Cadmium Accumulation in Cacao Plants (Theobroma cacao L.) under Drought Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Planting and Growth
2.4. Drought Stress Treatments
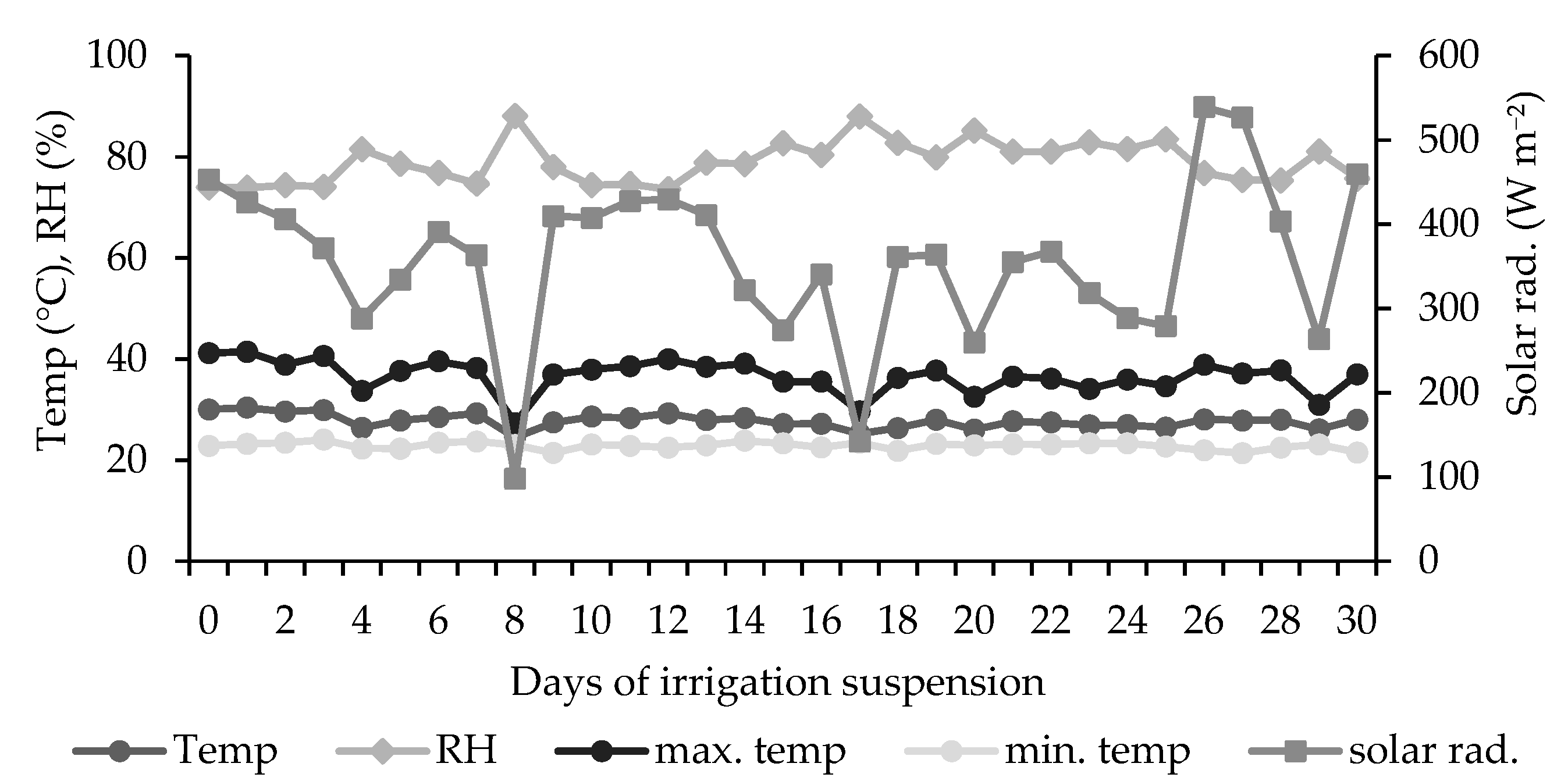
2.5. Environmental Conditions during the Experiment
2.6. Leaf Water Potential (Ψleaf)
2.7. Gas Exchange
2.8. Biomass Accumulation
2.9. Soil Cd Content
2.10. Plant Cd Content
2.11. Translocation Factor (TF)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Leaf Water Potential (Ψleaf)
3.2. Gas Exchange
3.3. Biomass Accumulation
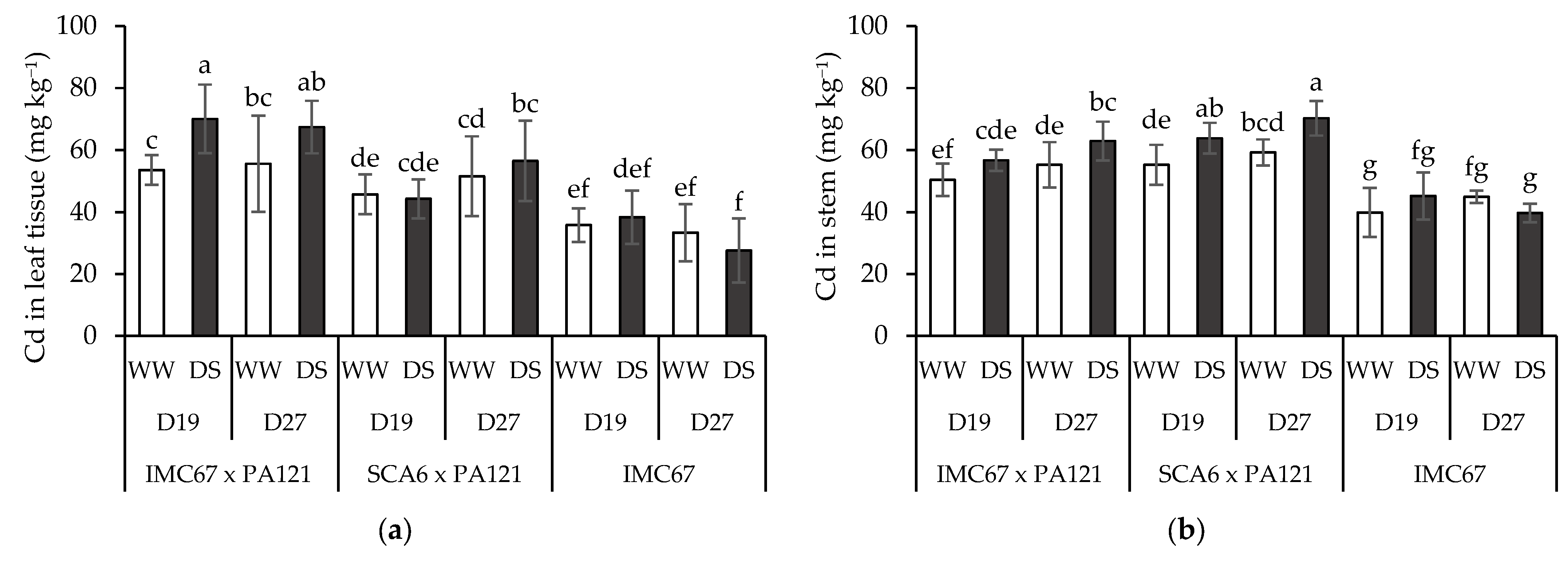
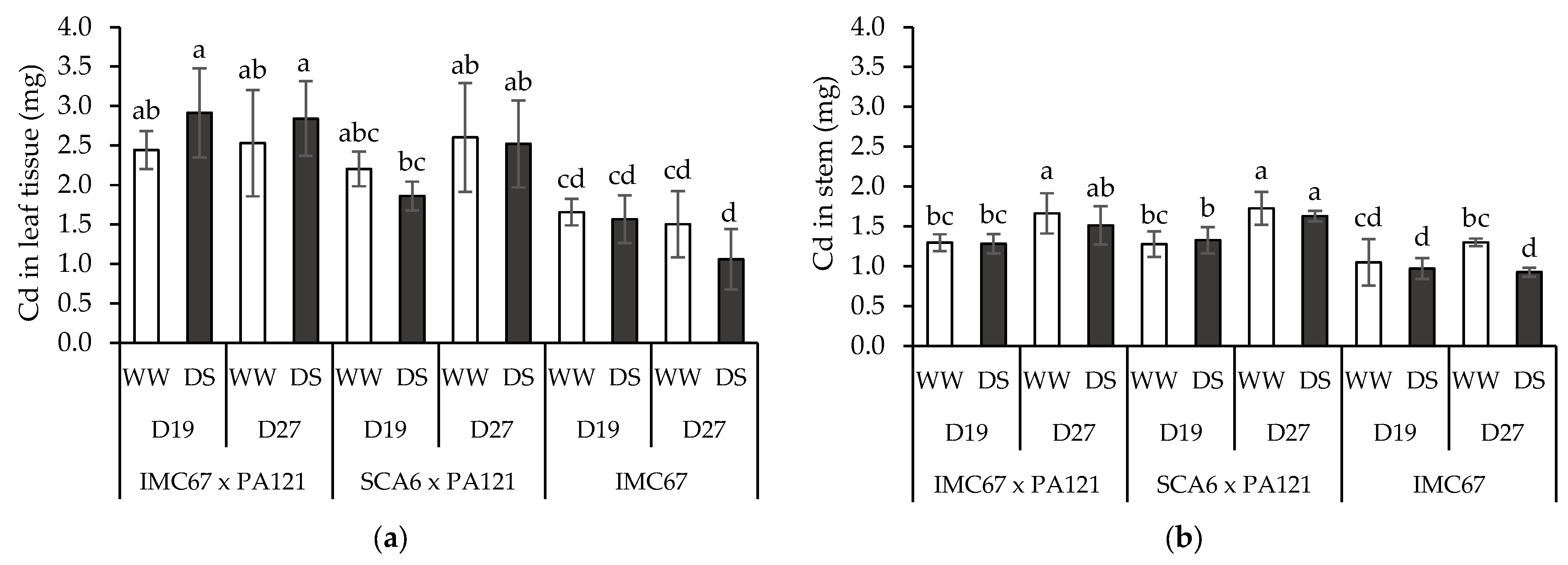
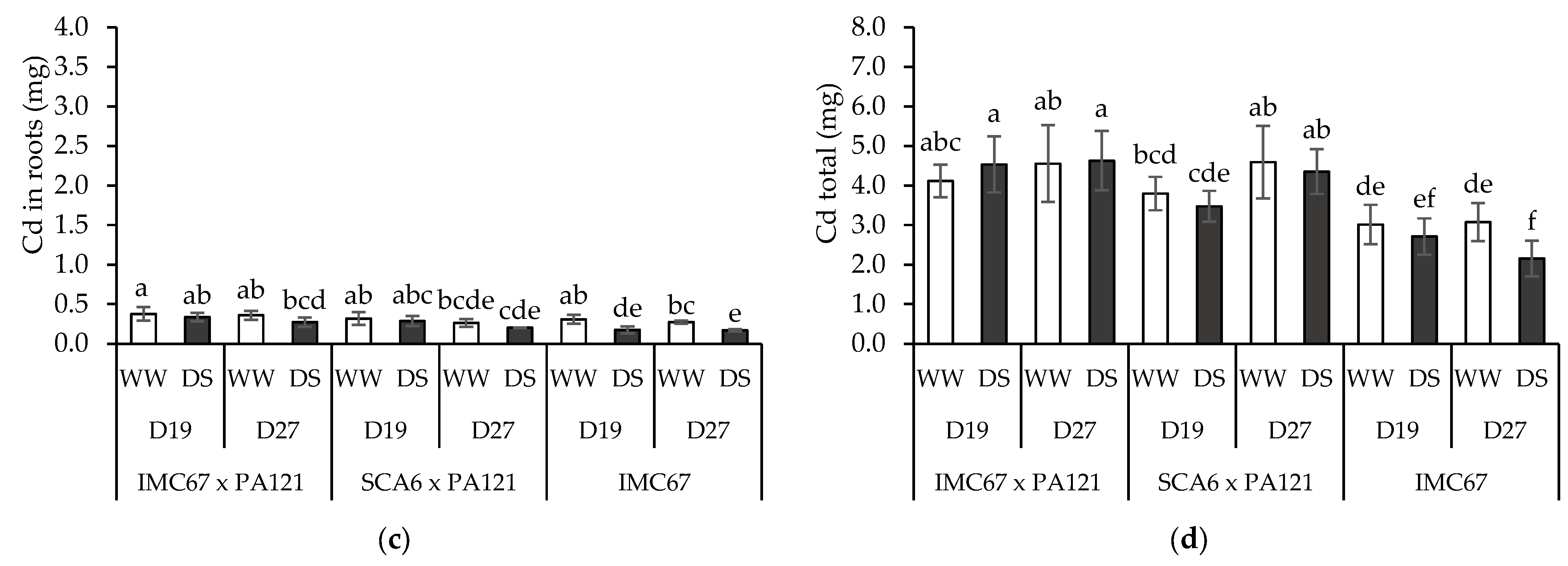
3.4. Plant Cd Content
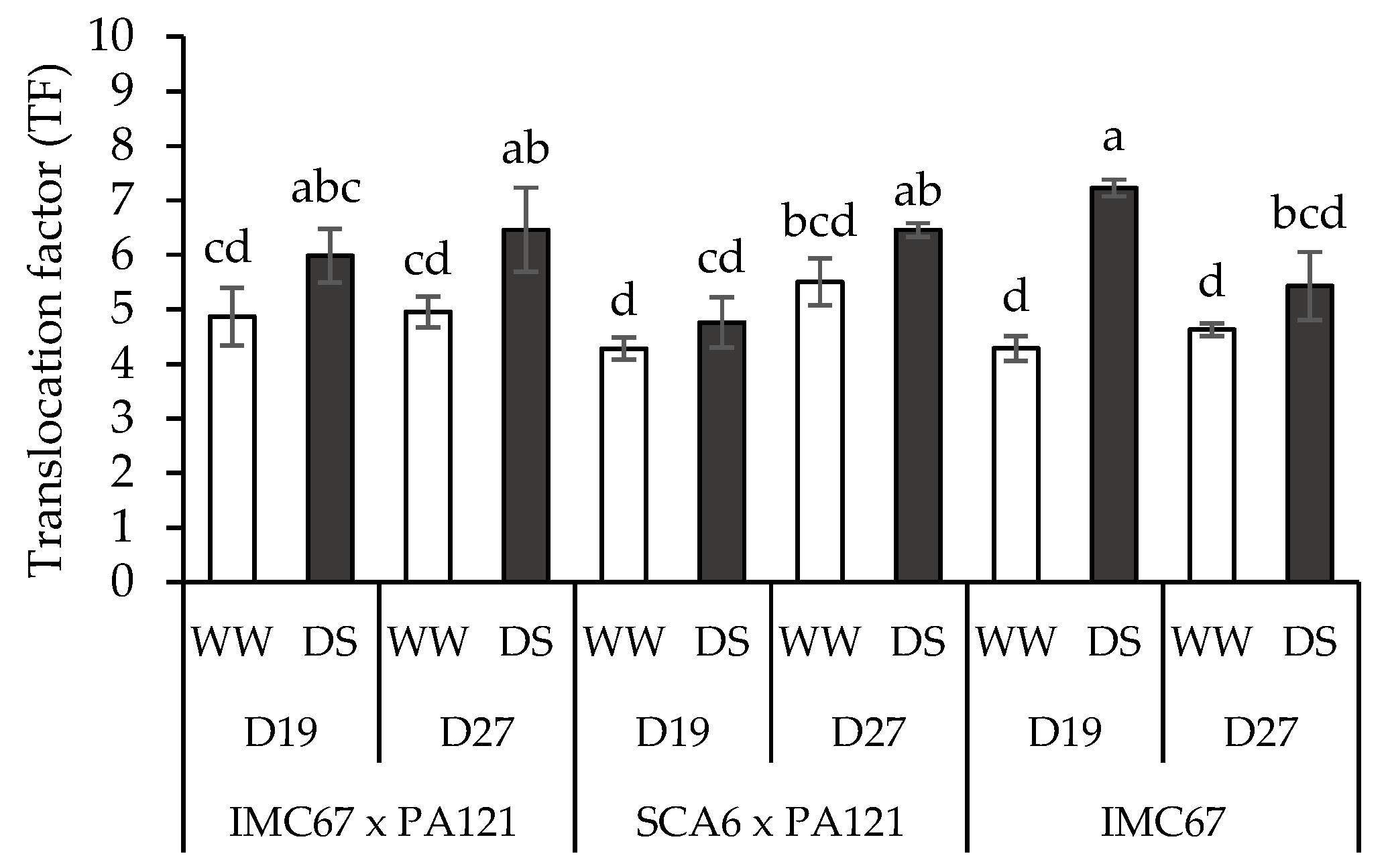
3.5. Translocation Factor (TF)
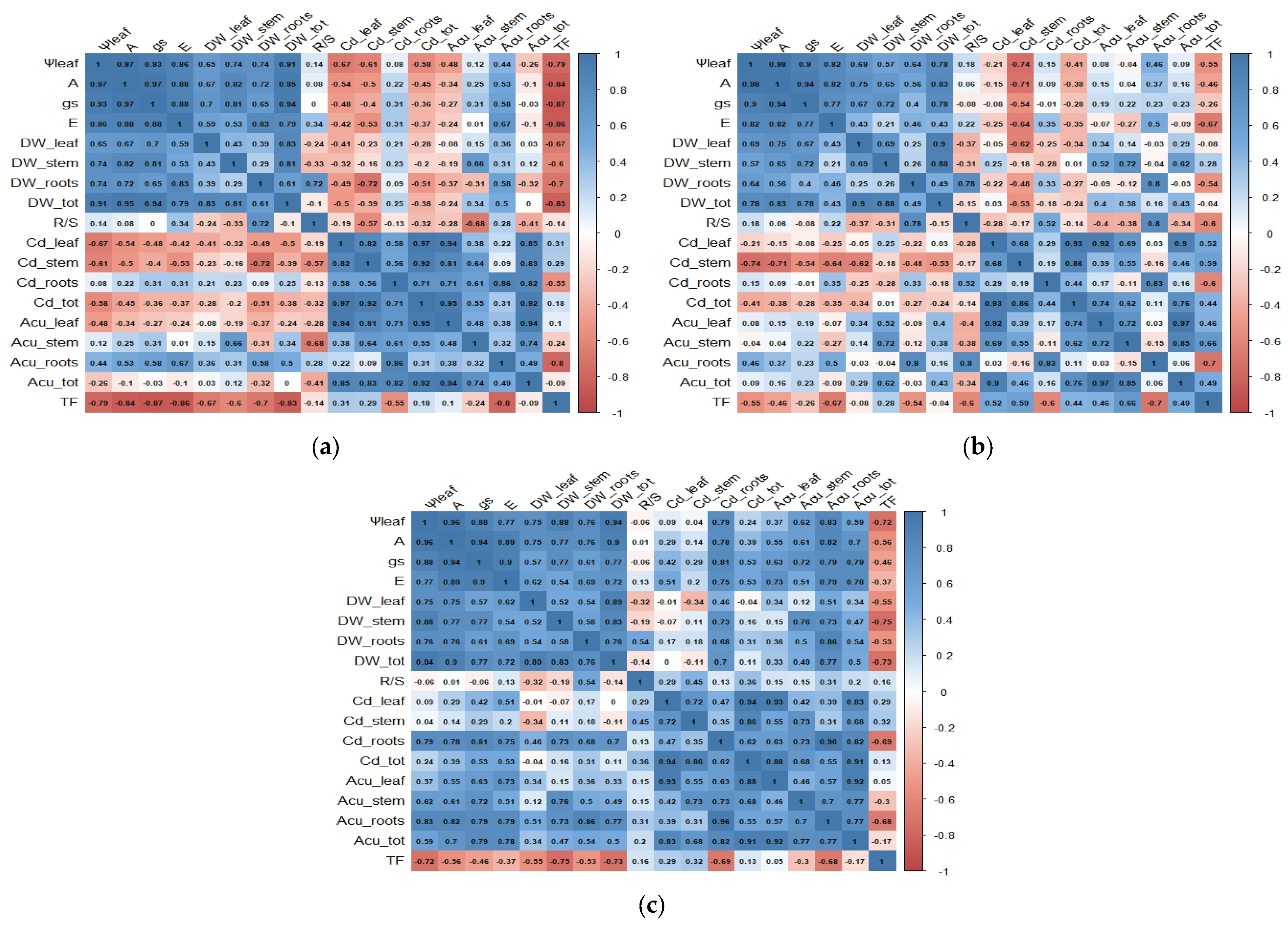
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gateau-Rey, L.; Tanner, E.V.J.; Rapidel, B.; Marelli, J.P.; Royaert, S. Climate Change Could Threaten Cocoa Production: Effects of 2015–2016 El Niño-Related Drought on Cocoa Agroforests in Bahia, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuidema, P.A.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Gerritsma, W.; Mommer, L.; Anten, N.P.R. A Physiological Production Model for Cocoa (Theobroma cacao): Model Presentation, Validation and Application. Agric. Syst. 2005, 84, 195–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahive, F.; Hadley, P.; Daymond, A.J. The Impact of Elevated CO2 and Water Deficit Stress on Growth and Photosynthesis of Juvenile Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.). Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Sicher, R.C.; Lary, D.; Strem, M.D.; Natarajan, S.; Bailey, B.A. The Drought Response of Theobroma cacao (Cacao) and the Regulation of Genes Involved in Polyamine Biosynthesis by Drought and Other Stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, E.; He, Z.L.; Stoffella, P.J.; Mylavarapu, R.S.; Li, Y.C.; Moyano, B.; Baligar, V.C. Concentration of Cadmium in Cacao Beans and Its Relationship with Soil Cadmium in Southern Ecuador. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florida Rofner, N. Revision Sobre Limites Máximos de Cadmio En Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.). Granja 2021, 34, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meter, A.; Atkinson, R.J.; Laliberte, B. Cadmium in Cacao from Latin America and the Caribbean—A Review of Research and Potential Mitigation Solutions; Bioversity International: Rome, Italy, 2019; ISBN 2013206534. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira de Araújo, R.; Furtado De Almeida, A.-A.; Pereira, L.S.; Mangabeira, P.A.O.; Souza, J.O.; Pirovani, C.P.; Ahnert, D.; Baligar, V.C. Photosynthetic, Antioxidative, Molecular and Ultrastructural Responses of Young Cacao Plants to Cd Toxicity in the Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.V.; De Almeida, A.-A.F.; Pirovani, C.P.; Reis, G.S.M.; Almeida, N.M.; Mangabeira, P.A.O. Morphological, Biochemical, Molecular and Ultrastructural Changes Induced by Cd Toxicity in Seedlings of Theobroma cacao L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Lennon, A.M.; Eudoxie, G.; Umaharan, P.; Campus, A. Genetic Variation in Bioaccumulation and Partitioning of Cadmium in Theobroma cacao L. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, N.M.; Furtado De Almeida, A.-A.; De Almeida, N.S.; Do Nascimento, L.J.; De Carvalho Neto, C.H.; Pirovani, C.P.; Ahnert, D.; Baligar, V.C. Scion-Rootstock Interaction and Tolerance to Cadmium Toxicity in Juvenile Theobroma cacao Plants. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 300, 111086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Paz, J.; Cortés, A.J.; Hernández-Varela, C.A.; Mejía-de-Tafur, M.S.; Rodriguez-Medina, C.; Baligar, V.C. Rootstock-Mediated Genetic Variance in Cadmium Uptake by Juvenile Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Genotypes, and Its Effect on Growth and Physiology. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo-Gardini, E.; Arévalo-Hernández, C.O.; Baligar, V.C.; He, Z.L. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Leaves and Beans of Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) in Major Cacao Growing Regions in Peru. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraza, F.; Moore, R.E.T.; Rehkämper, M.; Schreck, E.; Lefeuvre, G.; Kreissig, K.; Coles, B.J.; Maurice, L. Cadmium Isotope Fractionation in the Soil-Cacao Systems of Ecuador: A Pilot Field Study. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 34011–34022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furcal-Beriguete, P.; Torres-Morales, L.J. Determination of Cadmium Concentrations in Cocoa Plantations (Theobroma cacao L.) in Costa Rica. Tecnol. Marcha 2020, 33, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauddh, K.; Singh, R.P. Growth, Tolerance Efficiency and Phytoremediation Potential of Ricinus communis (L.) and Brassica juncea (L.) in Salinity and Drought Affected Cadmium Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 85, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Xia, S.; Ye, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z. PEG-Simulated Drought Stress Decreases Cadmium Accumulation in Castor Bean by Altering Root Morphology. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2015, 111, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünyayar, S.; Keleş, Y.; Çekiç, F.Ö. The Antioxidative Response of Two Tomato Species with Different Drought Tolerances as a Result of Drought and Cadmium Stress Combinations. Plant Soil Environ. 2005, 51, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, T.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Mahmood, A.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Arshad, M.; Qayyum, M.F. Biochar Application Increased the Growth and Yield and Reduced Cadmium in Drought Stressed Wheat Grown in an Aged Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Khan, Z.S.; Ali, S.; Hafeez, M.; Khalid, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Hussain, A.; Hussain, K.; Shahid Chatha, S.A.; Rizwan, M. Simultaneous Mitigation of Cadmium and Drought Stress in Wheat by Soil Application of Iron Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, W.; Anwar, S.; Zhao, Q.; Hussain, I.; Xie, F. Interactive Effect of Drought and Cadmium Stress on Soybean Root Morphology and Gene Expression. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 175, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, R.; Shi, G. Effects of Drought on the Accumulation and Redistribution of Cadmium in Peanuts at Different Developmental Stages. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 63, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wang, X.; Su, G.; Shi, G. Effects of Drought on Cadmium Accumulation in Peanuts Grown in a Contaminated Calcareous Soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18707–18717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, D.; Leon-Moreno, C.; Martínez, C.A.; Varón-Ramírez, V.M.; Araujo-Carrillo, G.A.; Vargas, R.; Quiroga-Mateus, R.; Zamora, A.; Rodríguez, E.A.G. The First National Survey of Cadmium in Cacao Farm Soil in Colombia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, C.; Lundy, M.; Läderach, P.; Castro, F. Global Climate Change Impacts on Cocoa. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Cocoa Research (ISCR), Lima, Peru, 13–17 November 2017; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, J.P.; López-Zuleta, S.; Quiroga-Mateus, R.Y.; Benavides-Erazo, J.; Chaali, N.; Bravo, D. Cadmium Distribution in Soils, Soil Litter and Cacao Beans: A Case Study from Colombia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 2455–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaraba, A.B.; Buriticá, Á.J.; Vega, F.N.; Urrego, J.E.; Bautista, J.F.; Puerta, J.A.; Yepes, J.E. Modelo Productivo Para el Cultivo de Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.)—Nutrición y Fertilización; Compañía Nacional de Chocolates: Lima, Peru, 2021; ISBN 9789585248588. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, I.C.; De Almeida, A.A.F.; Anhert, D.; Da Conceição, A.S.; Pirovani, C.P.; Pires, J.L.; Valle, R.R.; Baligar, V.C. Molecular, Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Theobroma cacao L. Genotypes to Soil Water Deficit. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaraba, A.B.; Buriticá, Á.J.; Vega, F.N.; Urrego, J.E.; Bautista, J.F.; Puerta, J.A.; Yepes, J.E. Modelo Productivo Para El Cultivo de Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.)—Origen, Botánica y Generalidades; Campaña Nacional de Chocolates—CNCH: Lima, Peru, 2021; ISBN 9789585341401. [Google Scholar]
- De Almeida, J.; Tezara, W.; Herrera, A. Physiological Responses to Drought and Experimental Water Deficit and Waterlogging of Four Clones of Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Selected for Cultivation in Venezuela. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, F.; Jaimez, R.E.; García-Nuñez, C.; Azócar, A.; Ramírez, M.E. Relaciones Hídricas e Intercambio de Gases En Theobroma cacao Var. Guasare Bajo Períodos de Deficit Hídrico. Rev. Fac. Agron. 2005, 22, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio Zambrano, M.A.; Castillo, D.A.; Rodríguez Pérez, L.; Terán, W. Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) Response to Water Stress: Physiological Characterization and Antioxidant Gene Expression Profiling in Commercial Clones. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 700855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Patra, A.; Singh Jatav, H.; Singh Jatav, S.; Kumar Singh, S.; Sathyanarayana, E.; Sudhanshu, V.; Singh, P. Toxicity of Cadmium in Soil-Plant-Human Continuum and Its Bioremediation Techniques; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020; ISBN 0000957720. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, J.G.; Churión, P.C.; Liendo, N.J.; López, V.H. Evaluación Del Contenido de Metales Pesados En Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) de Sabta Bárbara Del Zulia, Venezuela. Saber Univ. Oriente 2016, 28, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mattina, M.J.I.; Lannucci-Berger, W.; Musante, C.; White, J.C. Concurrent Plant Uptake of Heavy Metals and Persistent Organic Pollutants from Soil. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahive, F.; Hadley, P.; Daymond, A.J. The Physiological Responses of Cacao to the Environment and the Implications for Climate Change Resilience: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 39, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Joly, R.J.; Hahn, D.T. The Influence of Plant Water Deficit on Photosynthesis and Translocation of 14C-labeled Assimilates in Cacao Seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 1990, 78, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, V.; Laliberte, B. A Review of Research on the Effects of Drought and Temperature Stress and Increased CO2 on Theobroma cacao L., and the Role of Genetic Diversity to Address Climate Change; Bioversity International: Turrialba, Costa Rica, 2017; ISBN 9789292550745. [Google Scholar]
- Balasimha, D.; Daniel, E.V.; Bhat, P.G. Influence of Environmental Factors on Photosynthesis in Cocoa Trees. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1991, 55, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.K.V.; Lockwoods, G. The Water Relations and Irrigation Requeriments of Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.): A Review. Exp. Agric. 2011, 47, 635–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, O.; Jaimez, R.E.; Tezara, W.; Coronel, I.; Urich, R.; Espinoza, W. Comparative Photosynthesis, Water Relations, Growth and Survival Rates in Juvenile Criollo Cacao Cultivars (Theobroma cacao) during Dry and Wet Seasons. Exp. Agric. 2012, 48, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Dridi, J.; Gutiérrez, D.; Moret, D.; Irigoyen, J.J.; Moreno, M.A.; Gogorcena, Y. Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Responses in Four Prunus Rootstocks Submitted to Drought Stress. Tree Physiol. 2013, 33, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Ferri, E.; Moreno-Ortega, G.; Van Den Berg, N.; Pliego, C. Mild Water Stress-Induced Priming Enhance Tolerance to Rosellinia Necatrix in Susceptible Avocado Rootstocks. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, J.C.; Rodrigues, A.P.; Lidon, F.C.; Marques, L.M.C.; Leitão, A.E.; Fortunato, A.S.; Pais, I.P.; Silva, M.J.; Scotti-Campos, P.; Lopes, A.; et al. Stress Cross-Response of the Antioxidative System Promoted by Superimposed Drought and Cold Conditions in Coffea spp. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Jiang, W.; Xiukang, W.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.; Maqsood, M.F.; Ali, N.; Ishfaq, M.; Kaleem, M.; Haider, F.U.; et al. Cadmium Phytotoxicity, Tolerance, and Advanced Remediation Approaches in Agricultural Soils: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 773815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, K.F.; Hale, W.H.G.; Headley, A.D.; Athar, M. Heavy Metal Contamination of Roadside Soils of Northern England. Soil Water Res. 2006, 1, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alyemeni, M.N. Soil Cadmium Enrichment: Allocation and Plant Physiological Manifestations. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüello, D.; Chavez, E.; Lauryssen, F.; Vanderschueren, R.; Smolders, E.; Montalvo, D. Soil Properties and Agronomic Factors Affecting Cadmium Concentrations in Cacao Beans: A Nationwide Survey in Ecuador. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.B.M.; Furtado De Almeida, A.-A.; De Almeida Santos, N.; Pirovani, C.P. Tolerance Strategies and Factors That Influence the Cadmium Uptake by Cacao Tree. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, J.; Ac-Pangan, M.; Favoretto, V.R.; Taylor, A.J.; Engeseth, N.; Margenot, A.J. Drivers of Cadmium Accumulation in Theobroma cacao L. Beans: A Quantitative Synthesis of Soil-Plant Relationships across the Cacao Belt. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Rico-Medina, A.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. The Physiology of Plant Responses to Drought. Science 2020, 368, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouphael, Y.; Cardarelli, M.; Schwarz, D.; Franken, P.; Colla, G. Effects of Drought on Nutrient Uptake and Assimilation in Vegetable Crops. In Plant Responses to Drought Stress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 171–195. ISBN 9783642326530. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; He, Z.; Yang, X.; Stoffella, P.J.; Baligar, V.C. Soil Biogeochemistry, Plant Physiology, and Phytoremediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Soils. Adv. Agron. 2015, 134, 135–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, T.; Ishikawa, S. Genotypic Differences in Cadmium Concentration and Distribution of Soybean and Rice. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. Jpn. Int. Res. Cent. Agric. Sci. 2006, 40, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Clarke, J.M.; Duguid, S.; Chaney, R.L. Selection and Breeding of Plant Cultivars to Minimize Cadmium Accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M.; Farooq, M. Cadmium Toxicity in Plants: Impacts and Remediation Strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Peng, K.; Wang, A.; Lian, C.; Shen, Z. Cadmium Accumulation and Distribution in Populations of Phytolacca Americana L. and the Role of Transpiration. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, G. Variation in Cadmium Accumulation and Translocation among Peanut Cultivars as Affected by Iron Deficiency. Plant Soil 2013, 363, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, X. Cadmium Absorption and Transportation Pathways in Plants. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2017, 19, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.A.; Popova, L.P. Functions and Toxicity of Cadmium in Plants: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Turk. J. Bot. 2013, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirola, R.; Megharaj, M.; Palanisami, T.; Aryal, R.; Venkateswarlu, K. Ravi Naidu Evaluation of Metal Uptake Factors of Native Trees Colonizing an Abandoned Copper Mine—A Quest for Phytostabilization. J. Sustain. Min. 2015, 14, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, D.E.; Blaylock, M.; Kumar, N.P.B.A.; Dushenkov, V.; Ensley, B.D.; Chet, I.; Raskin, I. Phytoremediation: A Novel Strategy for the Removal of Toxic Metals from the Environment Using Plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, F.; Schreck, E.; Ev ^ Eque, T.L.; Uzu, G.; Opez, F.L.; Ruales, J.; Prunier, J.; Marquet, A.; Maurice, L. Cadmium Bioaccumulation and Gastric Bioaccessibility in Cacao: A Field Study in Areas Impacted by Oil Activities in Ecuador. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 950–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettens, S.; Vandecasteele, B.; De Vos, B.; Vansteenkiste, D.; Verschelde, P. Intra- and Inter-Annual Variation of Cd, Zn, Mn and Cu in Foliage of Poplars on Contaminated Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, S.; Mathur, V.; Garg, A.; Lenka, S.; Verma, K.; Agarwal, S. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Heavy Metal Uptake, Translocation and Tolerance in Hyperaccumulators-an Analysis Heavy Metal Tolerance in Hyperaccumulators. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Shen, W.; Du, L.; Wen, J.; Lin, J.; Li, R. Development and Chemical Characterization of Casparian Strips in the Roots of Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata). Trees—Struct. Funct. 2019, 33, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingorance, M.D.; Valdés, B.; Oliva, S.R. Strategies of Heavy Metal Uptake by Plants Growing under Industrial Emissions. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbruggen, N.; Hermans, C.; Schat, H. Mechanisms to Cope with Arsenic or Cadmium Excess in Plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, S.; Aarts, M.G.M.; Thomine, S.; Verbruggen, N. Plant Science: The Key to Preventing Slow Cadmium Poisoning. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Martinka, M.; Vaculík, M.; White, P.J. Root Responses to Cadmium in the Rhizosphere: A Review. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redjala, T.; Sterckeman, T.; Morel, J.L. Cadmium Uptake by Roots: Contribution of Apoplast and of High- and Low-Affinity Membrane Transport Systems. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbersen, N.; Gramlich, A.; Lopez, M.; Schwarz, G.; Hattendorf, B.; Gutierrez, O.; Schulin, R. Cadmium Accumulation and Allocation in Different Cacao Cultivars. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.E.T.; Ullah, I.; de Oliveira, V.H.; Hammond, S.J.; Strekopytov, S.; Tibbett, M.; Dunwell, J.M.; Rehkämper, M. Cadmium Isotope Fractionation Reveals Genetic Variation in Cd Uptake and Translocation by Theobroma cacao and Role of Natural Resistance-Associated Macrophage Protein 5 and Heavy Metal ATPase-Family Transporters. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.J.; Qiu, R.L.; Senthilkumar, P.; Jiang, D.; Chen, Z.W.; Tang, Y.T.; Liu, F.J. Tolerance, Accumulation and Distribution of Zinc and Cadmium in Hyperaccumulator Potentilla Griffithii. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 66, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.F.; Omelon, C.R.; Gordon, R.A.; Moser, D.; Macfie, S.M. Localization and Chemical Speciation of Cadmium in the Roots of Barley and Lettuce. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 100, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Uraguchi, S.; Ishikawa, S.; Arao, T. Xylem Loading Process Is a Critical Factor in Determining Cd Accumulation in the Shoots of Solanum melongena and Solanum torvum. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 67, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Silva, N.D.G.; Cholewa, E.; Ryser, P. Effects of Combined Drought and Heavy Metal Stresses on Xylem Structure and Hydraulic Conductivity in Red Maple (Acer rubrum L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5957–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
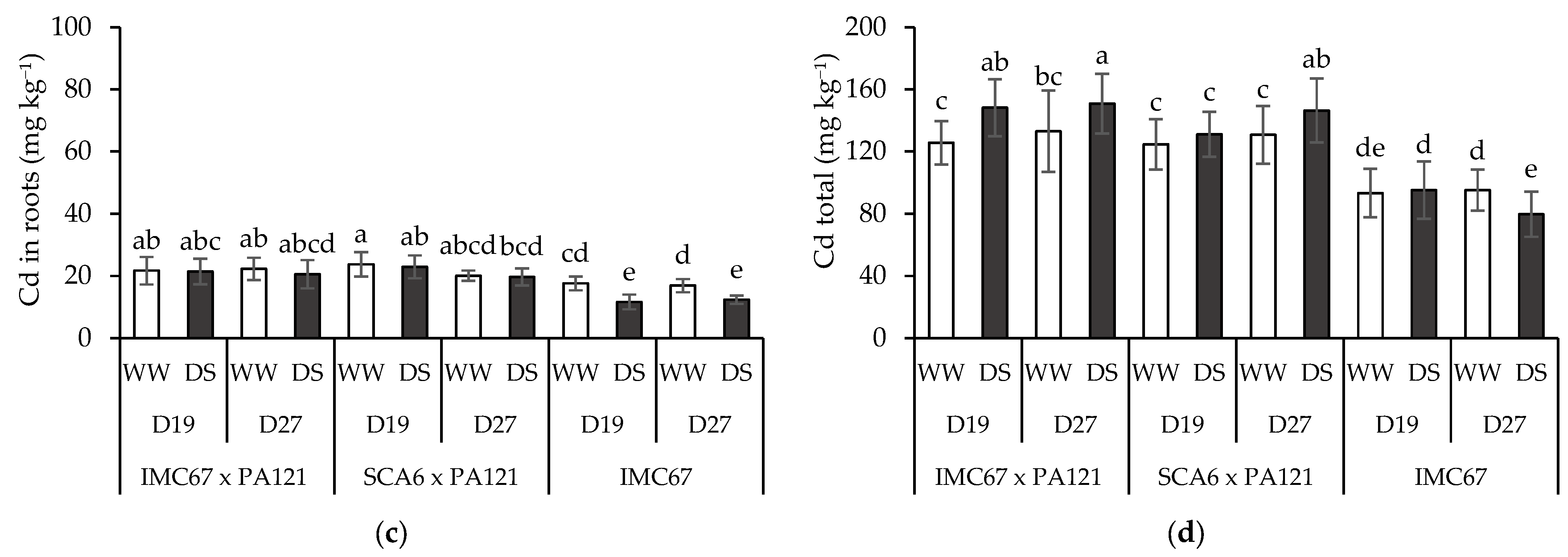
| Progeny | Ψleaf (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Stress | DS | DRH | ||
| IMC67 × PA121 | D19 | WW | −0.52 ± −0.10 ef | −0.34 ± −0.04 FG |
| DS | −1.87 ± −0.11 bc | −0.33 ± −0.04 FG | ||
| D27 | WW | −0.37 ± −0.12 fg | −0.42 ± −0.04 DE | |
| DS | −2.06 ± −0.13 a | −0.52 ± −0.06 BC | ||
| SCA6 × PA121 | D19 | WW | −0.47 ± −0.10 fg | −0.29 ± −0.06 G |
| DS | −1.51 ± −0.06 de | −0.37 ± −0.05 EF | ||
| D27 | WW | −0.31 ± −0.07 g | −0.61 ± −0.05 A | |
| DS | −2.09 ± −0.08 a | −0.62 ± −0.07 A | ||
| IMC67 | D19 | WW | −0.63 ± −0.06 e | −0.33 ± −0.06 EF |
| DS | −1.78 ± −0.13 c | −0.47 ± −0.06 CD | ||
| D27 | WW | −0.37 ± −0.10 fg | −0.57 ± −0.07 AB | |
| DS | −1.98 ± −0.10 ab | −0.54 ± −0.05 ABC | ||
| Progeny | Water Stress | A | gs | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µmol CO2 m−2 s−1) | (mol H2O m−2 s−1) | (mmol H2O m−2 s−1) | |||
| IMC67 × PA121 | D19 | WW | 7.46 ± 0.61 c | 0.07 ± 0.02 ab | 0.00167 ± 0.00032 ab |
| DS | 3.47 ± 0.53 e | 0.03 ± 0.01 c | 0.00077 ± 0.00033 fg | ||
| DRH | WW | 6.74 ± 0.7 B | 0.07 ± 0.02 ABC | 0.00153 ± 0.0005 ABC | |
| DS | 6.72 ± 0.63 BC | 0.07 ± 0.01 ABC | 0.00151 ± 0.00034 ABC | ||
| D27 | WW | 8.75 ± 0.41 ab | 0.08 ± 0.02 a | 0.00129 ± 0.00033 bcd | |
| DS | 2.14 ± 0.57 gh | 0.02 ± 0.01 c | 0.00037 ± 0.00021 gh | ||
| DRH | WW | 7.43 ± 0.8 AB | 0.07 ± 0.02 ABC | 0.00135 ± 0.00065 ABC | |
| DS | 7.31 ± 0.79 AB | 0.07 ± 0.02 ABC | 0.00148 ± 0.00076 ABC | ||
| SCA6 × PA121 | D19 | WW | 8.21 ± 0.63 b | 0.07 ± 0.02 ab | 0.00171 ± 0.00037 a |
| DS | 3.88 ± 0.47 e | 0.03 ± 0.01 c | 0.00085 ± 0.00024 ef | ||
| DRH | WW | 7.45 ± 0.63 AB | 0.08 ± 0.02 A | 0.00172 ± 0.00052 A | |
| DS | 6.71 ± 0.68 BC | 0.05 ± 0.01 C | 0.00088 ± 0.00025 C | ||
| D27 | WW | 9.08 ± 0.48 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 a | 0.00121 ± 0.0002 cde | |
| DS | 2.65 ± 0.61 fg | 0.03 ± 0.02 c | 0.00058 ± 0.00028 fgh | ||
| DRH | WW | 8.17 ± 0.83 BC | 0.08 ± 0.02 AB | 0.0018 ± 0.00078 AB | |
| DS | 6.89 ± 0.75 B | 0.07 ± 0.01 ABC | 0.00122 ± 0.00051 ABC | ||
| IMC67 | D19 | WW | 5.92 ± 0.5 d | 0.06 ± 0.02 b | 0.00148 ± 0.00043 abc |
| DS | 3.29 ± 0.37 ef | 0.03 ± 0.01 c | 0.00089 ± 0.00029 def | ||
| DRH | WW | 5.6 ± 0.68 D | 0.05 ± 0.02 BC | 0.00093 ± 0.00032 C | |
| DS | 5.82 ± 0.65 DC | 0.05 ± 0.01 C | 0.00089 ± 0.00021 C | ||
| D27 | WW | 6.33 ± 0.52 d | 0.07 ± 0.02 ab | 0.00122 ± 0.00042 cde | |
| DS | 1.54 ± 0.47 h | 0.02 ± 0.01 c | 0.00031 ± 0.0002 h | ||
| DRH | WW | 6.55 ± 0.69 BC | 0.06 ± 0.03 ABC | 0.00108 ± 0.00043 BC | |
| DS | 6.69 ± 0.6 BC | 0.07 ± 0.02 ABC | 0.00128 ±0.00035 ABC | ||
| Progeny | Water Stress | Biomass (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | Stem | Roots | R/S | Total | |||
| IMC67 × PA121 | D19 | WW | 45.58 ± 2.83 abc | 25.78 ± 2.25 bc | 17.36 ± 1.68 a | 0.24 ± 0.03 a | 88.72 ± 1.42 ab |
| DS | 41.44 ± 2.89 cd | 22.58 ± 1.15 cd | 15.78 ± 2.27 abc | 0.25 ± 0.03 a | 79.81 ± 4.45 cd | ||
| D27 | WW | 45.86 ± 3.93 abc | 30.08 ± 2.09 a | 16.13 ± 0.74 ab | 0.21 ± 0.02 abc | 92.07 ± 2.12 ab | |
| DS | 42.02 ± 2.69 bcd | 23.96 ± 1.85 cd | 13.32 ± 2.27 bcd | 0.20 ± 0.04 abcd | 79.29 ± 3.99 cd | ||
| SCA6 × PA121 | D19 | WW | 48.38 ± 2.93 abc | 23.08 ± 1.56 cd | 13.35 ± 2.10 bcd | 0.19 ± 0.03 bcd | 84.82 ± 2.97 bc |
| DS | 42.28 ± 3.53 bcd | 20.74 ± 1.92 d | 12.44 ± 1.47 cd | 0.20 ± 0.03 abcd | 75.46 ± 3.26 cd | ||
| D27 | WW | 50.35 ± 2.66 abc | 29.10 ± 2.22 ab | 13.12 ± 2.34 bcd | 0.17 ± 0.03 cd | 92.57 ± 4.69 ab | |
| DS | 44.70 ± 2.52 abcd | 23.25 ± 1.47 cd | 10.48 ± 1.99 d | 0.15 ± 0.03 d | 78.43 ± 3.95 cd | ||
| IMC67 | D19 | WW | 46.63 ± 4.53 abc | 26.05 ± 2.34 bc | 17.51 ± 1.18 a | 0.24 ± 0.02 ab | 90.19 ± 4.62 ab |
| DS | 41.13 ± 4.45 cd | 21.58 ± 1.94 d | 15.02 ± 1.22 abc | 0.24 ± 0.02 ab | 77.74 ± 4.33 cd | ||
| D27 | WW | 45.17 ± 3.06 abc | 28.94 ± 2.22 ab | 16.30 ± 1.74 ab | 0.22 ± 0.03 abc | 90.41 ± 4.54 ab | |
| DS | 38.50 ± 2.26 d | 23.36 ± 1.66 cd | 13.82 ± 1.58 bcd | 0.22 ± 0.02 ab | 75.67 ± 4.01 cd | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz-Álvarez, A.; Magnitskiy, S.; Silva-Arero, E.A.; Rodríguez-Medina, C.; Argout, X.; Castaño-Marín, Á.M. Cadmium Accumulation in Cacao Plants (Theobroma cacao L.) under Drought Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102490
Ortiz-Álvarez A, Magnitskiy S, Silva-Arero EA, Rodríguez-Medina C, Argout X, Castaño-Marín ÁM. Cadmium Accumulation in Cacao Plants (Theobroma cacao L.) under Drought Stress. Agronomy. 2023; 13(10):2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102490
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz-Álvarez, Antonio, Stanislav Magnitskiy, Elías Alexander Silva-Arero, Caren Rodríguez-Medina, Xavier Argout, and Ángela María Castaño-Marín. 2023. "Cadmium Accumulation in Cacao Plants (Theobroma cacao L.) under Drought Stress" Agronomy 13, no. 10: 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102490
APA StyleOrtiz-Álvarez, A., Magnitskiy, S., Silva-Arero, E. A., Rodríguez-Medina, C., Argout, X., & Castaño-Marín, Á. M. (2023). Cadmium Accumulation in Cacao Plants (Theobroma cacao L.) under Drought Stress. Agronomy, 13(10), 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102490






