The Carbon Footprint and Influencing Factors of the Main Grain Crops in the North China Plain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Calculation of Agricultural Carbon Emissions
3. Results
3.1. Crop Yield and Sown Area
3.2. Carbon Footprint
3.2.1. Area-Scaled Carbon Footprint
3.2.2. Yield-Scaled Carbon Footprint
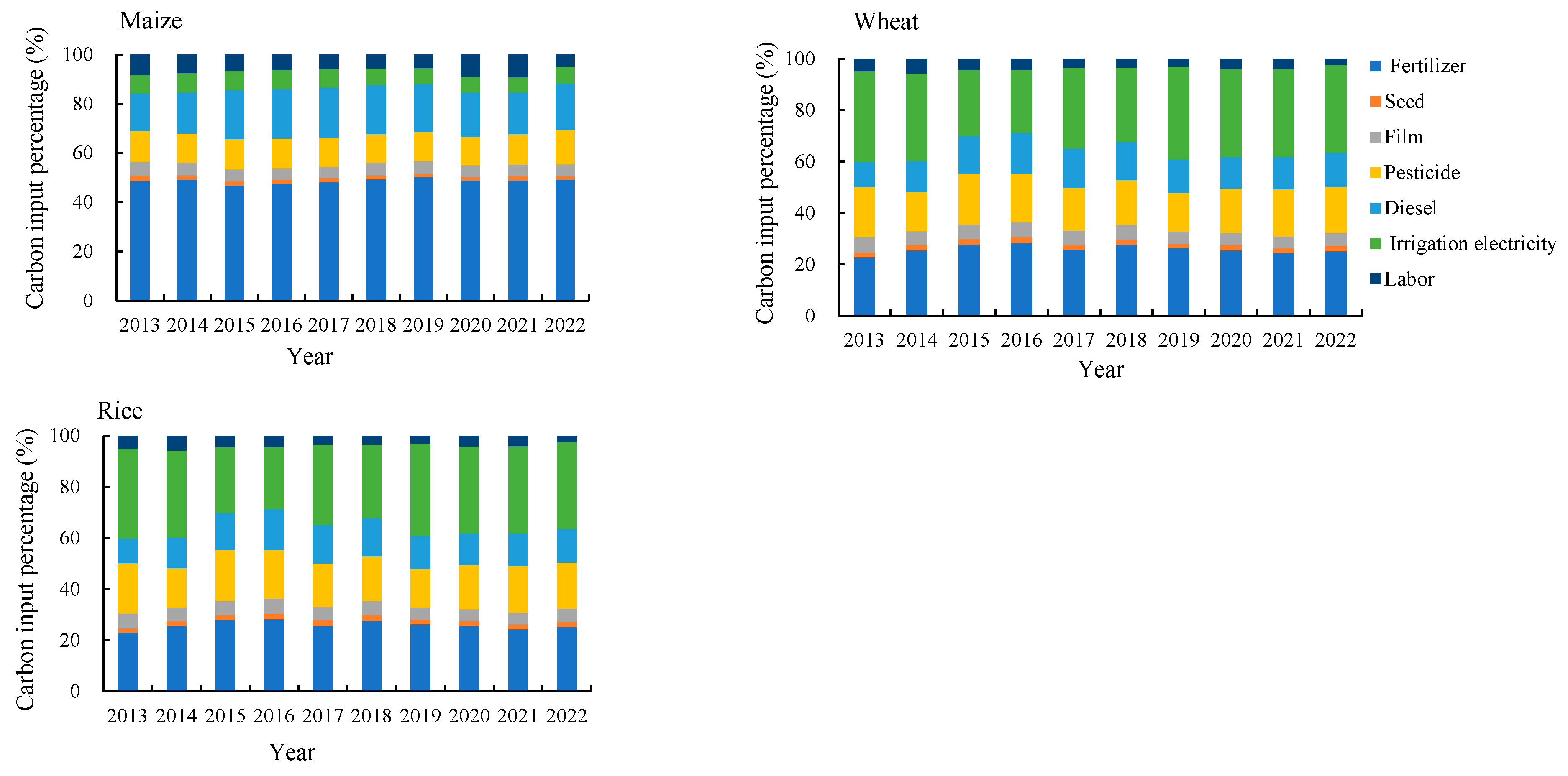
3.3. Agricultural Carbon Emissions from Different Agricultural Carbon Sources
3.4. Carbon Efficiency of Crop Production
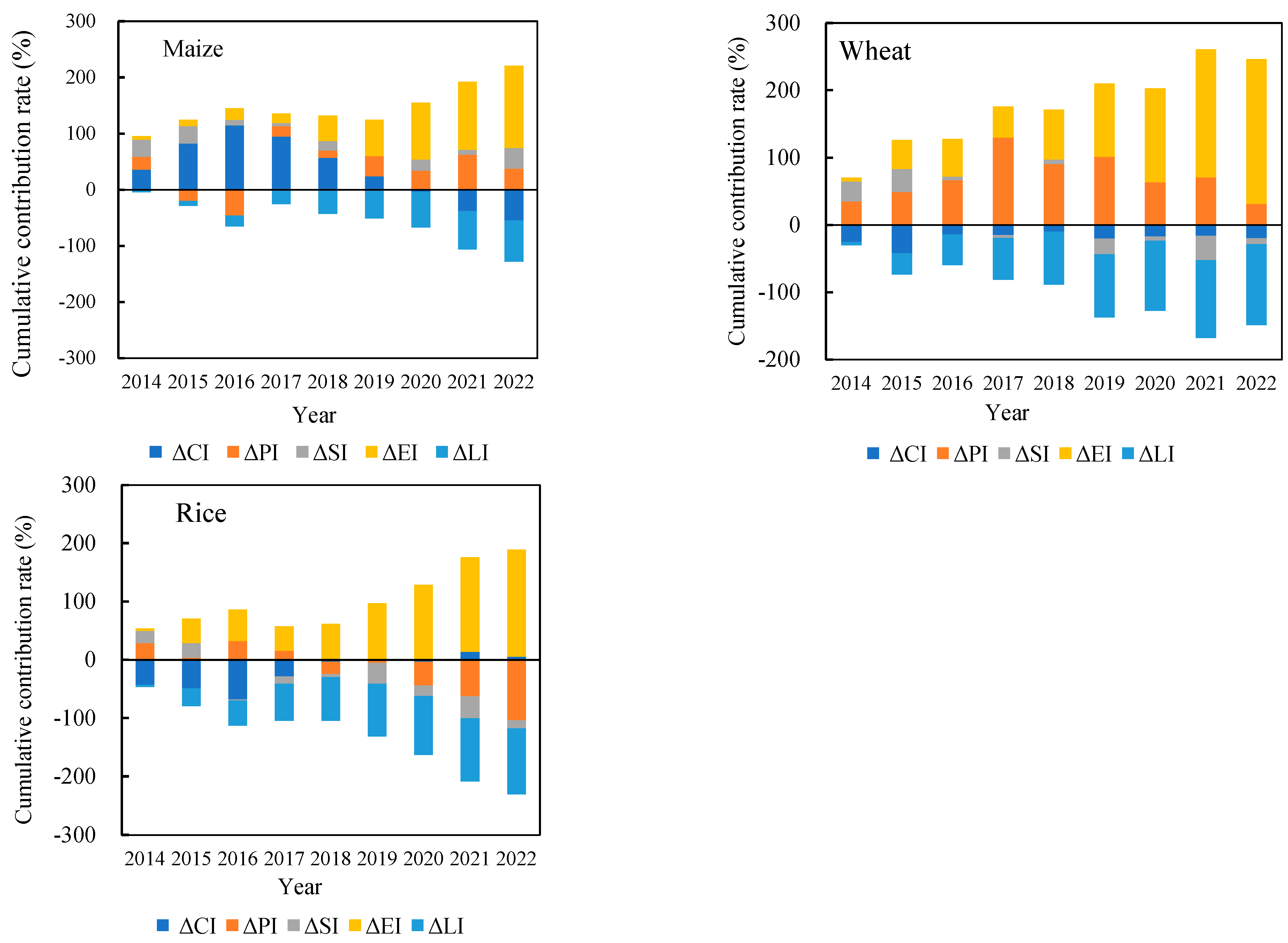
3.5. Main Influencing Factors of Agricultural Carbon Emissions
4. Discussions
4.1. Changes in Maize, Wheat, and Rice Yields, Sown Area, and Agricultural Inputs in the NCP
4.2. Changes in the CF of Maize, Wheat, and Rice Production in the NCP and Their Influence Factors
4.3. Carbon Emission Reduction Measures and Prospects for Grain Crops in the NCP
4.4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, M.; Chandler, R.E.; Cox, P.M.; Huthnance, J.M.; Rougier, J.; Stephenson, D.B. Quantifying future climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.J.; Smith, S.J.; Silva, R.A.; Naik, V.; Zhang, Y.; Adelman, Z.; Fry, M.M.; Anenberg, S.; Horowitz, L.W.; Lamarque, J.F. Co-benefits of mitigating global greenhouse gas emissions for future air quality and human health. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Masui, T. Achieving Carbon Emissions Peak in China by 2030: The Key Options and Economic Impacts. In Post-2020 Climate Action; Fujimori, S., Kainuma, M., Masui, T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, P.; Storelvmo, T.; Armour, K.; Collins, W.; Dufresne, J.L.; Frame, D.; Lunt, D.J.; Mauritsen, T.; Palmer, M.D.; Watanabe, M.; et al. The Earth’s Energy Budget, Climate Feedbacks, and Climate Sensitivity. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 923–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Campbell, B.M.; Ingram, J.S.I. Climate change and food systems. Annu. Rev. Env. Resour. 2012, 37, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhong, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xi, F.; Liu, S. Coupling and decoupling effects of agricultural carbon emissions in China and their driving factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 25280–25293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.A.; Kemp, S.; Williams, I. ‘Carbon footprinting’: Towards a universally accepted definition. Carbon Manag. 2011, 2, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Liang, C.; Hamel, C.; Cutforth, H.; Wang, H. Strategies for reducing the carbon footprint of field crops for semiarid areas. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Reducing agricultural carbon footprint through diversified crop rotation systems in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 76, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Pan, G.X.; Smith, P.; Luo, T.; Li, L.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Han, X.J.; Yan, M. Carbon footprint of China’s crop production-an estimation using agro statistics data over 1993–2007. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, F.; Han, W.; Li, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Lei, Y.; et al. Carbon footprint of cotton production in China: Composition, spatiotemporal changes and driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Dong, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, F.; Hu, Z. Dynamic Analysis of the Carbon Footprint in Winter Wheat Production Based on Lifecycle Assessment and the LMDI Model: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Bian, X. Carbon footprint analysis of farmland ecosystem in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 25, 203–208. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Carbon footprint analysis of crop production in North China Plain. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 83–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hillier, J.; Hawes, C.; Squire, G.; Hilton, A.; Wale, S.; Smith, P. The carbon footprints of food crop production. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2009, 7, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lei, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Dong, W.; Yang, Y. Changes in carbon dioxide emissions and LMDI-based impact factor decomposition: The Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region as a case. J. Arid Land 2014, 6, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). China Statistics Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Price Department of National Development and Reform Commission. The National Cost-Benefit Survey for Agricultural Product; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of China Price Yearbook. China Price Yearbook; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, L. Assessment of Agricultural Carbon Emissions and Their Spatiotemporal Changes in China, 1997–2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Niu, J. Water and Carbon Footprint and Layout Optimization of Major Grain Crops in the Northwest China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2024, 57, 1137–1152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Ou, Q.; Chen, Y. Decomposition of China’s CO2 emissions from agriculture utilizing an improved Kaya identity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 13000–13006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Liao, M.; Xie, X.; Guo, B.; Lu, X.; Qiu, H. Agricultural carbon emissions in Zhejiang Province, China (2001–2020): Changing trends, influencing factors, and has it achieved synergy with food security and economic development? Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Cao, B.; Tian, S.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Wheat yield improvements in China: Past trends and future directions. Field Crop Res. 2015, 177, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zou, J.; Chen, F.; Yin, X. Changes of the planting structure of major food and oil crops in China from 1951 to 2015. J. China Agric. Univ. 2019, 24, 183–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y. China’s water scarcity. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3185–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X. Analysis of ecosystem carbon footprint for three staple crop farmlands in China. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2024, 60, 575–584. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Yan, M.; Nayak, D.; Pan, G.X.; Smith, P.; Zheng, J.F.; Zheng, J.W. Carbon footprint of crop production in China: An analysis of National Statistics data. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 153, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, L.; Sun, B.; Kong, W.; Tang, S. Carbon footprint of crop production in China from 1993 to 2013 and its spatial distribution. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 2577–2587. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Shen, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W. Carbon footprint of grain production in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, C.S.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Jensen, T.L.; Fixen, P.E. Review of greenhouse gas emissions from crop production systems and fertilizer management effects. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, H.; Jain, N.; Bhatia, A.; Patel, J.; Aggarwal, P.K. Carbon footprints of Indian food items. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Qiu, J.; Yu, J. Impact of farmland characteristics on grain costs and benefits in the North China Plain. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.H.; Birchenall, J.A. Agricultural productivity, structural change, and economic growth in post-reform China. J. Dev. Econ. 2013, 104, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K.; Caglar, A.E. Investigating the EKC hypothesis with Renewable Energy Consumption, Human Capital, Globalization and Trade Openness for China: Evidence from Augmented ARDL Approach with a Structural Break. Energy 2021, 216, 119220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Davies, W.J.; Zhang, F. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartal, M.T.; Pata, U.K. Impacts of renewable energy, trade globalization, and technological innovation on environmental development in China: Evidence from various environmental indicators and novel quantile methods. Environ. Dev. 2023, 48, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.K.; Modi, B.; Pandey, H.P.; Subedi, A.; Aryal, G.; Pandey, M.; Shrestha, J. Diversified crop rotation: An approach for sustainable agriculture production. Adv. Agric. 2021, 2021, 8924087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Haberl, H.; Popp, A.; Erb, K.; Lauk, C.; Harper, R.; Tubiello, F.N.; de Siqueira Pinto, A.; Jafari, M.; Sohi, S.; et al. How much land-based greenhouse gas mitigation can be achieved without compromising food security and environmental goals? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2285–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Fan, M.; et al. Integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. Adv. Agron. 2012, 116, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Yan, X. Research progress and prospect of greenhouse gas emissions from the life-cycle production of food crops in China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 665–672. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Guo, D.; Han, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Xie, J.; Niu, J.; Yin, L. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Carbon Footprint of Main Crop Production in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Cai, Y.; Su, D.; Muneer, M.A.; Guo, M.; et al. Identifying the main crops and key factors determining the carbon footprint of crop production in China, 2001–2018. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 172, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Ti, C.; Li, B.; Xia, Y.; Yan, X. Greenhouse gas emissions and reactive nitrogen releases during the life-cycles of staple food production in China and their mitigation potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 556, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Du, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yao, C.; Sun, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Novel water-saving cultivation system maintains crop yield while reducing environmental costs in North China Plain. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 197, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Saetnan, E.; Cheng, K.; Wang, W.; Koslowski, F.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, J.K.; Liu, J.X.; Moran, D.; et al. Management opportunities to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from Chinese agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Li, D.; Lu, H.; Feng, S.; Nie, Q. Trends, distribution, and impact factors of carbon footprints of main grains production in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qiao, Y.; Lakshmanan, P.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.; Zhong, C.; Chen, X. Combing public-private partnership and large-scale farming increased net ecosystem carbon budget and reduced carbon footprint of maize production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 184, 106411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Lun, F.; Lu, M.; Sun, X.; Yang, P.; Wu, W.; Liu, J. Workable solutions for sustainably feeding the Chinese population. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 205, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Zhu, X.; Huang, S.; Linquist, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wassmann, R.; Minamikawa, K.; Martinez-Eixarch, M.; Yan, X.; Zhou, F.; et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation in rice agriculture. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Han, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Duan, X.; Zheng, H.; Miao, H. Soil carbon sequestrations by nitrogen fertilizer application, straw return and no-tillage in China’s cropland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
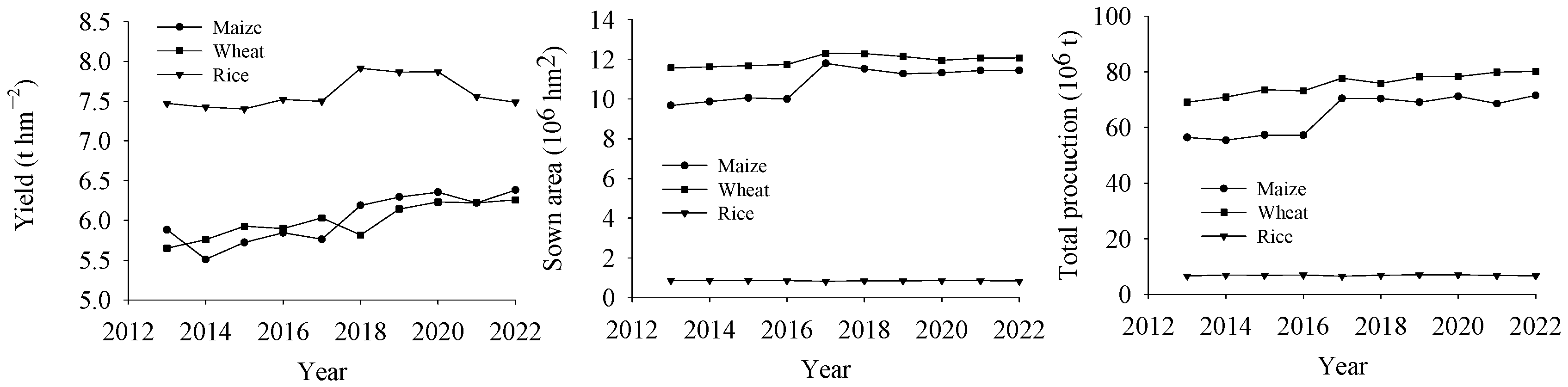
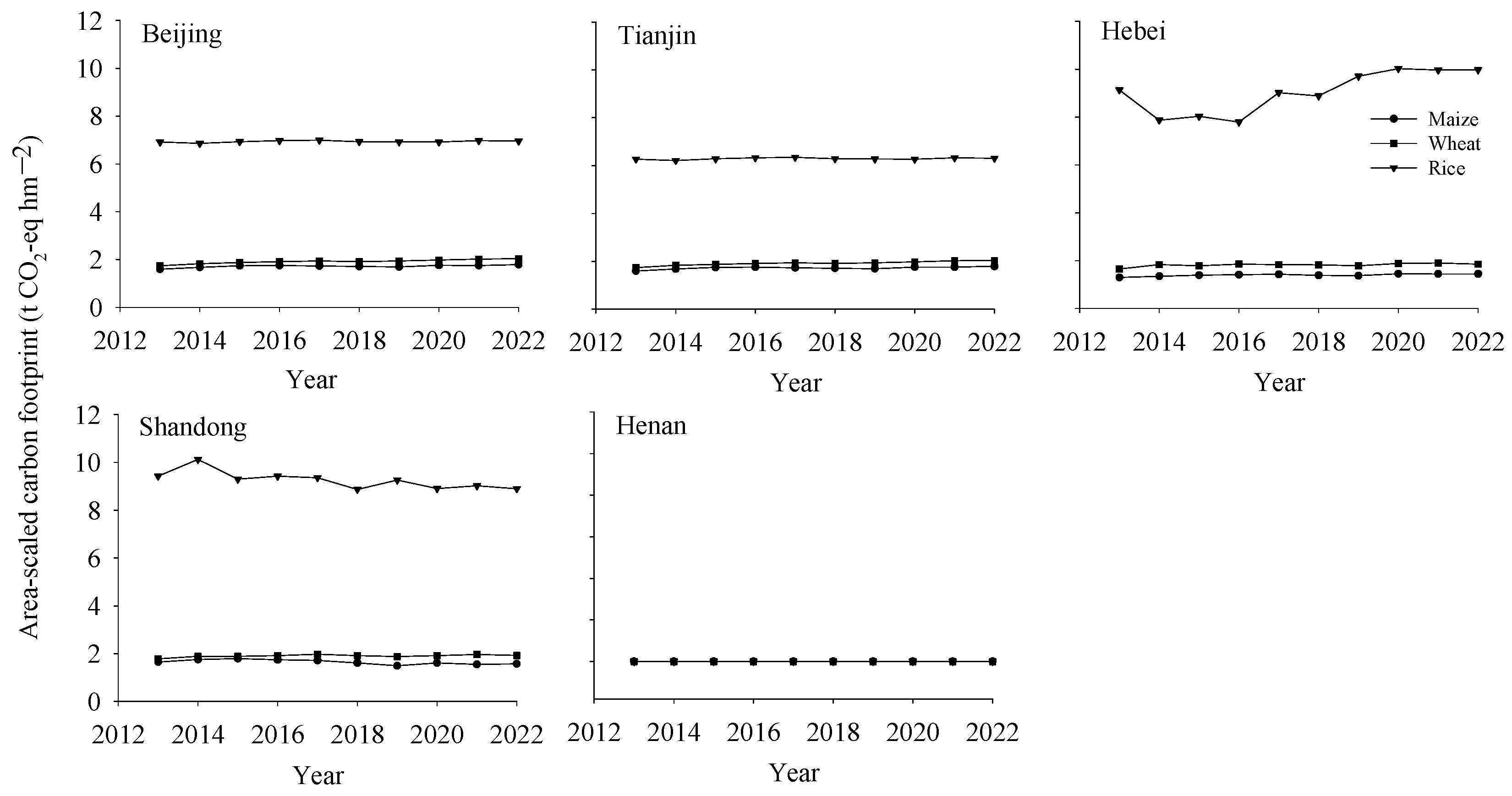
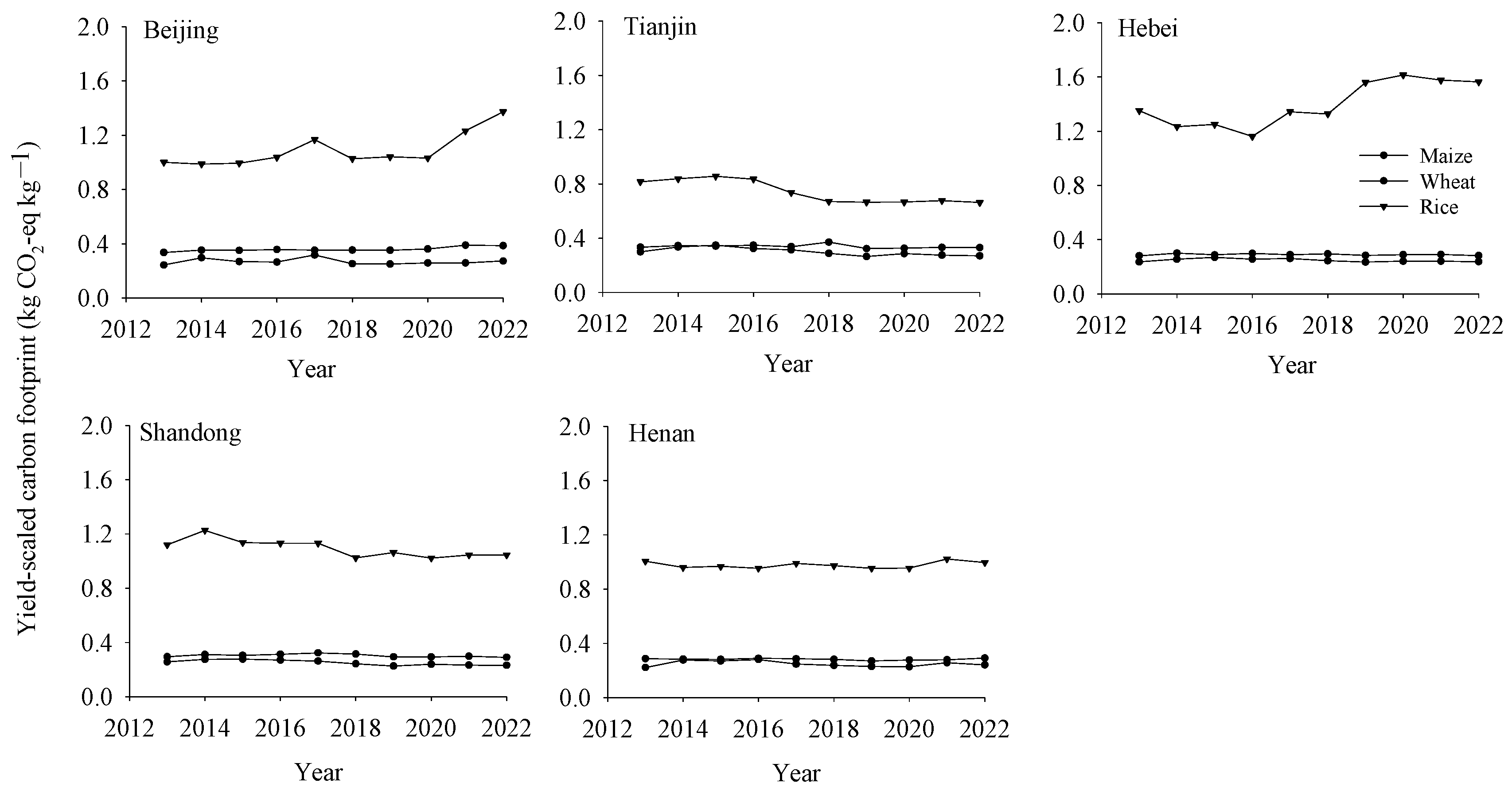
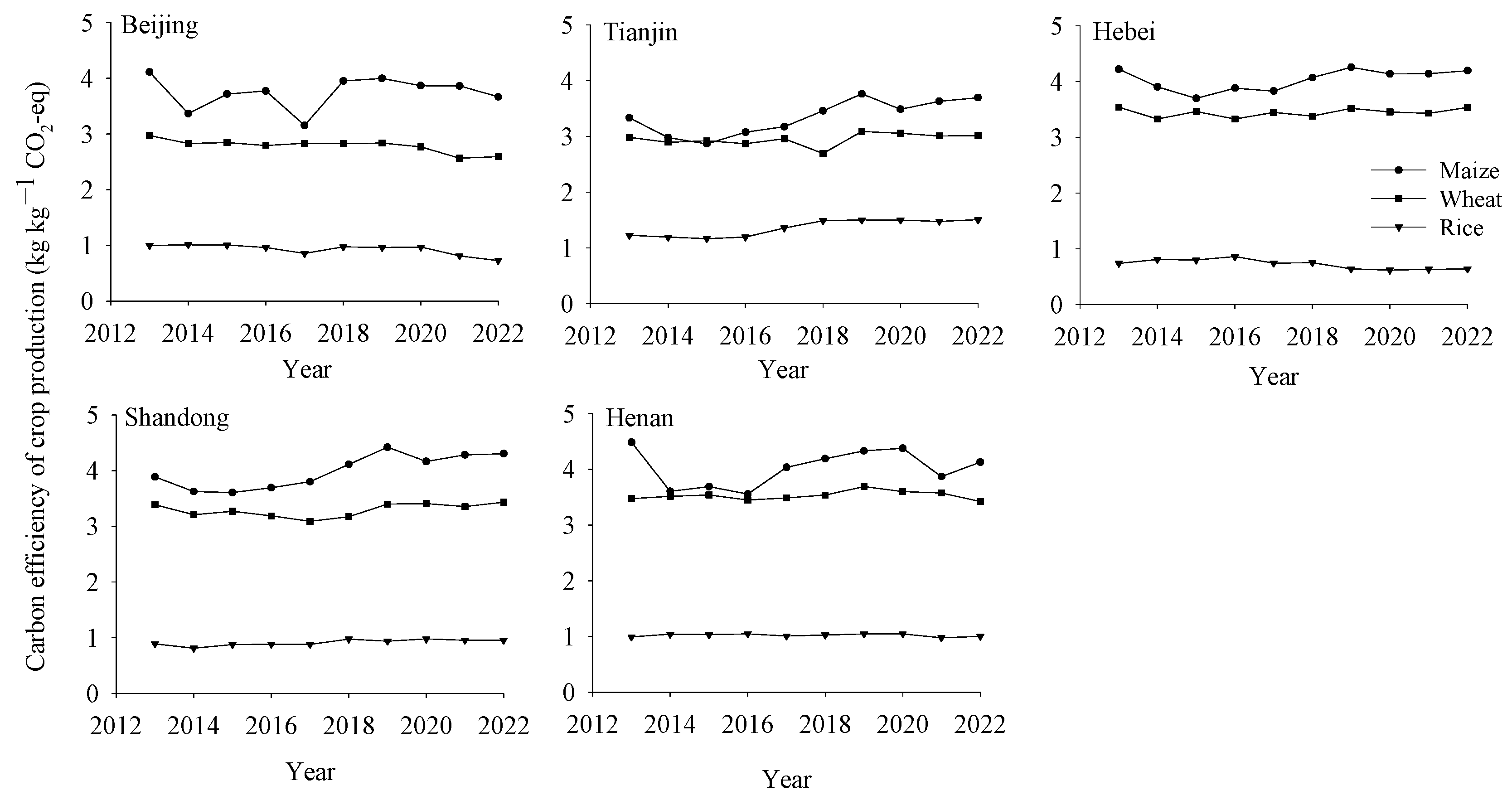
| Agricultural Input | Emission Factor | |
|---|---|---|
| Unit | Value | |
| Nitrogen fertilizer | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 1.53 |
| Phosphate fertilizer | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 1.63 |
| Potassic fertilizer | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 0.66 |
| Compound fertilizer | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 1.77 |
| Pesticide | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 12.5 |
| Electricity for irrigation | kg CO2-eq kWh−1 | 1.23 |
| Diesel | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 0.89 |
| Plastic film | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 22 |
| Seed | kg CO2-eq kg−1 | 0.58 |
| Labor | kg CO2-eq day−1 | 0.86 |
| Year | ΔCI | ΔPI | ΔSI | ΔEI | ΔLI | ΔCtotal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013–2014 | 53.5 | 34.7 | 45.7 | 8.8 | −7.2 | 135.5 |
| 2014–2015 | 521.2 | −486.0 | 6.9 | 60.5 | −43.3 | 59.2 |
| 2015–2016 | 69.3 | −54.6 | −46.0 | 20.4 | −22.2 | −33.0 |
| 2016–2017 | −177.0 | 565.3 | −32.9 | −35.9 | −58.2 | 261.2 |
| 2017–2018 | −202.0 | −30.8 | 57.9 | 153.3 | −90.4 | −112.0 |
| 2018–2019 | −249.3 | 174.1 | −126.8 | 144.5 | −61.6 | −119.1 |
| 2019–2020 | −173.6 | −15.9 | 130.2 | 231.6 | −82.3 | 89.9 |
| 2020–2021 | −272.3 | 227.1 | −93.1 | 158.8 | −34.4 | −14.0 |
| 2021–2022 | −77.6 | −117.1 | 132.8 | 118.6 | −23.6 | 33.1 |
| Total | −507.8 | 296.8 | 74.6 | 860.5 | −423.3 | 300.8 |
| Year | ΔCI | ΔPI | ΔSI | ΔEI | ΔLI | ΔCtotal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | −56.4 | 77.6 | 65.6 | 12.6 | −10.3 | 89.1 |
| 2015 | −36.8 | 31.9 | 9.5 | 83.5 | −59.8 | 28.3 |
| 2016 | 61.6 | 38.5 | −63.9 | 28.4 | −30.8 | 33.8 |
| 2017 | −3.7 | 300.6 | −44.3 | −48.3 | −78.3 | 126.0 |
| 2018 | 34.2 | −275.9 | 75.1 | 198.9 | −117.3 | −84.9 |
| 2019 | −56.7 | 61.8 | −170.7 | 194.6 | −83.0 | −54.0 |
| 2020 | 31.5 | −383.7 | 175.8 | 312.6 | −111.1 | 25.0 |
| 2021 | 3.8 | 29.7 | −125.6 | 214.1 | −46.4 | 75.6 |
| 2022 | −23.6 | −260.5 | 182.1 | 162.7 | −32.3 | 28.4 |
| Total | −46.0 | −379.9 | 103.6 | 1159.1 | −569.5 | 267.3 |
| Year | ΔCI | ΔPI | ΔSI | ΔEI | ΔLI | ΔCtotal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | −45.9 | 30.3 | 22.4 | 4.3 | −3.5 | 7.6 |
| 2015 | −4.2 | −18.3 | 3.1 | 27.7 | −19.8 | −11.5 |
| 2016 | −14.8 | 22.2 | −20.5 | 9.1 | −9.9 | −13.9 |
| 2017 | 46.9 | −20.1 | −13.3 | −14.5 | −23.6 | −24.7 |
| 2018 | 72.6 | −106.4 | 22.2 | 58.8 | −34.7 | 12.5 |
| 2019 | 2.1 | 31.2 | −53.1 | 60.5 | −25.8 | 15.0 |
| 2020 | −3.1 | −116.0 | 55.6 | 98.9 | −35.2 | 0.2 |
| 2021 | 34.1 | −44.5 | −39.0 | 66.4 | −14.4 | 2.7 |
| 2022 | −18.8 | −93.7 | 54.6 | 48.8 | −9.7 | −18.8 |
| Total | 68.9 | −315.3 | 32.1 | 360.0 | −176.6 | −30.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, B.; Yao, L.; Gao, X. The Carbon Footprint and Influencing Factors of the Main Grain Crops in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081720
Sun T, Li H, Wang C, Li R, Zhao Z, Guo B, Yao L, Gao X. The Carbon Footprint and Influencing Factors of the Main Grain Crops in the North China Plain. Agronomy. 2024; 14(8):1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081720
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tao, Hongjie Li, Congxin Wang, Ran Li, Zichao Zhao, Bing Guo, Li Yao, and Xinhao Gao. 2024. "The Carbon Footprint and Influencing Factors of the Main Grain Crops in the North China Plain" Agronomy 14, no. 8: 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081720
APA StyleSun, T., Li, H., Wang, C., Li, R., Zhao, Z., Guo, B., Yao, L., & Gao, X. (2024). The Carbon Footprint and Influencing Factors of the Main Grain Crops in the North China Plain. Agronomy, 14(8), 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081720






