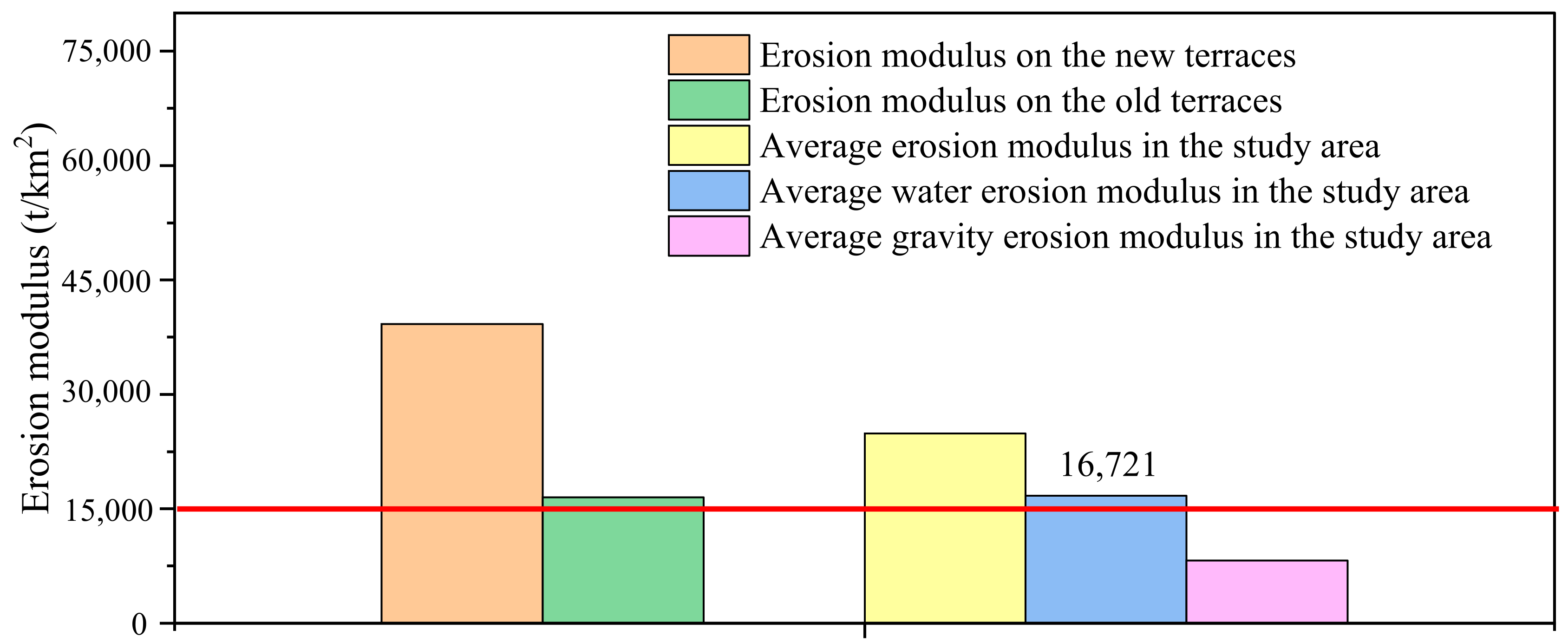
3.3.1. The Erosion Modulus
3.3.2. The Erosion Proportions
3.3.3. Erosion Moduli on the New and Old Terraces
4. Discussion
4.1. Terrace Erosion under Heavy Rainfalls
4.2. Factors Promoting Terrace Erosion under Heavy Rainfalls
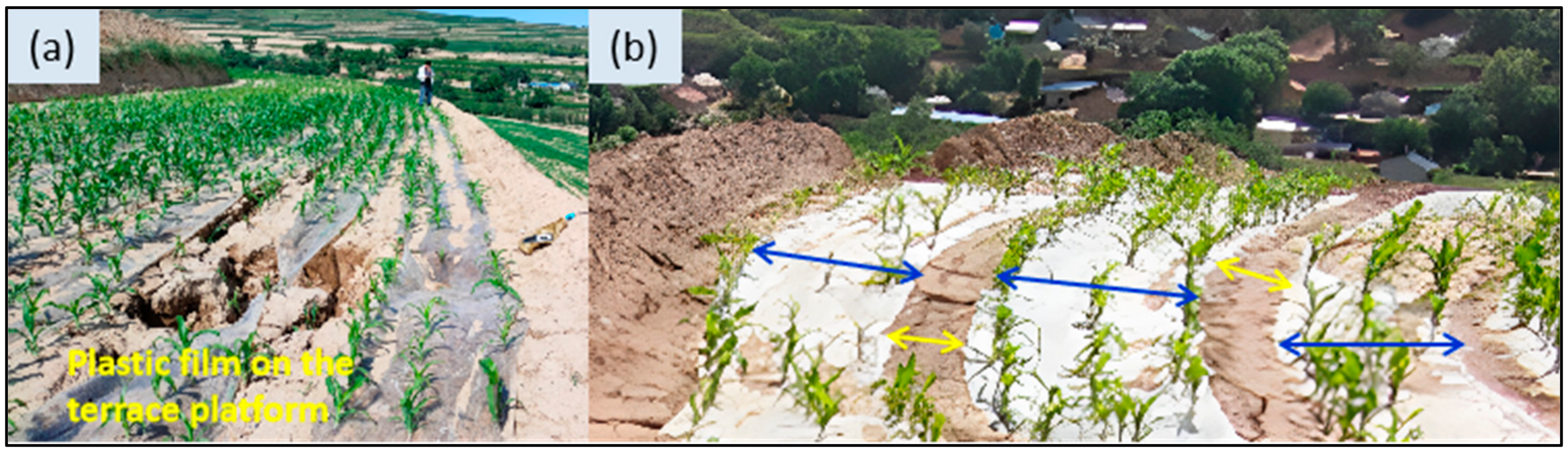
4.2.1. Plastic Film Mulching
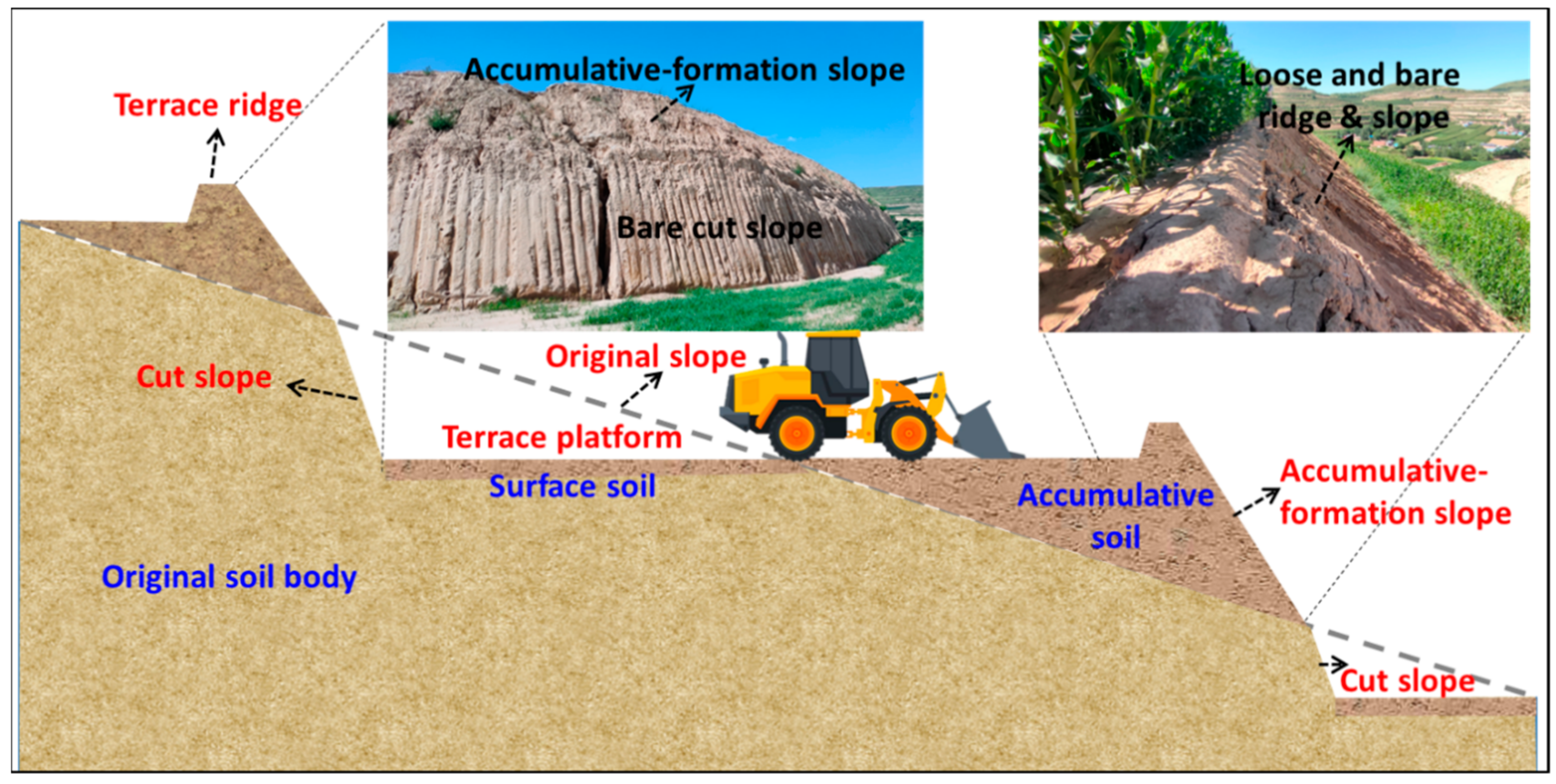
4.2.2. Loose and Bare Terrace Ridges and Walls
4.2.3. Inclined Terrace Platform and High Terrace Wall
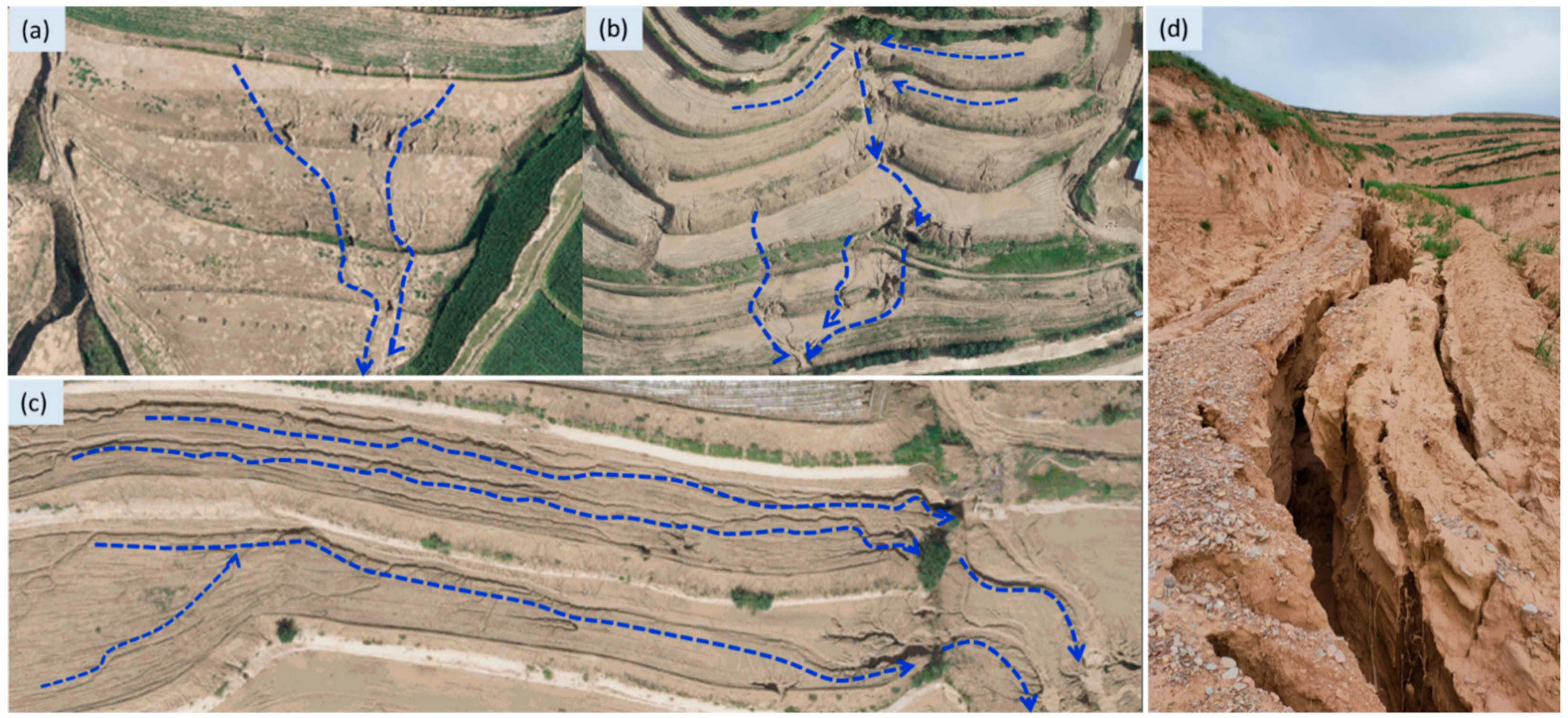
4.2.4. The Developing Flow and Sediment Delivery Paths
5. Recommendations for Erosion Control and Terrace Management
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, D. Advantages and disadvantages of terracing: A comprehensive review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta-analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; He, L.; Pei, Z.; Lv, D.; Lei, S.; Zhang, X. Investigation and Analysis of Damage of Horizontal Terraced Fields Under Extreme Rainstorm Conditions in the Loess PlateauTaking the 7·26 Torrential Rain in the Chabagou Watershed as an Example. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiao, J.; Ma, X.; Zhao, W.; Ling, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Han, J.; Du, P.; Cong, P.; et al. Investigation and analysis of typical rainstorm erosion and flood disaster on Loess Plateau in 2022. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Analysis of Rainstorm Erosion Disaster in Terrace Field in Loess Hilly and Gully Region. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 21, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Eldad, S.; Xu, C.; Xu, Z.; Gusarov, Y.; Haiman, M.; Argaman, E. Ancient agricultural terrace walls control floods and regulate the distribution of Asphodelus ramosus geophytes in the Israeli arid Negev. Catena 2024, 234, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Jacobson, P.J. Water and nutrient discharge to a high-value terrace-flood plain fen: Resilience and risk. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.J.; Koch, Z.G.; Compson, B.A.; Hungate, J.C. Ecosystem responses to restored flow in a travertine river. Freshw. Sci. 2018, 37, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Analysis on Soil and Water Conservation Benefits of Level Terrace Under Different Rainfall Condition in Loess Hilly Region. J. Soil Eros. Soil Water Conserv. 1999, 5, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, D.; Pan, C.; Jiang, Y. Effects of terrace on the precipitation-runoff process in the Chinese loess areas and application and improvement of SCS-CN model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Daryanto, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, G.; Feng, T. Global synthesis of the classifications, distributions, benefits and issues of terracing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 159, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Kasielke, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Zepp, H. May agricultural terraces induce gully erosion? A case study from the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.C.; Cots-Folch, R.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A. Sustainability of modern land terracing for vineyard plantation in a Mediterranean mountain environment—The case of the Priorat region (NE Spain). Geomorphology 2007, 86, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesschen, J.P.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Nieman, T. Erosion and terrace failure due to agricultural land abandonment in a semi-arid environment. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammeraat, E.L.H. Scale dependent thresholds in hydrological and erosion response of a semi-arid catchment in southeast Spain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Vanmaercke, M.; Jiao, J.; Bai, L.; Tang, B.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Quantifying the importance of different erosion processes and soil and water conservation measure collapses following an extreme rainstorm in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 34, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, B.; Cong, P.; Jiao, J.; Wang, C.; Dang, W.; Xing, X. Soil and water conservation survey after a heavy storm on 10th August, 2019 in Linqu, Shandong Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tang, C.J.; Shi, Z.H.; Yang, J. Efficacy of orchard terrace measures to minimize water erosion caused by extreme rainfall in the hilly region of China: Long-term continuous in situ observations. J Env. Manag. 2021, 278, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, C.; Pierluigi, B.; Claudia, S.; Ivano, R. Relationships between geo-hydrological processes induced by heavy rainfall and land-use: The case of 25 October 2011 in the Vernazza catchment (Cinque Terre, NW Italy). J. Maps 2013, 9, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, K.; Nishiwaki, S. The tendency of damage of stone walls in terrace fields in the northwestern Kumamoto City by the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake and heavy rain in 2016 and 2006. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 17, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-de-las-Heras, M.; Lindenberger, F.; Latron, J.; Lana-Renault, N.; Llorens, P.; Arnáez, J.; Romero-Díaz, A.; Gallart, F. Hydro-geomorphological consequences of the abandonment of agricultural terraces in the Mediterranean region: Key controlling factors and landscape stability patterns. Geomorphology 2019, 333, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ge, W.; Hei, Z.; Cong, C.; Ma, C.; Xie, M.; Liu, B.; Feng, W.; Wang, F.; Jiao, J. Agricultural land use and management weaken the soil erosion induced by extreme rainstorms. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, J.e.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Ssun, P.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Yanan Extreme Rainfall Characteristics and Impacts of Erosion Disasters on Terraces. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, B.; Yu, K.; Cong, P.; Dai, N. Investigation on erosion intensity of production roads under “7·13” rainstorm in 2020. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Dang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Li, X. Investigation and consideration of gravity erosion during July 15, 2022 rainstorm in Xiji County. Yellow River 2024, 46, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, B. Advancements and challenges in rill formation, morphology, measurement and modeling. Catena 2021, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, J.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Importance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, R.N.; Brooks, A.P.; Pietsch, T.J.; Spencer, J.R. What type of gully is that? The need for a classification of gullies. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 47, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.A.T. ‘Adhesion Flow’ and Regressive Gully-Head Expansion in Southern Brazil: Field Experiment Results. In Soil Erosion Research for the 21st Century, Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–5 January 2001; Ascough, J.C., II, Flanagan, D.C., Eds.; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Wang, W.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Lou, Y.; Guo, W.; Xiao, H. Headwall scour hole erosion and overhanging mass collapse play critical roles in gully head retreat on grassland under surface flow. Geomorphology 2022, 411, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Z.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, H.W.; Yan, Q.; Zhao, C.; Guo, W.Z. Which is more hazardous: Avalanche, landslide, or mudslide? Nat. Hazards 2015, 76, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, M.; Juneja, A. Sinkholes: Trigger, Development, and Subsidence—A Review; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.-Z.; Chen, Z.-X.; Wang, W.-L.; Gao, W.-W.; Guo, M.-M.; Kang, H.-L.; Li, P.-F.; Wang, W.-X.; Zhao, M. Telling a different story: The promote role of vegetation in the initiation of shallow landslides during rainfall on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geomorphology 2020, 350, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SL 190-2007; Standards for Classification and Gradation of Soil Erosion. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Lasanta, T.; Arnáez, J.; Oserín, M.; Ortigosa, L.M. Marginal Lands and Erosion in Terraced Fields in the Mediterranean Mountains. Mt. Res. Dev. 2001, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.R.; Sanleandro, P.M.; Soriano, A.S.; Serrato, F.B.; Faulkner, H. The causes of piping in a set of abandoned agricultural terraces in southeast Spain. Catena 2007, 69, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Akbar, J.; Zhang, S.; Che, C.; Zhang, M.; Cerdà, A.; Lupwayi, N. A review of preferential water flow in soil science. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 98, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M.; Errico, A.; Santoro, A.; Dani, A.; Preti, F. Terraced Landscapes and Hydrogeological Risk. Effects of Land Abandonment in Cinque Terre (Italy) during Severe Rainfall Events. Sustainability 2019, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Rickson, R.J.; Smith, C.J. Tolerable versus actual soil erosion rates in Europe. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 94, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapen, A.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; Gyssels, G.; Nachtergaele, J. Resistance of soils to concentrated flow erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2007, 80, 75–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Li, F.-M.; Zhang, F. Plastic film mulching increases crop yields and reduces global warming potential under future climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 349, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Che, J.; Ma, C. A Review of Plastic Film Mulching on Water, Heat, Nitrogen Balance, and Crop Growth in Farmland in China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanchi, S.; Freppaz, M.; Agnelli, A.; Reinsch, T.; Zanini, E. Properties, best management practices and conservation of terraced soils in Southern Europe (from Mediterranean areas to the Alps): A review. Quat. Int. 2012, 265, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lu, N.; Fu, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Tian, H. Hotspots, co-occurrence, and shifts of compound and cascading extreme climate events in Eurasian drylands. Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Nie, X.; et al. Complex vegetation patterns improve soil nutrients and maintain stoichiometric balance of terrace wall aggregates over long periods of vegetation recovery. Catena 2023, 227, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Watershed | Watershed Area /km2 | Terraced Area /km2 | Terrace Proportion /% | New Terrace area/km2 | Old Terrace area/km2 | New Terrace Proportion/% | Old Terrace Proportion/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lianjiacha | 1.37 | 0.67 | 48.9 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 53.2 | 46.8 |
| Wushicha | 1.71 | 0.85 | 49.7 | 0.26 | 0.59 | 30.3 | 69.7 |
| Xiemazui | 1.34 | 1.14 | 85.1 | 0.51 | 0.64 | 44.3 | 55.7 |
| Zhujiawan | 2.00 | 1.13 | 56.5 | 1.02 | 0.11 | 90.1 | 9.9 |
| Hainanwan | 3.02 | 2.04 | 67.6 | 0.00 | 2.04 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| Total | 9.44 | 5.83 | 61.7 | 2.15 | 3.69 | 36.8 | 63.2 |
| Research Sites | Environmental Conditions | Erosion Types | Erosion Modulus/(t/km2) or Other Erosion Characteristics | Resources | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ansai District, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province, China | Loess hilly and gully region, mid-temperate continental semi-arid monsoon climate, loessial soil | Sheet erosion, gully erosion, and sink hole erosion | 20,660 (average) 54,050 (maximum) | [5,23] |
| 2 | Zizhou County, Yulin City, Shaanxi Province, China | Loess hilly and gully region, temperate continental monsoon climate, loessial soil | Surface crust removal of the terrace wall, terrace wall collapse, ridge damage, and hole development of the terrace surface | 30,733 (average) 19,404 (newly machine-built terraces) 34,000–37,000 (old terraced farming, meadow fields, and forestland) 5958 (old terraced shrub field). | [3] |
| 3 | Yulin, Yan’an, Lvliang City, China | Loess hilly and gully region, temperate continental monsoon climate, loessal soil | Collapse, sink hole, and gully erosion | Damage to newly built terraces was significantly greater than that of old terraces | [4] |
| 4 | Weifang City, Shandong Province, China | Northern rocky mountain area of China, warm temperate monsoon subhumid continental climate, thin soils and high gravel concentration | Rill, gully, and embankment collapse | 9490 (the total value of rill/gully erosion and collapse) 8397 (average value of gravity erosion in terrace land) 4806 (the maximal value of rill/gully erosion) | [22] |
| 5 | Zizhou County, Yulin City, Shaanxi Province, China | Loess hilly and gully region, temperate continental monsoon climate, loessial soil | Rill, gully, collapse (and breach) | 22,991 (new terrace): 10,401 (water erosion), 11,640 (gravity erosion) 43,067 (old terrace): 1256 (water erosion), 41,811 (gravity erosion) | [16] |
| 6 | Cinque Terre, Northeastern Italy | Coastal region of La Spezia Province, Mediterranean climate, stone terrace walls | Landslides, mudflows of hillslopes with terraces, and gully and rill erosion. | Hundreds of shallow landslides, debris, and mudflow occurred. Several agricultural terraces failed. | [38] |
| 7 | Xiji County, Ningxia, China | Hilly Loess Plateau, temperate semi-arid continental climate, loessial soil | Rill, gully, scour hole, collapse, sink hole, and landslide of terrace wall | 39,252 (new terrace) 24,867 (old terrace) | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Han, L.; Wei, S. Soil Erosion Characteristics of the Agricultural Terrace Induced by Heavy Rainfalls on Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081840
Kang H, Wang W, Li L, Han L, Wei S. Soil Erosion Characteristics of the Agricultural Terrace Induced by Heavy Rainfalls on Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study. Agronomy. 2024; 14(8):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081840
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Hongliang, Wenlong Wang, Liangna Li, Lei Han, and Sihan Wei. 2024. "Soil Erosion Characteristics of the Agricultural Terrace Induced by Heavy Rainfalls on Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study" Agronomy 14, no. 8: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081840
APA StyleKang, H., Wang, W., Li, L., Han, L., & Wei, S. (2024). Soil Erosion Characteristics of the Agricultural Terrace Induced by Heavy Rainfalls on Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study. Agronomy, 14(8), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081840






