Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Soil Organic Matter Prediction Based on Combinatorial Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.1.1. Sample Collection and Measurement
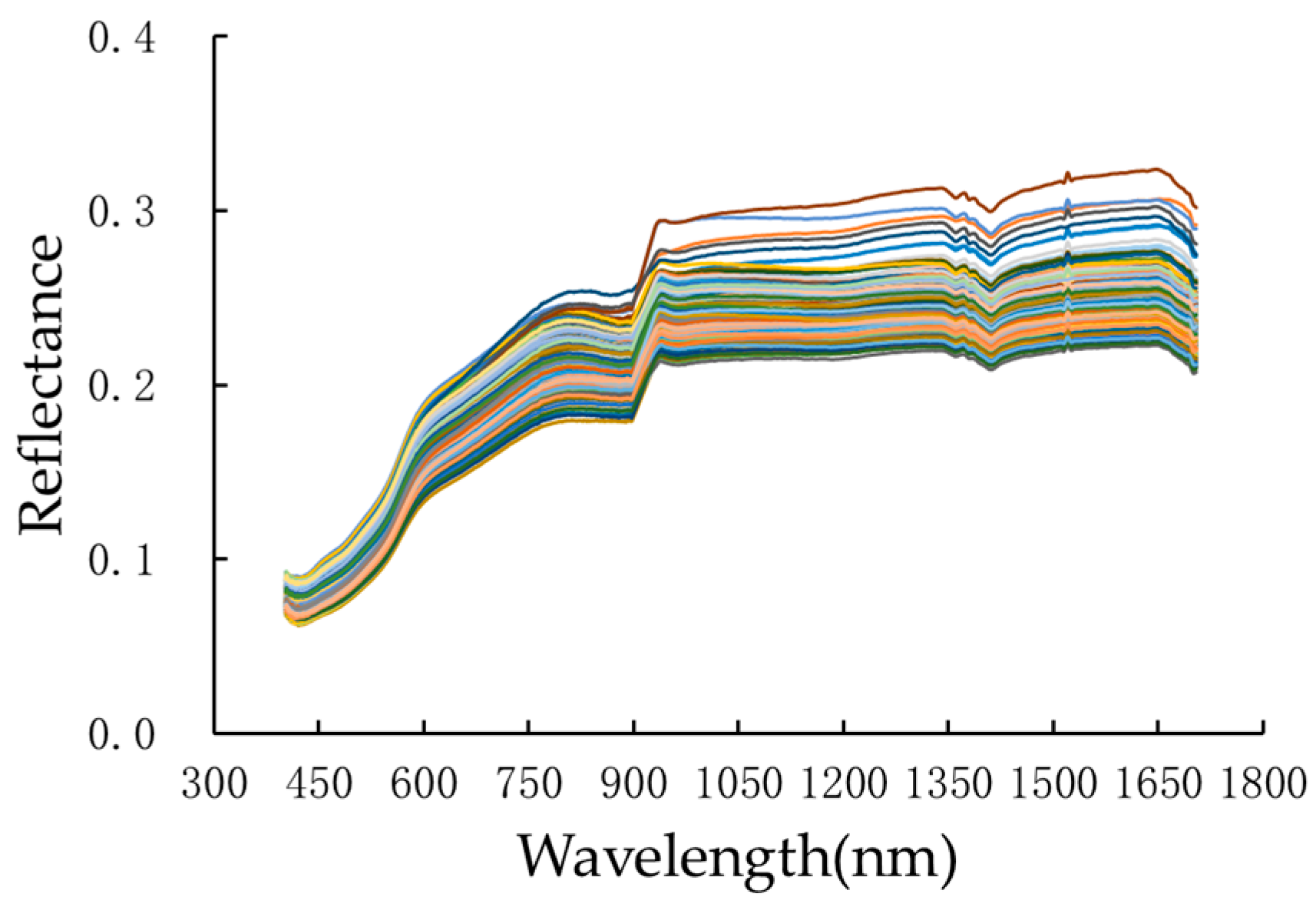
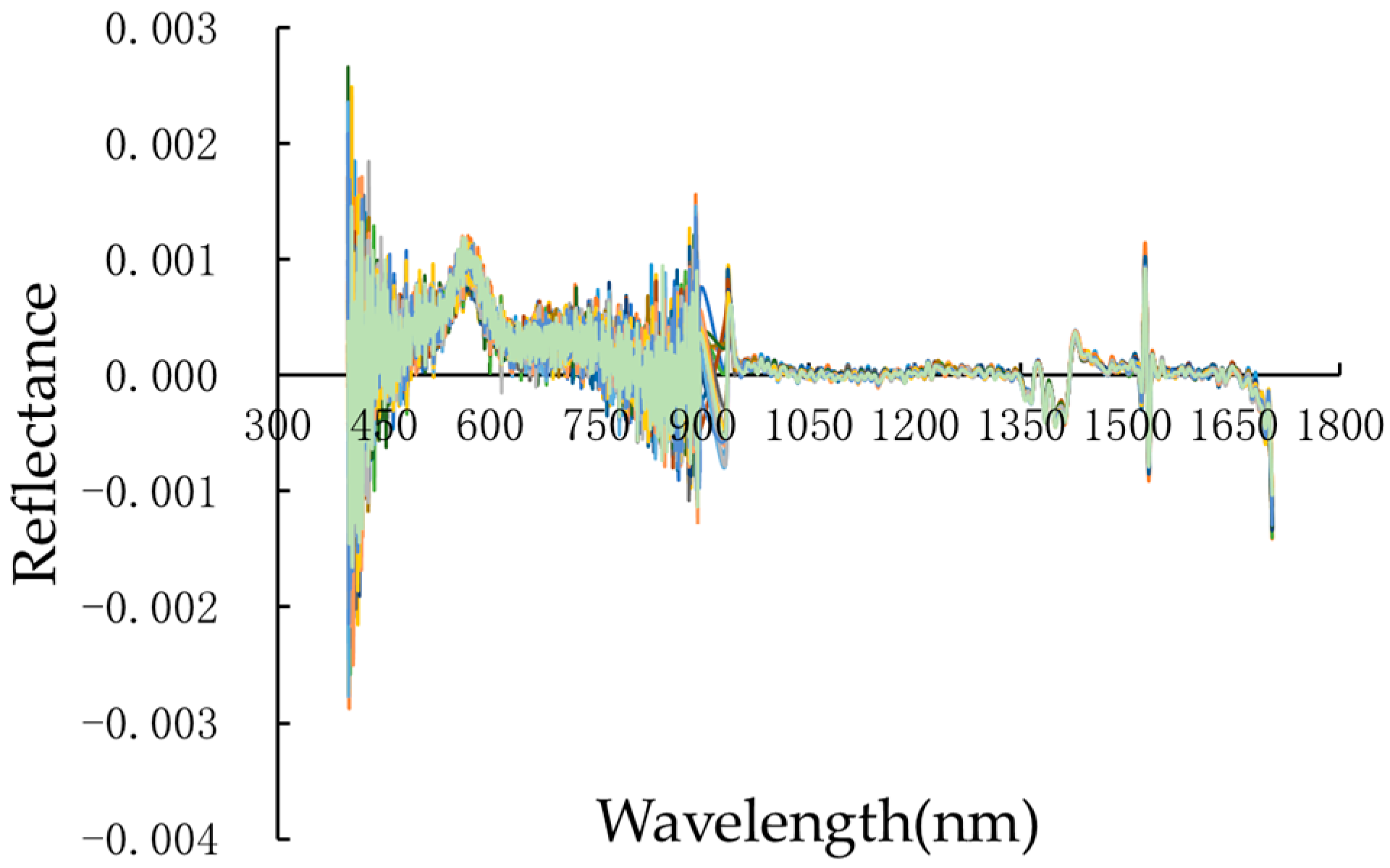
2.1.2. Hyperspectral Data Measurement and Preprocessing
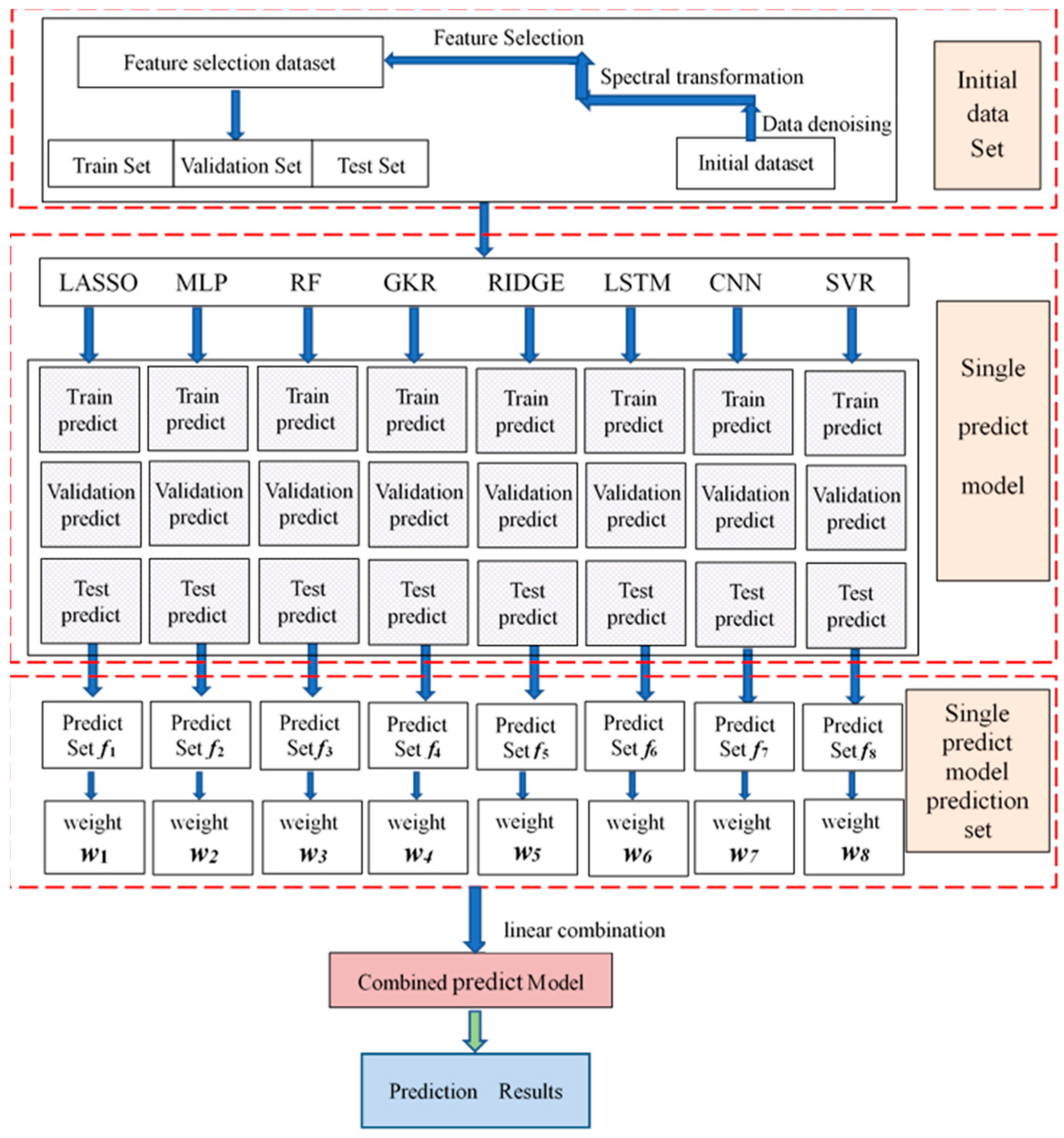
2.2. Construction of the Model
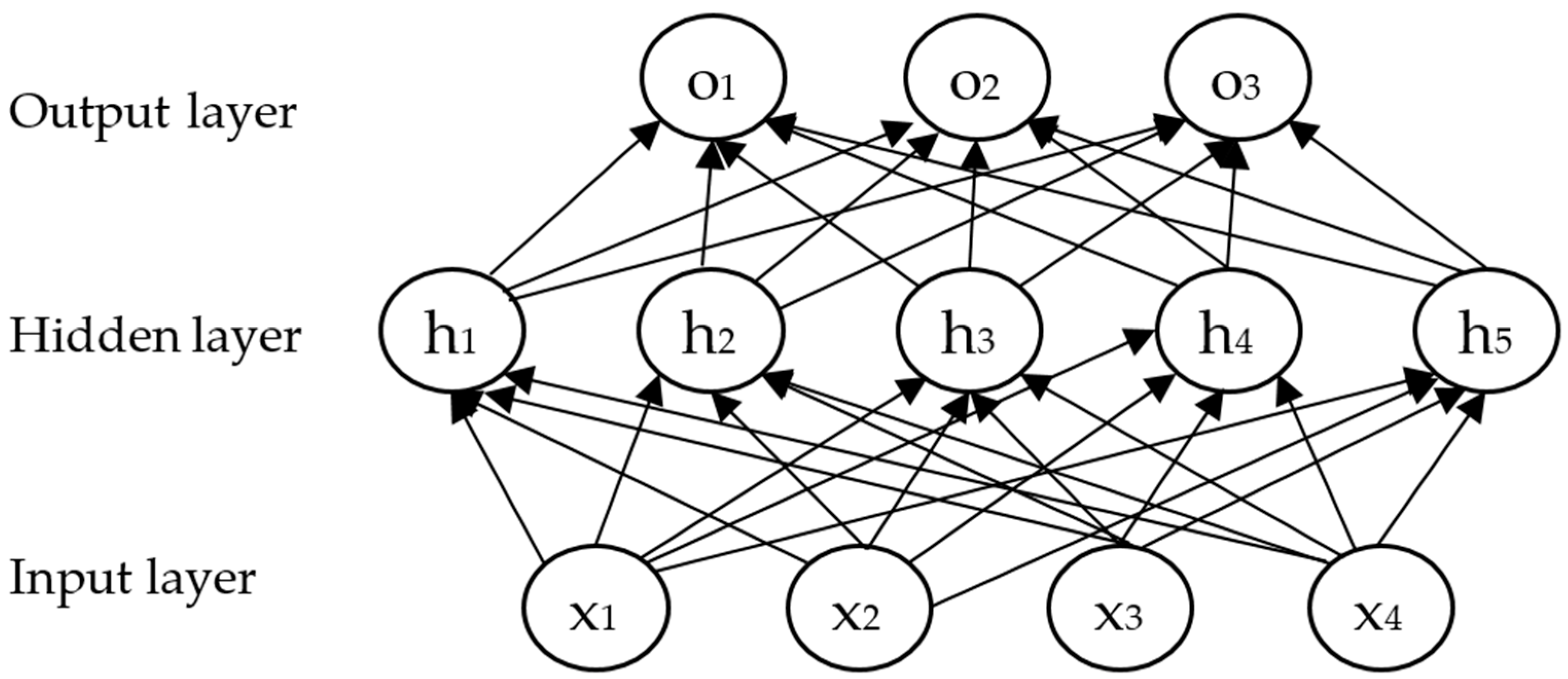
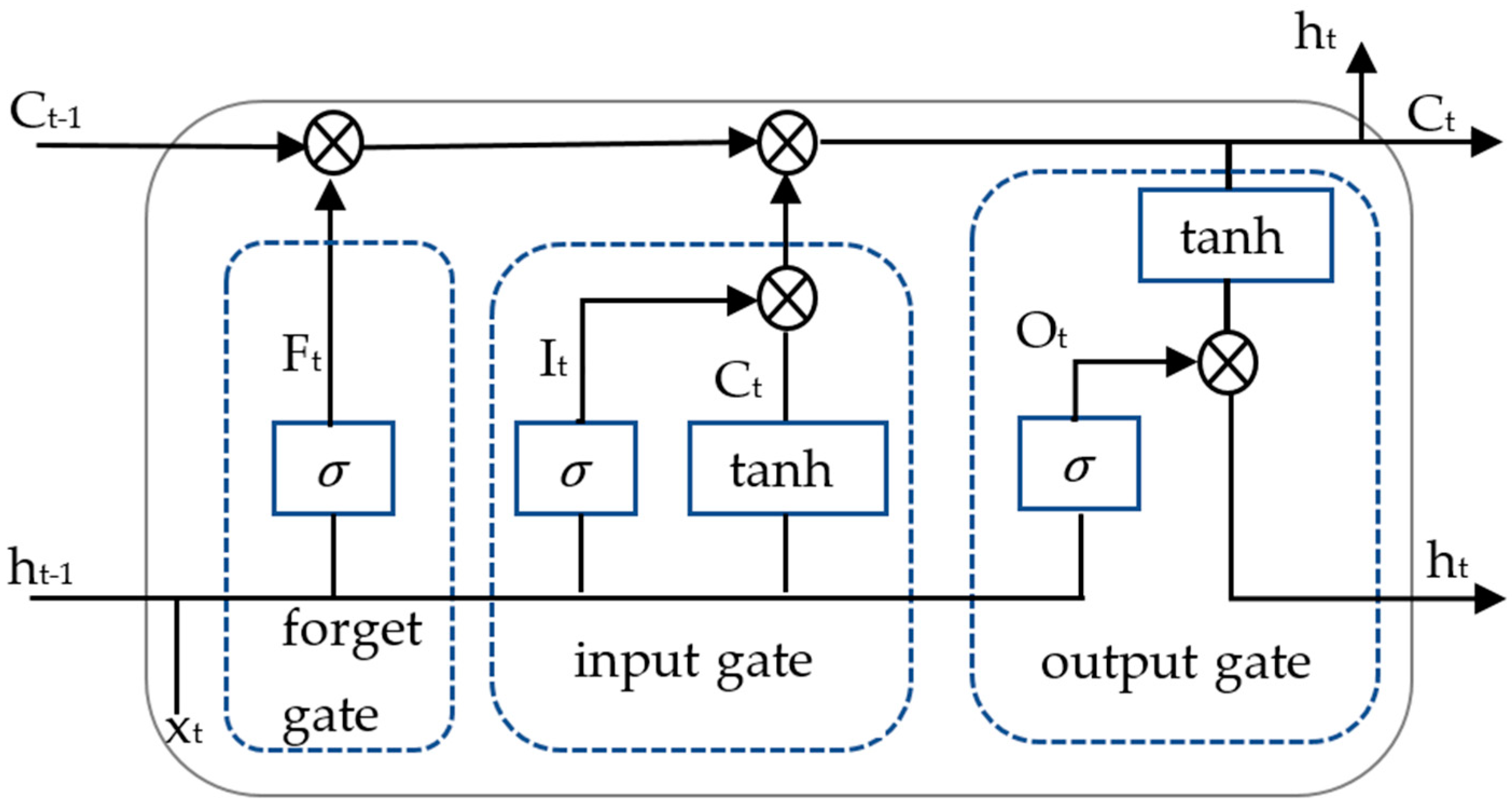
2.2.1. Single-Prediction Model Construction
2.2.2. Combinatorial Predictive Modeling
2.2.3. Calculation of Accuracy Validation Metrics
- (1)
- Calculate the combined predicted value ofwhere , , , are the weighting coefficients of m single-prediction methods and satisfy
- (2)
- Calculate the relative error and the prediction accuracy of the combination prediction for the tth sample
- (3)
- Calculate the combination-prediction validity Mwhere is the mathematical expectation of the sequence of prediction accuracy of the combination of prediction methods; is the standard deviation of the sequence of prediction accuracy of the combination of prediction methods, which is calculated using Equations (5) and (6), and and are the functions of weighting coefficients , , , of the various single-prediction methods, so that M is also a function of , , , , denoted as M(, , , ), denoted as M(, , , ), and the larger value of M indicates that the combination-prediction method is more effective. The combination-prediction model is calculated and obtained as follows:denoted as and are the minimum and maximum prediction validity of m prediction methods, respectively, and M is the prediction validity of the combination model. Then when M < , the combination-prediction model is an inferior combination prediction; when < M < , the combination-prediction model is a non-inferior combination prediction; when M > , the combination-prediction model is a superior combination prediction;
- (4)
- Approximate solution of the combined prediction model. Since the objective function is not derivable, i.e., the model is non-frivolous nonlinear programming, coupled with the fact that the computational complexity of the model is larger when n and m are larger, the non-frivolous nonlinear programming is transformed into frivolous nonlinear programming to solve the problem. The combined prediction model is equivalent to the following model (Equation (15)):where is a constant. The degree of inconsistency of the sign of the relative error of each single-prediction method in the same sample t is taken as different . The more serious the degree of inconsistency of the sign of the relative error is, the smaller the value of , and if it is completely consistent, then the value of is taken as 1. In this paper, the magnitude of is determined according to the ratio of the positive number and the negative number of the relative error in each method and takes a value of 0.9; is the correlation coefficient of the prediction accuracy sequence of the ith single-prediction method and the jth single-prediction method, and when ∈ (−1,1), the optimal solution of the combination-prediction model corresponding to the combination-prediction method is the superiority combination prediction. The optimal solution of the combination-prediction model is obtained based on the idea of a nonlinear programming solution.
2.2.4. The Planning and Solving Algorithm for the Combinatorial Predictive Modeling
3. Results
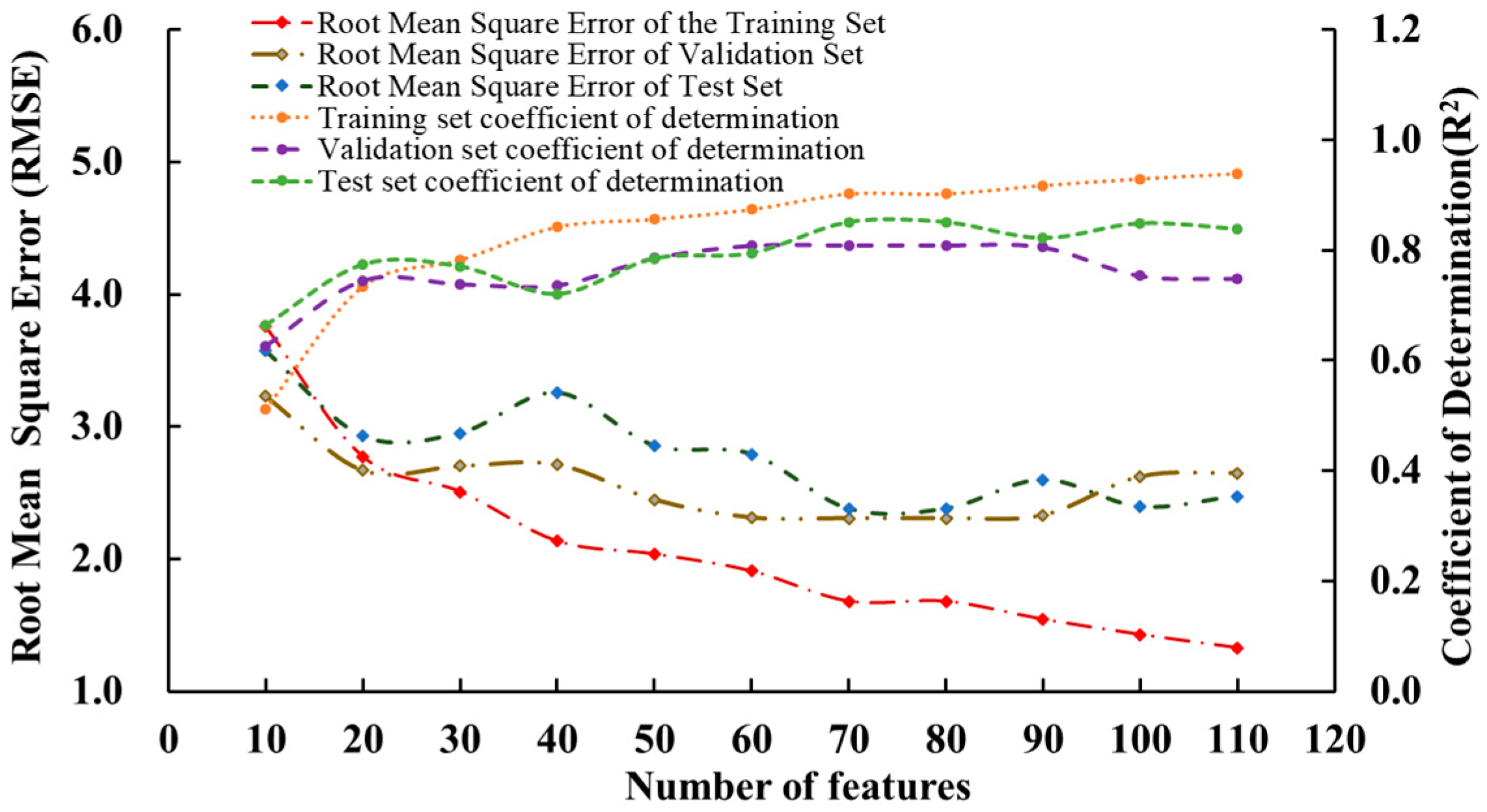
3.1. L1-Paradigm Hyperspectral Feature Selection
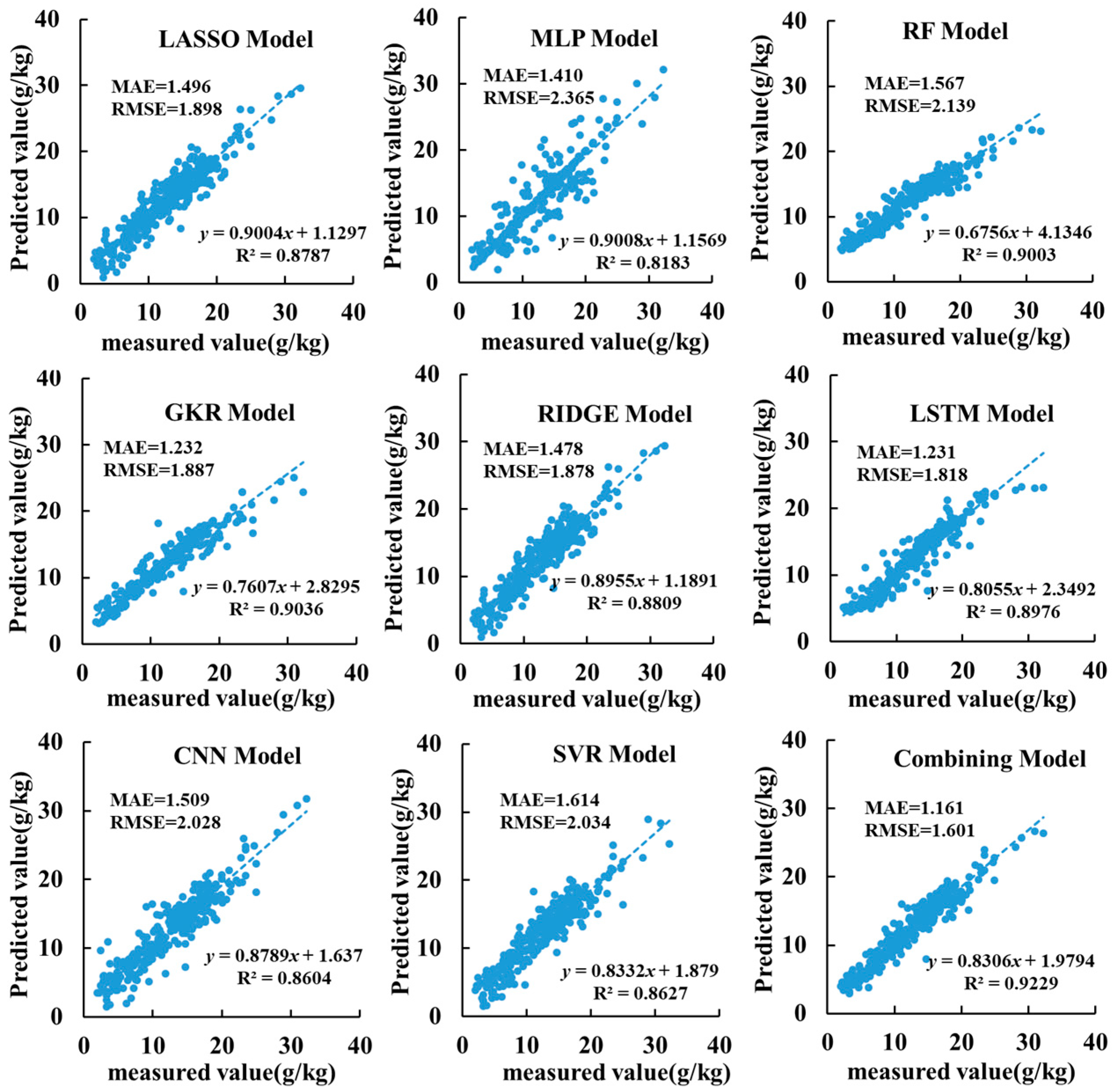
3.2. Results of Single-Prediction Model
3.3. Combined Prediction Model
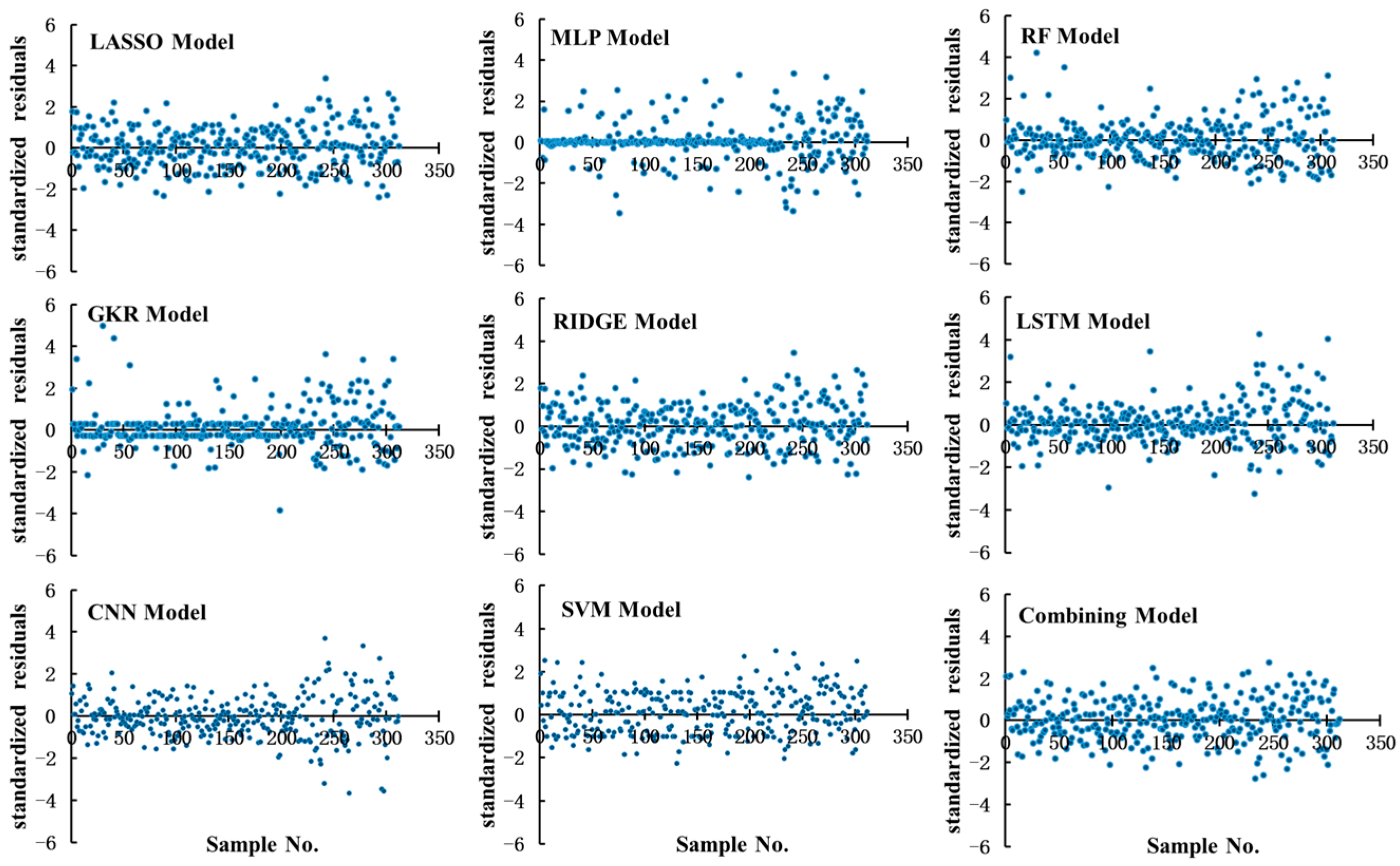
3.4. Residual Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, Y.; Wen, L.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Sun, X. Spatio-temporal Variability and Influencing Factors of Soil Organic Matter in Cultivated Land of Daxing District in Recent 40 Years. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 51, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y. Determination of soil organic matter content under forest based on different methods. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 3892–3901. [Google Scholar]
- Prathibha, S.R.; Hongal, A.; Jyothi, M.P. IOT Based Monitoring System in Smart Agriculture. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Recent Advances in Electronics and Communication Technology (ICRAECT), Bangalore, India, 16–17 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Xie, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, D.; Wang, S. Modeling for Soil Organic Matter Content Based on Hyperspectral Feature Indices. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2021, 58, 42–54. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Long, H.; He, J.; Mei, X.; Yang, G. Predicting soil organic matter contents in cultivated land using Google Earth Engine and machine learning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2022, 38, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, D.; Tan, K.; Lai, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, J. Semi-supervised DNN regression on airborne hyperspectral imagery for improved spatial soil properties prediction. Geoderma 2021, 1, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Zhen, G.; Xie, X.; Cui, X.; Shang, G. Prediction of Soil Organic Matter Using Visible-Short Near-Infrared Imaging Spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 3277–3281. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Laboratory assessment of three quantitative methods for estimating the organic matter content of soils in China based on visible/near-infrared reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2013, 202, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, L.; Yi, J.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, Y. Determination of Soil Organic Matter Content Based on Hyperspectral Wavelet Energy Features. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 3217–3222. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Bao, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X. Soil Organic Matter Prediction Model with Satellite Hyperspectral Image Based on Optimized Denoising Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lao, C.; Wang, H.; Arnon, K.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Estimation of Desert Soil Organic Matter through Hyperspectra Based on Fractional-Order Derivatives and SVMDA-RF. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, T.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Estimation of soil organic matter content in Yinchuan Plain based on fractional derivative combined with spectral indices. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 717–725. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Z.; Ji, W.; Luo, D.; Peng, J.; Feng, C. Hyperspectral Inversion of soil organic matter in Jujube Orchard in Southern Xinjiang Using CARS-BPNN. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, S.; Ding, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J. Estimation Method of VIS-NIR Spectroscopy for Soil Organic Matter Based on Sparse Networks. Laser Optoelectron. 2020, 57, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Meng, X.; Su, X.; Ma, T.; Liu, H.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Huo, H. Hyperspectral prediction on soil organic matter of different types using CARS algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, D.; Song, H.; Wang, G. VIS-NIR Hyperspectral Prediction of Soil Organic Matter Based on Stacking Generalization Model. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 909–910. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Xiao, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Yue, T. Soil organic matter content prediction using Vis-NIRS based on different wavelength optimization algorithms and inversion models. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.D.; Wang, Y.B.; Wang, R.J.; Wang, L.S.; Lu, C.P.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Song, L.T.; Liu, Y. Improvements of the Vis-NIRS Model in the Prediction of Soil Organic Matter Content Using Spectral Pretreatments, Sample Selection, and Wavelength Optimization. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 84, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shen, L.; Xie, H. Hyperspectral Estimation Model of Soil Organic Matter Content Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2021, 41, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Shang, X.; Miao, C.; Huang, C.; Lu, J. Hyperspectral estimation of soil organic matter based on particle swarm optimization neural network. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2019, 44, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Guo, D.; Li, G.; Guo, X.; Zhong, L.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, J.; Ye, Y. Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon Content in Jiangxi Province by Vis-NIR Spectroscopy Based on the CARS-BPNN Model. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 3738–3750. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Niu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Y. Anovel Hyperspectral prediction model of organic matter in red soil based on improved temporal convolutional network. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 2942–2951. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, X.; Jing, H.; Yao, X.; Yong, B.; Zhe, Y. Modeling and Prediction of Soil Organic Matter Content Based on Visible-Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Forests 2021, 12, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Ye, Y.; Sun, X.; Kuang, L. Spectrum Based Estimation of the Content of Soil Organic Matters in Mountain Red Soil Using RBF Combination Model. Sci. Silvae Sinivae 2018, 54, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Du, L.; Hong, J.; Wang, S.; Lian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Ye, L. Correlation between potassium dichromate external heating method and ASI for the determination of soil organic matter. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2020, 15, 122–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of potassium dichromate dosage on the determination of soil organic carbon by sulfur-chromium oxidation. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2011, 31, 57–58+65. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Fan, X.; Liao, Z. Dimension Reduction Model via Joint L1-trace Norms and Optimization Algorithm. J. China Railw. Soc. 2013, 35, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Luan, X.; Liu, F. Near Infrared Spectroscopic Modelling of Sodium Content in Oil Sands Based on Lasso Algorithm. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Ranstam, J.; Cook, J.A. LASSO regression. J. Br. Surg. 2018, 105, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xue, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z. Overview of deep learning. Appl. Res. Comput. 2012, 29, 2806–2810. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Z.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Meng, T.; Zhang, R.; Han, J.; Wang, N.; Xie, J. Estimation of soil organic matter content based on CARS algorithm coupled with random forest. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 258, 119823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B. Prediction model of network traffic based on combined kernel function Gaussian regression. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2015, 51, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Cao, L. Hyperspectral Inversion of Soil Organic Matter Content Based on a Combined Spectral Index Model. Sensors 2020, 20, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, X.; Ma, X. Application of Hyperspectral Technology Combined with Genetic Algorithm to Optimize Convolution Long- and Short-Memory Hybrid Neural Network Model in Soil Moisture and Organic Matter. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Han, F.; Guo, Q. Total organic carbon content prediction based on support-vector-regression machine with particle swarm optimization. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 180, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, D. Combination forecasting model based on forecasting effective measure with standard deviate. J. Syst. Eng. 2003, 18, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Mathieu, S.; Bin, F.; Tu, X. Prediction and evaluation of plasma arc reforming of naphthalene using a hybrid machine learning model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404 Pt A, 123965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, H.; Rui, Q. Research on Model Updating for Tracked Vehicle Dynamic Model Based on Generalized Reduced Gradient Method. J. Syst. Simul. 2012, 24, 774–779. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Liu, H. Black Soil Organic Matter Content Estimation Using Hybrid Selection Method Based on RF and GABPSO. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Guo, X.; Guo, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, M. Hyperspectral estimation of organic matter in red soil using different convolutional neural network models. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2021, 37, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Arnon, K.; Chen, J.; Han, W. Hyperspectral estimation of desert soil organic matter content based on gray correlation-ridge regression model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
| Organic Matter Content (g/kg) | Number of Samples | Minimum Value (g/kg) | Maximum Value (g/kg) | Mean Value (g/kg) | Standard Deviation (g/kg) | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0.000, 5.000] | 31 | 1.976 | 4.831 | 3.676 | 0.892 | 24.266 |
| (5.000, 10.000] | 67 | 5.051 | 9.882 | 7.901 | 1.335 | 16.897 |
| (10.000, 15.000] | 101 | 10.102 | 14.933 | 12.897 | 1.433 | 11.111 |
| (15.000, 20.000] | 92 | 15.153 | 19.984 | 17.068 | 1.335 | 7.822 |
| (20.000, 32.228] | 21 | 20.087 | 32.228 | 23.989 | 3.289 | 13.710 |
| (0.000, 32.228] | 312 | 1.976 | 32.228 | 12.885 | 5.441 | 42.227 |
| Model | Train Set | Validation Set | Test Set | DataSet | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | σ | M | E | σ | M | E | σ | M | E | σ | M | |
| LASSO | 0.865 | 0.155 | 0.731 | 0.836 | 0.153 | 0.708 | 0.802 | 0.220 | 0.626 | 0.853 | 0.163 | 0.714 |
| MLP | 0.908 | 0.179 | 0.746 | 0.777 | 0.201 | 0.621 | 0.773 | 0.163 | 0.647 | 0.869 | 0.192 | 0.702 |
| RF | 0.865 | 0.201 | 0.691 | 0.774 | 0.230 | 0.595 | 0.715 | 0.305 | 0.497 | 0.832 | 0.225 | 0.645 |
| GKR | 0.914 | 0.134 | 0.791 | 0.827 | 0.159 | 0.695 | 0.780 | 0.244 | 0.590 | 0.883 | 0.161 | 0.741 |
| Ridge | 0.865 | 0.155 | 0.731 | 0.839 | 0.152 | 0.712 | 0.805 | 0.218 | 0.630 | 0.854 | 0.163 | 0.715 |
| LSTM | 0.901 | 0.166 | 0.751 | 0.814 | 0.137 | 0.703 | 0.785 | 0.288 | 0.559 | 0.872 | 0.182 | 0.713 |
| CNN | 0.881 | 0.158 | 0.742 | 0.756 | 0.211 | 0.597 | 0.768 | 0.275 | 0.556 | 0.845 | 0.192 | 0.683 |
| SVR | 0.847 | 0.162 | 0.710 | 0.839 | 0.130 | 0.730 | 0.817 | 0.229 | 0.630 | 0.843 | 0.164 | 0.704 |
| Evaluating Indicator | LASSO | MLP | RF | GKR | Ridge | LSTM | CNN | SVR | Combining Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 0.853 | 0.869 | 0.832 | 0.883 | 0.854 | 0.872 | 0.845 | 0.843 | 0.893 |
| σ | 0.163 | 0.192 | 0.225 | 0.161 | 0.163 | 0.182 | 0.192 | 0.164 | 0.129 |
| M | 0.714 | 0.702 | 0.645 | 0.741 | 0.715 | 0.713 | 0.683 | 0.704 | 0.778 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, D. Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Soil Organic Matter Prediction Based on Combinatorial Modeling. Agronomy 2024, 14, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040789
Zhang X, Liu D, Ma J, Wang X, Li Z, Zheng D. Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Soil Organic Matter Prediction Based on Combinatorial Modeling. Agronomy. 2024; 14(4):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040789
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiuquan, Dequan Liu, Junwei Ma, Xiaolei Wang, Zhiwei Li, and Decong Zheng. 2024. "Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Soil Organic Matter Prediction Based on Combinatorial Modeling" Agronomy 14, no. 4: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040789
APA StyleZhang, X., Liu, D., Ma, J., Wang, X., Li, Z., & Zheng, D. (2024). Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Soil Organic Matter Prediction Based on Combinatorial Modeling. Agronomy, 14(4), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040789





