Soil Organic Matter Input Promotes Coastal Topsoil Desalinization by Altering the Salt Distribution in the Soil Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
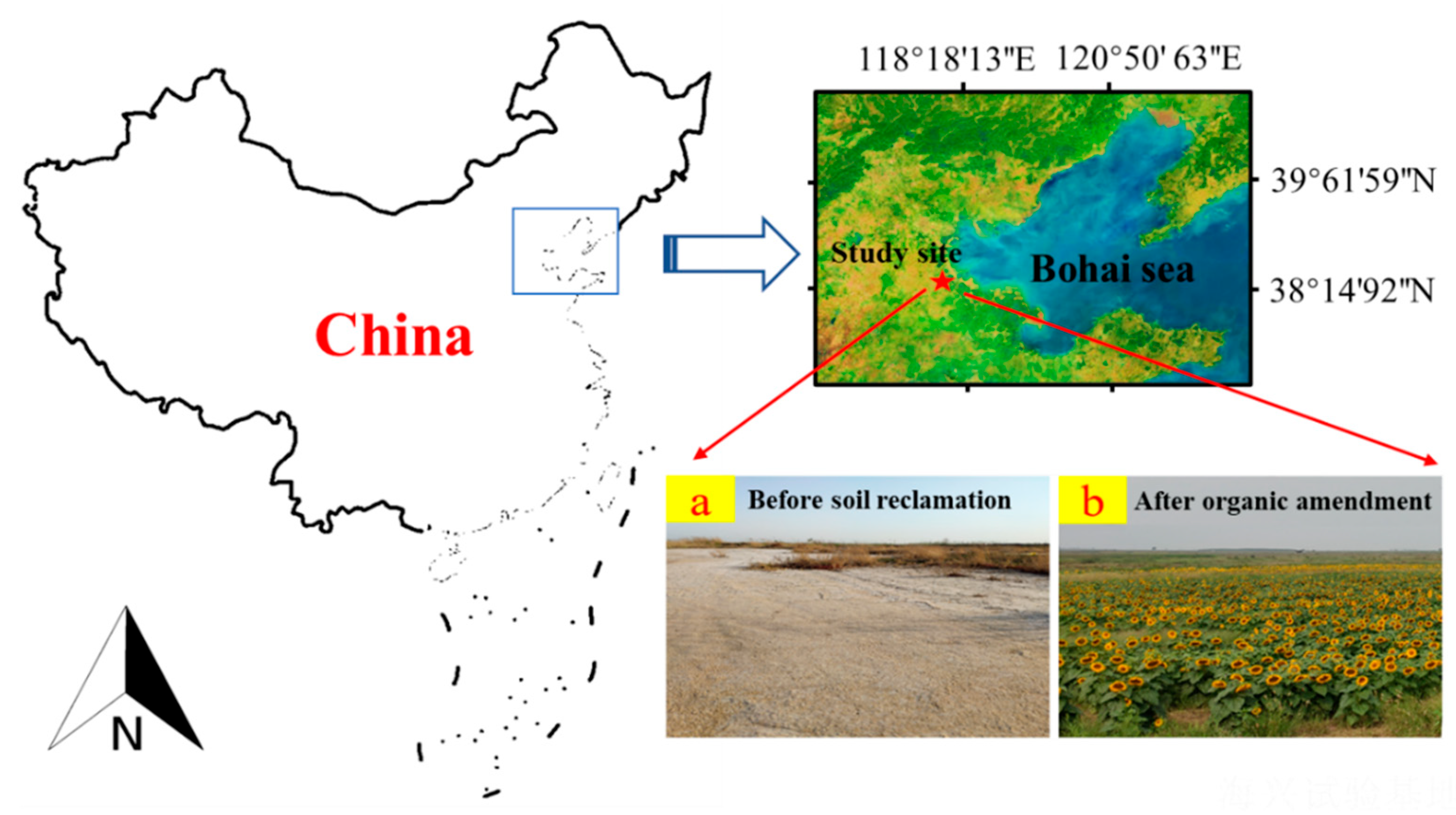
2.1. Experimental Site
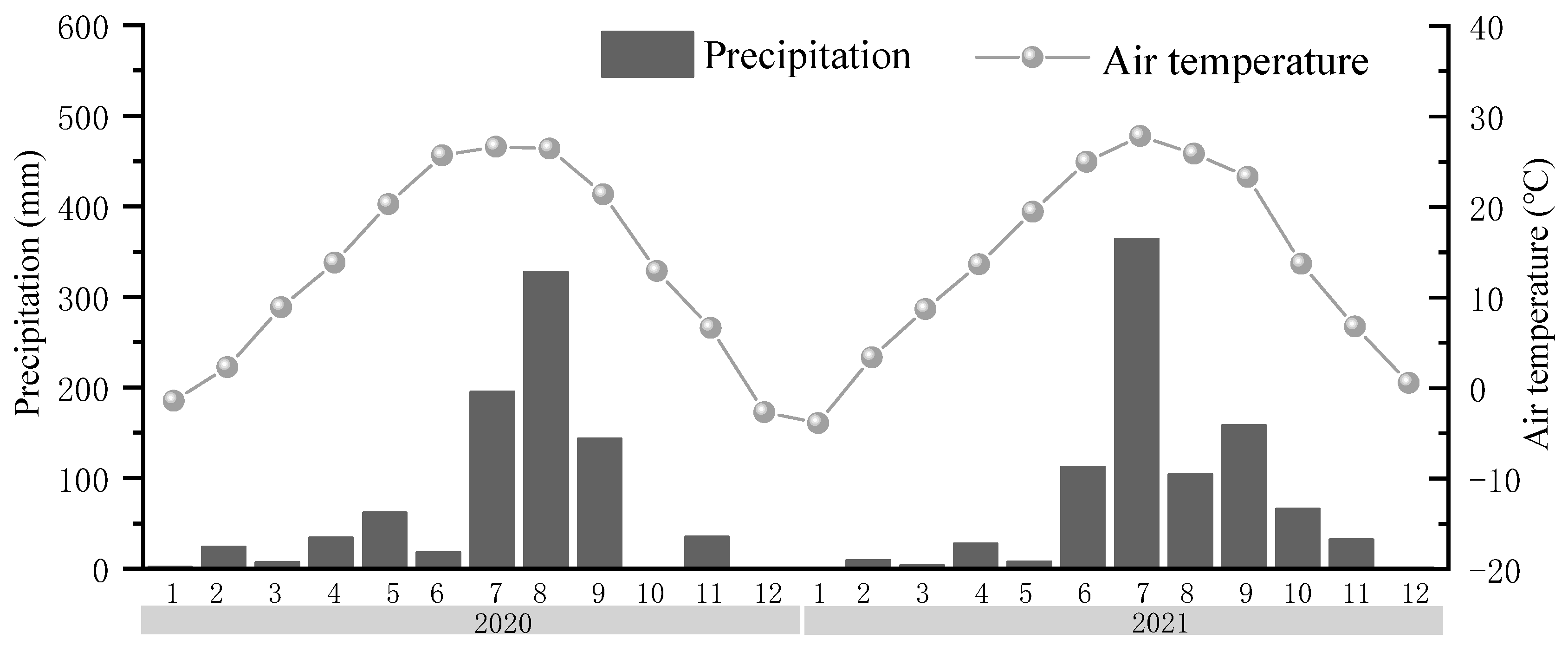
2.2. Field Observation
2.3. Soil Column Experiments
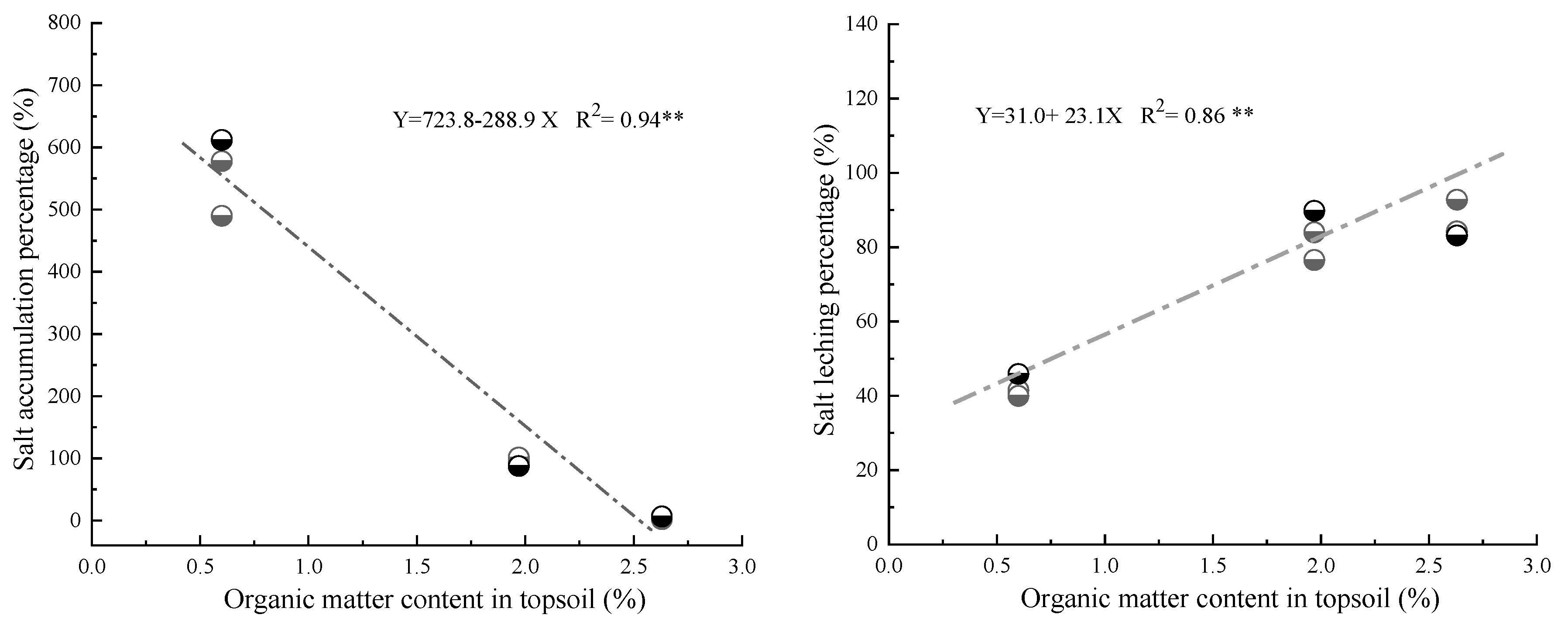
2.3.1. Salt Accumulation Experiment
2.3.2. Salt Leaching Experiment
2.4. Measurement
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
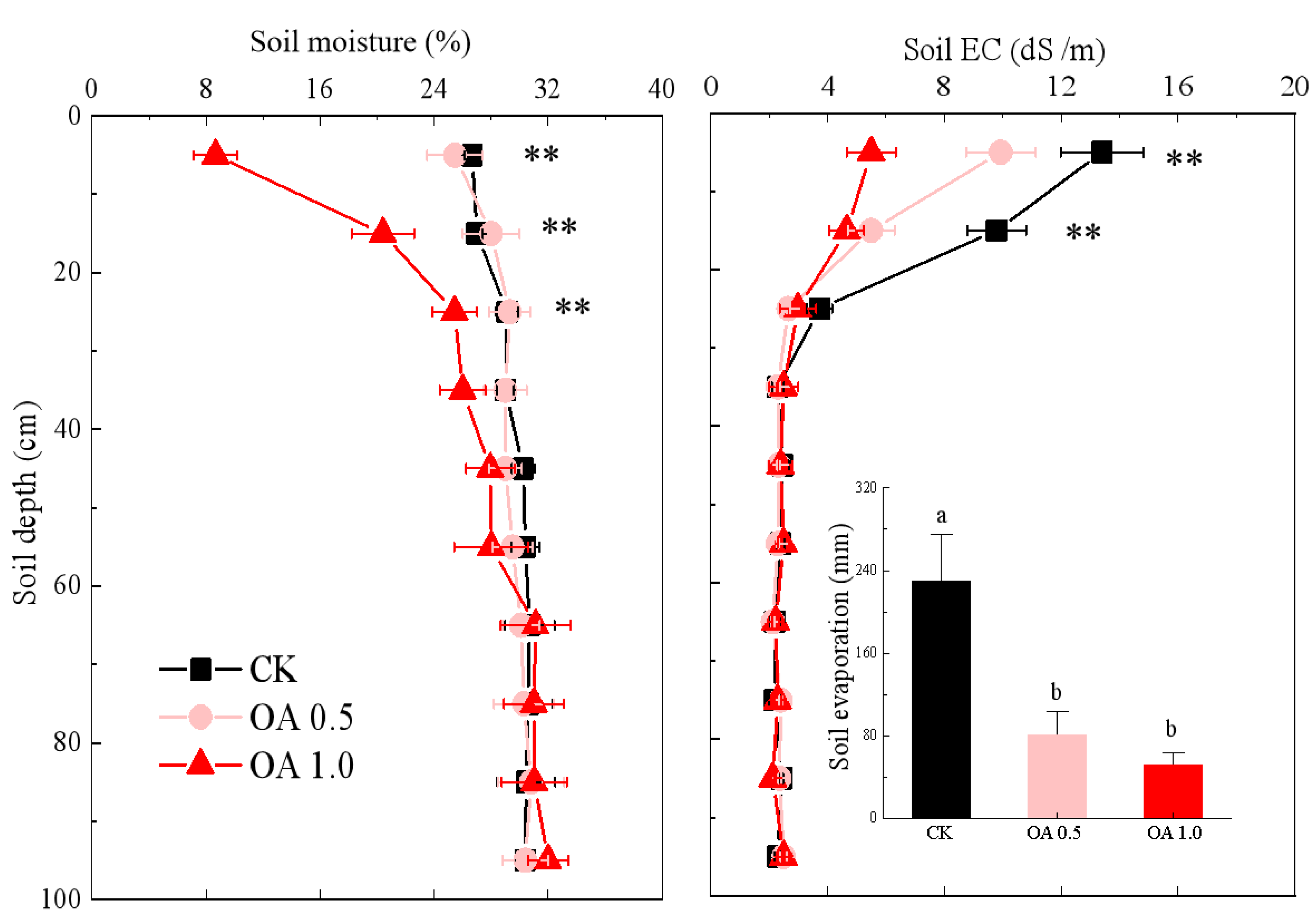
3.1. Changes in Soil Properties in Field Experiment
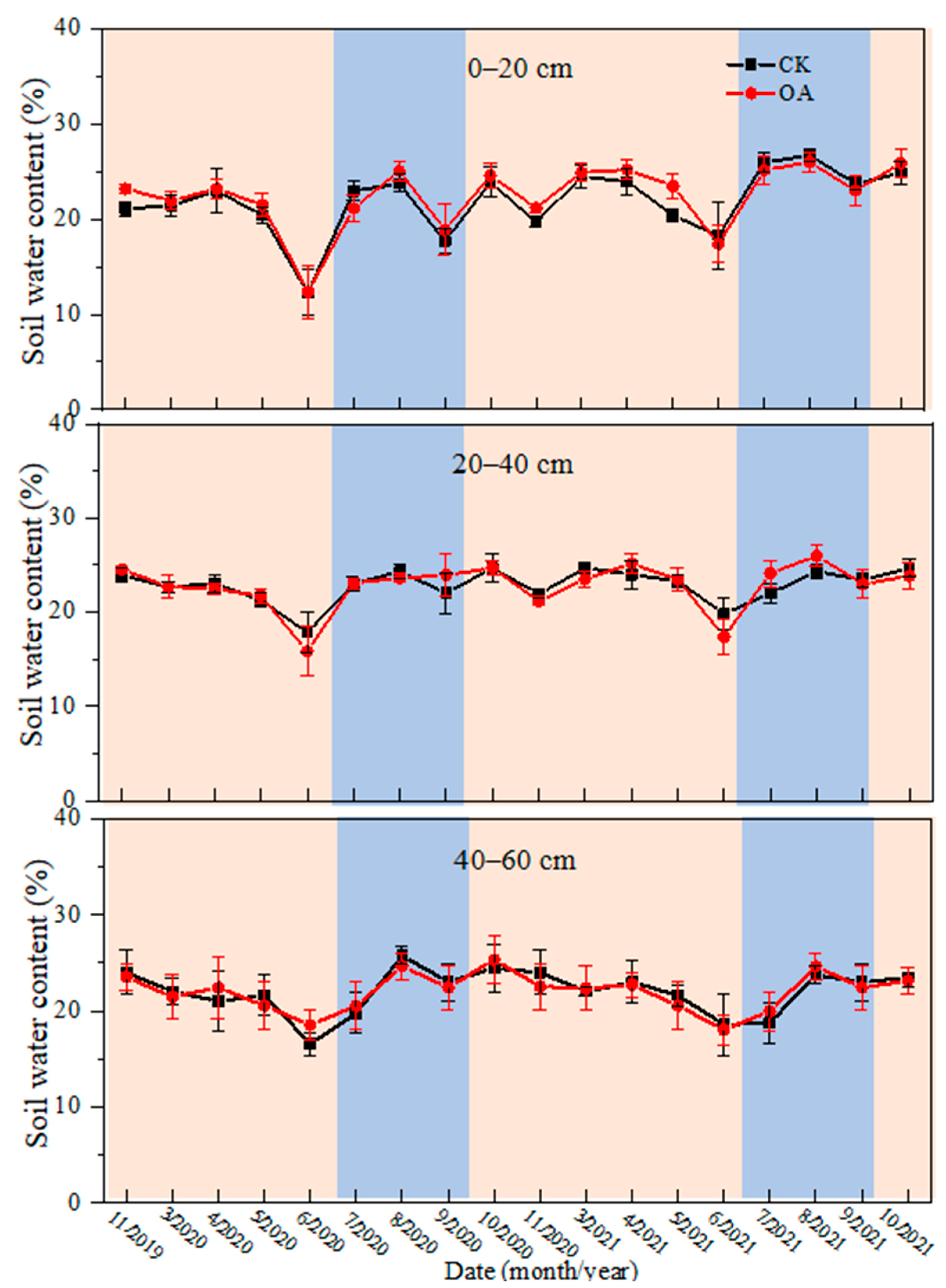
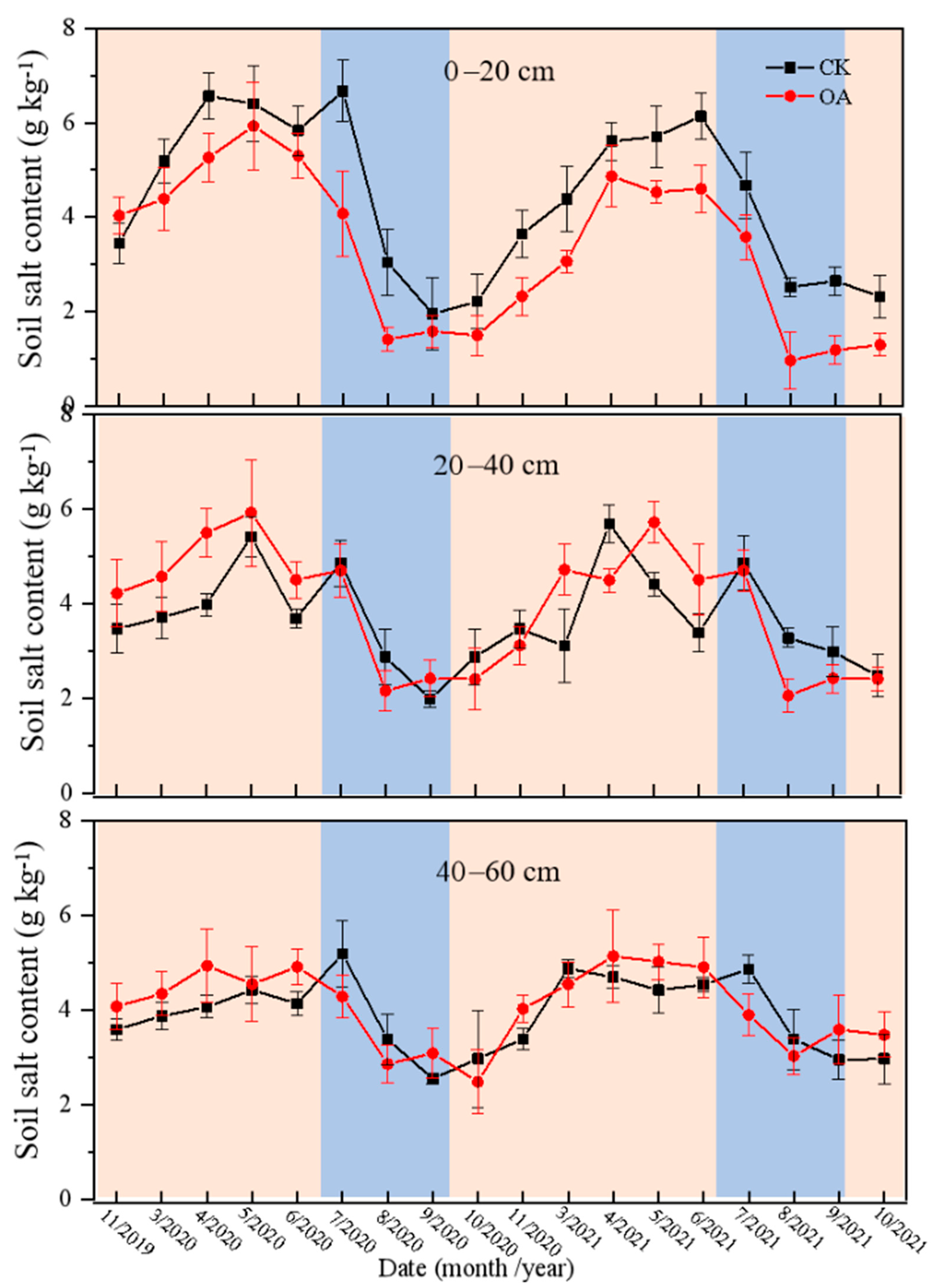
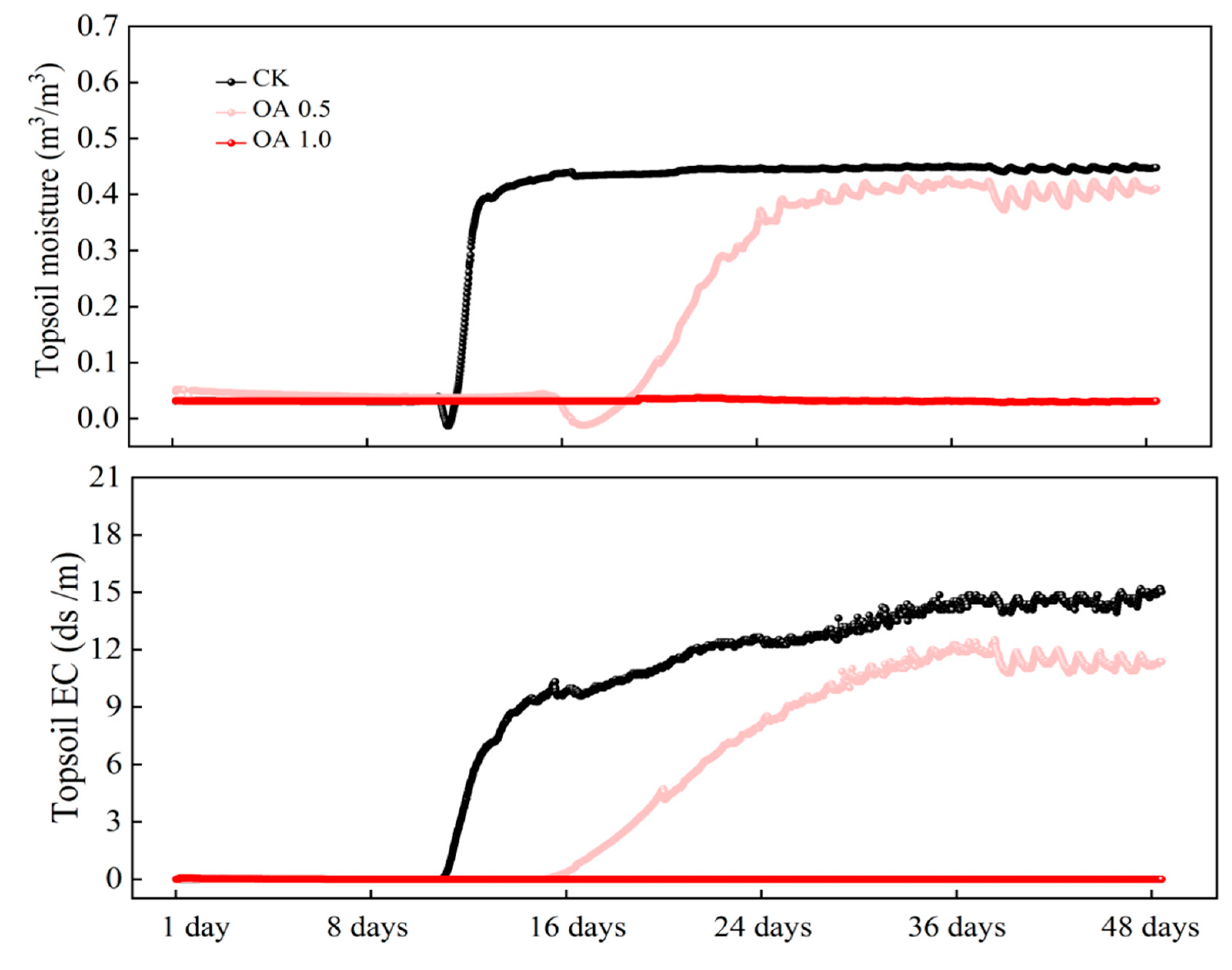
3.2. Soil Water and Salt Dynamics in Field Experiment
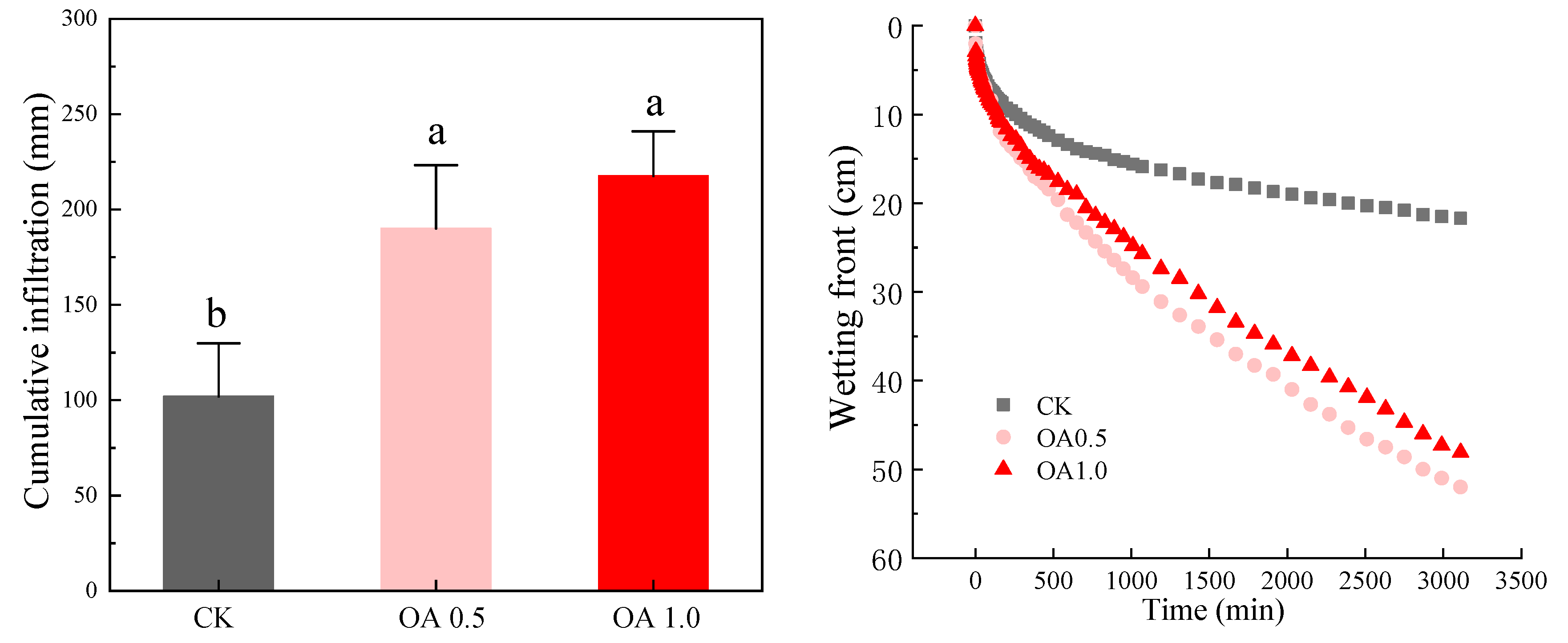
3.3. Soil Column Experiment: Salt Accumulation
3.4. Soil Column Experiment: Salt Leaching
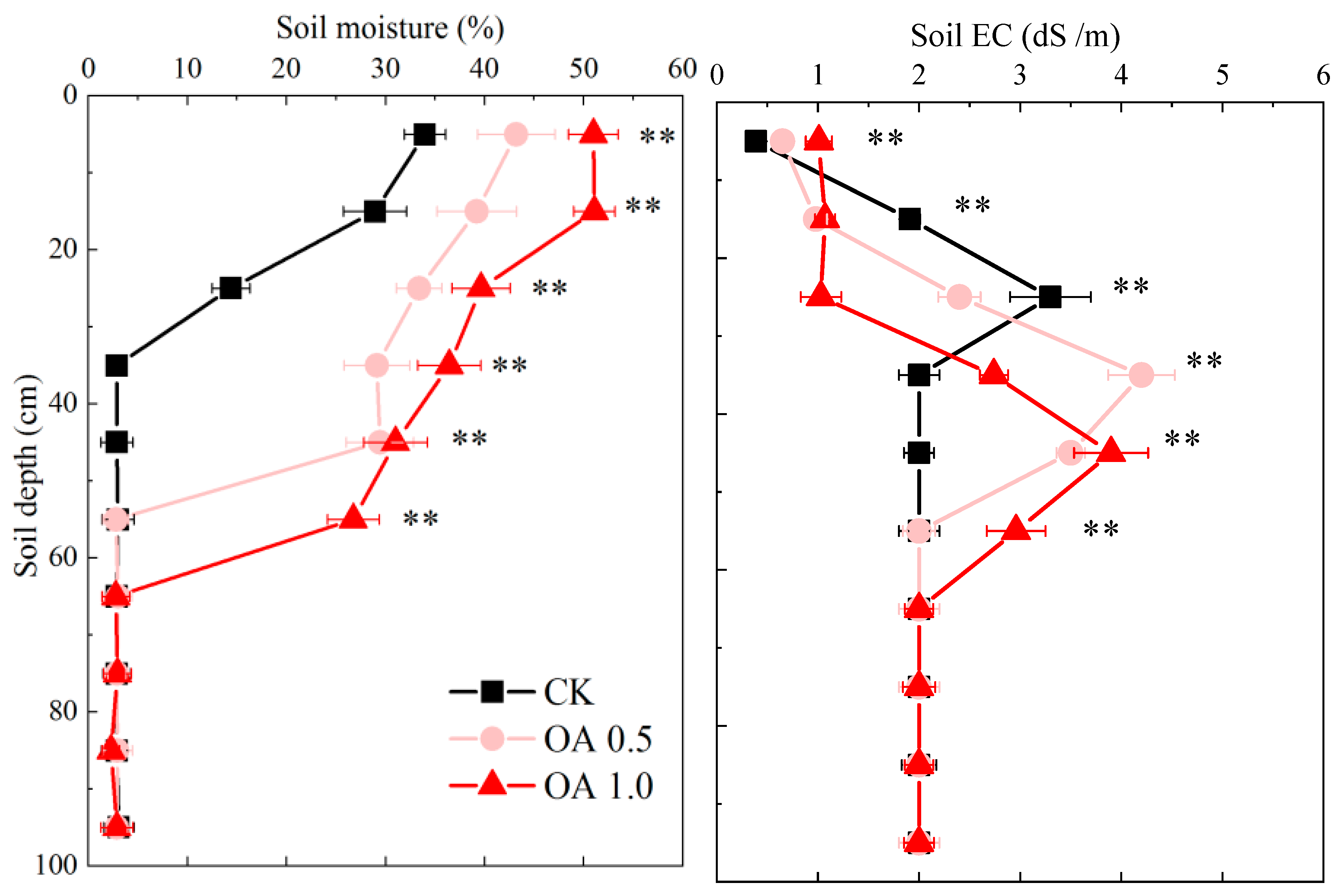
3.5. Changes in Salt Accumulation and Leaching in Topsoil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qadir, M.; Tubeileh, A.; Akhtar, J.; Larbi, A.; Minhas, P.S.; Khan, M.A. Productivity enhancement of salt-affected environments through crop diversification. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wei, B.; Xu, X.; Engel, B.; Li, G.; Huang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, G. Analyzing spatiotemporal characteristics of soil salinity in arid irrigated agro-ecosystems using integrated approaches. Geoderma 2019, 356, 113935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Han, D.; Song, X.; Trolle, D. Subsurface hydrological processes and groundwater residence time in a coastal alluvium aquifer: Evidence from environmental tracers (δ18O, δ2H, CFCs, 3H) combined with hydrochemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajiboland, R. Role of arbuscular mycorrhiza in amelioration of salinity. In Salt Stress in Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 301–354. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y. Forest and grass composite patterns improve the soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta, China. Geoderma 2019, 349, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Rico-Medina, A.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. The physiology of plant responses to drought. Science 2020, 368, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michot, D.; Walter, C.; Adam, I.; Guéro, Y. Digital assessment of soil-salinity dynamics after a major flood in the Niger River valley. Geoderma 2013, 207–208, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Li, J. Soil salinization of cultivated land in Shandong Province, China-Dynamics during the past 40 years. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.A.; Konukcu, F.; Gowing, J.W. Effect of watertable depth on evaporation and salt accumulation from saline groundwater. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypek, G.; Dogramaci, S.; Rouillard, A.; Grierson, P.F. Groundwater seepage controls salinity in a hydrologically terminal basin of semi-arid northwest Australia. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M. Evaluating the relative contribution of physiochemical and biological factors in ameliorating a saline-sodic soil amended with composts and biochar and leached with reclaimed water. Geoderma 2015, 259–260, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S.; Li, X. Effect of salinity on oleic sunflower (Helianthus annuus Linn.) under drip irrigation in arid area of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, C.; Hussain, T.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, K. Long-term effect of tamarisk plantation on soil physical properties and soil salt distribution in coastal saline land. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Liu, X.J. Infiltration of meltwater from frozen saline water located on the soil can result in reclamation of a coastal saline soil. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harttung, S.A.; Radabaugh, K.R.; Moyer, R.P.; Smoak, J.M.; Chambers, L.G. Coastal riverine wetland biogeochemistry follows soil organic matter distribution along a marsh-to-mangrove gradient (Florida, USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Y.; Yu, F. Biochar-compost addition benefits Phragmites australis growth and soil property in coastal wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shao, T.; Lv, Z.; Liu, A.; Long, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, X.; Rengel, Z. The mechanisms of improving coastal saline soils by planting rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cruzado, I.; Infante-Izquierdo, M.D.; Márquez-García, B.; Hermoso-López, V.; Polo, A.; Nieva, F.J.J.; Cartes-Barroso, J.B.; Castillo, J.M.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, A. Relationships between spatio-temporal changes in the sedimentary environment and halophytes zonation in salt marshes. Geoderma 2017, 305, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bian, X.; Yang, R.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B. Assessment of organic amendments for improving coastal saline soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3204–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Mei, X.; He, W.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Fan, T.L. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, L.; Vignozzi, N.; Miralles, I.; Solé-Benet, A. Organic amendments and mulches modify soil porosity and infiltration in semiarid mine soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Halim, A.A.; Lennartz, B. Amendment with sugarcane pith improves the hydrophysical characteristics of saline-sodic soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R.; Vitti, C. Use of organic amendments to reclaim saline and sodic soils: A review. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2019, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, A.N.; Iwai, C.B.; Saenjan, P. Soil properties and maize growth in saline and non-saline soils using cassava-industrial waste compost and vermicompost with or without earthworms. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitran, T.; Pabitra, K.M.; Nirmalendu, B.; Sunanda, B.; Biswapati, M. Organic amendments influence on soil biological indices and yield in rice-based cropping system in coastal sundarbans of India. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 48, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.Y.; Singh, K.; Pankaj, U.; Verma, S.K.; Verma, R.K.; Patra, D.D. Effect of organic amendments and microbial application on sodic soil properties and growth of an aromatic crop. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Chen, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. Coastal saline soil aggregate formation and salt distribution are affected by straw and nitrogen application: A 4-year field study. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Lv, X.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Shi, J. Impact of saline soil improvement measures on salt content in the abandonment-reclamation process. Soil Res. 2021, 208, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Approaches and Research Progresses of Marginal Land Productivity Expansion and Ecological Benefit Improvement in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 336–348. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; An, P.; Li, X.; Guo, K.; Yang, C.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of soil water and salinity after establishment of dense-foliage Tamarix chinensis on coastal saline land. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 121, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, M.; Cheng, F.; Coxixo, A.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Factors driving the relationships between vegetation and soil properties in the Yellow River Delta, China. Catena 2018, 165, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Du, Z.; Guo, K.; Liu, X. Irrigation with freezing saline water for 6 years alters salt ion distribution within soil aggregates. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Techniques for Measuring Soil Physical Properties; MAFF Reference Book 441; HMSO: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, R.Q.; Rolim, M.M.; de Lima, R.P.; Tavares, U.E.; Pedrosa, E.M.R.; Cherubin, M.R. Soil physical changes induced by sugarcane cultivation in the Atlantic Forest biome, northeastern Brazil. Geoderma 2020, 370, 114353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, W.D.; Chepil, W.S. Size distribution of aggregation. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Black, C.A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Liu, X.J. Dynamics of meltwater quality and quantity during saline ice melting and its effects on the infiltration and desalinization of coastal saline soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 139, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.S. Handbook of Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.J.; Sun, H.Y.; Wang, J.T.; Liu, X.J.; Singh, B.P. Wheat-derived soil organic carbon accumulates more than its maize counterpart in a wheat–maize cropping system after 21 years. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 71, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassel, D.K.; Nielsen, D.R. Field capacity and available water capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis. 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; ASA-SSSA Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 901–924. [Google Scholar]
- Canfora, L.; Bacci, G.; Pinzari, F.; Papa, G.L.; Dazzi, C.; Benedetti, A. Salinity and bacterial diversity: To what extent does the concentration of salt affect the bacterial community in a saline soil? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, C.; Cardinale, M.; Ratering, S.; Steffens, D.; Jung, S.; Montoya, A.M.Z.; Geissler-Plaum, R.; Schnell, S. Plant growth-promoting effects of Hartmannibacter diazotrophicus on summer barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under salt stress. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 95, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, Z.; Huang, J.; Hussain, S.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X.; Jin, Q. Biochar alleviated the salt stress of induced saline paddy soil and improved the biochemical characteristics of rice seedlings differing in salt tolerance. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowing, J.W.; Konukcu, F.; Rose, D.A. Evaporative flux from a shallow watertable: The influence of a vapour–liquid phase transition. J. Hydrol. 2006, 321, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phogat, V.; Skewes, M.A.; Cox, J.W.; Sanderson, G.; Alam, J.; Šimůnek, J. Seasonal simulation of water, salinity and nitrate dynamics under drip irrigated mandarin (Citrus reticulata) and assessing management options for drainage and nitrate leaching. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; She, D.; Mu, X. Water flow and salt transport in bare saline-sodic soils subjected to evaporation and intermittent irrigation with saline/distilled water. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1204–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.B.; Gail, M.H.; Derek, A.H.; Wuhuan, Z.; James, A.S. Green stormwater infrastructure redirects deicing salt from surface water to groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138736. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, J.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z. Effects of biochar application on phreatic water evaporation and water-salt distribution in coastal saline soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Endo, K.N.; Guodong, C. Soil carbon in desertified land in relation to site characteristics. Geoderma 2002, 106, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Slater, A.G. Incorporating organic soil into a global climate model. Clim. Dyn. 2008, 30, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Z.; Liang, L. Effect of straw incorporation on soil moisture, evapotranspiration, and rainfall-use efficiency of maize under dryland farming. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Ge, Y.; Sun, L. Effects of soil reclamation on the oat cultivation in the newly reclaimed coastal land, eastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandana, S.; Thomas, B.; Sven, A.; Lucy, P.R. The effect of soil physical amendments on reclamation of a saline-sodic soil: Simulation of salt leaching using HYDRUS-1D. Soil Res. 2018, 56, 829–845. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W. Short-term effects of biochar and gypsum on soil hydraulic properties and sodicity in a saline-alkali soil. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.; Eugene, D.U.; Moshe, S. Shrubs enhance resilience of a semi-arid ecosystem by engineering and regrowth. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 330–339. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Sela, S.; Svoray, T.; Assouline, S. The role of soil-surface sealing, microtopography, and vegetation patches in rainfall-runoff processes in semiarid areas. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 5585–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, E.; Abdellatif, E.; Hudson, W.P.; Ahmed, L.; Mostafa, B. A review of organic and inorganic amendments to treat saline-sodic soils: Emphasis on waste valorization for a circular economy approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171087. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ferreira, J.; Wang, M.; Na, J.; Huang, J.; Liang, Z. Long-term combined effects of tillage and rice cultivation with phosphogypsum or farmyard manure on the concentration of salts, minerals, and heavy metals of saline-sodic paddy fields in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Properties | Materials | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Sample | Organic Fertilizer | Groundwater | |
| Organic matter (%) | 0.60 ± 0.02 | 49.25 ± 0.45 | – |
| pH | 6.74 ± 0.10 | 5.83 ± 0.05 | 7.36 ± 0.09 |
| EC (dS /m) | 2.01 ± 0.03 | 9.82 ± 0.64 | 32.2 ± 1.37 |
| Main ion content (g/kg) | |||
| HCO3− | 0.37 ± 0.09 | 1.29 ± 0.28 | 0.12 ± 0.02 |
| Cl− | 4.96 ± 0.60 | 3.90 ± 0.79 | 12.27 ± 1.20 |
| SO42− | 1.25 ± 0.72 | 9.59 ± 1.12 | 0.18 ± 0.47 |
| Ca2+ | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 1.64 ± 0.73 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| Mg2+ | 0.21 ± 0.09 | 2.14 ± 0.54 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Na+ and K+ | 3.40 ± 0.21 | 0.53 ± 0.09 | 7.95 ± 0.29 |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Treatments | BD (g/cm3) | Porosity Indicator (m3/m3) | TP (%) | SWSC (-) | SHC (cm/h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macro-(MA) | Meso-(ME) | Micro-(MI) | ||||||
| 0–20 | CK | 1.40 ± 0.02 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | 47.16 ± 1.71 b | 0.73 ± 0.04 a | 1.84 ± 0.34 b |
| 0–20 | OA | 1.24 ± 0.03 b | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 53.21 ± 0.95 a | 0.67 ± 0.02 b | 5.43 ± 1.31 a |
| 20–40 | CK/OA | 1.46 ± 0.06 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.09 | 44.90 ± 2.03 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 1.75 ± 0.14 |
| 40–60 | CK/OA | 1.49 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 43.77 ± 1.16 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 1.69 ± 0.47 |
| Soil Depth (cm) | Treatments | SOC (g/kg) | Soil Aggregate Size Percentage (%) | MWD (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | SA | LA + SA | MI | CS | ||||
| 0–20 | CK | 5.49 ± 0.41 b | 4.30 ± 1.53 b | 31.46 ± 1.80 b | 35.76 ± 1.72 b | 30.22 ± 1.75 a | 33.52 ± 3.97 a | 24.65 ± 2.12 b |
| 0–20 | OA | 6.69 ± 0.23 a | 7.82 ± 1.60 a | 49.09 ± 3.18 a | 56.91 ± 3.93 a | 21.40 ± 1.50 b | 21.69 ± 4.88 b | 37.55 ± 3.23 a |
| 20–40 | CK/OA | 4.01 ± 0.62 | 1.68 ± 0.98 | 18.41 ± 2.32 | 20.09 ± 2.44 | 30.14 ± 2.01 | 49.78 ± 6.09 | 19.83 ± 2.42 |
| 40–60 | CK/OA | 3.64 ± 0.21 | 0.78 ± 0.43 | 40.65 ± 8.04 | 4.145 ± 2.57 | 35.97 ± 7.04 | 22.59 ± 3.40 | 21.53 ± 3.05 |
| Infiltration Rate (mm/min) | CK | OA 0.5 | OA 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial stage | 2.95 ±0.26 c | 3.58 ± 0.44 a | 3.01 ± 0.21 b |
| Stable stage | 0.08 ±0.01 c | 0.21 ± 0.05 b | 0.31 ± 0.03 a |
| Treatment | Stage | Cation (g kg−1) | Anion (g kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ and K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | ||
| CK | Before EXP | 3.40 ± 0.21 b | 0.14 ± 0.03 b | 0.21 ± 0.09 b | 4.96 ± 0.60 b | 1.25 ± 0.72 b | 0.37 ± 0.09 ab |
| After EXP 1 | 7.43 ± 0.24 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 0.48 ± 0.08 a | 11.31 ± 0.79 a | 1.82 ± 0.29 a | 0.42 ± 0.03 a | |
| After EXP 2 | 2.68 ± 0.60 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 c | 4.05 ± 0.51 b | 0.14 ± 0.02 c | 0.32 ± 0.02 b | |
| OA 0.5 | Before EXP | 2.74 ± 0.23 b | 0.80 ± 0.09 a | 0.73 ± 0.11 a | 4.26 ± 0.61 b | 4.80 ± 0.35 a | 0.55 ± 0.11 ab |
| After EXP 1 | 4.12 ± 0.67 a | 1.09 ± 0.34 a | 0.84 ± 0.14 a | 6.48 ± 1.05 a | 4.86 ± 0.48 a | 0.67 ± 0.13 a | |
| After EXP 2 | 1.90 ± 0.39 c | 0.06 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | 2.55 ± 0.34 c | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 0.42 ± 0.03 b | |
| OA 1.0 | Before EXP | 2.30 ± 0.15 a | 1.08 ± 0.22 a | 1.02 ± 0.16 a | 4.12 ± 0.33 a | 6.63 ± 1.06 a | 0.67 ± 0.20 a |
| After EXP 1 | 2.44 ± 0.51 ab | 1.18 ± 0.86 a | 1.05 ± 0.12 a | 4.02 ± 1.50 a | 6.27 ± 0.67 a | 0.81 ± 0.23 a | |
| After EXP 2 | 1.20 ± 0.12 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 2.91 ± 0.28 b | 0.48 ± 0.05 b | 0.31 ± 0.01 b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, K.; Fan, F.; Liu, S.; Jia, S. Soil Organic Matter Input Promotes Coastal Topsoil Desalinization by Altering the Salt Distribution in the Soil Profile. Agronomy 2024, 14, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050942
Li J, Li W, Feng X, Liu X, Guo K, Fan F, Liu S, Jia S. Soil Organic Matter Input Promotes Coastal Topsoil Desalinization by Altering the Salt Distribution in the Soil Profile. Agronomy. 2024; 14(5):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050942
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingsong, Weiliu Li, Xiaohui Feng, Xiaojing Liu, Kai Guo, Fengcui Fan, Shengyao Liu, and Songnan Jia. 2024. "Soil Organic Matter Input Promotes Coastal Topsoil Desalinization by Altering the Salt Distribution in the Soil Profile" Agronomy 14, no. 5: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050942
APA StyleLi, J., Li, W., Feng, X., Liu, X., Guo, K., Fan, F., Liu, S., & Jia, S. (2024). Soil Organic Matter Input Promotes Coastal Topsoil Desalinization by Altering the Salt Distribution in the Soil Profile. Agronomy, 14(5), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050942





