Toward the Development of Garlic Varieties: The First Attempts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
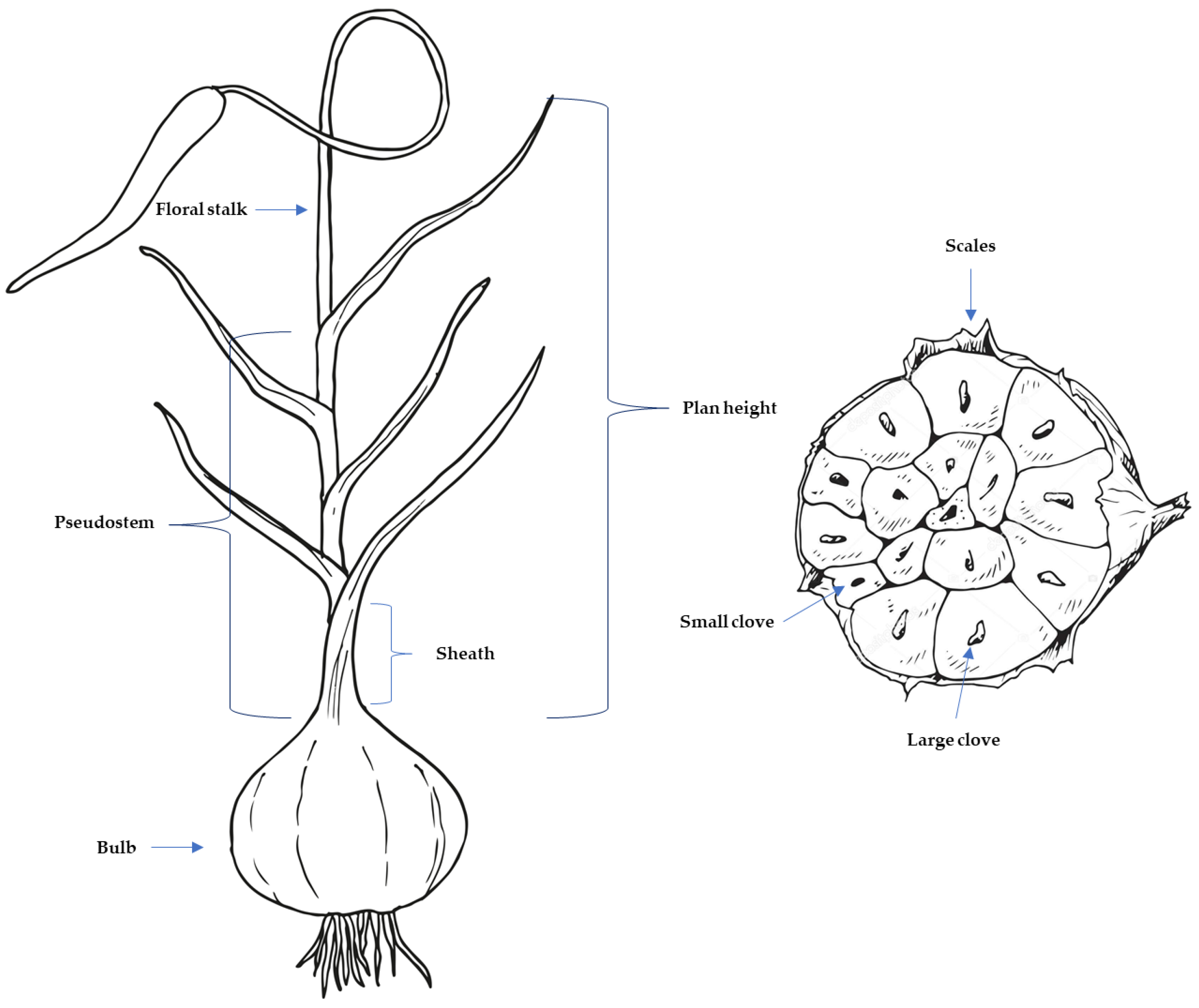
2.1. Plant Material and Statements for the Field Trials
2.2. Phenotypic Selection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
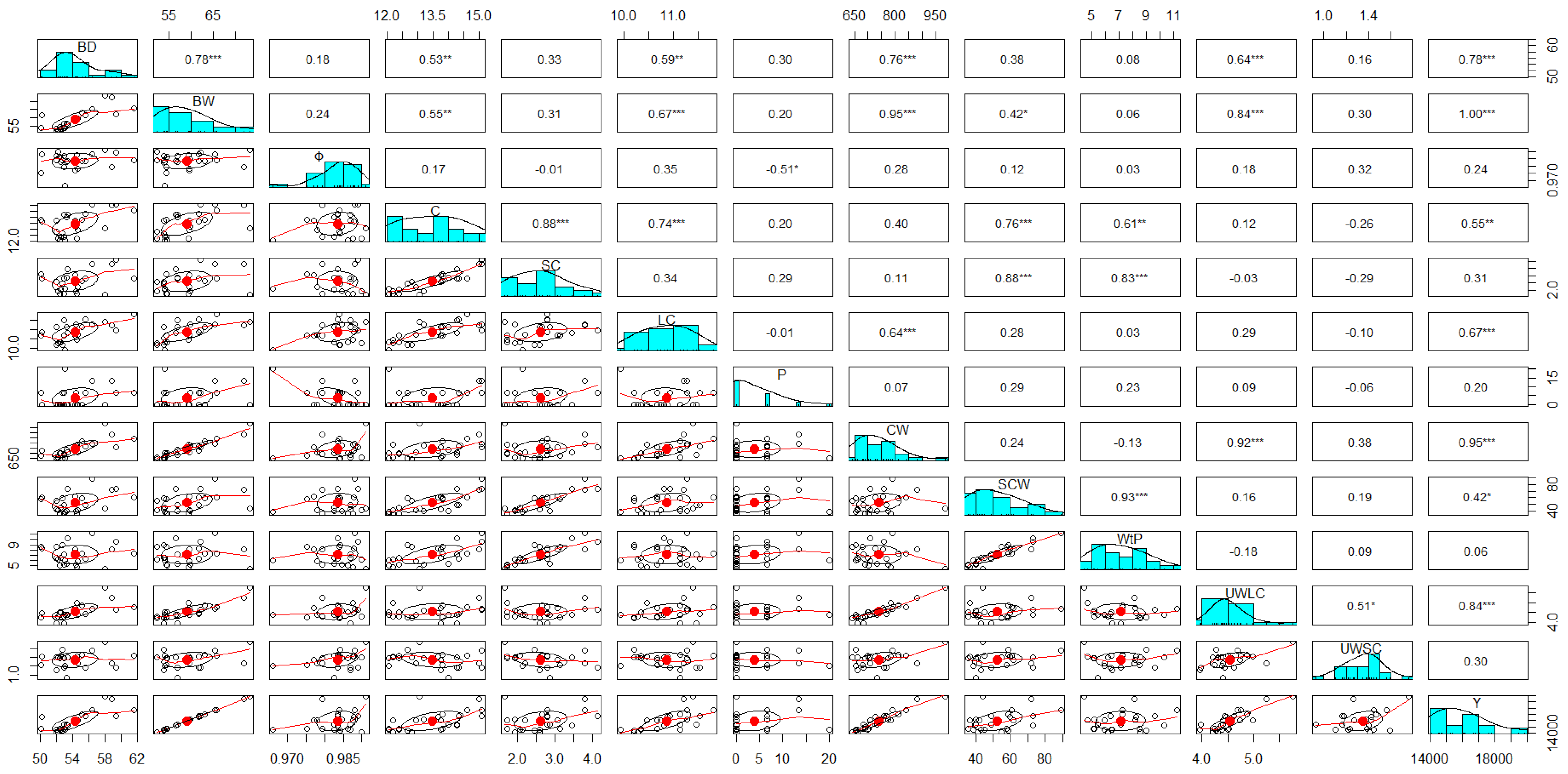
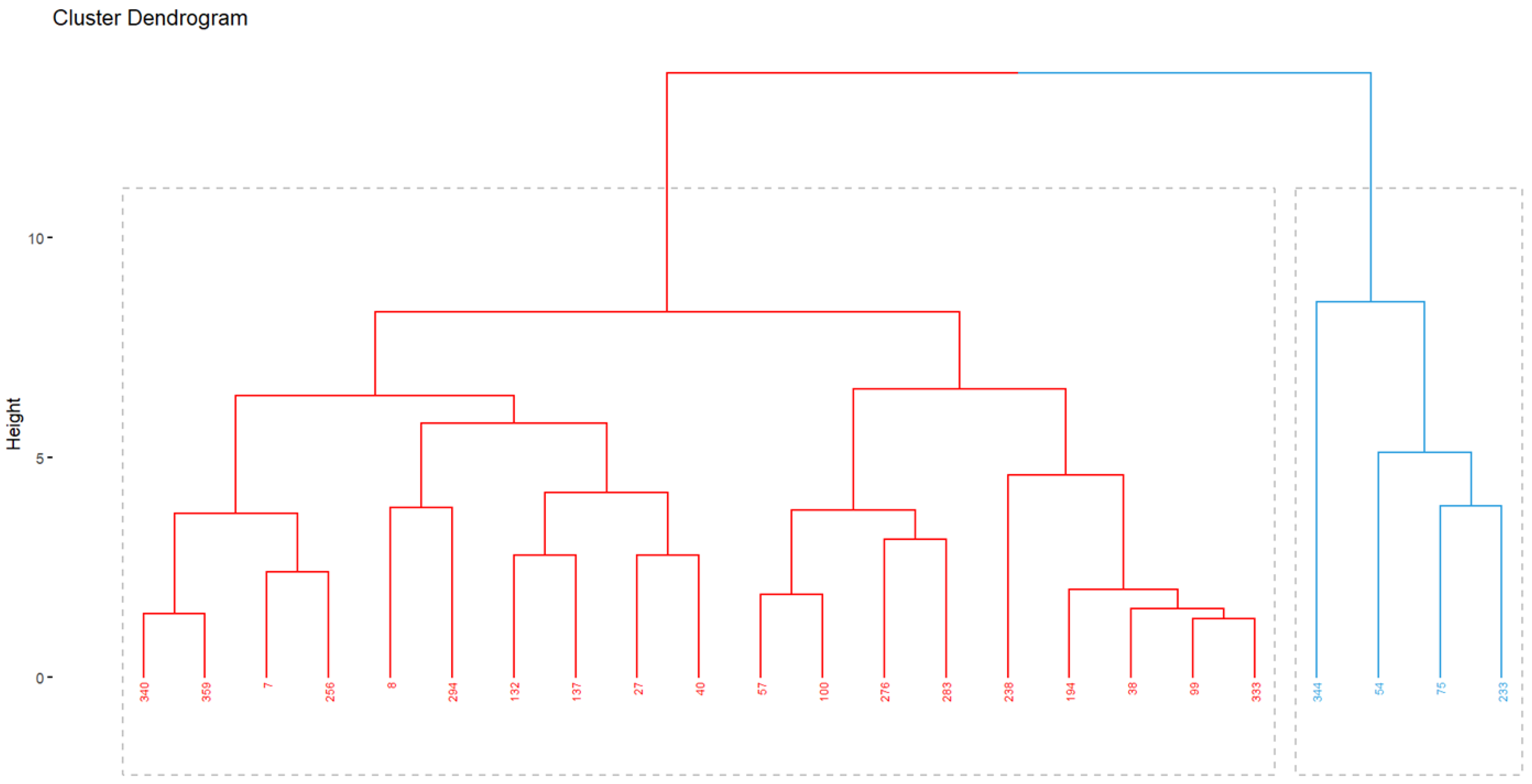
3. Results
3.1. The First Trial: Season 2021–2022
3.2. The Second Trial: Season 2022–2023
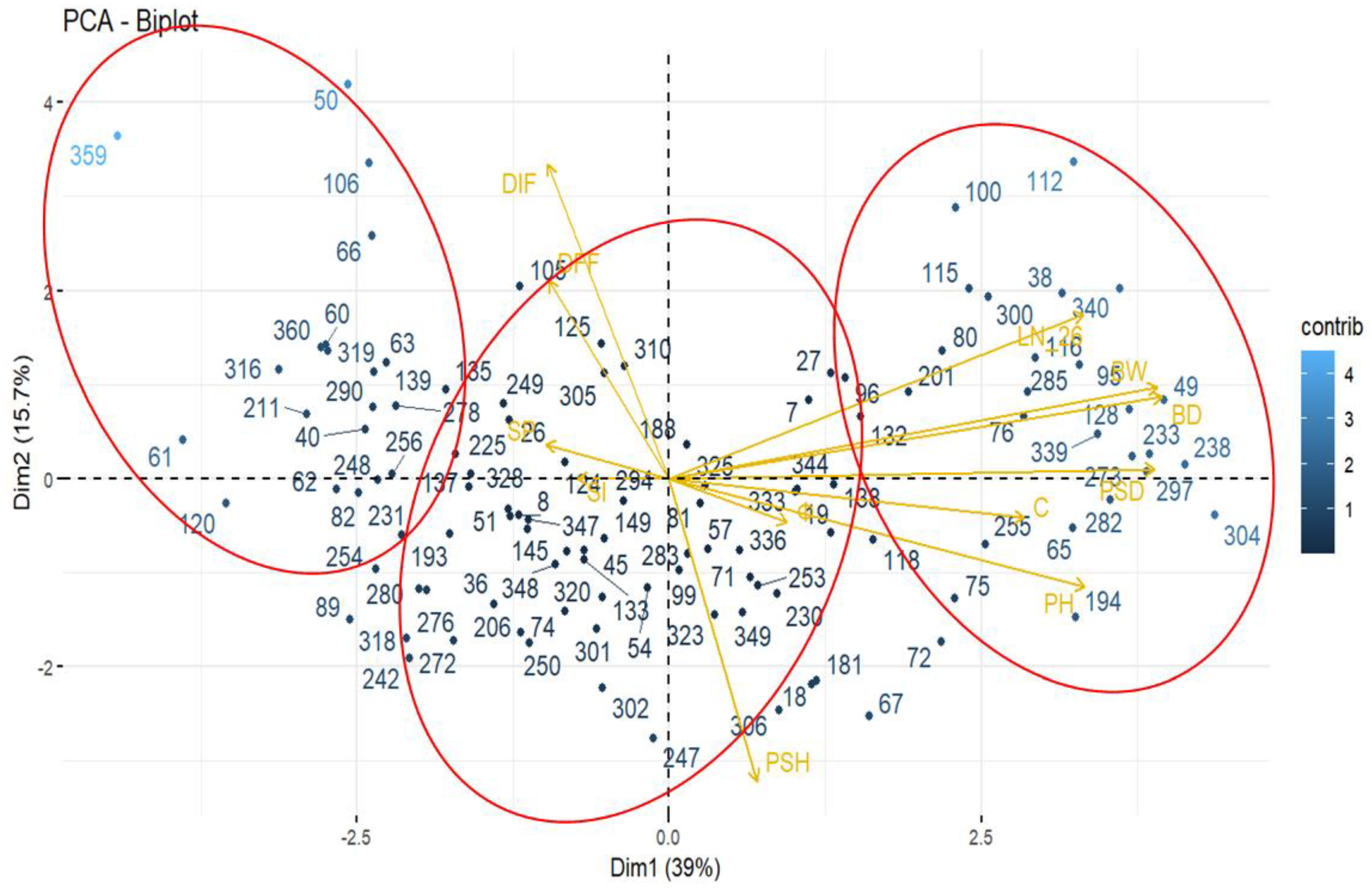
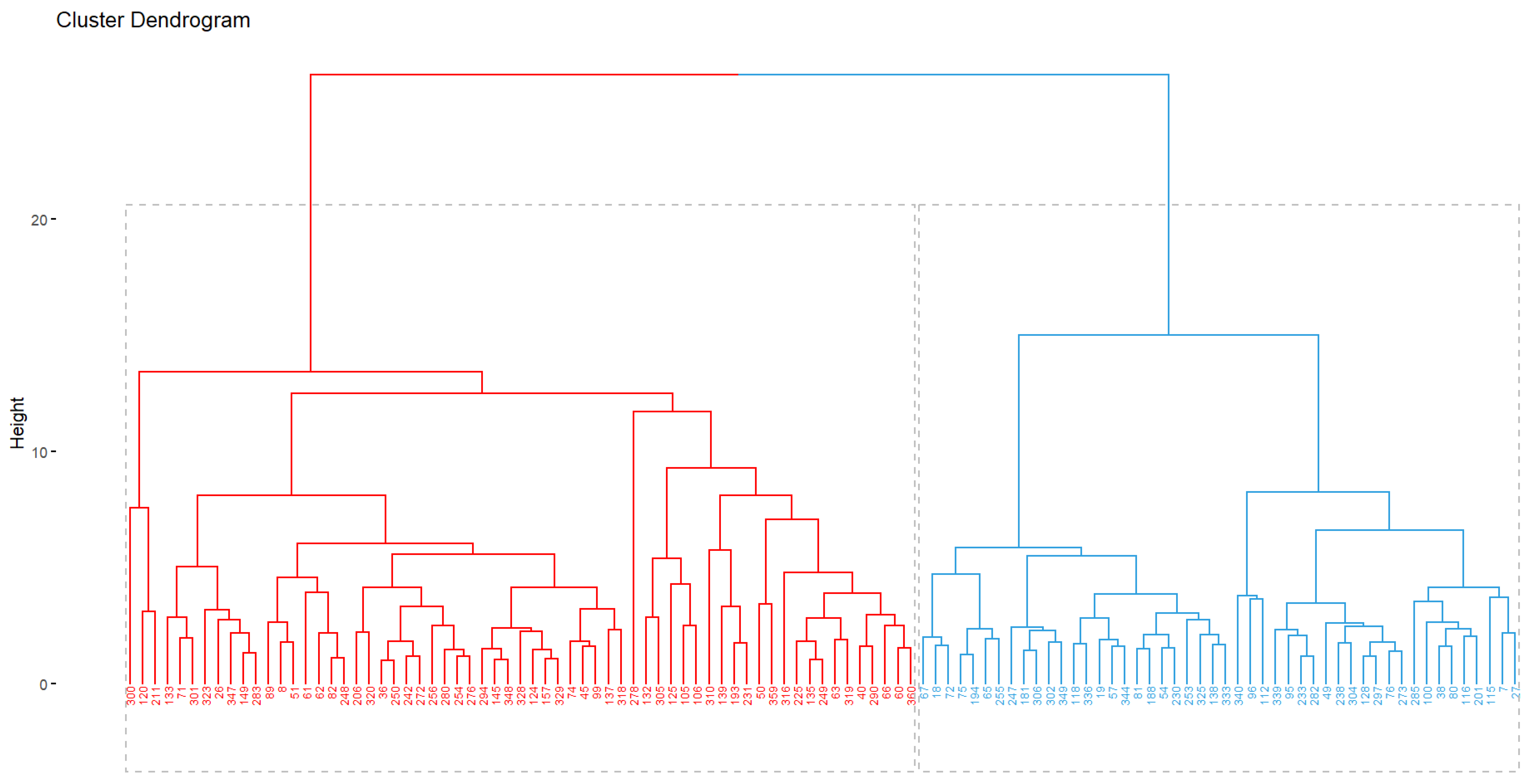
3.3. Interaction Genotype–Environment (G × E)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- APG. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 161, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, M.W.; Reveal, J.L.; Fay, M.F.A. Subfamilial classification for the expanded asparagalean families Amaryllidaceae, Asparagaceae and Xanthorrhoeaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 161, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haston, E.; Richardson, J.E.; Stevens, P.F.; Chase, M.W.; Harris, D.J. The Linear Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (LAPG) III: A linear sequence of the families in APG III. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2009, 161, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Zhou, S.D.; He, X.J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wei, X.Q. Phylogeny and biogeography of Allium (Amaryllidaceae: Allieae) based on nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer and chloroplast rps16 sequences, focusing on the inclusion of species endemic to China. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Giussani, L.M.; Jang, C.G.; Oh, B.U.; Cota-Sánchez, J.H. Systematics of disjunct northeastern Asian and northern north American Allium (Amaryllidaceae). Botany 2012, 90, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, R.M.; Friesen, N. Evolution, domestication and taxonomy. In Allium Crop Science: Recent Advances; Rabinowitch, H.D., Currah, L., Eds.; CABI publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 5–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenetsky, R.; Khassanov, F.; Rabinowitch, H.D.; Auger, J.; Kik, C. Garlic biodiversity and genetic resources. Med. Aromat. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, P.W.; Jenderek, M.M. Flowering, seed production, and the genesis of garlic breeding. In Plant Breeding Reviews, 23; Janik, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 211–244. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, R.K.; Cavagnaro, P.F.; Singh, H.; Mandal, S. History, evolution and domestication of garlic: A review. Plant Syst. Evol. 2023, 309, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.W. The Origins and Distribution of Garlic: How Many Garlics Are There? Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/midwest-area/madison-wi/vegetable-crops-research/docs/simon-garlic-origins/ (accessed on 3 March 2020).
- Shemesh-Mayer, E.; Kamenetsky-Goldstein, R. Traditional and Novel Approaches in Garlic (Allium sativum L.) Breeding. In Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Vegetable Crops. Bulb, Roots and Tubers; Al-Khairy, J.M., Mohan Jain, S., Jhonson, D.V., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 8, pp. 3–49. [Google Scholar]
- Etoh, T. Fertility of the garlic clones collected in Soviet Central Asia. Hort. J. 1986, 55, 312–319. [Google Scholar]
- Lallemand, J.; Messian, C.M.; Briand, F.; Etoh, T. Delimitation of varietal groups in garlic (Allium sativum L.) by morphological, physiological and biochemical. characters. In Proceedings of the I International Symposium on Edible Alliaceae, Mendoza, Argentina, 14–18 March 1994; Burba, J.L., Galmarini, C.R., Eds.; ISHS Acta Horticulturae: Leuven, Belgium, 1997; Volume 433, pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Chovelon, V.; Souche, S.; Delecolle, B.; Etoh, T.; Messiaen, C.M.; Lot, H. Resistance to onion yellow dwarf virus and leek yellow stripe virus found in a fertile garlic clone. In Proceeding of the II International Symposium on Edible Alliaceae, Adelaide, Australia, 10–13 November 1997; Armstrong, J., Ed.; ISHS Acta Horticulturae: Leuven, Belgium, 2001; Volume 555, pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Safadi, B.; Arabi, M.I.E.; Ayyoubi, Z. Differences in quantitative and qualitative characteristics of local and introduced cultivars and mutated lines of garlic. J. Veg. Crop Prod. 2003, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burba, J.L.; Portela, J.A.; Lanzavechia, S. Argentine garlic I: A wide offer of clonal cultivars. In Proceedings of the IV International Symposium on Edible Alliaceae, Beijing, China, 21–26 April 2004; Guangshu, L., Ed.; ISHS Acta Horticulturae: Leuven, Belgium, 2005; Volume 688, pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, G.M.; Stern, D. Phenotypic characteristics of ten garlic cultivars grown at different North American locations. HortScience 2009, 44, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lampasona, S.; Asprelli, P.; Burba, J.L. Genetic analysis of a garlic (Allium sativum L.) germplasm collection from Argentina. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 138, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Resistance and clonal selection among Allium sativum L. germplasm resources to Delia antiqua M. and its correlation with allicin content. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2830–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, K.; Salinas, M.C.; Acuña, C.V.; Bannoud, F.; Beretta, V.; Garcia-Lampasona, S.; Burba, J.L.; Galmarini, C.R.; Cavagnaro, P.F. Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure in a garlic (Allium sativum L.) germplasm collection varying in bulb content of pyruvate, phenolics, and solids. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Carvalho, J.; de Jager, V.; van Gurp, T.P.; Wagemaker, N.C.A.M.; Verhoeven, K.J.F. Recent and dynamic transposable elements contribute to genomic divergence under asexuality. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, N.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Qiao, X.; Lu, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of garlic (Allium sativum) provides insights into genome evolution and allicin biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1328–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajo Morado de Las Pedroñeras. Description. EC No: ES/PGI/005/0228/12.03.2002. GI 1204. The International Appellations of Origin; World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Peña-Iglesias, A. El ajo: Virosis, fisiopatías y selección clonal y sanitaria. II: Científico-experimental. Boletín Sanid. Vegetal. Plagas 1988, 14, 493–553. [Google Scholar]
- RAEA. Ensayo de variedades comerciales de ajo. Campaña 2005–2006. Instituto de Investigación de Formación Agraria y Pesquera. Consejería de Innovación, Ciencia y Empresa. Consejería de Agricultura y Pesca. Junta de Andalucía, 2006; pp. 1–92. Available online: https://www.juntadeandalucia.es/export/drupaljda/1337163241RAEA_Ajo_2006.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Bhojwani, S.S.; Cohen, D.; Fry, P.R. Production of virus-free garlic and field performance of micropropagated plants. Sci. Hortic. 1982, 18, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R. A language and environment for statistical computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peña, E.A.; Slate, E.H. Global validation of linear model assumptions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2006, 101, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczak, M.; Tomczak, E. The need to report effect size estimates revisited. An overview of some recommended measures of effect size. Trends Sport. Sci. 2014, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sawilowsky, S.S. New effect size rules of thumb. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2009, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: A Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, M.D.; García Lampasona, S. Before-after analysis of genetic and epigenetic markers in garlic: A 13-year experiment. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figliuolo, G.; Candido, V.; Logozzo, G.; Miccolis, V.; Spagnoletti Zeuli, P.L. Genetic evaluation of cultivated garlic germplasm (Allium sativum L. and A. ampeloprasum L.). Euphytica 2001, 121, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragas, R.E.G.; Padron, F.K.J.R.; Ruedas, M.Y.A.D. Analysis of the morpho-anatomical traits of four major garlic (Allium sativum L.) cultivars in the Philippines. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, A.P.; Khar, A.; Mahajan, V.; Gupta, A.; Singh, M. Study on dispersion of genetic variation among Indian garlic ecotypes using agro morphological traits. Indian. J. Gen. Plant Breed. 2020, 80, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khar, A.; Hirata, S.; Abdelrahman, M.; Shigyo, M.; Singh, H. Breeding and genomic approaches for climate-resilient garlic. In Genomic Designing of Climate-Smart Vegetable Crops; Chittaranjan, K., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 359–383. [Google Scholar]
- Baghalian, K.; Ziai, S.A.; Naghavi, M.R.; Badi, H.N.; Khalighi, A. Evaluation of allicin content and botanical traits in Iranian garlic (Allium sativum L.) ecotypes. Sci. Hortic. 2005, 103, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthee, D.R.; Kc, R.B.; Regmi, H.N.; Subedi, P.P.; Bhattarai, S.; Dhakal, J. Diversity analysis of garlic (Allium sativum L.) germplasms available in Nepal based on morphological characters. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbes, N.; Arnault, I.; Auger, J.; Dridi, B.A.M.; Hannachi, C. Agro-morphological markers and organo-sulphur compounds to assess diversity in Tunisian garlic landraces. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 148, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchorzewska, D.; Bocianowski, J.; Najda, A.; Dąbrowska, A.; Winiarczyk, K. Effect of environment fluctuations on biomass and allicin level in Allium sativum (cv. Harnas, Arkus) and Allium ampeloprasum var. ampeloprasum (GHG-L). J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2017, 90, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Casals, J.; Rivera, A.; Campo, S.; Aymerich, E.; Isern, H.; Fenero, D.; Garriga, A.; Palou, A.; Monfort, A.; Howad, W.; et al. Phenotypic diversity and distinctiveness of the Belltall garlic landrace. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1004069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, S.; Regasa, T.; Yirgu, M. Influence of clove weight and planting depth on yield and yield components of garlic (Allium sativum L.). American-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2017, 17, 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- IPGRI; ECP/GR; AVRDC. Descriptors for Allium (Allium spp.); International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy; European Cooperative Programme for Crop Genetic Resources Networks (ECP/GR), Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center: Taiwan, China, 2001; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Quintero, J.J. El Cultivo del Ajo; Hojas Divulgadoras, Ministerio de Agricultura: Pesca y Alimentación, España, 1984; Volume 1/84, pp. 1–16. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/ministerio/pags/biblioteca/hojas/hd_1984_01.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Hoopes, R.W.; Plaisted, R.L. Potato. In Principles of Cultivar Development: Crop Species; Fehr, W.R., Ed.; Macmillan Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 2, pp. 385–436. [Google Scholar]
- Tascón Rodríguez, C.; Morales, D.A.; Ríos Mesa, D.J. Caracterización morfológica preliminar de un grupo de ajos de la Isla de Tenerife. In XXXVI Seminario de Técnicos y Especialistas en Horticultura: Ibiza, 2006; Centro de Publicaciones Agrarias: Pesqueras y Alimentarias, España, 2007; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, W.; Shen, X.; Yang, Y.; Qi, F.; Liu, Y.; Meng, H. Analysis of the genetic diversity of garlic (Allium sativum L.) by simple sequence repeat and inter simple sequence repeat analysis and agro-morphological traits. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 55, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, C.; Fassou, G.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Lamari, F.N.; Bebeli, P.J.; Papasotiropoulos, V. Evaluation of the genetic diversity of Greek garlic (Allium sativum L.) accessions using DNA markers and association with phenotypic and chemical variation. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, F.G.; Mossie, G.A.; Fita, G.T. Evaluation of garlic genotypes for yield performance and stability using GGE biplot analysis and genotype by environment interaction. Plant Genet. Resour. 2023, 21, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dependent Variables | F Value | df | Signif. (p) | ω2 | 95% CI ω2 ** | Interpretation of Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSH | 6.631 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.54 | (0.41–1.00) | Medium |
| PSD | 8.216 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.60 | (0.50–1.00) | Medium |
| LN_26 | 5.030 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.45 | (0.29–1.00) | Small |
| PH | 7.843 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.58 | (0.48–1.00) | Medium |
| BD | 12.230 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.70 | (0.63–1.00) | Medium |
| Φ * | 148.100 | 102 | <0.01 | 0.27 | (0.36–0.48) | Small |
| BW | 12.540 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.70 | (0.64–1.00) | Medium |
| C | 6.296 | 102 | <0.001 | 0.52 | (0.39–1.00) | Medium |
| Dependent Variables | F Value | df | Signif. (p) | ω2 | 95% CI ω2 * | Interpretation of Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD | 8.254 | 23 | <0.001 | 0.32 | (0.22, 1.00) | Small |
| Φ | 2.326 | 23 | <0.001 | 0.08 | (0.00, 1.00) | Very Small |
| BW | 5.330 | 23 | <0.001 | 0.22 | (0.11, 1.00) | Small |
| C | 8.883 | 23 | <0.001 | 0.33 | (0.24, 1.00) | Small |
| SC | 8.018 | 23 | <0.001 | 0.31 | (0.21, 1.00) | Small |
| LC | 3.225 | 23 | <0.001 | 0.12 | (0.02, 1.00) | Small |
| Family | Yield (kg ha−1) | Grouping of Families by Yield | Bulb Size Category (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F < 37 mm | E 37–45 mm | D 45–50 mm | C 50–55 mm | B 55–60 mm | A >60 mm | |||
| 38 | 14,112 | I | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 60.0 | 20.0 | 0.0 |
| 57 | 14,490 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 53.3 | 26.7 | 0.0 | |
| 99 | 14,724 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 13.3 | 66.7 | 13.3 | 0.0 | |
| 100 | 14,112 | 0.0 | 13.3 | 26.7 | 26.7 | 26.7 | 6.7 | |
| 194 | 14,652 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.3 | 73.3 | 6.7 | 6.7 | |
| 238 | 14,562 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 26.7 | 53.3 | 13.3 | 6.7 | |
| 256 | 15,372 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 46.7 | 33.3 | 0.0 | |
| 276 | 15,228 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 60.0 | 33.3 | 0.0 | |
| 283 | 14,670 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 53.3 | 26.7 | 13.3 | 0.0 | |
| 333 | 14,544 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 73.3 | 20.0 | 0.0 | |
| 340 | 15,336 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.3 | 46.7 | 40.0 | 0.0 | |
| 359 | 14,508 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 13.3 | 66.7 | 13.3 | 0.0 | |
| 7 | 16,668 | II | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 53.3 | 6.7 |
| 8 | 16,092 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 26.7 | 46.7 | 6.7 | |
| 27 | 16,650 | 0.0 | 13.3 | 26.7 | 53.3 | 6.7 | 0.0 | |
| 40 | 17,028 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 40.0 | 46.7 | 6.7 | |
| 132 | 16,056 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.3 | 46.7 | 26.7 | 13.3 | |
| 137 | 16,146 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.7 | 53.3 | 40.0 | 0.0 | |
| 233 | 16,776 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 33.3 | 46.7 | |
| 294 | 16,092 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 53.3 | 46.7 | 0.0 | |
| 54 | 17,640 | III | 0.0 | 0.0 | 13.3 | 20.0 | 40.0 | 26.7 |
| 75 | 19,458 | IV | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 66.7 | 33.3 |
| 344 | 19,800 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 20.0 | 66.7 | 13.3 | |
| Dependent Variable | Variation Factor | F Value | df | Signif. (p) | ω2 | 95% CI ω2 * | Interpretation of Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulb Diameter | |||||||
| F | 8.750 | 22 | <0.001 | 0.27 | (0.18, 1.00) | Small | |
| L | 824.089 | 1 | <0.001 | 0.64 | (0.60, 1.00) | Medium | |
| F × L | 9.725 | 22 | <0.001 | 0.30 | (0.21, 1.00) | Small | |
| Sphericity | |||||||
| F | 1.507 | 22 | n.s. | 0.02 | (0.00, 1.00) | Very small | |
| L | 69.445 | 1 | <0.001 | 0.13 | (0.08, 1.00) | Small | |
| F × L | 2.256 | 22 | <0.01 | 0.06 | (0.00, 1.00) | Very small | |
| Bulb Weight | |||||||
| F | 6.296 | 22 | <0.001 | 0.20 | (0.12, 1.00) | Small | |
| L | 429.649 | 1 | <0.001 | 0.49 | (0.43, 1.00) | Small | |
| F × L | 8.750 | 22 | <0.001 | 0.27 | (0.18, 1.00) | Small | |
| Number of Cloves | |||||||
| F | 7.859 | 22 | <0.001 | 0.25 | (0.16, 1.00) | Small | |
| L | 256.415 | 1 | <0.001 | 0.36 | (0.30, 1.00) | Small | |
| F × L | 5.255 | 22 | <0.001 | 0.17 | (0.08, 1.00) | Small | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Licea-Moreno, R.J.; Rodríguez-Haro, Á.; Marín-Martínez, J.A. Toward the Development of Garlic Varieties: The First Attempts. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081812
Licea-Moreno RJ, Rodríguez-Haro Á, Marín-Martínez JA. Toward the Development of Garlic Varieties: The First Attempts. Agronomy. 2024; 14(8):1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081812
Chicago/Turabian StyleLicea-Moreno, Ricardo Julián, Ángeles Rodríguez-Haro, and Juan Antonio Marín-Martínez. 2024. "Toward the Development of Garlic Varieties: The First Attempts" Agronomy 14, no. 8: 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081812
APA StyleLicea-Moreno, R. J., Rodríguez-Haro, Á., & Marín-Martínez, J. A. (2024). Toward the Development of Garlic Varieties: The First Attempts. Agronomy, 14(8), 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081812







