Organic Fertilizer with High Nutrient Levels Affected Peanut-Growing Soil Bacteria More Than Fungi at Low Doses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Overview and Experimental Design
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.4. Analysis of Soil Enzyme Activity
2.5. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
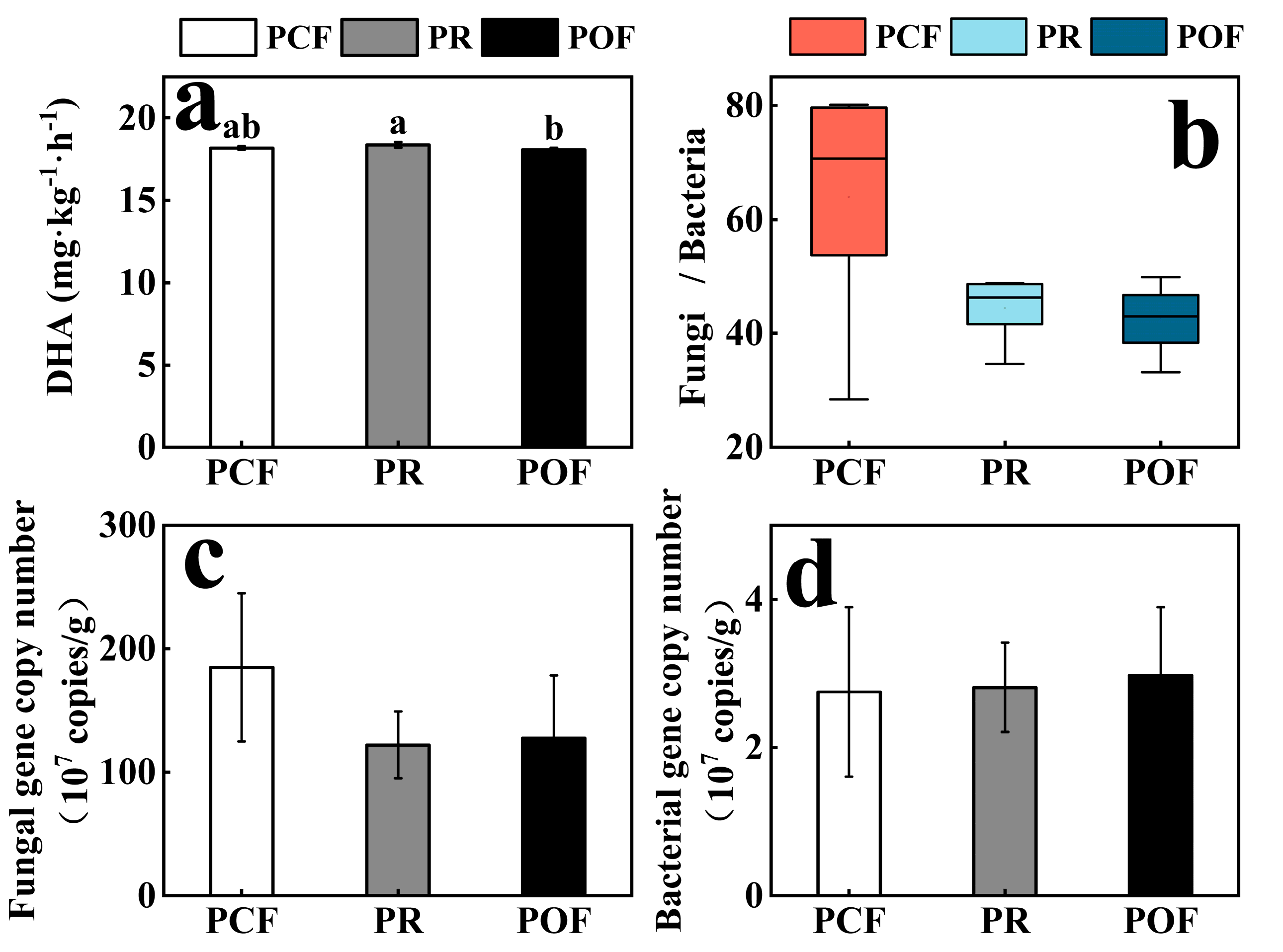
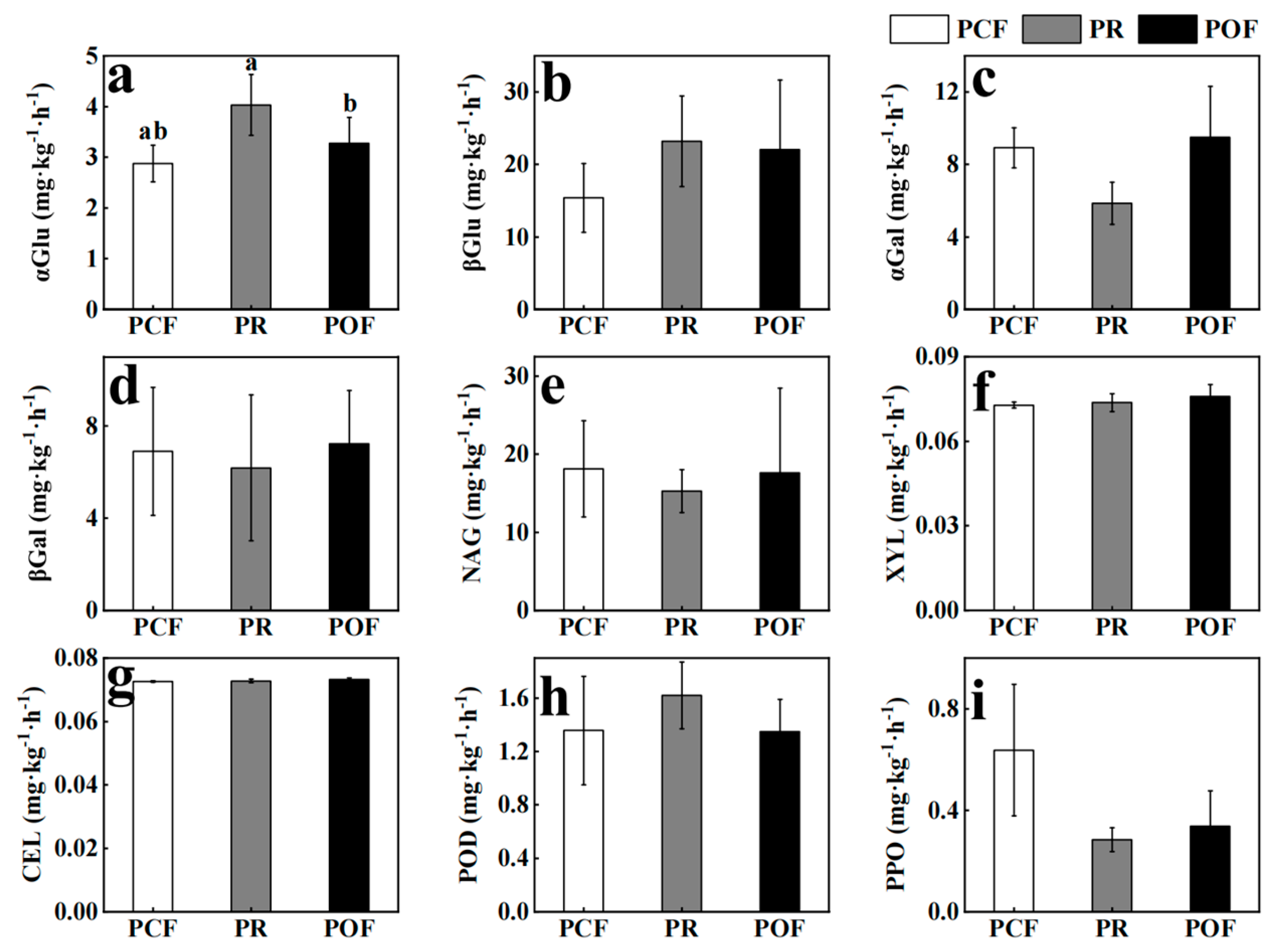
3.1. Effects of Low-Dose Organic Fertilizer on Soil Microbial Activities and Absolute Abundances
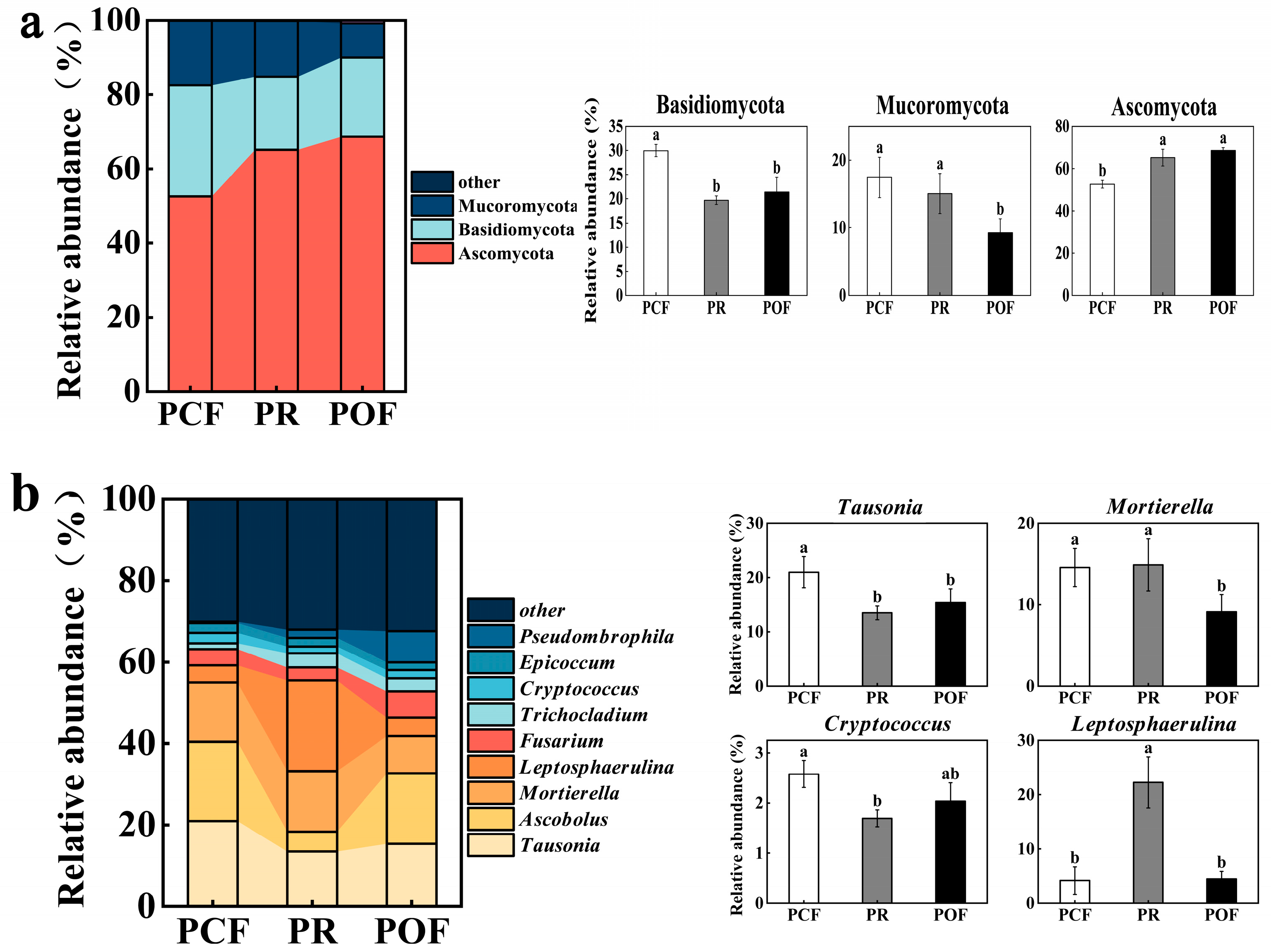
3.2. Effects of Low-Dose Organic Fertilizer on Soil Microbial Diversity and Structures
3.3. Correlation Analysis between Soil Microbial Communities, Chemical Properties, and Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Organic Fertilizer Treatment on Basic Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activities of Soil
4.2. Effect of Organic Fertilizer Treatments on Soil Microbial Community Activity, Abundance, Diversity, and Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, S.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Lin, J. Impact of virtual water export on water resource security associated with the energy and food bases in Northeast China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 180, 121635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tong, L.; Mei, L. The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Xiong, S.; Huang, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Cui, J.; et al. Rates and causes of black soil erosion in Northeast China. Catena 2022, 214, 106250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, J.; Wu, K.; Kang, L. Cultivated land use zoning based on soil function evaluation from the perspective of black soil protection. Land 2021, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Nie, R.; Du, G. Responses of Soil Collembolans to Land Degradation in a Black Soil Region in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, J. A multi-faceted, location-specific assessment of land degradation threats to peri-urban agriculture at a traditional grain base in northeastern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 111000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, M.; Shi, A.; Awais, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; Shabbir, A.; Faheem, M.; Wei, W.; Ye, L. Ultra-high temperature aerobic fermentation pretreatment composting: Parameters optimization, mechanisms and compost quality assessment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Zou, X.; Cheng, T.; Li, J. Aerobic co-composting of mature compost with cattle manure: Organic matter conversion and microbial community characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 382, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, W.; Wang, X.; Gabauer, W.; Ortner, M.; Li, Z. Tackling ammonia inhibition for efficient biogas production from chicken manure: Status and technical trends in Europe and China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; Various Issues; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Long-term effects of optimized fertilization, tillage and crop rotation on soil fertility, crop yield and economic profit on the Loess Plateau. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 143, 126731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, R.; Liu, K.; Oladele, O.; Xu, Z.; Lal, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. Management-induced changes in soil organic carbon and related crop yield dynamics in China’s cropland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 3575–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdeniz, N. A systematic review of biochar use in animal waste composting. Waste Manag. 2019, 88, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedizzi, C.; Noya, I.; Sarli, J.; González-García, S.; Lema, J.; Moreira, M.; Carballa, M. Environmental assessment of alternative treatment schemes for energy and nutrient recovery from livestock manure. Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohi, M.; Arif, M.S.; Guillaume, T.; Yasmeen, T.; Riaz, M.; Shakoor, A.; Farooq, T.; Shahzad, S.; Bragazza, L. Role of fertilization regime on soil carbon sequestration and crop yield in a maize-cowpea intercropping system on low fertility soils. Geoderma 2022, 428, 116152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of farmland scale on farmers’ application behavior with organic fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, S.; Fu, X.; Feng, S.; Zhuang, Z. A sustainable agricultural supply chain considering substituting organic manure for chemical fertilizer. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Liang, Y.; Wakelin, S.A.; Chu, G. Supplementing chemical fertilizer with an organic component increases soil biological function and quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wu, Z.; You, Z.; Yi, X.; Ni, K.; Guo, S.; Ruan, J. Effects of organic substitution for synthetic N fertilizer on soil bacterial diversity and community composition: A 10-year field trial in a tea plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Fei, J.; Luo, G. Biochar amendments combined with organic fertilizer improve maize productivity and mitigate nutrient loss by regulating the C–N–P stoichiometry of soil, microbiome, and enzymes. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zeng, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, B. Research Status on Environmental Control Technologies and Intelligent Equipment for Livestock and Poultry Production. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2019, 34, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y. Intelligent control system of integrated environmental protection equipment for livestock and poultry manure treatment. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Sustainable Technology and Management (ICSTM 2023), SPI.E., Dongguan, China, 21–23 July 2023; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mengqi, Z.; Shi, A.; Ajmal, M.; Ye, L.; Awais, M. Comprehensive review on agricultural waste utilization and high-temperature fermentation and composting. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 5445–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, X.; Fei, J.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Coupling amendment of biochar and organic fertilizers increases maize yield and phosphorus uptake by regulating soil phosphatase activity and phosphorus-acquiring microbiota. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Cai, J.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Shao, X.; Fu, C.; Li, C.; Deng, R.; Huang, J.; Ruan, Y.; et al. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer and slow-release fertilizer benefits soil microbial diversity and pineapple fruit yield in the tropics. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J. Reduced chemical fertilizer combined with bio-organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and yield and quality of lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 863325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiflu, A.; Beyene, S. Effects of different land use systems on selected soil properties in South Ethiopia. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2013, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, O.; Bolat, I. The effect of different land uses on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in Bartın province. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2008, 32, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Chen, G.; Meng, T.; Li, C.; Feng, G.; Si, B.; Siddique, K. Effect of different vegetation restoration on soil properties in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2023, 220, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punithavathi, M.; Vasanthakumar, R.; Mariappan, V.N. Studies on drought tolerant and high yielding groundnut varieties in Perambalur district. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2021, 12, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, D.; Hu, J.; Xia, G.; Pan, B. Modeling and assessing water and nitrogen use and crop growth of peanut in semi-arid areas of Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhao, J.; Li, y.; Li, X. Effects of soil tillage, management practices, and mulching film application on soil health and peanut yield in a continuous cropping system. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 570924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1983; Volume 9, pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Kuo, S., Ed.; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 869–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koralage, I.; Silva, N.; De Silva, C. The determination of available phosphorus in soil: A quick and simple method. OUSL J. 2015, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Dippold, M.A.; An, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Loeppmann, S. Extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry: The effect of soil microbial element limitation during leaf litter decomposition. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; Volume 5, pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry of microbial organic nutrient acquisition in soil and sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, L.; Whitelaw-Weckert, M.; Orchard, B. Consecutive applications of brassica green manures and seed meal enhances suppression of Meloidogyne javanica and increases yield of Vitis vinifera cv Semillon. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 47, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Crop yield, plant nutrient uptake and soil physicochemical properties under organic soil amendments and nitrogen fertilization on Nitisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Saha, S.; Mina, B.; Pande, H.; Kundu, S.; Gupta, H.S. Influence of organic amendments on growth, yield and quality of wheat and on soil properties during transition to organic production. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2008, 82, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.K.; Labanya, R.; Joshi, H.C. Influence of long-term chemical fertilizers and organic manures on soil fertility—A review. Univers. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Chetani, R. A review on the effect of organic and chemical fertilizers on plants. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol 2017, 5, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Z. Organic amendments affect phosphorus sorption characteristics in a paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 175, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M. Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, A.; Claassens, A.; Wehner, F. Effect of direct nitrogen and potassium and residual phosphorus fertilizers on soil chemical properties, microbial components and maize yield under long-term crop rotation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 35, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Káš, M.; Mühlbachová, G.; Kusá, H.; Pechová, M. Soil phosphorus and potassium availability in long-term field experiments with organic and mineral fertilization. Plant Soil Environ. 2016, 62, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, X.; Li, M. Effects of different fertilization treatments on inter-root soil nutrients and fungal communities of ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ grapes. Microbiol. Bull. 2023, 50, 4876–4893. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, K.; Kapoor, K.K.; Gupta, A.P. Impact of organic manures with and without mineral fertilizers on soil chemical and biological properties under tropical conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, C.; Fangueiro, D.; Mota, M.; Martins, M.; Braga, R.P.; Ribeiro, H. Partial replacement of chemical fertilizers with animal manures in an apple orchard: Effects on crop performance and soil fertility. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 322, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Barrow, N. Soil pH-nutrient relationships: The diagram. Plant Soil 2023, 486, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.G.; Hoeft, R.G. Managing soil pH and crop nutrients. Ill. Agron. Handb. 2009, 24, 91–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fageria, N.K.; Nascente, A.S. Management of soil acidity of South American soils for sustainable crop production. Adv. Agron. 2014, 128, 221–275. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Responses of soil bacterial communities, enzyme activities, and nutrients to agricultural-to-natural ecosystem conversion in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monreal, C.M.; Bergstrom, D. Soil enzymatic factors expressing the influence of land use, tillage system and texture on soil biochemical quality. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2000, 80, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, E. Soil biota, ecosystem services and land productivity. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Aizpurua, A.; Riga, P.; Albizu, I.; Amézaga, I.; Garbisu, C. Soil enzyme activities as biological indicators of soil health. Rev. Environ. Health 2003, 18, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utobo, E.; Tewari, L. Soil enzymes as bioindicators of soil ecosystem status. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Gurung, N.; Ray, S.; Bose, S.; Rai, V. A broader view: Microbial enzymes and their relevance in industries, medicine, and beyond. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 329121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Smith, M.; Penn, C.; Cheary, B.S.; Conaghan, K.J. Nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium applied individually or as a slow release or controlled release fertilizer increase growth and yield and affect macronutrient and micronutrient concentration and content of field-grown tomato plants. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 211, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Lin, Q.; An, J.; Xu, S.; Xie, X.; Geng, J. Combining organic fertilizer with controlled-release urea to reduce nitrogen leaching and promote wheat yields. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 802137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.; Krasnov, G.; Semenov, V.; Ksenofontova, N.; Zinyakova, N.B.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Does fresh farmyard manure introduce surviving microbes into soil or activate soil-borne microbiota? J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, T.M.; Acosta-Martínez, V.; Calderón, F.; Jackson, L.E. Soil enzyme activities, microbial communities, and carbon and nitrogen availability in organic agroecosystems across an intensively-managed agricultural landscape. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Noll, L.; Böckle, T.; Dietrich, M.; Wanek, W. Soil multifunctionality is affected by the soil environment and by microbial community composition and diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Tian, G.; Semenov, A.M.; Bruggen, A.H.C. Short-term fluctuations of sugar beet damping-off by Pythium ultimum in relation to changes in bacterial communities after organic amendments to two soils. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering fungal: Bacterial dominance in soils–methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, F.; Cadisch, G. The molecular microbial perspective of organic matter turnover and nutrient cycling in tropical agroecosystems-What do we know? Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolińska, A.; Stępniewska, Z. Dehydrogenase activity in the soil environment. Dehydrogenases 2012, 10, 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- García, C.; Hernandez, T.; Costa, F. Potential use of dehydrogenase activity as an index of microbial activity in degraded soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1997, 28, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezińska, M.; Stępniewska, Z.; Stępniewski, W. Soil oxygen status and dehydrogenase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunniyi, J.E. Effects of Clay and Organic Matter Amendments on Water and Nutrient Retention of Sandy Soils; University of Warwick: Coventry, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Hartemink, A.E. Soil and environmental issues in sandy soils. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalev, S.D.; Toor, G.S. The Composition of Soils and sediments, Green Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 339–357. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.; Yu, B.; Wang, B.; George, T.S.; Yin, H.; Li, D.; Song, A. Microbial mechanisms of the contrast residue decomposition and priming effect in soils with different organic and chemical fertilization histories. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, D.; Zhou, W.; Huang, S. Distinct responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to changes in fertilization regime and crop rotation. Geoderma 2018, 319, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, A.; Jones, C.; Jacobsen, J. Basic soil properties. Soil Water Manag. Modul. 2005, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, M.D.; Yadav, R.K.; Narjary, B.; Yadav, G.; Jat, H.S.; Sheoran, P.; Moharana, P. Municipal solid waste (MSW): Strategies to improve salt affected soil sustainability: A review. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, T.T.; Bouvier, C.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, T.; Henry-des-Tureaux, T.; Janeau, J.L.; Jouquet, P. Influence of buffalo manure, compost, vermicompost and biochar amendments on bacterial and viral communities in soil and adjacent aquatic systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 73, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Yao, Y.; Raza, W.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Application of bioorganic fertilizer significantly increased apple yields and shaped bacterial community structure in orchard soil. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, S.; Brankatschk, R.; Dümig, A.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Schloter, M.; Zeyer, J. The role of microorganisms at different stages of ecosystem development for soil formation. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3983–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, V.; Rehman, A.; Mishra, A.; Chauhan, P.S.; Nautiyal, C.S. Changes in bacterial community structure of agricultural land due to long-term organic and chemical amendments. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Bai, J.-L.; Yang, H.-T.; Zhang, W.D.; Xiong, Y.W.; Ding, P.; Qin, S. Phylogenetic diversity and investigation of plant growth-promoting traits of actinobacteria in coastal salt marsh plant rhizospheres from Jiangsu, China. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrar, A.M.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Méheust, R.; Diamond, S.; Starr, E.P.; Banfield, J.F. Bacterial secondary metabolite biosynthetic potential in soil varies with phylum, depth, and vegetation type. MBio 2020, 11, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Shah, S.T.; Ullah, I.; Ullah, L.; Mohamed, H.I. Microbial bioactive compounds produced by endophytes (bacteria and fungi) and their uses in plant health. In Plant Growth-Promoting Microbes for Sustainable Biotic and Abiotic Stress Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 285–318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Guan, D.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Qin, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.; Cao, F.; Shen, D.; et al. Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatment | N (kg·ha−1) | P2O5 (kg·ha−1) | K2O (kg·ha−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | OM | F | OM | F | OM | |
| PCF | 200 | 0 | 300 | 0 | 250 | 0 |
| PR | 100 | 106.9 | 150 | 123.9 | 125 | 68.6 |
| POF | 0 | 213.8 | 0 | 247.8 | 0 | 137.2 |
| Treatment | pH | SOC | TN | TP | TK | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | |||||||
| Soil | 6.38 | 5.00 | // | // | // | 41.06 | 51.85 | 104.55 |
| Organic Fertilizer | 8.1 | 393.0 | 47.5 | 55.1 | 30.5 | // | // | // |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zhao, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, H.; Jiang, N.; et al. Organic Fertilizer with High Nutrient Levels Affected Peanut-Growing Soil Bacteria More Than Fungi at Low Doses. Agronomy 2024, 14, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040765
Zhang X, Li P, Zhao M, Wang S, Sun B, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chen Z, Xie H, Jiang N, et al. Organic Fertilizer with High Nutrient Levels Affected Peanut-Growing Soil Bacteria More Than Fungi at Low Doses. Agronomy. 2024; 14(4):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040765
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xianying, Pengcheng Li, Mingyi Zhao, Shuqiang Wang, Baoyi Sun, Yulan Zhang, Yonghuan Wang, Zhenhua Chen, Hongtu Xie, Nan Jiang, and et al. 2024. "Organic Fertilizer with High Nutrient Levels Affected Peanut-Growing Soil Bacteria More Than Fungi at Low Doses" Agronomy 14, no. 4: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040765
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, P., Zhao, M., Wang, S., Sun, B., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, Z., Xie, H., Jiang, N., & Li, T. (2024). Organic Fertilizer with High Nutrient Levels Affected Peanut-Growing Soil Bacteria More Than Fungi at Low Doses. Agronomy, 14(4), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040765






