Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nitrogen Dynamics: Effects of Maize Straw Incorporation Under Contrasting Nitrogen Fertilization Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Acquisition and Implementation of Experiment
2.2. Gas Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Soil Sampling and Measurements
2.4. Data Management and Analysis
3. Results
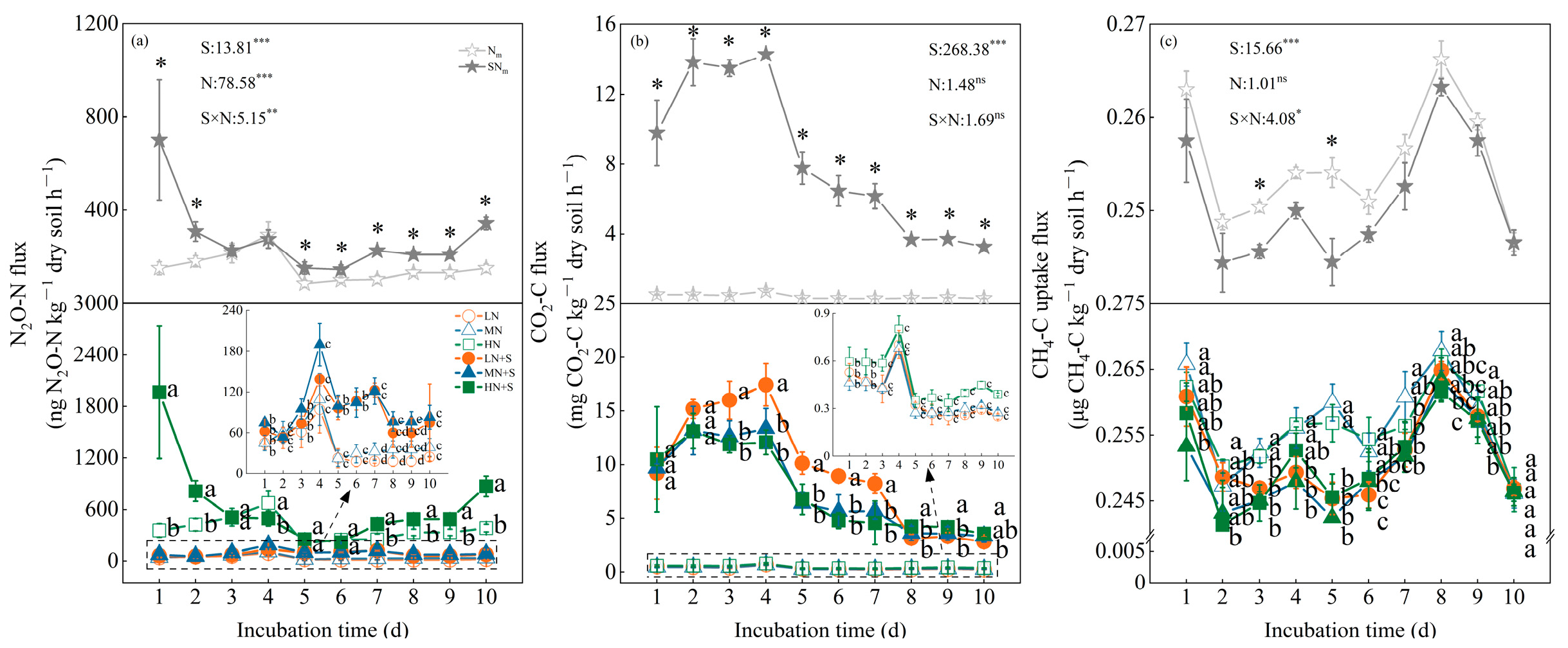
3.1. Greenhouse Gas Flux Dynamic Depends on N Fertilization and Straw Incorporation
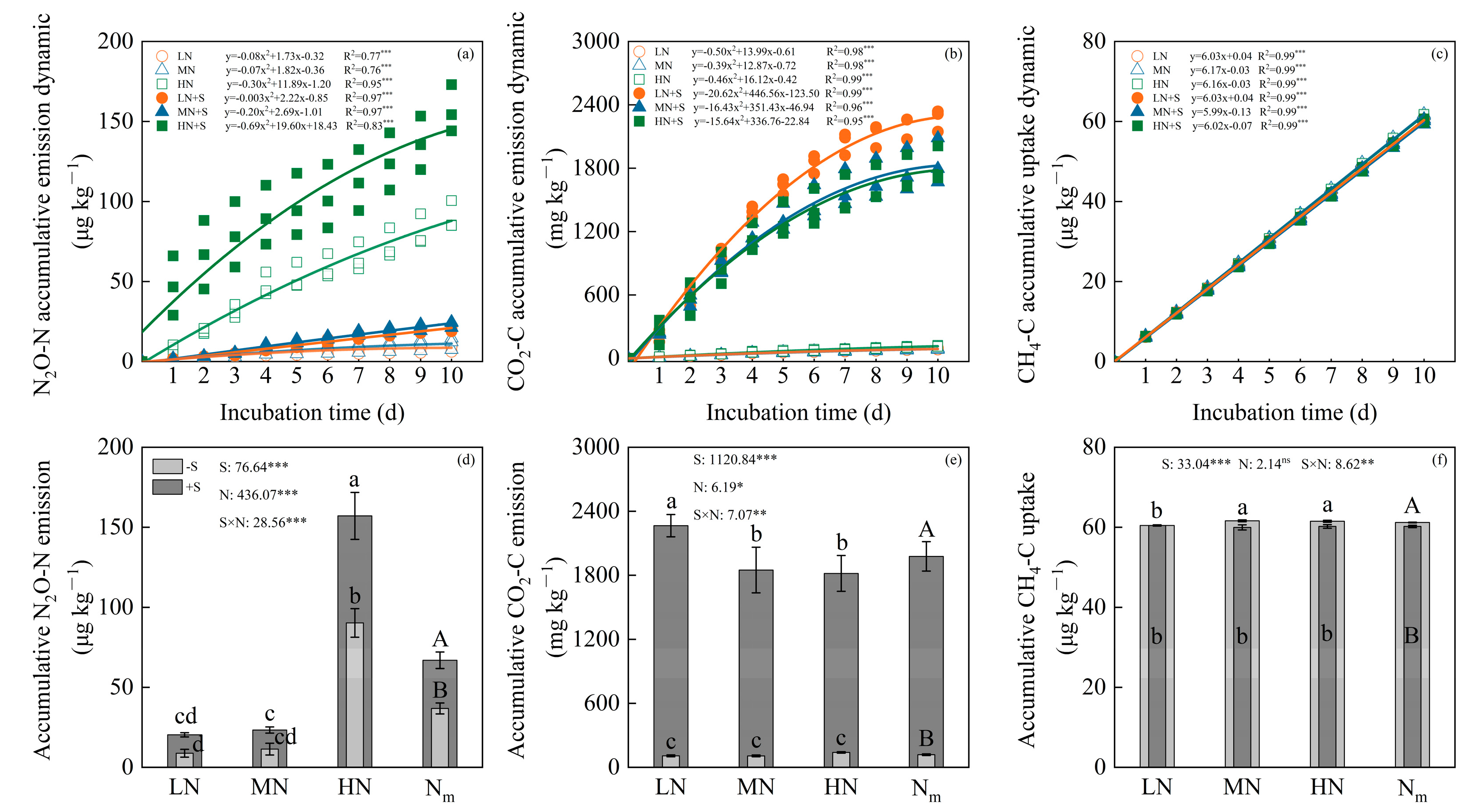
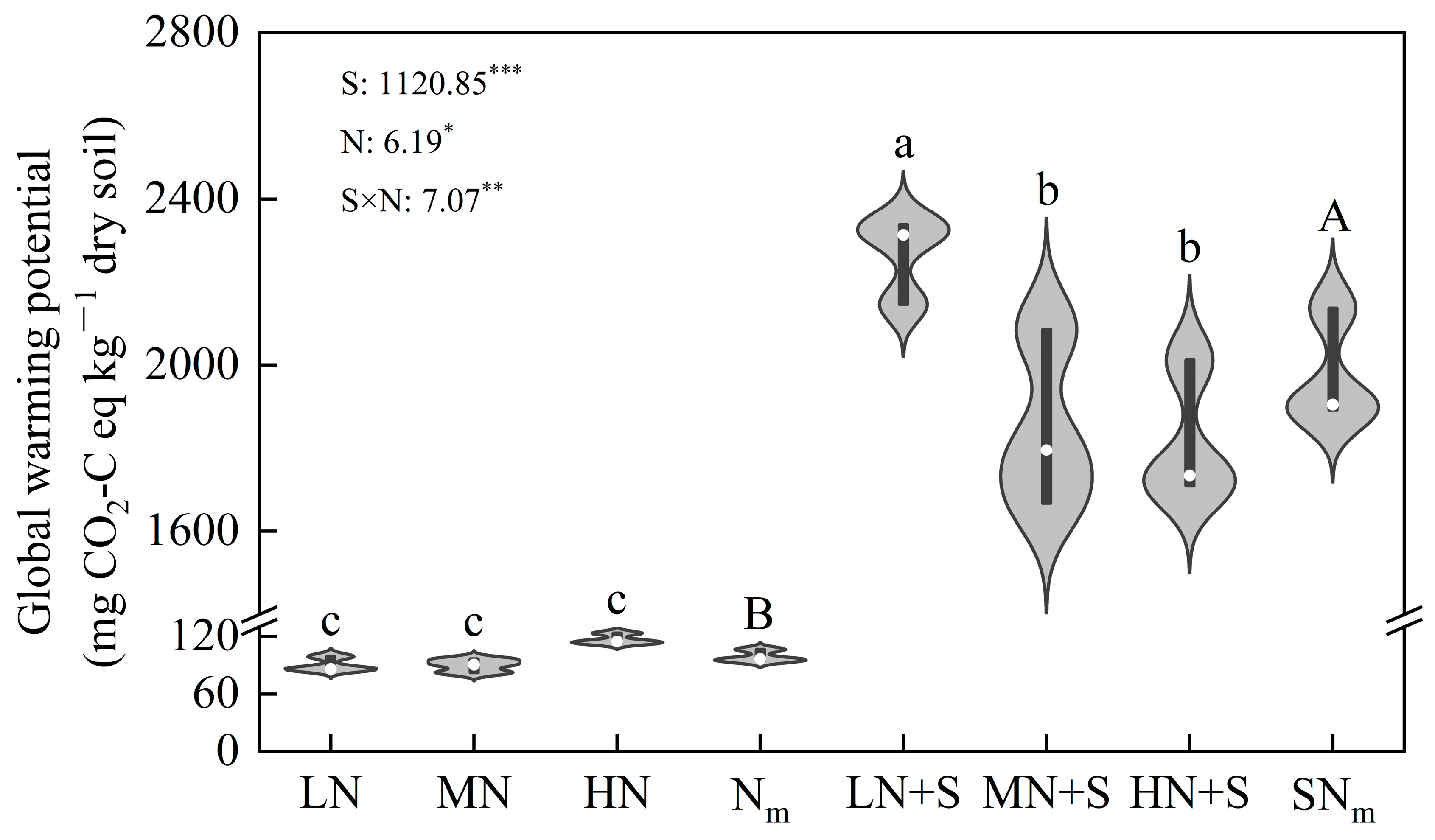
3.2. Accumulative GHGs and GWP Relied on N Fertilization and Straw Incorporation
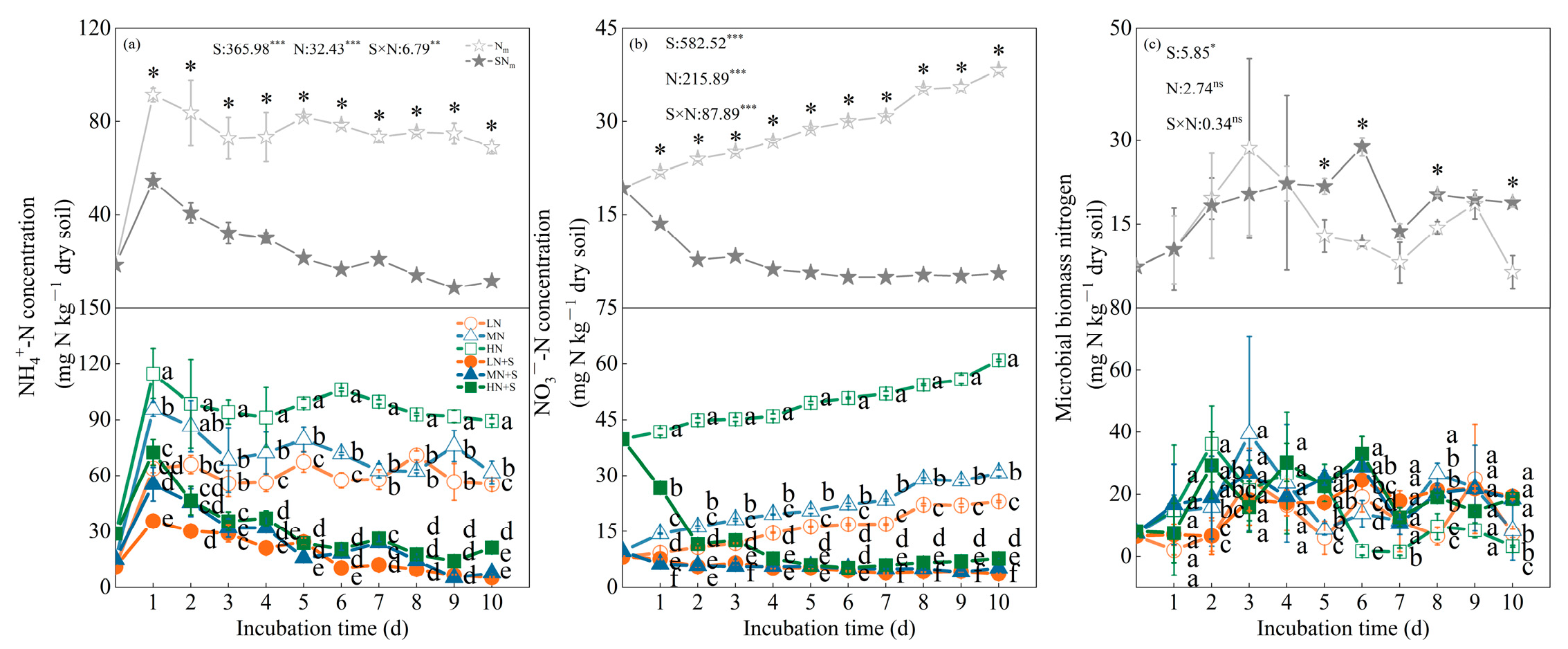
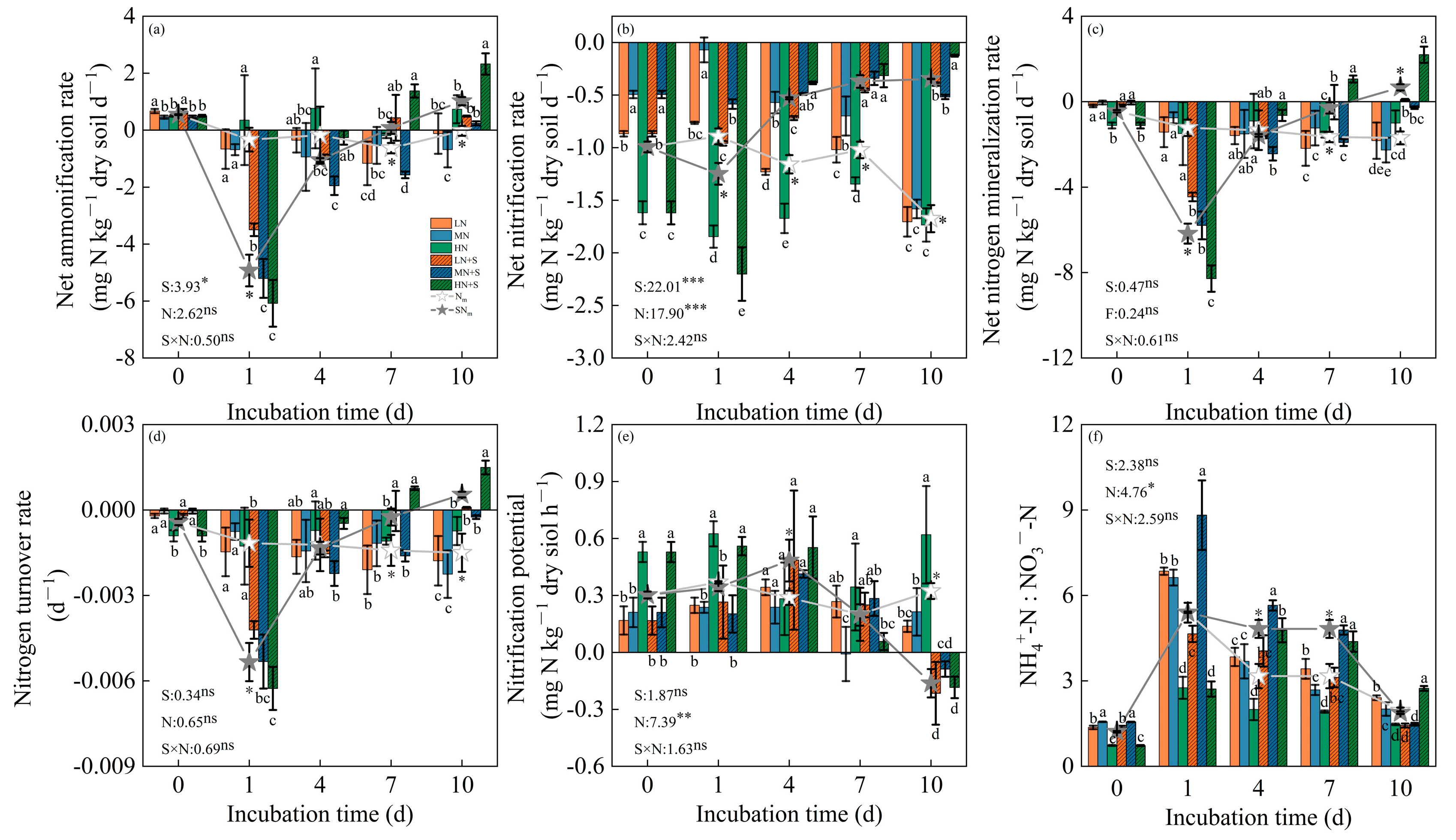
3.3. Soil Labile N Dynamic and Related N Turnover Capacity of Different N and Straw Management
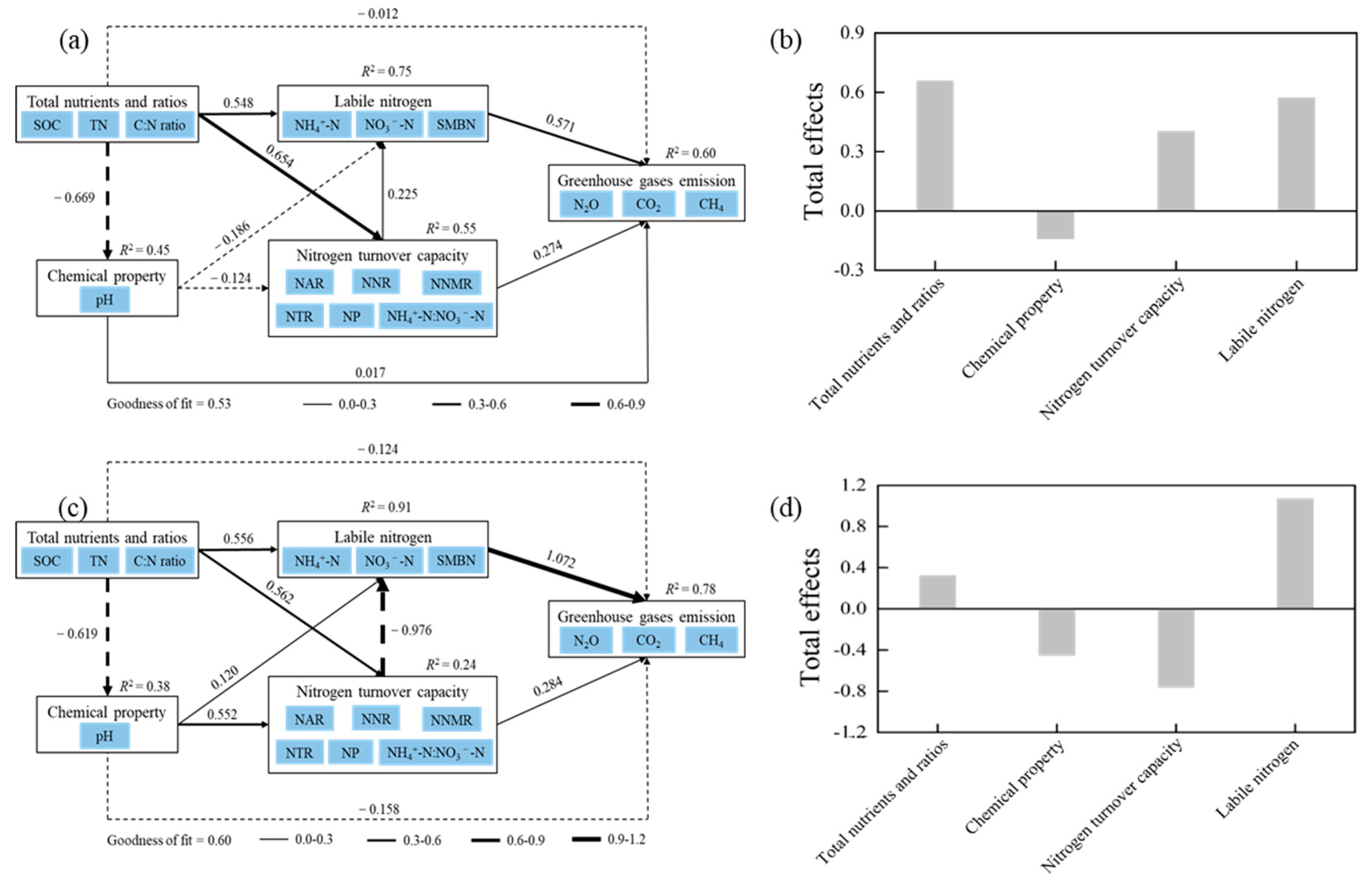
3.4. Relationships Between GHGs and Soil Properties
3.5. Soil Nitrogen and Carbon Balance in Incubation Microcosm
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Straw Amendment and N Level on Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions
4.2. Effects of Straw Incorporation and N Fertilization on Soil Labile N and N Turnover Capacity
4.3. Effects of Straw Incorporation and N Level on Soil N and C Pools Trade-Off
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. World crop residues production and implications of its use as a biofuel. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT Database 2023; Production: Crops and livestock products; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Zhuang, D.F.; Fu, J.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Wen, K.G. Bioenergy potential from crop residues in China: Availability and distribution. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2012, 16, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Guo, R.; Naseer, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.L.; Ren, X.L. Long-term straw incorporation regulates greenhouse gas emissions from biodegradable film farmland, improves ecosystem carbon budget and sustainable maize productivity. Field Crop Res. 2023, 295, 108890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Muhammad, I.; Chi, Y.X.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.B. Straw return and nitrogen fertilization regulate soil greenhouse gas emissions and global warming potential in dual maize cropping system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.W.; Khan, K.; Yang, L.; Pan, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.B. Continuous Straw Returning Combined with Nitrogen Application Improve Soil Properties and Yield of Double Cropping Maize in Subtropical Regions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Baath, E. Fungal and bacterial growth in soil with plant materials of different C/N ratios. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, N.; Guppy, C.; Herridge, D.; Schwenke, G. Influence of source and quality of plant residues on emissions of N2O and CO2 from a fertile, acidic Black Vertisol. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Q.; Liu, E.K.; Tian, Q.Z.; Yan, C.R.; Zhang, Y.Q. Soil nitrogen dynamics and crop residues. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Liu, T.; Peng, Q.A.; Shaaban, M.; Hu, R.G. Effect of straw returning in winter fallow in Chinese rice fields on greenhouse gas emissions: Evidence from an incubation study. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C.M. Effects of straw carbon input on carbon dynamics in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.J.; Wang, B.J.; Gu, Z.H.; Tao, B.R.; Zhang, Z.W.; Hu, S.J.; Zhu, L.Q.; Meng, Y.L. Effects of different straw returning modes on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yields in a rice-wheat rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 223, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Wei, Z.J.; Well, R.; Shan, J.; Yan, X.Y.; Bol, R.; Senbayram, M. Straw amendment with nitrate-N decreased N2O/(N2O+N2) ratio but increased soil N2O emission: A case study of direct soil-born N2 measurements. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.C.; Xu, G.X.; Luo, M.; Xu, C.; Ci, E.; Gao, M. Variation in N2O emission and N2O related microbial functional genes in straw- and biochar-amended and non-amended soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 137, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Yu, J.G.; Zhao, Y.H.; Chang, Z.Z.; Shi, X.X.; Ma, L.Q.; Li, H.B. Straw enhanced CO2 and CH4 but decreased N2O emissions from flooded paddy soils: Changes in microbial community compositions. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 174, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hang, X.N.; Lamine, S.M.; Jiang, Y.; Afreh, D.; Qian, H.Y.; Feng, X.M.; Zheng, C.Y.; Deng, A.X.; Song, Z.W.; et al. Interactive effects of straw incorporation and tillage on crop yield and greenhouse gas emissions in double rice cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 250, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: How well do we understand the processes and their controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, D.M.; Dolfing, J.; Wrage, N.; Van Groenigen, J.W. Nitrifier denitrification as a distinct and significant source of nitrous oxide from soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, W.G.; Yue, S.C.; Li, S.Q.; Huang, H.Z.; Shen, Y.F. Characteristics of N2O production and transport within soil profiles subjected to different nitrogen application rates in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, I.A.; Dieleman, W.; Luyssaert, S.; Subke, J.A.; Reichstein, M.; Ceulemans, R.; Ciais, P.; Dolman, A.J.; Grace, J.; Matteucci, G.; et al. Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.R.; Senbayram, M.; Blagodatsky, S.; Myachina, O.; Dittert, K.; Lin, X.G.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil C and N availability determine the priming effect: Microbial N mining and stoichiometric decomposition theories. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.Q.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Datta, A.; Pan, T.; Zeng, C.S.; Bartrons, M.; Peñuelas, J. Rice straw incorporation affects global warming potential differently in early vs. late cropping seasons in Southeastern China. Field Crop Res. 2015, 181, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.; Kong, F.X.; Lv, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.G.; Meng, Y.L. Responses of greenhouse gas emissions to different straw management methods with the same amount of carbon input in cotton field. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, Y.M.; Tong, Y.A.; Gao, P.C.; Ju, X.T. Coupled effects of straw and nitrogen management on N2O and CH4 emissions of rainfed agriculture in Northwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 157, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, L.; Billen, G.; Grizzetti, B.; Anglade, J.; Garnier, J. 50 year trends in nitrogen use efficiency of world cropping systems: The relationship between yield and nitrogen input to cropland. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Batjes, N.H. Emissions of N2O and NO from fertilized fields: Summary of available measurement data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, M.J.; Hsu, J. Coupling of nitrous oxide and methane by global atmospheric chemistry. Science 2010, 330, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Meng, Y.; Chen, G.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.H. Impact of maize growth on N2O emission from farmland soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, S.L.; Parihar, C.M.; Dey, A.; Nayak, H.S.; Ghosh, A.; Pariha, N.; Goswami, A.K.; Singh, A.K. Dynamics and temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon mineralization under medium-term conservation agriculture as affected by residue and nitrogen management options. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Sui, P.X.; Lian, H.L.; Li, Y.N.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, H.R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xu, Y.Y.; Gong, X.W.; Qi, H.; et al. Tillage with straw incorporation reduces the optimal nitrogen rate for maize production by affecting crop uptake, utility efficiency, and the soil balance of nitrogen. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 2825–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.R.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.Y.; Jiang, Y. Variations in soil bacterial taxonomic profiles and putative functions in response to straw incorporation combined with N fertilization during the maize growing season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 283, 106578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.H.; Cai, Y.J.; Chen, Z.M.; Luo, J.F.; Di, H.J.; Yu, H.Y.; Zhu, A.N.; Ding, W.X. No-tillage did not increase organic carbon storage but stimulated N2O emissions in an intensively cultivated sandy loam soil: A negative climate effect. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliher, F.M.; Sherlock, R.; Clough, T.J.; Premaratne, M.; Laughlin, R.J.; McGeough, K.L.; Harvey, M.J.; McMillan, A.M.S.; Reid, A.; Saggar, S. Air sample collection, storage and analysis. In Nitrous Oxide Chamber Methodology Guidelines, 1st ed.; de Klein, C.A.M., Harvey, M.J., Eds.; Ministry for Primary Industries: Wellington, New Zealand, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 56–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Che, Y.Y.; Zhang, F.G.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.H. Effects of biochar, N fertilizer, and crop residues on greenhouse gas emissions from acidic soils. Clean-Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Liang, C.; He, H.B.; Zhang, X.D. Variations in Soil Microbial Communities and Residues Along an Altitude Gradient on the Northern Slope of Changbai Mountain, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.C.; Stark, J.M.; Daridson, E.A.; Firestone, M.K. Nitrogen mineralization, immobilization, and nitrification. In Method of Soil Analysis, 1st ed.; Weaver, R.W., Angle, J.S., Bottomley, P.S., Eds.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; Volume 2, pp. 985–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Zeng, Z.Q.; Tian, D.S.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, B.X.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Quan, Q.; Chen, W.N.; Yang, J.L.; Meng, C.; et al. Global variations and controlling factors of soil nitrogen turnover rate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobke, S.; Senbayram, M.; Pfeiffer, B.; Nacke, H.; Dittert, K. Post-harvest N2O and CO2 emissions related to plant residue incorporation of oilseed rape and barley straw depend on soil NO3− content. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.C.; Qiu, S.J.; Xu, X.P.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Zhang, S.Q.; He, P. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Reichel, R.; Xu, Z.F.; Vereecken, H.; Bruggemann, N. Return of crop residues to arable land stimulates N2O emission but mitigates NO3− leaching: A meta–analysis. Agron. Sutain Dev. 2021, 41, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groenigen, J.W.; Huygens, D.; Boeckx, P.; Kuyper, T.W.; Lubbers, I.M.; Rutting, T.; Groffman, P.M. The soil N cycle: New insights and key challenges. Soil 2015, 1, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, C.; Clough, T.J.; Grace, P.R.; Rowlings, D.W.; Scheer, C. Soil type, bulk density and drainage effects on relative gas diffusivity and N2O emissions. Soil Res. 2020, 58, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Senbayram, M.; Well, R.; Bruggemann, N.; Pfeiffer, B.; Loick, N.; Stempfhuber, B.; Dittert, K.; Bol, R. Nitrification inhibitors mitigate N2O emissions more effectively under straw-induced conditions favoring denitrification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, R.; Wei, J.; Islam, M.S.; Schmid, C.; Wissel, H.; Schröder, P.; Schloter, M.; Brüggemann, N. Potential of wheat straw, spruce sawdust, and lignin as high organic carbon soil amendments to improve agricultural nitrogen retention capacity: An incubation study. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendecke, J.W.; Axelson, R.D.; Pepper, I.L. Soil microbial activity as an indicator of soil fertility: Long-term effects of municipal sewage sludge on an arid soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.D.; Fan, P.; Xi, B.D.; Tan, W.B. Effects of microplastics on soil organic carbon and greenhouse gas emissions in the context of straw incorporation: A comparison with different types of soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Friedel, J.K.; Stahr, K. Review of mechanisms and quantification of priming effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatsky, S.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Yuyukina, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Model of apparent and real priming effects: Linking microbial activity with soil organic matter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhao, X.L.; Lu, D.J.; Zhou, J.M.; Li, C.Z. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Barot, S. Size and functional diversity of microbe populations control plant persistence and long-term soil carbon accumulation. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, G.Q.; Xu, W.H.; Boutton, T.W.; Zhuge, Y.P.; Bai, E. Effects of nitrogen addition on soil organic carbon mineralization after maize stalk addition. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 89, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wu, L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Khalid, M.S.; Younas, A.; Lin, S.; Zhao, J.; Bashir, S.; et al. The interactive effects of dolomite application and straw incorporation on soil N2O emissions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, R.L.; Li, Q.X.; Yang, Z.L. Effects of straw application on nitrate leaching in fields in the Yellow River irrigation zone of Ningxia, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollmann, A.; Conrad, R. Influence of O2 availability on NO and N2O release by nitrification and denitrification in soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1998, 4, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Liu, R.; Ju, X.T. Effect of carbon rate and type amended with ammonium or nitrate on nitrous oxide emissions in a strong ammonia oxidation soil. J. Soil Sediment. 2020, 20, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.B.; Meng, T.Z.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhong, W.H.; Mueller, C.; Cai, Z.C. Fungi-dominant heterotrophic nitrification in a subtropical forest soil of China. J. Soil Sediments 2015, 15, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cai, Z.C.; Chang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.B. Wheat straw and its biochar have contrasting effects on inorganic N retention and N2O production in a cultivated Black Chernozem. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, K.L.; McCartney, D.M. Effect of C:N ratio on microbial activity and N retention: Bench-scale study using pulp and paper biosolids. Compost. Sci. Util. 2000, 8, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.S.; Ren, L.X.; Li, Z.P.; Zhang, T.L.; Inubushi, K. Effect of rice residues on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions from a paddy soil of subtropical China. Water Air Soil Poll. 2006, 178, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Yang, B.; Dai, Y.J.; Xu, M.M.; Koide, R.T.; Wang, X.H.; Liu, J.; Bian, X.M. Soil nitrogen retention is increased by ditch-buried straw return in a rice-wheat rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 69, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Tian, H.Q.; Hui, D.F. Convergence in the relationship of CO2 and N2O exchanges between soil and atmosphere within terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.F.; Cheng, G.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, M.; Feng, H.; Dyck, M.; Sun, B.H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.X.; Chen, J.; et al. Contrasting effects of straw and straw-derived biochar application on net global warming potential in the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crop Res. 2017, 205, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Applied Substance | SOC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | C:N | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | NH4+-N: NO3−-N | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straw | 420.8 | 11.6 | 36.4 | 264.0 | 692.0 | 0.4 | - | |
| Soil | LN | 9.3 b | 0.9b | 9.9 a | 11.3 c | 8.3 c | 1.4 b | 5.8 a |
| MN | 10.6 b | 1.0b | 10.2 a | 15.1 b | 9.7 b | 1.6 a | 5.4 a | |
| HN | 15.5 a | 1.2a | 12.7 a | 28.9 a | 39.7 a | 0.7c | 5.0 a | |
| Treatment | Initial | Input | Ideal TN (mg) | Δ NH4+-N (mg) | Δ NO3−-N (mg) | Δ Mineral-N (mg) | N2O-N (μg) | Balance (μg) | R1 (‱) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN (mg) | NH4+-N (mg) | NO3−-N (mg) | NH4+-N (mg) | Straw-N (mg) | |||||||||
| −S | LN | 28.30 b | 0.34 c | 0.25 c | 1.50 | – | 29.80 d | 1.32 b | 0.44 b | 1.77 c | 0.27 d | 1499.73 b | 0.09 c |
| MN | 31.20 b | 0.45 b | 0.29 b | 1.50 | – | 32.70 cd | 1.40 b | 0.63 a | 2.03 b | 0.34 cd | 1499.66 b | 0.10 c | |
| HN | 37.30 a | 0.87 a | 1.19 a | 1.50 | – | 38.80 b | 1.82 a | 0.64 a | 2.45 a | 2.71 b | 1497.29 b | 0.70 b | |
| Nm | 32.27 A | 0.55 A | 0.58 A | 1.50 | – | 33.77 B | 1.51 A | 0.57 A | 2.08 A | 1.11 B | 1498.89 B | 0.30 A | |
| +S | LN | 28.30 b | 0.34 c | 0.25 c | 1.50 | 6.95 | 36.75 bc | −0.18 c | −0.14 c | −0.31 d | 0.61 cd | 8453.39 a | 0.17 c |
| MN | 31.20 b | 0.45 b | 0.29 b | 1.50 | 6.95 | 39.65 b | −0.22 c | −0.13 c | −0.35 d | 0.70 c | 8453.30 a | 0.18 c | |
| HN | 37.30 a | 0.87 a | 1.19 a | 1.50 | 6.95 | 45.75 a | −0.23 c | −0.96 d | −1.19 e | 4.71 a | 8449.29 a | 1.04 a | |
| Nm | 32.27 A | 0.55 A | 0.58 A | 1.50 | 6.95 | 40.72 A | −0.21 B | −0.41 B | −0.62 B | 2.01 A | 8451.99 A | 0.46 A | |
| Treatment | Initial TC (g) | Input Straw-C (g) | Ideal TC (g) | CO2-C (mg) | CH4-C (μg) | Balance (mg) | R2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −S | LN | 0.28 b | - | 0.28 c | 2.71 c | 1.814 b | −2.707 c | 0.97 d |
| MN | 0.32 b | - | 0.32 c | 2.69 c | 1.849 a | −2.691 c | 0.85 d | |
| HN | 0.46 a | - | 0.46 b | 3.51 c | 1.846 a | −3.506 c | 0.77 d | |
| Nm | 0.35 A | - | 0.35 B | 2.97 B | 1.836 A | −2.968 B | 0.86 B | |
| +S | LN | 0.28 b | 0.25 | 0.53 b | 67.97 a | 1.814 b | 184.51 b | 12.79 a |
| MN | 0.32 b | 0.25 | 0.57 b | 55.49 b | 1.799 b | 196.99 a | 9.74 b | |
| HN | 0.46 a | 0.25 | 0.71 a | 54.55 b | 1.807 b | 197.93 a | 7.63 c | |
| Nm | 0.35 A | 0.25 | 0.60 A | 59.34 A | 1.807 B | 193.14 A | 10.05 A | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Shang, J.; Wang, X.; Ye, R.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gong, X.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nitrogen Dynamics: Effects of Maize Straw Incorporation Under Contrasting Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122996
Wang Z, Shang J, Wang X, Ye R, Zhao D, Li X, Yang Y, Zhang H, Gong X, Jiang Y, et al. Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nitrogen Dynamics: Effects of Maize Straw Incorporation Under Contrasting Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122996
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhengyu, Jiaxin Shang, Xuelian Wang, Rongqi Ye, Dan Zhao, Xiangyu Li, Yadong Yang, Hongyu Zhang, Xiangwei Gong, Ying Jiang, and et al. 2024. "Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nitrogen Dynamics: Effects of Maize Straw Incorporation Under Contrasting Nitrogen Fertilization Levels" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122996
APA StyleWang, Z., Shang, J., Wang, X., Ye, R., Zhao, D., Li, X., Yang, Y., Zhang, H., Gong, X., Jiang, Y., & Qi, H. (2024). Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Nitrogen Dynamics: Effects of Maize Straw Incorporation Under Contrasting Nitrogen Fertilization Levels. Agronomy, 14(12), 2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122996







