Influence of Water Erosion on Soil Aggregates and Organic Matter in Arable Chernozems: Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Indicators of Soil Structure
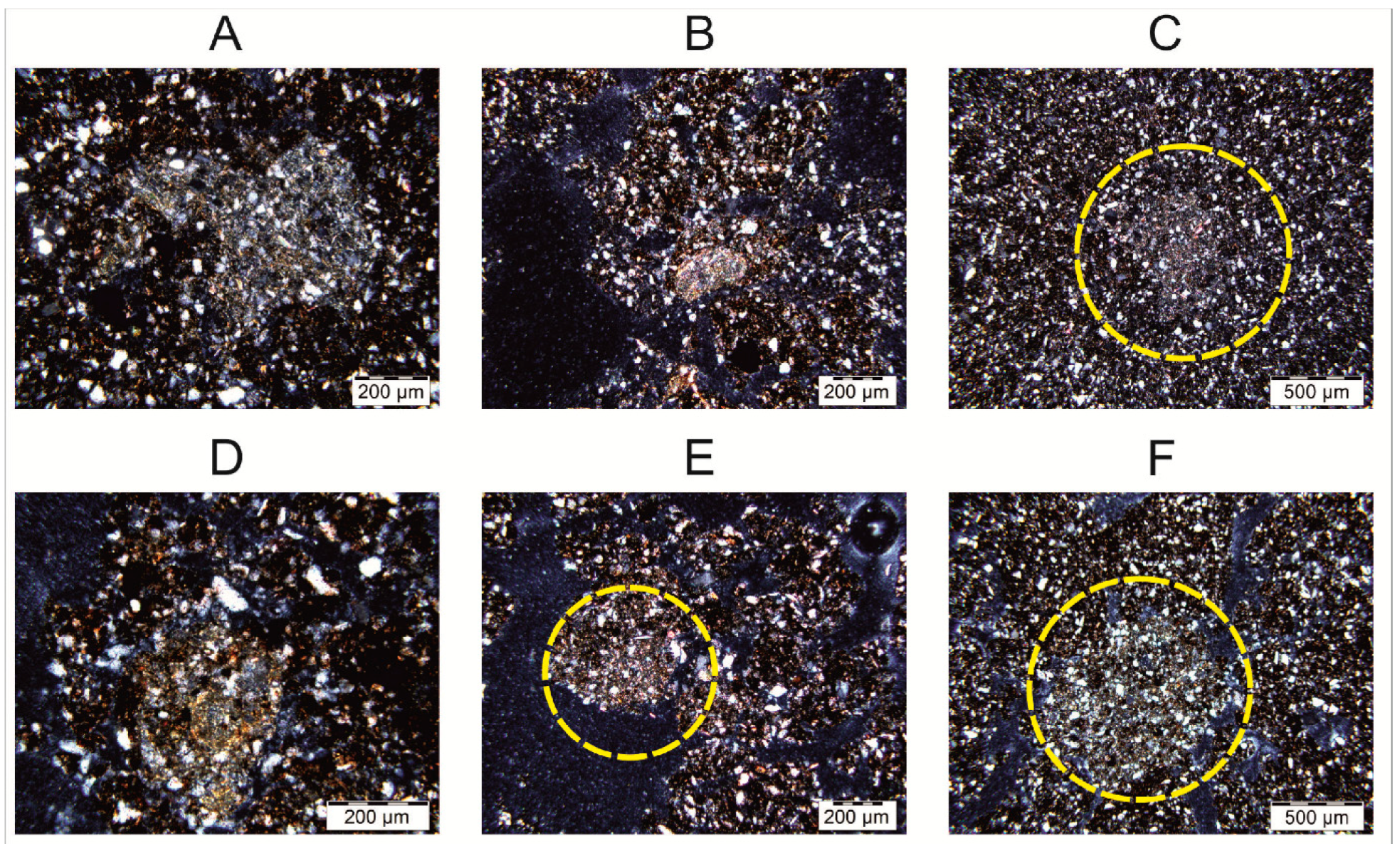
3.2. Micromorphological Features of Material and SOM
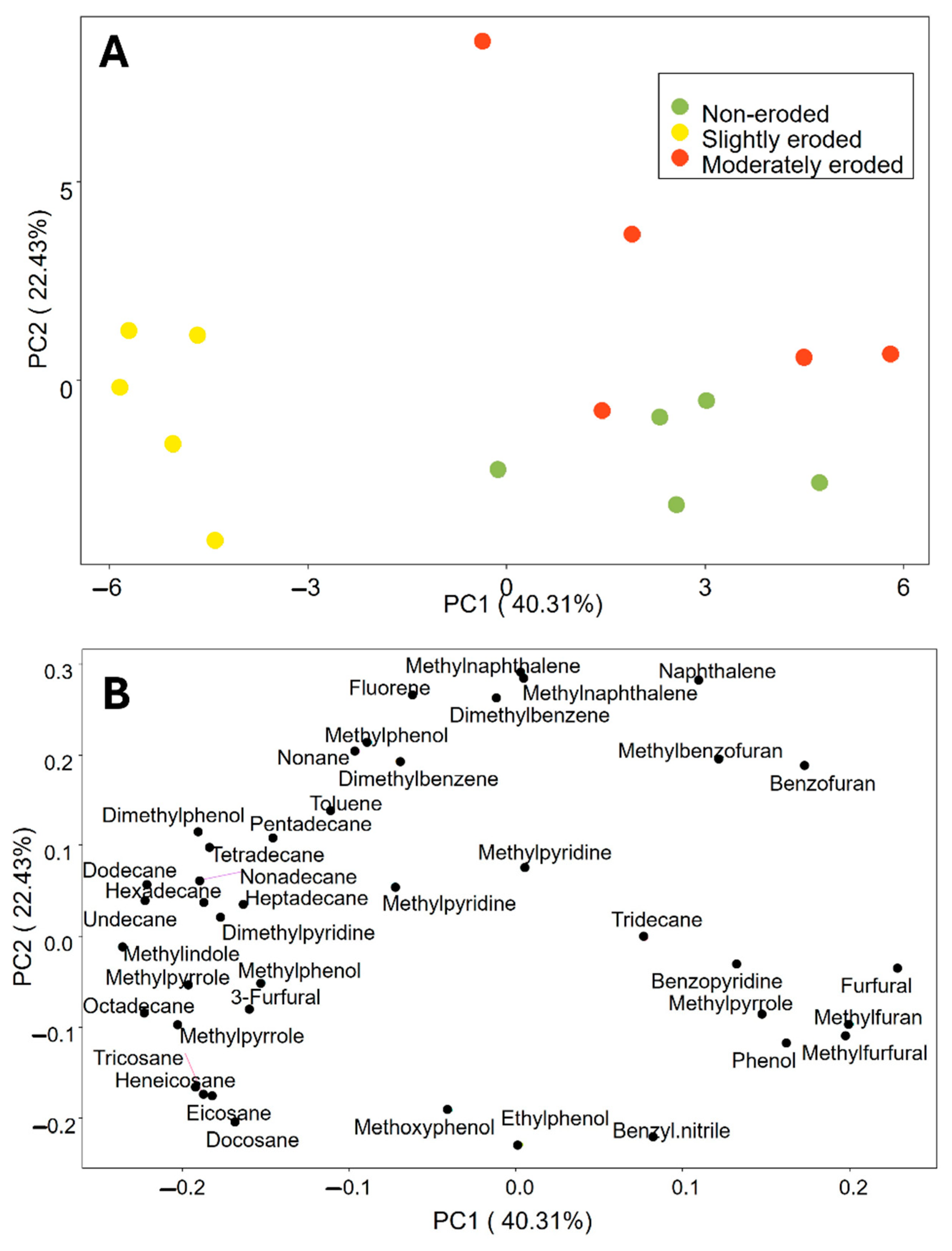
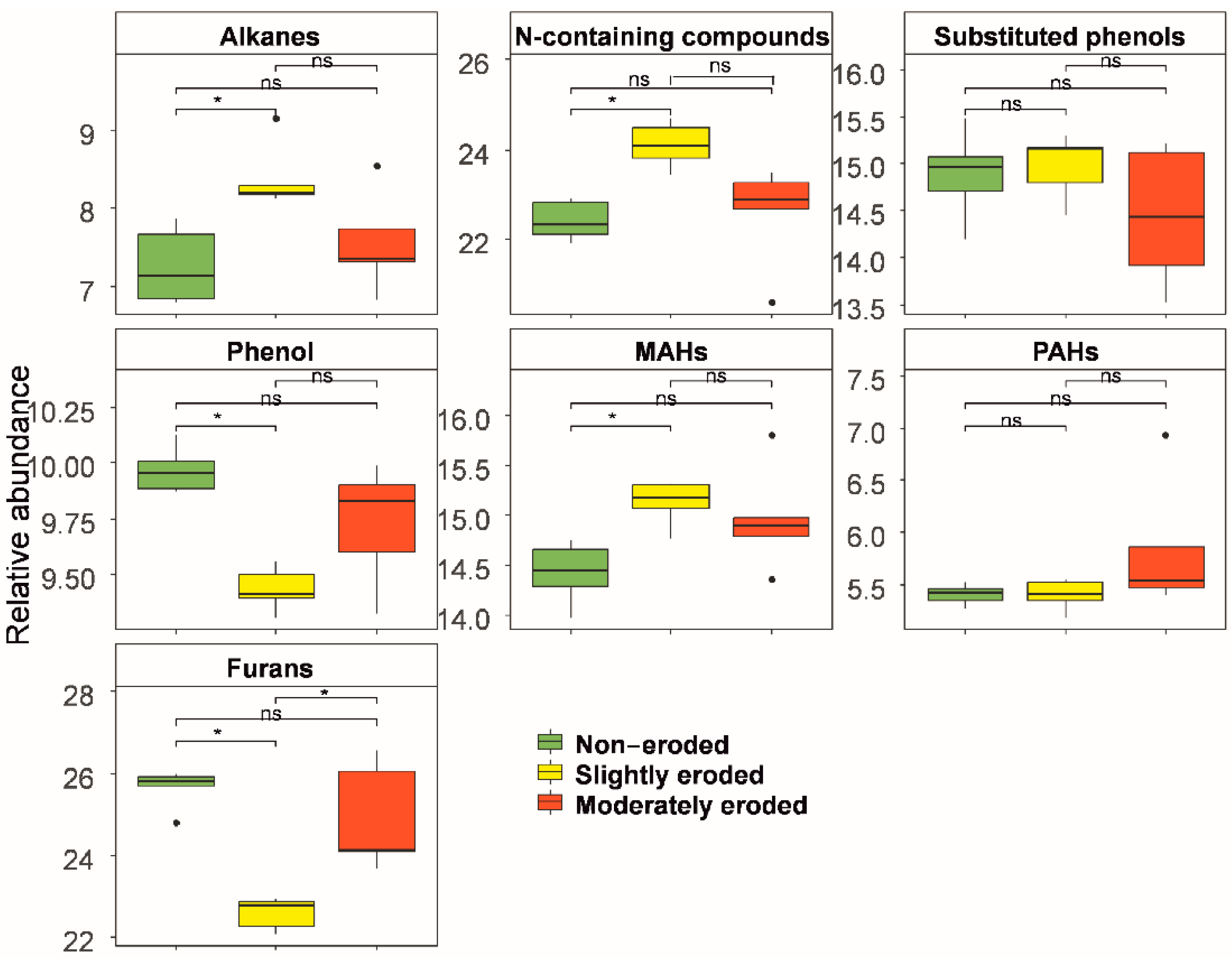
3.3. SOM Content and Composition According to Chemical Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Indicators of Soil Structure
4.2. Micromorphological Features of Aggregates and SOM
4.3. Organic Matter Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO Global Status of Black Soils. Available online: https://doi.org/10.4060/cc3124en (accessed on 22 May 2024).
- Doetterl, S.; Van Oost, K.; Six, J. Towards constraining the magnitude of global agricultural sediment and soil organic carbon fluxes. Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 2012, 37, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.; Gersmehl, P. Soil Erosion, T Values, and Sustainability: A Review and Exercise. J. Geogr. 1993, 92, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Du, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, G. An overview of soil loss tolerance. Catena 2009, 78, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chornyy, S.; Poliashenko, N. Determination of Soil-loss Tolerance for Chernozem of Right-Bank Ukraine. In Soil Science Working for a Living; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 109–119. ISBN 9783319454177. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsov, M.S.; Abdulkhanova, D.R. Soil loss tolerance in the central chernozemic region of the European part of Russia. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2013, 46, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, V.N.; Collins, A.L.; Dobrovolskaya, N.G.; Bazhenova, O.I.; Ryzhov, Y.V.; Sidorchuk, A.Y. Soil loss on the arable lands of the forest-steppe and steppe zones of European Russia and Siberia during the period of intensive agriculture. Geoderma 2021, 381, 114678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Chang, X.; Huang, J.; Nie, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, J. Soil erosion-related dynamics of soil bacterial communities and microbial respiration. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, M.; Augustin, J. Erosion effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics on cultivated slopes: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2021, 397, 115045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, D. Source identification and chemical compositions of particulate and mineral-associated organic matter in the deposited sediments of a dam-controlled watershed. Catena 2022, 219, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandl, G.; Baum, C.; Heckrath, G.; Greve, M.H.; Kanal, A.; Mander, Ü.; Maliszewska-Kordybach, B.; Niedzwiecki, J.; Eckhardt, K.-U.; Leinweber, P. Erosion Induced Heterogeneity of Soil Organic Matter in Catenae from the Baltic Sea Catchment. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleymanov, A.; Gabbasova, I.; Suleymanov, R.; Abakumov, E.; Polyakov, V.; Liebelt, P. Mapping soil organic carbon under erosion processes using remote sensing. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2021, 70, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.V.; Fridland, V.M.; Ivanova, E.N.; Rozov, N.N.; Nosin, V.A.; Friev, T.A. Classification of Soils of the USSR; Kolos: Moscow, Russia, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB World Reference Base for Soil Resources. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zaslavskiy, M.N. Soil Erosion; Vyshaya Shkola: Moscow, Russia, 1983; Available online: https://search.rsl.ru/ru/record/01001139700 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Motrevich, V.P. Agrarian History of Russia (IX–XX Centuries); Ural Agrarian Publishing House: Ekaterinburg, Russia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bazdyrev, G.I.; Loshakov, V.G.; Puponin, A.I.; Rassadin, A.Y.; Safonov, A.F.; Tulikov, A.M. Agriculture; Maksimova, A.S., Ed.; Kolos: Moscow, Russia, 2000; Available online: https://djvu.online/file/peNXsxT6xqqUJ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Vadyunina, A.F.; Korchagina, Z.A. Methods for Studying the Physical Properties of Soils; Agropromizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1986; Available online: https://djvu.online/file/SHzvgCKRn9d2D (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Derzhavin, L.M.; Samokhvalova, S.G.; Sokolova, N.V.; Orlova, A.N.; Habarova, K.A.; Prizhukova, V.G.; Ya, P.S. Soils. Methods for Determination of Organic Matter; Russian Institute of Standardisation: Moscow, Russia, 2021; Available online: https://files.stroyinf.ru/Data/758/75803.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Stoops, G.J. Guidelines for Analysis and Description of Soil and Regolith Thin Sections; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-89118-842-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikova, O.O.; Kust, P.G.; Romanis, T.V.; Lebedeva, M.P. Methodical Guidance for Computer Analysis of Images of Soil Thin Sections Using the Thixomet Pro Software; Ivanov, A.L., Ed.; MBA Publishing House LLC: Moscow, Russia, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, A.A.; Laponogov, I.; Zhang, Z.; Doran, S.L.F.; Belluomo, I.; Veselkov, D.; Bittremieux, W.; Nothias, L.F.; Nothias-Esposito, M.; Maloney, K.N.; et al. Auto-deconvolution and molecular networking of gas chromatography–mass spectrometry data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Rosa, J.M.; González-Pérez, J.A.; González-Vázquez, R.; Knicker, H.; López-Capel, E.; Manning, D.A.C.; González-Vila, F.J. Use of pyrolysis/GC–MS combined with thermal analysis to monitor C and N changes in soil organic matter from a Mediterranean fire affected forest. Catena 2008, 74, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R package version. Media. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/dplyr/dplyr.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr. R Package version 0.4.0. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggpubr/index.html (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Ogle, D.H.; Doll, J.C.; Wheeler, A.P.; Dinno, A. fcaR. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.FSA (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Dinno, A. Nonparametric Pairwise Multiple Comparisons in Independent Groups using Dunn’s Test. Stata J. Promot. Commun. Stat. Stata 2015, 15, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, N.; Monger, H.C.; Canti, M.G. Calcium Carbonate Features. In Interpretation of Micromorphological Features of Soils and Regoliths; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 149–194. ISBN 9780444531568. [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk, H.; Świtoniak, M. Time of aggregate destruction as a parameter of soil water stability within an agricultural hummocky moraine landscape in northern Poland. Bull. Geogr. Phys. Geogr. Ser. 2022, 23, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziuk, H.; Świtoniak, M. The Effect of Erosional Transformation of Soil Cover on the Stability of Soil Aggregates within Young Hummocky Moraine Landscapes in Northern Poland. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, E.V. Interrelation of the Humus and Structural State in Eroded Chernozems in the Slope Agroecosystems on the Central Chernozemc Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Russian State Agrarian University—Moscow Timiryazev Agricultural Academy (RSAU–MTAA), Moscow, Russia, 2017. Available online: https://search.rsl.ru/ru/record/01006657681 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Shein, E.V. The particle-size distribution in soils: Problems of the methods of study, interpretation of the results, and classification. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2009, 42, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamontov, V.G.; Kogut, B.M.; Rodionova, L.P.; Ryzhkov, O.V. Influence of agricultural using on the structural condition of typical chernozem and content of organic carbon in aggregates of different sizes and quality. Timiryazev Agric. Acad. 2016, 6, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A.N.; Yarilova, E.A. Main features of microtexture of chernozems of the Central Chernozem regions. Pochvovedenie 1978, 5, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimova, M.I.; Gubin, S.V.; Shoba, S.A. Micromorphology of Soils of Natural Zones of the USSR; Dobrovolskiy, G.V., Ed.; Pusshchino Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Pusshchino, Russia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sanzharova, S.I.; Bgantsev, V.N.; Skvortsova, E.B. Structural state of typical chernozem of different duration of agricultural use. In Micromorphology of Anthropogenically Modified Soils; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1988; pp. 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovik, E.V.; Dubovik, D.V. Relationships between the Organic Carbon Content and Structural State of Typical Chernozem. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyutenko, N.P.; Glazunov, G.P.; Sanzharov, A.I.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Afonchenkov, N.V.; Oleshitskiy, V.V. Influence of the degree of erodibility on the indicators of ecological state of chernozem soils. Dostizhenie Nauk. Tekhnologii APK 2015, 29, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kukharuk, N.S.; Chendev, Y.G.; Petin, A.N. Micromorphologic features of organic matter during agrogenic transformation of soils in the forest-steppe zone. Nauchniye Vedom. BelSU. Seriya Estestv. Nauk. 2011, 15, 168–179. [Google Scholar]
- Babel, U. Vergleich von mikrogefügemerkmalen einiger humus-bildungen mit hilfe einer schätzmethode. Geoderma 1967, 1, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemyeva, Z.S.; Danchenko, N.N.; Kirillova, N.P.; Masyutenko, N.P.; Dubovik, E.V.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Kogut, B.M. The Effect of Erosion Processes on the Content and Composition of Organic Matter in Macro-and Microaggregates of Haplic Chernozem. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Kunkel, V.; Wells, T.; Martinez, C. Soil organic carbon and soil erosion—Understanding change at the large catchment scale. Geoderma 2019, 343, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, G.; Szabó, J.; Szalai, Z.; Mészáros, E.; Madarász, B.; Centeri, C.; Szabó, B.; Németh, T.; Sipos, P. Changes in organic carbon concentration and organic matter compound of erosion-delivered soil aggregates. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R.; Al-Kaisi, M.; Lal, R.; Cihacek, L. Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics in Eroding and Depositional Landscapes. Open J. Soil Sci. 2016, 6, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panova, I.G.; Demidov, V.V.; Shulga, P.S.; Ilyasov, L.O.; Butilkina, M.A.; Yaroslavov, A.A. Interpolyelectrolyte complexes as effective structure-forming agents for Chernozem soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xia, L.; Meng, D.; Wu, L.; Song, S.; Sancheze, R.M.T.; Farias, M.E. Rapid artificial biocrust development by cyanobacterial inoculation and clay amendment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 3728–3743, Erratum in Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5152–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Berhe, A.A.; Zeng, G.; Xiao, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, H. Chemical characterization and source identification of organic matter in eroded sediments: Role of land use and erosion intensity. Chem. Geol. 2019, 506, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozentsvet, O.A.; Fedoseeva, E.V.; Terekhova, V.A. Lipid biomarkers in ecological assessment of soil biota: Analysis of fatty acids. Usp. Sovrem. Biol. 2019, 139, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jansen, B.; Absalah, S.; Kalbitz, K.; Chunga Castro, F.O.; Cammeraat, E.L.H. Soil organic carbon content and mineralization controlled by the composition, origin and molecular diversity of organic matter: A study in tropical alpine grasslands. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkels, F.M.S.A.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Kuhn, N.J. The fate of soil organic carbon upon erosion, transport and deposition in agricultural landscapes—A review of different concepts. Geomorphology 2014, 226, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinweber, P.; Walley, F.; Kruse, J.; Jandl, G.; Eckhardt, K.-U.; Blyth, R.I.R.; Regier, T. Cultivation Affects Soil Organic Nitrogen: Pyrolysis-Mass Spectrometry and Nitrogen K-edge XANES Spectroscopy Evidence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Jimenez, C.; De Leeuw, J.W. Chemical characterization of soil organic matter fractions by analytical pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1986, 9, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buurman, P.; Peterse, F.; Almendros Martin, G. Soil organic matter chemistry in allophanic soils: A pyrolysis-GC/MS study of a Costa Rican Andosol catena. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 1330–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, S.; Rumpel, C.; MChunu, C.; Chaplot, V. Carbon mineralization and lignin content of eroded sediments from a grazed watershed of South-Africa. Geoderma 2011, 167–168, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenberger, G.; Rodionov, A.; Shibistova, O.; Grabe, M.; Kasansky, O.A.; Fuchs, H.; Mikheyeva, N.; Zrazhevskaya, G.; Flessa, H. Storage and mobility of black carbon in permafrost soils of the forest tundra ecotone in Northern Siberia. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, C.; Chaplot, V.; Planchon, O.; Bernadou, J.; Valentin, C.; Mariotti, A. Preferential erosion of black carbon on steep slopes with slash and burn agriculture. Catena 2006, 65, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, C. Biochar transport in terrestrial ecosystems: Fate and impact. In Biochar for Environmental Management; Lehmann, J., Joseph, S., Eds.; Earthscan: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 313–330. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Chang, X.; Huang, B.; Nie, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J. The mineralization and sequestration of organic carbon in relation to agricultural soil erosion. Geoderma 2018, 329, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, D.; Marol, C.; Balabane, M.; Balesdent, J. The turnover of carbohydrate carbon in a cultivated soil estimated by 13 C natural abundances. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerke, J. Carbon Accumulation in Arable Soils: Mechanisms and the Effect of Cultivation Practices and Organic Fertilizers. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunina, A.; Kuzyakov, Y. Sugars in soil and sweets for microorganisms: Review of origin, content, composition and fate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Challenges and opportunities in soil organic matter research. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, G.; Mueller, K.E.; Nierop, K.G.J.; Simpson, M.J. Plant- or microbial-derived? A review on the molecular composition of stabilized soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Chernozems | SC | WS | MWDa, mm | MWDwa, mm | MWDww, mm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | Cv | M | Cv | M | Cv | M | Cv | M | Cv | |
| Non-eroded | 2.7 a | 21 | 1.5 a | 19 | 3.4 a | 26 | 0.3 a | 8 | 1.3 a | 53 |
| Slightly eroded | 3.0 a | 23 | 2.5 b | 32 | 3.5 a | 30 | 0.4 a | 39 | 3.1 a | 69 |
| Moderately eroded | 1.7 a | 59 | 2.7 b | 38 | 4.6 a | 38 | 0.3 a | 20 | 2.4 a | 53 |
| Ap Horizon | Non-Eroded | Slightly Eroded | Moderately Eroded |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uppermost | 19.3 a | 9.1 a | 8.6 a |
| Lowermost | 24.6 a | 9.2 b | 13.0 b |
| Chernozems | Sampling Depth, cm | SOC, % | Average SOC 2017–2018, 0–30 cm, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | |||
| Non-eroded | 0–10 | 2.92 | 2.72 | 2.90 a |
| 10–20 | 2.93 | 2.84 | ||
| 20–30 | 2.98 | 3.00 | ||
| Slightly eroded | 0–10 | 2.85 | 2.44 | 2.74 ab |
| 10–20 | 2.87 | 2.75 | ||
| 20–30 | 2.87 | 2.63 | ||
| Moderately eroded | 0–10 | 2.65 | 2.38 | 2.52 b |
| 10–20 | 2.70 | 2.51 | ||
| 20–30 | 2.70 | 2.20 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plotnikova, O.O.; Demidov, V.V.; Farkhodov, Y.R.; Tsymbarovich, P.R.; Semenkov, I.N. Influence of Water Erosion on Soil Aggregates and Organic Matter in Arable Chernozems: Case Study. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081607
Plotnikova OO, Demidov VV, Farkhodov YR, Tsymbarovich PR, Semenkov IN. Influence of Water Erosion on Soil Aggregates and Organic Matter in Arable Chernozems: Case Study. Agronomy. 2024; 14(8):1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081607
Chicago/Turabian StylePlotnikova, O. O., V. V. Demidov, Yu. R. Farkhodov, P. R. Tsymbarovich, and I. N. Semenkov. 2024. "Influence of Water Erosion on Soil Aggregates and Organic Matter in Arable Chernozems: Case Study" Agronomy 14, no. 8: 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081607
APA StylePlotnikova, O. O., Demidov, V. V., Farkhodov, Y. R., Tsymbarovich, P. R., & Semenkov, I. N. (2024). Influence of Water Erosion on Soil Aggregates and Organic Matter in Arable Chernozems: Case Study. Agronomy, 14(8), 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14081607







