Exogenous Si Mitigates the Effects of Cinnamic-Acid-Induced Stress by Regulating Carbon Metabolism and Photosynthetic Pigments in Cucumber Seedlings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation of Test Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
- (1)
- CK: 1/2 Yamazaki nutrient solution;
- (2)
- Si: 1/2 Yamazaki nutrient solution + 1.0 mM Si;
- (3)
- CA: 1/2 Yamazaki nutrient solution + 0.8 mM CA;
- (4)
- CA + Si: 1/2 Yamazaki nutrient solution + 0.8 mM CA + 1.0 mM Si.
2.3. Measurement Index and Method
2.3.1. Pigment Content
2.3.2. Activity of Key Enzymes of Photosynthesis
2.3.3. Carbohydrate Content of Cucumber Leaves and Roots
2.3.4. Enzyme Activities Related to Carbon Metabolism in Cucumber Leaves and Roots
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
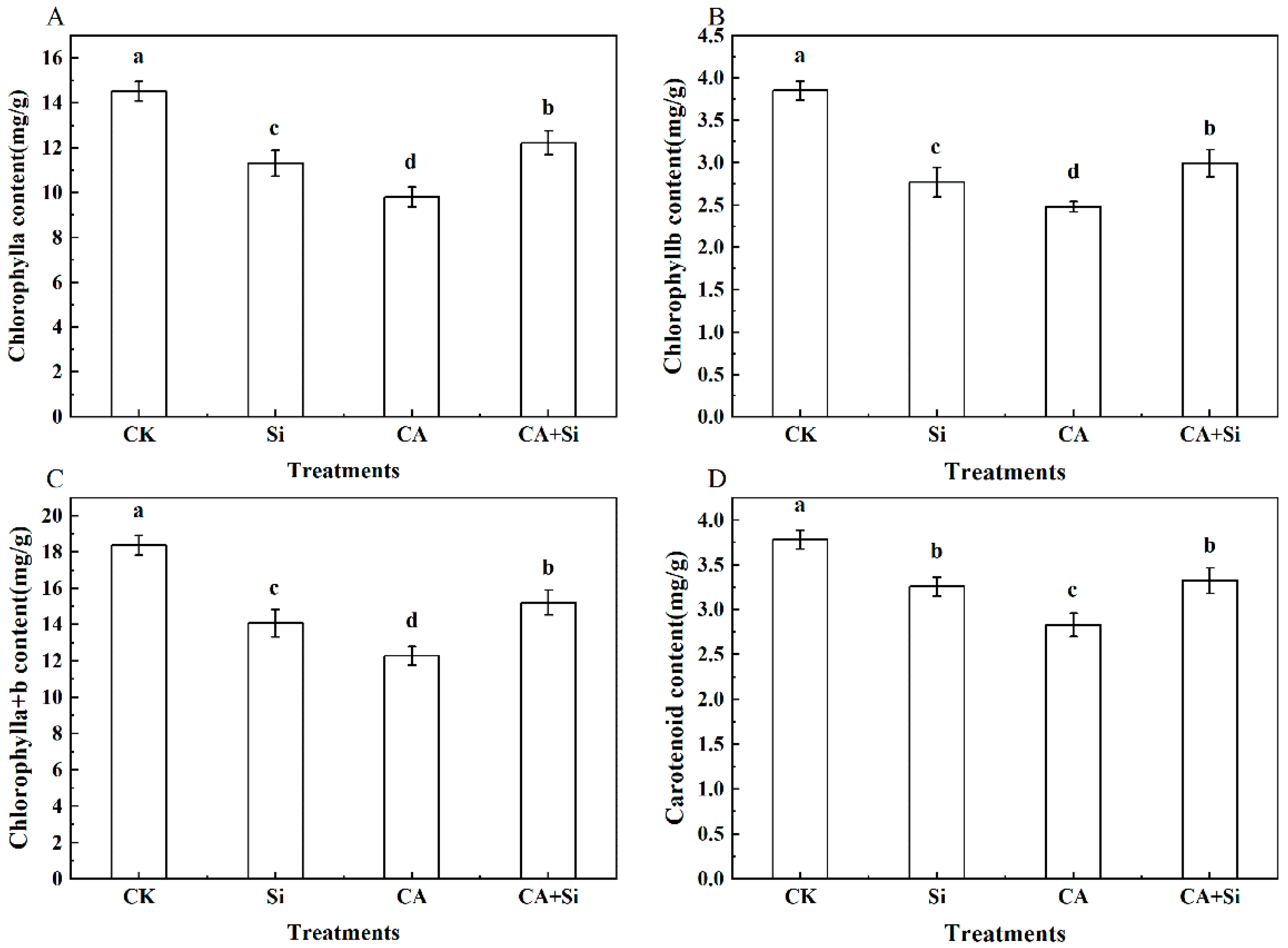
3.1. Effect of Si on the Photosynthetic Pigment Content of Cucumber Leaves under CA-Induced Stress
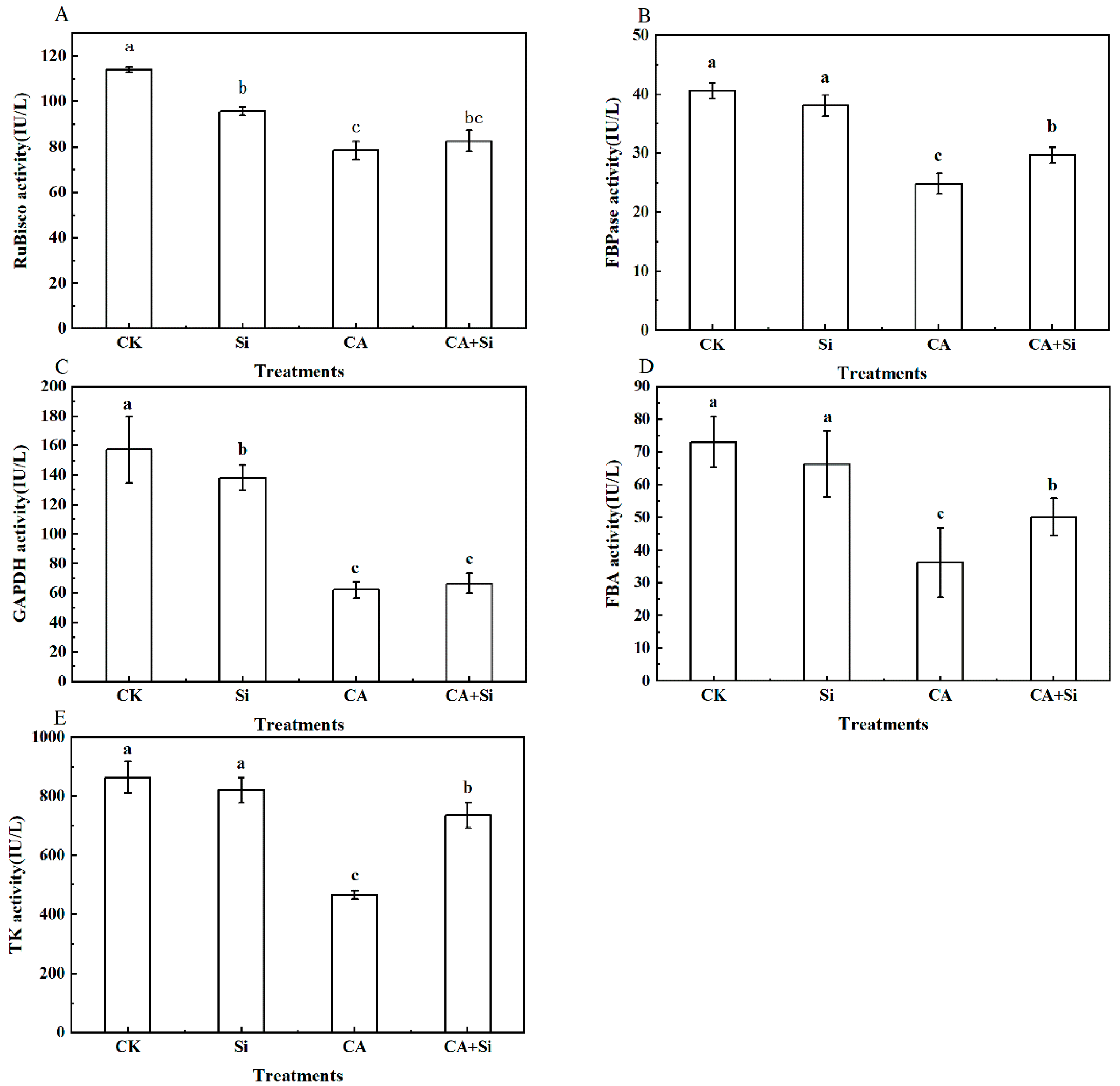
3.2. Effect of Si on the Activity of the Key Enzymes of Photosynthesis in Cucumber Leaves under CA-Induced Stress
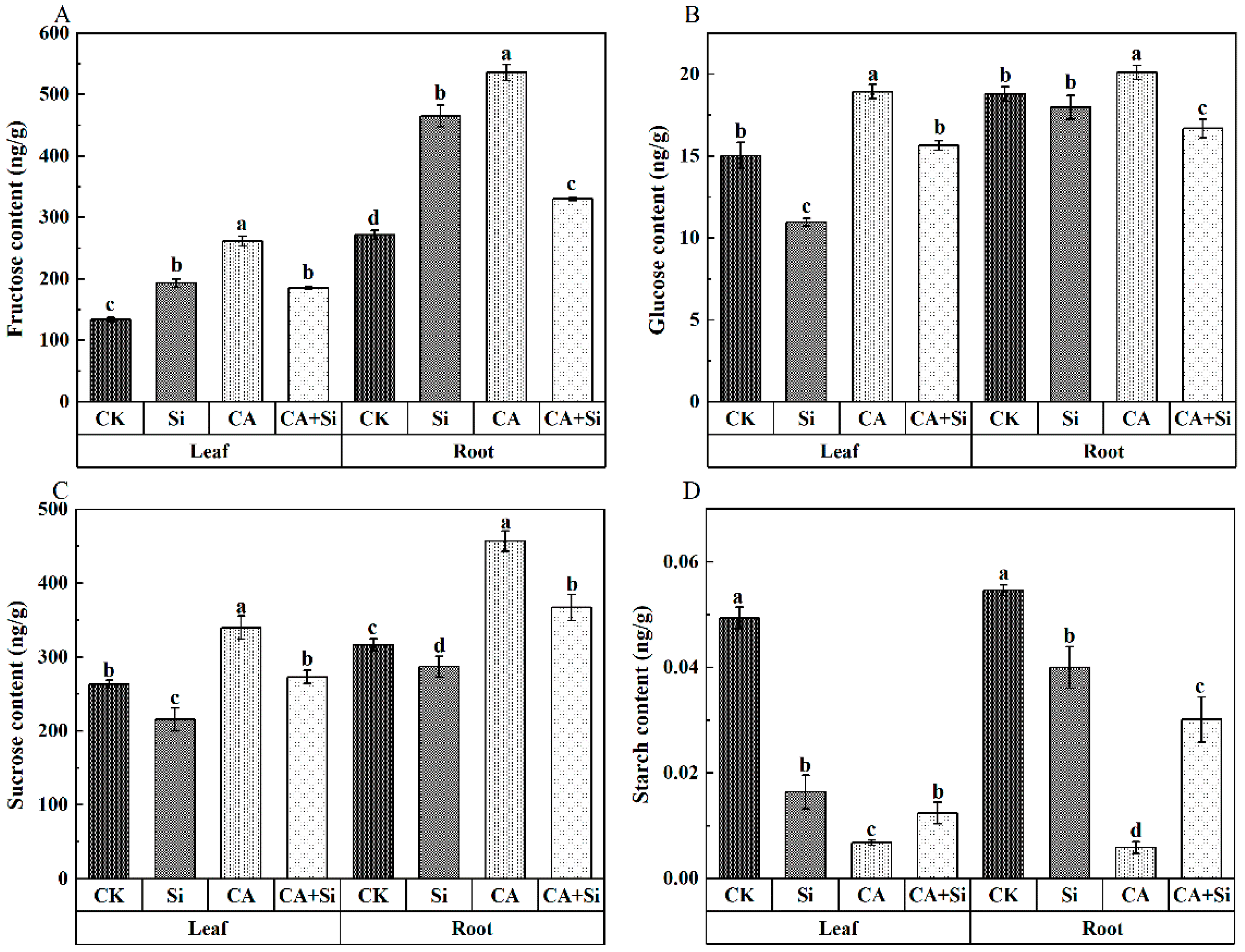
3.3. Effect of Si on the Carbohydrate Contents of Cucumber Leaves and Roots under CA-Induced Stress
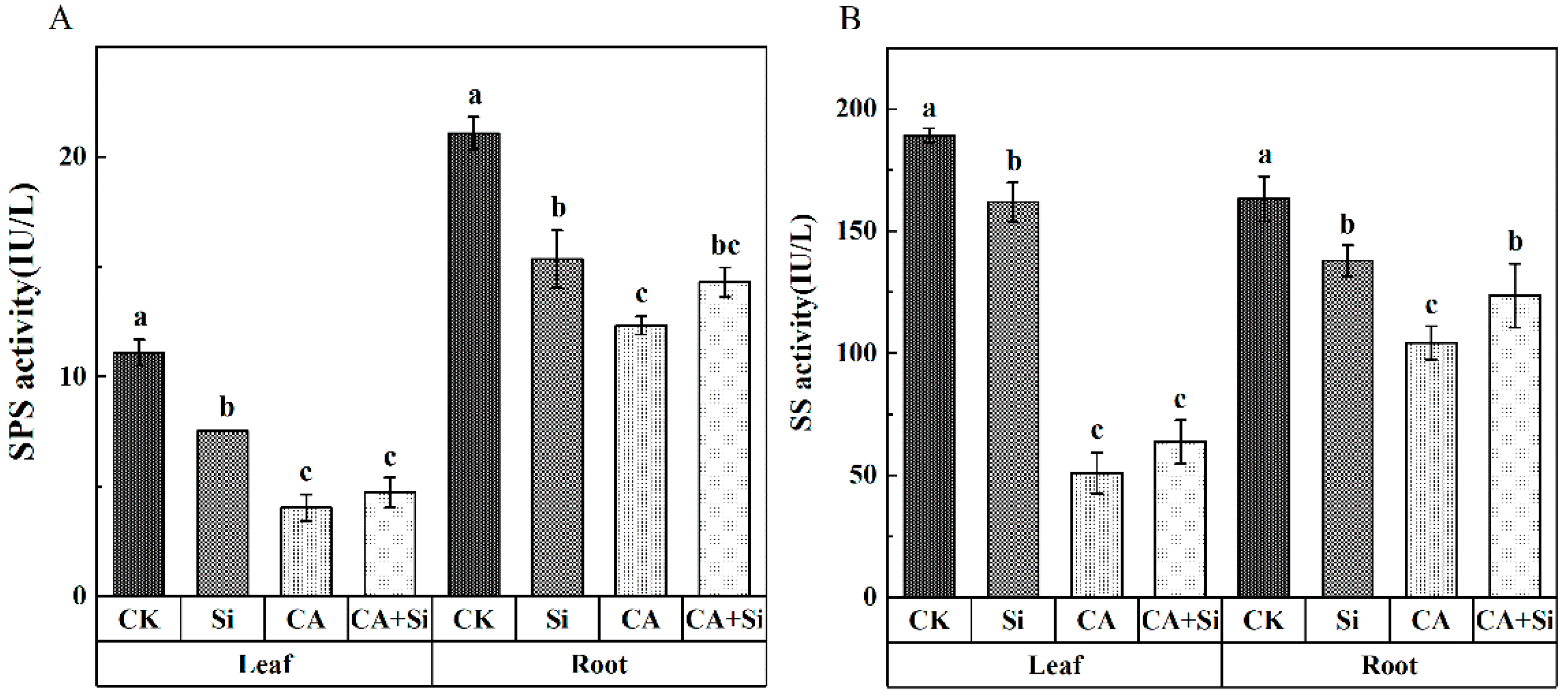
3.4. Effect of Si on the Activities of SPS and SS in Cucumber Leaves and Roots under CA-Induced Stress
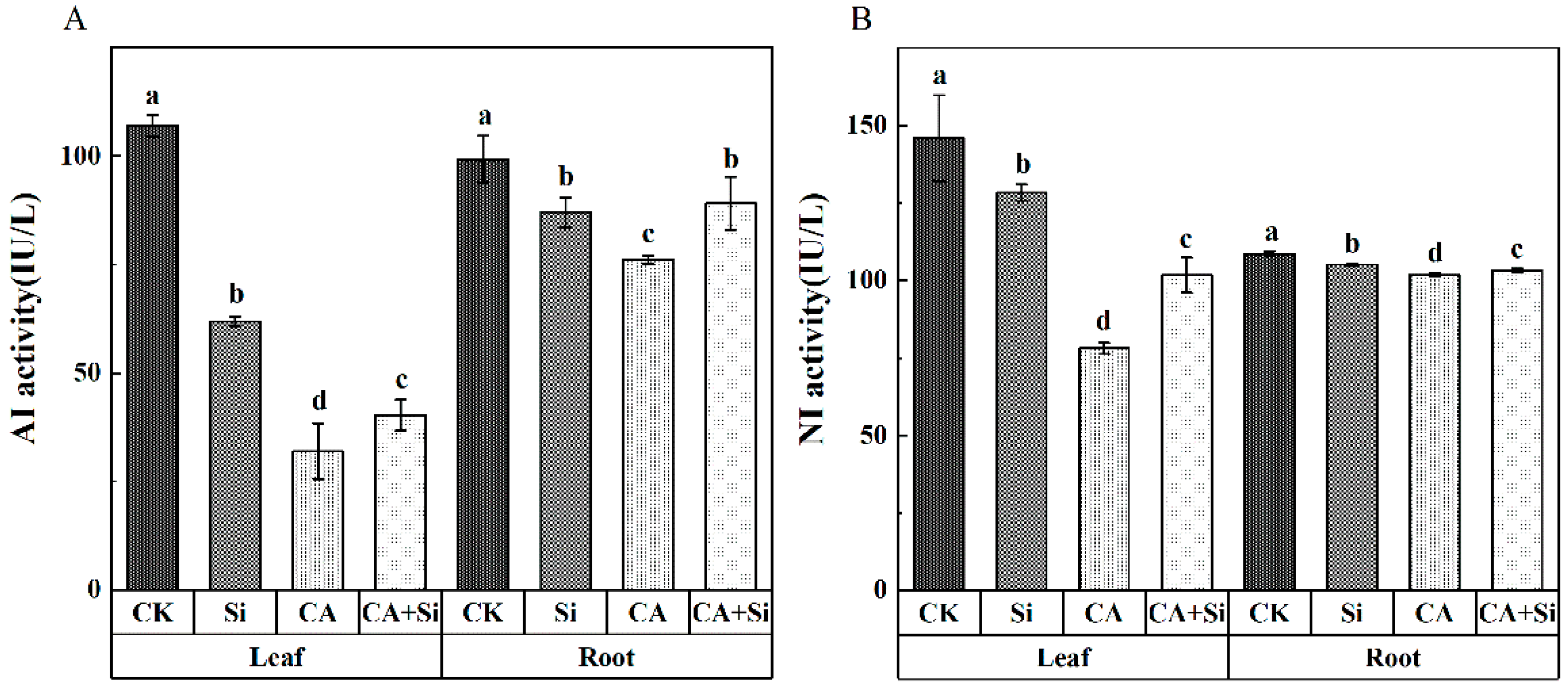
3.5. Effects of Si on the Activities of AI and NI in Cucumber Leaves and Roots under CA-Induced Stress
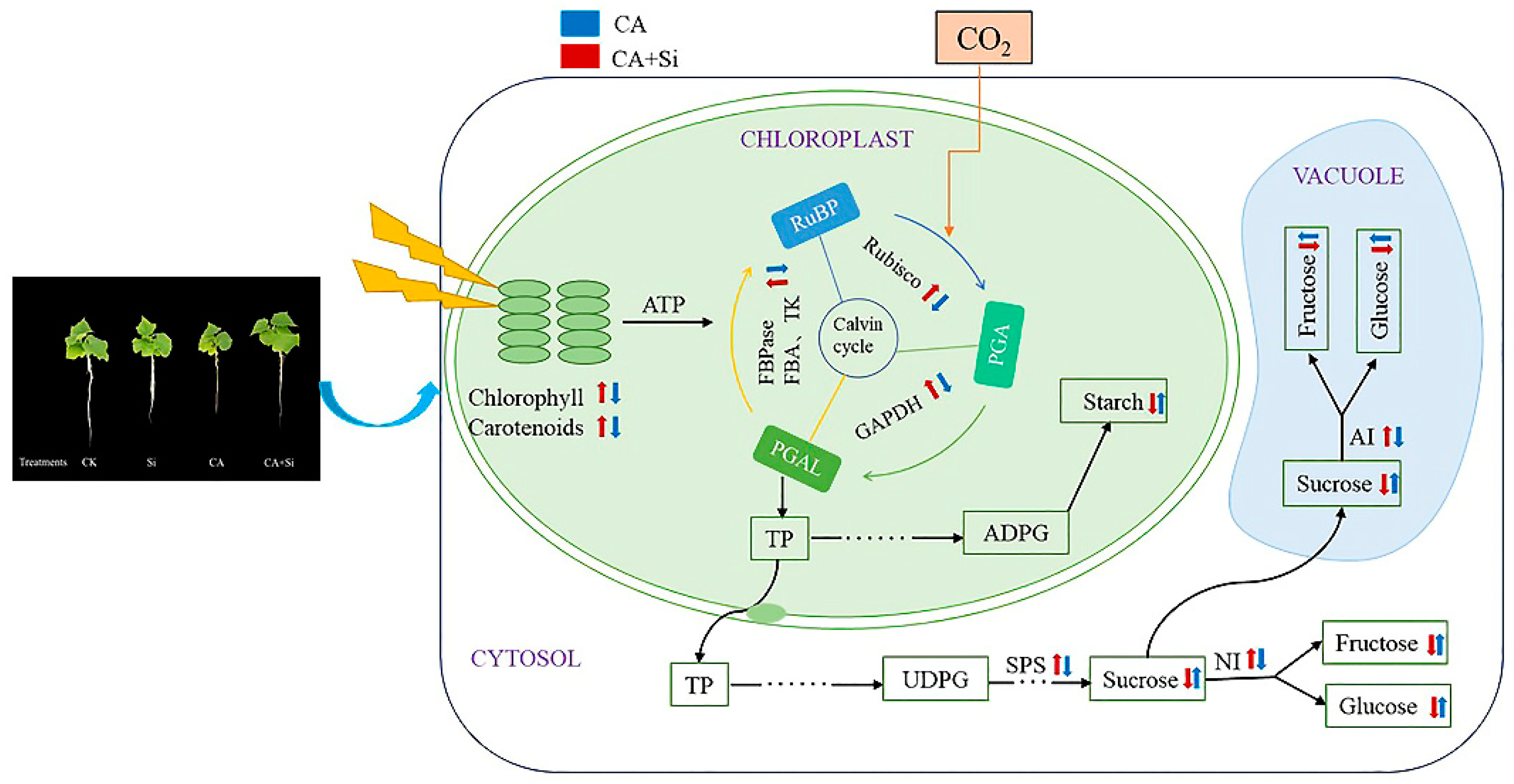
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kato-Noguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; Okuda, N. Involvement of an autotoxic compound in asparagus decline. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 224, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, C.L.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q. Physiological basis of different allelopathic reactions of cucumber and figleaf gourd plants to cinnamic acid. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajjou, L.; Duval, M.; Gallardo, K.; Catusse, J.; Bally, J.; Job, C.; Job, D. Seed germination and vigor. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoilova, I.; Krastanov, A.; Yanakieva, I.; Kratchanova, M.; Yemendjiev, H. Biodegradation of mixed phenolic compounds by Aspergillus awamori NRRL 3112. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 60, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Xue, C. Effect of cinnamic acid on soil microbial characteristics in the cucumber rhizosphere. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2009, 45, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Yu, J.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zou, L. Incidence of Fusarium wilt in Cucumis sativus L. is promoted by cinnamic acid, an autotoxin in root exudates. Plant Soil 2004, 263, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Bie, Z. Cinnamic acid-inhibited ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity is mediated through decreased spermine and changes in the ratio of polyamines in cowpea. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.T.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Exogenously applied spermidine confers protection against cinnamic acid-mediated oxidative stress in Pisum sativum. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Singh, H.; Singh, A.; Hussain, I.; Singh, N. Salicylic acid induced changes on some physiological parameters symptomatic for oxidative stress in maize (Zea mays L.) grown under cinnamic acid stress. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2018, 44, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, V.; Dotaniya, M.; Coumar, V.; Rajendiran, S.; Kundu, S.; Subba Rao, A. A case for silicon fertilization to improve crop yields in tropical soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 84, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yongchao, L.; Miroslav, N.; Richard, B.; Haijun, G.; Alin, S. Silicon in Agriculture. In From Theory to Practice; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, M.H.; Al-Whaibi, M.H. Role of nano-SiO2 in germination of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum seeds Mill.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dar, F.A.; Tahir, I.; Hakeem, K.R.; Rehman, R.U. Silicon Application Enhances the Photosynthetic Pigments and Phenolic/Flavonoid Content by Modulating the Phenylpropanoid Pathway in Common Buckwheat under Aluminium Stress. Silicon 2022, 14, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, S.; Tanaka, K.; Fujihara, S.; Itai, A.; Den, X.; Zhang, S. Silicon-mediated changes in polyamines participate in silicon-induced salt tolerance in Sorghum bicolor L. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerriero, G.; Hausman, J.-F.; Legay, S. Silicon and the plant extracellular matrix. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Khan, A.L.; Waqas, M.; Lee, I.-J. Silicon regulates antioxidant activities of crop plants under abiotic-induced oxidative stress: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.H.I.; Gong, H.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Li, H.L.; Hu, Y.H.; Wang, Y.C. Beneficial effects of silicon on photosynthesis of tomato seedlings under water stress. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raessler, M.; Wissuwa, B.; Breul, A.; Unger, W.; Grimm, T. Chromatographic analysis of major non-structural carbohydrates in several wood species–an analytical approach for higher accuracy of data. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, S.; Jiang, C.; Sun, H.; Feng, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhuang, X. Transcriptomic sequencing and co-expression network analysis on key genes and pathways regulating nitrogen use efficiency in myriophyllum aquaticum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Pan, K.; Zhu, T.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. Carbon and nitrogen metabolism in leaves and roots of dwarf bamboo (Fargesia denudata Yi) subjected to drought for two consecutive years during sprouting period. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 33, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttens, A.; Gross, E.M. Sucrose modifies growth and physiology in axenically grown Myriophyllum spicatum with potential effects on the response to pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Mumtaz, M.; Manzoor, S.; Shuxian, L.; Ahmed, I.; Skalicky, M.; Liu, W. Foliar application of silicon improves growth of soybean by enhancing carbon metabolism under shading conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q. Silicon alleviates salinity stress in licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) by regulating carbon and nitrogen metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Si, J.; Römheld, V. Silicon uptake and transport is an active process in Cucumis sativus. New Phytol. 2005, 167, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitani, N.; Yamaji, N.; Ago, Y.; Iwasaki, K.; Ma, J.F. Isolation and functional characterization of an influx silicon transporter in two pumpkin cultivars contrasting in silicon accumulation. Plant J. 2011, 66, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Nascimento, C.W.A.; de Souza Nunes, G.H.; Preston, H.A.F.; da Silva, F.B.V.; Preston, W.; Loureiro, F.L.C. Influence of silicon fertilization on nutrient accumulation, yield and fruit quality of melon grown in Northeastern Brazil. Silicon 2020, 12, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.S.; da Silva Lobato, A.K.; Tan, D.K.Y.; da Costa, D.V.; Uchoa, E.B.; do Nascimento Ferreira, R.; Silva Guedes, E.M. Positive interference of silicon on water relations, nitrogen metabolism, and osmotic adjustment in two pepper (‘capsicum annuum’) cultivars under water deficit. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Luo, S.; Dawuda, M.M.; Gao, X.; Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Yu, J. Exogenous silicon enhances the systemic defense of cucumber leaves and roots against CA-induced autotoxicity stress by regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and photosystem II. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, J.; Merckx, R. An improved colorimetric method to quantify sugar content of plant tissue. J. Exp. Bot. 1993, 44, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Bi, X.; Gao, W. Allelopathic effect of p-coumaric acid on American ginseng and its physiological mechanism. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 3006–3013. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, R.; Xiao, X.; Liao, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Xie, J. Exogenous Si alleviation of autotoxicity in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seed germination is correlated with changes in carbohydrate metabolism. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 37, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsomino, A.; Araniti, F.; Lupini, A.; Princi, G.; Petrovičová, B.; Abenavoli, M.R. Phenolic acids in plant-soil interactions: A microcosm experiment. JA I 2015, 1, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Abenavoli, M.; Lupini, A.; Oliva, S.; Sorgonà, A. Allelochemical effects on net nitrate uptake and plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity in maize seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2010, 54, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkosky, R.R.; Einhellig, F.A.; Butler, J.L. Caffeic acid-induced changes in plant–water relationships and photosynthesis in leafy spurge Euphorbia esula. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 2095–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.; Singh, S. Cinnamic acid induced changes in reactive oxygen species scavenging enzymes and protein profile in maize (Zea mays L.) plants grown under salt stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2013, 19, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Shi, Q.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Yang, F.; Xu, H. Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 123, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M.; Dubey, N.K.; Chauhan, D.K. Silicon nanoparticles more effectively alleviated UV-B stress than silicon in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 110, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, D.; Chen, G. Silicon improves photosynthetic performance by optimizing thylakoid membrane protein components in rice under drought stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 158, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Caemmerer, S.V.; Farquhar, G.D. Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves. Planta 1981, 153, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Fukui, Y. Possible role of NAD-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in growth promotion of Arabidopsis seedlings by low levels of selenium. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Guo, S.; Sun, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, Y.; Abou El-Yazied, A.; Hasan, M.M. Melatonin-mediated photosynthetic performance of tomato seedlings under high-temperature stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghsoudi, K.; Emam, Y.; Pessarakli, M. Effect of silicon on photosynthetic gas exchange, photosynthetic pigments, cell membrane stability and relative water content of different wheat cultivars under drought stress conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raines, C.A. The Calvin cycle revisited. Photosynth. Res. 2003, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Azher Nawaz, M.; Li, F.; Bai, L.; Li, J. Brassinosteroids regulate antioxidant system and protect chloroplast ultrastructure of autotoxicity-stressed cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings. Agronomy 2019, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boriboonkaset, T.; Theerawitaya, C.; Yamada, N.; Pichakum, A.; Supaibulwatana, K.; Cha-Um, S.; Kirdmanee, C. Regulation of some carbohydrate metabolism-related genes, starch and soluble sugar contents, photosynthetic activities and yield attributes of two contrasting rice genotypes subjected to salt stress. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Ma, N.; Yang, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M. Effect of ammonia stress on carbon metabolism in tolerant aquatic plant—Myriophyllum aquaticum. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, Z. Ammonia stress on the carbon metabolism of Ceratophyllum demersum. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiboland, R.; Cherghvareh, L.; Dashtebani, F. Effect of silicon supplementation on wheat plants under salt stress. J. Plant Process Funct. 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, D.; Pei, Z.; Naeem, M.; Gong, H.; Zhou, W. Silicon alleviates PEG-induced water-deficit stress in upland rice seedlings by enhancing osmotic adjustment. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2012, 198, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Tanaka, K.; Oka, M. Application of silicon improves salt tolerance through ameliorating osmotic and ionic stresses in the seedling of Sorghum bicolor. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 3099–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashida, Y.; Hirose, T.; Okamura, M.; Hibara, K.-I.; Ohsugi, R.; Aoki, N. A reduction of sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS) activity affects sucrose/starch ratio in leaves but does not inhibit normal plant growth in rice. Plant Sci. 2016, 253, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhu, X.; Jia, H.; Wang, C. Research advances on physiological function of plant sucrose synthase. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2017, 40, 759–768. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfig, K.B.; Gabler, A.; Simon, U.K.; Luschin-Ebengreuth, N.; Hatz, M.; Berger, S.; Muhammad, N.; Zeier, J.; Sinha, A.K.; Roitsch, T. Post-translational derepression of invertase activity in source leaves via down-regulation of invertase inhibitor expression is part of the plant defense response. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chia, L.; McRae, D.; Thompson, J. Light-dependence of paraquat-initiated membrane deterioration in bean plants. Evid. Involv. Superoxide. Physiol. Plant. 1982, 56, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Lang, D.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Silicon alleviates salt and drought stress of Glycyrrhiza uralensis plants by improving photosynthesis and water status. Biol. Plant 2020, 64, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Olvera, S.M.; Trejo-Téllez, L.I.; Gómez-Merino, F.C.; Ruíz-Posadas, L.D.M.; Alcántar-González, E.G.; Saucedo-Veloz, C. Silicon Stimulates Plant Growth and Metabolism in Rice Plants under Conventional and Osmotic Stress Conditions. Plants 2021, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Wang, X.; Li, N. Plant Physiology; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2009; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, J.; Jin, L.; Meng, X.; Jin, N.; Wang, S.; Hu, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Luo, S.; Yu, J. Exogenous Si Mitigates the Effects of Cinnamic-Acid-Induced Stress by Regulating Carbon Metabolism and Photosynthetic Pigments in Cucumber Seedlings. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071569
Lyu J, Jin L, Meng X, Jin N, Wang S, Hu L, Zhang G, Wu Y, Luo S, Yu J. Exogenous Si Mitigates the Effects of Cinnamic-Acid-Induced Stress by Regulating Carbon Metabolism and Photosynthetic Pigments in Cucumber Seedlings. Agronomy. 2022; 12(7):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071569
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Jian, Li Jin, Xin Meng, Ning Jin, Shuya Wang, Linli Hu, Guobin Zhang, Yue Wu, Shilei Luo, and Jihua Yu. 2022. "Exogenous Si Mitigates the Effects of Cinnamic-Acid-Induced Stress by Regulating Carbon Metabolism and Photosynthetic Pigments in Cucumber Seedlings" Agronomy 12, no. 7: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071569
APA StyleLyu, J., Jin, L., Meng, X., Jin, N., Wang, S., Hu, L., Zhang, G., Wu, Y., Luo, S., & Yu, J. (2022). Exogenous Si Mitigates the Effects of Cinnamic-Acid-Induced Stress by Regulating Carbon Metabolism and Photosynthetic Pigments in Cucumber Seedlings. Agronomy, 12(7), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071569





