Study on the Appropriate Degree of Water-Saving Measures in Arid Irrigated Areas Considering Groundwater Level
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Regional Problem
2.3. Data Sources
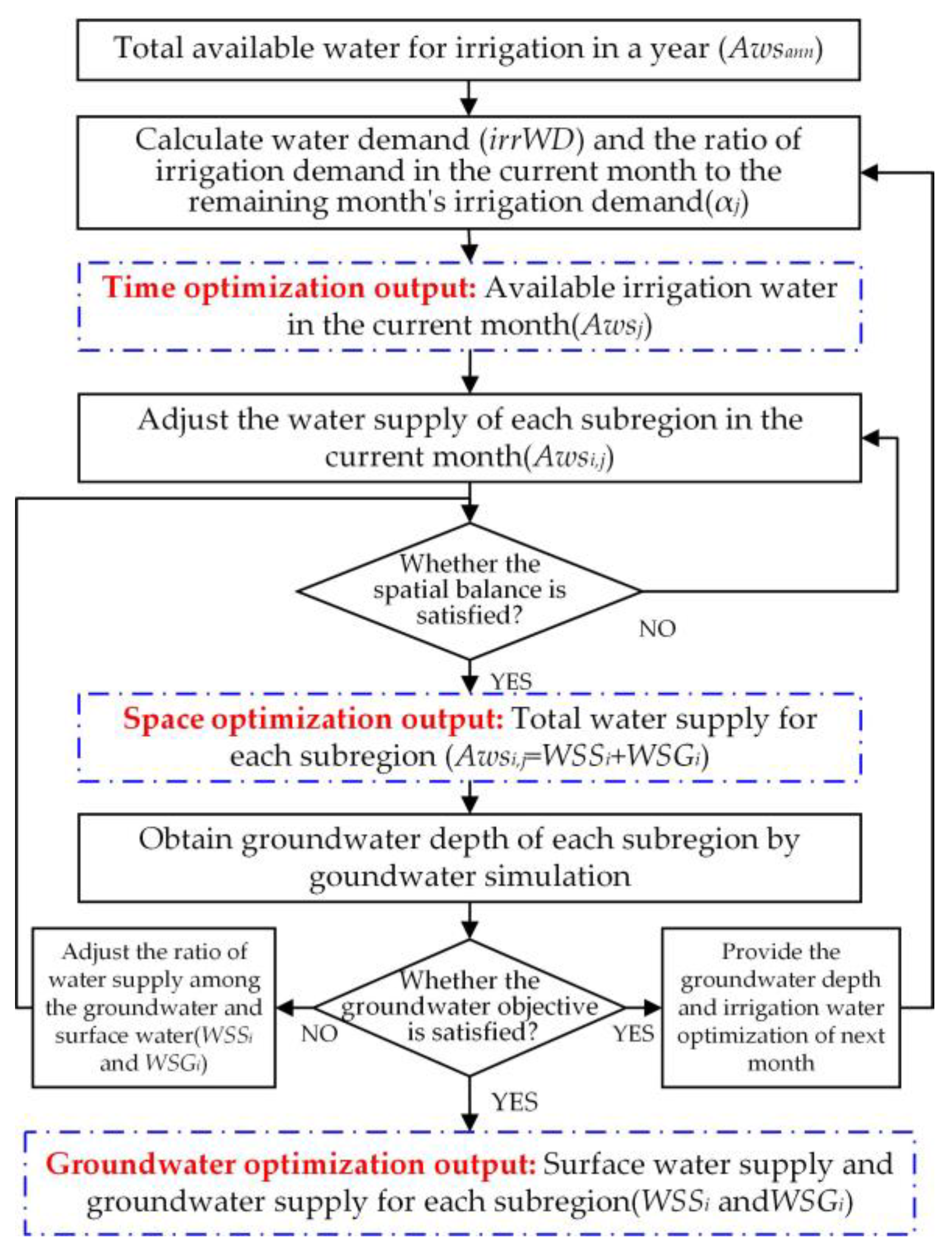
3. Method
3.1. The Optimal Allocation Method of Water Resources
3.2. The Scenarios of Water-Saving Measures
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation of the Effect of Single Water-Saving Schemes
4.1.1. The Impact of Single Water-Saving Schemes on Water Scarcity and Water Shortage Rate
4.1.2. The Response of Changes in Groundwater to Different Single Water-Saving Schemes
4.1.3. The Comprehensive Evaluation of the Effect of Single Water-Saving Schemes
4.2. Estimated of the Effect of Comprehensive Water-Saving Measure Schemes
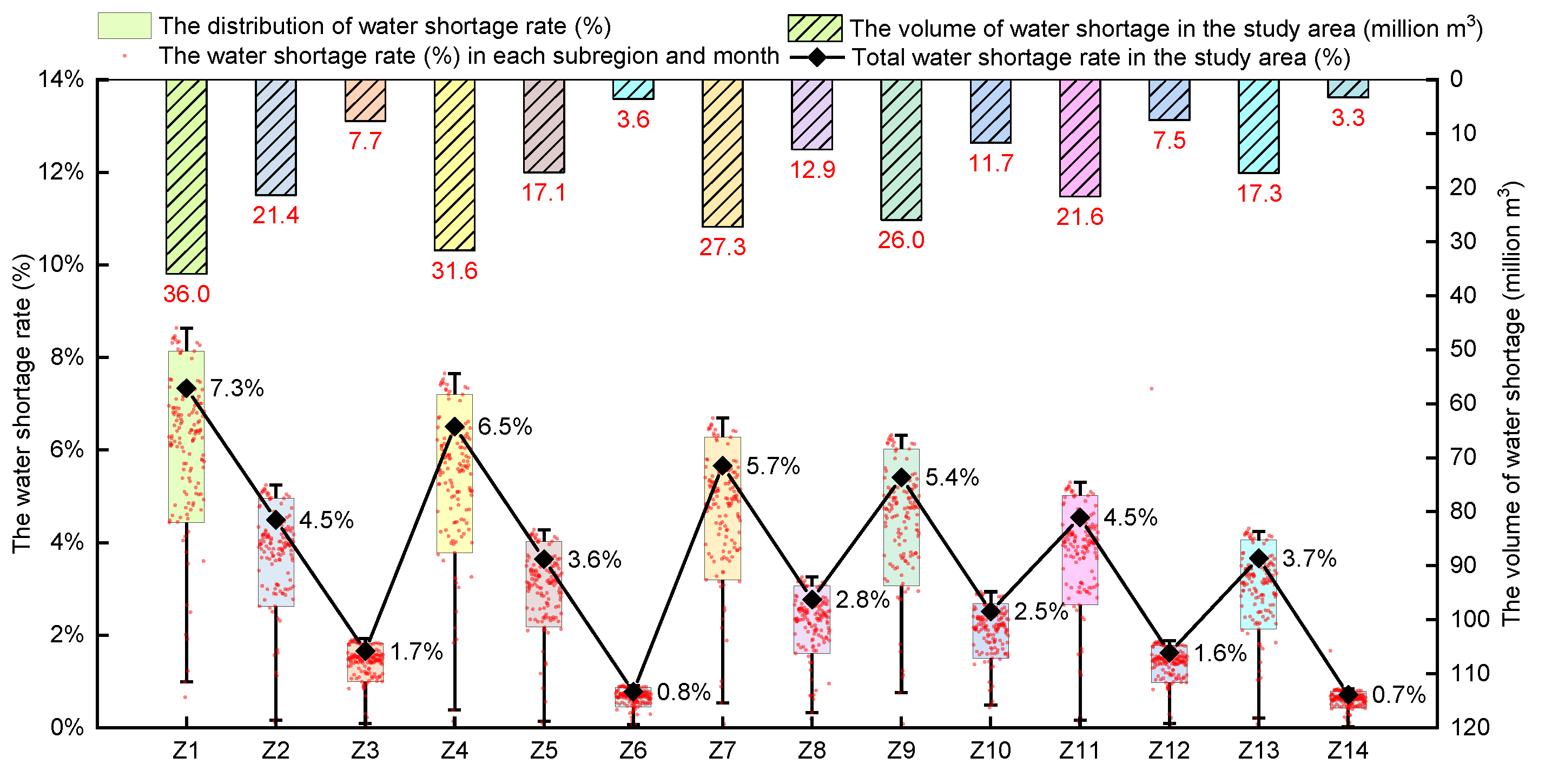
4.2.1. The Impact of Comprehensive Water-Saving Schemes on Water Scarcity and Water Shortage Rate
4.2.2. The Response of Changes in Groundwater to Different Comprehensive Water-Saving Schemes
4.2.3. The Selection of the Comprehensive Water-Saving Schemes for the Future
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Men, X. Study on the Matching Method of Agricultural Water and Land Resources from the Perspective of Total Water Footprint. Water 2022, 14, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Liu, H.; He, X.; Tian, Z. Integrating Blue and Greens Water to Identify Matching Characteristics of Agricultural Water and Land Resources in China. Water 2022, 14, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Study on agricultural cultivation development layout based on the matching characteristic of water and land resources in North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Rosengrant, M.W. Water scarcity and food security: Alternative futures for the 21st century. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.A.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Lundy, M.E. Targeted irrigation expands scope for winter cereal production in water-limited areas of California’s San Joaquin Valley. Agric. Syst. 2023, 210, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fei, L.; Li, S.; Xue, C.; Shi, Z.; Hinkelmann, R. Development of “water-suitable” agriculture based on a statistical analysis of factors affecting irrigation water demand. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, S. Estimation of regional irrigation water requirement and water supply risk in the arid region of Northwestern China 1989–2010. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.W. Priorities for irrigated agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, L.; Maucieri, C.; Borin, M. A Tool for the Evaluation of Irrigation Water Quality in the Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Agronomy 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, M. Water supply and water allocation strategy in the arid US West: Evidence from the Eastern Snake River Plain Aquifer. Reg. Environ. Change 2015, 16, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Ling, Y.; De Wulf, A.; De Maeyer, P. The conflicts of agricultural water supply and demand under climate change in a typical arid land watershed of Central Asia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, D.; Woltering, L.; Ndjeunga, J.; Wani, S.P. Innovative and sustainable approaches for agricultural water management in the drylands of the developing world. Acta Hortic. 2011, 922, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Xu, E. Spatiotemporal Changes in the Geographic Imbalances between Crop Production and Farmland-Water Resources in China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Blanco, C.D.; Sapino, F. Economic Sustainability of Irrigation-Dependent Ecosystem Services Under Growing Water Scarcity. Insights From the Reno River in Italy. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Chang, C.; Du, J.; Gao, D. A spatial-temporal optimal allocation method of irrigation water resources considering groundwater level. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S. Accelerating modernization of irrigation districts to make up shortfall of national food security. China Water Resour. 2020, 9, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Z.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Huang, J.; Li, B. China’s water for food under growing water scarcity. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. Water resources strategy and agricultural development in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1709–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Jia, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Agricultural water resource in China and strategic measures for its efficient utilization. Strateg. Study CAE 2018, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaid, H.I.; Caldwell, R.R. Evaluating the impact of irrigation on surface water-groundwater interaction and stream temperature in an agricultural watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Thorp, K.R.; van Oel, P.R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y. Environmental impact assessment of water-saving irrigation systems across 60 irrigation construction projects in northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Qu, Z.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the groundwater dynamics and impacts of water saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Guan, H.; Huo, Z.; Wang, F.; Huang, G.; Boll, J. Water saving practices enhance regional efficiency of water consumption and water productivity in an arid agricultural area with shallow groundwater. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanja Mrazovac, K.; Staletović, N.; Abulsba, K.S.; Dagali, K.S. Possibility of the Application of Danube, Sava and Morava River Area Shallow Aquifer Groundwater (Serbia) in the Irrigation Purposes. Water Resour. 2019, 46, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Tian, L.; Li, X.; He, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Xue, L.; Li, P. Numerical assessment of the effect of water-saving irrigation on the water cycle at the Manas River Basin oasis, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazoumou, Y.; Favreau, G.; Adamou, M.M.; Maïnassara, I. La petite irrigation par les eaux souterraines, une solution durable contre la pauvreté et les crises alimentaires au Niger? Cah. Agric. 2016, 25, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Hashemi, H.; Bouri, S. Soil salinization and critical shallow groundwater depth under saline irrigation condition in a Saharan irrigated land. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qian, H.; Wu, J. Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, S.; Xiao, S.; Ren, W.; Qu, W.; Zhang, Q. Natural-human driving factors of groundwater salinization in a long-term irrigation area. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabad, F.A.; Hakimzadeh, M.A.; Shojaei, S. The impact of drought and decline in groundwater levels on the spread of sand dunes in the plain in Iran. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 5, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, M.M.; Sweet, S.B.; Ulrich, C.; Howard, J. A Transdisciplinary Approach to Characterize Hydrological Controls on Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystem Health. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lv, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q. Intra-annual variation in the attribution of runoff evolution in the Yellow River source area. Catena 2023, 225, 107032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Abd El-Hamid, H.T. Remote Sensing Inversion for Simulation of Soil Salinization Based on Hyperspectral Data and Ground Analysis in Yinchuan, China. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 4641–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Using HJ-I satellite remote sensing data to surveying the Saline soil distribution in Yinchuan Plain of China. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, L.; Tian, J.; Si, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Evolution of Groundwater in Yinchuan Oasis at the Upper Reaches of the Yellow River after Water-Saving Transformation and Its Driving Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Yan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, W. A new method for quantifying threshold water tables in a phreatic aquifer feeding an irrigation district in northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noory, H.; Liaghat, A.-M.; Chaichi, M.R.; Parsinejad, M. Effects of water table management on soil salinity and alfalfa yield in a semi-arid climate. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 27, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri-Kuehni, S.M.S.; Raaijmakers, B.; Kurz, T.; Or, D.; Helmig, R.; Shokri, N. Water Table Depth and Soil Salinization: From Pore-Scale Processes to Field-Scale Responses. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gao, Q. Water-Saving Irrigation Promotion and Food Security: A Study for China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ren, J. Efficiency Analysis of the Input for Water-Saving Agriculture in China. Water 2020, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H. Analysis on the status of water-saving irrigation techniques and its development trends in China. Soil. Fertil. Sci. China 2006, 5, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Singh, R.M. Groundwater Assessment in a Canal Command Area for Sustainable Irrigation in a Part of the Indo-Gangetic Alluvial Plain. Curr. Sci. 2017, 112, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smout, I.K.; Gorantiwar, S.D. Multilevel Approach for Optimizing Land and Water Resources and Irrigation Deliveries for Tertiary Units in Large Irrigation Schemes. I: Method. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, A.; Molden, D.; Khamzina, T.; Platonov, A.; Ivanov, Y. A water accounting procedure to determine the water savings potential of the Fergana Valley. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Water-Saving Measures and Types | Water-Saving Degrees | Single Schemes | Comprehensive Schemes (Z1–Z7) | ||||||
| Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | Z4 | Z5 | Z6 | Z7 | |||
| The benchmark scheme (S0) | |||||||||
| Planting structure adjustment (non-engineering measure) | Replace 50% area of rice with corn | S1 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Replace 75% area of rice with corn | S2 | ||||||||
| Efficient water-saving irrigation (engineering measure) | DY (70%), PY (30%) | S3 | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| DY (80%), PY (35%) | S4 | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| DY (90%), PY (40%) | S5 | √ | |||||||
| Channel lining to improve water utilization efficiency of channel (engineering measure) | Improve to 0.62 | S6 | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Improve to 0.64 | S7 | √ | √ | ||||||
| Improve to 0.66 | S8 | √ | √ | ||||||
| Controlled irrigation of rice (non-engineering measure) | Irrigation not exceeding 11.85 thousand m3/ha | S9 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Water-Saving Measures and Types | Water-Saving Degrees | Single Schemes | Comprehensive Schemes (Z8–Z14) | ||||||
| Z8 | Z9 | Z10 | Z11 | Z12 | Z13 | Z14 | |||
| The benchmark scheme (S0) | |||||||||
| Planting structure adjustment (non-engineering measure) | Replace 50% area of rice with corn | S1 | √ | ||||||
| Replace 75% area of rice with corn | S2 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Efficient water-saving irrigation (engineering measure) | DY (70%), PY (30%) | S3 | √ | √ | |||||
| DY (80%), PY (35%) | S4 | √ | √ | ||||||
| DY (90%), PY (40%) | S5 | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Channel lining to improve water utilization efficiency of channel (engineering measure) | Improve to 0.62 | S6 | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Improve to 0.64 | S7 | √ | √ | √ | √ | ||||
| Improve to 0.66 | S8 | ||||||||
| Controlled irrigation of rice (non-engineering measure) | Irrigation not exceeding 11.85 thousand m3/ha | S9 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Yang, G.; Chang, C.; Wang, H.; Jin, X.; Peng, Z. Study on the Appropriate Degree of Water-Saving Measures in Arid Irrigated Areas Considering Groundwater Level. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081611
Li S, Yang G, Chang C, Wang H, Jin X, Peng Z. Study on the Appropriate Degree of Water-Saving Measures in Arid Irrigated Areas Considering Groundwater Level. Agronomy. 2024; 14(8):1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081611
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuoyang, Guiyu Yang, Cui Chang, Hao Wang, Xiaohui Jin, and Zhigong Peng. 2024. "Study on the Appropriate Degree of Water-Saving Measures in Arid Irrigated Areas Considering Groundwater Level" Agronomy 14, no. 8: 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081611
APA StyleLi, S., Yang, G., Chang, C., Wang, H., Jin, X., & Peng, Z. (2024). Study on the Appropriate Degree of Water-Saving Measures in Arid Irrigated Areas Considering Groundwater Level. Agronomy, 14(8), 1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081611








