Comprehensive Identification of Rhubarb Species Based on DNA Barcoding and Multiple-Indicator Quantification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. DNA Barcoding Analysis
2.4. Anthraquinones Extraction and Analysis Conditions
2.5. Sennosides Extraction and Analysis Conditions
2.6. Proteins Extraction and Analysis Conditions
2.7. Polysaccharides Extraction and Analysis Conditions
2.8. Data Analysis of Each Component
3. Results
3.1. DNA Barcoding Sequence Characterization
3.2. Genetic Distance Analysis
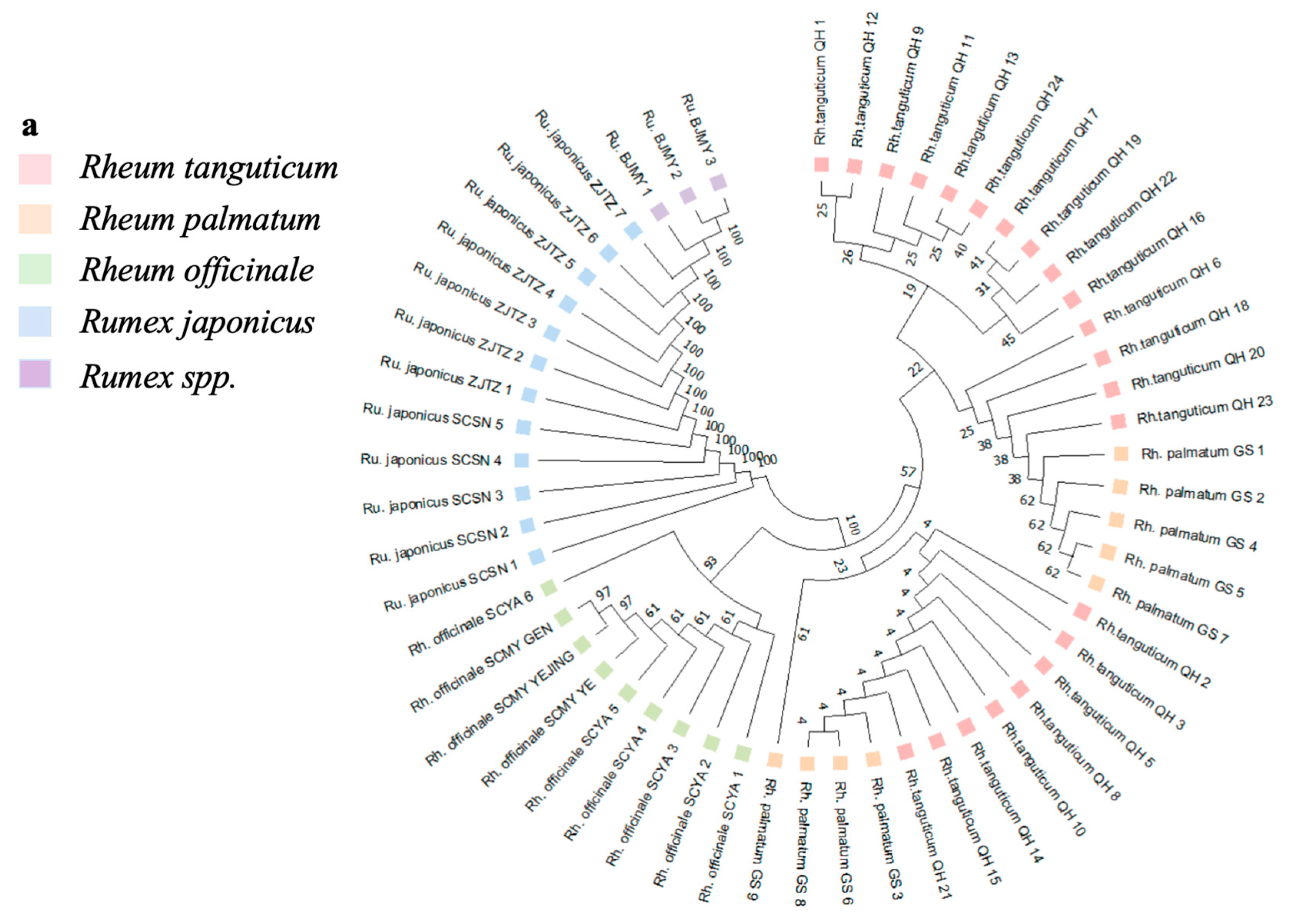
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
3.4. Determination of Medicinal Components in Rhubarb
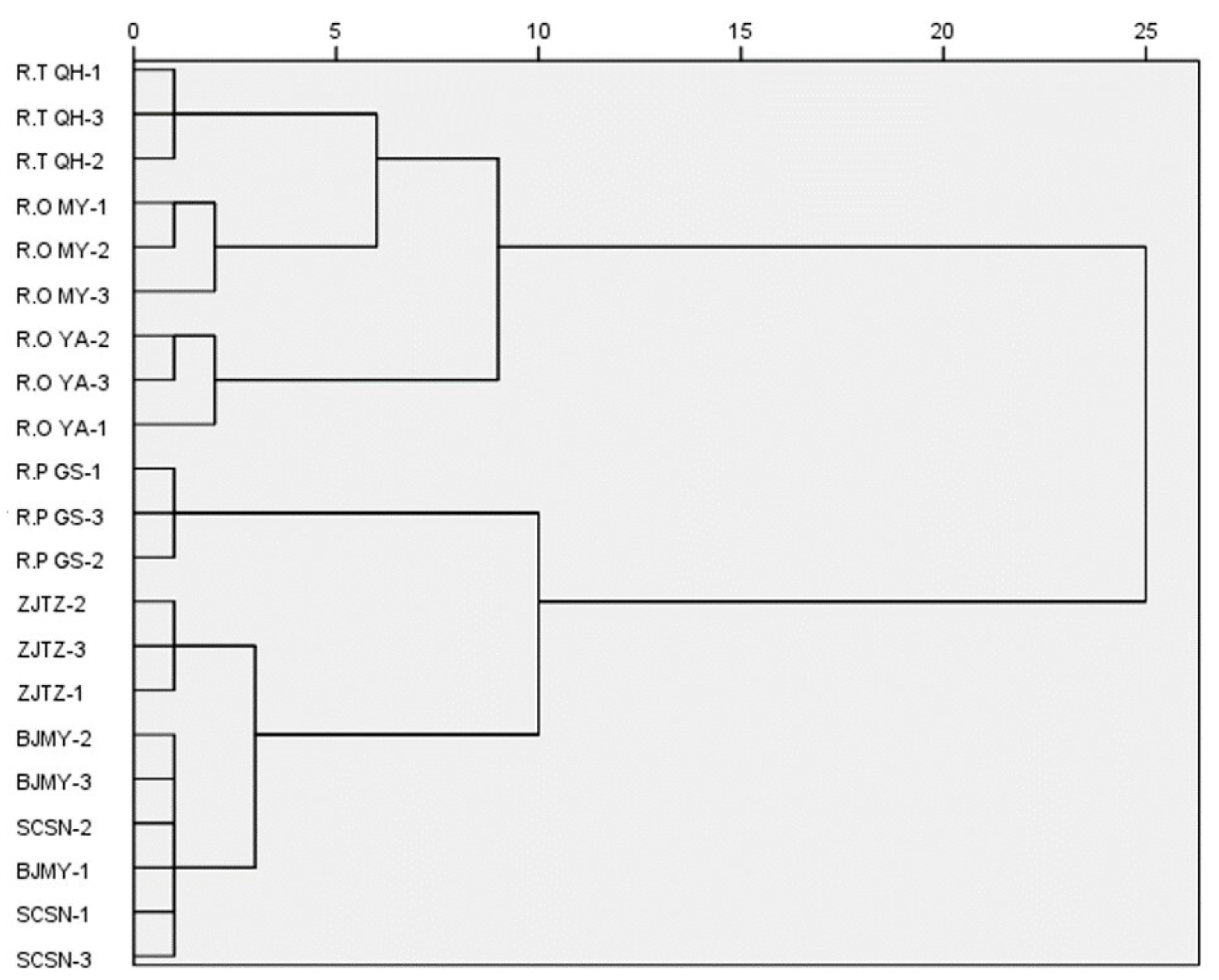
3.5. Cluster Analysis
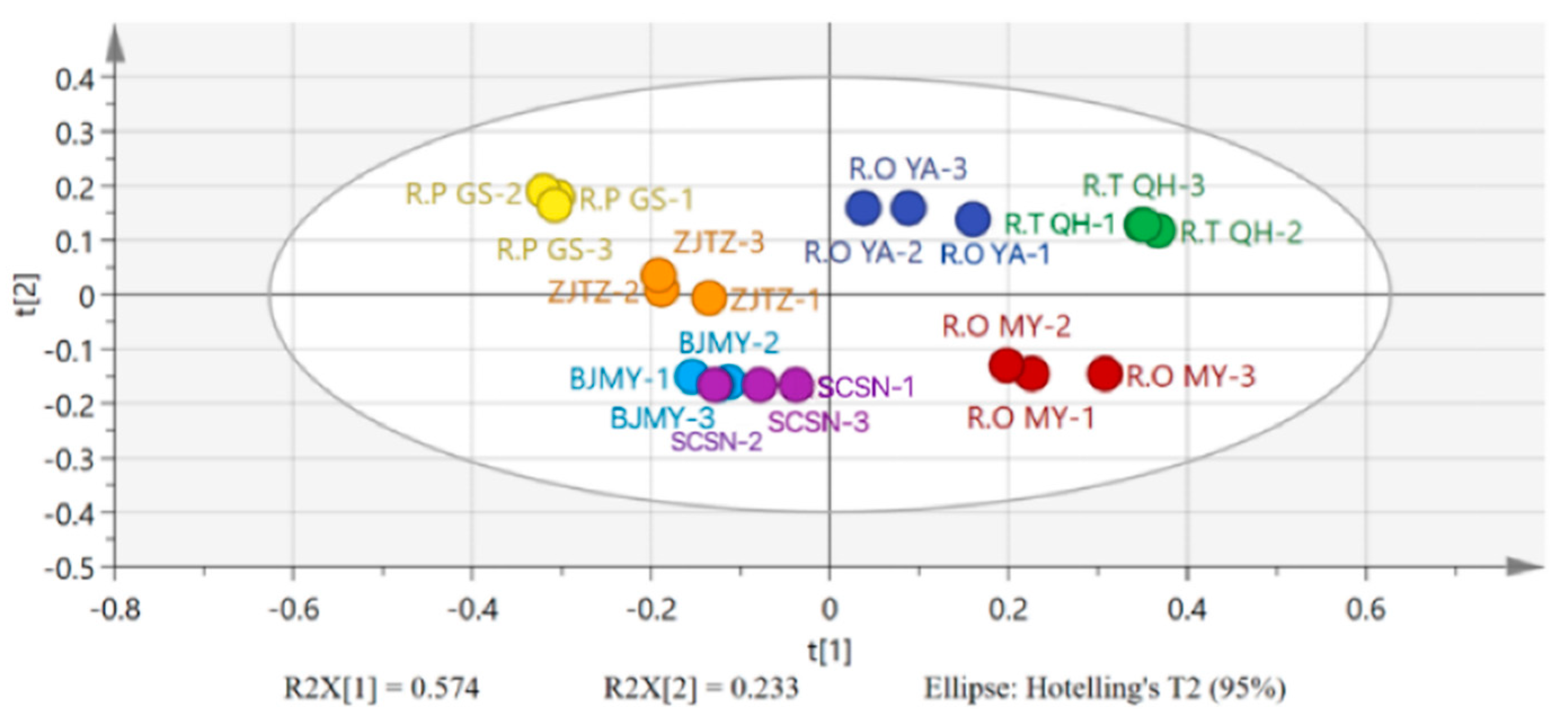
3.6. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- State Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 Edition, Part I); China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.J.; Yao, J.J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. Research progress on authenticity identification and quality control methods of Rhubarb. China Pharm. 2019, 30, 2583–2589. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-L.; Yao, H.; Han, J.-P.; Xin, T.-Y.; Pang, X.-H.; Shi, L.-C.; Luo, K.; Song, J.-Y.; Hou, D.-Y.; Shi, S.-M.; et al. Principles for molecular identification of traditional Chinese materia medica using DNA barcoding. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2013, 38, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.M.; Pan, M.J.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.Q. Application of molecular identification techniques in Chinese materia medica. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2016, 17, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.-W.; Liao, B.-S.; Luo, L.; Ren, Y.-Y. Species identification of poisonous medicinal plant using DNA barcoding. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyaningis, R.; Compto, L.J.; Rahay, S.; Brehm, J.M.; Maxte, N. DNA Barcoding Medicinal Plant Species from Indonesia. Plants 2022, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.P.; Cui, Y.X.; Chen, X.L.; Xu, Z.C.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.Y.; Yao, H. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of the medicinal plant Arctium lappa. Genome 2020, 63, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shang, F. The complete chloroplast genome of Ulmus mianzhuensis with insights into structural variations, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic relationships of Ulmus (Ulmaceae). BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Zou, X.L.; Baskaran, X.R.; Li, Q.; Xing, H.T.; Li, H.L. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Zingiber teres S. Q. Tong & Y. M. Xia (Zingiberaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2023, 8, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Nie, J.; Xiao, L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, B. Comparative Chloroplast Genome Analysis of Rhubarb Botanical Origins and the Development of Specific Identification Markers. Molecules 2018, 23, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, X. Complete chloroplast genome sequence determination of Rheum species and comparative chloroplast genomics for the members of Rumiceae. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.M.; Zen, Y.; Yang, C.F.; Li, M.J.; Li, J.P.; Liu, L.K. High-throughput sequencing of complete chloroplast genome of Rheum tanguticum and its application in species identification. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2019, 50, 5545–5553. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, H.; Tao, X.; Xia, S.; Qu, J.; Song, H.; Liu, J.; Shang, D. Emodin Alleviates Sodium Taurocholate-Induced Pancreatic Acinar Cell Injury via MicroRNA-30a-5p-Mediated Inhibition of High-Temperature Requirement A/Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Inflammatory Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.M.; Peng, F.H.; Zhong, Y.P.; Chen, Y.H.; Tang, M.; Li, D.R. Rhein suppresses matrix metalloproteinase production by regulating the Rac1/ROS/MAPK/AP-1 pathway in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, L.; Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, D.; Sun, Q.; Wu, J.; Cao, S. Free Total Rhubarb Anthraquinones Protect Intestinal Injury via Regulation of the Intestinal Immune Response in a Rat Model of Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keser, S.; Keser, F.; Karatepe, M.; Kaygili, O.; Tekin, S.; Turkoglu, I.; Demir, E.; Yilmaz, O.; Kirbag, S.; Sandal, S. Bioactive contents, In vitro antiradical, antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of rhubarb (Rheum ribes L.) extracts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 3353–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, W.X.; Guo, W.D.; Lei, T.; Ouyang, J.Y.; Zhao, H.; Zou, H.Y. Evaluation of Quality Coherence of Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. from Different Producing Areas Based on HPLC Fingerprint and PCA. Chin. J. Inf. TCM 2017, 24, 1005–5304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.Q.; Gao, X.M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.L.; Di, L.Q. Quality analysis of Caulis Bambusae in Taeniam from different origins by HPLC coupled with chemometrics. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 0523–2670. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.H.; Xu, K.; Yuan, X.M.; Ding, B.; Wang, L.P.; Xu, L.; Yang, B.G.; Liu, Y.H.; Fan, J.W. Based on UHPLC multi-component determination and principal component analysis Quality evaluation of Jinteng Qingbi granules. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 44, 0254–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.L.; Li, Y.R.; Hong, X. Quality evaluation of Scutellaria barbata based on combination of chromatographic fingerprints and multi-component quantitative analysis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2023, 54, 670–676. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.H.; Tang, X.J.; Huang, L.Q. Study on extraction methods of DNA from Chinese medicinal materials containing starch and polysaccharides. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2006, 16, 1365–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.Y.; Ding, Y.M.; Tang, J.C.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhao, T.; Liu, F.; Liu, F.B.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.L. Effects of growth year and specification grade on content of active compounds of Rheum tanguticum. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 45, 842–849+854. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, D.M.; Liu, J.L.; Deng, S.F.; Sun, Y.J.; Wang, Y.L. Determination and analysis of main nutrients in Angelica sinensis roots, stems and leaves. J. Gansu Univ. Chin. Med. 2021, 38, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.H. The Component Analysis of Rheum officinale Baill and the Biotransformation of the Conjugated Anthraquinone; Shaanxi University of Technology: Hanzhong, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.H.; Wu, H.W.; Li, G.F.; Yang, X.R.; Li, X.W.; Song, Q.J.; Li, Y.; Li, W.F. Study on content of total polyphenols and total anthraquinones in rhubarb and its spectrum-effect relationship of anti-oxidation in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2022, 34, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, G.Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Man, J.H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; et al. Screening of specific DNA barcode, identification of germplasm resources, andanalysis of genetic diversity of Atractylodes chinenesis. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2023, 58, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Yin, G.Y.; Chen, Y.; Man, J.H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; et al. Specific DNA barcodes, germplasm resources, and genetic diversity of Eleutherococcus senticosus. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2023, 48, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Brach, A.R.; Song, H. eFloras: New directions for online floras exemplified by the Flora of China Project. Taxon 2006, 55, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Yang, M.; Liu, J. Molecular phylogeny, recent radiation and evolution of gross morphology of the rhubarb genus Rheum (Polygonaceae) inferred from chloroplast DNA trn LF sequences. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, A.; Wan, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J. Rapid radiation of Rheum (Polygonaceae) and parallel evolution of morphological traits. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2012, 63, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, A. Phylogeny of Rheum (Polygonaceae) based on CPDNA TRNS-G sequences. Pak. J. Bot. 2020, 52, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Milne, R. Multiple ITS Copies Reveal Extensive Hybridization within Rheum (Polygonaceae), a Genus That Has Undergone Rapid Radiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanping, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. New occurrence of B chromosomes in Rheum tanguticum Maxim. ex Balf.(Polygonaceae). Caryologia 2011, 64, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Xing, L.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Z.; et al. The haplotype-resolved genome assembly of autotetraploid rhubarb Rheum officinale provides insights into its genome evolution and massive accumulation of anthraquinones. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.H.; Zhao, M.J.; Dang, J.; Luo, L.; Yan, P.A.; Yuan, A.; Li, Y.X.; Peng, C. Comparision of contents of thirteen components in different origins of Rhei Radix et Rhizoma based on principal component analysis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 4994–4999. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.Q.; Tian, J.; Feng, R.Z.; Zhou, W.H.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of quality of Rhubarb based on principal component and cluster analysis. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Medica 2019, 30, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. UPLC fingerprint combined with principal component analysis for quality control of Rheum palmatum. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Kou, L.; Li, X.R.; Kang, S.H. General situation of extraction method, structure and pharmacological activity of rhubarb polysaccharide. Shangdong Chem. Ind. 2022, 51, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.M.; Luo, S.N.; Wei, M.; Zhu, D.Q.; He, G.M.; Luo, W.A.; Yang, R.P. Study on quality evaluation of different origins of Rhei Radix et Rhizoma Based on multivariate statistical analysis fingerprints and multi-component quantitative analysis. J. Nanjing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 37, 83–90. [Google Scholar]


| Species | Sample Code | Origin | Number of Samples | Form of Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rheum tanguticum | Rh. tanguticum QH | Qinghai | 22 | Roots |
| Rheum officinale | Rh. officinale SCYA | Ya’an, Sichuan | 6 | Roots |
| Rheum officinale | Rh. officinale SCMY | Mianyang, Sichuan | 3 | Root, leaf, stem |
| Rheum palmatum | Rh. palmatum GS | Gansu | 9 | Roots |
| Rumex japonicus | Ru. japonicus ZJTZ | Zhejiang | 7 | Roots |
| Rumex japonicus | Ru. japonicus SCSN | Sichuan | 5 | Roots |
| Rumex spp. | Ru. BJMY | Beijing | 3 | Roots |
| Primer | Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Amplification Condition | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| rps3-rpl22-F | CAACGAGTCACACACTAAG | 94 °C 5 min; (94 °C 30 s, 50 °C 30 s, 72 °C 70 s, 35 cycles); 72 °C 10 min. | 1044 bp |
| rps3-rpl22-R | CTAAACACAATAGAGGGTTCG | ||
| rpl16-F | CCTATTACAGAACCGGAC | 94 °C 5 min; (94 °C 30 s, 51 °C 30 s, 72 °C 60 s, 35 cycles); 72 °C 10 min. | 973 bp |
| rpl16-R | CTTAGTGTGTGACTCGTT |
| Sample | Interspecific Genetic Divergences | Intraspecific Genetic Divergences | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh.T | Rh.P | Rh.O | ||
| Rh. tanguticum | 0–0.0060 | |||
| Rh. palmatum | 0–0.0060 | 0–0.0012 | ||
| Rh. officinale | 0.0060–0.0108 | 0.0060–0.0084 | 0–0.0012 | |
| Ru. | 0.0205–0.0254 | 0.0205–0.0218 | 0.0242–0.0254 | 0.0000 |
| Sample | Interspecific Genetic Divergences | Intraspecific Genetic Divergences | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh.T | Rh.P | Rh.O | ||
| Rh. tanguticum | 0–0.0012 | |||
| Rh. palmatum | 0–0.0024 | 0–0.0012 | ||
| Rh. officinale | 0.0024–0.0048 | 0.0024–0.0048 | 0–0.0012 | |
| Ru. | 0.0804–0.0845 | 0.0804–0.0860 | 0.0804–0.0863 | 0–0.0013 |
| Components | Regression Equation | Range | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aloe-emodin | y = 25.067x − 3952.5 | 0.5–50 μg/mL | 1.0000 |
| Rhein | y = 10.158x + 5820.2 | 0.1–120 μg/mL | 0.9992 |
| Emodin | y = 30.231x − 15713 | 1–50 μg/mL | 0.9995 |
| Chrysophanol | y = 29.666x − 5833.3 | 1–100 μg/mL | 0.9995 |
| Physcion | y = 16.549x − 3540.7 | 1–100 μg/mL | 0.9998 |
| Sennoside A | y = 6029.3x – 20.076 | 1–300 μg/mL | 0.9991 |
| Sennoside B | y = 9731.7x – 22.576 | 1–100 μg/mL | 0.9991 |
| Proteins | y = 0.5592x + 0.0096 | 0.0059–1.1800 mg/mL | 0.9987 |
| Polysaccharides | y = 6.3011x − 0.0751 | 0.01–0.70 mg/mL | 0.9953 |
| Total Anthraquinones | Free Anthraquinones | Combination Anthraquinones | Sennoside B | Sennoside A | Total Sennosides | Polysaccharides | Proteins | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh. tanguticum QH | 3.896 ± 0.035 | 1.260 ± 0.045 | 2.636 ± 0.063 | 0.057 ± 0.001 | 0.308 ± 0.002 | 0.365 ± 0.002 | 12.842 ± 0.223 | 2.175 ± 0.072 |
| Rh. officinale SCYA | 0.826 ± 0.007 | 0.607 ± 0.009 | 0.219 ± 0.002 | 0.061 ± 0.001 | 0.072 ± 0.004 | 0.132 ± 0.005 | 10.950 ± 1.467 | 5.769 ± 0.109 |
| Rh. officinale SCMY | 0.668 ± 0.012 | 0.581 ± 0.009 | 0.087 ± 0.007 | 0.074 ± 0.001 | 0.061 ± 0.007 | 0.135 ± 0.007 | 15.942 ± 1.358 | 1.435 ± 0.180 |
| Rh. palmatum GS | 0.976 ± 0.019 | 0.372 ± 0.007 | 0.604 ± 0.018 | 0.059 ± 0.001 | 0.063 ± 0.003 | 0.122 ± 0.003 | 1.245 ± 0.149 | 4.797 ± 0.180 |
| Ru. BJMY | 0.605 ± 0.014 | 0.178 ± 0.004 | 0.427 ± 0.014 | - | 0.061 ± 0.004 | 0.061 ± 0.004 | 5.772 ± 0.487 | 0.172 ± 0.072 |
| Ru. japonicus SCSN | 0.600 ± 0.013 | 0.441 ± 0.006 | 0.159 ± 0.009 | 0.046 ± 0.001 | 0.073 ± 0.002 | 0.119 ± 0.002 | 7.725 ± 1.084 | 0.148 ± 0.109 |
| Ru. japonicus ZJTZ | 0.926 ± 0.015 | 0.627 ± 0.009 | 0.299 ± 0.023 | 0.054 ± 0.001 | 0.065 ± 0.007 | 0.119 ± 0.007 | 3.870 ± 0.717 | 2.461 ± 0.258 |
| Principal Component | Initial Eigenvalue | Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variance Contribution Rate (%) | Cumulative Variance Contribution Rate (%) | Total | Variance Contribution Rate (%) | Cumulative Variance Contribution Rate (%) | |
| 1 | 5.103 | 63.786 | 63.786 | 5.103 | 63.786 | 63.786 |
| 2 | 1.541 | 19.267 | 83.053 | 1.541 | 19.267 | 83.053 |
| 3 | 0.957 | 11.964 | 95.017 | |||
| 4 | 0.333 | 4.165 | 99.182 | |||
| 5 | 0.056 | 0.696 | 99.878 | |||
| 6 | 0.010 | 0.122 | 100.000 | |||
| 7 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 100.000 | |||
| 8 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 100.000 | |||
| Factor | Principal Component Load Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| Total sennosides | 0.996 | −0.006 |
| Total anthraquinones | 0.972 | −0.165 |
| Sennoside A | 0.970 | −0.223 |
| Free anthraquinones | 0.963 | 0.149 |
| Combination anthraquinones | 0.924 | −0.274 |
| Polysaccharides | 0.552 | 0.199 |
| Sennoside B | 0.363 | 0.848 |
| Proteins | 0.095 | 0.780 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shen, L.; Lu, Y.; Lin, J.; Tang, F.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, C.; et al. Comprehensive Identification of Rhubarb Species Based on DNA Barcoding and Multiple-Indicator Quantification. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081746
Wang Y, Yang L, Yang Z, Zhang M, Shen L, Lu Y, Lin J, Tang F, Jiang Q, Zhu C, et al. Comprehensive Identification of Rhubarb Species Based on DNA Barcoding and Multiple-Indicator Quantification. Agronomy. 2024; 14(8):1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081746
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yifan, Lin Yang, Zhao Yang, Min Zhang, Luyi Shen, Yiwen Lu, Jing Lin, Fan Tang, Qiong Jiang, Cheng Zhu, and et al. 2024. "Comprehensive Identification of Rhubarb Species Based on DNA Barcoding and Multiple-Indicator Quantification" Agronomy 14, no. 8: 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081746
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, L., Yang, Z., Zhang, M., Shen, L., Lu, Y., Lin, J., Tang, F., Jiang, Q., Zhu, C., Zhang, L., & Ding, Y. (2024). Comprehensive Identification of Rhubarb Species Based on DNA Barcoding and Multiple-Indicator Quantification. Agronomy, 14(8), 1746. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081746





