Multigenerational Insecticide Hormesis Enhances Fitness Traits in a Key Egg Parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis Ishii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Environment
2.2. Insect Colonies
2.2.1. Rearing of the Factitious Host, Corcyra cephalonica
2.2.2. Rearing of the Egg Parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis
2.3. Insecticide
2.4. Toxicity Assay
2.5. Multigenerational Sublethal Effects of Imidacloprid on the Demographic Traits of T. chilonis
2.5.1. Egg to Adult Developmental Time
2.5.2. Adult Fecundity and Longevity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity Assay of Imidacloprid on T. chilonis Adults
3.2. Multigenerational Sublethal Effects of Imidacloprid on the Biological Traits of T. chilonis
3.3. Multigenerational Sublethal Effects of Imidacloprid on the Population Traits of T. chilonis
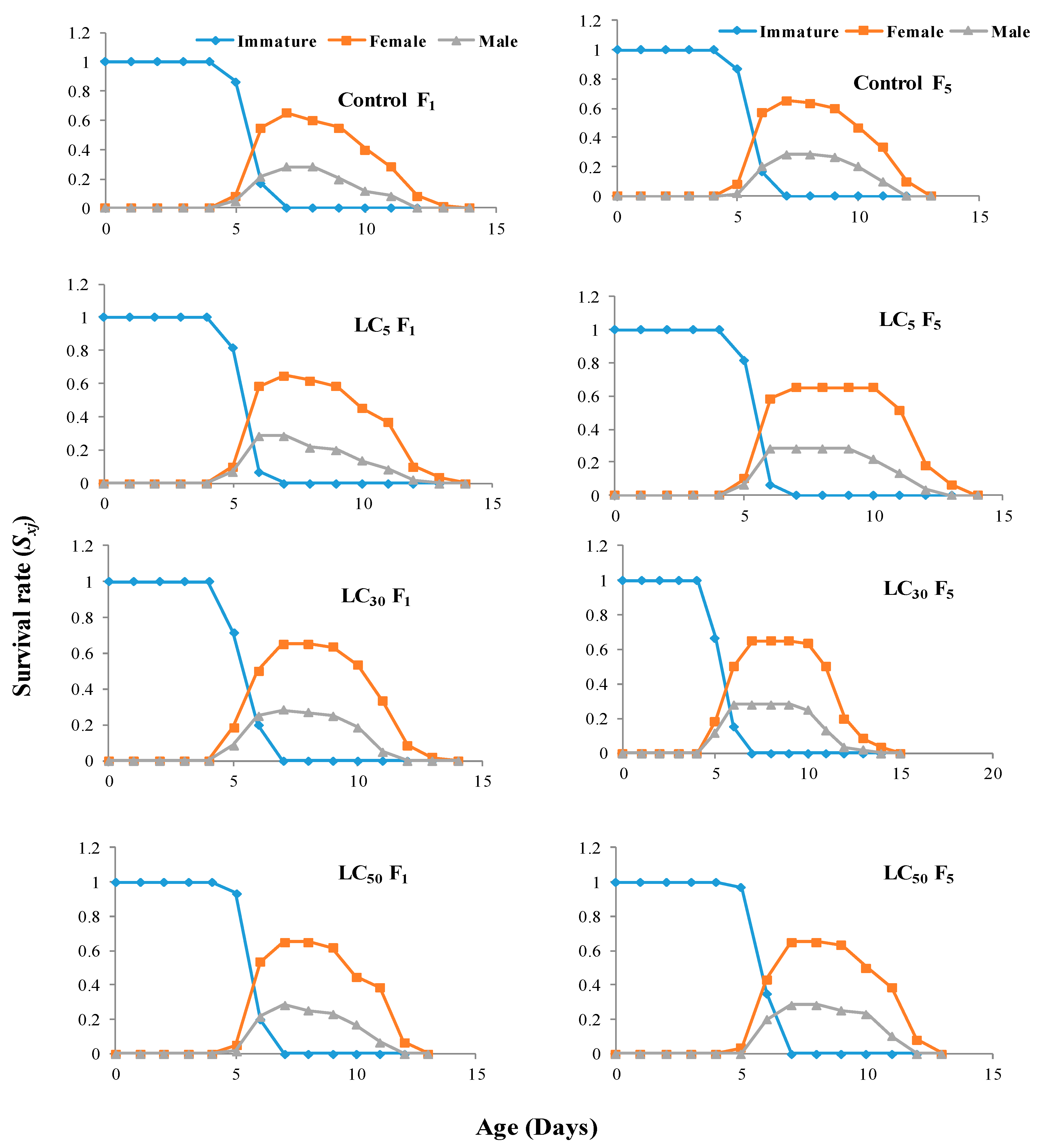
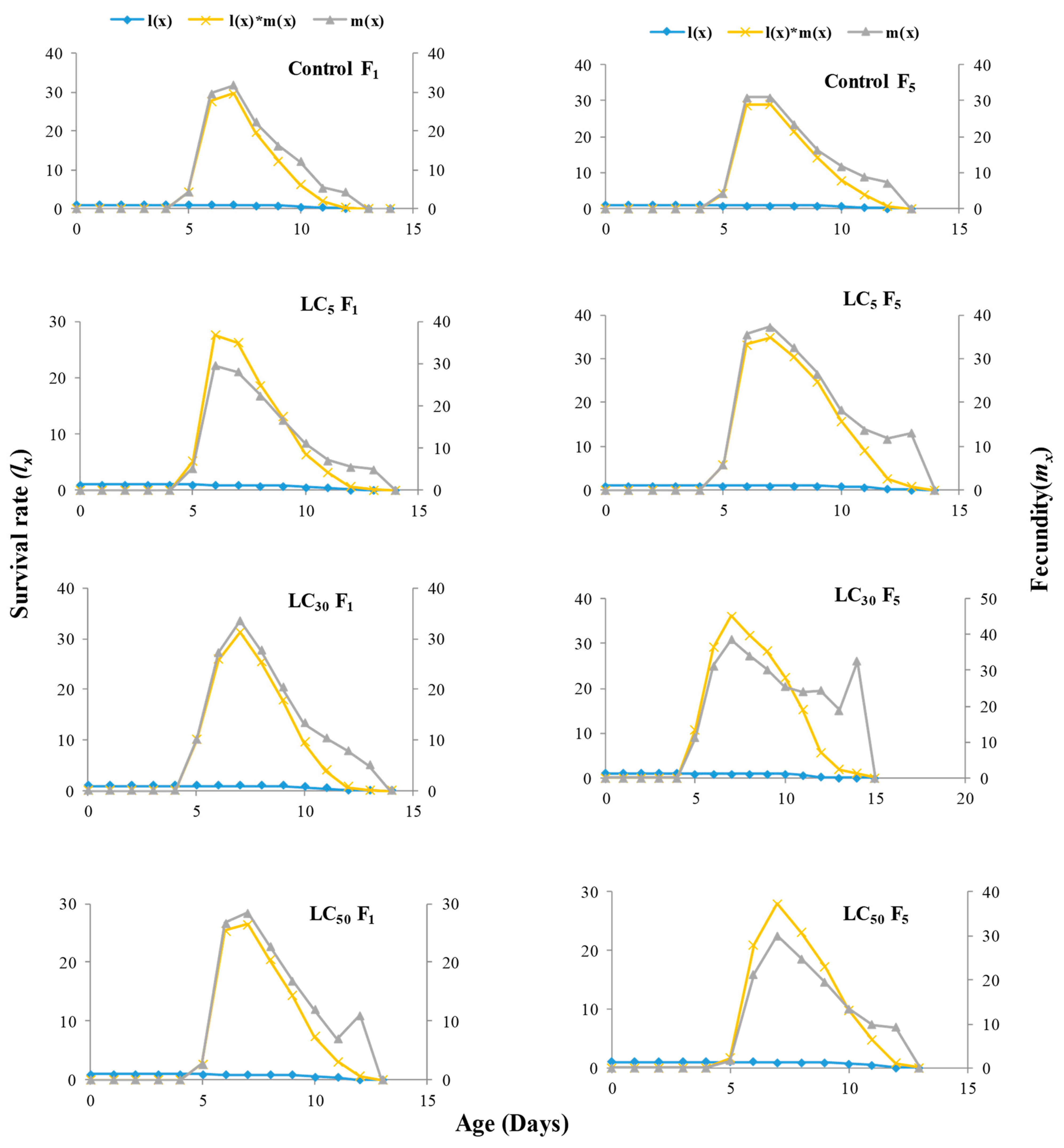
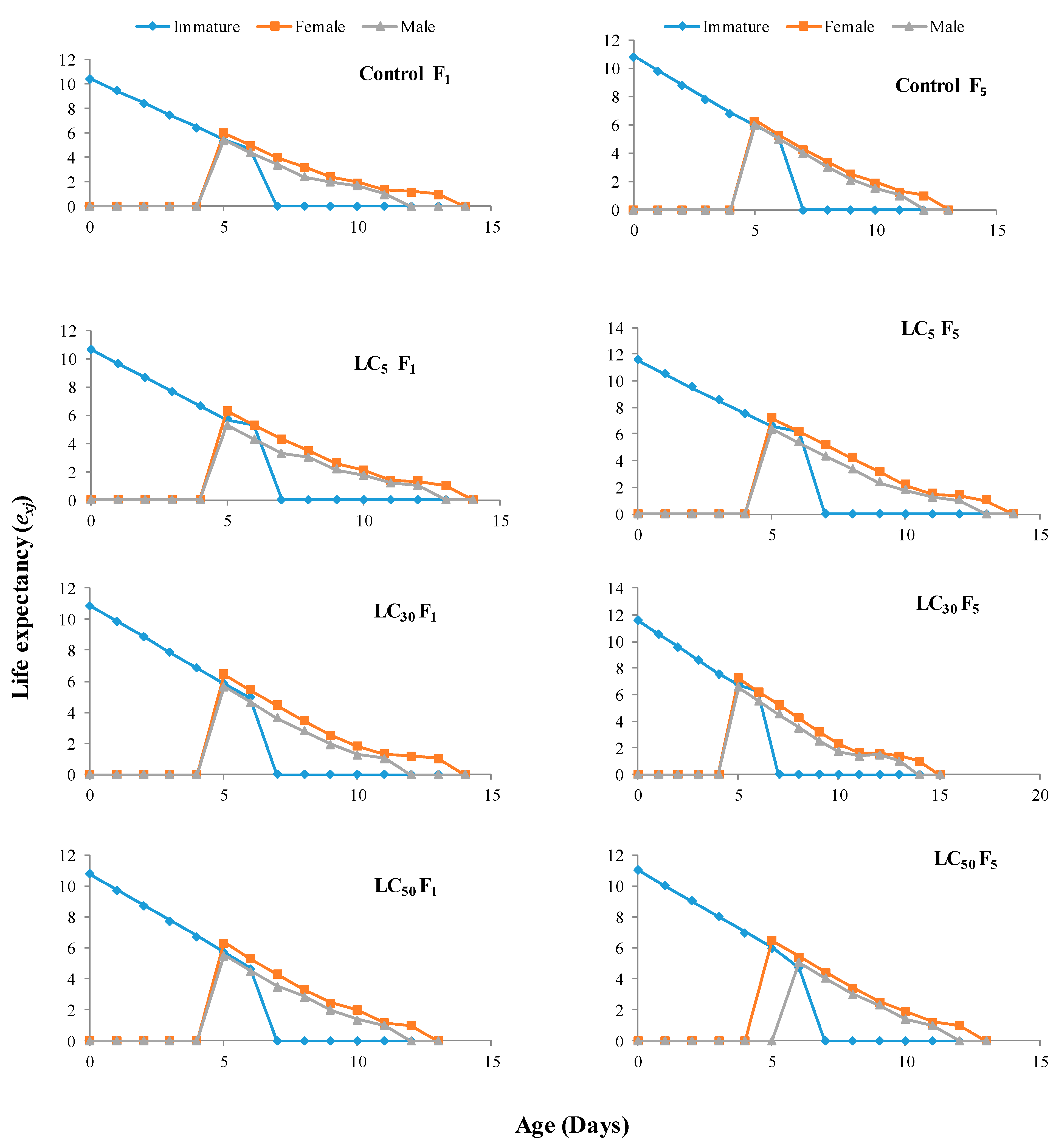
3.4. Multigenerational Sublethal Effects of Imidacloprid on the Age–Stage Specific Survival Rate, Fecundity, and Life Expectancy of T. chilonis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prakash, A.; Bentur, J.; Prasad, M.S.; Tanwar, R.; Sharma, O.; Bhagat, S.; Sehgal, M.; Singh, S.; Singh, M.; Chattopadhyay, C. Integrated Pest Management for Rice; National Centre for Integrated Pest Management: New Delhi, India, 2014; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Fahad, S.; Saud, S.; Akhter, A.; Bajwa, A.A.; Hassan, S.; Battaglia, M.; Adnan, M.; Wahid, F.; Datta, R.; Babur, E. Bio-based integrated pest management in rice: An agro-ecosystems friendly approach for agricultural sustainability. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2021, 20, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, R.; Zhao, X.; Wu, C.; Cang, T.; Wang, Q. Insecticide toxic effects on Trichogramma ostriniae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ge, L.; Liu, F.; Song, Q.; Stanley, D. Pesticide-induced planthopper population resurgence in rice cropping systems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.-M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Cutler, G.C. Insecticide-induced hormesis and arthropod pest management. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preetha, G.; Stanley, J.; Suresh, S.; Samiyappan, R. Risk assessment of insecticides used in rice on miridbug, Cyrtorhinus lividipennis Reuter, the important predator of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stal.). Chemosphere 2010, 80, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Fauvergue, X.; Dechaume-Moncharmont, F.-X.; Kerhoas, L.; Ballanger, Y.; Kaiser, L. Diaeretiella rapae limits Myzus persicae populations after applications of deltamethrin in oilseed rape. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, M.N.; Schneider, M.I.; Desneux, N.; González, B.; Ronco, A.E. Impact of the neonicotinoid acetamiprid on immature stages of the predator Eriopis connexa (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.-L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.-W.; Desneux, N.; He, Y.-X.; Weng, Q.-Y. Lethal and sublethal effects of thiamethoxam on the whitefly predator Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) through different exposure routes. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Ali, E.; Li, W.; He, B.; Gong, P.; Xu, P.; Li, J.; Wan, H. Sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the development and reproduction of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Crop Prot. 2019, 118, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Imidacloprid-induced hormesis effects on demographic traits of the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-Y.; Yang, X.-M.; Sun, L.-J.; Zhao, C.-D.; Chi, H.; Zheng, C.-Y. Sublethal effect of spirotetramat on the life table and population growth of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Ramirez-Romero, R.; Kaiser, L. Multistep bioassay to predict recolonization potential of emerging parasitoids after a pesticide treatment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2006, 25, 2675–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Gao, Y. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the population development of western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Insects 2019, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Shu, R.; Gong, P.; Li, W.; Wan, H.; Li, J. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of triflumezopyrim on the biological traits of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)(Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Crop Prot. 2019, 117, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Tariq, K.; Ali, A.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Clothianidin-induced sublethal effects and expression changes of vitellogenin and ecdysone receptors genes in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; You, M.; Atlihan, R.; Smith, C.L.; Kavousi, A.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Güncan, A.; Tuan, S.-J.; Fu, J.-W.; Xu, Y.-Y. Age-stage, two-sex life table: An introduction to theory, data analysis, and application. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Desneux, N.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Khattak, A.M.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Acetamiprid-induced hormetic effects and vitellogenin gene (Vg) expression in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Atlihan, R.; Chi, H.; Chu, D. Demographic analysis of progeny fitness and timing of resurgence of Laodelphax striatellus after insecticides exposure. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 39, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wyckhuys, K.A.; Liang, H.; Desneux, N.; Lu, Y. Lethal and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on Helicoverpa armigera adults enhance the potential for use in ‘attract-and-kill’control strategies. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, G.C. Insects, insecticides and hormesis: Evidence and considerations for study. Dose-Response 2013, 11, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, E.A.; El-Sherif, S.A.; Mokbel, E.-S. Flupyradifurone induces transgenerational hormesis effects in the cowpea aphid, Aphis craccivora. Ecotoxicology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, G.C.; Amichot, M.; Benelli, G.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Qu, Y.; Rix, R.R.; Ullah, F.; Desneux, N. Hormesis and insects: Effects and interactions in agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Rix, R.R.; Cutler, G.C. Pesticide-induced hormesis in arthropods: Towards biological systems. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2022, 29, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, D.B.; Suh, C.P.; Mccravy, K.W.; Berisford, C.W.; Debarr, G.L. Evaluation of inundative releases of Trichogramma exiguum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) for suppression of Nantucket pine tip moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) in pine (Pinaceae) plantations. Can. Entomol. 2000, 132, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabello, T.; Gámez, M.; Varga, Z.; Garay, J.; Carreño, R.; Gallego, J.; Fernández, F.; Vila, E. Selection of Trichogramma spp. (Hym.: Trichogrammatidae) for the biological control of Tuta absoluta (Lep.: Gelechiidae) in greenhouses by an entomo-ecological simulation model. IOBC/WPRS Bull 2012, 80, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chailleux, A.; Biondi, A.; Han, P.; Tabone, E.; Desneux, N. Suitability of the pest–plant system Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae)–tomato for Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) parasitoids and insights for biological control. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, L.; Cascone, P.; Giorgini, M.; Michelozzi, M.; Rodrigues, H.S.; Spiezia, G.; Iodice, L.; Guerrieri, E. Relative importance of host and plant semiochemicals in the foraging behavior of Trichogramma achaeae, an egg parasitoid of Tuta absoluta. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozad-Bonab, Z.; Hejazi, M.J.; Iranipour, S.; Arzanlou, M.; Biondi, A. Lethal and sublethal effects of synthetic and bio-insecticides on Trichogramma brassicae parasitizing Tuta absoluta. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.-S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Desneux, N. Biological control with Trichogramma in China: History, present status, and perspectives. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.-C.; Du, W.-M.; Zang, L.-S.; Ruan, C.-C.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zou, Z.; Monticelli, L.S.; Harwood, J.D.; Desneux, N. Multi-parasitism: A promising approach to simultaneously produce Trichogramma chilonis and T. dendrolimi on eggsof Antheraea pernyi. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.-X.; Jaworski, C.; Desneux, N.; Zhang, F.; Yang, P.-Y.; Wang, S. Long-term, large-scale releases of Trichogramma promote pesticide decrease in maize in northeastern China. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.; Hoffmann, M.P.; Pitcher, S.A.; Harper, J.K. Integrating insecticides and Trichogramma ostriniae to control European corn borer in sweet corn: Economic analysis. Biol. Control 2011, 56, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thany, S.H. Neonicotinoid insecticides. In Insect Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, F.; Ou, J. Global pesticide consumption and pollution: With China as a focus. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Vernon, R.S.; van Herk, W.G.; Clodius, M.; Harding, C. Crop protection and mortality of Agriotes obscurus wireworms with blended insecticidal wheat seed treatments. J. Pest Sci. 2013, 86, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuelher, E.S.; da Silva, É.H.; Rodrigues, H.S.; Hirose, E.; Guedes, R.N.C.; Oliveira, E.E. Area-wide spatial survey of the likelihood of insecticide control failure in the neotropical brown stink bug Euschistus heros. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decourtye, A.; Henry, M.; Desneux, N. Overhaul pesticide testing on bees. Nature 2013, 497, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondeau, G.; Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Tennekes, H.A.; Decourtye, A.; Ramírez-Romero, R.; Desneux, N. Delayed and time-cumulative toxicity of imidacloprid in bees, ants and termites. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Goka, K.; Hayasaka, D. Contamination of the aquatic environment with neonicotinoids and its implication for ecosystems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappington, J.D. Imidacloprid alters ant sociobehavioral traits at environmentally relevant concentrations. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jam, N.A.; Saber, M. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on the functional response of the aphid parasitoid, Lysiphlebus fabarum. Entomol. Gen. 2018, 38, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.B.; Sahu, M.; Ullah, F.; Patil, N.B.; Adak, T.; Pokhare, S.; Mahendiran, A.; Rath, P.C. Insecticide-induced hormesis in a factitious host, Corcyra cephalonica, stimulates the development of its gregarious ecto-parasitoid, Habrobracon hebetor. Biol. Control 2021, 160, 104680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, B.; Pandi, G.G.P.; Ullah, F.; Patil, N.B.; Sahu, M.; Adak, T.; Pokhare, S.; Yadav, M.K.; Mahendiran, A.; Mittapelly, P.; et al. Performance of Trichogramma japonicum under field conditions as a function of the factitious host species used for mass rearing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256246. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.-S.; He, Y.-R.; Guo, X.-L.; Luo, Y.-L. Acute toxicities and sublethal effects of some conventional insecticides on Trichogramma chilonis (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Pino, M.; Gallego, J.R.; Hernández Suárez, E.; Cabello, T. Effect of temperature on life history and parasitization behavior of Trichogramma achaeae Nagaraja and Nagarkatti (Hym.: Trichogrammatidae). Insects 2020, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Biondi, A.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.; Song, D. Sublethal and hormesis effects of imidacloprid on the soybean aphid Aphis glycines. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, L. The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J. Anim. Ecol. 1948, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-B.; Chi, H. Assessing the application of the jackknife and bootstrap techniques to the estimation of the variability of the net reproductive rate and gross reproductive rate: A case study in Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Agric. 2012, 61, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Preetha, G.; Stanley, J.; Suresh, S.; Kuttalam, S.; Samiyappan, R. Toxicity of selected insecticides to Trichogramma chilonis: Assessing their safety in the rice ecosystem. Phytoparasitica 2009, 37, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.; Smagghe, G.; Stark, J.; Desneux, N. Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayyanath, M.-M.; Cutler, G.C.; Scott-Dupree, C.D.; Sibley, P.K. Transgenerational shifts in reproduction hormesis in green peach aphid exposed to low concentrations of imidacloprid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74532. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Shi, X.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X. Effects of spirotetramat treatments on fecundity and carboxylesterase expression of Aphis gossypii Glover. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhu, H.; Lu, Y. Imidacloprid-induced hormesis on the fecundity and juvenile hormone levels of the green peach aphid Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyanath, M.-M.; Scott-Dupree, C.D.; Cutler, G.C. Effect of low doses of precocene on reproduction and gene expression in green peach aphid. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ma, K.; Chi, H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, X. Transgenerational hormetic effects of sublethal dose of flupyradifurone on the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Qi, Y.; Desneux, N.; Shi, X.; Biondi, A.; Gao, X. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of short-term and chronic exposures to the neonicotinoid nitenpyram on the cotton aphid Aphis gossypii. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.; Magalhaes, L.; Cosme, L. Stimulatory sublethal response of a generalist predator to permethrin: Hormesis, hormoligosis, or homeostatic regulation? J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.I.A.; Ramalho, F.d.S.; Bandeira, C.d.M.; Malaquias, J.B.; Zanuncio, J.C. Age-dependent fecundity of Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas)(Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) with sublethal doses of gammacyhalothrin. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2009, 52, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, A.; Salerno, G.; Onofri, A.; Conti, E. Sub-lethal effects of two pyrethroids on biological parameters and behavioral responses to host cues in the egg parasitoid Telenomus busseolae. Biol. Control 2010, 53, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.P.-C.; Orr, D.B.; Van Duyn, J.W. Effect of insecticides on Trichogramma exiguum (Trichogrammatidae: Hymenoptera) preimaginal development and adult survival. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.A.; Reis, P.R.; Rocha, L.C.D.; Moraes, J.; Fuini, L.; Ecole, C.C. Side-effects of insecticides used in tomato fields on Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera, Trichogrammatidae). Acta Sci. 2003, 25, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.A.; Farias, E.S.; Andrade, E.D.; Carvalho, V.C.; Carvalho, G.A. Lethal, sublethal and transgenerational effects of insecticides labeled for cotton on immature Trichogramma pretiosum. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabebordbar, F.; Shishehbor, P.; Ziaee, M.; Sohrabi, F. Lethal and sublethal effects of two new insecticides spirotetramat and flupyradifurone in comparison to conventional insecticide deltamethrin on Trichogramma evanescens (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsaeyan, E.; Saber, M.; Safavi, S.A.; Poorjavad, N.; Biondi, A. Side effects of chlorantraniliprole, phosalone and spinosad on the egg parasitoid, Trichogramma brassicae. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Insecticide | n | Slope ± SE | LC5 µg·L−1 (95% CL) | LC30 µg·L−1 (95% CL) | LC50 µg·L−1 (95% CL) | LC90 µg·L1 (95% CL) | χ2 (df) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imidacloprid | 300 | 1.189 ± 0.055 | 0.07 (0.01–0.2) | 0.6 (0.3–1) | 2 (0.9–3) | 20 (9–60) | 12.196 (3) |
| Biological Parameters | Generations | Mean ± SE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LC5 | LC30 | LC50 | ||
| Immature | F1 | 6.03 ± 7.55 aA | 5.89 ± 0.06 aA | 5.91 ± 0.09 aA | 6.12 ± 6.71 aA |
| F5 | 6.07 ± 7.05 aA | 5.89 ± 0.06 aA | 5.84 ± 0.09 aB | 6.28 ± 7.01 aA | |
| Pre-adult (days) | F1 | 0.93 ± 0.03 aA | 0.93 ± 0.03 aA | 0.93 ± 0.03 aA | 0.93 ± 3.22 aA |
| F5 | 0.93 ± 0.03 aA | 0.93 ± 0.03 aA | 0.93 ± 0.03 aA | 0.93 ± 3.20 aA | |
| Adult longevity (days) | F1 | 4.76 ± 0.17 aA | 5.11 ± 0.19 bA | 5.30 ± 0.12 bA | 4.96 ± 0.15 aA |
| F5 | 5.12 ± 0.15 aB | 6.03 ± 0.12 aA | 6.18 ± 0.12 aA | 5.05 ± 0.12 aA | |
| Total longevity (days) | F1 | 10.48 ±0.23 aA | 10.65 ± 0.26 bA | 10.87 ± 0.22 bA | 10.77 ± 0.22 aA |
| F5 | 10.82 ± 0.23 aB | 11.52 ± 0.23 aA | 11.58 ± 0.25 aA | 11.03 ± 0.19 aA | |
| TPOP (days) | F1 | 6.02 ± 0.08 aA | 5.95 ± 0.08 aA | 5.95 ± 0.11 aA | 6.28 ± 0.08 aA |
| F5 | 5.99 ± 0.08 aA | 5.95 ± 0.08 aA | 5.95 ± 0.11 aA | 6.28 ± 0.08 aA | |
| Oviposition days | F1 | 4.85 ± 0.21 aA | 5.18± 0.22 bA | 5.39 ± 0.14 bA | 5.10 ± 0.16 aA |
| F5 | 5.28 ± 0.18 aB | 6.15 ±0.14 aA | 6.26 ± 0.13 aA | 5.13 ± 0.15 aA | |
| Fecundity (offspring/individual) | F1 | 156.64 ± 5.23 aA | 155.89 ± 9.24 bA | 191.43 ± 5.67 bA | 154.95 ± 8.31 aA |
| F5 | 169.26 ± 4.95 aB | 241.51 ±5.39 aA | 281.05 ± 8.49 aA | 163.43 ± 6.65 aA | |
| Population Parameters | Generations | Mean ± SE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | LC5 | LC30 | LC50 | ||
| r (d−1) | F1 | 0.59 ± 0.01 aA | 0.59 ± 0.01 aA | 0.61 ± 0.02 aA | 0.57 ± 0.01 aA |
| F5 | 0.59 ±0.01 aA | 0.62 ± 0.01 aA | 0.63 ± 0.02 aA | 0.56 ± 0.01 aA | |
| λ (d−1) | F1 | 1.79 ± 0.03 aA | 1.79 ± 0.03 aA | 1.84 ± 0.03 aA | 1.77 ±0.03 aA |
| F5 | 1.80± 0.03 aA | 1.86 ± 0.03 aA | 1.88 ± 0.03 aA | 1.76 ± 0.02 aA | |
| R0(offspring/individual) | F1 | 101.82 ± 10.21 aA | 101.33 ± 11.32 bA | 124.43 ± 12.36 bA | 100.72 ± 10.94 aA |
| F5 | 110.02 ± 10.93 aB | 156.98 ± 15.32 aA | 182.68 ± 18.23 aA | 106.23 ± 10.93 aA | |
| T (days) | F1 | 7.89 ± 0.1 aA | 7.88± 0.11 aA | 7.88 ± 0.12 aA | 8.05 ±0.10 aA |
| F5 | 7.96 ± 0.09 aA | 8.15± 0.09 aA | 8.21 ± 0.13 aA | 8.27 ± 0.09 aA | |
| GRR (offspring/individual) | F1 | 125.7 ± 11.07 aA | 130.91 ± 12.83 bA | 155.03 ± 13.70 bA | 127.5 ±11.89 aA |
| F5 | 133.94 ± 11.71 aB | 194.4 ± 15.91 aA | 270.91 ± 26.75 aA | 129.59 ±11.99 aA | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ray, A.; Gadratagi, B.-G.; Rana, D.K.; Ullah, F.; Adak, T.; Govindharaj, G.-P.-P.; Patil, N.B.; Mahendiran, A.; Desneux, N.; Rath, P.C. Multigenerational Insecticide Hormesis Enhances Fitness Traits in a Key Egg Parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis Ishii. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061392
Ray A, Gadratagi B-G, Rana DK, Ullah F, Adak T, Govindharaj G-P-P, Patil NB, Mahendiran A, Desneux N, Rath PC. Multigenerational Insecticide Hormesis Enhances Fitness Traits in a Key Egg Parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis Ishii. Agronomy. 2022; 12(6):1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061392
Chicago/Turabian StyleRay, Aishwarya, Basana-Gowda Gadratagi, Dhanendra Kumar Rana, Farman Ullah, Totan Adak, Guru-Pirasanna-Pandi Govindharaj, Naveenkumar B Patil, Annamalai Mahendiran, Nicolas Desneux, and Prakash Chandra Rath. 2022. "Multigenerational Insecticide Hormesis Enhances Fitness Traits in a Key Egg Parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis Ishii" Agronomy 12, no. 6: 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061392
APA StyleRay, A., Gadratagi, B.-G., Rana, D. K., Ullah, F., Adak, T., Govindharaj, G.-P.-P., Patil, N. B., Mahendiran, A., Desneux, N., & Rath, P. C. (2022). Multigenerational Insecticide Hormesis Enhances Fitness Traits in a Key Egg Parasitoid, Trichogramma chilonis Ishii. Agronomy, 12(6), 1392. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12061392









