Abstract
To compare the differences in the soil microbial community structure in yellow soil paddy fields after the long-term application of chemical fertilizer, the role and mechanism of chemical fertilizer in maintaining soil microbial diversity were analyzed, and a theoretical basis for fertilization management in farmlands was provided. In this study, long-term experiments were conducted at the Scientific Observation and Experimental Station of the Arable Land Conservation and Agricultural Environment (Guizhou), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. Soil samples were collected from five treatments: fertilizer N, P, and K (NPK); fertilizer P and K (PK); fertilizer N and K (NK); fertilizer N and P (NP); and no fertilizer (CK). High-throughput sequencing technology was used to analyze the microbial composition and diversity of the colonies, and the influencing factors are discussed. An analysis of the soil bacterial α diversity indices under the different fertilization treatments revealed that the long-term application of NPK fertilizers had less of an effect on the soil bacterial α diversity indices than did the CK. The long-term application of chemical fertilizers significantly reduced the soil bacterial Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson indices, while there was no significant difference in the bacterial Pielou e index among the treatments. The long-term application of chemical fertilizers significantly increased the soil fungal Chao1 index, but the effects on the other indices were not significant (p < 0.05). An analysis of the bacterial and fungal species under different fertilization treatments showed found that compared with CK, the long-term application of chemical fertilizer increased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria to varying degrees while reducing the relative abundance of Chloroflexi. The impact of other phyla was relatively small, and the difference in the relative abundance of fungi was not significant (p < 0.05). Principal component analysis revealed that, at the genus level, the bacterial and fungal community structures in the CK and NK treatments were relatively independent, while those in the NPK, PK, and NP treatments were similar. Random forest analysis revealed that OM, TP, and TK are the dominant factors that affect soil bacteria α diversity. The dominant factors affecting fungi α diversity are pH, OM, and AK. Redundancy analysis indicated that AK and TP were the main factors affecting bacterial community structure, while AP, AK, and pH were the main factors affecting fungal community structure. The conclusion drawn from this study is that the long-term application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer; phosphorus and potassium fertilizer; and nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer can improve soil fertility, alter the soil environment, enhance microbial diversity, and improve the microbial community structure in yellow soil paddy fields, promoting soil ecosystem stability and health.
1. Introduction
Chemical fertilizer is an important contributor to global agricultural production and plays an important role in promoting high and stable food production and improving soil fertility [1,2]. In recent years, with the increasing call for the use of green agriculture, the popularity of organic fertilizers has been increasing annually, and the amount of chemical fertilizer applied has significantly decreased [3]. However, for various reasons including socioeconomic and soil biophysical factors, some regions still rely solely on the application of chemical fertilizers to ensure food production [4,5]. Microorganisms play a crucial role in material transformation and energy transfer in soil ecosystems. The application of chemical fertilizers can alter the structure and functional diversity of microbial communities, thereby affecting soil fertility and productivity [6,7,8]. Compared with no fertilization or the biased application of chemical fertilizers, reasonable fertilization can improve the soil microbial community structure, and the balanced application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is more conducive to the construction of a good microbial community structure [9,10]. However, relevant research has confirmed the positive effects of nitrogen fertilizer, phosphorus fertilizer, and potassium fertilizer applied alone or in combination on microbial growth and reproduction [11,12,13]. Excessive fertilization can reduce the relative abundance, richness, and diversity of soil microorganisms [14]. Compared with insufficient fertilization, excessive fertilization has a more significant negative impact on microorganisms [15,16,17].
Researchers have further explored the reasons why the application of chemical fertilizers affects soil microorganisms. Numerous studies have shown that chemical fertilizer input mainly affects the growth and activity of microorganisms by altering the amount of nutrients in the soil [18,19]. The reasonable application of chemical fertilizers can effectively supplement the absorption of large amounts of nutrients from the soil due to crop growth and development and alleviate the limitation of soil nutrient loss on microbial growth [20,21]. The excessive application of chemical fertilizers can lead to soil nutrient imbalances. For example, the excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer can cause an imbalance in the soil carbon-to-nitrogen ratio and nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio, affecting the abundance and activity of microorganisms that dominate carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus turnover; damaging the structure of microbial communities; and leading to an imbalance in the microbial community structure [22]. The structure of soil microbial communities is influenced not only by fertilizer type, fertilizer amount, and combinations of fertilizer types [23,24], but also by factors such as soil type [25], climate conditions [26], and crop type [27]. Therefore, studying the impact of fertilizer application on soil microorganisms according to local conditions has practical significance for regional farmland soil fertilization and the efficient utilization of fertilizers.
Yellow soil is a zonal soil formed under the perennial humid bioclimatic conditions of subtropical regions and is the main cultivated soil in southwestern China. Among them, the yellow soil area in Guizhou accounts for 25.3% of the national total and 46.4% of the total soil area in Guizhou, playing a crucial role in agricultural production in the region [28]. Currently, research on the impact of fertilizer application on yellow soil microorganisms has focused mainly on increasing the application of organic fertilizers, while there is relatively little research on the effects of long-term fertilizer application. Related studies have focused mainly on the differences in microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus contents under different fertilizer applications or on the differences in the community structure of soil bacteria or fungi [29,30,31]. The impact of chemical fertilizer application on the microbial community structure of yellow soil is not sufficiently systematic or detailed, and the differences in bacterial and fungal community composition characteristics under long-term chemical fertilizer application are not yet clear. Therefore, this study relies on the long-term positioning experiment of the Scientific Observing and Experimental Station of Arable Land Conservation and Agricultural Environment, Ministry of Agriculture, and uses Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technology to explore the impact of different long-term fertilizer application modes on the microbial community structure of yellow paddy soil and to understand its main influencing factors, providing a scientific basis for the healthy management of farmland in yellow soil areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
The experimental site is in the long-term fertilizer positioning experimental field (106°39′52″ E, 26°29′49″ N) of the Guizhou Farmland Conservation and Scientific Observing and Experimental Station of Arable Land Conservation and Agricultural Environment, Ministry of Agriculture within the Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences in Huaxi District, Guiyang City, Guizhou Province. It is located in the yellow soil hilly area of central Guizhou Province, with an average elevation of 1071 m, and has a subtropical monsoon climate. The average temperature in 2019 was 15.43 °C, with an annual rainfall of 1151.26 mm. The specific results are shown in Figure 1. The soil type is anthrosols formed on the yellow soil parent material, and the parent material is residual deposits of Triassic limestone and sand shale. The experiment began construction and leveling in 1994 and was officially launched in 1995, with a total area of 201 m2 in each residential area. The soil chemical properties before the experiment were as follows: pH, 6.75; organic matter (OM), 44.50 g∙kg−1; total nitrogen (TN), 1.96 g∙kg−1; total phosphorus (TP), 2.30 g∙kg−1; total potassium (TK), 13.8 g∙kg−1; alkaline nitrogen (AN), 134 mg∙kg−1; available phosphorus (AP), 13.4 mg∙kg−1; and available potassium (AK), 294 mg∙kg−1.
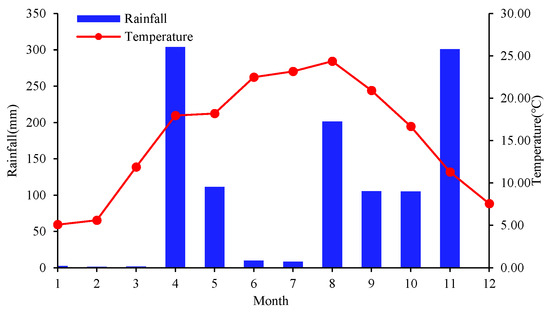
Figure 1.
Monthly rainfall and temperature situation of the experimental site in 2019.
Fourteen treatments were used in the experiment: (1) rice/wheat rotation; (2) rice/rapeseed rotation; (3) 25% organic substitution; (4) 50% organic substitution; (5) 100% organic fertilizer; (6) no fertilization; (7) nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer and 100% organic fertilizer; (8) nitrogen fertilizer; (9) nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer; (10) nitrogen and potassium fertilizer; (11) nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer; (12) phosphorus and potassium fertilizer; (13) rice/green manure rotation; and (14) winter fallow. The purpose of this study was to explore the effect of a single application of chemical fertilizer on soil microbial community characteristics by selecting the 5 treatments with chemical fertilizers—(1) nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer (NPK), (2) phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (PK), (3) nitrogen and potassium fertilizer (NK), (4) nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer (NP), and (5) no fertilization (CK)—for analysis and discussion. According to the soil testing formula for rice in the yellow soil area of Guizhou and the average rice yield, the nitrogen/phosphorus/potassium fertilizer ratio was set to N:P2O5:K2O = 2:1:1. The specific fertilization amounts are shown in Table 1. Fertilizers included urea (N 46%), superphosphate (P2O5 16%), and potassium chloride (K2O 60%). The planting system was for one season of middle-season rice. Before transplanting, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were applied as base fertilizers according to the treatment, and fertilizer was applied twice with urea during the rice growth period.

Table 1.
Test treatment and annual fertilization amount.
2.2. Test Method
2.2.1. Sampling
After the rice harvest in November 2019, the soil bulk density was measured, and soil samples were collected from the cultivated layer (0–20 cm). In the S-shaped method, soil samples were randomly mixed from 5 sites, with 3 replicates for each treatment. After mixing evenly, impurities were removed through a 2 mm sieve. A portion was stored in a −80 °C refrigerator for the extraction of soil DNA, while the remaining portion was air-dried, and the soil nutrients were measured.
2.2.2. Soil Microbial Assay
Total genomic DNA was extracted from the samples using an OMEGA Soil DNA Kit (M563M563 5-02) (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions, and the DNA was stored at −20 °C until further analysis. The quantity and quality of the extracted DNA were measured using a NanoDrop NC2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and agarose gel electrophoresis, respectively. The V3-V4 region of bacterial 16S rRNA was amplified by 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGGAGGCAGCA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′), and the ITS region of fungal rRNA was amplified by ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGGAGATAA-3′) and ITS2R (5′-GCTGGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′). For PCR, NEBQ5 DNA high-fidelity polymerase was used. After configuring the required components for PCR, the template DNA was denatured at 98 °C for 5 min, and then the amplification cycle was started. In each cycle, the temperature was first held at 98 °C for 30 s to denature the template, and then decreased to 53 °C (fungal 55 °C) and held for 30 s (fungal 45 s) to allow the primer and template to fully anneal. The temperature was maintained at 72 °C for 45 s to extend the primer on the template, synthesize DNA, and complete one cycle. The mixture was cycled 25 times (28 times for fungi) to enrich a large amount of amplified DNA fragments. Finally, the mixture was maintained at 72 °C for 5 min to allow the product to extend completely, after which it was stored at 12 °C. The amplification products were subjected to 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, and the target fragments were cut and then recovered with an Axygen gel recovery kit. Library construction was completed using Illumina’s TruSeq Nano DNA LT Library Prep Kit in San Diego, CA, USA.
2.2.3. Determination of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
The soil pH was determined by the potential method with a water-to-soil ratio of 2.5:1 [32]. The total organic carbon in the soil was determined by the potassium dichromate method [33], the total nitrogen was determined by the semi-trace Kjeldahl method [33], the alkaline nitrogen was determined by the alkaline diffusion method [33], the total phosphorus and available phosphorus were determined by UV–visible spectrophotometry [33], and the total potassium and available potassium were determined by flame spectrophotometry [33].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Alpha diversity index analysis: First, QIIME (v1.8.0, http://qimei.org/, accessed on 14 November 2019) was used. The software randomly sampled the total number of sequences for each sample in the ASV abundance matrix at different depths. A sparse curve was drawn based on the number of sequences extracted at each depth and their corresponding ASV numbers to evaluate whether the current sequencing depth of each sample was sufficient to reflect the microbial diversity contained in the community sample. Second, to compare the diversity of different samples, the ASV abundance matrix was randomly flattened at 95% of the sequence size of the sample with the lowest sequence size among all samples to correct for differences in diversity between samples caused by sequencing depth. Subsequently, QIIME software was used to calculate seven diversity indices for each sample, including the Chao1 index, Shannon index, Simpson index, and Pielou e index.
Taxonomic composition analysis: Based on the ASV classification and classification status identification results, the specific species composition of each sample at each classification level can be obtained. The different classification levels—phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species—are equivalent to viewing the community composition structure at different resolutions. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 20.0 software, and one-way ANOVA was used to calculate significant differences (Duncan’s test; p < 0.05 indicated a significant difference, and p < 0.01 indicated an extremely significant difference). Canoco 5.0 was used for principal component analysis (PCA) and redundancy analysis (RDA), the Spsspro online platform was used for random forest regression analysis, and Origin 2021 and Excel 2010 were used to construct charts.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Soil Nutrients
Long-term fertilization changed the chemical properties of the soil (Table 2). Compared with no fertilization (CK), fertilization resulted in a varying degree of decrease in soil pH, with a decrease of 0.13–0.28. Among them, the application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer (NPK) and nitrogen, and potassium fertilizer (NK) resulted in greater reductions. The application of phosphorus fertilizers (NPK, PK, and NP) significantly increased the total phosphorus and available phosphorus contents in the soil, which were 20.48%~28.92% and 85.23%~125.69% greater than those in the CK, respectively. There was no significant difference between the nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer (NP) treatments and the CK. The results also showed that compared with nitrogen, and phosphorus fertilizer (NP) treatment, the application of potassium fertilizer (NPK, PK, or NK) significantly increased the soil available potassium content, but there was no significant difference in the total potassium content between the treatments. In addition, there was no significant difference in the effects of fertilization on the contents of soil organic matter, total nitrogen, or alkaline nitrogen.

Table 2.
Fertilization treatment effects on soil physical and chemical properties.
3.2. Different Long-Term Fertilization Effects on Soil Microorganisms and the Impact of Diversity
Fertilization affected the soil bacterial Chao1 index, Shannon index, and Simpson index, but had a relatively small impact on the Pielou e index (Table 3). Compared with CK, the application of nitrogen and potassium fertilizer (NK) significantly reduced the soil bacterial Chao1 index, Shannon index, and Simpson index by 21.86%, 3.44%, and 0.10%, respectively. The application of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (PK) significantly reduced the soil bacterial Shannon index by 1.93%, while in the other treatments, the difference between the diversity index and CK was not significant. Fertilization affected the soil fungal Chao1 index. Compared with CK, the application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer (NPK) significantly increased the soil fungal Chao1 index by 41.85%, while for the fungi in the other treatments, the difference in the diversity index was not significant.

Table 3.
Soil bacterial and fungal α diversity indices as affected by different fertilization treatments.
3.3. Response of the Microbial Community Composition to Long-Term Fertilization
At the phylum level, a total of 47 bacterial groups were obtained, including 10 groups with relative abundances >1%, accounting for 95.60% to 96.93% of the bacterial population (Figure 2a). The dominant bacterial phyla (with a relative abundance >10%) were composed mostly of Acidobacteria (31.81~33.65%), Proteobacteria (22.81~27.16%), and Chloroflexi (20.15~24.30%), accounting for a total of 79.17~80.30% of the bacterial population. Rokubacteria accounted for 3.94~4.49%, Actinobacteria accounted for 3.45~3.91%, Gemmatimonadetes accounted for 2.74~2.94%, Nitrospinae accounted for 1.79~2.13%, Bacteroidetes accounted for 1.26~1.64%, Latescibacteria accounted for 1.38~1.71%, and Nitrospirae accounted for 0.92~1.08%, with these groups accounting for a total of 16.33~16.94% of the bacterial population. Compared with the CK, the application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer (NPK), phosphorus and potassium fertilizer (PK), and nitrogen and potassium fertilizer (NK) significantly increased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria by 19.08%, 11.45%, and 14.76%, respectively. The application of nitrogen and potassium fertilizer (NK) significantly reduced the relative abundance of Chloroflexi, which decreased by 17.07% compared to the CK. In addition, there was a significant difference in the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes between the nitrogen and potassium fertilizer (NK) and the nitrogen phosphorus fertilizer (NP) treatments, with values of 1.27% and 1.64%, respectively. At the class level, a total of 156 bacterial taxa were obtained, with 17 taxa having an average relative abundance greater than 1% (Figure 2b). Among them, the relative abundances of Subgroup 6, Anaerolineae, Gammaproteobacteria, Deltaproteobacteria, KD4-96, Blastocatella (Subgroup 4), Alphaprotobacteria, NC10, and Holophagae were 16.40~18.43%, 10.91~14.75%, 8.68~11.66%, 9.91~11.05%, 4.15~4.94%, 4.14~4.93%, 4.20~4.60%, 3.94~4.49%, and 2.92~5.04%, respectively, while the relative abundances of the other groups were between 0.91% and 2.67%. Compared with CK, all fertilization treatments significantly reduced the relative abundance of Acidimicrobiia; nitrogen and potassium fertilizer (NK) reduced the relative abundance of Subgroup 6 and Anaerolineae while increasing the relative abundance of Gammaproteobacteria and Blastocatella (Subgroup 4); nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer (NPK) increased the relative abundance of Gammaproteobacteria and Blastocatella (Subgroup 4); and the differences in the other bacterial classes were not significant.
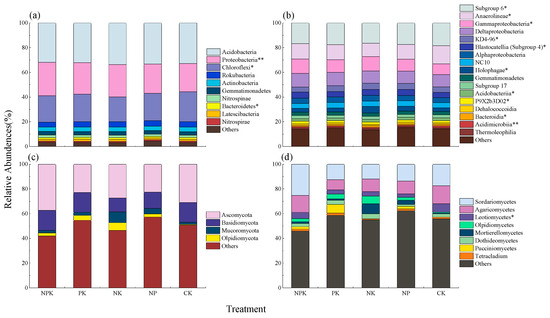
Figure 2.
Bacterial relative abundance at the phylum and class levels. (a,b) represent the phyla and class of bacteria, respectively, and (c,d) represent the phyla and class of fungi, respectively. Asterisks indicate significant differences in relative abundance among the different treatments, where * represents p < 0.05 and ** represents p < 0.01.
At the phylum level, a total of eight fungal taxa were obtained, including four taxa with relative abundances >1% (Figure 2c). Among them, the major phyla (with a relative abundance >10%) were Ascomycota (22.69~37.26%), Basidiomycota (11.18~16.34%), Zygomycota (1.74~8.74%), and Olpidiomycota (0.52~6.22%), with a total relative abundance of 42.67~58.06%. There was no significant difference in the relative abundance of fungi among the treatments. At the class level, a total of 32 fungal taxa were obtained, including eight taxa with relative abundances >1% (Figure 2d). Compared with CK, nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer (NP) reduced the relative abundance of Leotiomycetes, while there was no significant difference in the relative abundance of other fungal taxa.
Principal component analysis was used to analyze the differences in community composition among the different treatments (Figure 3). At the bacterial phylum level, the community compositions of the CK and NPK treatments were relatively similar, while those of the PK, NK, and NP treatments were relatively similar. The explanatory power of the variation in the bacterial community structure composition of the first and second principal component axes was 20.32% and 16.57%, respectively, totaling 36.89% (Figure 3a). At the genus level, the community structures of the CK and NK treatments were completely independent, while those of the NPK, PK, and NP treatments were relatively similar, with a genus-level explanatory power of 30.19% (Figure 3b). At the fungal phylum level, the community structure in the CK treatment was independent, and those of other fertilization treatments were similar. The explanatory power of the first and second principal component axes was 51.86% and 27.90%, respectively, totaling 79.76% (Figure 3c). The community structure of fungi is similar to that of bacteria, with an explanatory power of 26.72% (Figure 3d).
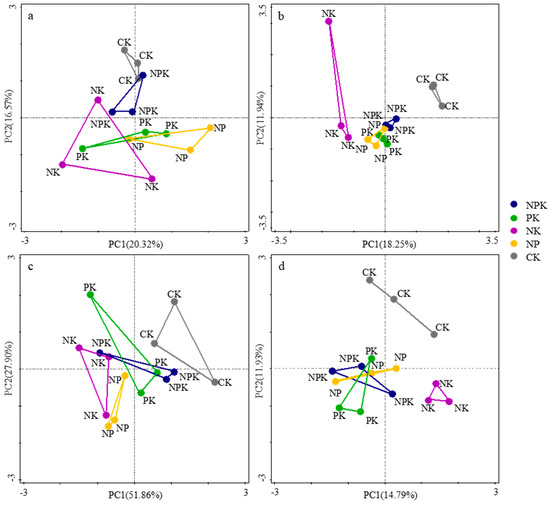
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis at the phylum and genus levels for different treatments. (a,b) represent the phyla and genera of bacteria, while (c,d) represent the phyla and genera of fungi, respectively.
3.4. Relationships between the Microbial α Diversity Index and Soil Environmental Factors
A random forest regression model was used to analyze the impact of various soil environmental factors on microorganisms. The importance of the diversity index was determined (Figure 4). According to Figure 4a, the order of importance of various environmental factors that affect the Chao1 index of soil bacteria was as follows: total phosphorus (TP) > available potassium (AK) > total potassium (TK) > pH > organic matter (OM) > alkaline nitrogen (AN) > available phosphorus (AP). TP and AK were the major factors, with importance values of 49.90% and 20.10%, respectively, and the importance of the other factors ranged from 1.50% to 8.10%. AK and TK were the dominant factors affecting the Shannon index and Simpson index, while AK, AP, and OM were the major factors affecting the Pielou e index. According to Figure 4b, OM and AP were the dominant factors affecting the Chao1 index of soil fungi, with importance values of 49.70% and 18.20%, respectively; AK, OM, and pH were the dominant factors affecting the Shannon, Simpson, and Pielou e indices, with importance values ranging from 13.10% to 38.20%.
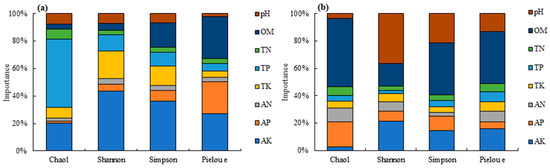
Figure 4.
Impact on soil microorganisms and the importance of each eigenvalue on α diversity indices. (a,b) represent bacteria and fungi, respectively.
3.5. Relationships between Microbial Community Structure and Soil Environmental Factors
Redundancy analysis was used to analyze the impact of soil physicochemical properties on the bacterial and fungal community structures at the genus level (Figure 5, Table 4). The results showed that in the conditional restriction analysis, AK and TP were the main factors affecting the level of bacterial genera, and the explanatory power of the first and second axes in the RDA was 12.37% and 10.57%, respectively. At the fungal genus level, the first and second axis interpretability of the RDA were 12.70% and 10.45%, respectively, with AP, AK, and pH being the main influencing factors.
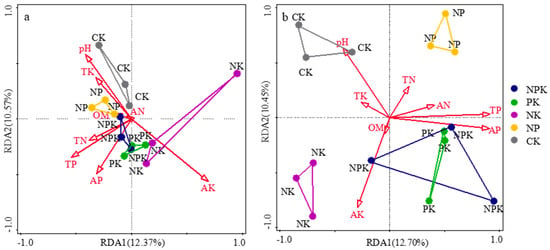
Figure 5.
Different processing methods based on a phylum-level redundancy analysis diagram. (a,b) represent bacteria and fungi, respectively.

Table 4.
Environmental factor impact indicators based on genus-level redundancy analysis.
4. Discussion
The soil microbial α diversity index is an important indicator for characterizing the diversity of soil bacterial communities and ecosystem stability [34,35]. The results of this study showed that the bacterial α diversity index of the NPK treatment was not significantly different from that of the CK, and the bacterial α diversity indices of all other fertilization treatments decreased, which indicated that the balanced application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers barely affected the diversity of the soil bacteria, whereas the PK, NK, and NP treatments limited the growth and reproduction of soil bacteria, and the Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson indices decreased (Table 3). This may be because the balanced application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers provides a good growth environment for soil bacteria, while the soil environment under long-term fertilizer bias is not balanced in nutrients, which is not conducive to bacterial growth [36,37,38]. The Chao1, Shannon, Simpson, and Pielou e indices of bacteria were the highest under NPK, followed by NP and PK, and the lowest under NK, indicating that the application of phosphorus fertilizer promoted the growth of bacteria in yellow soil rice fields by increasing the soil P content, thereby increasing bacterial diversity (Table 2). The research results of Li [39] and Wasaki [40] are consistent with those of this study. However, Li [20] reported that the long-term application of NK increased the soil microbial composition and diversity, while the PK and NP treatments had the opposite effect. This contradiction may be related to differences in soil fertility levels and the duration of field trials. Fungi account for a large proportion of soil microbial communities, and their diversity is important in soil environmental quality assessments [41]. For the fungal α diversity indices, the trends of the different treatments differed from those of bacteria; long-term fertilization increased the Chao1 index of soil fungi, but had less effect on the Shannon, Simpson, and Pielou e indices, and the Chao1 index of fungi in the NPK treatment was significantly greater than that in the CK treatment (Table 3). This once again proved that nutrient inputs balance soil fungal diversity; therefore, balanced fertilization is the recommended fertilization method for increasing microbial diversity.
The different fertilizers affected the structure of the soil bacterial communities, and, in general, the major fungal and bacterial communities were similar among the treatments, but there were differences in relative abundance (Figure 2). The major phyla (with a relative abundance >10%) of the different fertilizer treatments were Acidobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Chloroflexi, which were similar to the major taxa of the rice soil bacterial community identified by Wang [42]. This may be because the experimental soils were all paddy-neutral soils and were in the same mid-latitude subtropical monsoon climate with similar hydrothermal conditions, resulting in high similarity in the soil bacterial community structure and dominant flora. Proteobacteria, Nitrospira, Firmicutes, and Actinobacteria are considered copiotrophic taxa, while Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Chlorobacteria, and Aspergillus are typical oligotrophic taxa [43]. In this study, compared with CK, long-term fertilization increased the relative abundance of Proteobacteria to varying degrees. The relative abundance in the fertilization treatment group decreased in the order NPK > NK > PK > NP > CK. The relative abundance of Bacteroidetes was lowest in the NP treatment without potassium, while the relative abundance of Chloroflexi was lowest in the NK treatment without phosphorus. The reason for this difference may be that different nutrient fertilizers cause significant changes in the relative abundance of specific bacterial communities [44]. In terms of the relative abundance of fungi, Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were the major phyla, which agrees with the findings of Wang [45]. However, the statistically nonsignificant differences at the fungal phylum level among the experimental treatments in this study indicated that the relative abundance of fungi was less affected by fertilizer application. According to the cluster analysis at the phylum and genus levels, there were significant differences in the distribution of bacterial and fungal species among the five treatments (Figure 3). The application of chemical fertilizers not only affects the relative abundance of microorganisms in the yellow soil of rice fields, but also affects the distribution of microbial species. At the genus level, the distributions of the bacterial and fungal communities in the different treatments showed that those in the CK and NK treatments were relatively independent, while those in the NPK, NP, and PK treatments were similar. This confirms that the application of phosphorus fertilizer is an important reason for changes in the structure of microbial communities [46].
Many studies have shown that soil microbial diversity is more significantly affected by indicators related to soil fertility [47]. In this study, the long-term application of different fertilizers significantly changed the soil properties, among which available potassium, total phosphorus, organic matter, and pH were the factors affecting bacteria. The major factors affecting fungi diversity included organic matter, pH, and available potassium. The main factor affecting microorganisms was diversity, but the soil total nitrogen and available nitrogen content also had an impact. Moreover, the impact of the diversity index on microorganisms was relatively small (Figure 4). This differs from the results of other related studies. Geng [48] reported that AP and C/N are the main driving factors of the α diversity of bacteria and fungi, respectively, with more research indicating that soil pH is the strongest factor affecting microbial diversity changes [49,50]. The reason for the differences in soil microorganisms is that the physical and chemical properties of the soil at different experimental points have different responses to fertilization. However, in this study, the tested soil was relatively rich in nitrogen, and the effect of fertilization on soil nitrogen was relatively small. Therefore, the difference in the impact on microbial diversity and community structure was not significant. The redundancy analysis results indicate that fertilization affects the bacterial community structure by altering soil AK and TP, while altering AP, AK, and pH affects the fungal community structure. This is related to microorganism α diversity. The results of the random forest analysis of the diversity indices and soil environmental factors were similar, indicating that the structure of the soil microbial community is closely related to diversity.
5. Conclusions
In the yellow soil area of Guizhou, the long-term application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer, and nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer can improve the fertility of paddy fields in yellow soil, enhance microbial diversity, and improve the microbial community structure, which has positive significance for promoting soil ecosystem stability and health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Y.Y., X.H., Y.L. (Yu Li) and T.J.; methodology: X.H.; software, Y.Y., Y.L. (Yanling Liu) and Y.Z.; validation: X.H., Y.L. (Yu Li), Y.L. (Yanling Liu), Y.Z., H.Z., H.X. and S.Z.; formal analysis: Y.Y., Y.L. (Yanling Liu) and Y.Z.; resources: X.H., Y.L. (Yu Li) and T.J.; writing—original draft preparation: Y.Y.; writing—review and editing: Y.L. (Yu Li), Y.L. (Yanling Liu), Y.Z., H.Z., H.X. and S.Z.; supervision: X.H.; project administration: Y.Y.; funding acquisition: Y.Y., Y.L. (Yanling Liu), Y.Z. and Y.L. (Yu Li); data collection: H.Z., H.X. and S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Youth Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences ([2022]20) by Y.Y, the Post subsidy project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China ([2021]26) by Y.Y, the Research and Development Fund Project of Guizhou Institute of Soil and Fertilizer ([2022]12) by Y.Y., the Natural Science Foundation Project of Guizhou province (ZK[2024]ZD082) by Y.L. (Yanling Liu), the Youth Science and Technology Fund of Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences ([2021]12) by Y.Z., the Germplasm Resource Project Special of Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences ([2023]12) by Y.L. (Yu Li), and the Science and Technology Innovation Project Special of Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences ([2023]13, [2022]09) by Y.L. (Yanling Liu) and Y.L. (Yu Li).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Garba, H.N.; Liu, Y.R.; Zhang, S.X.; Liu, K.L.; Huang, J.; Lv, Z.Z.; Hou, H.Q.; Lan, X.J.; Ji, J.H.; Han, T.F.; et al. Long-term effect of fertilizations on yield sustainability, soil organic carbon sequestration and apparent phosphorus balance in acidic paddy soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 4282–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, J.; Ahmad, S.; Malik, M. Nitrogenous fertilizers: Impact on environment sustainability, mitigation strategies, and challenges. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, J.B. Conventional, organic and conservation agriculture: Production and environmental impact. Sustain. Agric. Rev. 2012, 8, 149–165. [Google Scholar]
- Thiombiano, B.A.; Le, Q.B.; Ouédraogo, D. The role of responsive heterogeneity in sub-Saharan smallholder farming sustainability: Socio-economic and biophysical determinants of mineral and organic fertilizers used in South Western Burkina Faso. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2023, 21, 2219921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconnier, G.N.; Cardinael, R.; Corbeels, M.; Baudron, F.; Chivenge, P.; Couëdel, A.; Ripoche, A.; Affholder, F.; Naudin, K.; Benaillon, E.; et al. The input reduction principle of agroecology is wrong when it comes to mineral fertilizer use in sub-Saharan Africa. Outlook Agric. 2023, 52, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degens, B.P.; Schipper, L.A.; Sparling, G.P.; Vojvodic-Vukovic, M. Decreases in organic C reserves in soils can reduce the catabolic diversity of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Su, T.; Han, H.L.; Tan, H.P.; Bao, F.; Zhao, F.C. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil microbial community structure, labile organic carbon and nitrogen and enzyme activity in paddy field and upland. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2019, 10, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hicks, L.C.; Rousk, K.; Rinnan, R.; Rousk, J. Soil microbial responses to 28 years of nutrient fertilization in a Subarctic heath. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Wang, S.P.; Jia, S.G.; Gao, Q. Effect of 25-year fertilization on soil microbial biomass and community structure in a continuous corn cropping system. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 61, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Liu, K.L.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, H.Q.; Shen, R.F. Balanced fertilization over four decades has sustained soil microbial communities and improved soil fertility and rice productivity in red paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.Q.; Sun, J.W.; Wang, X.B.; Zhou, W. Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 2011, 173, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilova, L.P.; Banetskaya, E.V. The effect of long-term use of fertilizers on soil-dwelling micromycetes of meadow chernozem soil in wheat crops. Agrokhimiya 2023, 7, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, K.V.; Morachevskaya, E.V.; Vlasova, A.P.; Manucharova, N.A. Microbiological activity of chernozem in the combined use of potassium chloride with nitrogen fertilizers. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2023, 56, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ai, C.; Huang, S.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Jia, L.L.; Jia, J.C.; Zhou, W.; He, P. The responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community composition under nitrogen addition in an upland soil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enebe, M.C.; Babalola, O.O. Effects of inorganic and organic treatments on the microbial community of maize rhizosphere by a shotgun metagenomics approach. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokovic, N.; Jacimovic, G.; Sikiric, B.; Ciric, V.; Ugrenovic, V.; Zhapparova, A.; Saljnikov, E. Changes in Eutric Cambisol due to long-term mineral fertilisation: A case study in Serbia. Ital. J. Agron. 2022, 17, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Lazicki, P.A.; Scow, K.M. Mineral nitrogen input decreases microbial biomass in soils under grasslands but not annual crops. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 106, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, M.; Deen, W.; Drijber, R.; McPherson, M.; Stengel, A.; Dunfield, K. Long-term N inputs shape microbial communities more strongly than current-year inputs in soils under 10-year continuous corn cropping. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Gan, G.Y.; Zeng, Q.Q. Impacts of long-term fertilization on crop yield and microbial communities under rice–rapeseed rotation. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.F.; Luo, P.Y.; Yang, J.F.; Irfan, M.; Zhang, S.Y.; An, N.; Dai, J.; Han, X.R. Effect of long-term fertilization on ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms and nitrification in brown soil of northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.H.; Gan, B.P.; Li, Q.; Xiao, W.F.; Song, X.Z. Effects of Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Addition on Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activity and Stoichiometry in Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) Forests. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 834184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaswar, M.; Ahmed, W.; Jing, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.L.; Zhang, L.; Han, T.F.; Du, J.X.; Ali, S.; Ur-Rahim, H.; et al. Interaction of soil microbial communities and phosphorus fractions under long-term fertilization in paddy soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.; Pascual, J.A.; López-García, A.; Romo-Vaquero, M.; De Santiago, A.; Ros, M.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Alguacil, M.D. Effects of inorganic and compost tea fertilizers application on the taxonomic and functional microbial diversity of the purslane rhizosphere. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1159823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evdokimova, E.V.; Gladkov, G.V.; Kuzina, N.I.; Ivanova, E.A.; Kimeklis, A.K.; Zverev, A.O. The difference between cellulolytic culturomes and microbiomes inhabiting two contrasting soil types. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil microbiomes and climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Devi, R.; Kumar, S.; Sheikh, I.; Kour, D.; Yadav, A.N. Microbial consortium with nitrogen fixing and mineral solubilizing attributes for growth of barley. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.M. Moisture Dynamic in Yellow Soil and Its Environment Factors in Karst Mountainous Area of Guizhou. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Huang, X.C.; Zhu, H.Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.R.; Liu, Y.L.; Jiang, T.M. Bacterial community structure and composition under long-term combined application of organic and inorganic fertilizers in a yellow paddy soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2022, 28, 984–992. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Bai, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.R.; Huang, X.C.; Zhang, W.A.; Jiang, T.M. Responses of soil microbial biomass C and P to different long-term fertilization treatments in the yellow paddy soil. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Wei, Q.Q.; Gou, J.L. Effects of Short-term Application of Moutai Lees Biochar on Nutrients and Fungal Community Structure in Yellow Soil of Guizhou. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67404–67413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 1377-2007; Determination of pH in Soil pH. Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Bao, S.D. An Exploratory Method for Fractionation of Organic Phosphorus from Grassland Soils; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Custer, G.E.; Diepen, L.T.A.V. Plant invasion has limited impact on soil microbial a-diversity: A meta-analysis. Diversity 2020, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.E.; Martiny, J.B.H. Alpha-, beta-, and gamma-diversity of bacteria varies across habitats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.; Freitas, H. Long-Term Effects of Fertilization on Soil Organism Diversity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.P.; Zhang, P.; Riggins, C.W.; Zabaloy, M.C.; Rodríguez-Zas, S.; Villami, M.B. Long-term N fertilization decreased diversity and altered the composition of soil bacterial and archaeal communities. Agronomy 2019, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, J.; Park, K.C. Long-term effects of imbalanced fertilization on the composition and diversity of soil bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Luo, Z.Z.; Li, L.L.; Niu, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.Q.; He, R.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Nian, L.L. Long-term phosphorus fertilization reveals the phosphorus limitation shaping the soil micro-food web stability in the Loess Plateau. Front. Micobiol. 2024, 14, 1256269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasaki, J.; Sakaguchi, J.; Yamamura, T.; Ito, S.; Shinano, T.; Osaki, M. P and N deficiency change the relative abundance and function of rhizosphere microorganisms during cluster root development of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2018, 64, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, G.H.; Chen, L.; Han, W.Y.; Wang, D.B. Plant diversity is coupled with soil fungal diversity in a natural temperate steppe of northeastern China. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhu, Z.J.; Qian, X.Q.; Wang, G.L. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with application of different organic fertilizers on soil bacterial community structure during rice season. Soils 2021, 53, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Knight, R. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. Isme J. 2011, 6, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miransari, M. Soil microbes and plant fertilization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Song, Y.; Ma, T.F.; Raza, W.; Li, J.; Howland, J.G.; Huang, Q.W.; Shen, Q.R. Impacts of inorganic and organic fertilization treatments on bacterial and fungal communities in a paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 112, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Yang, M.; Hao, Z.H.; Wang, X.L.; Shi, Y. Synergistic phosphate fertilizer effects on soil nutrient and microbial diversity in wheat. Agon. J. 2023, 115, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.R.; Fan, Z.W.; An, T.X.; Kai, L.; Zhou, F.; Wu, K.X.; Wu, B.Z.; Fullen, M.A. Long-term fertilizer use altered soil microbial community structure but not alpha-diversity in subtropical southwestern China. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2022, 55, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.T.; Wang, X.D.; Shi, S.B.; Ye, Z.Q.; Zhou, W.J. Effect of combined application of fungal residue and chemical fertilizer on soil microbial community composition and diversity in paddy soil. Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y. Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholier, T.; Lavrinienko, A.; Brila, I.; Tukalenko, E.; Hindström, R.; Vasylenko, A.; Cayol, C.; Ecke, F.; Singh, N.J.; Forsman, J.T.; et al. Urban forest soils harbour distinct and more diverse communities of bacteria and fungi compared to less disturbed forest soils. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).