Abstract
Maize/peanut intercropping may improve soil health through reducing nitrogen (N) fertilization. However, the effects of maize/peanut intercropping combined with reduced N fertilization on the soil fungal community structure have not been well reported. Using a long-term localized micro-zone experiment, we investigated the combined effects of intercropping and N fertilizer application on soil fungal community diversity and composition. Three cropping patterns (maize/peanut intercropping, maize monoculture, and peanut monoculture) and three N application levels (0 kg·hm−2, 150 kg·hm−2, and 300 kg·hm−2) were assessed. The results showed that the total numbers of fungal species and unique species (operational taxonomic units, OTUs) in both maize and peanut soils tended to first increase and then decrease with increasing N application. Compared with monoculture, the numbers of total OTUs and unique OTUs in intercropped maize soil decreased by 4.14% and 12.79%, respectively, but the total numbers of OTUs and unique OTUs in peanut soil increased by 1.08% and 3.78%, respectively. With increasing N application, the soil fungal Ace and Chao indices of maize soil first increased and then decreased, while the fungal Shannon, Ace, and Chao indices of peanut soil decreased. Compared with the monoculture system, intercropping significantly reduced the maize soil fungal Ace and Chao indices but increased the peanut soil fungal Shannon, Ace, and Chao indices. Nitrogen application and intercropping significantly altered the fungal community structure of maize soil, while N application had no significant effect on the fungal community structure of peanut soil, though intercropping significantly changed the fungal community structure of peanut soil. At the phylum level, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Mortierellomycota, unclassified_k_Fungi, and Chytridiomycota were the dominant taxa. Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that soil nitrate (NO3−) content was the main environmental factor shaping the soil fungal community. In conclusion, excessive N fertilization (300 kg·hm−2) can reduce soil fungal community diversity; maize/peanut intercropping reversed the negative effect of N application on fungal community of peanut soil, but not that of maize soil. Soil NO3− content is the primary environmental driver of soil fungal communities.
1. Introduction
Intercropping is a quintessential cultivation pattern in traditional Chinese agriculture, known to increase aboveground biodiversity, strengthen complementary advantages between crops, improve resource utilization efficiency, and enhance farmland productivity [1,2]. Nitrogen (N) fertilizer application is a common measure to maintain crop yield, but long-term excessive use can lead to soil acidification, decreased soil microbial diversity, and altered soil microbial community structure [3,4]. Therefore, reducing chemical N fertilizer input has become an important national policy in China. Legume/cereal intercropping, such as maize/peanut intercropping, can reduce fertilizer input by promoting biological N fixation in legumes, while increasing aboveground biodiversity may affect soil N cycling by regulating the composition of soil microorganisms [5,6,7]. Studying the effects of legume/cereal intercropping with different N fertilizer levels on soil microbial composition and structure can reveal the mechanisms by which this practice promotes N use efficiency and is of great significance for the ecological evaluation and promotion of intercropping systems.
Legume/cereal intercropping is one of the common intercropping patterns [8]. It directly or indirectly affects soil microbial community diversity and composition by altering soil aggregate structure, nutrient availability, water redistribution, and root exudates [9,10]. Studies have shown that most intercropping systems can increase bacterial and fungal diversity by improving the availability of nutrients in soil and the diversity of root exudates [11,12]. Nitrogen has significant effects on microbial growth and metabolism [13]. In N-limited ecosystems, N fertilizer application can alleviate microbial N limitation, thereby changing community structure and diversity. In high-N-input systems, soil pH changes become the primary factor shaping the structure and diversity of soil microbial communities [4]. Shifts in microbial community diversity and composition feed back on soil nutrient cycling and ecosystem balance [14].
Maintaining higher soil microbial diversity and a good community structure is crucial for soil health management. In intercropping systems, changes in soil chemical properties, aggregates, and the quantity and composition of root exudates alter soil microbial communities [8]. Previous studies on legume/cereal intercropping systems have focused on bacterial communities, but fungi have stronger N uptake capacities and environmental tolerance [15,16]. However, the effects of legume/cereal intercropping on the diversity and composition of soil fungal communities, as well as the mechanisms by which N application levels affect fungal community diversity and composition in the legume/cereal intercropping system, remain unclear.
This study focuses on the soil fungal community in a maize/peanut intercropping system under different N levels. We hypothesize that: (1) N application will decrease fungal alpha diversity, while intercropping will increase it; (2) community composition will be strongly affected by N, but more similar between maize and peanut soils in the intercropping system. The study aims to investigate the impacts of intercropping and N application on soil fungal community diversity and composition, and the factors driving changes in soil fungal community structure, providing a theoretical basis for ecological evaluation and N regulation in maize/peanut intercropping.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
The maize/peanut intercropping micro-plot experiment was started in May 2015 at the Liaoning Academy of Agricultural Sciences (41°49′ N, 123°33′ E) located in Shenyang city, Liaoning Province, Northeastern China. This region has a temperate sub-humid monsoon climate with mean annual precipitation of 574–684 mm and rainfall concentrated mainly from June to September, accounting for approximately 85% of the total annual precipitation. The experimental site was located at an altitude of 54.4 m a.s.l with an accumulated temperature above 10 °C of 3350 °C, mean annual evaporation of 1440 mm, mean annual temperature of 7.0–8.1 °C and a frost-free period of 148–180 days. The soil was brown earth according to the Chinese Soil Taxonomy [17], with a soil bulk density of 1.38 g·cm−3, organic matter of 15.2 g·kg−1, total N of 0.62 g·kg−1, available phosphorus of 25.4 mg·kg−1, and available potassium of 64.3 mg·kg−1.
2.2. Experimental Design
The field experiment included three cropping systems: maize monoculture (SM), peanut monoculture (SP), and maize/peanut intercropping (IM, intercropped maize; IP, intercropped peanut). In the monoculture systems, four rows of either maize or peanuts were planted. The intercropping system consisted of two rows of maize alternating with two rows of peanuts, with each crop occupying 50% of the planting area. Each cropping system was nested with three N application levels: 0 kg N·hm−2 (N0), 150 kg N·hm−2 (N1), and 300 kg N·hm−2 (N2). All plots received 90 kg P2O5·hm−2 and 105 kg K2O·hm−2, with urea (46% N), calcium superphosphate (12% P2O5), and potassium sulfate (50% K2O) used as the N, P, and K fertilizers, respectively. The fertilizers were applied in furrows before sowing. The nine treatment combinations were arranged in a randomized complete block design with three replications. Each plot measured 8 m2 (length 4 m and width 2 m) and was separated from adjacent plots with a 1 m deep polypropylene board.
For both the monoculture and intercropping systems, the row spacing was 0.5 m. The planting spacings were 0.33 m and 0.13 m for maize and peanut, respectively. The sowing density was 6 seeds·m−2 (one seed per hole) for maize and 30 seeds·m−2 (two seeds per hole) for peanut. The maize and peanut varieties were “Zhengdan 958” (developed by Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China) and “Baisha 1016” (developed by Baisha Farm in Guangdong Province, China), respectively. Sowing took place in mid-May, and the crops were harvested at the end of September each year.
2.3. Sample Collection and Soil Property Measurement Methods
On 24 August 2019, soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm soil layer during the peanut pod setting stage. In the intercropping plots, soils were sampled from the peanut (or maize) plants rows closed to maize (or peanut) plants; 4 plants per row were sampled. The loosely adhering soil was shaken off the roots and sieved through a 2 mm mesh. Soil samples from the same plants within each plot were mixed and divided into two portions (see Supplementary Figure S1A). In the monoculture plots, two plants were sampled from each of the two inner rows (see Supplementary Figure S1B,C). One portion of the soil samples was stored at 4 °C for determination of ammonium and nitrate contents, while the other portion was air-dried in the shade for determination of organic matter, total N, available phosphorus, available potassium, and pH. The remaining rhizosphere soils from the same plants in each plot were then homogenized and stored at −80 °C for fungal community analysis.
The soil chemical properties were determined according to the methods described by Lu [18]. Soil organic matter was determined using the potassium dichromate oxidation method. Total N was analyzed with an elemental analyzer (Elementar III, Hanau, Germany). Available phosphorus was extracted with 0.5 mol·L−1 NaHCO3 and determined using the molybdenum blue colorimetric method. Available potassium was extracted with 1 mol·L−1 NH4OAc and measured via flame photometry. Soil pH was determined in a 1:5 (w/w) soil-water suspension using a Leici SJ-3F pH meter. Fresh soil samples were extracted with 0.01 mol·L−1 CaCl2, in a 5:1 water-to-soil ratio, and the concentrations of ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3−) were determined using an automatic flow analyzer (AA3, SEAL Company, Norderstedt, Germany).
Total DNA was extracted from 0.5 g fresh soil using the Fast DNA® SPIN Kit for Soil. The purity and concentration of DNA were measured with a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer, and integrity was assessed via 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The fungal ITS1 region was amplified using the primers ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS2R (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′) with barcodes synthesized for PCR amplification using an ABI GeneAmp® 9700 instrument. The reaction system (20 μL) included 2 μL of 10× buffer, 2 μL of 2.5 mmol·L−1 dNTPs, 0.8 μL each of 5 μmol·L−1 forward and reverse primers, 0.2 μL of rTaq polymerase, 0.2 μL of BSA, 10 ng of DNA template, and ddH2O. Cycling conditions were 95 °C for 3 min, followed by cycling (95 °C for 30 s, annealing temperature for 30 s, 72 °C for 45 s) and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min, followed by cooling to 10 °C. The PCR products were checked under 2% agarose gel electrophoresis, and qualified products were recovered via gel extraction and mixed in appropriate proportions for sequencing.
The ITS sequences were sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq PE300 platform (San Diego, CA, USA) at the Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The raw paired-end reads were combined using Flash software (version 1.2.11). Barcodes and primers were removed and duplicate sequences were eliminated using QIIME (version 1.9.1) [19]. Chimeric sequences were then identified and excluded from the dataset using Usearch (version 7.0, http://drive5.com/uparse/ (accessed on 10 May 2024)) [20]. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were defined at a 97% similarity threshold using Uparse (version 7.0.1090) [21]. Taxonomic classification was conducted using UNITE (version 8.0) databases. QIIME was used to assign classifications with a threshold value of 0.8. Before estimating α-diversity, the dataset was rarified to the lowest read count present in all soil samples.
2.4. Data Analysis
Mothur Version 2.0.4 “https://mothur.org/wiki/otu-based_approaches/ (accessed on 16th October 2020)” was used to calculate fungal alpha diversity indices based on the rarefied OTU data. Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) was performed on the rarefied OTU data using the Bray–Curtis distance algorithm of the “vagen” package in the R statistical software (version 3.4.2 (http://cran.rproject.org/). Adonis inter-group difference tests were conducted to assess the effects of N application and intercropping on fungal community structure based on the Bray–Curtis distance. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was used to identify the main soil properties shaping the fungal community. To detect treatment effects, two-way ANOVA with Duncan’s test (p < 0.05) was carried out in SPSS Statistics 17.0.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
Compared with the absence of N application (N0), N1 did not show a significant impact on nitrate and ammonium content in maize soils (either in monoculture or intercropping) but significantly reduced the content of available phosphorus (Table 1). On the other hand, N2 led to significant increases in nitrate and ammonium content, while significantly reducing the content of available phosphorus. N1 and N2 significantly reduced the pH of monoculture maize soil (Table 1, p < 0.050), while having no significant effect on the pH of intercropping maize soil. Intercropping significantly affected the nitrate content, available phosphorus content, and pH of maize soil (Table 1, p < 0.05). Maize/peanut intercropping increased the pH of maize soil and significantly increased the available phosphorus content across all N application levels. The content of available phosphorus and organic matter decreased with increased N fertilization levels. The content of available potassium increased with increased N application levels. Compared with monoculture, intercropping significantly increased the nitrate, available phosphorus, available potassium, total N, and pH in peanut soil under all three N fertilization levels.

Table 1.
Basic soil properties under different treatments.
3.2. Soil Fungal Alpha Diversity
As shown in Figure 1, the rarefaction curves for maize and peanut soil tended to plateau, indicating that the sequencing depth was sufficient and the gene sequences in the samples can reasonably reflect the real situation of the soil fungal communities. This suggests that the sampling and sequencing efforts adequately captured the diversity and richness of the soil fungal communities in this study.
Figure 1.
Rarefaction curves of maize (A) and peanut (B) soil fungi sequencing were generated for the Sobs index at the OTU level under different treatments. The numbers 0, 1, 2 in the legends refer to 0, 150, 300 kg·hm−2 nitrogen application.
Nitrogen fertilization and intercropping had no significant effect on the Shannon index of the fungal community in maize soil (Figure 2A; p > 0.05). However, they had a significant effect on the Ace and Chao indices of the fungal community (Figure 2C,E; p < 0.01). Compared with N0, N1 increased the fungal Ace and Chao indices in maize soil, while N2 decreased these indices. The Ace and Chao indices of fungal communities in maize soil in the intercropping system were significantly lower than those in monoculture, across all N fertilization levels. The average Ace indices for SM and IM were 985.98 and 887.74, respectively. Similarly, the average Chao index for SM was 1008.89, compared with 896.76 for IM. Pearson correlation analysis between fungal alpha diversity indices and soil chemical properties showed that, in maize soil, only available potassium was significantly negatively correlated with the Ace index (Table 2). No other soil chemical properties demonstrated significant correlation with the fungal diversity indices.
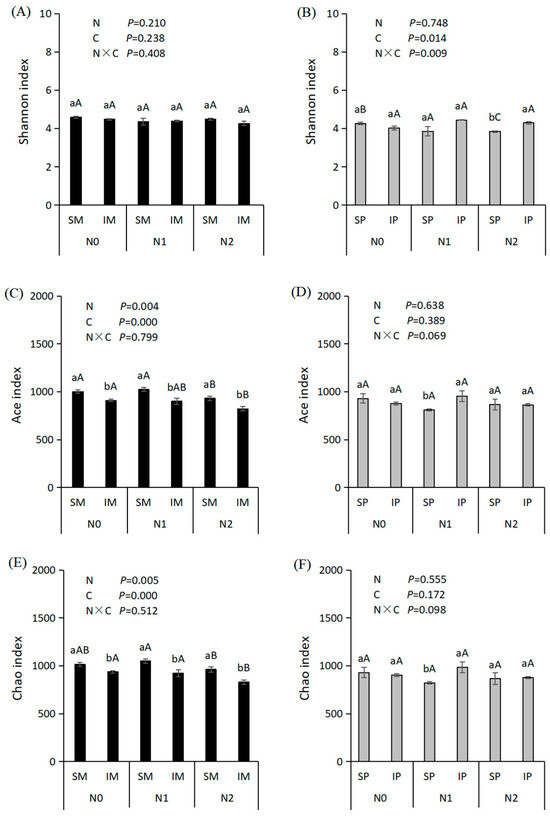
Figure 2.
Fungal alpha diversity of maize (A,C,E) and peanut (B,D,F) soil under different treatments. N, nitrogen application effect; C, cropping pattern effect; N × C, the interaction effect of N fertilization and cropping pattern. The different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between monoculture and intercropping system under the same N fertilization leavel at 0.05 level, and the different capital letters indicate a significant difference between different N fertilization levels under the same cropping pattern at 0.05 level.

Table 2.
Pearson correlation coefficients of soil fungal alpha diversity indexes and chemical properties.
The impact of N fertilization on fungal Shannon, Ace, and Chao indices in peanut soil appeared to be relatively minor, with no significant differences existing among the N0, N1, and N2 treatments (Figure 2B,D,F; p > 0.05). Compared with monoculture, intercropping significantly increased the fungal Shannon index in peanut soil (p < 0.05), with average values of 3.98 and 4.25 for SP and IP, respectively. However, the effects varied across N application levels. Under the N0 treatment, the fungal Shannon, Ace, and Chao indices in intercropped peanut soil were lower than those in the monoculture, while under N1 and N2 treatments, the fungal Shannon, Ace, and Chao indices in the intercropped peanut soil were higher than those in the monoculture. This indicates that both N application and intercropping altered the fungal community diversity and richness in the peanut soil. In the peanut soil, only ammonium content showed a significant negative correlation with the Ace index (Table 2).
3.3. Soil Fungal Community Structure
The fungal community structure similarity among all treatments was analyzed at the OTU level, and Venn diagrams were constructed to visualize the overlap (Figure 3A,B). For maize soil, a total of 631–685 OTUs were identified across all treatments, with 457 OTUs shared among all treatments and 174–228 OTUs unique to specific treatments. The total numbers of OTUs and unique OTUs under each N treatment followed the pattern N1 > N0 > N2, with average values of 673, 667, and 646 for total OTUs and 216, 210, and 189 for unique OTUs, respectively. The overall OTU numbers were higher in SM compared with IM, with average values of 676 and 648, respectively. Similarly, the number of unique OTUs was higher in SM compared with IM, with average values of 219 and 191, respectively. In peanut soil, 462 OTUs were shared among all treatments, and 169–225 OTUs were unique to each treatment. Similar to maize soil, the total numbers of OTUs and unique OTUs in peanut soil demonstrated the pattern N1 > N0 > N2, with total OTU numbers of 659.5, 653, and 642, and unique OTU numbers of 197.5, 191, and 177, respectively. The total numbers of OTUs and unique OTUs were higher in IP compared with SP, with total OTU numbers of 654 and 647, and unique OTU numbers of 192 and 185, respectively.
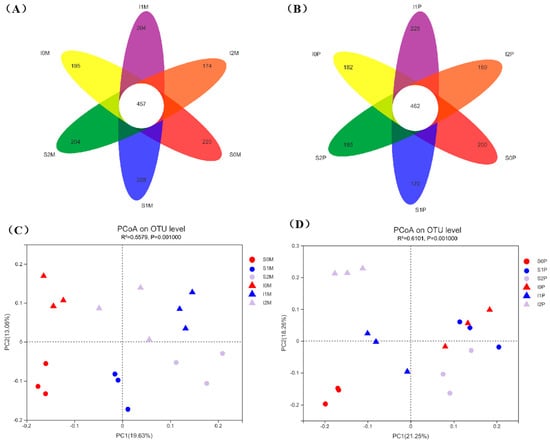
Figure 3.
Venn diagram (A,B) and PCoA diagram (C,D) of soil fungal community of maize and peanut. The numbers 0 (red color), 1 (blue color), 2 (purple color) in the legends refer to 0, 150, 300 kg·hm−2 nitrogen application.
In maize soil, the fungal community structure was significantly separated between N0 (red), N1 (blue), and N2 (purple), while the separation between N1 and N2 was less apparent (Figure 3C). The fungal communities of maize soil under intercropping and monoculture exhibited distinct distribution along the PC2 axis, indicating that N fertilization and intercropping significantly altered the structure of maize soil fungal communities, although N fertilization alone did not exert a significant effect on the fungal community structure. There was no clear separation between N0, N1, and N2, but significant separation was evident between fungal communities under monoculture and intercropping at each level of N fertilization (Figure 3D).
3.4. Relative Abundance of Soil Fungal Taxa
In the maize soil, the dominant fungal taxa were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Mortierellomycota, unclassified_k_Fungi, and Chytridiomycota (relative abundances > 1%), accounting for approximately 98.77% to 99.82% of the total fungal taxa (Figure 4A). Ascomycota was the most abundant phylum, ranging from 59.06% to 71.91%, followed by Basidiomycota, which ranged from 7.70% to 19.54%. The relative abundance of Ascomycota and Chytridiomycota first decreased followed by an increase with increasing N fertilization levels. The relative abundance of Ascomycota was 70.74%, 59.84%, and 61.60% in N0, N1, and N2, respectively, while that of Chytridiomycota was 0.48%, 0.40%, and 2.43%, respectively. Conversely, the relative abundance of Basidiomycota was 8.23%, 19.53%, and 17.75%, and that of unclassified_k_Fungi was 4.86%, 6.86%, and 5.91% in N0, N1, and N2, respectively. Compared with the maize monoculture, intercropping increased the relative abundance of Mortierellomycota from 11.48% to 14.92% in maize soil, while decreasing the relative abundance of Ascomycota, unclassified_k_Fungi, and Chytridiomycota.
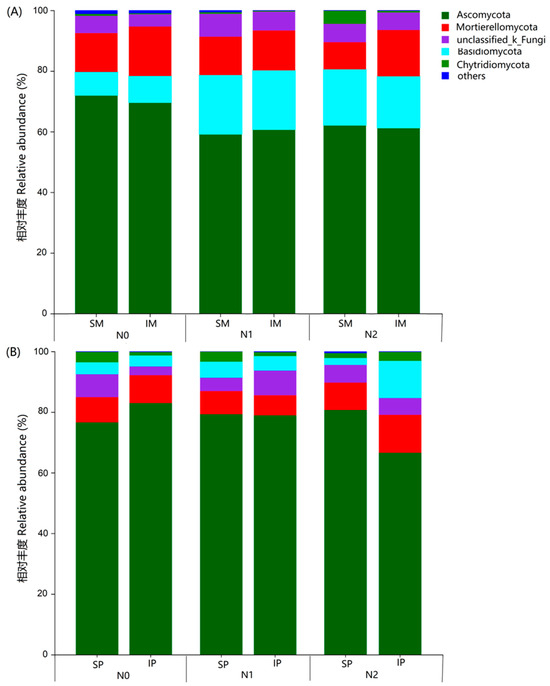
Figure 4.
Relative abundance of fungi in maize (A) and peanut (B) soils at phylum taxonomy level under different treatments.
In the peanut soil, the dominant fungal taxa were Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, unclassified_k_Fungi, Basidiomycota, and Chytridiomycota (with relative abundances > 1%), accounting for approximately 99.40% to 99.90% of the total fungal taxa (Figure 4B). Ascomycota was the most abundant taxon, ranging from 66.57% to 82.95%, followed by Mortierellomycota, ranging from 6.63% to 12.47%. With increasing levels of N fertilization, the relative abundance of Ascomycota decreased from 79.77% to 73.61%, while the relative abundance of Basidiomycota increased from 3.78% to 7.27%. The relative abundance of Mortierellomycota initially decreased and then increased, while the relative abundance of unclassified_k_Fungi initially increased and then decreased. Compared with monoculture, intercropping decreased the relative abundance of Ascomycota and Chytridiomycota, but increased the relative abundance of Basidiomycota and Mortierellomycota in the peanut soil.
Along the RDA1 axis, the fungal communities of N0 (red), N1 (blue), and N2 (purple) were distinctly separated, while there was no significant separation between monoculture and intercropping in the maize soil (Figure 5A). The selected soil chemical properties could explain 62.9% of the total variation in fungal community composition in the maize soil. Nitrate (NO3−, Table 3, F = 8.37, p = 0.002) was the main factor influencing the fungal community composition in maize soil, with an explanatory power of 34.3%.
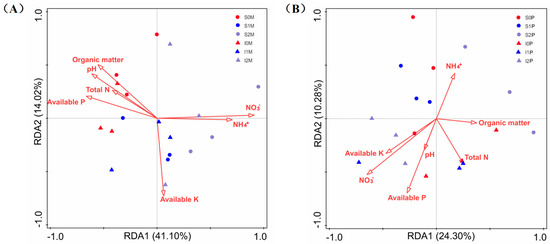
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of fungal community in maize (A) and peanut (B) soils.

Table 3.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of fungal community.
Monoculture and intercropping were distinctly separated along the RDA2 axis, while there was no significant separation among N0, N1, and N2 in the peanut soil (Figure 5B). The soil chemical properties’ total explanation for the variation in fungal community composition in peanut soil was 46.1%. Nitrate (NO3−, Table 3, F = 2.75, p = 0.032) was the main factor influencing the fungal community composition in peanut soil, with an explanatory power of 14.7%.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Maize/Peanut Intercropping and Nitrogen Application on Soil Chemical Properties
Our study indicates that N fertilization significantly increased the nitrate content in maize soil while decreasing the available phosphorus content. However, maize/peanut intercropping can mitigate this change induced by N fertilization. However, contrary to maize soil, the nitrate N content in peanut soil was not influenced by N fertilization, but maize/peanut intercropping increased the nitrate N content in peanut soil. The variation in nitrate content in the soil depends on the crop’s absorption capacity and N cycling processes in the soil. Previous reports show that N fertilization can increase nitrate content in soil [22,23]. In this study, the decrease in nitrate content in maize soil under intercropping conditions may be attributed to the promotion of maize growth by intercropping, leading to increased N absorption by maize [24]. Meanwhile, the increase in nitrate content in peanut soil under intercropping conditions may be due to the higher abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and the nitrification potential in intercropped peanut soil compared with monoculture peanut soil, thus increasing the potential for ammonium oxidation to nitrate [25]. Studies have shown that cereal/legume intercropping can increase the activity of soil phosphatase [26], significantly increase the available phosphorus content in the rhizosphere soil of crops [27,28], alleviate phosphorus limitation in low-phosphorus soil [29], and improve the efficiency of phosphorus fertilizer utilization [30], which is consistent with the results of this study.
4.2. Effects of Maize/Peanut Intercropping and Nitrogen Fertilization on Soil Fungal Diversity
Soil microbial diversity plays a pivotal role in maintaining the multifunctionality and health of soil. The loss of microbial diversity can have detrimental effects on soil fertility, organic matter content, and biological control, thereby reducing soil multifunctionality [31,32]. The Ace and Chao indices quantify the richness of species in microbial communities, while the Shannon index indicates species diversity within the community. Inconsistent with our first hypothesis, low N fertilization (150 kg·hm−2) increased fungal richness (Ace and Chao indices) in maize soil, while high N fertilization (300 kg·hm−2) significantly reduced fungal richness in maize soil. However, N fertilization did not affect the Shannon index, indicating a minimal impact of N fertilization on fungal species diversity. Moderate N application was beneficial for increasing soil fungal species richness, reflected in the results presented in the Venn diagram. Similar to our findings, Liao et al. [33] found that moderate N fertilization resulted in the highest Chao index of fungi in soil, possibly due to the increased aboveground biomass and soluble organic carbon content below ground. However, in this study, intercropping reduced fungal species richness, species numbers, and unique species numbers in maize soil but significantly increased fungal species richness, diversity, species numbers, and unique species numbers in peanut soil. Additionally, no consistent environmental factors affecting fungal diversity were found. Combining with previous studies [9,34], we infer that the interaction between maize and peanut (including aboveground resource competition and belowground root interaction) is a crucial factor influencing soil fungal diversity. Maize/peanut intercropping reduced fungal community diversity in maize soil, possibly due to the proliferation of certain microorganisms and inhibition of the growth of others [35]. In intercropping systems, the increase in fungal community richness and diversity in peanut soil indicates enhanced functional redundancy among various microbial groups, which can help mitigate the impact of fluctuations in certain microbial groups on soil ecosystem multifunctionality and maintain soil health in peanut soil [32]. This is beneficial for alleviating the problem of continuous cropping obstacles in peanut soil [36]. Therefore, from the perspective of soil fungal diversity, maize/peanut intercropping can be a valuable practice in agricultural systems to maintain the ecological function of peanut soil.
4.3. Impact of Maize/Peanut Intercropping and Nitrogen Fertilization on Soil Fungal Community Composition
Consistent with the second hypothesis, the fungal community composition was significantly different between N application levels in the maize soil. In this study, at the phylum level, five dominant fungal phyla (relative abundance > 1%) were detected in both maize and peanut soils, namely Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Mortierellomycota, unclassified_k_Fungi, and Chytridiomycota, accounting for 98.77–99.82% and 99.40–99.90% of the total fungal abundance, respectively. Studies have shown that the abundance of Ascomycota is mainly regulated by N content in soils [37]. Compared with low N fertilization, high N fertilization increased the abundance of Ascomycota [3], while excessive N fertilization, such as N application exceeding 300 kg·hm−2, inhibited the growth of this fungal phylum [22]. However, in this study, with increasing N application, the relative abundance of Ascomycota in the maize soil showed an initial decreasing trend followed by an increase, while it decreased in peanut soil. This may be due to significant differences in the responses of various microorganisms at lower taxonomic levels to N fertilization. For example, different genera within Ascomycota, such as Cenococcum, Hypocrea, and Phialophora, exhibit varying responses to N [38]. Long-term monoculture (i.e., continuous cropping) leads to imbalances in the soil microbial community structure, inhibiting the growth of beneficial bacteria and promoting colonization by pathogenic fungi [39]. In this study, compared with maize and peanut monoculture, intercropping reduced the abundance of Ascomycota in both maize and peanut soils, while the relative abundance of Mortierellomycota increased. Yuan et al. [40] showed that the relative abundance of Ascomycota was higher in soils with wilt disease, while Mortierellomycota were more abundant in healthy soils. This suggests that maize/peanut intercropping has the potential to improve soil fungal community composition and enhance soil disease resistance.
This study indicates that soil nitrate content is an important environmental factor influencing fungal community composition. Deng et al. [22] reported that soil nitrate content is a major factor influencing changes in soil fungal community structure, which is consistent with the results of this study. In intercropping systems, maize roots can extend into the peanut rhizosphere [41], absorbing nitrate from the peanut rhizosphere, thereby affecting the composition of peanut rhizosphere microorganisms, demonstrating the intercropping effect.
5. Conclusions
The impact of N fertilization and intercropping on fungal richness, species number, and diversity in soils can be substantial. Increased N fertilization initially raised fungal richness and species numbers in maize soil, followed by a subsequent decrease, while fungal diversity and richness in peanut soil tended to decrease. Intercropping significantly reduced fungal richness, total species numbers, and unique species numbers in maize soil, while it increased fungal diversity, richness, total species numbers, and unique species numbers in peanut soil. Nitrogen fertilization and intercropping significantly altered the fungal community structure in maize soil, whereas N fertilization had no significant effect on the fungal community structure in peanut soil. Intercropping, however, altered the fungal community structure in peanut soil. Nitrogen fertilization and intercropping significantly affected the species richness of fungi in maize and peanut soil. Redundancy analysis indicated that nitrate content was the primary environmental factor influencing soil fungal community composition. Our results provide valuable insights into the dynamics of fungal communities in response to N fertilization and intercropping. These results suggest that moderate N application in maize/peanut intercropping systems is conducive to fostering healthy soil for peanut cultivation, which may lead to increased yields. These findings highlight the potential benefits of employing such holistic agricultural practices to maintain soil health and enhance crop production.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy14051053/s1, Figure S1: Diagram of experimental design and soil sampling spot.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. and F.Z.; methodology, Y.Z.; software, Y.Z.; validation, F.Z., W.B. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, Z.Z.; investigation, W.B.; resources, C.F.; data curation, Q.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. and F.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.S. and L.F.; visualization, Y.Z. and F.Z.; supervision, Z.S. and L.F.; funding acquisition, Z.S. and L.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number U21A20217, 32272234), the National Key Research and Development Program (grant number 2023YFD1500901, 2022YFD1500601), the Shenyang Science and Technology Plan (grant number RC230406), the Presidential Foundation of the Liaoning Academy of Agricultural Sciences (grant number 2024YQ0401), and the Liaoning Province Science and Technology Plan (2023020443-JH1/10401).
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Martin-Guay, M.O.; Paquette, A.; Dupras, J.; Rivest, D. The new green revolution: Sustainable intensification of agriculture by intercropping. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Bao, X.G.; Sun, J.H.; Yang, S.C.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.B.; Wu, J.P.; Liu, X.R.; Tian, X.L.; et al. Long-term increased grain yield and soil fertility from intercropping. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paungfoo-Lonhienne, C.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Kasinadhuni, N.R.P.; Lonhienne, T.G.A.; Robinson, N.; Hugenholtz, P.; Ragan, M.A.; Schmidt, S. Nitrogen fertilizer dose alters fungal communities in sugarcane soil and rhizosphere. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guan, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Qin, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Shen, D.; et al. Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.N.; Sun, Y.M.; Wang, E.T.; Yang, J.S.; Yuan, H.L.; Scow, K.M. Effects of intercropping and Rhizobial inoculation on the ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in rhizospheres of maize and faba bean plants. App. Soil Ecol. 2014, 85, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Study on Nitrogen Uptake and Rhizosphere Azotobacter Diversity in Maize/Soybea Intercropping by Nitrogen Fertilizer. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Huang, G.Q.; Bian, X.M.; Jiang, X.H.; Zhao, Q.G. Effects of intercropping on quality and yield of maize grain, microorganism quantity, and enzyme activities in soils. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 7082–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, L. Intercropping enhances agroecosystem services and functioning: Current knowledge and perspectives. Chin. J. Eco-Agr. 2016, 24, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.L.; Wang, C.B.; Bao, X.G.; Wang, P.; Li, X.F.; Yang, S.C.; Ding, G.C.; Christie, P.; Li, L. Crop diversity facilitates soil aggregation in relation to soil microbial community composition driven by intercropping. Plant Soil. 2019, 436, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandra, G.; Kristin, K.; Bernd, W.; Birgit, P.; Rolf, D.; Stefan, V.; Franziska, W. The effects of cropping regimes on fungal and bacterial communities of wheat and faba bean in a greenhouse pot experiment differ between plant species and compartment. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.X.; Pan, X.H.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Xiao, Y.P.; Liu, R.G.; Wang, R.Q.; Lü, F.J. Effects of nitrogen application and cassava-peanut intercropping on cassava nutrient accumulation and system nutrient utilization. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 3275–3290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Yi, W.B.; Li, H.; Chen, L.K.; Zhao, P.; Long, G.Q. Effects of intercropping and nitrogen application on soil microbial metabolic functional diversity in a maize cropping soil. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 33, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Li, C.J.; Li, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, F.S. Effects of interspecific interactions and nitrogen fertilization rates on the agoronmic and nodulation characteristics of intercropped faba bean. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2009, 42, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, L.; Xiao, J.X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, K.X. Rhizosphere biological processes of legume//cereal intercropping systems: A review. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2016, 33, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peršoh, D. Plant associated fungal communities in the light of meta omics. Fungal Divers. 2015, 75, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Bailey, M.; Craig, H.; Girlanda, M.; Gweon, H.S.; Hallin, S.; Kaisermann, A.; Keitn, A.M.; Kretzschmar, M.; et al. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooperative Research Group on Chinese Soil Taxonomy. Chinese Soil Taxonomy; Science Press: Beijing, China; New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.L.; Luo, C.Y.; Qiu, H.Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.H.; Fu, X.; Shen, Q.R. Effects of continuous application of different nitrogen rates on fungal community structure in potato rhizosphere in semi-arid area of Gansu Province. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2020, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.H.; Xiang, X.L.; Lei, F.; Zou, Q.S.; Ai, D.L.; Zheng, T.; Huang, X.L.; Fan, G.Q. Relationship between rhizosphere fungal community and wheat yield under straw mulching combined with nitrogen fertilizer. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 8751–8761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.L.; Bao, X.G.; Song, J.L.; Sun, J.H.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.S.; Li, Q.J.; Zhou, L.L. Effect of long-term fertilizer application on yield, nitrogen uptake and soil NO3−-N accumulation in wheat/maize intercropping. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2004, 10, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yi, W.B.; Wang, D.; Wu, K.X.; Zhao, P.; Long, G.Q.; Tang, L. Effects of intercropping on soil nitrification and nitrogen supply in potato field. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.S.; Wu, L.K.; Chen, J.; Khan, M.A.; Luo, X.M.; Lin, W.X. Biochemical and microbial properties of rhizospheres under maize/peanut intercropping. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.F.; Qin, X.M.; Nong, Y.Q.; Lu, J.M.; Qin, H.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Li, J.T.; Wei, J.J. Effects of maize and soybean intercropping on inorganic phosphorus forms and available phosphorus in red soil under different phosphorus levels. Soils 2022, 54, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Xiao, J.X.; Tang, L.; Zheng, Y. Effects of wheat and faba bean intercropping on the available phosphorus contents in rhizospheric soil and phosphorus uptake by crops under different phosphorus levels. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Layati, M.; Bargaz, A.; Belarbi, B.; Lazali, M.; Benlahrech, S.; Tellah, S.; Kaci, G.; Drevon, J.; Ounane, S.M. The intercropping common bean with maize improves the rhizobial efficiency, resource use and grain yield under low phosphorus availability. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 72, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Shen, J.; Van Der Werf, W.; Zhang, F. Intercropping legumes and cereals increases phosphorus use efficiency; a meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2021, 460, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.C.; Smith, K.L. Soil microbial diversity and the sustainability of agricultural soils. Plant Soil 1995, 170, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffrie, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial eco systems. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C. Nitrogen fertilization increases fungal diversity and abundance of saprotrophs while reducing nitrogen fixation potential in a semiarid grassland. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K. Study on the Mechanism of Maize-Peanut Intercropping to Alleviate the Obstacle of Peanut Continuous Cropping. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.M.; Chen, X.M.; Liang, Y.J.; Huo, X.J.; Zhang, C.H.; Duan, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Yuan, L. Effects of crop rotation on soil nutrient, microbial activity and bacterial community structure. Acta Pratacul. Sin. 2015, 24, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.K.; Liu, P.; Zhao, H.J.; Song, X.Z.; Lin, H.T.; Shen, Y.W.; Li, L.; Wan, S.B. Effects of maize root exudates on allelopathy of phenolic acids in soil of continuous cropping peanut. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Henault, C.; Aamor, A.; Bdioui, N.; Bloor, J.M.G.; Maire, V.; Mary, B.; Revaillot, S.; Maron, P.A. Fungi mediate long term sequestration of carbon and nitrogen in soil through their priming effect. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, E.W.; Frey, S.D.; Sadowsky, J.J.; Diepen, L.T.A.V.; Pringle, A. Chronic nitrogen additions fundamentally restructure the soil fungal community in a temperate forest. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 23, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.D.; Li, X.G.; Ding, C.F.; Han, Z.M.; Wang, X.X. Microzone distribution characteristics of soil microbial community with peanut cropping system, monocropping or rotation. Soil J. 2019, 56, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wen, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.L.; Penton, C.R.; Thomashow, L.S.; Shen, Q.R. Predicting disease occurrence with high accuracy based on soil macroecological patterns of Fusarium wilt. ISME J. 2020, 14, 2936–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.L.; Sun, Z.X.; Bai, W.; Feng, L.S.; Cai, Q.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z. Spatial distribution characteristics of root system and the yield in maize-peanut intercropping system. J. Maize Sci. 2016, 24, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).